FeCeOx Supported Ni, Sn Catalysts for the High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
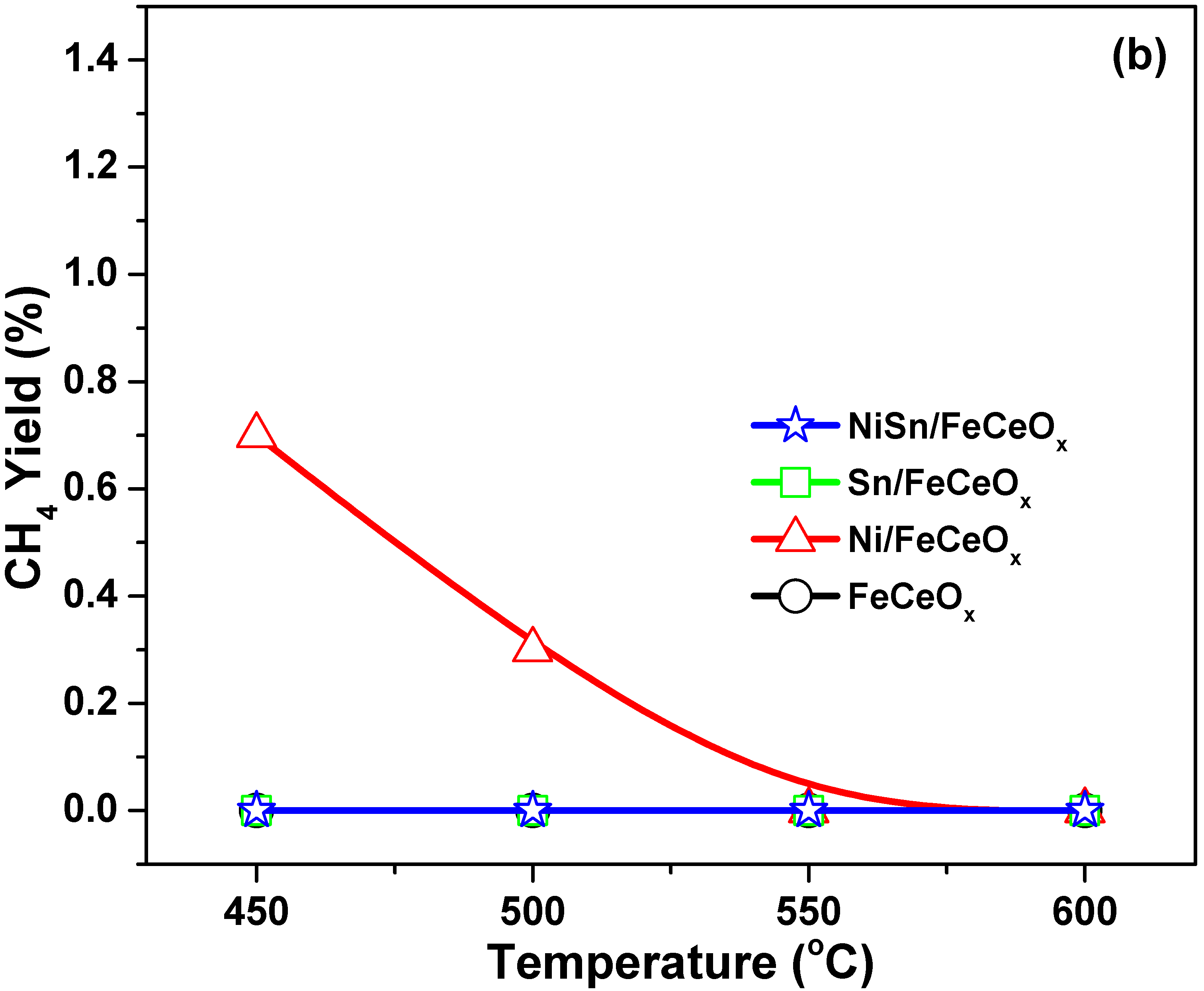
2.1. Catalytic Activity, Selectivity, and Stability
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
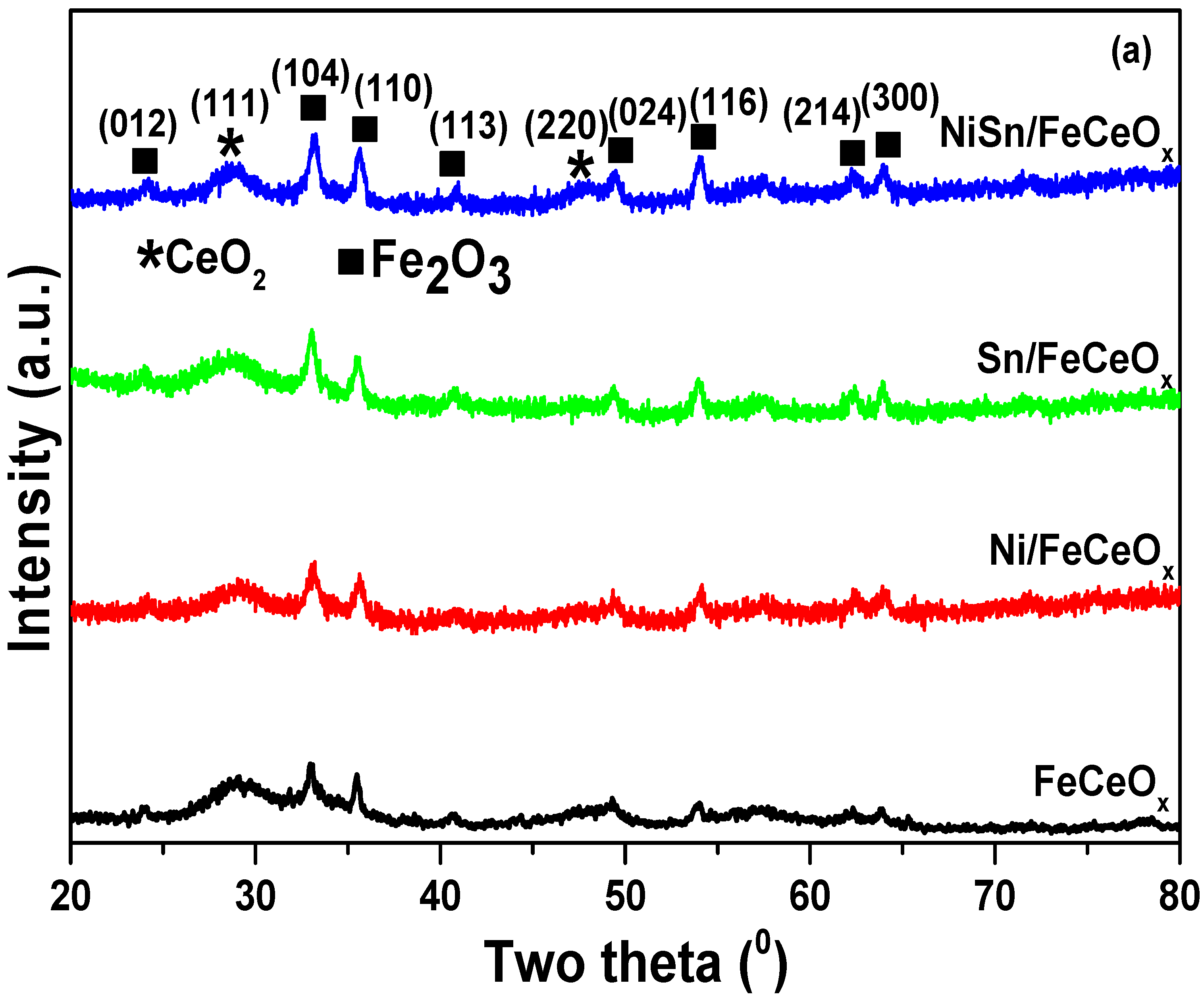
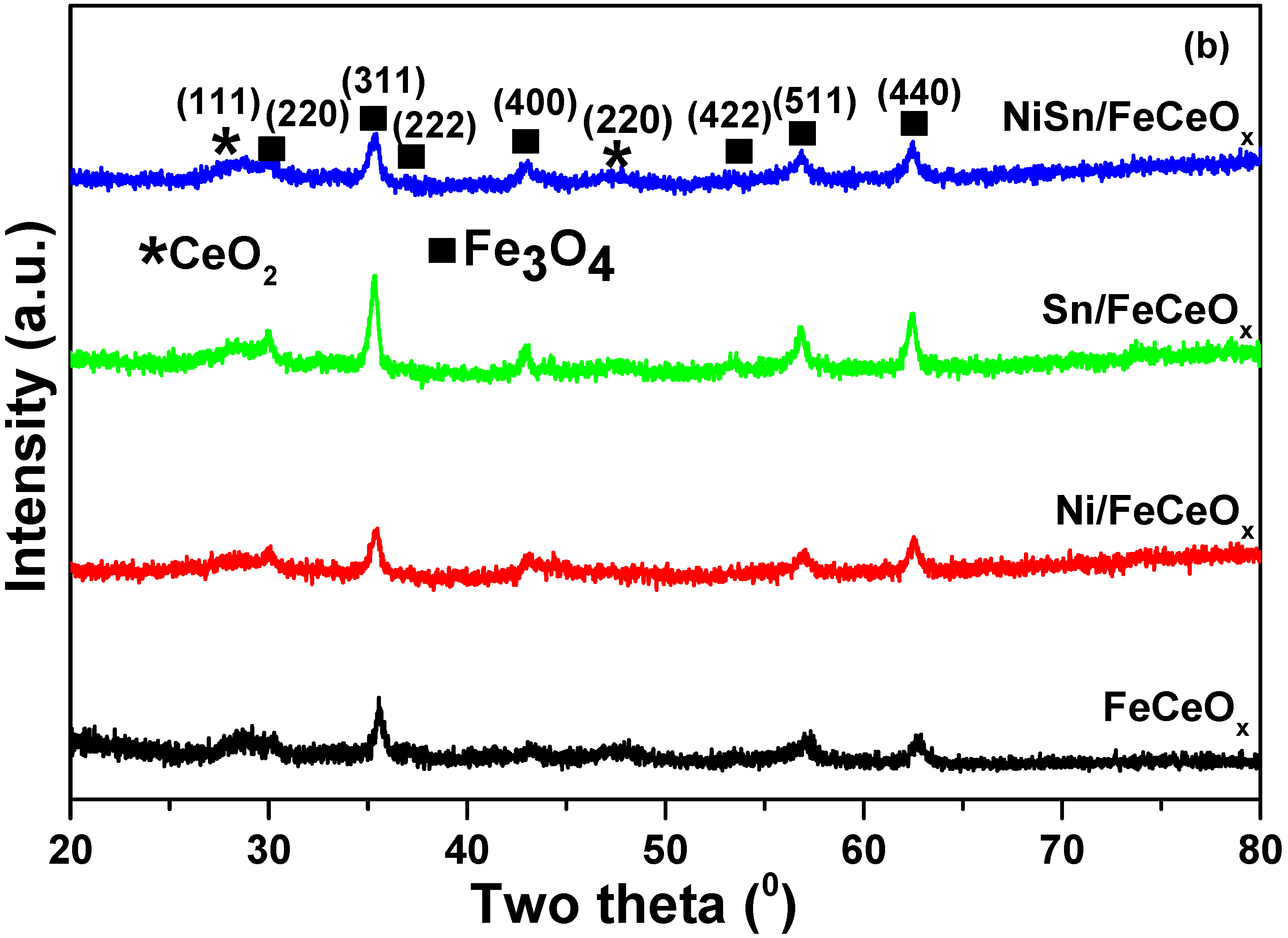
2.2.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Measurement
2.2.2. BET Surface Area and Scanning Electron Microscopy/Elemental Mapping (SEM/EDS)
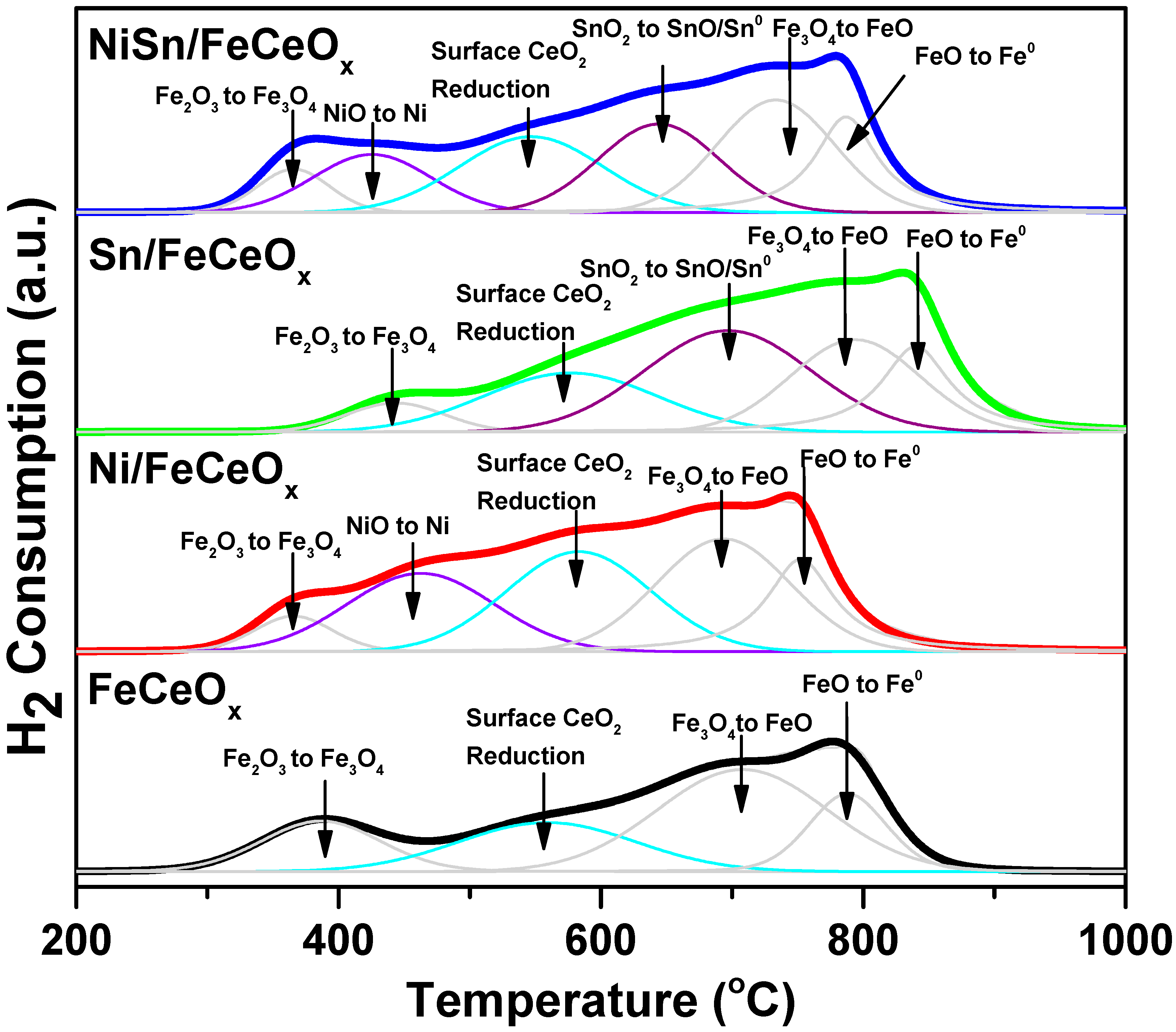
2.2.3. H2-Temperature-Programmed Reduction (H2-TPR) Measurement
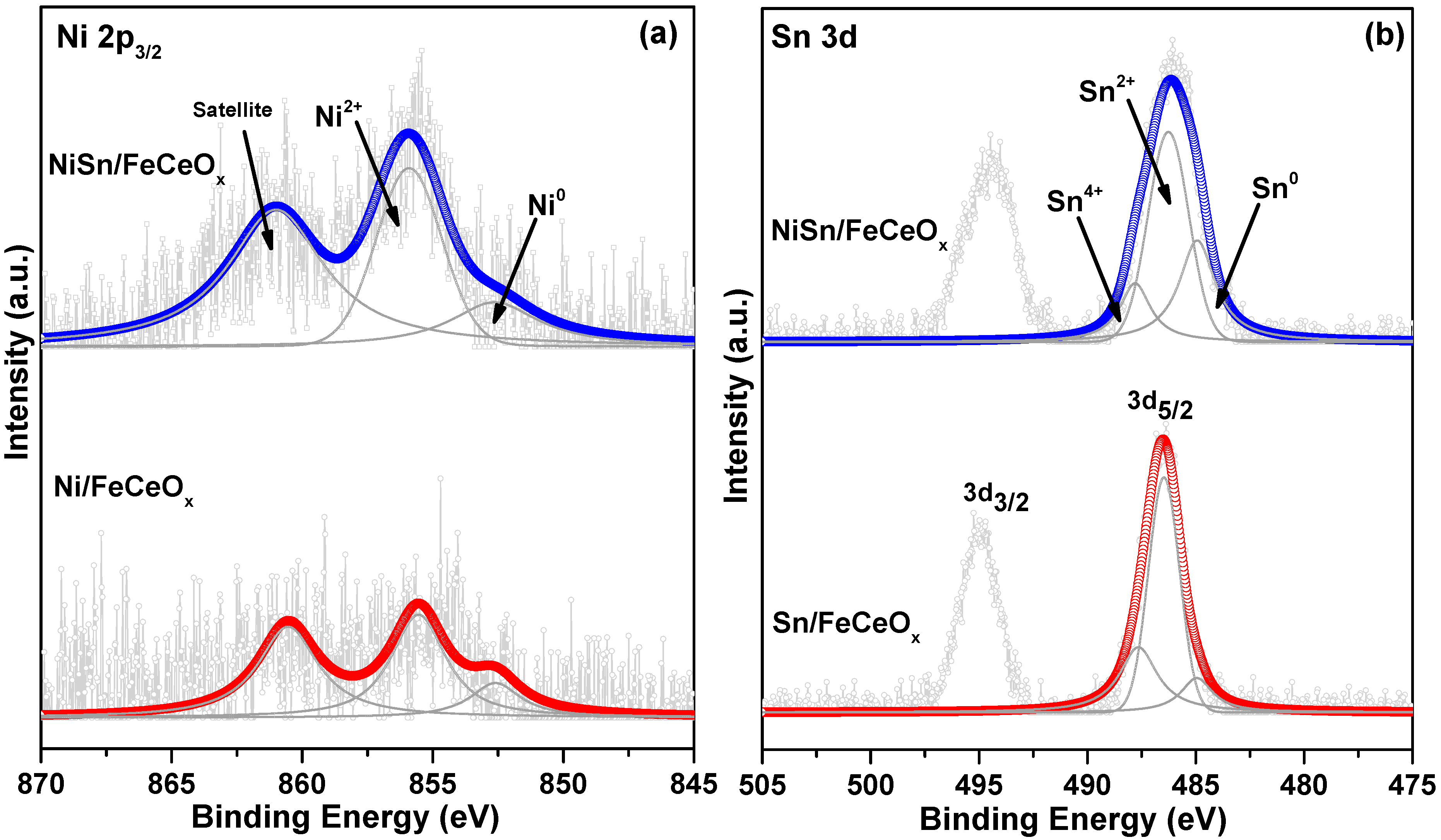
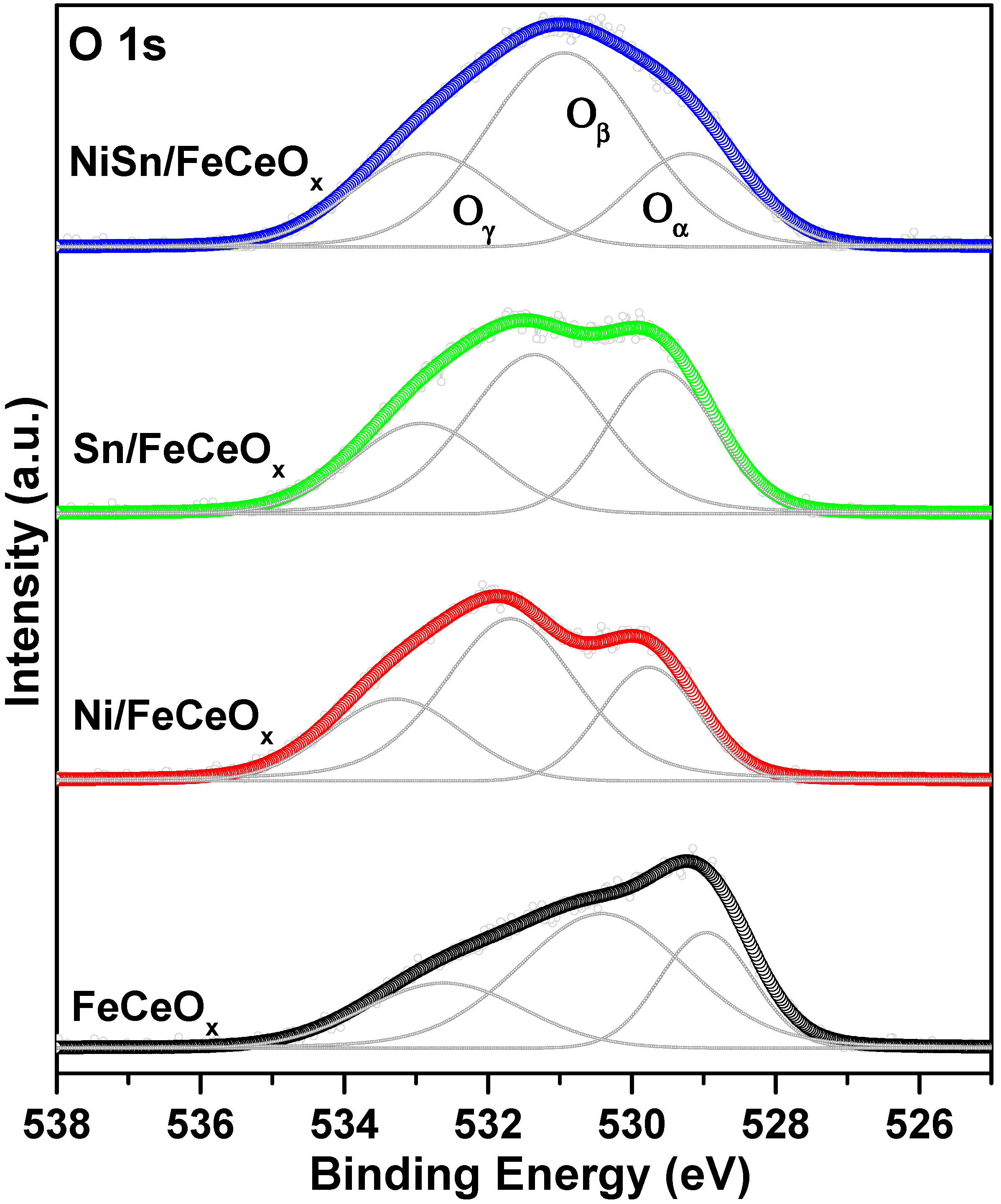
2.2.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Measurement
2.3. Structure–Activity Relationship
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Catalysts
3.2. Catalysts Characterizations
3.3. Catalytic Activity Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vovchok, D.; Guild, C.J.; Dissanayake, S.; Llorca, J.; Stavitski, E.; Liu, Z.; Palomino, R.M.; Waluyo, I.; Li, Y.; Frenkel, A.I.; et al. In Situ Characterization of Mesoporous Co/CeO2 Catalysts for the High-Temperature Water-Gas Shift. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 8998–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, I.; Acar, C. Review and Evaluation of Hydrogen Production Methods for Better Sustainability. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 11094–11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Jeong, D.-W.; Shim, J.-O.; Jang, W.-J.; Lee, Y.-L.; Rode, C.V.; Roh, H.