Stereolithography 3D-Printed Catalytically Active Devices in Organic Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
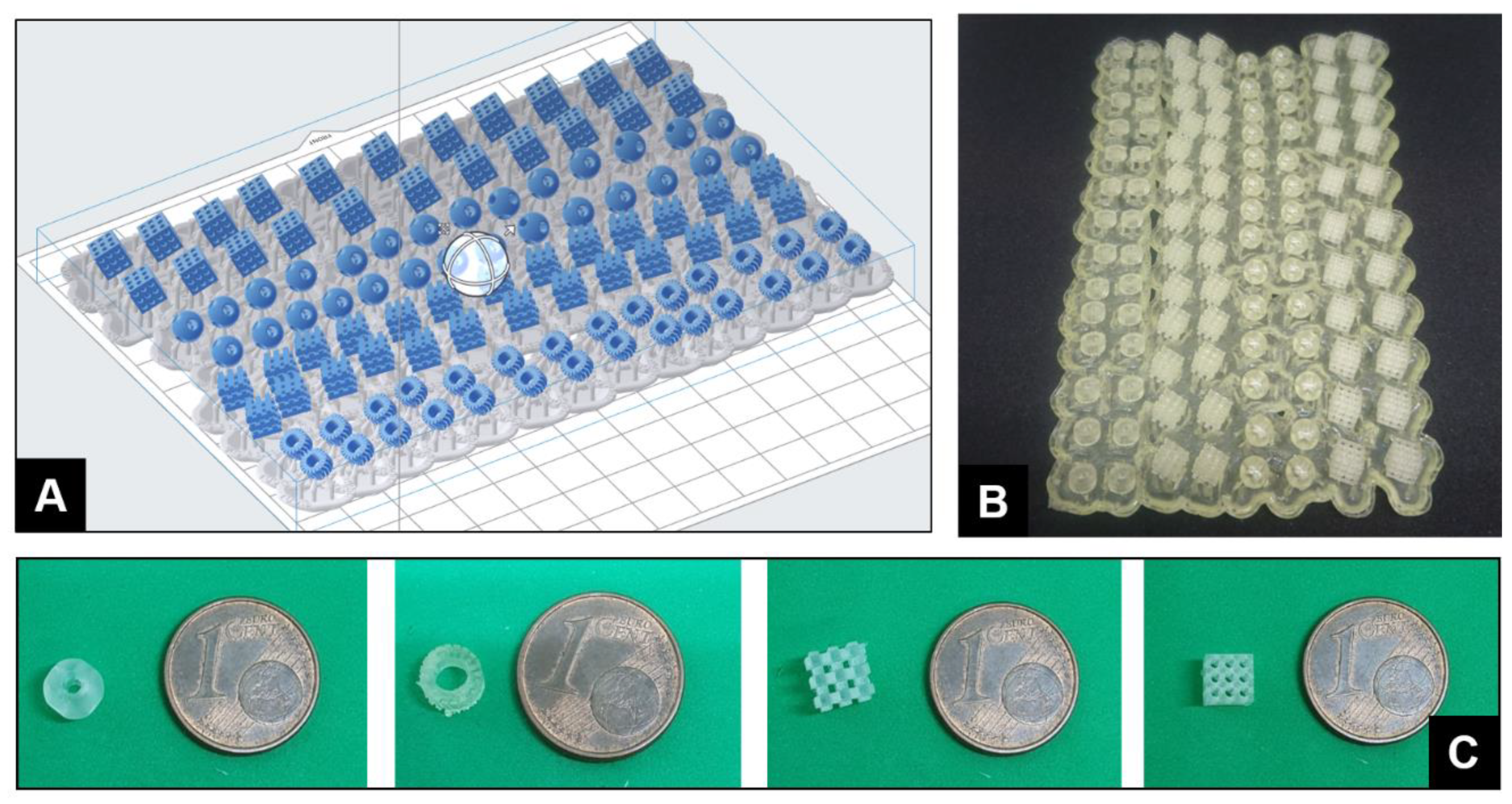
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References and Note
- Chaudhary, R.; Doggalli, N.; Chandrakant, H.V.; Patil, K. Current and evolving applications of three-dimensional printing in forensic odontology: A review. Int. J. Forensic Odontol. 2018, 3, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A.; Marti Marti, B.; Sauret-Jackson, V.; Darwood, A. 3D printing in dentistry. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 219, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Dong, H.; Su, J.; Han, J.; Song, B.; Wei, Q.; Shi, Y. A Review of 3D Printing Technology for Medical Applications. Engineering 2018, 4, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froes, F.; Boye, R. (Eds.) Additive Manufacturing for the Aerospace Industry, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.C.; Sheikh, A.A. 3D printing in aerospace and its long-term sustainability. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2015, 10, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, Y.L.; Yeong, W.Y. Additive manufacture of fashion and jewellery products: A mini review. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2014, 9, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Seong, H.; Her, Y.; Chun, J. A study of the development and improvement of fashion products using a FDM type 3D printer. Fash. Text. 2019, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B. Model Building and Slicing in Food 3D Printing Processes: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2019, 18, 1052–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Qu, M.; Zhang, H.; Lim, Y. 3D Printing and Buildings: A Technology Review and Future Outlook. Technol. Archit. Des. 2018, 2, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartings, M.R.; Ahmed, Z. Chemistry from 3D printed objects. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.M.; Ng, S.H.; Li, K.H.; Yoon, Y.J. 3D printed microfluidics for biological applications. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3627–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel, A.J.; Rimington, R.P.; Lewis, M.P.; Christie, S.D.R. 3D printing for chemical, pharmaceutical and biological applications. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Puglisi, A.; Benaglia, M. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D Printing in Organic Synthesis. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Three-Dimensional Printing in Analytical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 2865–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldbaur, A.; Rapp, H.; Lange, K.; Rapp, B.E. Let there be chip-towards rapid prototyping of microfluidic devices: One-step manufacturing processes. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2681–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel, A.J.; Edmondson, S.; Christie, S.D.; Goodridge, R.D.; Bibb, R.J.; Thurstans, M. Design and additive manufacture for flow chemistry. