Deactivation of a Vanadium-Based SCR Catalyst Used in a Biogas-Powered Euro VI Heavy-Duty Engine Installation
Abstract
1. Introduction
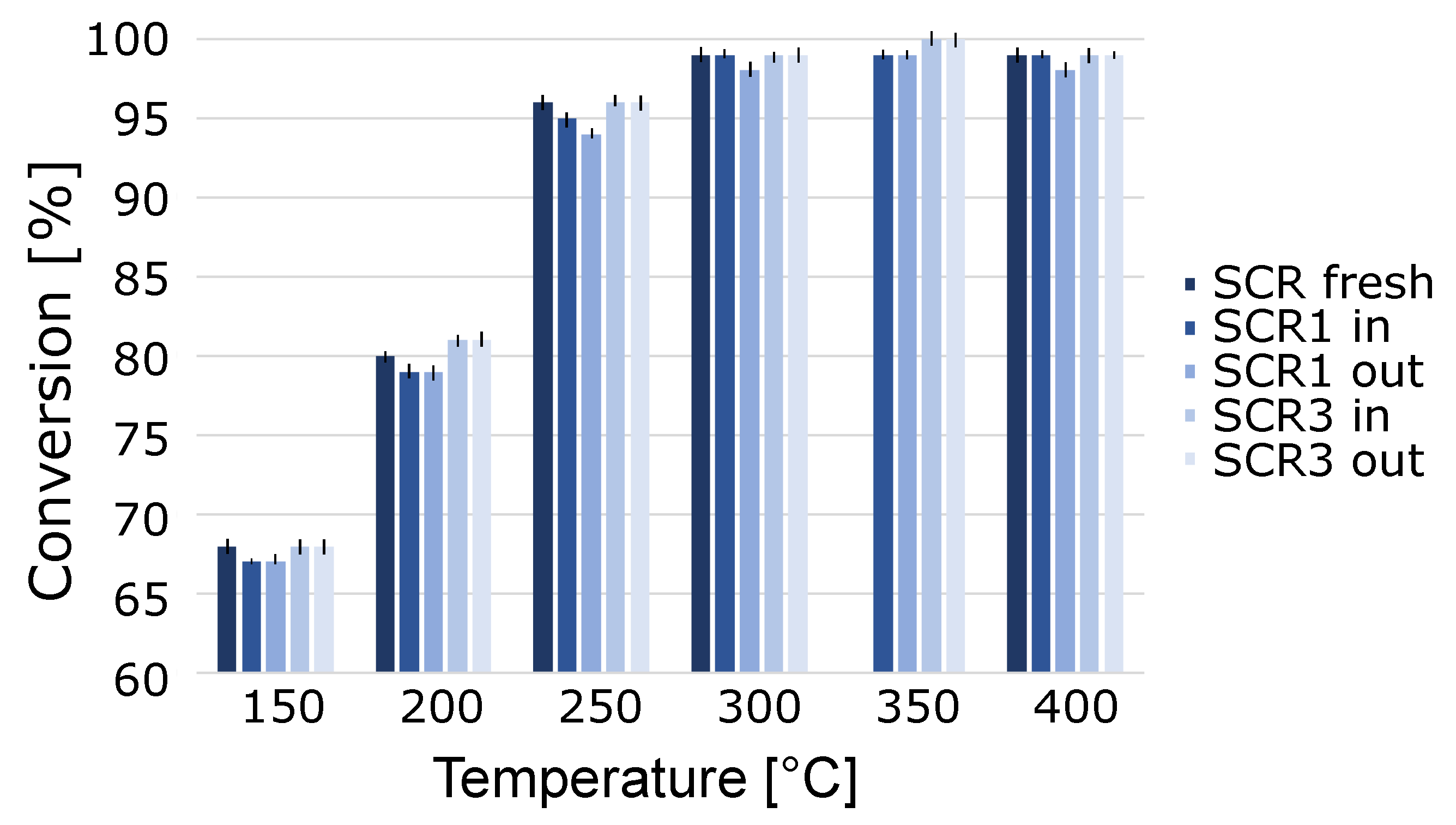
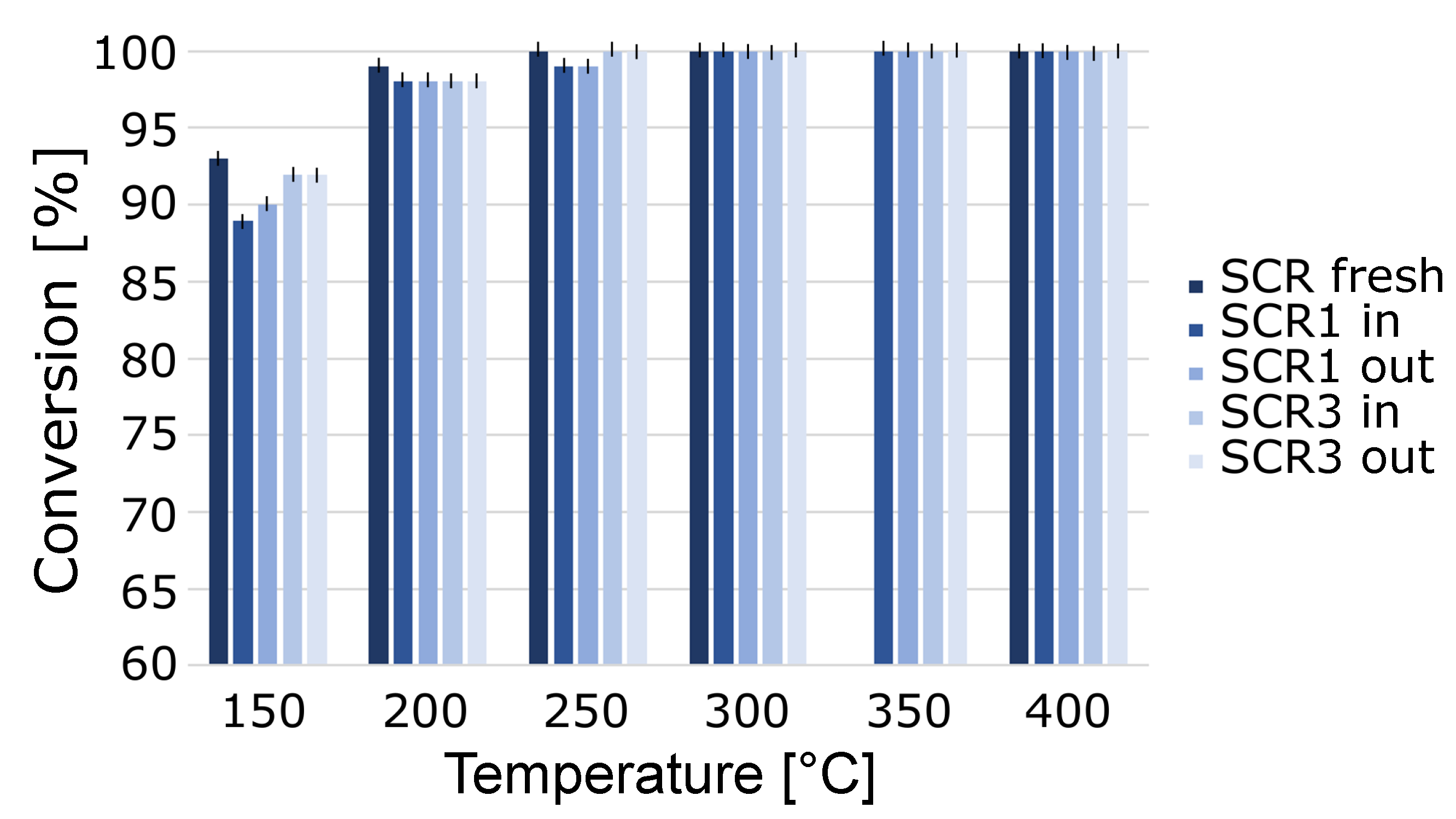
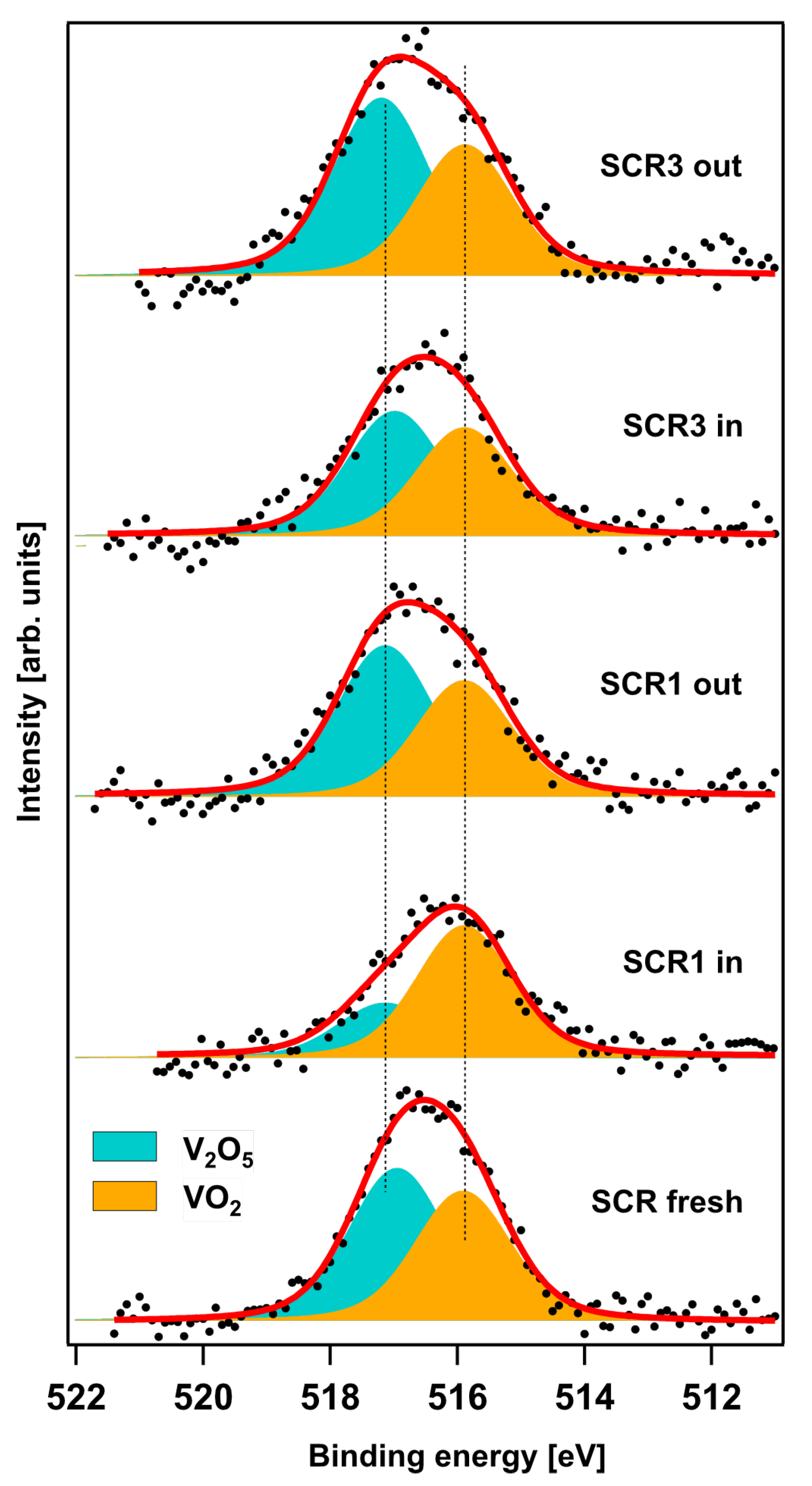
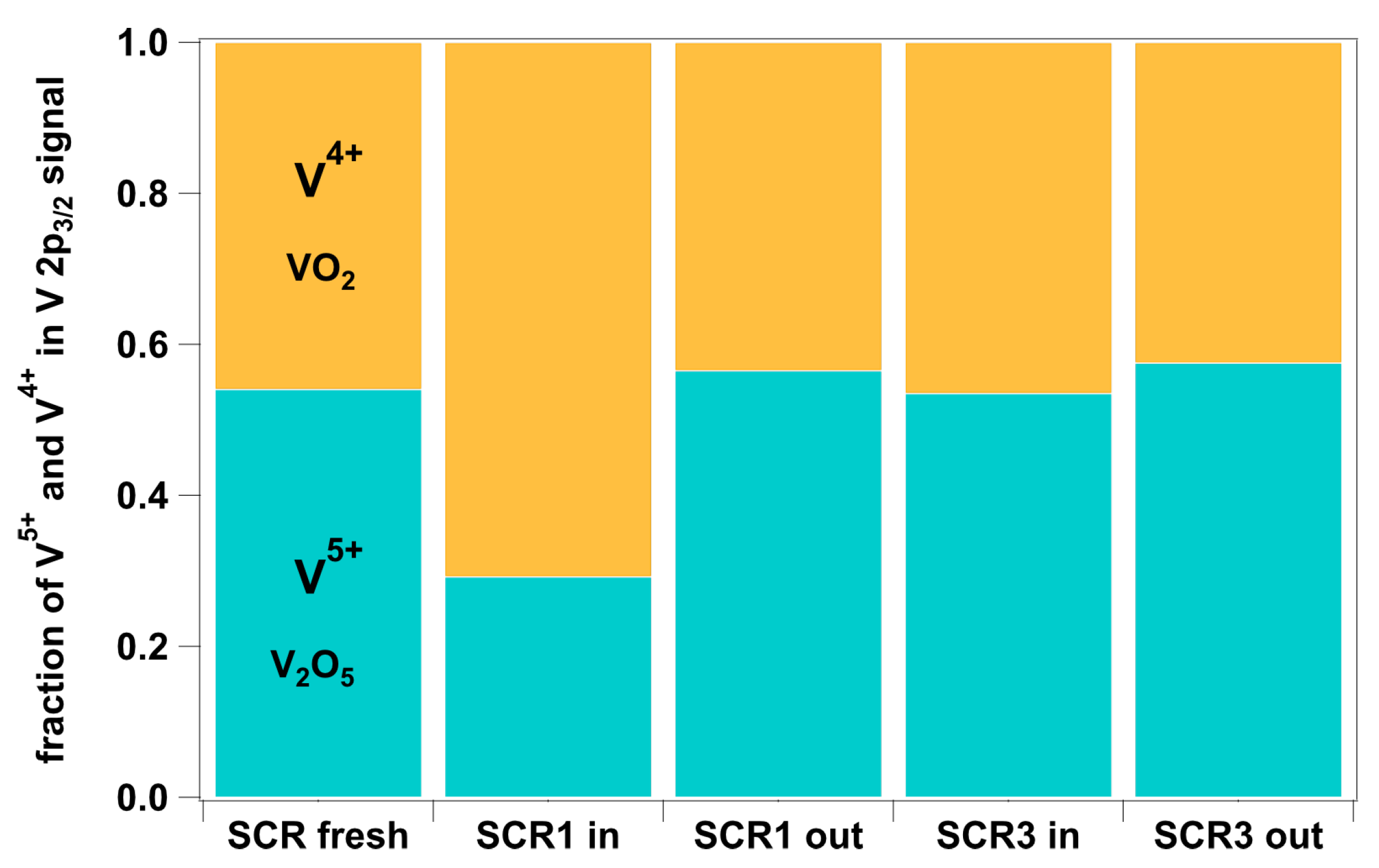
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Material
3.2. SCR Performance
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Regulation (EU) 2019/631. Official Journal of the European Union: Brussels, 2019. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32019R0631 (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Regulations No 595/2009; Official Journal of the European Union: Brussels, 2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2009/595/oj (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Binder, A.J.; Toops, T.J.; Unocic, R.R.; Parks, J.E., II; Dai, S. Low-Temperature CO Oxidation over a Ternary Oxide Catalyst with High Resistance to Hydrocarbon Inhibition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13263–13267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlin, S.; Nilsson, M.; Bäckström, D.; Bergman, S.L.; Bengtsson, E.; Bernasek, S.L.; Pettersson, L.J. Multivariate analysis of the effect of biodiesel-derived contaminants on V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 183, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiodo, V.; Maisano, S.; Zafarana, G.; Urbani, F. Effect of pollutants on biogas steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koebel, M.; Strutz, E.O. Thermal and Hydrolytic Decomposition of Urea for Automotive Selective Catalytic Reduction Systems: Thermochemical and Practical Aspects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2003, 42, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadas, M.; Kröcher, O.; Elsener, M.; Wokaun, A.; Söger, N.; Pfeifer, M.; Demel, Y.; Mussmann, L. Influence of NO2 on the selective catalytic reduction of NO with ammonia over Fe-ZSM5. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 67, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammershøi, P.S.; Jensen, A.D.; Janssens, T.V. Impact of SO2-poisoning over the lifetime of a Cu-CHA catalyst for NH3-SCR. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 238, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammershøi, P.S.; Jangjou, Y.; Epling, W.S.; Jensen, A.D.; Janssens, T.V. Reversible and irreversible deactivation of Cu-CHA NH3-SCRcatalysts by SO2 and SO3. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 226, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezcano-Gonzalez, I.; Deka, U.; van der Bij, H.; Paalanen, P.; Arstad, B.; Weckhuysen, B.; Beale, A. Chemical deactivation of Cu-SSZ-13 ammonia selective catalytic reduction (NH3-SCR) systems. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 154–155, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Shi, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; He, H. Deactivation of Cu-SSZ-13 in the presence of SO2 during hydrothermal