-S. Hydrogen Production by the Water-Gas Shift Reaction using CuNi/Fe2O3 Catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasamy, C.; Wagner, J.P. Water Gas Shift Catalysis. Catal. Rev. 2009, 51, 325–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-W.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Eom, H.-J.; Moon, D.J.; Lee, K.-Y. The Review of Cr-Free Fe-based Catalysts for High-Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reactions. Catal. Today 2013, 210, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damma, D.; Smirniotis, P.G. Recent Advances in Iron-Based High-Temperature Water-Gas Shift Catalysis for Hydrogen Production. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2018, 21, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, A.A.; Vásquez, R.S.; Rajendran, J.; Li, M.; Berger, R.J.; Delgado, J.J.; Kapteijn, F.; Makkee, M. The Role of Rhodium in the Mechanism of the Water–Gas Shift over Zirconia Supported Iron Oxide. J. Catal. 2014, 313, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, J.; Wai, M.H.; Kawi, S. Nickel-based Catalysts for High-temperature Water Gas Shift Reaction-Methane Suppression. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 3927–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Biswas, P.; Guliants, V.V.; Misture, S. Hydrogen Production by Water–Gas Shift Reaction over Bimetallic Cu–Ni Catalysts Supported on La-Doped Mesoporous Ceria. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 387, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, E.T.; Oemar, U.; Tan, X.R.; Du, Y.; Borgna, A.; Hidajat, K.; Kawi, S. Bimetallic Ni–Cu Catalyst Supported on CeO2 for High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction: Methane Suppression via Enhanced CO Adsorption. J. Catal. 