Abstract
We introduce a model for studying the evolutionary dynamics of Poker. Notably, despite its wide diffusion and the raised scientific interest around it, Poker still represents an open challenge. Recent attempts for uncovering its real nature, based on statistical physics, showed that Poker in some conditions can be considered as a skill game. In addition, preliminary investigations reported a neat difference between tournaments and ‘cash game’ challenges, i.e., between the two main configurations for playing Poker. Notably, these previous models analyzed populations composed of rational and irrational agents, identifying in the former those that play Poker by using a mathematical strategy, while in the latter those playing randomly. Remarkably, tournaments require very few rational agents to make Poker a skill game, while ‘cash game’ may require several rational agents for not being classified as gambling. In addition, when the agent interactions are based on the ‘cash game’ configuration, the population shows an interesting bistable behavior that deserves further attention. In the proposed model, we aim to study the evolutionary dynamics of Poker by using the framework of Evolutionary Game Theory, in order to get further insights on its nature, and for better clarifying those points that remained open in the previous works (as the mentioned bistable behavior). In particular, we analyze the dynamics of an agent population composed of rational and irrational agents, that modify their behavior driven by two possible mechanisms: self-evaluation of the gained payoff, and social imitation. Results allow to identify a relation between the mechanisms for updating the agents’ behavior and the final equilibrium of the population. Moreover, the proposed model provides further details on the bistable behavior observed in the ‘cash game’ configuration.
PACS:
89.20.-a
1. Introduction
Poker is one of the most famous card games and constitutes also an open challenge for artificial intelligence and game theory [1,2,3,4]. In last years, mainly due to the advent of online gaming platforms, Poker has widely increased its popularity and its prestige, up to be considered even as a profession. However, in this scenario, an important question is still feeding an old debate: ‘Is Poker a Skill Game?’. This question has not yet a clear and shared answer, and its relevance is given by the related implications, spanning from legal aspects to healthcare problems [5,6,7]. For instance, considering Poker as gambling would entail the need to include it in the list of dangerous activities, i.e., those that can lead to the emergence of an addiction, and that can require clinical treatments. It is worth to emphasize that the utilization of money and the influence of luck, barely measurable, represent two main elements that support its classification as ‘gambling’. On the other hand, the possibility to apply a rational strategy (e.g., based on mathematics) for improving the success probabilities, suggests that Poker can be really considered as a ‘skill game’, e.g., like Chess. In order to shed some light on this issue, two recent works [8,9] analyzed the dynamics of an agent population, whose interactions were based on a simplified version of Poker. In particular, these mentioned models consider agents behaving in two possible ways: ‘rational’ and ‘irrational’. Rational agents are those that play Poker following a mathematical strategy, while irrational agents are those that play randomly. In particular, in the model presented in [9] agents can modify their strategy and the whole dynamics has been studied by a compartmental approach. The latter, as some models defined in epidemiology (e.g., SIS (Susceptible-Infected-Susceptible) model [10]), allows to provide a macroscopical description of the population, and it has been named RIR model (i.e., Rational-Irrational-Rational). It is worth noting that the RIR model [9] (see Appendix A for a full description) has been studied in two different configurations: full challenge and one-round challenge. Full challenges entail each interaction lasts until the winner gains all the money of its opponent, thus different rounds can be required. Instead, the second configuration (i.e., one-round challenge) entails each interaction lasts for only one betting round. After each interaction, in both configurations, the amount of money of each player is set to the initial value. In addition, each interaction considers only two agents at time, i.e., it is a pairwise interaction defined ‘heads-up’ in the Poker jargon. Here, the full challenge configuration can be related to Poker tournaments, while the one-round challenge can be related to the ‘cash game’ variant. Since agents modify their behavior by imitating that of the winner, after each challenge a well mixed population reaches an ordered phase, i.e., after a number of interactions all agents share the same strategy. Remarkably, the full challenge configuration indicates that even with very few rational agents in the population, at , the final ordered phase is always composed of rational agents. A more complex situation is observed in the case of one-round challenges, since a bistable behavior emerges. In particular, considering the same initial density of rational agents, it is possible to reach both equilibria, i.e., full rational and full irrational. Clearly, increasing the amount of rational agents at the beginning of the challenge, increases the number of final equilibria corresponding to full rational. As result the emergence of the bistable behavior described in [9] still deserves attention. It is also worth to highlight that the statistical physics approach to Poker, presented in these models [8,9], leads to two main conclusions: (1) the nature of Poker strongly depends on the player’s behavior and (2) Poker tournaments can