aging. Catal. Today 2019, 320, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, H.; Takahashi, K.; Odenbrand, I. Surface acid property and its relation to SCR activity of phosphorus added to commercial V2O5(WO3)/TiO2 catalyst. Catal. Lett. 1998, 53, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, M.; Kern, P.; Heinzelmann, T.; Lucas, M.; Claus, P. High-throughput study of the effects of inorganic additives and poisons on NH3-SCR catalysts—Part I: V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 95, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, D.; Czekaj, I.; Kröcher, O. Chemical deactivation of V2O5/WO3–TiO2 SCR catalysts by additives and impurities from fuels, lubrication oils and urea solution: Part II. Characterization study of the effect of alkali and alkaline earth metals. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 77, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Ge, M. The poisoning effect of alkali metals doping over nanoV2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeman, P.; Arnby, K.; Marsh, P.; Newman, C.; Smedler, G. Optimization of an SCR Catalyst System to Meet EUIV Heavy Duty Diesel Legislation. In Proceedings of the 2008 SAE International Powertrains, Fuels and Lubricants Congress, Berlin, Germany, 16–18 June 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granestrand, J.; Dahlin, S.; Immele, O.; Schmalhorst, L.; Lantto, C.; Nilsson, M.; París, R.S.; Regali, F.; Pettersson, L.J. Catalytic aftertreatment systems for trucks fueled by biofuels—Aspects on the impact of fuel quality on catalyst deactivation. RSC Catal. 