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4583–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fu, J.-Z.; Gao, Q.; Qiu, J.-J. Developments of 3D Printing Microfluidics and Applications in Chemistry and Biology: A Review. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1658–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, T.; Harding, M.J.; Harris, R.A.; Friel, R.J.; Christie, S.D. Customisable 3D printed microfluidics for integrated analysis and optimisation. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3362–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Porta, R.; Brenna, D.; Puglisi, A.; Benaglia, M. Stereoselective Catalytic Synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Homemade 3D-Printed Mesoreactors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4290–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Benaglia, M.; Brenna, D.; Porta, R.; Orlandi, M. Three Dimensional (3D) Printing: A Straightforward, User-Friendly Protocol To Convert Virtual Chemical Models to Real-Life Objects. J. Chem. Educ. 2015, 92, 1398–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Dozzi, M.V.; Puglisi, A.; Pagani, M. 3D-printed, home-made, UV-LED photoreactor as a simple and economic tool to perform photochemical reactions in high school laboratories. Chem. Teach. Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Bradbury, T.J.; Bebb, T.J.; Iskra, J.; Surprenant, H.L.; West, T.G. Three-Dimensional Printing System and Equipment Assembly. US Patent 9,908,293, 6 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Melchels, F.P.; Feijen, J.; Grijpma, D.W. A review on stereolithography and its applications in biomedical engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6121–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaglia, M.; Puglisi, A.; Cozzi, F. Polymer-supported organic catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 3401–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubio, C.R.; Azuaje, J.; Escalante, L.; Coelho, A.; Guitian, F.; Sotelo, E.; Gil, A. 3D printing of a heterogeneous copper-based catalyst. J. Catal. 2016, 334, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuaje, J.; Tubio, C.R.; Escalante, L.; Gomez, M.; Guitian, F.; Coelho, A.; Caamano, O.; Gil, A.; Sotelo, E. An efficient and recyclable 3D printed alpha-Al2O3 catalyst for the multicomponent assembly of bioactive heterocycles. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 530, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, S.; Penny, M.; Dos Santos, B.S.; Patel, B. Three-Dimensional Printing of Impregnated Plastic for Chemical Reactions. Patent application WO2017158336A1, 21 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, A.; Herrera, R.P.; Dessole, G. H-Bonding Organocatalysed Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of Aromatic and Heteroaromatic Systems with Nitroolefins. Synlett 2004, 13, 2374–2378. [Google Scholar]
- These Informations are Described in the Safety Data Sheet. Available online: https://formlabs-media.formlabs.com/datasheets/Clear_Resin_Technical.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- See the Supporting Information for further details.