be classified as ‘skill game’, while ‘cash-game’ challenges composed of few rounds make Poker similar to gambling. In this work, we aim to obtain further insights on Poker by using an approach based on the Evolutionary Game Theory (hereinafter EGT) [11,12,13,14,15,16]. EGT represents the attempt to study the evolutionary dynamics of a population by the framework of game theory [17,18], and taking into account the Darwinian theory of natural evolution. Evolutionary games can be used for studying a number of scenarios, spanning from socio-economic dynamics to biological systems [11,14,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31]. The proposed model aims to study the equilibria that can be reached in a population, considering rational and irrational agents, by focusing on two degrees of freedom: the imitation probability and the success probability of rational agents . The first degree (i.e., ) indicates the probability to modify a behavior (e.g., from rational to irrational) by imitating the opponent, while indicates the success probability of rational agents when play against irrational ones. Thus, as below explained, we can avoid to focus on full challenges or on one-round challenges, because on varying the value of we are able to consider different cases, i.e., from short to long-lasting challenges. Here, it is important to evaluate the influence of the imitation probability since in real Poker challenges, it is not always possible to imitate the winner (e.g., players can decide to hide the own cards when the opponent folds). In addition, cash-game challenges can last few or many rounds, therefore the success probability varies over time. In order to take into account also the second observation, we studied also the case with a variable value of (during the same challenge). In doing so, we observed the same bistable behavior found in one-round challenges of [9]. Then, we compared the outcomes of the two models, i.e., the new one and the previous one presented in [9]. To conclude, it is worth to note that the proposed model constitutes a new application of EGT, and allows to reach further insights for understanding the nature of Poker. In addition, our results shed more light on the bistable behavior reported in [9]. The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the proposed model. Section 3 shows results of numerical simulations. Eventually, Section 4 ends the paper. In addition, since the model presented in [9] is often adopted as reference, it is fully described in Appendix A.
2. Materials and Methods
In this section, we present the proposed model. We considered an agent population whose interactions are based on a simple game inspired from Poker (in particular focusing on the variant named Texas Hold’em—see [32]). The agents may follow two different strategies: rational and irrational. Rational agents are those that take actions according to a mathematical strategy, i.e., those that aim to maximize the probability to succeed by a ‘rational’ mindset. Irrational agents, on the contrary, are those that take actions randomly, i.e., without to consider the value of their own cards nor other strategies. According to results achieved in previous works [8,9], the winning probability of rational agents depends on the duration of a challenge. Notably, rational agents have high probability to succeed against irrational agents when the amount of rounds that constitute a challenge increases. For instance, if challenges terminate when one agent wins all the money of its opponent, the success probability of rational agents increases up to . At the same time, when a challenge is composed of only one round, a rational agent succeeds against an irrational one with a probability close to . In the case the agents modify their strategy, imitating that of their winning opponent, a mixed population (i.e., composed of of rational agents at ) can reach two different equilibria: full rational and full irrational. As previously discussed, in real scenarios the behavior of the winner is not always disclosed. Thus, the imitation probability, on average, is much smaller than 1. In order to analyze a system, taking into account this last observation, we introduce a model inspired from EGT where agents play Poker and modify their strategy according to the following mechanisms: imitation and payoff evaluation. The former can be adopted when the winning opponent reveals its strategy, while the latter entails to modify a behavior according to the amount of the gained payoff. Thus, if after an iteration the agent’s payoff decreases, it is more likely a rational agent becomes irrational, and vice versa. From the EGT perspective, the two updating mechanisms allow to implement a ’strategy revision phase’. Notably, in the case a losing agent (say y) decides to imitate its opponent (say x), it computes the transition probability (from rational to irrational, and vice versa) by using a Fermi-like equation [20] which reads
where and indicate the strategy of the agents x and y, respectively, meanwhile and indicate their payoff; the constant K parametrizes the uncertainty in adopting a strategy. By using , we implement a strategy revision phase with a very small amount of irrationality [33]. Instead, when an agent does not imitate its opponent, it changes its strategy according to the following probability
where indicates the transition probability of the y-th agent to modify its strategy (from rational to irrational, and vice versa), indicates its payoff divided by constant equal to 4. In particular, at each iteration, the two agents are randomly selected and they play with 4 opponents. In addition, since we studied both the well-mixed configuration and the spatially structured configuration, we highlight that in the second case the two randomly selected agents, and their opponents, are nearest neighbors.