2014, 314, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, E.T.; Oemar, U.; Ang, M.L.; Hidajat, K.; Kawi, S. Highly Active and Stable Bimetallic Nickel–Copper Core–Ceria Shell Catalyst for High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 3358–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayakul, K.; Srithanratana, T.; Hengrasmee, S. Catalytic Activities of Re–Ni/CeO2 Bimetallic Catalysts for Water Gas Shift Reaction. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Miyao, T.; Higashiyama, K.; Yamashita, H.; Watanabe, M. Preparation of a Mesoporous Ceria–Zirconia Supported Ni–Fe Catalyst for the High Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerveny, L. (Ed.) Catalytic Hydrogenation. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 27, pp. 1–677. [Google Scholar]
- Masai, M.; Honda, K.; Kubota, A.; Ohnaka, S.; Nishikawa, Y.; Nakahara, K.; Kishi, K.; Ikeda, S. Dehydrogenation and Hydrogenation Activity of Palladium-Tin-Silica and Nickel-Tin-Silica. J. Catal. 1977, 50, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengne, A.M.; Samal, A.K.; Enakonda, L.R.; Harb, M.; Gevers, L.E.; Anjum, D.H.; Hedhili, M.N.; Saih, Y.; Huang, K.-W.; Basset, J.-M. Ni−Sn-Supported ZrO2 Catalysts Modified by Indium for Selective CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3688–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, G.W.; Shabaker, J.; Dumesic, J. Raney Ni-Sn Catalyst for H2 Production from Biomass-derived Hydrocarbons. Science 2003, 300, 2075–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Porosoff, M.D.; Chen, J.G. Effects