- 123d Design, Version 2.2.14. The Software Is Not More Accessible from Autodesk, but It Can Be Downloaded from Other Sources. Available online: https://www.download-3d.com (accessed on 1 September 2019).


| Sample | Thiourea (weight %) | Catalyst Loading (mmol/g) | UV Polymerization Occurred |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resin 1 | 1 | 0.019 | Yes |
| Resin 2 | 5 | 0.111 | Yes |
| Resin 3 | 10 | 0.222 | Yes |
| Resin 4 | 15 | 0.299 | Yes |
| Resin 5 | 20 | 0.389 | Yes |
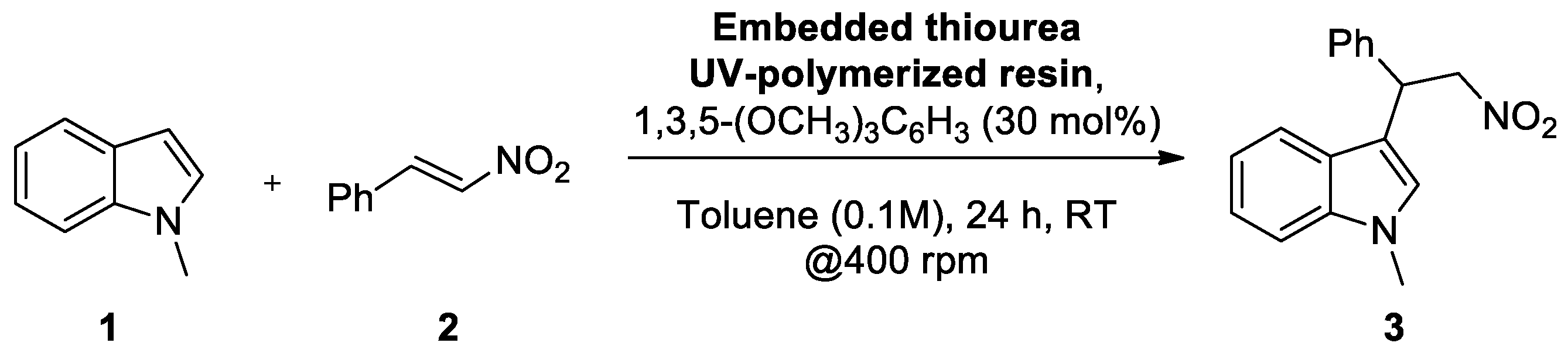
| Entry | Thiourea Loading (wt %) | Embedded-Catalyst/Substrate Ratio (mol/mol) | Yield 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - |
| 2 | 1 | 0.1 | - |
| 3 | 5 | 0.1 | - |
| 4 | 10 | 0.1 | - |
| 5 | 10 | 0.3 | - |
| 6 | 10 | 0.5 | - |
| 7 | 10 | 1 | 23 |
| 8 | 15 | 0.3 | - |
| 9 | 15 | 0.5 | 7 |
| 10 | 15 | 1 | 60 |
| 11 | 20 | 0.1 | 7 |
| 12 | 20 | 0.2 | 14 |
| 13 | 20 | 0.5 | 25 |
| 14 | 20 | 1 | 49 |
| 15 | 20 | 2 | 53 |
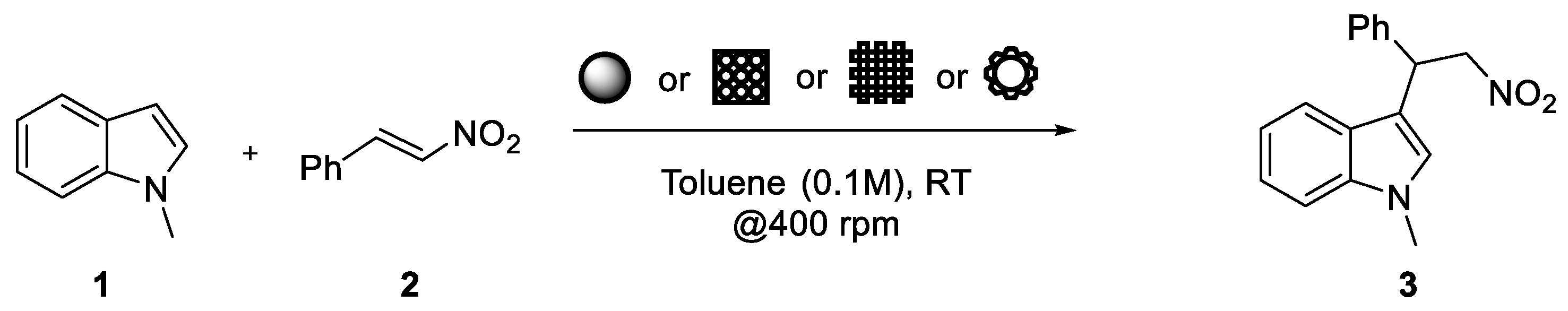
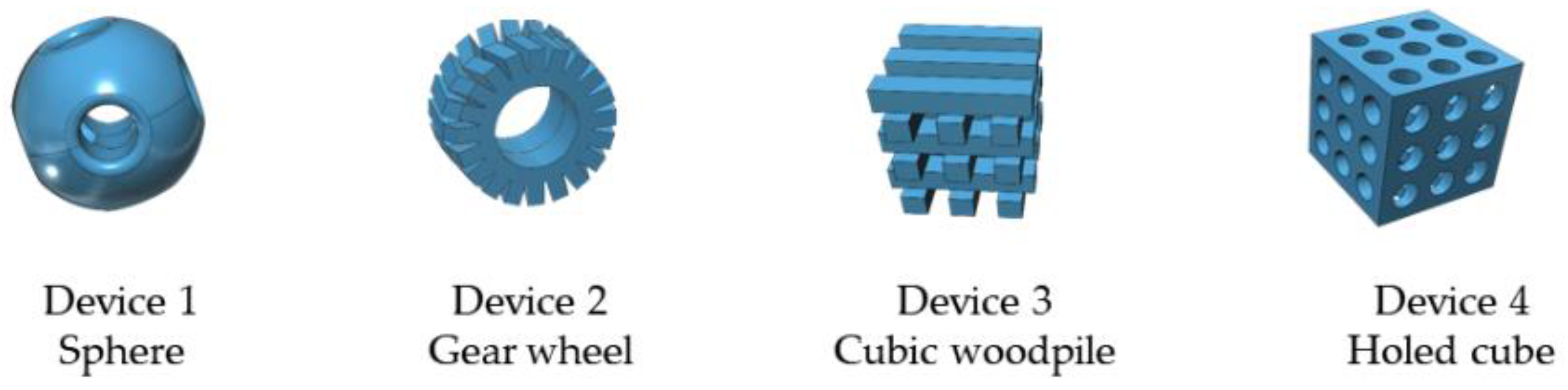
| Entry | Device Shape | Thiourea Loading (% w/w) | Catalyst/Substrate Ratio (mol/mol) | 24 h Yield (%) 1 | 90 h Yield (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 10 | 1 | 5 | 10 |
