Gender Differences in Yielding to Social Influence: An Impunity Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
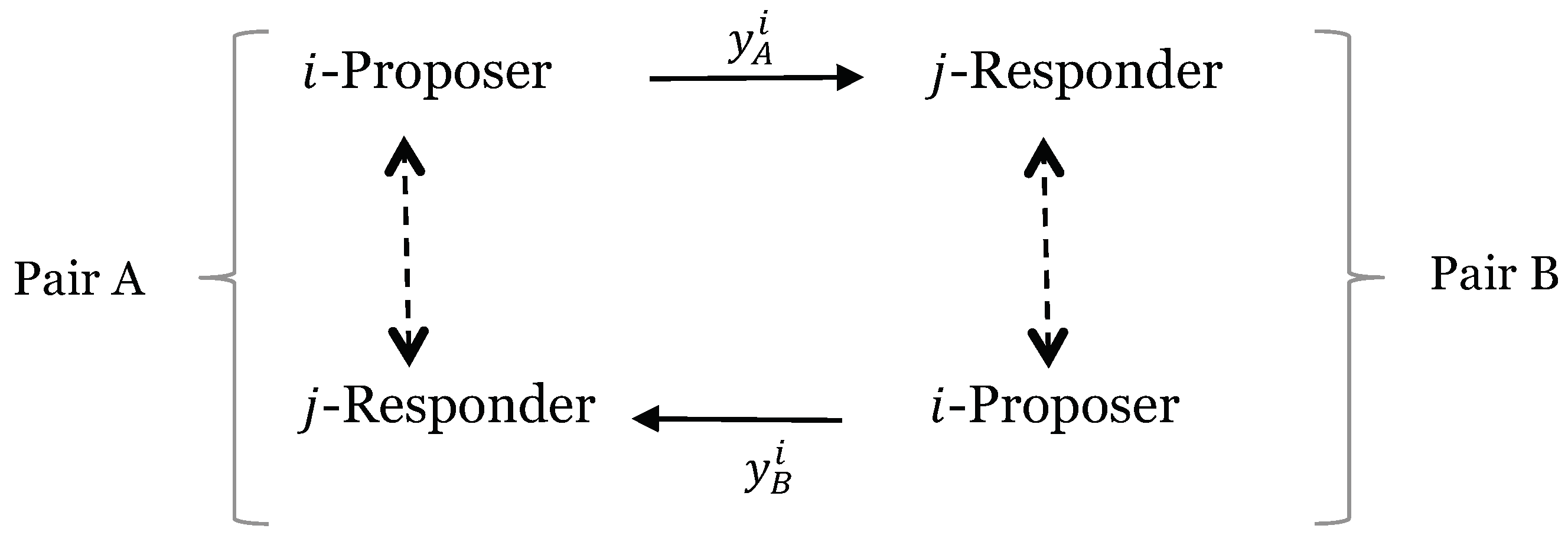
2. Experimental Design and Protocol
3. Results
Gender Effects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- first, you have to decide, individually and independently, how much of your endowment you to want to give to a responder (different from your paired participant) if you will be selected as a proposer. If you are an O(dd) participant, you can choose one between these numbers . If you are an E(ven) participant, you can choose one of the numbers .Observe that both types of participants have the same number of possible choices, i.e., twelve, and that the difference between the minimum and the maximum choice, i.e., 22€, is the same for both types of participant.
- Second, you have to decide, individually and independently, how much you want to update your initial proposal if you will be selected as a proposer in the two following situations:
- -
- the proposal of your paired participant is larger than yours; in this case you can either confirm or increase your initial proposal;
- -
- the proposal of your paired participant is smaller than your; in this case you can either confirm or decrease your initial proposal.
Remember that in each of the two cases, your updated proposal can only be an odd number or even number depending on whether you are an O or an E candidate.Note: Beware that you will be asked to update your initial proposal before knowing if the other has decided to propose more than you or less than you. - Third, you have to decide, individually and independently, what proposals you will accept if you will be selected as a responder. In particular, you have to decide an acceptance threshold such that all proposals larger than the threshold will be accepted and all proposals lower than the threshold will be rejected.Remember that the acceptance threshold can only be an odd number or even number depending on whether you are an O or an E candidate.
- adjust the proposals of each participant depending on whether the initial proposal of the paired participant is larger or smaller than the own one;
- select, for each pair of participant, who is the proposer and who is the responder;
- randomly match each proposer with a responder from a different pair than the initial one and, similarly, randomly match each responder with a proposer from a different pair than the initial one.
