Assessing an Integral Treatment for Landfill Leachate Reverse Osmosis Concentrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
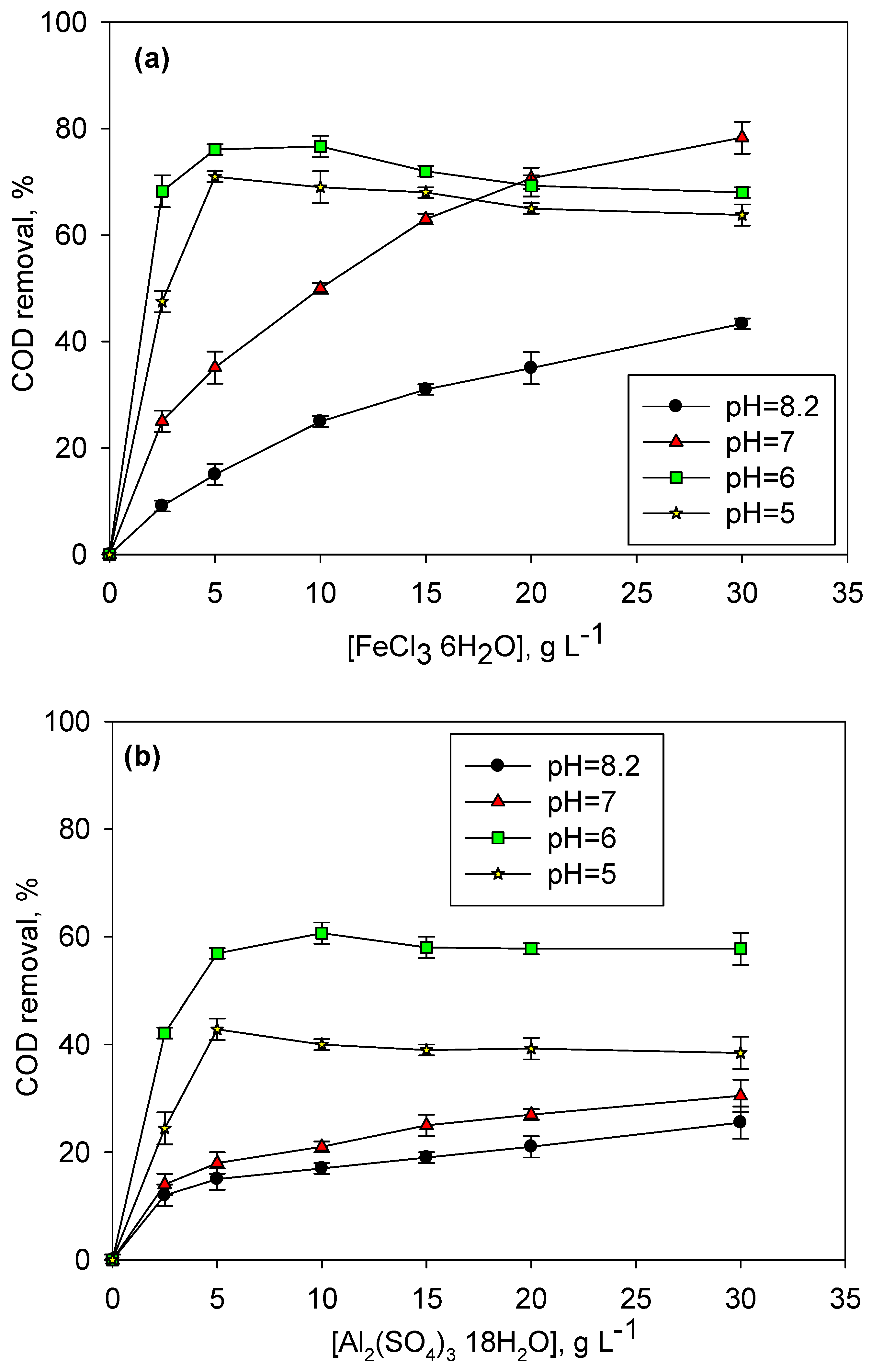
2.1. Coagulation Pretreatment, Effect of pH and Coagulant Dosage
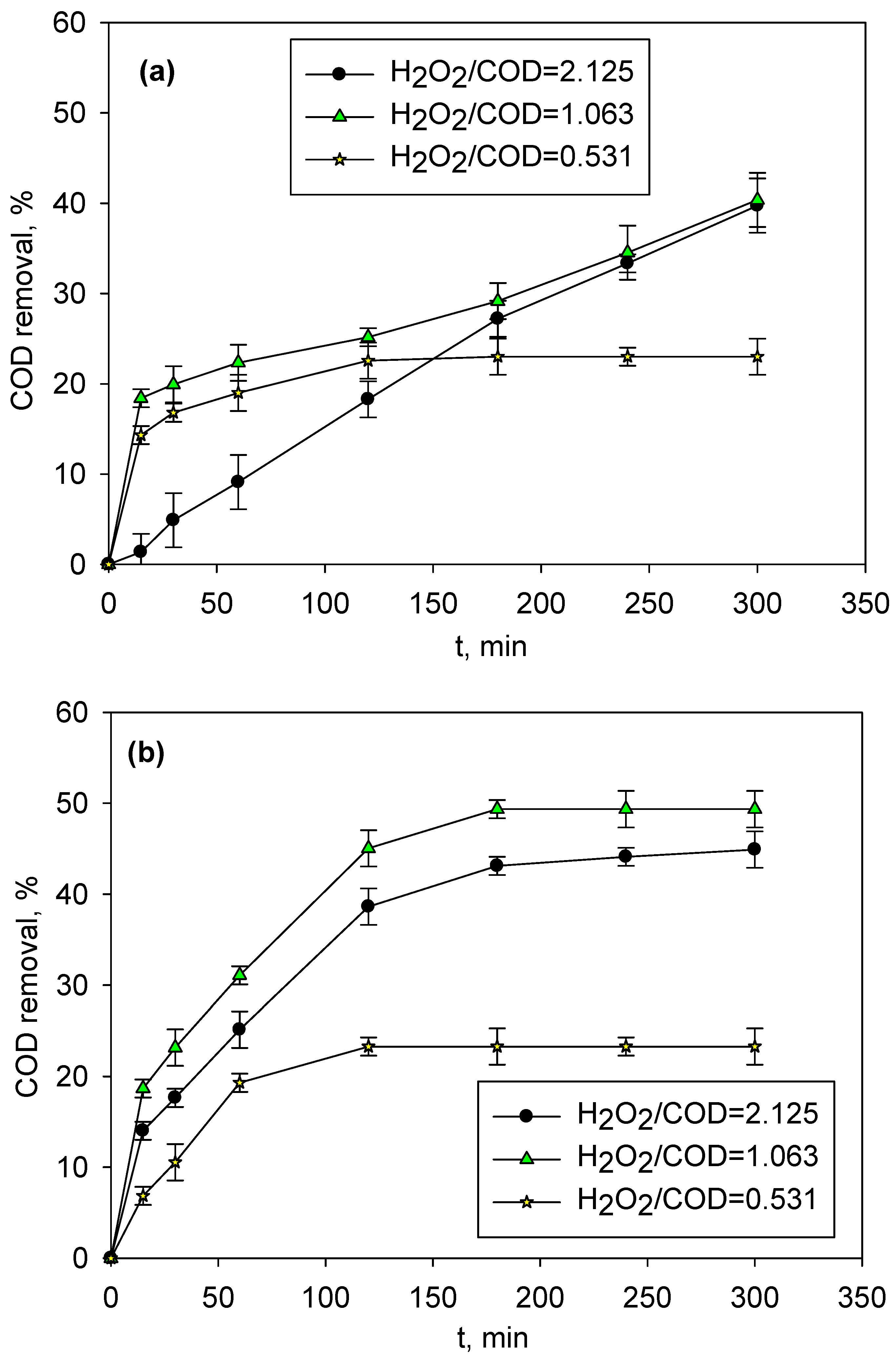
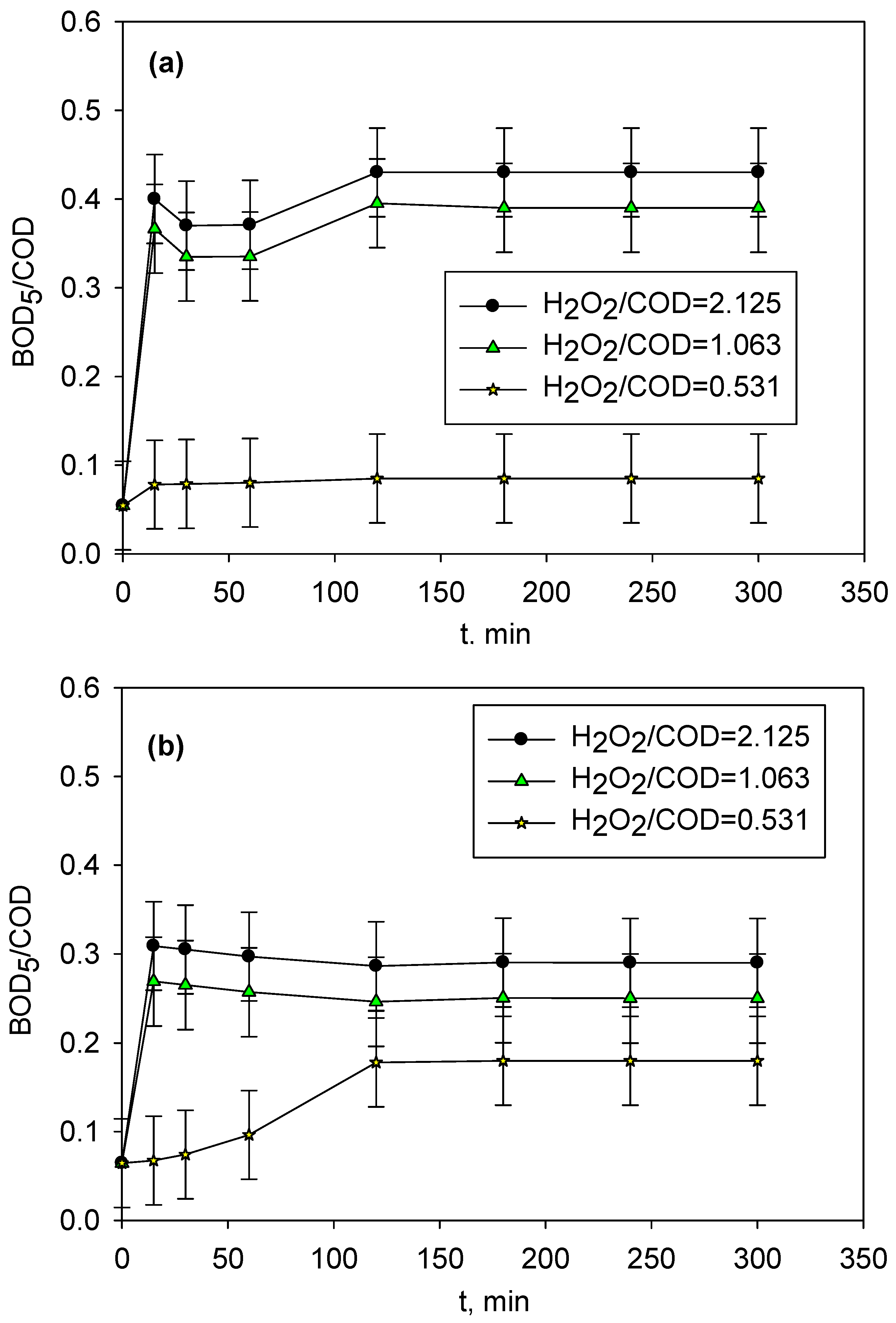
2.2. Photo-Fenton Treatment
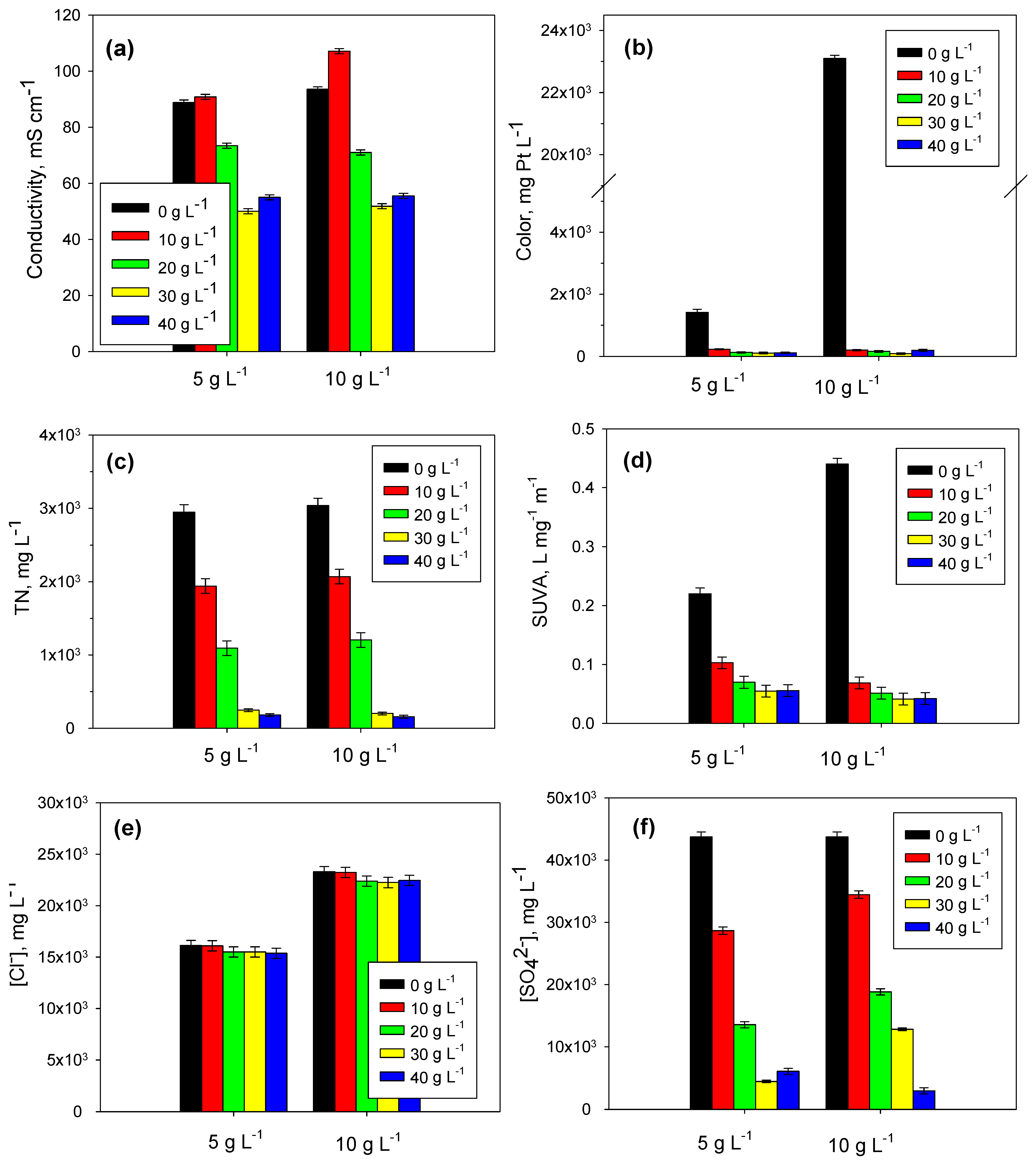
2.3. Lime Treatment
2.4. Economic Assessment
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Landfill Leachate ROC
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Analytical Determinations and Data Processing
3.4. Coagulation/Flocculation Pretreatment
3.5. Photo-Fenton Treatment
3.6. Lime Precipitation Step
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koc-Jurczyk, J.; Jurczyk, L. Biological treatment of landfill leachate at elevated temperature in the presence of polyurethane foam of various porosity. Clean Soil Air Water 2017, 45, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.L.; Hong, Y.; Pan, S.; Huang, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, W. Full-scale treatment of landfill leachate by using the mechanical vapor recompression combined with coagulation pretreatment. Waste Manag. 2017, 66, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, C.Y.; Budiman, P.M.; Shak, K.P.Y.; Wu, T.Y. Recent advancement of oagulation-flocculation and its application in wastewater treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4363–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torretta, V.; Ferronato, N.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Tolkou, A.K.; Airoldi, M. Novel and conventional technologies for landfill leachates treatment: A Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.A. Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4141–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebouet, D.; Schlumpf, J.P.; Jaouen, P.; Quemeneur, F. Stabilized landfill leachate treatment by combined physicochemical–nanofiltration processes. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2935–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohdziewicz, J.; Bodzek, M.; Górska, J. Application of pressure-driven membrane techniques to biological treatment of landfill leachate. Process. Biochem. 