A Cellulose Electrolysis Cell with Metal-Free Carbon Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
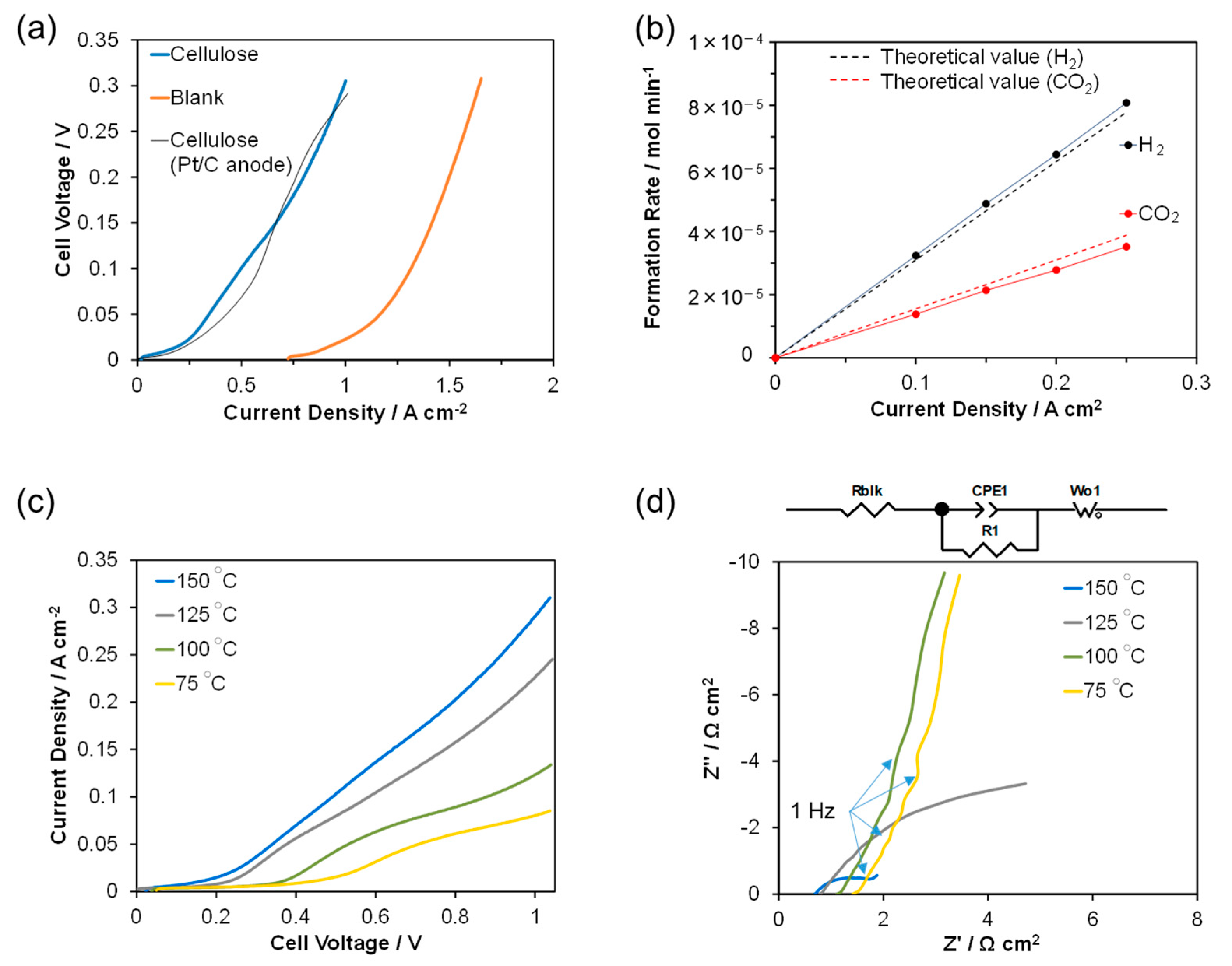
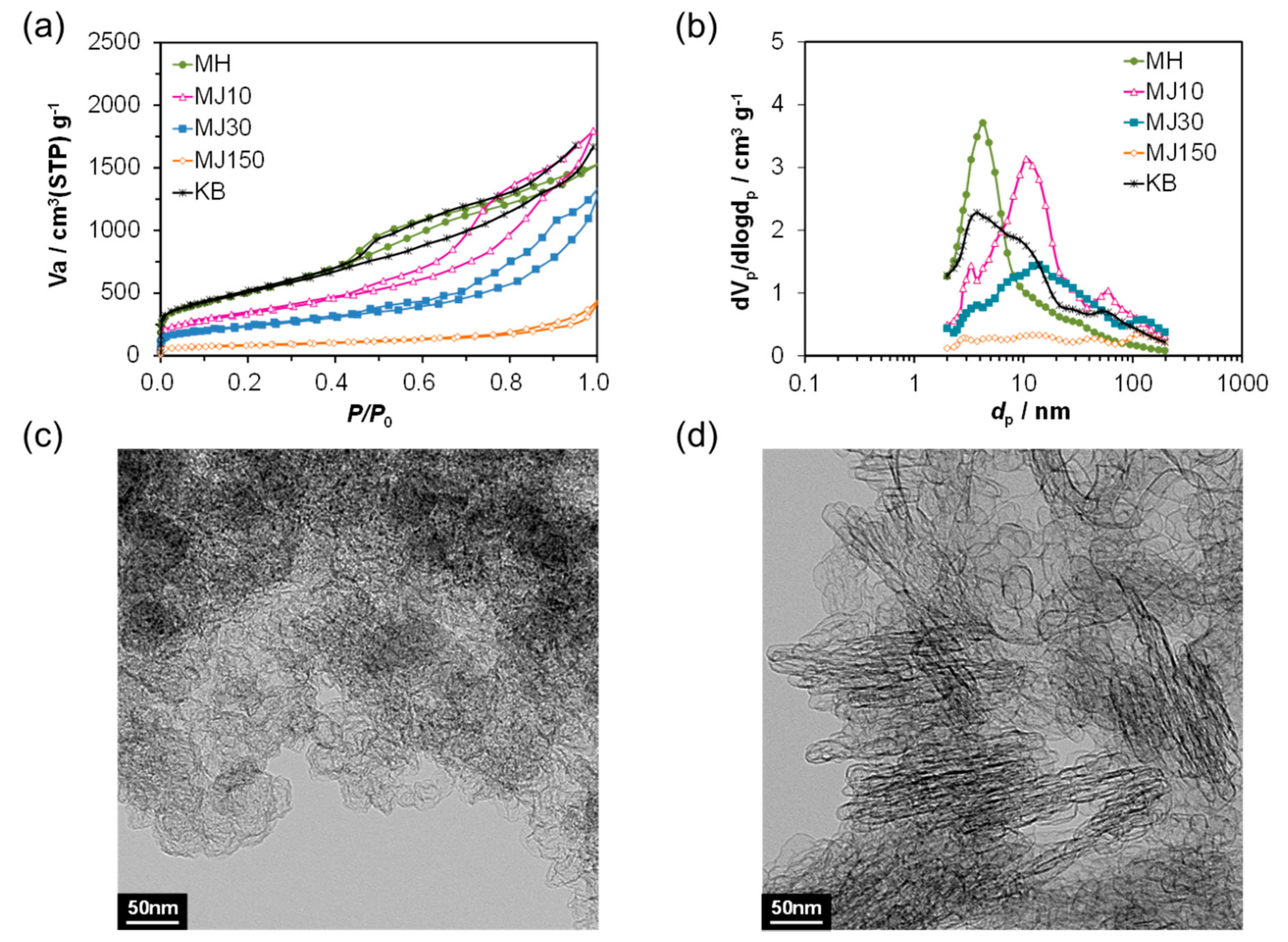
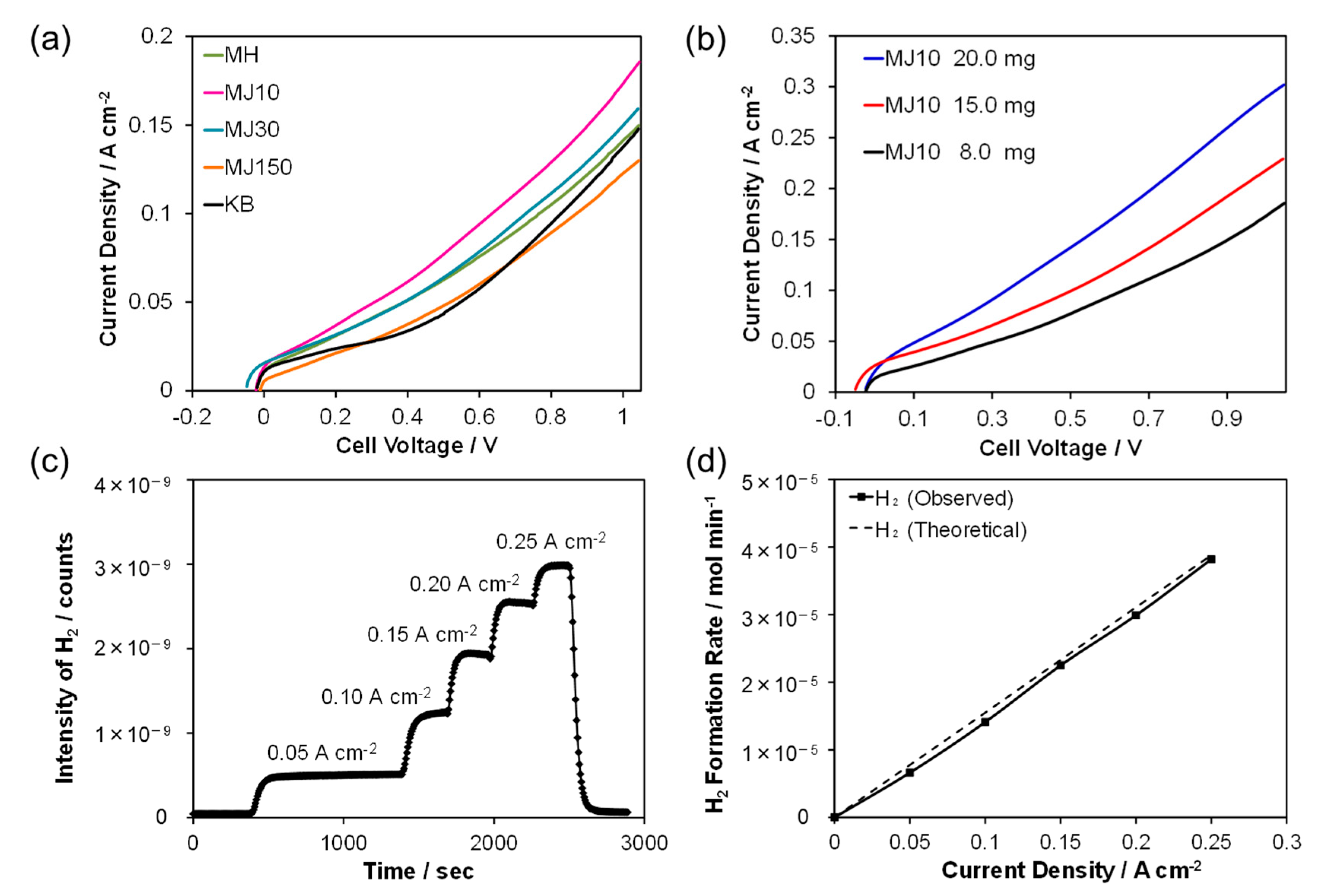
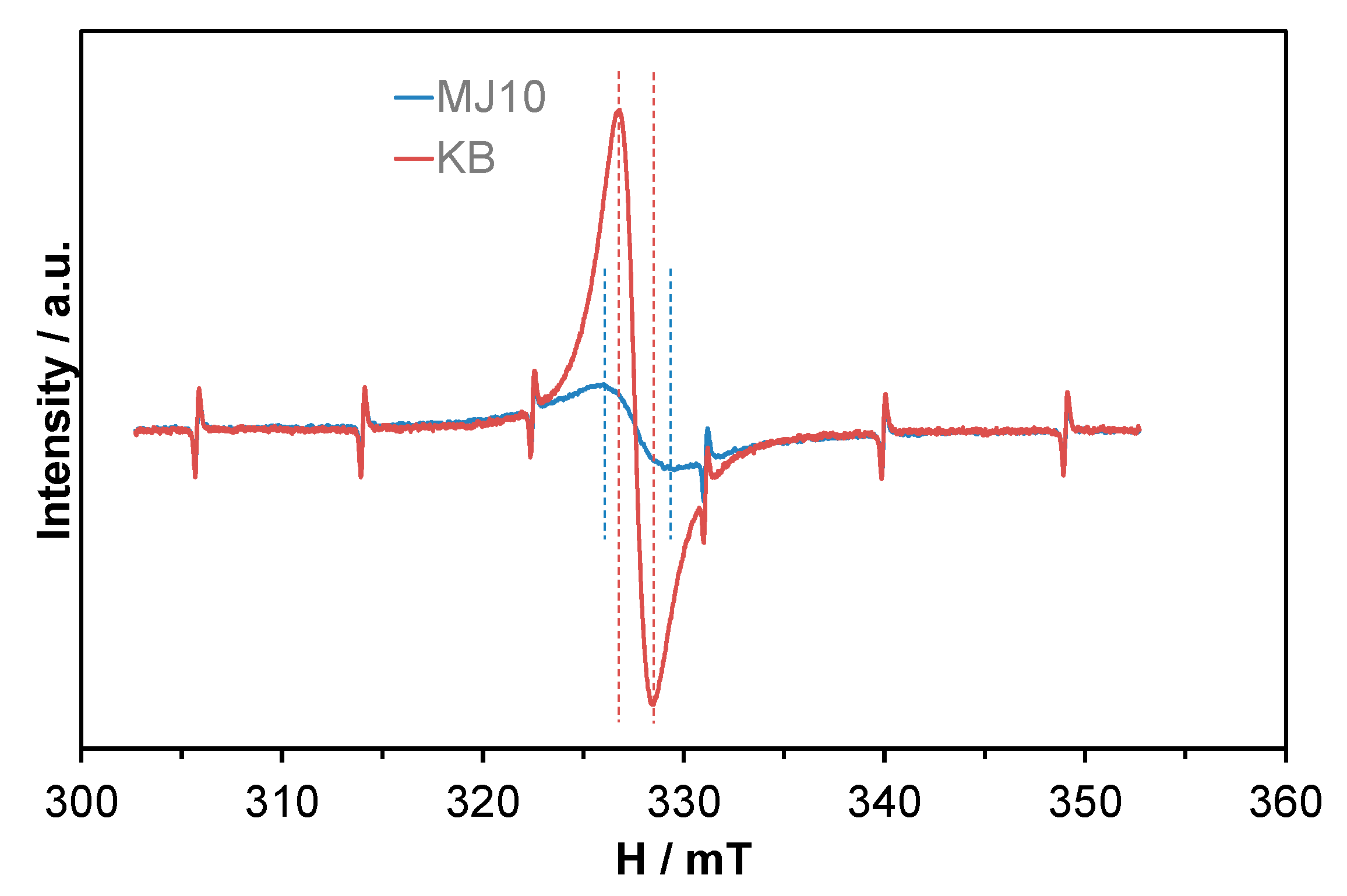
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, G.; Shobana, S.; Chen, W.H.; Bach, Q.V.; Kim, S.H.; Atabani, A.E.; Chang, J.S. A review of thermochemical conversion of microalgal biomass for biofuels: Chemistry and processes. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 44–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, N.; Sivasankari, S.; Kiran, G.; Ninawe, A.; Selvin, J. Utilization of bioresources for sustainable biofuels: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, R.A.; Rodionova, M.V.; Zharmukhamedov, S.K.; Veziroglu, T.N.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. Biofuel production from plant and algal biomass. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 17257–17273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainaina, S.; Horvath, I.S.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Biochemicals from food waste and recalcitrant biomass via syngas fermentation: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Gallegos, A.; Ahmad, Z.; Asgher, M.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Lignocellulose: A sustainable material to produce value-added products with a zero-waste approach—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, C.; Jaubert, T.; Baranton, S.; Coutanceau, C. Clean hydrogen generation through the electrocatalytic oxidation of ethanol in a proton exchange membrane electrolysis cell (PEMEC): Effect of the nature and structure of the catalytic anode. J. Power Sources 2014, 245, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, I.; Shipman, M.A.; Symes, M.D. Earth-abundant