2018, 30, 64–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröcher, O.; Elsener, M. Chemical deactivation of V2O5/WO3–TiO2 SCR catalysts by additives and impurities from fuels, lubrication oils, and urea solution: I. Catalytic studies. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 77, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, J.; Avila, P.; Barthelemy, C.; Bahamonde, A.; Odriozola, J.; Banda, J.G.D.L.; Heinemann, H. Influence of phosphorus in vanadium-containing catalysts for NOx removal. Appl. Catal. 1989, 55, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellino, F.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Jensen, A.D.; Johnsson, J.E.; Fehrmann, R. Deactivation of vanadia-based commercial SCR catalysts by polyphosphoric acids. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2008, 83, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englund, J.; Xie, K.; Dahlin, S.; Schaefer, A.; Jing, D.; Shwan, S.; Andersson, L.; Carlsson, P.A.; Pettersson, L.J.; Skoglundh, M. Deactivation of a Pd/Pt Bimetallic Oxidation Catalyst Used in a Biogas-Powered Euro VI Heavy-Duty Engine Installation. Catalysts 2019, 9, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iojoiu, E.; Lauga, V.; Abboud, J.; Legros, G.; Bonnety, J.; Da Costa, P.; Schobing, J.; Brillard, A.; Leyssens, G.; Tschamber, V.; et al. Biofuel Impact on Diesel Engine After-Treatment: Deactivation Mechanisms and Soot Reactivity. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2018, 4, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silversmit, G.; Depla, D.; Poelman, H.; Marin, G.B.; De Gryse, R. Determination of the V2p XPS binding energies for different vanadium oxidation states (V5+ to V0+). J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2004, 135, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Wang, Z.M.; Ma, M.S.; Li, S. X-ray photoemission studies of praseodymium thin films on SiO2/Si(100). J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 5857–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupin, J.C.; Gonbeau, D.; Vinatier, P.; Levasseur, A. Systematic XPS studies of metal oxides, hydroxides and peroxides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannisto, H.; Ingelsten, H.H.; Skoglundh, M. Ag-Al2O3 catalysts for lean NOx reduction—Influence of preparation method and reductant. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 302, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; E’Sobol, P.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elmer Corporation: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.L.; Papp, T. Widths of the Atomic K–N7 Levels. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2001, 77, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


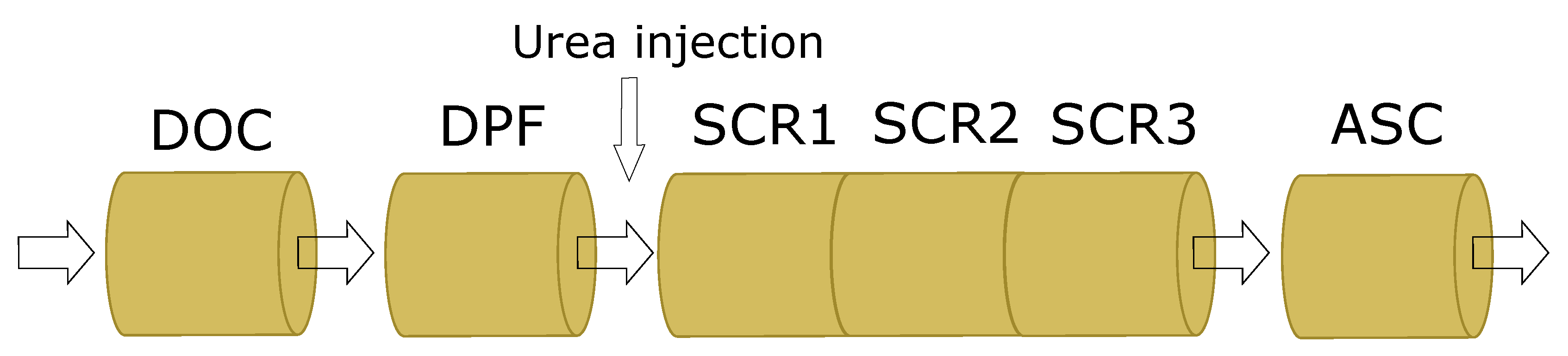
| Sample Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SCR fresh | Fresh sample of the SCR catalyst |
| SCR1 in | Inlet sample of the first consecutive engine-bench aged SCR catalyst |