Now, it is worth to highlight that the payoff of this game is very simple: when an agent wins a challenge, its payoff increases of 1, whereas each time it loses a challenge the payoff decreases of 1. Thus, the mathematical definition of the payoff reads: , with outcome of the i-th challenge and equal to , i.e., if successful, otherwise . According to these rules, we considered the evolution of a population on varying and (i.e., imitation probability and success probability of rational agents). We recall that when two agents of the same kind face each other, both have the same probability to succeed (i.e., ). Eventually, it is worth to emphasize that the strategy imitation takes place only after comparing the payoffs of the two considered agents. For example, if the agent y is undergoing a strategy revision phase with , it will imitate the agent x only after evaluating the payoff difference, as defined in (1). For instance, if y wins 3 out of 4 challenges, losing only against the agent x that, in turn, wins only against y and loses all the other challenges, is clearly bigger than . Accordingly, the probability that the agent y imitates x is very low even if . Finally, we highlight that the well-mixed configuration allows to perform a mean field analysis of the system, while the other one allows to evaluate the role of an interaction topology (e.g., [34]). Remarkably, even a simple topology, like a regular square lattice, can be strongly relevant in in the dynamics of some games, a for instance the Public Goods Game (see [33]). Summarizing, our population evolves according to the following steps:
- At , set a number of rational and irrational agents in the population;
- select randomly one agent x, and select randomly one opponent y (being a neighbor in the case of the lattice topology);
- each selected agent plays the game with all its four opponents (randomly composed in the well mixed case), then computes its payoff;
- agent y performs the strategy revision phase according , then adopting Equations (1) or (2), to compute the weight probability to change its behavior/strategy;
- repeat from (2) until an ordered phase is reached, or up to a limited number of time steps elapsed.
Then, before to show results of numerical simulations, we highlight that the maximum number of time steps has been set to .
3. Results
Let us start considering the results achieved in [9], where a well-mixed population played both full and one-round challenges—see Figure 1.
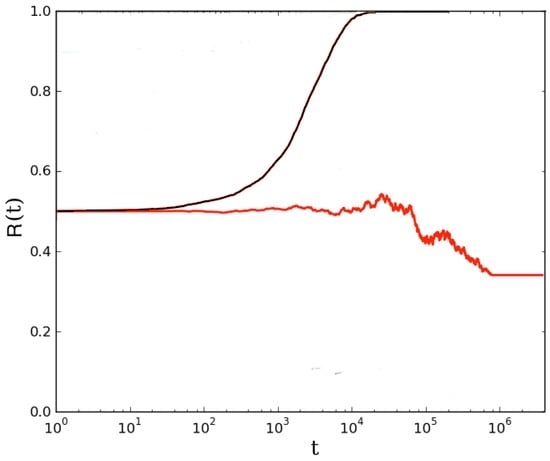
Figure 1.