- -
- O(dd) proposers will be matched with E(ven) receivers and that E(ven) proposers will be matched with O(dd) receivers;
- ●
- the proposal communicated to the receiver will be the adjusted one (and not the initial one).
- if you are a proposer, your payoff will be equal to your endowment minus your offer both in case the offer is above or below the responder’s acceptance threshold.
- if you are a receiver, your payoff will be equal to
- ∘
- the proposer’s proposal if this is larger than your acceptance threshold;
- ∘
- equal to zero if the proposal is smaller than your acceptance threshold.
- -
- if you are proposer or responder;
- -
- if your are a proposer, you will be communicated that you were selected as a proposer and you will be informed about your final payoff and the payoff of the responder who received your proposal;
- -
- if you are a receiver, you will be communicated that you were selected as a receiver and you will be informed about your final payoff.
References
- Vesterlund, L. Using Experimental Methods to Understand Why and How We Give to Charity. In The Handbook of Experimental Economics; Kagel, J.H., Roth, A.E., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Borghans, L.; Golsteyn, B.; Heckman, J.; Meijers, H. Gender differences in risk aversion and ambiguity aversion. J. Econ. Eur. Assoc. 2009, 7, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, D. Social dilemma cooperation (unlike Dictator Game giving) is intuitive for men as well as women. J. Exp. Soc. Psycol. 2017, 73, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederle, M.; Vesterlund, L. Do women shy away from competition? Do men compete too much? Q. J. Econ. 2007, 122, 1067–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, C.L.; Demiral, E.E.; Mollerstrom, J. No Gender Difference in Willingness to Compete When Competing against Self. Am. Econ. Rev. 2017, 107, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güth, W.; Kocher, M.G. More than thirty years of ultimatum bargaining experiments: Motives, variations, and a survey of the recent literature. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2014, 108, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, D.; Galliera, A.; Güth, W.; Panaccione, L. A hybrid public good experiment eliciting multi-dimensional choice data. J. Econ. Psychol. 