| SCR1 out | Outlet sample of the first consecutive engine-bench aged SCR catalyst |
| SCR3 in | Inlet sample of the third and last consecutive engine-bench aged SCR catalyst |
| SCR3 out | Outlet sample of the third and last consecutive engine-bench aged SCR catalyst |
| DPF in | Inlet sample of the engine-bench aged DPF |
| DPF out | Outlet sample of the engine-bench aged DPF |
| Sample | Desorbed Amount of NH3 [% of SCR Fresh] | Tmax [°C] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCR fresh | 100 | 236 | |
| SCR1 in | 76 | 253 | |
| SCR1 out | 48 | 229 | |
| SCR3 in | 87 | 238 | |
| SCR3 out | 48 | 226 |
| Sample | Phosphorus [%] | Sulfur [ppm] | Calcium [ppm] | Zinc [ppm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCR fresh | 0.19 * | 400 | 1.7 | - |
| SCR1 in | 0.17 * | 630 | 1.5 | - |
| SCR1 out | 0.20 * | 820 | 1.6 | - |
| SCR3 in | 0.18 * | 650 | 1.5 | - |
| SCR3 out | 0.18 * | 840 | 1.6 | - |
| DPF in | 0.06 * | 890 | 380 | 160 |
| DPF out | 0.09 * | 1300 | 1000 | 480 |
| DOC fresh ** | 0.00 | 0 | 280 | - |
| DOC in ** | 0.18 | 2700 | 470 | - |
| DOC out ** | 0.04 | 2500 | 320 | - |
| Step | NO [vol.-ppm] | NO2 [vol.-ppm] | NH3 [vol.-ppm] | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1000 | - | 1100 | Standard SCR |
| 2 | 500 | 500 | 1100 | Fast SCR |
| 3 | 250 | 750 | 1100 | NO2-rich SCR |
| 4 | - | - | 1000 | NH3 oxidation |
| 5 | - | - | - | Cooling to 150 °C in pure argon |
| 6 | - | - | 400 | NH3 adsorption for TPD |