Mean field analysis of a population playing Poker. Amount of rational agents over time ( indicates rational, irrational) in the two different configurations analyzed in [9], for the case with an equal starting density of rational and irrational agents. Black line indicates the result achieved with full challenges. Red line indicates the result achieved with one-round challenges. Results have been averaged over different simulation runs.
In particular, considering the same starting conditions, as the initial density of rational agents in the population, Figure 1 clearly indicates that full challenges support rational agents (i.e., all agents become rational after a number of time steps), while one-round challenges entail sometimes rational succeed, other times all the population turns to irrational (i.e., irrational succeed). As previously discussed, the bistable behavior of the population playing one-round challenges needs further attention, in order to better understand the related motivation. According to the investigations performed in [8,9], rational agents have about to succeed in full challenges, and about in one-round challenges. Therefore, increasing the number of rounds from 1 to ∞ entails to support rationals. In addition, the model presented in [9] considers that agents modify their behavior by imitating the winning opponents. So, in order to represent scenarios closer to real challenges, it is important to observe that players are not always able to imitate their opponent because the latter can also keep hidden her/his own cards (notably, only in particular conditions players have to show their cards). Accordingly, here we analyze the evolutionary model of Poker on varying two relevant parameters: the imitation probability (i.e., ) and the success probability of rational agents (i.e., ). Figure 2 shows results of numerical simulations performed on a well mixed population with N = 10,000 agents.
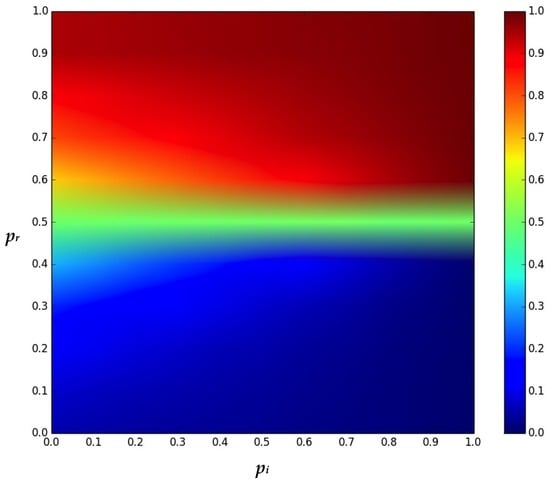
Figure 2.
Strategy distribution in the proposed model, on varying the degrees of freedom and , i.e., the imitation probability and the probability a rational agent succeeds over an irrational one, respectively. Red indicates full rational, while blue full irrational. Results have been averaged over 100 simulation runs.
Since some games, as the Public Goods Game, show a different behavior in networked topologies [33,35,36,37,38,39,40,41], we studied the proposed model also in a regular square lattice with periodic boundary conditions. Remarkably, we did not find any particular difference between the the well-mixed case and the lattice topology, as reported in Figure 3 that shows very small and non-correlated values.
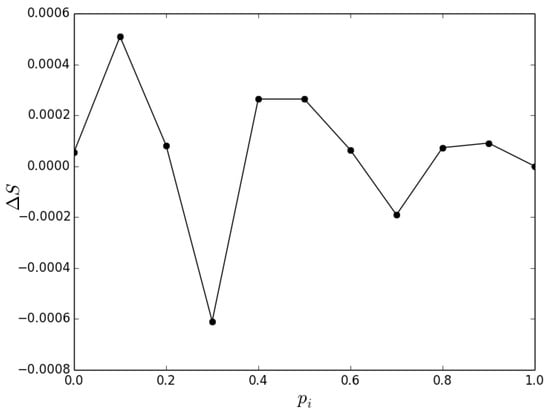
Figure 3.
Average difference, in the summation of states ( indicates rational, irrational), obtained on varying the imitation probability, between results achieved in a well mixed population and in a structured population (i.e., regular square lattice with periodic boundary conditions). Results have been averaged over 100 simulation runs.
