Electrochemical Fingerprint of CuS-Hexagonal Chemistry from (Bis(N-1,4-Phenyl-N-(4-Morpholinedithiocarbamato) Copper(II) Complexes) as Photon Absorber in Quantum-Dot/Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
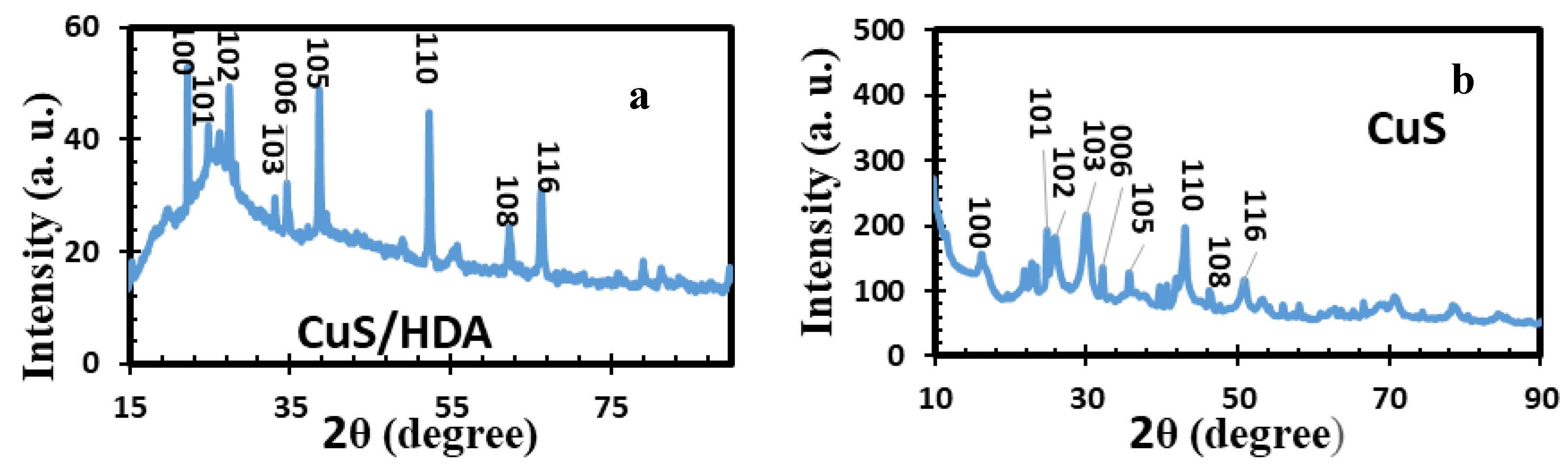
2.1. X-Ray Diffraction of Metal Sulfide Nanoparticles
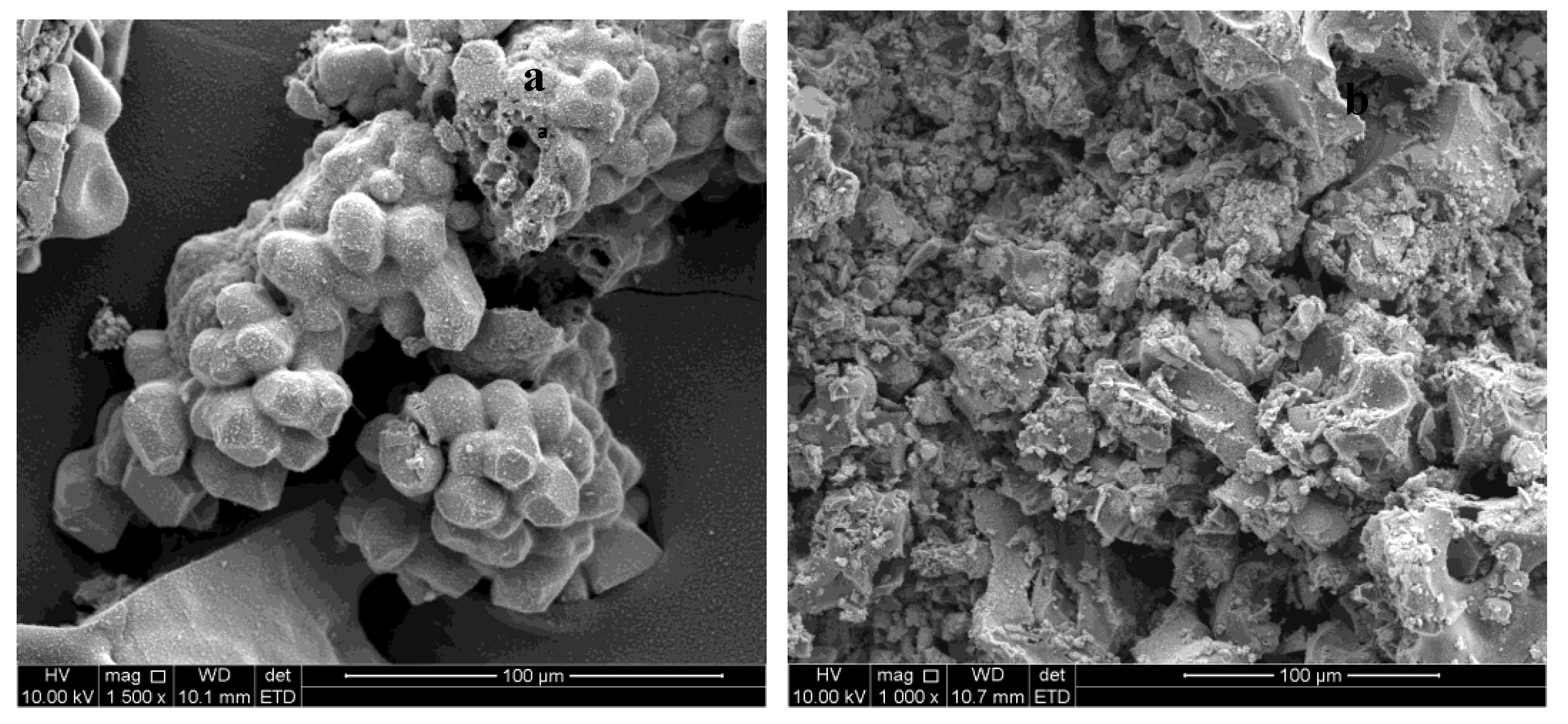
2.2. SEM of Metal Sulfide Nanoparticles
2.3. Atomic-Force Microscopy of Metal Sulfide Nanoparticles
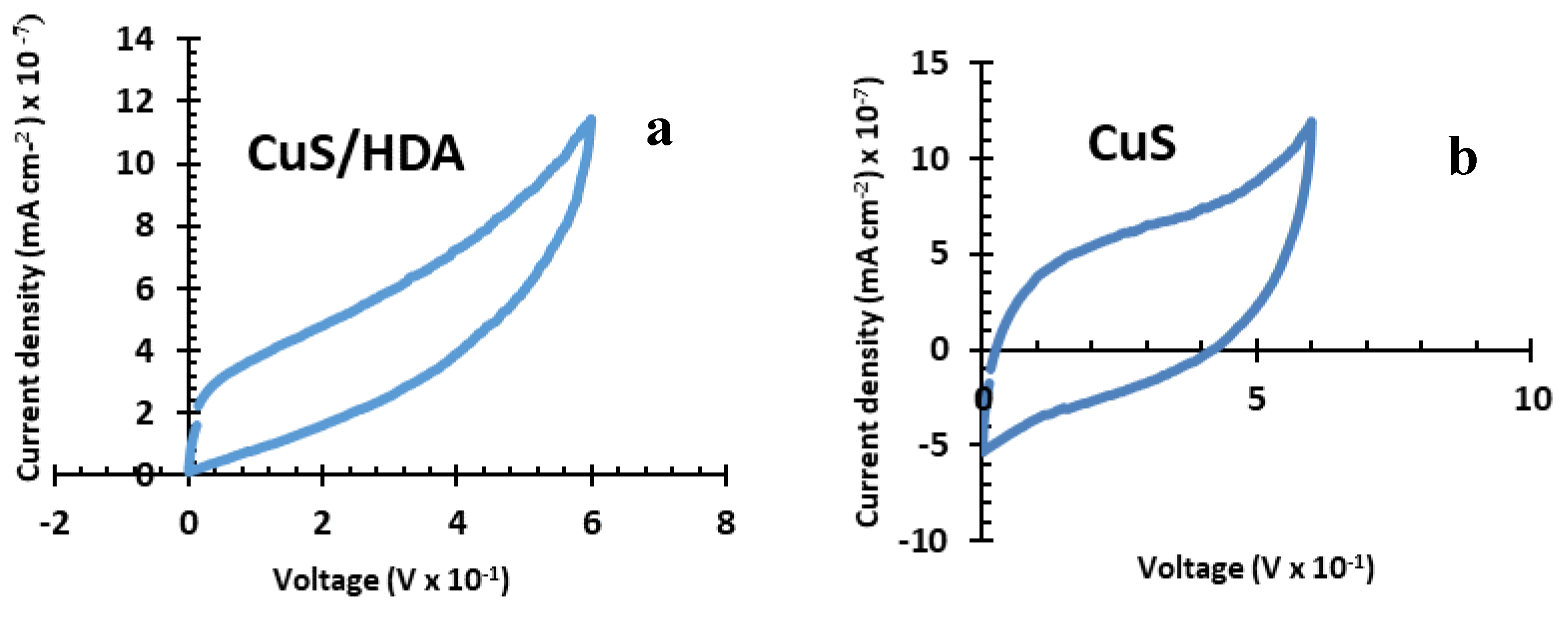
2.4. Cyclic-Voltammetry Results
2.5. Electrochemical-Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
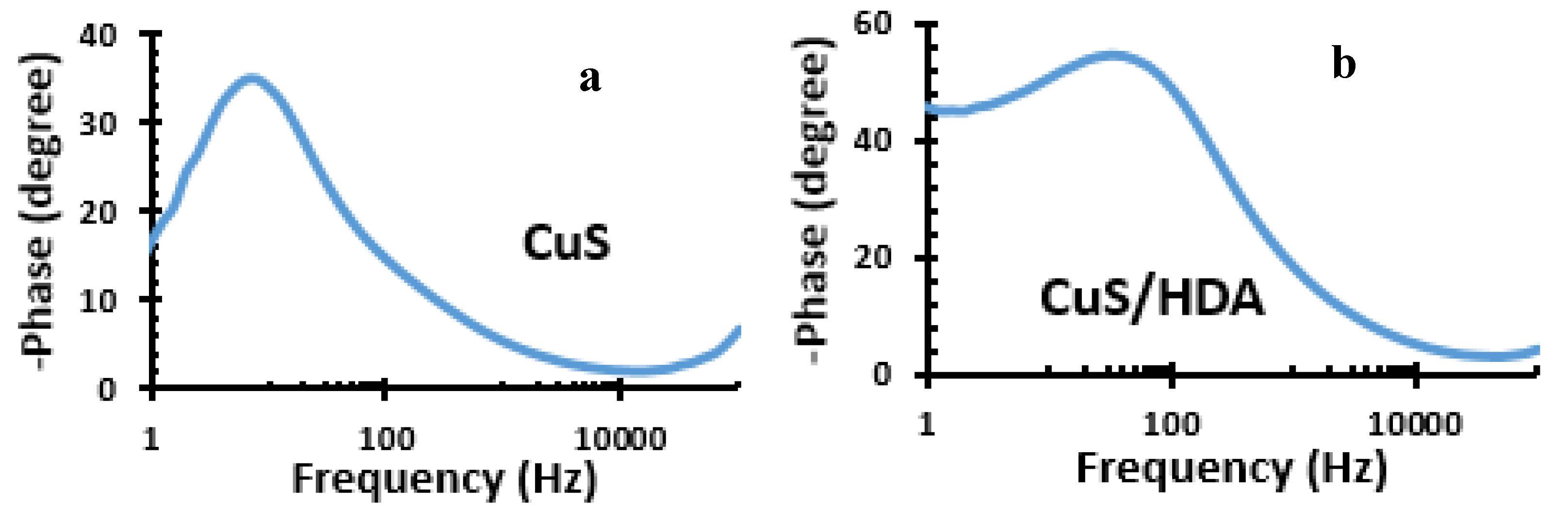
2.6. Bode Plot of Metal Sulfide Nanoparticles
2.7. I–V Results
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of CuS Nanoparticles with HDA Capping Agent
3.3. Synthesis of CuS Nanoparticles without HDA Capping Agent
3.4. Solar-Cell Fabrication and Assembly
3.5. Characterisation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundu, J.; Khilari, S.; Bhunia, K.; Pradhan, D. Ni-Doped CuS as an efficient electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetzel, M.; Janssen, R.A.; Mitzi, D.B.; Sargent, E.H. Materials interface engineering for solution-processed photovoltaics. Nature 2012, 488, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreos, A.; Börjesson, K.; Wang, Z.; Roffey, A.; Norwood, Z.; Kushnir, D.; Moth-Poulsen, K. Exploring the potential of a hybrid device combining solar water heating and molecular solar thermal energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiti, A.K. Tidal power technology review with potential applications in Gulf Stream. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singal, S.K. Operation of hydro power plants-a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.K. Solar power generation by PV (photovoltaic) technology: A review. Energy 2013, 53, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Hussain, A.; Ahmed, R.; Wang, M.K.; Zhao, C.; Haq, B.U.; Fu, Y.Q. Advances in nanostructured thin film materials for solar cell applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, W.A. A review on solar cells from Si-single crystals to porous materials and quantum dots. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.H.; Protesescu, L.; Kovalenko, M.V.; Loi, M.A. Sensitized solar cells with colloidal PbS–CdS core–shell quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ji, H.; Yu, P.; Wang, Z. Recent progress towards quantum dot solar cells with enhanced optical absorption. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pan, Z.; Zhong, X. CuInSe2 and CuInSe2–ZnS based high efficiency “green” quantum dot sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Q.; He, B.; Yu, L. Recent advances in critical materials for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17497–17510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, D.