2016, 56, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, G.E.; Katok, E. An experimental test for gender differences in beneficent behavior. Econ. Lett. 1995, 48, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, C.C.; Grossman, P.J. Are women less selfish than men?: Evidence from dictator experiments. Econ. J. 1998, 108, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, J.; Vesterlund, L. Which is the fair sex? Gender differences in altruism. Q. J. Econ. 2001, 116, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruttel, L.; Stolley, F. Gender Differences in the Responce to Decision Power and Responsability—Framings Effects in a Dictator Game. Games 2018, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederle, M. Gender. In The Handbook of Experimental Economics; Kagel, J.H., Roth, A.E., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rand, D.; Brescoll, V.; Everett, J.; Capraro, V.; Barcelo, H. Social heuristics and social roles: Intuition favors altruism for women but not for men. J. Exp. Psycol. Gen. 2016, 145, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brañas-Garza, P.; Capraro, V.; Rascón-Ramírez, E. Gender differences in altruism on Mechanical Turk: Expectations and actual behavior. Econ. Lett. 2018, 170, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, E.; Houser, D. Emotion Expression in Human Punishment Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7398–7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbacher, U. z-Tree: Zurich toolbox for ready-made economic experiments. Exp. Econ. 2007, 10, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, B. Subject Pool Recruitment Procedures: Organizing Experiments with ORSEE. J. Econ. Sci. Assoc. 2015, 1, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, D.; Galliera, A.; Güth, W.; Panaccione, L. Intention-Based Sharing. Games 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adda, G.; Capraro, V.; Tavoni, M. Push, don’t nudge: Behavioral spillovers and policy instruments. Econ. Lett. 2017, 154, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmat, G.; Petrongolo, B. Gender and the labor market: What we have learned from field and lab experiments? Labor Econ. 2014, 30, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. | |
| 2. | For example, Bolton and Katok [8] found no gender differences, Eckel and Grossman [9] that female participants are more generous and less likely to reject offers, Andreoni and Versterlund [10] that female participants are more generous than male ones, Bruttel and Stolley [11] show that men are more reactive to their responsibility for the receiver’s payoff, whereas women react more to strategic power and freedom of choice. For a survey, see Niederle [12]. |