of Oxide Supports on the Water-Gas Shift Reaction over Pt−Ni Bimetallic Catalysts: Activity and Methanation Inhibition. Catal. Today 2014, 233, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.K.; Gunasekara, K.; Boolchand, P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Cr- and Ce-Doped Ferrite Catalysts for the High Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction: TPR and Mossbauer Spectroscopic Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damma, D.; Jampaiah, D.; Welton, A.; Boolchand, P.; Arvanitis, A.; Dong, J.; Smirniotis, P.G. Effect of Nb Modification on the Structural and Catalytic Property of Fe/Nb/M (M = Mn, Co, Ni, and Cu) Catalyst for High Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction. Catal. Today 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.; Jeong, D.-W.; Jang, W.-J.; Rode, C.V.; Roh, H.-S. Mesoporous NiCu–CeO2 Oxide Catalysts for High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, D.; Thrimurthulu, G.; Smirniotis, P.G.; Reddy, B.M. Nanocrystalline Alumina-Supported Ceria–Praseodymia Solid Solutions: Structural Characteristics and Catalytic CO Oxidation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 44826–44837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, D.; Reddy, L.H.; Kuntaiah, K.; Reddy, B.M. Design of Novel Ceria-Based Nano-Oxides for CO Oxidation and Other Catalytic Applications. Indian J. Chem. 2012, 51A, 186–195. [Google Scholar]