catalysts for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni-Urtiaga, A.; Presvytes, D.; Scott, K. Solid acids as electrolyte materials for proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 3358–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbir, F. PEM electrolysis for production of hydrogen from renewable energy sources. Sol. Energy 2005, 78, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Aili, D.; Li, Q.; Christensen, E.; Jensen, J.O.; Zhang, W.; Hansen, M.K.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Bjerrum, N.J. Oxygen evolution catalysts on supports with a 3-D ordered array structure and intrinsic proton conductivity for proton exchange membrane steam electrolysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.K.; Aili, D.; Christensen, E.; Pan, C.; Eriksen, S.; Jensen, J.O.; Barner, J.H.V.; Li, Q.F.; Bjerrum, N.J. PEM steam electrolysis at 130 °C using a phosphoric acid doped short side chain PFSA membrane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 10992–11000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Lavacchi, A.; Miller, H.A.; Bevilacqua, M.; Filippi, J.; Innocenti, M.; Marchionni, A.; Oberhauser, W.; Wang, L.; Vizza, F. Nanotechnology makes biomass electrolysis more energy efficient than water electrolysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caravaca, A.; Sapountzi, F.M.; De Lucas-Consuegra, A.; Molina-Mora, C.; Dorado, F.; Valverde, J.L. Electrochemical reforming of ethanol-water solutions for pure H2 production in a PEM electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 9504–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaca, A.; Garcia-Lorefice, W.E.; Gil, S.; de Lucas-Consuegra, A.; Vernoux, P. Towards a sustainable technology for H2 production: Direct lignin electrolysis in a continuous-flow polymer electrolyte membrane reactor. Electrochem. Commun. 