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Stamplecoskie, K.G.; Kamat, P.V. Size-dependent photovoltaic performance of CuInS2 quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 7221–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sun, J.; Guo, P.C.; Yang, Z.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.F. Enhancement in efficiency of CdS/CdSe quantum dots-sensitized solar cells based on ZnO nanostructures by introduction of MnS layer. Mater. Lett. 2018, 215, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwafemi, O.S. Quantum dots for solar cell applications. In Nanomaterials for Solar Cell Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 377–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isac, L.; Cazan, C.; Alexandru, E.; Andronic, L. Copper Sulfide Based Heterojunctions as Photocatalysts for Dyes Photodegradation. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y.; Guo, K.; Hu, F. Novel method of constructing CdS/ZnS heterojunction for high performance and stable photocatalytic activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 380, 111859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, C.; Ibanez, M.; Dobrozhan, O.; Singh, A.; Cabot, A.; Ryan, K.M. Compound copper chalcogenide nanocrystals. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 5865–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Swihart, M.T. Plasmonic copper sulfide-based materials: A brief Introduction to their synthesis, doping, alloying, and applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 13435–13447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Sakamoto, M.; Matsunaga, H.; Vequizo, J.J.M.; Yamakata, A.; Haruta, M.; Kurata, H.; Ota, W.; Sato, T.; Teranishi, T. Near infrared light induced plasmonic hot hole transfer at a nano-heterointerface. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Stam, W.; Gudjonsdottir, S.; Evers, W.H.; Houtepen, A.J. Switching between plasmonic and fluorescent copper sulfide nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13208–13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Swihart, M.T. Reversible crystal phase interconversion between covellite CuS and high chalcocite Cu2S nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 4783–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toe, C.Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, H.; Scott, J.; Amal, R.; Ng, Y.H. Transformation of cuprous oxide into hollow copper sulfide cubes for photocatalytic hydrogen generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 14072–14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Shao, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Ding, M.; Huang, J.; Xu, X. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of CdS decorated CuS microflower-like structures for enhanced photocatalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, L.; Sheng, Y. Durable superhydrophobic cotton textiles with ultraviolet-blocking property and photocatalysis based on flower-like copper sulfide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 6714–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethravathi, C.; Rajamathi, J.T.; Rajamathi, M. Microwave-assisted synthesis of porous aggregates of CuS nanoparticles for sunlight photocatalysis. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 4825–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xin, Y.; Chai, C.; Chen, Q. Construction of immobilized CuS/TiO2 nanobelts heterojunction photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of enrofloxacin: Synthesis, characterization, influencing factors and mechanism insight. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rühle, S.; Shalom, M.; Zaban, A. Quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. ChemPhysChem. 2010, 11, 2290–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.L.; Mbese, J.Z.; Agoro, M.A. The Frontiers of Nanomaterials (SnS, PbS and CuS) for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Applications: An Exciting New Infrared Material. Molecules 2019, 24, 4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, G.; Zou, H.; Shi, J. Amylose-directed synthesis of CuS composite nanowires and microspheres. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, S.H.; Deshpande, M.P.; Tailor, J.P. Characterization of CuS nanocrystalline thin films synthesized by chemical bath deposition and dip coating techniques. Thin Solid Film. 2014, 550, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzari, M.; Abaab, M.; Rezig, B.; Brunel, M. Effect of substrate thermal gradient on as-grown CuInS2 properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 1997, 32, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi-Kamazani, M.; Zarghami, Z.; Salavati-Niasari, M. Facile and novel chemical synthesis, characterization, and formation mechanism of copper sulfide (Cu2S, Cu2S/CuS, CuS) nanostructures for increasing the efficiency of solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. 