- Devaiah, D.; Smirniotis, P.G. Effects of the Ce and Cr Contents in Fe−Ce−Cr Ferrite Spinels on the High-Temperature Water−Gas Shift Reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, Z.; Xie, H.; Maeda, N.; Miao, L.; Wang, Z. Insight Into the Mesoporous FexCe1−xO2−δ Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3: Regulable Structure and Activity. J. Catal. 2016, 338, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, R.; Zhou, W. A Wire-Shaped Supercapacitor in Micrometer Size Based on Fe3O4 Nanosheet Arrays on Fe Wire. Nano Micro Lett. 2017, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, A.; Weiss, W.; Van Hove, M.A.; Somorjai, G.A. Magnetite Fe3O4(111): Surface Structure by LEED Crystallography and Energetic. Surf. Sci. 1994, 302, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.-W.; Jha, A.; Jang, W.-J.; Han, W.-B.; Roh, H.-S. Performance of Spinel Ferrite Catalysts Integrated with Mesoporous Al2O3 in the High Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 265, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damma, D.; Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P.G. High-Temperature Water-Gas Shift over Fe/Ce/Co Spinel Catalysts: Study of the Promotional Effect of Ce and Co. Mol. Catal. 2018, 451, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andana, T.; Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Russo, N.; Fino, D.; Pirone, R. Nanostructured Ceria-Praseodymia Catalysts for Diesel Soot Combustion. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 197, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-O.; Na, H.-S.; Jha, A.; Jang, W.J.; Jeong, D.-W.; Nah, I.W.; Jeon, B.-H.; Roh, H.-S. Effect of Preparation Method on the Oxygen Vacancy Concentration of CeO2-Promoted Cu/γ-Al2O3 Catalysts for HTS Reactions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouotou, P.M.; Vieker, H.; Tian, Z.Y.; Ngamou, P.H.T.; Kasmi, A.E.; Beyer, A.