| 2 |  | 10 | 2 | 17 | 31 |
| 3 |  | 15 | 0.5 | 6 | 37 |
| 4 |  | 15 | 1 | 40 | 60 |
| 5 |  | 15 | 2 | 36 | 56 |
| 6 |  | 10 | 1 | 13 | 74 |
| 7 |  | 15 | 1 | 23 | 79 |
| 8 |  | 15 | 1 | 33 | 56 |
| 9 |  | 15 | 1 | 11 | 38 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rossi, S.; Puglisi, A.; Raimondi, L.M.; Benaglia, M. Stereolithography 3D-Printed Catalytically Active Devices in Organic Synthesis. Catalysts 2020, 10, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010109
Rossi S, Puglisi A, Raimondi LM, Benaglia M. Stereolithography 3D-Printed Catalytically Active Devices in Organic Synthesis. Catalysts. 2020; 10(1):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010109
Chicago/Turabian StyleRossi, Sergio, Alessandra Puglisi, Laura Maria Raimondi, and Maurizio Benaglia. 2020. "Stereolithography 3D-Printed Catalytically Active Devices in Organic Synthesis" Catalysts 10, no. 1: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010109
APA StyleRossi, S., Puglisi, A., Raimondi, L. M., & Benaglia, M. (2020). Stereolithography 3D-Printed Catalytically Active Devices in Organic Synthesis. Catalysts, 10(1), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010109