Then, we considered different initial densities of rational agents (i.e., ) and, as for games like the Public Goods Game, we found that the process is independent from the value of , i.e., the latter does not affect the outcomes. Eventually, as anticipated before, in order to make the model closer to real scenarios we analyzed it on varying the value of during the same simulation (showing in the plot the average result, as for the other cases)—see Figure 4. In particular, at each time step, the value of can be , or , both with equal probability (i.e., ).
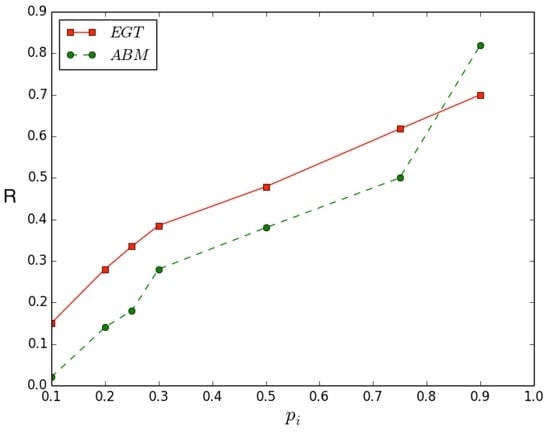
Figure 4.
Comparison between the outcomes achieved in the model described in [9], defined as ABM (i.e. Agent-Based Model) in the legend, and those achieved in this work, defined as EGT (i.e., Evolutionary Game Theory) in the legend. Amount of rational agents R ( indicates rational, irrational). In particular, this analysis aims to evaluate if one-round challenges analyzed in [9] behave like an EGT-based model with a varying (i.e., probability of success of rational agents). Results have been averaged over 100 simulation runs.
It is worth to observe that results achieved with one-round challenges in [9] are very similar to those achieved on varying during the same simulation. Therefore, in our view, the bistable behavior is due to the variation, along the same challenge, of the success probability of rational agents. In particular, the bistable behavior reported in [9], may reflect the fact that strong card combinations, being opportunities for those that play by using a mathematical strategy (i.e., rational agents), are not very frequent (as real Poker players usually know from direct experience, and as the theory of probability suggests given the structure of ‘playing cards’ used in Poker). Thus, several times rational agents fold without to participate. So, since one-round challenges entail a loser imitates the winner, a rational agent many times becomes irrational for this reason, i.e., for the low rate of good own cards (defined as hand in the Poker jargon). Finally, it is worth to point out that this last observation can be, in principle, provided only considering the probability laws, and the dynamics of the model described in [9]. However, the evolutionary model here presented is able to prove it by the numerical simulation.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
In this work we propose a model based on EGT for studying the dynamics of Poker, considering a simplified version of this game. In particular, our agents are provided with two behaviors (or strategies), i.e., rational and irrational, and we analyze the evolution of the population in function of two degrees of freedom: the imitation probability and the success probability of rational agents. We remind that rational agents represent players that take decisions using a mathematical based strategy, while irrational agents are those that play randomly. In addition, since our agents can modify their strategy over time, they undergo a ’strategy revision phase’, whose aim is to increase their payoff. In particular, according to an imitation probability, losing agents may assume the strategy of their opponents, or they evaluate to change strategy considering the trend of their payoff. In the first case, they know the strategy of their opponent, while in the second case they do not. Before to discuss about the achieved results, we deem relevant to clarify an important conceptual point: even if the proposed model is based on EGT, it does not constitute a dilemma game, like for instance the Prisoner’s dilemma [12,19,42,43] and the Public Goods Game [33,44,45]. Notably, agents do not have to chose between their own benefit and that of their community of belonging. So, we analyzed the equilibria reached by the population, both in the mean-field and in a structured configuration, on varying the degrees of freedom before illustrated. In general, we found only two final equilibria: full rational and full irrational, even with an imitation probability equal to zero. It is worth to point out that when is equal to 1, an absorbing state characterized by a full order is highly expected, as demonstrated in a number of models embodying an imitative mechanism (the most simple example is the voter model [46]). According to this observation, and as shown in Figure 2, the transition between full irrational to full rational appears quite smooth for close to zero, and becomes more sharp increasing up to 1, where a critical threshold, i.e., , between the two regimes can be clearly identified. Although further analyzes are mandatory for classifying the observed phase transition, on a quality level we can state that for low a second order phase transition occurs, while for high emerges a first order phase transition. Now, we recall that in the proposed model