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K. Structure–Activity Relation of Spinel-Type Co–Fe Oxides for Low-Temperature CO Oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 3359–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zou, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Dong, X.; Gao, F.; Deng, Y.; Tang, C.; Chen, Z.; et al. Correlation Between the Physicochemical Properties and Catalytic Performances of CexSn1–xO2 Mixed Oxides for NO Reduction by CO. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 144, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, X.; Han, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of La, Ce, and Y Oxides on SnO2 Catalysts for CO and CH4 Oxidation. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2025–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, K.G.; Babich, I.V.; Seshan, K.; Lefferts, L. Bifunctional Catalysts for Single-Stage Water–Gas Shift Reaction in Fuel Cell Applications.: Part 1. Effect of the Support on the Reaction Sequence. J. Catal. 2007, 251, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabow, L.; Xu, Y.; Mavrikakis, M. Lattice Strain Effects on CO Oxidation on Pt(111). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 3369–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shan, J.; Tao, F. The Role of Copper in Catalytic Performance of a Fe–Cu–Al–O Catalyst for Water Gas Shift Reaction. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4385–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio, L.; Zhou, G.; González, I.D.; Estrella, M.; Hanson, J.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Navarro, R.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. In Situ Characterization of Pt Catalysts Supported on Ceria Modified TiO2 for the WGS Reaction: Influence of Ceria Loading. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, S.; Shimizu, T.; Otsuka, K. Complete Removal of Carbon Monoxide in Hydrogen-Rich Gas Stream through Methanation over Supported Metal Catalysts. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2004, 29, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamaras, C.M.; Americanou, S.; Efstathiou, A.M. “Redox” vs “Associative Formate with –OH Group Regeneration” WGS Reaction Mechanism on Pt/CeO2: Effect of Platinum Particle Size. J. Catal. 2011, 279, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigos, J.M.; Brooks, C.J.; Jacobs, G.; Davis, B.H. Low Temperature Water-Gas Shift: Characterization of Pt-Based ZrO2 Catalyst Promoted with Na Discovered by Combinatorial Methods. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 319, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulou, P.; Chistodoulakis, A.; Kondarides, D.I.; Boghosian, S. Particle Size Effects on the Reducibility of Titanium Dioxide and its Relation to the Water–Gas Shift Activity of Pt/TiO2 Catalysts. J. Catal. 2006, 240, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Catalysts | Crystallite Size (nm) a | Lattice Strain b | Lattice Parameter (Å) c |
|---|---|---|---|
| FeCeOx | 13.0 | 0.011 | 8.3738 |
| Ni/FeCeOx | 11.7 | 0.013 | 8.3931 |
| Sn/FeCeOx | 15.5 | 0.004 | 8.4118 |