| 3. | Participants additionally received a show-up fee of 3 euro. |
| 4. | Based on rematching groups with four participants, but without informing participants about this restricted rematching. Each proposer candidate is matched with a different one to set the conditional choice and never repeats one round with the same one. No specific restriction was made on the matching between actual proposer and responder. |
| 5. | Randomly endowing one candidate of one pair determines also the role of the other pair with respect to be an odd/even player. |
| 6. | The translated instructions for the impunity game are reported in Appendix A. |
| 7. | Sessions are not gender-balanced to avoid possible demand effects which could arise from participants’ awareness of such a balance. |
| 8. | A related work is d’Adda et al. [19] where authors find that dictators respond to social influence (although they do not analyse conditioning and gender differences). |
| 9. | Our companion study (Di Cagno et al. [18]) does not focus on gender effects but on how weakest social influence is moderated by sanctioning in sharing games with and without monitoring proposer generosity as well as by experience with such games. Both studies together confirm Results 1 and 2. |
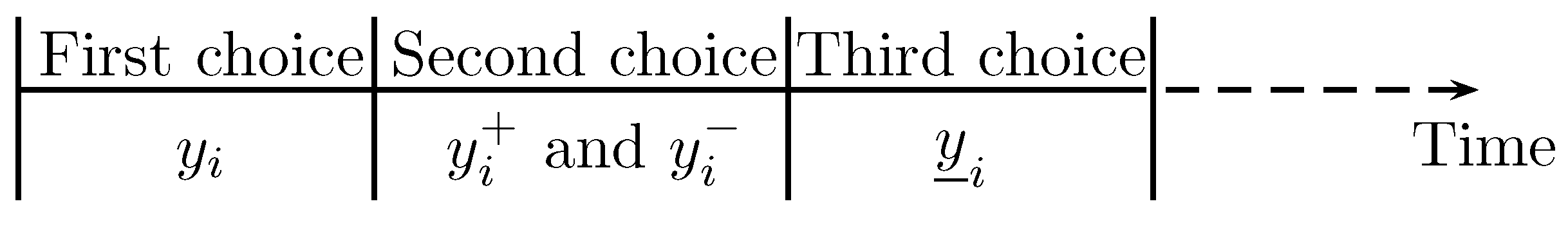
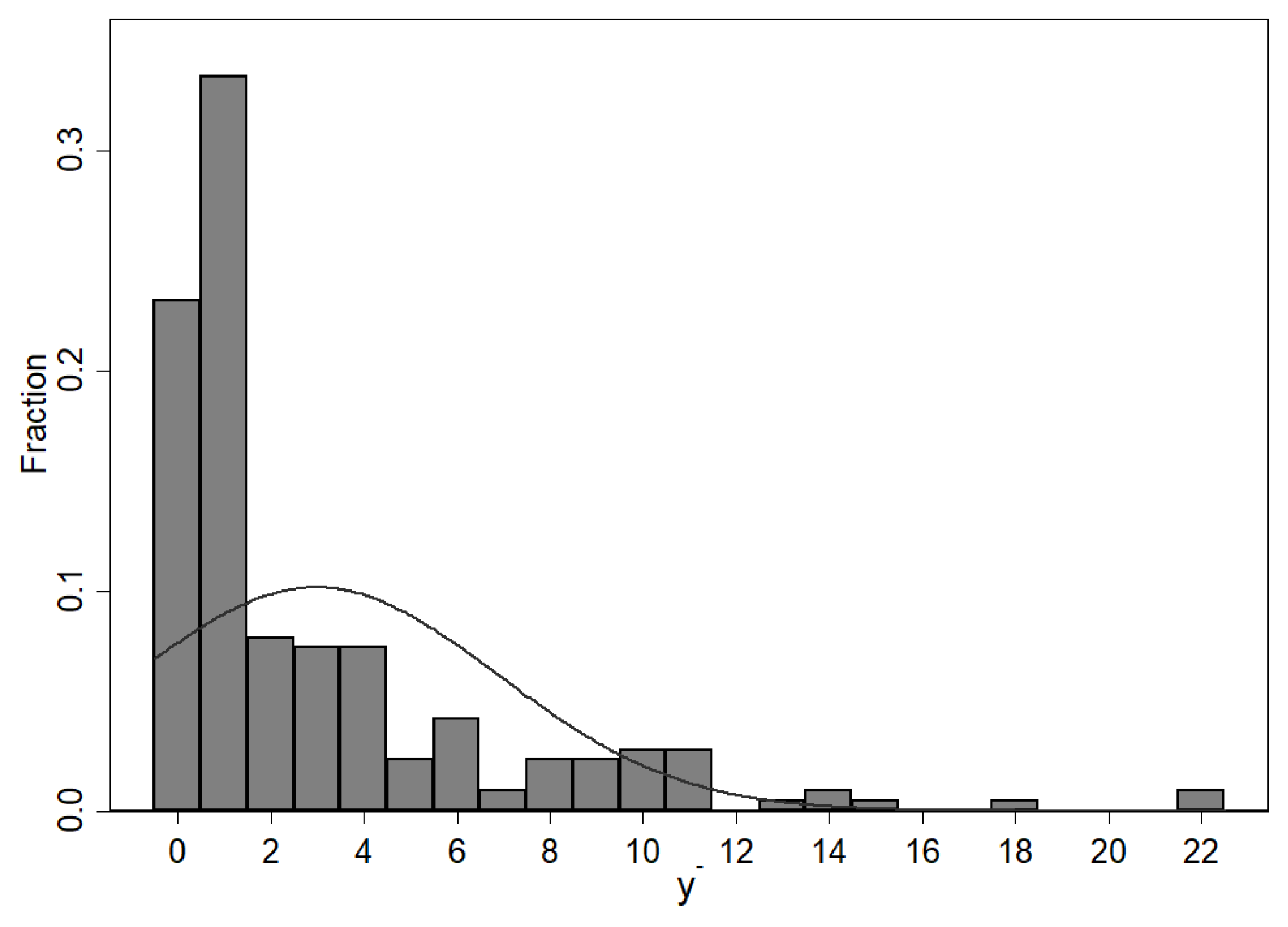
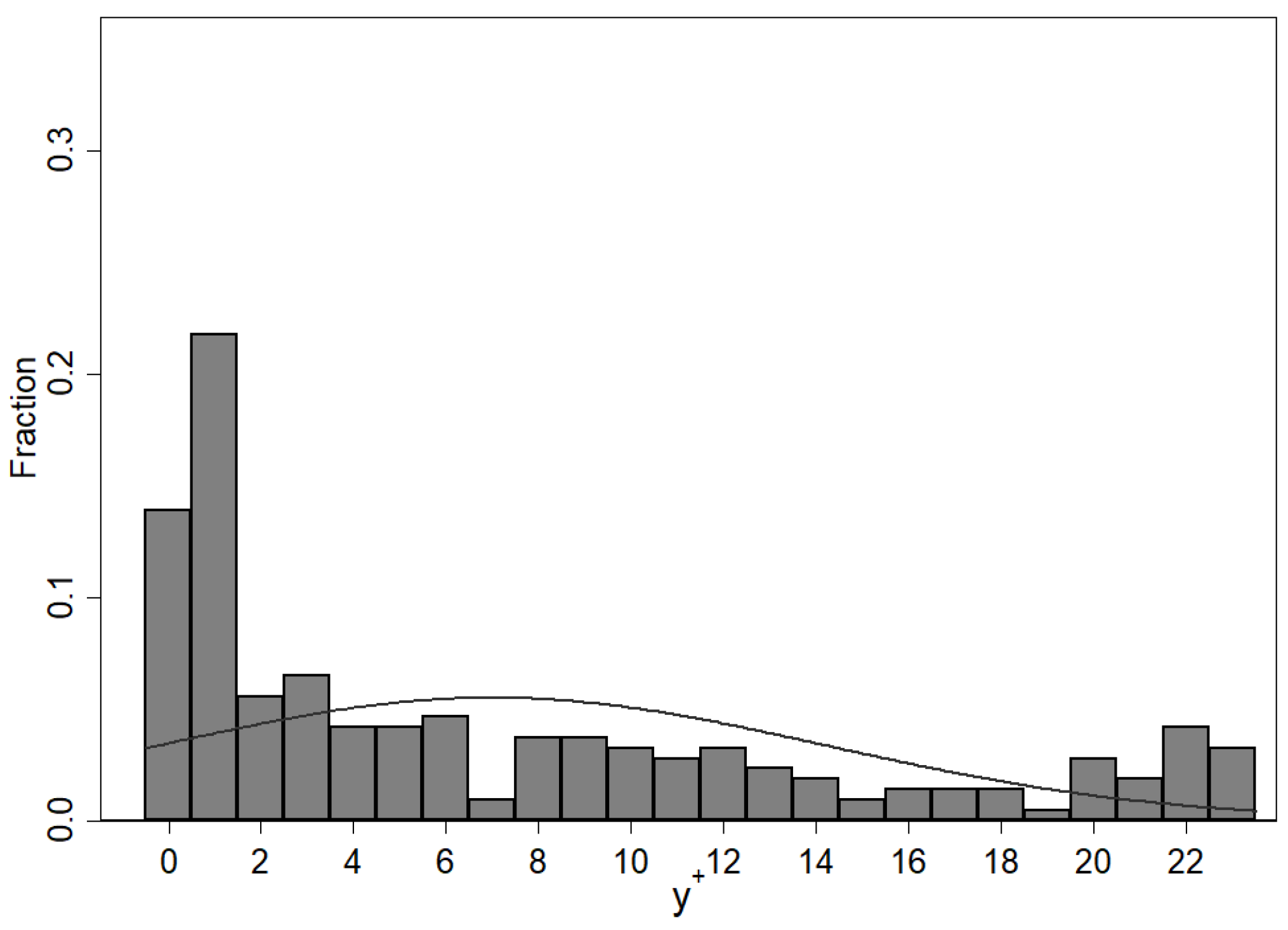
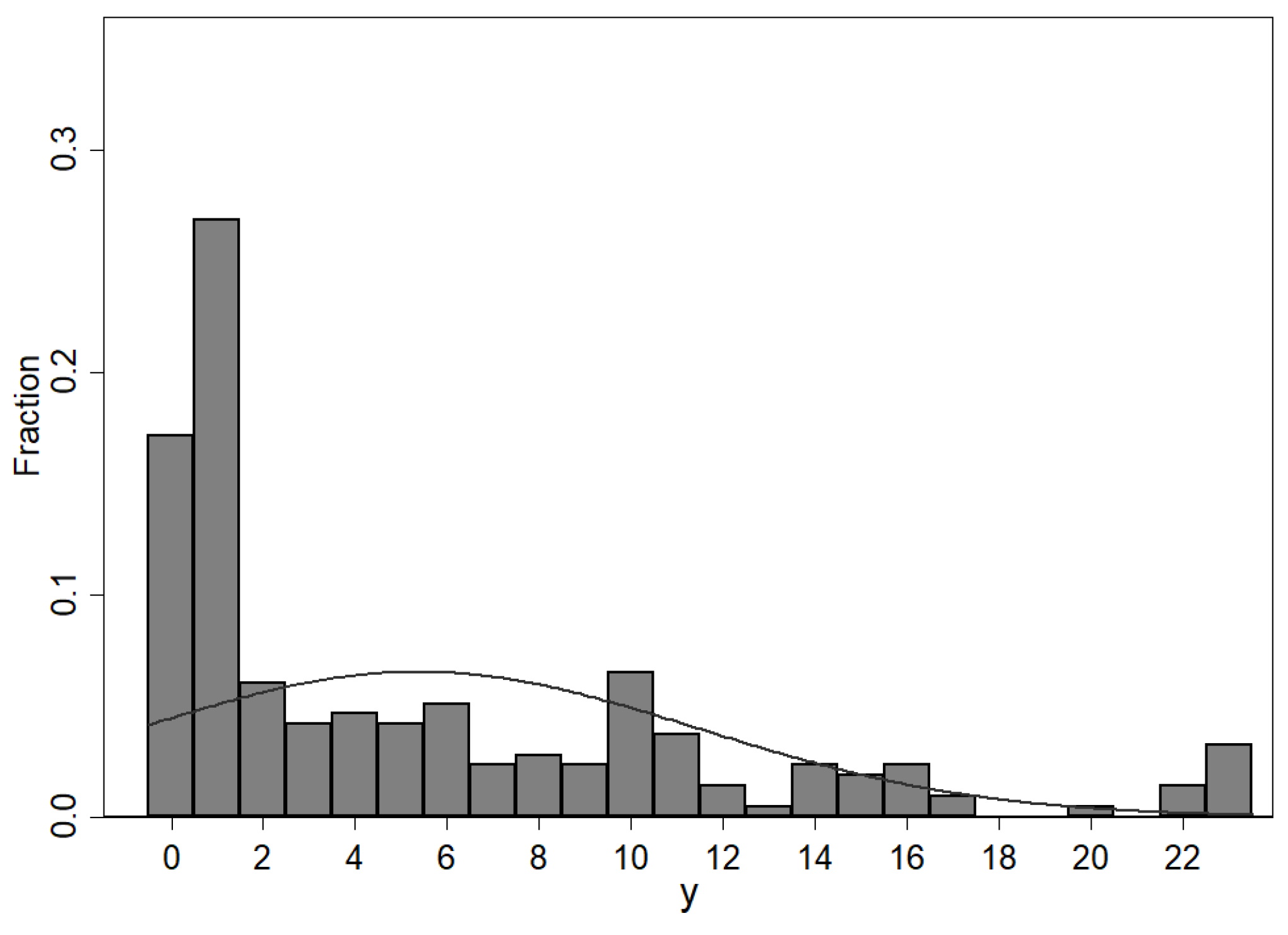
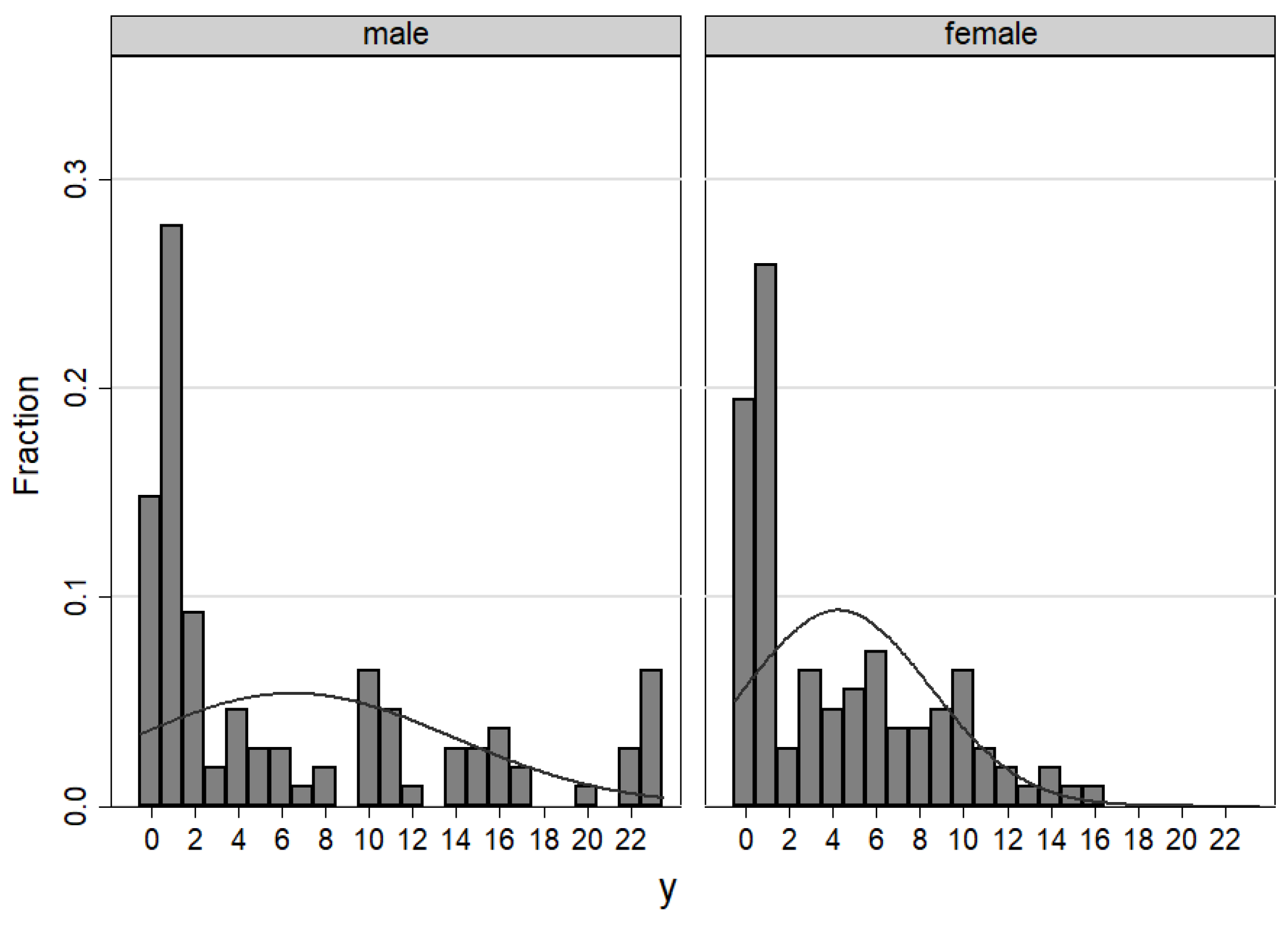
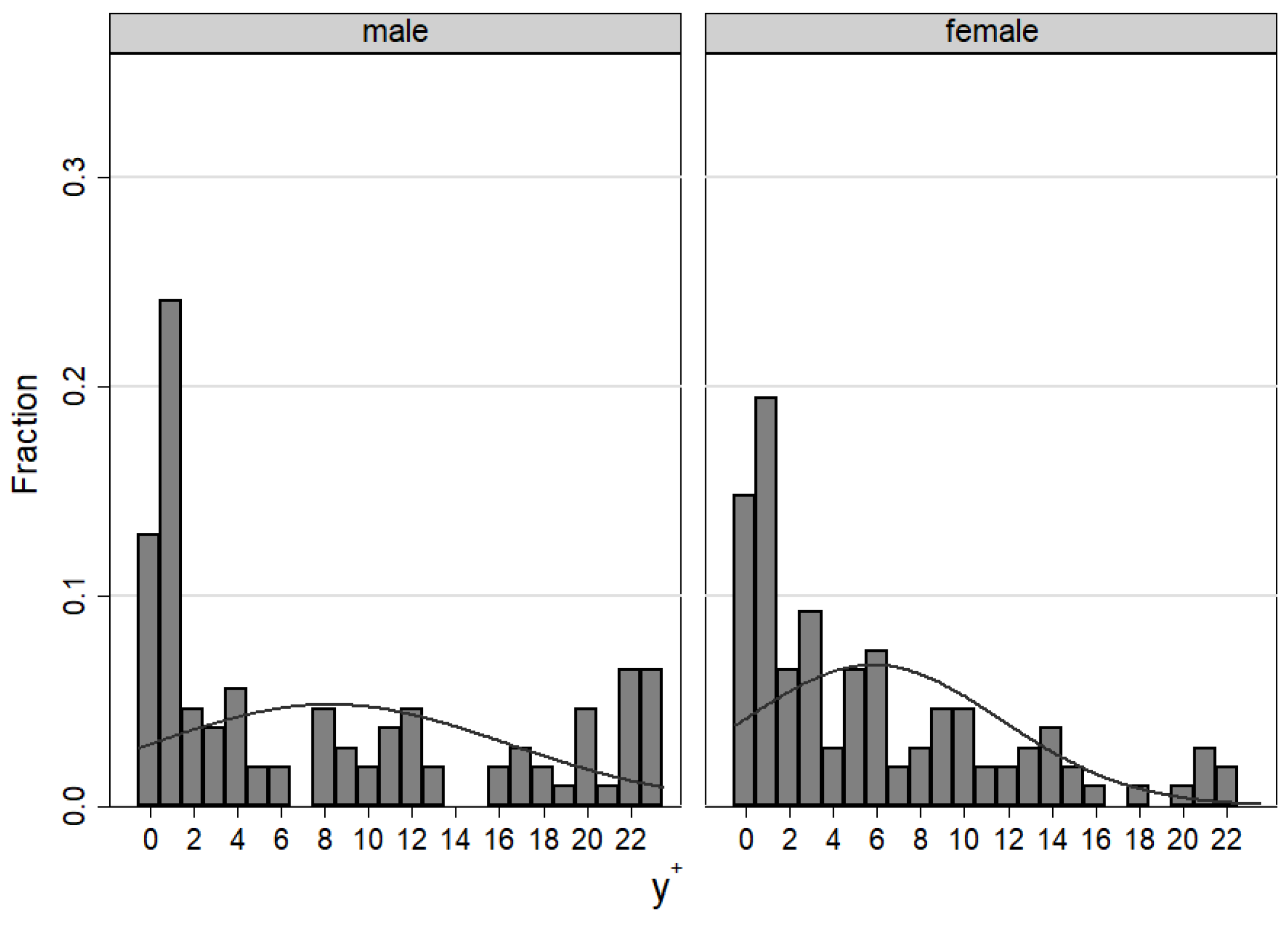
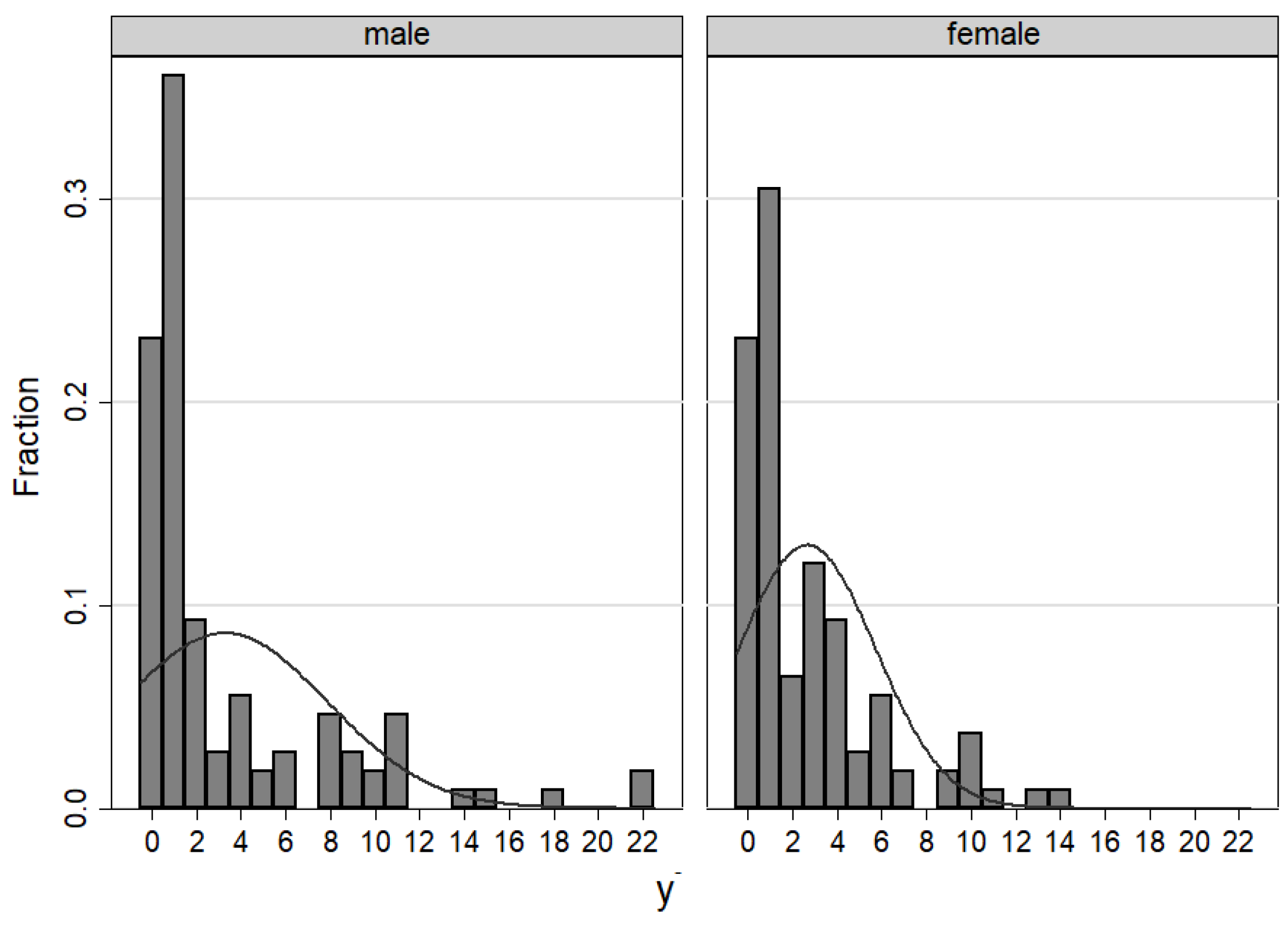
| y | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 5.361 | 6.991 | 2.963 | 2.176 | 1.630 | 2.398 | 3.185 |
| Std. Dev. | 6.123 | 7.268 | 3.929 | 2.173 | 3.212 | 4.344 | 5.706 |
| Min | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | -10 |
| Max | 23 | 23 | 22 | 13 | 20 | 22 | 22 |
| Paired t-test | |||||||
| () | () | () | () | ||||
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.031 | |||
| y | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| Mean | 6.491 | 4.231 | 8.194 | 5.787 | 3.269 | 2.657 | 7.136 | 5.080 | 4.926 | 3.130 | 2.602 | 1.750 |
| Std. Dev. | 7.392 | 4.255 | 8.244 | 5.936 | 4.623 | 3.076 | 5.197 | 3.036 | 6.496 | 4.377 | 3.318 | 2.019 |
| obs | 108 | 108 | 108 | 108 | 108 | 108 | 44 | 54 | 108 | 108 | 108 | 108 |
| Paired t-test () | ||||||||||||
| p-value | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.254 | 0.020 | 0.018 | 0.024 | ||||||
| % | % | % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 6.5 | 43.5 | 50.0 | 3.889 | 4.407 |
| Female | 13.0 | 40.7 | 46.3 | 2.500 | 3.148 |
| Paired t-test () | |||||
| p-value | 0.070 | 0.083 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Cagno, D.; Galliera, A.; Güth, W.; Panaccione, L. Gender Differences in Yielding to Social Influence: An Impunity Experiment. Games 2018, 9, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/g9040086
Di Cagno D, Galliera A, Güth W, Panaccione L. Gender Differences in Yielding to Social Influence: An Impunity Experiment. Games. 2018; 9(4):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/g9040086
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Cagno, Daniela, Arianna Galliera, Werner Güth, and Luca Panaccione. 2018. "Gender Differences in Yielding to Social Influence: An Impunity Experiment" Games 9, no. 4: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/g9040086
APA StyleDi Cagno, D., Galliera, A., Güth, W., & Panaccione, L. (2018). Gender Differences in Yielding to Social Influence: An Impunity Experiment. Games, 9(4), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/g9040086