2016, 120, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveenkumar, P.; Kalaignan, G.P.; Arulmani, S.; Anandan, S. Solvothermal synthesis of CuS/Cu (OH)2 nanocomposite electrode materials for supercapacitor applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 16853–16863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, Y.W.; Do, K.; Ko, J.; Im, S.S. Camphorsulfonic acid-doped polyaniline transparent counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22743–22748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.; Durga, I.K.; Kang, T.S.; Kim, S.K.; Punnoose, D.; Gopi, C.V.; Reddy, A.E.; Krishna, T.N.V.; Kim, H.J. Enhancing the photovoltaic performance and stability of QDSSCs using surface reinforced Pt nanostructures with controllable morphology and superior electrocatalysis via cost-effective chemical bath deposition. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 3450–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Douri, Y.; Khasawneh, Q.; Kiwan, S.; Hashim, U.; Hamid, S.A.; Reshak, A.H.; Bouhemadou, A.; Ameri, M.; Khenata, R. Structural and optical insights to enhance solar cell performance of CdS nanostructures. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 82, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.K.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, Y.G. Synthesis of copper sulfide nanowire arrays for high-performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 139, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgrishi, N.; Rountree, K.J.; McCarthy, B.D.; Rountree, E.S.; Eisenhart, T.T.; Dempsey, J.L. A practical beginner’s guide to cyclic voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ 2018, 95, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.J. In situ growth of hierarchical mesoporous NiCo2S4@MnO2 arrays on nickel foam for high-performance supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 166, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, U.; Öksüzoğlu, R.M.; Baykul, M.C. Deposition potential dependence of composition, microstructure, and surface morphology of electrodeposited Ni–Cu alloy films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 23, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metosen, A.; Bin, A.N.S.; Pang, S.C.; Chin, S.F. Nanostructured multilayer composite films of manganese dioxide/nickel/copper sulfide deposited on polyethylene terephthalate supporting substrate. J. Nanomater. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himasree, P.; Durga, I.K.; Krishna, T.N.V.; Rao, S.S.; Gopi, C.V.M.; Revathi, S.; Prabakar, K.; Kim, H.J. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of CuS@MnS on Ni foam for high performance supercapacitor electrode material. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 305, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, W.; Ma, J.; Mhaisalkar, S.; Maria, T.L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hng, H.H.; et al. Synthesis of porous NiO nanocrystals with controllable surface area and their application as supercapacitor electrodes. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gund, G.S.; Dubal, D.P.; Jambure, S.B.; Shinde, S.S.; Lokhande, C.D. Temperature influence on morphological progress of Ni(OH)2 thin films and its subsequent effect on electrochemical supercapacitive properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 4793–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.; Lin, J.Y.; Tai, S.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, J. A catalytic composite film of MoS2/graphene flake as a counter electrode for Pt-free dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 85, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.P.; Teng, H.; Lee, Y.L. Highly electrocatalytic carbon black/copper sulfide composite counter electrodes fabricated by a facile method for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 23146–23157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, S.S.; Dehghani, H. Ca-doped CuS/graphene sheet nanocomposite as a highly catalytic counter electrode for improving quantum dot-sensitized solar cell performance. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 10880–10886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Tai, S.Y.; Chou, S.W.; Yu, Y.C.; Chang, K.D.; Wang, S.; Chien, F.S.S.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, T.W. Facile synthesis of MoS2/graphene nanocomposite with high catalytic activity toward triiodide reduction in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21057–21064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.A.; Kalode, P.Y.; Mane, R.S.; Shinde, D.V.; Doyoung, A.; Keumnam, C.; Sung, M.M.; Ambade, S.B.; Han, S.H. Highly efficient and stable DSSCs of wet-chemically synthesized MoS2 counter electrode. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 5256–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnezhad, M.; Selopal, G.S.; Alsayyari, N.; Akilimali, R.; Navarro-Pardo, F.; Wang, Z.M.; Stansfield, B.; Zhao, H.; Rosei, F. CuS/Graphene Nanocomposite as a Transparent Conducting Oxide and Pt-Free Counter Electrode for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, H3065–H3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.T.; Yang, H.; Sun, X.F.; Xian, T. Preparation and promising application of novel LaFeO3 /BiOBr heterojunction photocatalysts for photocatalytic and photo-Fenton removal of dyes. Opt. Mater. 2020, 100, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, H.; Chen, C.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, X. Irradiation assisted polyacrylamide gel route for the synthesize of the Mg1–xCoxAl2O4 nano-photocatalysts and its optical and photocatalytic performances. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Xian, T.; Yang, H. In Situ Construction of CNT/CuS Hybrids and Their Application in Photodegradation for Removing Organic Dyes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Liang, C.P.; Huang, H.S.; Chen, J.G.; Vittal, R.; Lin, C.Y.; Wu, K.C.W.; Ho, K.C. Electrophoretic deposition of mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles consisting of primary anatase nanocrystallites on a plastic substrate for flexible dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 8346–8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; Gopi, C.V.; Kim, S.K.; Son, M.K.; Jeong, M.S.; Savariraj, A.D.; Prabakar, K.; Kim, H.J. Cobalt sulfide thin film as an efficient counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 133, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulasi-Varma, C.V.; Rao, S.S.; Kumar, C.S.S.P.; Gopi, C.V.; Durga, I.K.; Kim, S.K.; Punnoose, D.; Kim, H.J. Enhanced photovoltaic performance and time varied controllable growth of a CuS nanoplatelet structured thin film and its application as an efficient counter electrode for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells via a cost-effective chemical bath deposition. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 19330–19343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.; Punnoose, D.; Tulasivarma, C.V.; Kumar, C.P.; Gopi, C.V.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, H.J. A strategy to enhance the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells by the highly efficient TiO2/ZnS photoanode. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.G.; Kang, M.G.; Kim, K.M.; Ryu, K.S.; Chang, S.H.; Kim, D.K.; Van de Lagemaat, J.; Benkstein, K.D.; Frank, A.J. Morphological and photoelectrochemical characterization of core- shell nanoparticle films for dye-sensitized solar cells: Zn−O type shell on SnO2 and TiO2 cores. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4246–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Teng, C.Y.; Li, T.L.; Lee, Y.L.; Teng, H. Photoactive p-type PbS as a counter electrode for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kumar, C.S.P.; Punnoose, D.; Kim, S.K.; Gopi, C.V.; Rao, S.S. Facile chemical bath deposition of CuS nano peas like structure as a high efficient counter electrode for quantum-dot sensitized solar cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 739, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Niu, H.; Ji, F.; Wan, L.; Mao, X.; Guo, H.; Xu, J.; Cao, G. Band-structure tailoring and surface passivation for highly efficient near-infrared responsive PbS quantum dot photovoltaics. J. Power Sources 2016, 333, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhyuddin, M.; Ahsan, M.T.; Ali, I.; Khan, T.F.; Akram, M.A.; Basit, M.A. A new insight into solar paint concept: Regeneration of CuS nanoparticles for paintable counter electrodes in QDSSCs. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalanur, S.S.; Chae, S.Y.; Joo, O.S. Transparent Cu1. 8S and CuS thin films on FTO as efficient counter electrode for quantum dot solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 103, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbese, J.Z.; Ajibade, P.A.; Matebese, F.; Agoro, M.A. Optical and Structural Properties of TOPO/HDA Capped CuS-Nanocrystals via Thermal Decomposition of Bis(N-Diisopropyldithiocarbamate)Cu(II) Complex. J. Nano Res. 2019, 59, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.L.; Mbese, J.Z.; Agoro, M.A.; Taziwa, R. Optical and structural-chemistry of SnS nanocrystals prepared by thermal decomposition of bis(N-di-isopropyl-N-octyldithiocarbamato)tin(II) complex for promising materials in solar cell applications. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2020, 52, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dye | Photoanode | Electrolyte | CEs | JSC (mA/cm2) | VOC (mV) | FF | η (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUS/HDA | TiO2 | HI-30 | Pt | 1.78 | 0.877 | 0.1 | 0.15 |
| CUS | TiO2 | HI-30 | Pt | 0.64 | 0.068 | 0.3 | 0.01 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agoro, M.A.; Meyer, E.L.; Mbese, J.Z.; Manu, K. Electrochemical Fingerprint of CuS-Hexagonal Chemistry from (Bis(N-1,4-Phenyl-N-(4-Morpholinedithiocarbamato) Copper(II) Complexes) as Photon Absorber in Quantum-Dot/Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells. Catalysts 2020, 10, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030300
Agoro MA, Meyer EL, Mbese JZ, Manu K. Electrochemical Fingerprint of CuS-Hexagonal Chemistry from (Bis(N-1,4-Phenyl-N-(4-Morpholinedithiocarbamato) Copper(II) Complexes) as Photon Absorber in Quantum-Dot/Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells. Catalysts. 2020; 10(3):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030300
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgoro, Mojeed Adedoyin, Edson Leroy Meyer, Johannes Zanoxolo Mbese, and Kwabena Manu. 2020. "Electrochemical Fingerprint of CuS-Hexagonal Chemistry from (Bis(N-1,4-Phenyl-N-(4-Morpholinedithiocarbamato) Copper(II) Complexes) as Photon Absorber in Quantum-Dot/Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells" Catalysts 10, no. 3: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030300
APA StyleAgoro, M. A., Meyer, E. L., Mbese, J. Z., & Manu, K. (2020). Electrochemical Fingerprint of CuS-Hexagonal Chemistry from (Bis(N-1,4-Phenyl-N-(4-Morpholinedithiocarbamato) Copper(II) Complexes) as Photon Absorber in Quantum-Dot/Dye-Sensitised Solar Cells. Catalysts, 10(3), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10030300