2001, 36, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Holz, F. Landfill leachate treatment by reverse osmosis. In Effective Industrial Membrane Processes: Benefits and Opportunities; Turner, M.K., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Lejon, L.; Vandecasteele, C. Reuse, treatment, and discharge of the concentrate of pressure-driven membrane processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3733–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Jung, C.; Trzopek, A.; Torrens, K.; Deng, Y. Characterization of ultraviolet-quenching dissolved organic matter (DOM) in mature and young leachates before and after biological pre-treatment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskander, S.M.; Novak, J.T.; Brazilb, B.; He, Z. Percarbonate oxidation of landfill leachates towards removal of ultraviolet quenchers. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2017, 3, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Long, H.Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Y. Electrochemical oxidation of biological pretreated and membrane separated landfill leachate concentrates on boron doped diamond. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 377, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, L.; Cossu, R.; Raga, R.; Pivato, A.; Lavagnolo, M.C. Recirculation of reverse osmosis concentrate in lab-scale anaerobic and aerobic landfill simulation reactors. Waste Manag. 2016, 56, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrò, P.S.; Gentili, E.; Meoni, C.; Orsi, S.; Komilis, D. Effect of the recirculation of a reverse osmosis concentrate on leachate generation: A case study in an Italian landfill. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labiadh, L.; Fernandes, A.; Ciriaco, L.; Pacheco, M.J.; Gadri, A.; Ammar, S. Electrochemical treatment of concentrate from reverse osmosis of sanitary landfill leachate. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talalaj, I.A.; Biedka, P. Impact of concentrated leachate recirculation on effectiveness of leachate treatment by reverse osmosis. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.X.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, Y. Treatment of landfill leachate RO concentrate by VMD. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Circuits and Systems, Madrid, Spain, 20–21 July 2015; Volume 9, pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.Q.; Yang, J.M.