| NiSn/FeCeOx | 10.5 | 0.017 | 8.4091 |
| Catalysts | Wt % a | BET SA (m2/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Ce | Ni | Sn | Fresh | Reduced | |
| FeCeOx | 83.82 (83.33) | 16.18 (16.67) | - | - | 115 | 101 |
| Ni/FeCeOx | 74.13 (75) | 15.64 (15) | 10.23 (10) | - | 85 | 73 |
| Sn/FeCeOx | 74.57 (75) | 14.87 (15) | - | 10.56 (10) | 70 | 62 |
| NiSn/FeCeOx | 75.18 (75) | 14.92 (15) | 5.07 (5) | 4.83 (5) | 94 | 85 |
| Catalysts | Fe3+/Fe2+ | Ce4+/Ce3+ | Ni0/Ni2+ | Sn0/Sn2++Sn4+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeCeOx | 1.65 | 2.77 | - | - |
| Ni/FeCeOx | 1.78 | 2.94 | 0.32 | - |
| Sn/FeCeOx | 1.76 | 3.57 | - | 0.12 |
| NiSn/FeCeOx | 1.80 | 5.26 | 0.45 | 0.32 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Damma, D.; Smirniotis, P.G. FeCeOx Supported Ni, Sn Catalysts for the High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts 2020, 10, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060639
Damma D, Smirniotis PG. FeCeOx Supported Ni, Sn Catalysts for the High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts. 2020; 10(6):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060639
Chicago/Turabian StyleDamma, Devaiah, and Panagiotis G. Smirniotis. 2020. "FeCeOx Supported Ni, Sn Catalysts for the High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction" Catalysts 10, no. 6: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060639
APA StyleDamma, D., & Smirniotis, P. G. (2020). FeCeOx Supported Ni, Sn Catalysts for the High-Temperature Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Catalysts, 10(6), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10060639