2019, 100, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Ito, M.; Nagao, M.; Fukui, M.; Teranishi, S. Direct electrolysis of waste newspaper for sustainable hydrogen production: An oxygen-functionalized porous carbon anode. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 231, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Ito, M.; Ma, Q.; Nagao, M.; Fukui, M.; Teranishi, S. Efficient hydrogen production by direct electrolysis of waste biomass at intermediate temperatures. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9360–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.B.; Xia, B.Y.; Yu, L.; Yu, X.Y.; Lou, X.W. Porous molybdenum carbide nano-octahedrons synthesized via confined carburization in metal-organic frameworks for efficient hydrogen production. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Regmi, Y.N.; Leonard, B.M. Multiple phases of molybdenum carbide as electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6407–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, H.; Guo, X. WC nanocrystals grown on vertically aligned carbon nanotubes: An efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5125–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; You, B.; Sheng, M.; Sun, Y. Electrodeposited cobalt-phosphorous-derived films as competent bifunctional catalysts for overall water splitting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6251–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A.M.; Sun, X. Self-supported nanoporous cobalt phosphide nanowire arrays: An efficient 3D hydrogen-evolving cathode over the wide range of pH 0–14. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7587–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, S.K.; Lovley, D.R. Electricity generation by direct oxidation of glucose in mediatorless microbial fuel cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibino, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Lv, P.; Nagao, M.; Teranishi, S.; Mori, T. An intermediate-temperature biomass fuel cell using wood sawdust and pulp directly as fuel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, F557–F563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Wang, X.T.; Sui, D.; Zhang, T.F.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.H.; Ge, Z.; Xie, Y.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, Y.X.; et al. High-temperature-endurable, flexible supercapacitors: Performance and degradation mechanism. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulepp, M.; Leis, J.; Lätt, M.; Miller, F.; Rumma, K.; Lust, E.; Burke, A.F. The advanced carbide-derived carbon-based supercapacitor. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, A.; Christy, M.; Hwang, Y.J.; Lim, Y.R.; Kim, P.; Nahm, K.S. Improved electrocatalytic activity of carbon materials by nitrogen doping. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wei, Z.D.; Chen, S.G.; Qi, X.Q.; Yang, T.; Hu, J.S.; Wang, D.; Wan, L.J.; Alvi, S.F.; Li, L. Space-confinement-induced synthesis of pyridinic- and pyrrolic-nitrogen-doped graphene for the catalysis of oxygen reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11755–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignaszak, A.; Ye, S.Y.; Gyenge, E. A study of the catalytic interface for O2 electroreduction on Pt: The interaction between carbon support meso/microstructure and ionomer (Nafion) distribution. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, D.; Kurosawatsu, K.; Uota, M.; Karashima, T.; Otsubo, M.; Honda, C.; Sung, Y.M. Space charge distributions of an electric double layer capacitor with carbon nanotubes electrode. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 4234–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.J.; Li, R.C.; Qiu, J.S.; Xie, K.; Ling, P.H.; Yu, M.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zheng, M.D. Synthesis of mesoporous carbons for supercapacitors from coal tar pitch by coupling microwave-assisted KOH activation with a MgO template. Carbon 2012, 50, 4911–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, T.; Tsumura, T.; Toyoda, M.; Przepiórski, J.; Morawski, A.W.; Konno, H.; Inagaki, M. A review of the control of pore structure in MgO-templated nanoporous carbons. Carbon 2010, 48, 2690–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Gas adsorption characterization of ordered organic-inorganic nanocomposite materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.B.; Zhao, T.S. Mesoporous carbon with uniquely combined electrochemical and mass transport characteristics for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Nishanth, K.G.; Selvarani, G.; Sridhar, P.; Pitchumani, S.; Shukla, A.K. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells employing electrodes with gas-diffusion layers of mesoporous carbon derived from a sol–gel route. Carbon 2009, 47, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikander, K.; Ekstrom, H.; Palmqvist, A.E.C.; Lundblad, A.; Holmberg, K.; Lindbergh, G. Alternative catalysts and carbon support material for PEMFC. Fuel Cells 2006, 6, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Shin, J.-K.; Eun, K.Y.; Lee, K.-R.; Yoon, K.H. Defect density and atomic bond structure of tetrahedral amorphous carbon ta-C films prepared by filtered vacuum arc process. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 4829–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Acik, M.; Takai, K.; Lu, J.; Hao, S.-J.