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.M.; Li, X.K.; Wang, Q.Z.; Pan, X.J. Co-bioevaporation treatment of concentrated landfill leachate with addition of food waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 130, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagastyo, A.Y.; Radjenovic, J.; Mu, Y.; Rozendal, R.A.; Batstone, D.J.; Rabaey, K. Electrochemical oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrate on mixed metal oxide (MMO) titanium coated electrodes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, G.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Urtiaga, A.M.; Ortiz, I. Electro-oxidation of reverse osmosis concentrates generated in tertiary water treatment. Water Res. 2010, 44, 2763–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, B.; Pan, Z. Treatment of landfill leachate reverse osmosis concentrate by catalytic ozonation with γ-Al2O3. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Ziyang, L.; Hui, W.; Gholami, A. Concentrated landfill leachate treatment by electro-ozonation. In Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Water and Wastewater Treatment; Aziz, H.A., Abu Amr, S.S., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 150–170. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.H.; Xue, W.J.; Yang, S.Q.; Tu, J.L.; Guo, X.L.; Liu, Z.Q. Electrochemical/peroxydisulfate/Fe3+ treatment of landfill leachate nanofiltration concentrate after ultrafiltration. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, W.C.; Lia, X.F.; Wang, W.M.; Line, H.C.; Zhang, L.C. Ultrafast activation efficiency of three peroxides by Fe78Si9B13 metallic glass under photo-enhanced catalytic oxidation: A comparative study. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 221, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, D.; Cortijo, M.; Huang, C.P. Optimizing the treatment of landfill leachate by conventional Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Lu, J.; Zhang, L.C. Compelling rejuvenated catalytic performance in metallic glasses. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Lin, P.; Cui, Z.; Chu, C.; Shen, B. Investigation of FePC amorphous alloys with self-renewing behaviour for highly efficient decolorization of methylene blue. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.B.; López, J.C.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Pérez, J.S. A comparative study of different tests for biodegradability enhancement determination during AOP treatment of recalcitrant toxic aqueous solutions. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paździor, K.; Bilińska, L.; Ledakowicz, S. A review of the existing and emerging technologies in the combination of AOPs and biological processes in industrial textile wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Roddick, F.; Fan, L.H. Recent advancements in the treatment of municipal wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate—An overview. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 193–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dialynas, E.; Mantzavinos, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Advanced treatment of the reverse osmosis concentrate produced during reclamation of municipal wastewater. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4603–4608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Impact of salinity and pH on the UVC/H2O2 treatment of reverse osmosis concentrate produced from municipal wastewater reclamation. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3229–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Pan, Y.; Xiang, X. Oxidation of acidic dye Eosin Y by the solar photo-Fenton processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Alias, S.; Adlan, M.N.; Faridah; Asaari, A.H.; Zahari, M.S. Colour removal from landfill leachate by coagulation and flocculation processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Lim, T.T.; Chin, S.S.; Fane, A.G. Treatment of organics in reverse osmosis concentrate from a municipal wastewater reclamation plant: Feasibility test of advanced oxidation processes with/without pretreatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, V.; Palanivelu, K. The role of ferrous ion in Fenton and photo-Fenton processes for the degradation of phenol. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarzadeh-Amiri, A.; Bolton, J.R.; Cater, S.R. Ferrioxalate-mediated photodegradation of organic pollutants in contaminated water. Water Res. 1997, 31, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, D.; Cortijo, M.; Huang, C.P. The role of iron on the degradation and mineralization of organic compounds using conventional Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, C.; de Torres-Socias, E.; Peres, J.A.; Maldonado, M.I.; Oller, I.; Malato, S.; Lucas, M.S. Mature landfill leachate treatment by coagulation/flocculation combined with Fenton and solar photo-Fenton processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Treatment process adapted to stabilized leachates: Lime precipitation–prefiltration–reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 313, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejera, J.; Miranda, R.; Hermosilla, D.; Urra, I.; Negro, C.; Blanco, A. Treatment of a mature landfill leachate: Comparison between homogeneous and heterogeneous photo-Fenton with different pretreatments. Water 2019, 11, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Amor, C.; Fernandes, J.R.; Tavares, P.B.