setting to 1 does not ensure that, during an iteration, one agent imitates another one. The motivation is that the imitation takes place with a probability depending on the payoff difference between the selected agents. For instance, if and the agent undergoing the ‘strategy revision phase’ achieved a payoff higher than that of its opponent, the imitation process does not take place. The role of a pure imitative mechanism has been investigated in [47], where authors analyzed the link between the Public Goods Game and the voter model. Notably, a voter model like mechanism emerges in the Public Goods Game at high temperature, i.e., when agents change strategy without to consider the payoff differences. Moreover, it is worth to recall that results shown in Figure 2 are independent from the initial density of rational agents. Eventually, considering the results achieved on varying the during each challenge, we found that they are very similar to those achieved by the ‘one-round’ configuration of the model presented in [9]. Therefore, the observed bistable behavior of the population can be explained by the fact that during a challenge, rational agents fold weak hands and, according to the theory of probability (see also the Sklansky tables [32]), there are many more weak hands than strong ones. To conclude, results achieved by numerical simulations allow to get further insights on the game of Poker, showing the relevance of models based on EGT and, in addition, allow to shed light on the bistable behavior reported in [9]. As for future work, we deem relevant to analyze the proposed model by arranging agents on more complex topologies, as scale-free networks.
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank the National Group of Mathematical Physics (GNFM-INdAM) for supporting his work.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EGT | Evolutionary Game Theory |
| RIR | Rational-Irrational-Rational |
| SIS | Susceptible-Infected-Susceptible |
| ABM | Agent-Based Model |
Appendix A
Here, we provide a full description of the RIR model presented in [9]. The RIR model implements ‘heads-up’ challenges, so that only two agents are considered at each time step. Agents can be rational and irrational. The former play according rules based on the Sklansky tables [32], while the latter (i.e., irrational) play randomly. The duration of a challenge spans from 1 to n rounds. Thus the RIR mainly refers to the Poker format known as ‘cash game’ (even if, in principle, can be adapted also for representing tournaments). The population evolves following the dynamics of the voter model [46], so that each agent has a state representing its behavior (i.e., rational or irrational): (rational) and (irrational), that varies according to its interactions. Notably, losers imitate their opponents (i.e., the winners). The success probability of rational agents against irrational ones (i.e., ), strongly depends on the number of rounds. In particular, when the challenge terminates once one agent wins all the money of its opponent, i.e., for , , as computed in [42]. Thus, for , a ‘heads-up’ poker challenge (involving the agents x and y) is reduced to a coin flip with winning probabilities
and . Recalling that that ’cash game’ challenges can last from 1 to n rounds, two main cases are considered:
- (a) : full challenge;
- (b) : one round.
Agents start a new challenge always with the same amount of money (called ‘starting stack’), regardless of their previous result. Moreover, in the ‘cash game’ format the minimal amount of a bet does not increase over time (as it occurs in Poker tournaments). Then, the ‘starting stack’ has been set to 10,000 and the minimal fee to pay (at each round) to 100. Remarkably, both considered cases, i.e., a and b, aim to represent real scenarios. Notably, the case b refers to the so called ‘rush poker’, and it is worth to highlight that Equation (A1) cannot be used, since it holds only for full challenges (i.e., case a). For the first case (i.e., a), it is possible to define a mean field approximation [48] considering the provided winning probabilities (A1). Since agents can change strategy/state over time, the dynamics of the population can be described by the following system of equations
with and density of rational and irrational agents, respectively. The parameters a and b represent the winning probabilities of each species (i.e., rational and irrational), then and . In the case b, the winning probabilities of rational agents cannot be defined a priori as for the case a. Therefore, numerical simulations are mandatory in order to study the final equilibrium of the population. To conclude it is worth to note that, since the Sklansky tables [32] suggest to play usually with a small set of hands, many rounds are won by irrational agents due to the several ‘fold’ actions performed by rational agents.
