A Comparative Study on Oxidation of Acidic Red 18 by Persulfate with Ferrous and Ferric Ions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
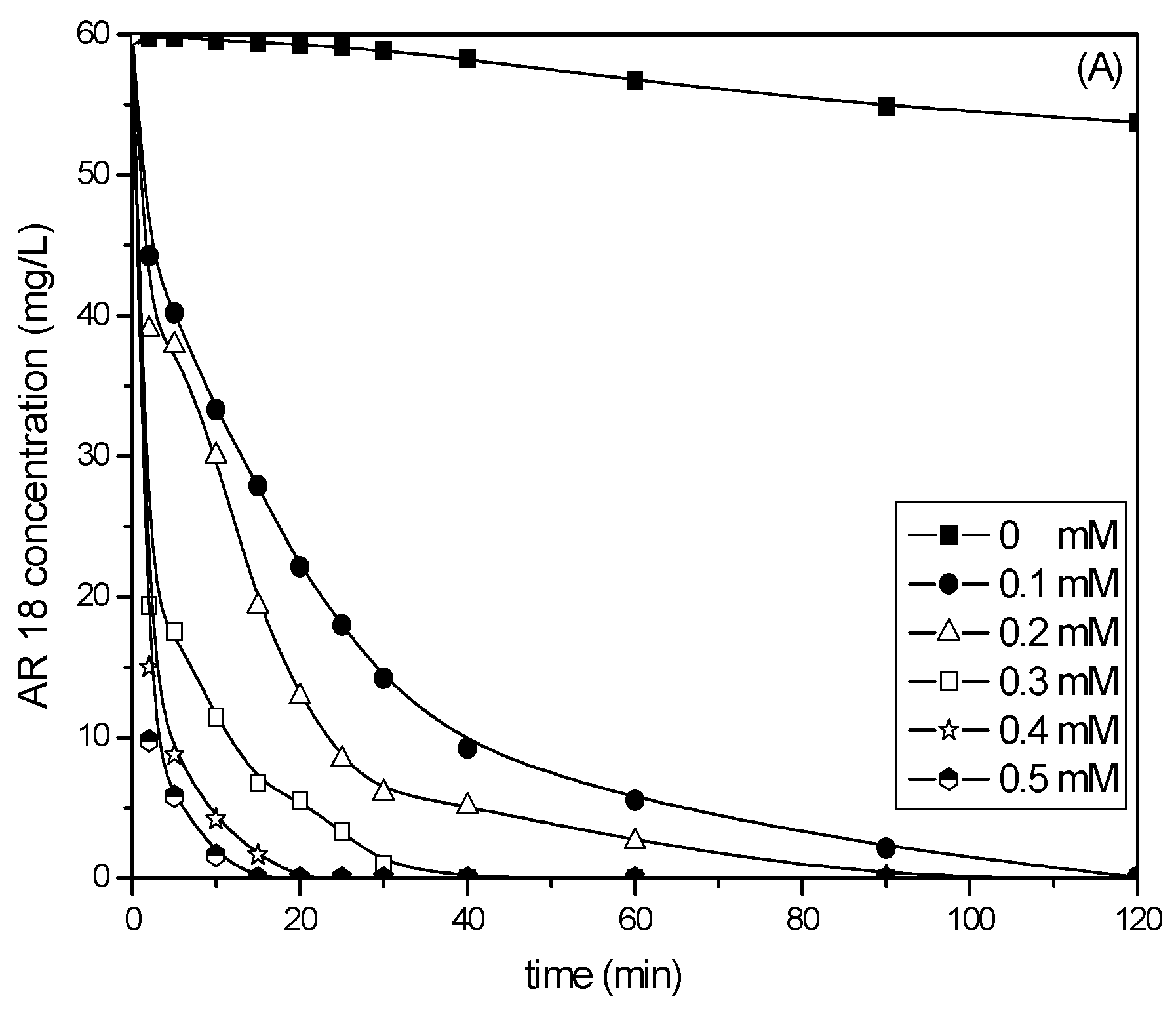
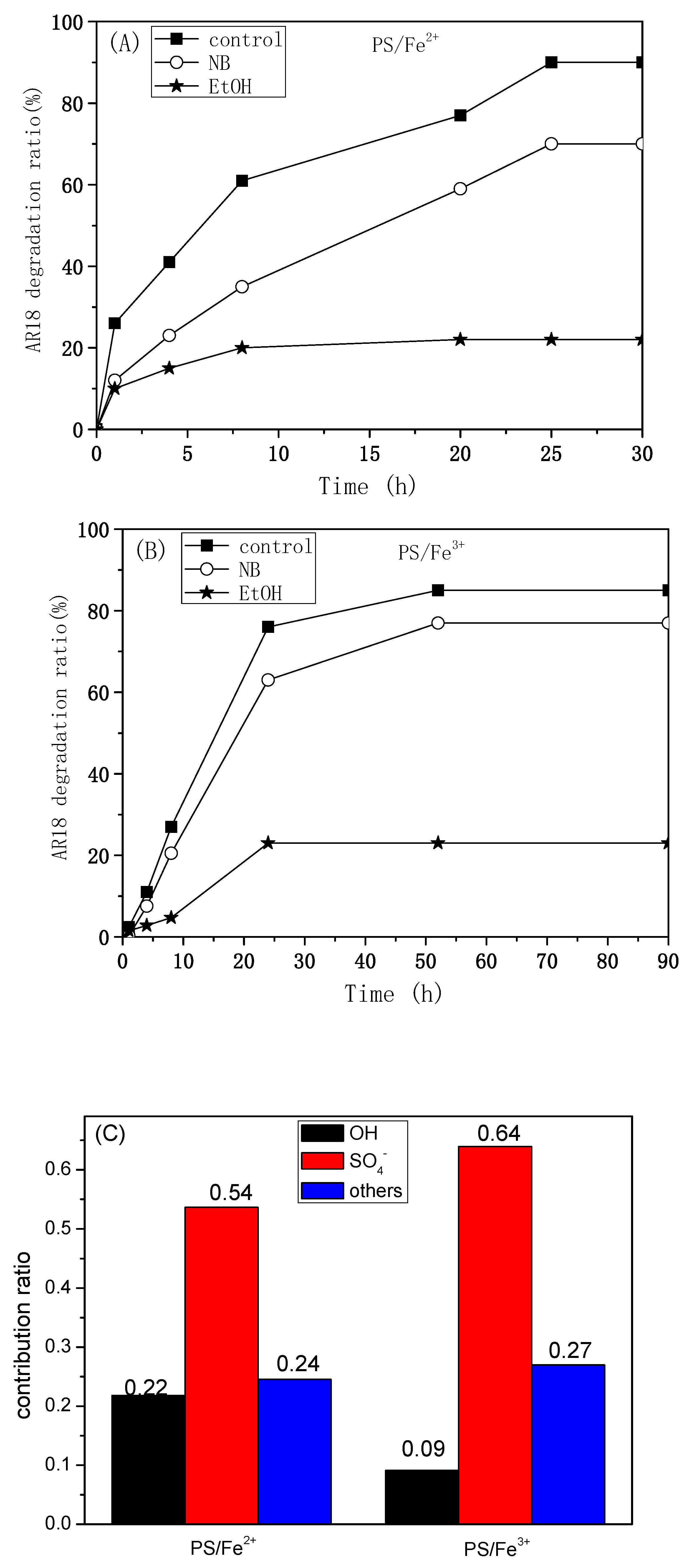
2.1. Comparison of PS/Fe2+ and PS/Fe3+ Processes
2.2. Effect of the Initial pH
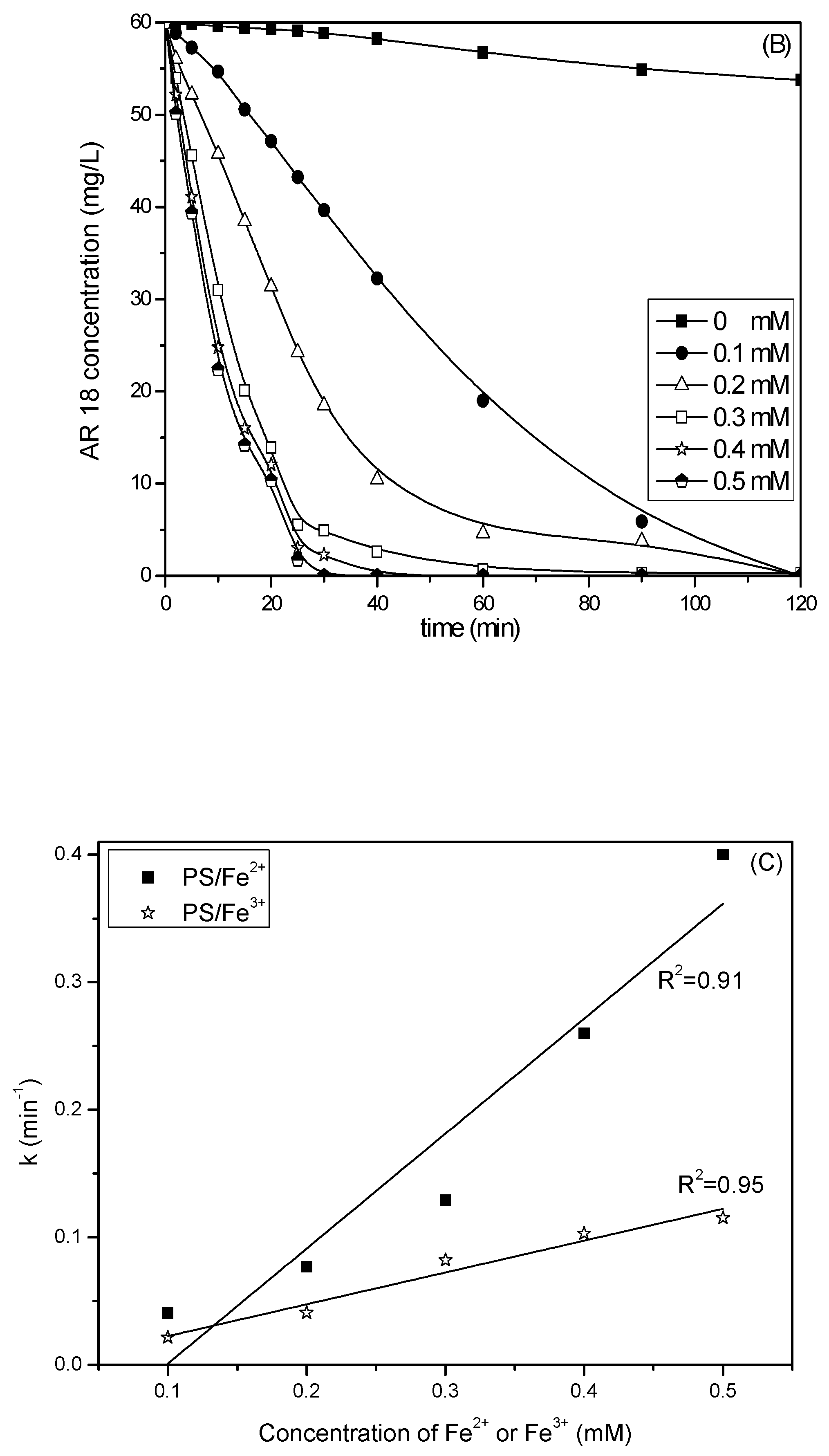
2.3. Effect of Fe2+ or Fe3+ Concentration
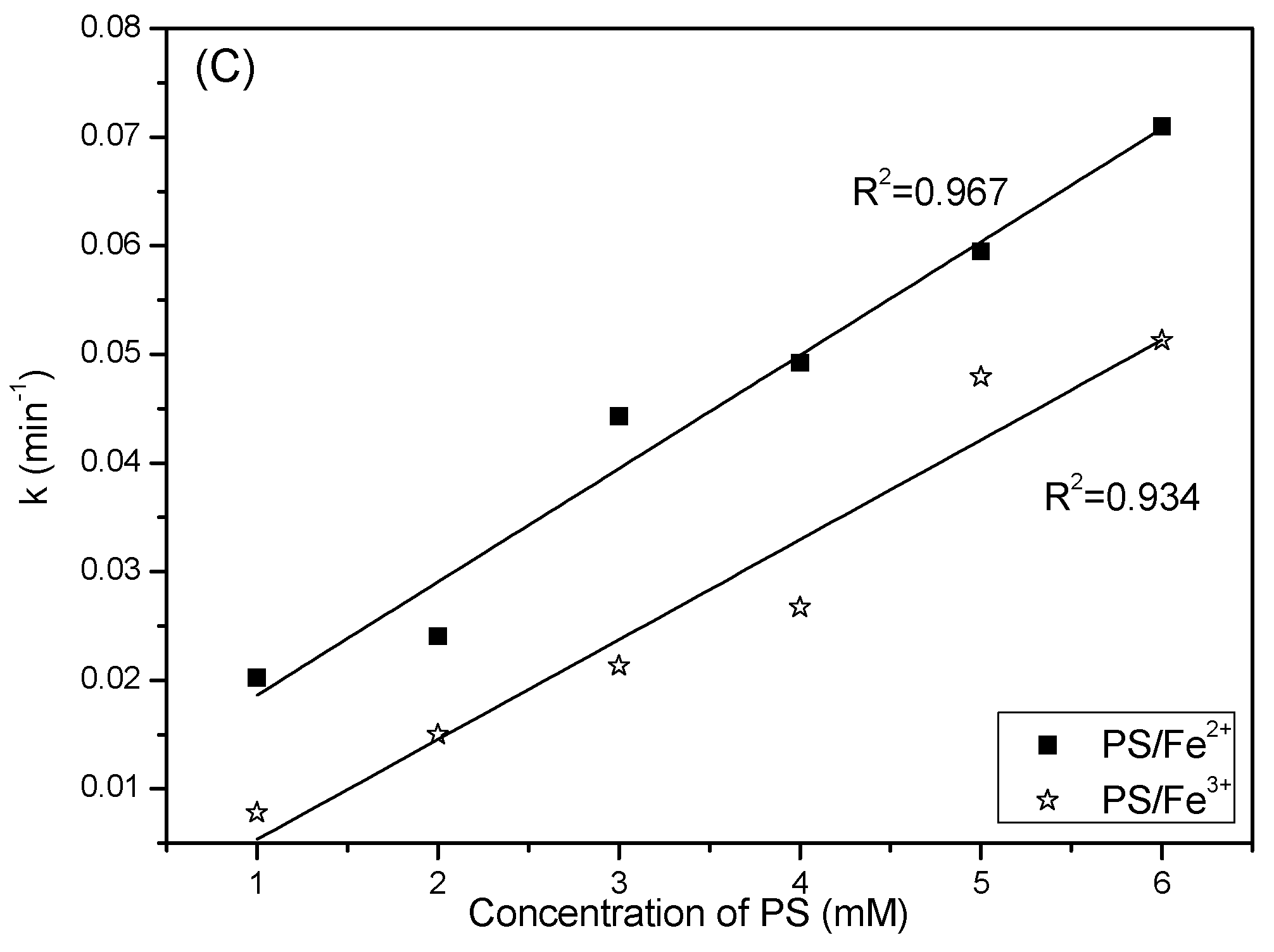
2.4. Effect of PS Concentration
2.5. AR18 Mineralization and Radical Detection
2.5.1. Mineralization of AR18
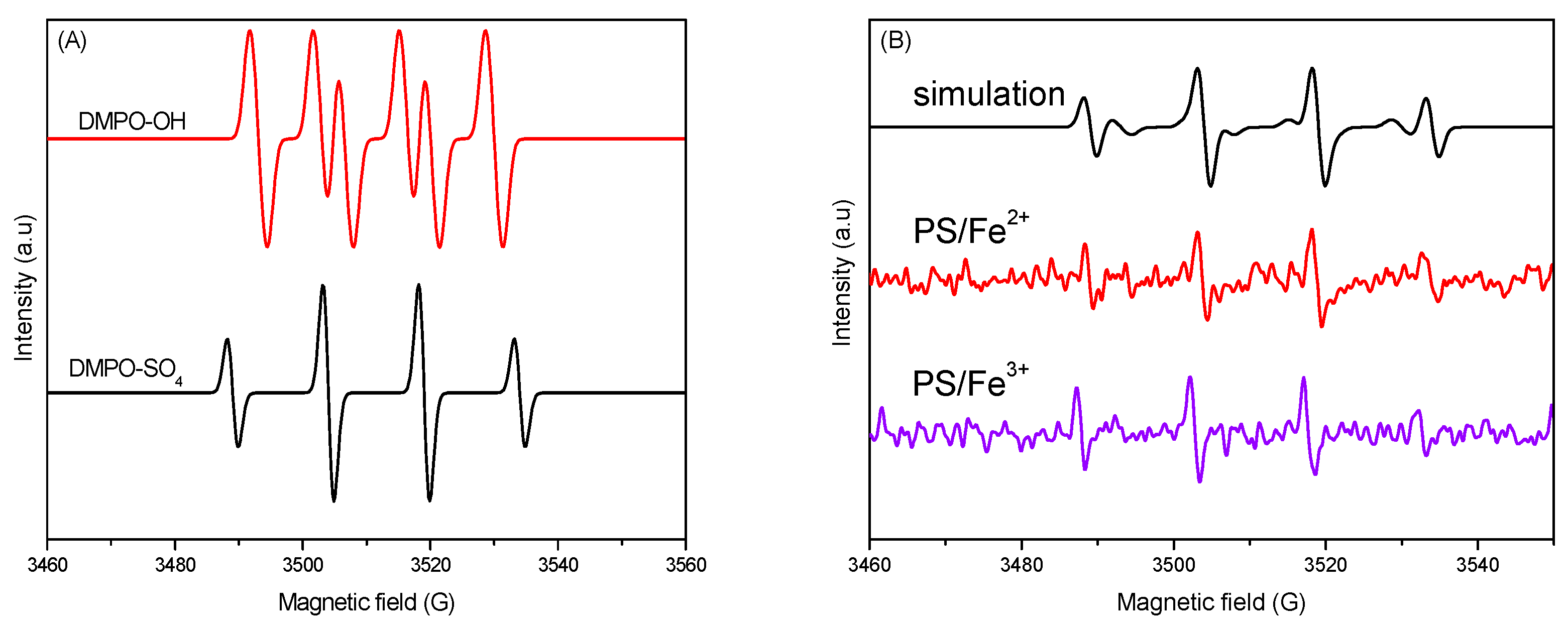
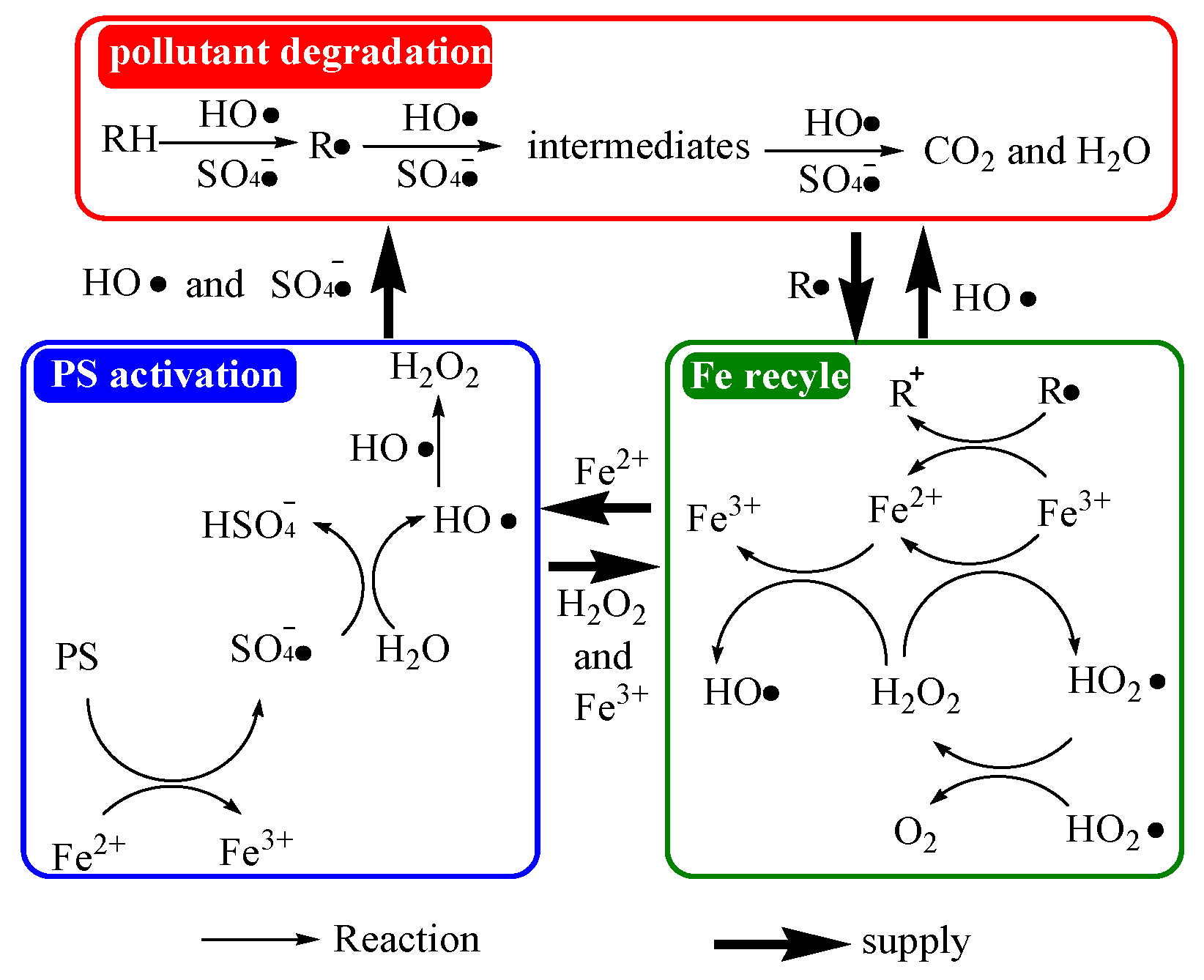
2.5.2. EPR Radical Detection and AR18 Degradation Mechanism
2.5.3. Quenching Experiments
3. Materials and Methods
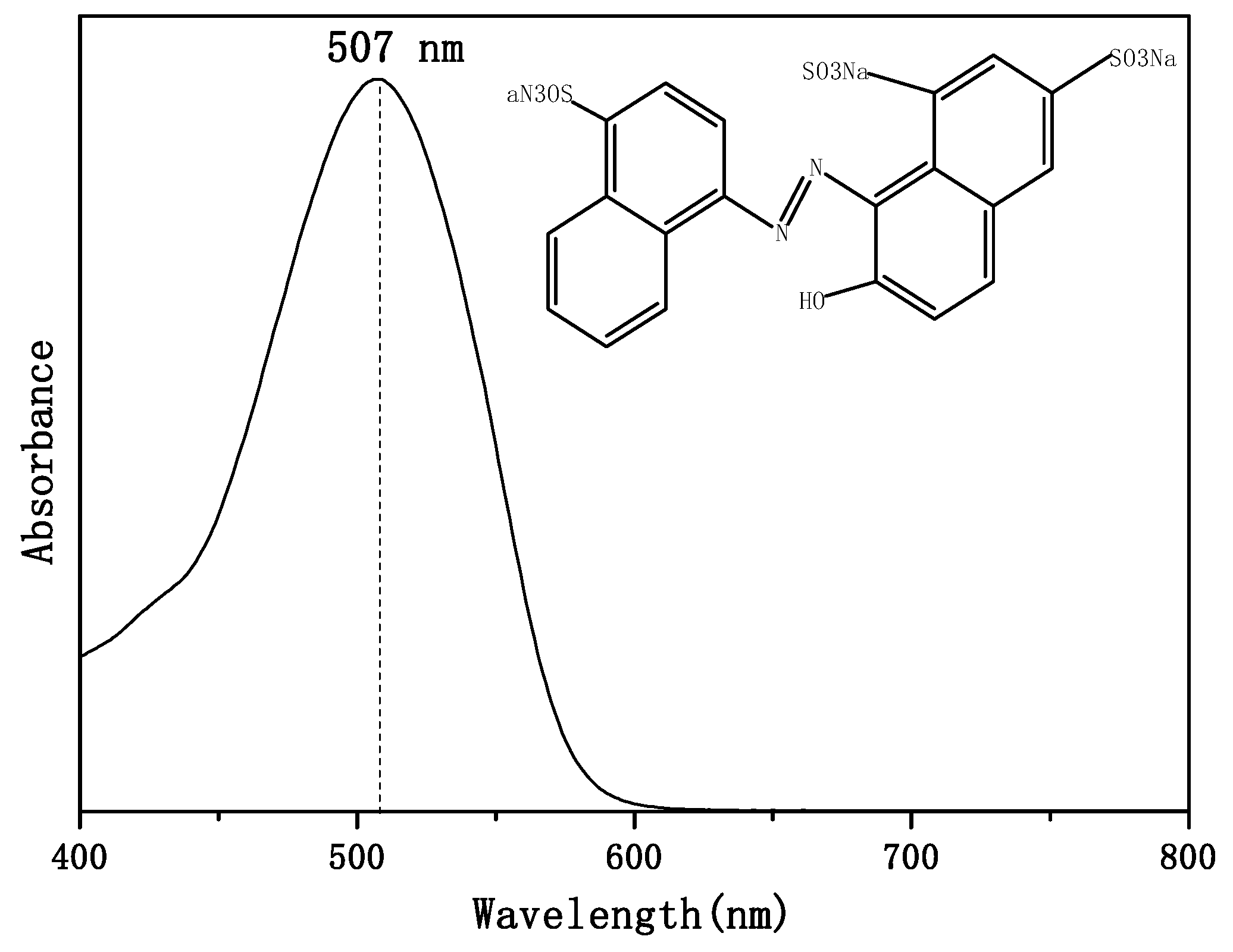
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Procedures
3.3. Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabra, A.N.; Khandare, R.V.; Waghmode, T.R.; Govindwar, S.P. Phytoremediation of textile effluent and mixture of structurally different dyes by Glandularia pulchella (Sweet) Tronc. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, D.; Hong, S.; Khan, S.; Darya, B.; Lee, J.; Chung, J.; Cho, S. Investigation of the synergistic effect of sonolysis and photocatalysis of titanium dioxide for organic dye degradation. Catalysts 2020, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Shen, S. Electrocatalytic degradation of azo dye by vanadium-doped TiO2 nanocatalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Xiao, L.; Jiang, R.; Zeng, G.M.; Liu, L. Efficient decolorization of azo dye solution by visible light-induced photocatalytic process using SnO2/ZnO heterojunction immobilized in chitosan matrix. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Thakur, V.; Gajbe, V. Adsorptive removal of toxic azo dye amido black 10B by hen feather. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2013, 20, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, B.; De, M.I.; Vegliò, F. Fenton treatment of complex industrial wastewater: Optimization of process conditions by surface response method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.D.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Zhou, D.M. Superoxide radical driving the activation of persulfate by magnetite nanoparticles: Implications for the degradation of PCBs. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2013, 129, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.H.; Dietrich, A.M.; Tanko, J.M. Simultaneous degradation of disinfection byproducts and earthy-musty odorants by the UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.C.; Gao, Z.; Qu, H.L.; Li, J.W.; Wang, X.X.; Li, P.; Liu, H. A new insight into Fenton and Fenton-like processes for water treatment: Part II. Influence of organic compounds on Fe(III)/Fe(II) interconversion and the course of reactions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W.; Shao, X.; Niu, R. Degradation efficiencies of azo dye Acid Orange 7 by the interaction of heat, UV and anions with common oxidants: Persulfate, peroxymonosulfate and hydrogen peroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Mechanism of persulfate activation by phenols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5864–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liao, X.; Yan, X.; Huling, S.G.; Chai, T.; Tao, H. Effect and mechanism of persulfate activated by different methods for PAHs removal in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.K.; Chu, W.; Graham, N. The aqueous degradation of butylated hydroxyanisole by UV/S2O82-: Study of reaction mechanisms via dimerization and mineralization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, W.