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Treatment of crystallized-fruit wastewater by UV-A LED photo-Fenton and coagulation–flocculation. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.I.; Silva, T.F.C.V.; Duarte, M.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Vilar, V.J.P. Cost-effective solar collector to promote photo-Fenton reactions: A case study on the treatment of urban mature leachate. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.F.; Fonseca, A.; Saraiva, I.; Boaventura, R.A.; Vilar, V.J. Scale-up and cost analysis of a photo-Fenton system for sanitary landfill leachate treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.W.K.; van Leeuwen, J.A.; Fabris, R.; Drikas, M. Optimised coagulation using aluminium sulfate for the removal of dissolved organic carbon. Desalination 2009, 245, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renou, S.; Givaudan, J.G.; Poulain, S.; Dirassouyan, F.; Moulin, P. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 150, 468–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacardit, J.; Stötzner, J.; Chamarro, E.; Esplugas, S. Effect of salinity on the photo-Fenton process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 7615–7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.J.; Oo, M.H.; Kekre, K.A.; Knops, F.; Miller, P. Impact of coagulation pH on enhanced removal of natural organic matter in treatment of reservoir water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 49, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Wen, P.; Li, Q. Degradation of refractory organic contaminants in membrane concentrates from landfill leachate by a combined coagulation-ozonation process. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biglarijoo, N.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Ehteshami, M.; Ghaznavi, S.M. Optimization of Fenton process using response surface methodology and analytic hierarchy process for landfill leachate treatment. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 104, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermosilla, D.; Merayo, N.; Ordóñez, R.; Blanco, A. Optimization of conventional Fenton and ultraviolet-assisted oxidation processes for the treatment of reverse osmosis retentate from a paper mill. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chiu, H.M.; Shiau, C.S.; Yeh, R.Y.L.; Hung, Y.T. Degradation and sludge production of textile dyes by Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Dyes Pigm. 2007, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskander, S.M.; Zhao, R.; Pathak, A.; Gupta, A.; Pruden, A.; Novak, J.T.; He, Z. A review of landfill leachate induced ultraviolet quenching substances: Sources, characteristics, and treatment. Water Res. 2018, 145, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Hazra, T.; Dutta, A. Sustainable treatment of municipal landfill leachate by combined association of air stripping, Fenton oxidation, and enhanced coagulation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA; AWWA; WPCF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pobiner, H. Determination of hydroperoxides in hydrocarbon by conversion to hydrogen peroxide and measurement by titanium complexing. Anal. Chem. 1961, 33, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhu, X.; Butler, E.C. Comparison of four advanced oxidation processes for the removal of naphthenic acids from model oil sands process water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatchard, C.; Parker, C.A. A new sensitive chemical actinometer. II. Potassium ferrioxalate as a standard chemical actinometer. Proc. R. Soc. A. 1956, 235, 518–536. [Google Scholar]
- Montalti, M.; Credi, A.; Prodi, L.; Gandolfi, M.T. Handbook of Photochemistry, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; p. 650. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter 1 (LLROC) | Value 2 | Parameter (Dissolved Fraction) | Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.13 ± 0.10 | Chloride, mg L−1 | 8968 ± 897 |
| Conductivity, mS cm−1 | 87.30 ± 0.90 | Sulfate, mg L−1 | 2431 ± 243 |
| UV-254, cm−1 | 150 ± 10 | Aluminum, mg L−1 | 4.20 ± 0.60 |
| Color, mg Pt L−1 | 28,100 ± 900 | Iron, mg L−1 | 2.30 ± 0.30 |
| COD, mg O2 L−1 | 21,220 ± 750 | Chromium, mg L−1 | 1.00 ± 0.20 |
| BOD5, mg O2 L−1 | 1273 ± 100 | Sodium, mg L−1 | 6769 ± 677 |
| BOD5/COD | 0.06 ± 0.01 | Potassium, mg L−1 | 3157 ± 316 |
| TOC, mg C L−1 | 9980 ± 150 | Magnesium, mg L−1 | 245 ± 25 |
| TS, mg L−1 | 51,270 ± 1620 | Calcium, mg L−1 | 19 ± 2 |
| TSS, mg L−1 | 360 ± 32 | Silicon, mg L−1 | 29 ± 3 |