| 7 | - | - | - | Argon flush |
| 8 | - | - | - | NH3 desorption at a heating rate of 10 °C/min to 500 °C |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Englund, J.; Dahlin, S.; Schaefer, A.; Xie, K.; Andersson, L.; Shwan, S.; Carlsson, P.-A.; Pettersson, L.J.; Skoglundh, M. Deactivation of a Vanadium-Based SCR Catalyst Used in a Biogas-Powered Euro VI Heavy-Duty Engine Installation. Catalysts 2020, 10, 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050552
Englund J, Dahlin S, Schaefer A, Xie K, Andersson L, Shwan S, Carlsson P-A, Pettersson LJ, Skoglundh M. Deactivation of a Vanadium-Based SCR Catalyst Used in a Biogas-Powered Euro VI Heavy-Duty Engine Installation. Catalysts. 2020; 10(5):552. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050552
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnglund, Johanna, Sandra Dahlin, Andreas Schaefer, Kunpeng Xie, Lennart Andersson, Soran Shwan, Per-Anders Carlsson, Lars J. Pettersson, and Magnus Skoglundh. 2020. "Deactivation of a Vanadium-Based SCR Catalyst Used in a Biogas-Powered Euro VI Heavy-Duty Engine Installation" Catalysts 10, no. 5: 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050552
APA StyleEnglund, J., Dahlin, S., Schaefer, A., Xie, K., Andersson, L., Shwan, S., Carlsson, P.-A., Pettersson, L. J., & Skoglundh, M. (2020). Deactivation of a Vanadium-Based SCR Catalyst Used in a Biogas-Powered Euro VI Heavy-Duty Engine Installation. Catalysts, 10(5), 552. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10050552