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, P.; Bao, Q.; Enoki, T.; Chabal, Y.J.; et al. Probing the catalytic activity of porous graphene oxide and the origin of this behavior. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Xu, C.; Wu, X. Intermediate temperature proton-conducting membrane electrolytes for fuel cells. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2014, 3, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibino, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nagao, M.; Kawasaki, S. High-temperature supercapacitor with a proton-conducting metal pyrophosphate electrolyte. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Vp (cm3 g−1) (BJH) | dp (nm) (BJH) | dav (nm) (BJH) | SBET (m2 g−1) (BET) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB | 2.40 | 3.80 | 5.90 | 1830 |
| MH | 2.25 | 4.20 | 4.80 | 1875 |
| MJ10 | 2.71 | 10.6 | 8.60 | 1223 |
| MJ30 | 1.76 | 13.9 | 9.30 | 830 |
| MJ150 | 0.53 | - | 10.0 | 282 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Nagao, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Jin, Y.; Hibino, T. A Cellulose Electrolysis Cell with Metal-Free Carbon Electrodes. Catalysts 2020, 10, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010106
Li Y, Nagao M, Kobayashi K, Jin Y, Hibino T. A Cellulose Electrolysis Cell with Metal-Free Carbon Electrodes. Catalysts. 2020; 10(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010106
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yaorong, Masahiro Nagao, Kazuyo Kobayashi, Yongcheng Jin, and Takashi Hibino. 2020. "A Cellulose Electrolysis Cell with Metal-Free Carbon Electrodes" Catalysts 10, no. 1: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010106
APA StyleLi, Y., Nagao, M., Kobayashi, K., Jin, Y., & Hibino, T. (2020). A Cellulose Electrolysis Cell with Metal-Free Carbon Electrodes. Catalysts, 10(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010106