| TDS, mg L−1 | 50,910 ± 1230 | Zinc, mg L−1 | 0.60 ± 0.09 |
| Alkalinity, mg CaCO3 L−1 | 44,125 ± 1023 | Nickel, mg L−1 | 0.38 ± 0.06 |
| TNb, mg N L−1 | 3000 ± 150 | Strontium, mg L−1 | 1.50 ± 0.30 |
| Parameters 1 | LLROC 2 | Al2(SO4)3·18H2O 2 | FeCl3·6H2O 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2SO4, g L−1 | - | 25 | 25 |
| Initial coagulation pH | 8.13 ± 0.10 | 6.00 ± 0.10 | 6.00 ± 0.10 |
| Final pH | 8.13 ± 0.10 | 4.99 ± 0.10 | 4.07 ± 0.10 |
| Conductivity, mS cm−1 | 87.30 ± 0.90 | 90.20 ± 0.90 | 92.30 ± 0.90 |
| COD, mg O2 L−1 | 21,220 ± 1000 | 8488 ± 700 (60%) 1 | 5092 ± 500 (76%) |
| TOC, mg C L−1 | 9980 ± 100 | 3493± 100 (65%) | 2495 ± 100 (75%) |
| UV-254, cm−1 | 150 ± 10 | 49 ± 1 (67%) | 16 ± 1 (89%) |
| SUVA, L mg−1 m−1 | 1.50 ± 0.50 | 1.40 ± 0.50 (7%) | 0.64 ± 0.50 (57%) |
| Color, mg Pt L−1 | 28,100 ± 1000 | 7700 ± 400 (73%) | 2160 ± 200 (92%) |
| BOD5/COD | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| Treatment Costs | 100 W Mercury Lamp | UVA LED Lamp |
|---|---|---|
| Power consumption, € m−3 | 15.8 | 13.2 |
| Hydrogen peroxide, € m−3 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Photo-Fenton, € m−3 | 17.7 | 15.1 |
| Pre-treatment, € m−3 | 4.2 | 4.2 |
| Post-treatment, € m−3 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
| Total, € m−3 | 25.8 | 23.2 |
| Total, € kg COD | 1.4 | 1.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tejera, J.; Hermosilla, D.; Miranda, R.; Gascó, A.; Alonso, V.; Negro, C.; Blanco, Á. Assessing an Integral Treatment for Landfill Leachate Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121389
Tejera J, Hermosilla D, Miranda R, Gascó A, Alonso V, Negro C, Blanco Á. Assessing an Integral Treatment for Landfill Leachate Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Catalysts. 2020; 10(12):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121389
Chicago/Turabian StyleTejera, Javier, Daphne Hermosilla, Ruben Miranda, Antonio Gascó, Víctor Alonso, Carlos Negro, and Ángeles Blanco. 2020. "Assessing an Integral Treatment for Landfill Leachate Reverse Osmosis Concentrate" Catalysts 10, no. 12: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121389
APA StyleTejera, J., Hermosilla, D., Miranda, R., Gascó, A., Alonso, V., Negro, C., & Blanco, Á. (2020). Assessing an Integral Treatment for Landfill Leachate Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Catalysts, 10(12), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10121389