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X. Ferrous-activated persulfate oxidation of arsenic (III) and diuron in aquatic system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 265, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazime, R.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Ferronato, C.; Huynh, T.K.X.; Jaber, F.; Chovelon, J.M. Optimization of imazalil removal in the system UV/TiO2/K2S2O8 using a response surface methodology (RSM). Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2013, 132–133, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hou, H.; Fujii, A.; Hosomi, M.; Li, F.S. Degradation of 1,4-dioxane in water with heat- and Fe2+-activated persulfate oxidation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2014, 21, 7457–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, S.; Vasquez, L.; Costa, D.; Romero, A.; Santos, A. Oxidation of Orange G by persulfate activated by Fe(II), Fe(III) and zero valent iron (ZVI). Chemosphere 2014, 101, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, O.S.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Mechanism of base activation of persulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6423–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Wei, G.; Zhang, W.Y.; Shan, L. A novel advanced oxidation process to degrade organic pollutants in wastewater: Microwave-activated persulfate oxidation. J. Environ. Sci. China 2009, 21, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Bruell, C.J.; Marley, M.C.; Sperry, K.L. Persulfate oxidation for in situ remediation of TCE. I. Activated by ferrous ion with and without a persulfate—Thiosulfate redox couple. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.R.; Li, X.Z. Degradation of azo dye Orange G in aqueous solutions by persulfate with ferrous ion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.X.; Wu, Y.L.; Wang, P.; Li, H.J.; Dong, W.B. Degradation of bisphenol A in aqueous solution by persulfate activated with ferrous ion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2013, 20, 4947–4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A review of classic Fenton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.C.; Pang, S.Y.; Ouyang, F.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J. A new insight into Fenton and Fenton-like processes for water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ferronato, C.; Salvador, A.; Yang, X.; Chovelon, J. Degradation of ciprofloxacin and sulfamethoxazole by ferrous-activated persulfate—Implications for remediation of groundwater contaminated by antibiotics. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Park, J.M.; Park, H.S.; Yoon, C. Oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol by persulfate activated with heat, Fe2+, and zero-valent iron. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Zhao, D.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, P.Y.; Dong, C.X. Enhanced degradation of ortho-nitrochlorobenzene by the combined system of zero-valent iron reduction and persulfate oxidation in soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R 2014, 21, 5132–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Liang, R.; Zhang, X.; Kurdi, S.; Luong, D.; Huang, H.; Peng, P.; Marzbanrad, E.; Oakes, K.D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of dyes by TiO2 nanobelts with hierarchical structures. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 256, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Shin, D.S.; Lee, J.K. Treatment of high-strength animal industrial wastewater using photo-assisted fenton oxidation coupled to photocatalytic technology. Water 2019, 11, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Radical generation by the interaction of transition metals with common oxidants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 3705–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crimi, M.L.; Taylor, J. Experimental evaluation of catalyzed hydrogen peroxide and sodium persulfate for destruction of BTEX contaminants. Soil Sediment Contam. 2007, 16, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masomboon, N.; Ratanatamskul, C.; Lu, M.C. Chemical oxidation of 2,6-dimethylaniline in the fenton process. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8629–8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Santos, A.; Vicente, F.; Gonzalez, C. Diuron abatement using activated persulphate: Effect of pH, Fe(II) and oxidant dosage. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.J.; Wang, Z.S.; Bruell, C.J. Influence of pH on persulfate oxidation of TCE at ambient temperatures. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, E.; Rosen, G.M.; Rauckman, E.J. Spin trapping—Kinetics of the reaction of superoxide and hydroxyl radicals with nitrones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4994–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranguelova, K.; Rice, A.B.; Khajo, A.; Triquigneaux, M.; Garantziotis, S.; Magliozzo, R.S.; Mason, R.P. Formation of reactive sulfite-derived free radicals by the activation of human neutrophils: An ESR study. Free Radical Bio. Med. 2012, 52, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.J.; Su, H.W. Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, L. A Comparative Study on Oxidation of Acidic Red 18 by Persulfate with Ferrous and Ferric Ions. Catalysts 2020, 10, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060698
Li X, Yuan L, Zhao L. A Comparative Study on Oxidation of Acidic Red 18 by Persulfate with Ferrous and Ferric Ions. Catalysts. 2020; 10(6):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060698
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Lijing Yuan, and Liangfu Zhao. 2020. "A Comparative Study on Oxidation of Acidic Red 18 by Persulfate with Ferrous and Ferric Ions" Catalysts 10, no. 6: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060698
APA StyleLi, X., Yuan, L., & Zhao, L. (2020). A Comparative Study on Oxidation of Acidic Red 18 by Persulfate with Ferrous and Ferric Ions. Catalysts, 10(6), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060698