References
- Bowling, M.; Burch, N.; Johanson, M.; Tammelin, O. Heads-up limit hold’em poker is solved. Science 2015, 347, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahl, F.A. A Reinforcement Learning Algorithm Applied to Simplified Two-Player Texas Hold’em Poker. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Machine Learning: ECML 2001—LNCS, Freiburg, Germany, 5–7 September 2001; Volume 2167, pp. 85–96.
- Teofilo, L.F.; Reis, L.P.; Lopes Cardoso, H. Computing card probabilities in Texas Hold’em. In Proceedings of the 2013 8th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Lisboa, Portugal, 19–22 June 2013; pp. 1–6.
- Seale, D.A.; Phelan, S.E. Bluffing and betting behavior in a simplified poker game. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2010, 23, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannum, R.C.; Cabot, A.N. Toward Legalization of Poker: The Skill vs. Chance Debate. UNLV Gaming Res. Rev. J. 2009, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, J.M.; Dhar, Z.; Verbiest, T. Poker and the Law: Is It a Game of Skill or Chance and Legally Does It Matter? Gaming Law Rev. 2007, 11, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabot, A.; Hannum, R. Poker: Public Policy, Law, Mathematics, and the Future of an American Tradition. TM Cooley Law Rev. 2005, 22, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Javarone, M.A. Poker as a Skill Game: Rational versus Irrational Behaviors. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2015, 2015, P03018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javarone, M.A. Is Poker a Skill Game? New Insights from Statistical Physics. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2015, 110, 58003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, Y.; Vazquez, A. Disease spreading in structured scale-free networks. Eur. Phys. J. B 2003, 31, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perc, M.; Grigolini, P. Collective behavior and evolutionary games—An introduction. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2013, 56, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Conformity enhances network reciprocity in evolutionary social dilemmas. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20141299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julia, P.C.; Gomez-Gardenes, J.; Traulsen, A.; Moreno, Y. Evolutionary game dynamics in a growing structured population. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 083031. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, E.; Hauert, C.; Nowak, M.A. Evolutionary dynamics on graphs. Nature 2004, 433, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M.A.; Wardil, L.; Perc, M.; da Silva, J.K.L. Stochastic win-stay-lose-shift strategy with dynamic aspirations in evolutionary social dilemmas. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 94, 032317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Zealots tame oscillations in the spatial rock-paper-scissors game. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 062307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, A.M. Game Theory and Its Applications; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Galam, S.; Walliser, B. Ising model versus normal form game. Physica A 2010, 389, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perc, M.; Szolnoki, A. Social diversity and promotion of cooperation in the spatial prisoner’s dilemma. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 77, 011904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Interdependent network reciprocity in evolutionary games. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szolnoki, A.; Xie, N.-G.; Wang, C.; Perc, M. Imitating emotions instead of strategies in spatial games elevates social welfare. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 96, 38002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perc, M.; Szolnoki, A. Self-organization of punishment in structured populations. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 043013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolnoki, A.; Szabo, G.; Perc, M. Phase diagrams for the spatial public goods game with pool punishment. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 0361101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D. On economic applications of evolutionary game theory. J. Evol. Econ. 1998, 8, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.; de Figueiredo, L.; Schroeter, A.; Kaleta, C. Combining metabolic pathway analysis with evolutionary game theory. Explaining the occurrence of low-yield pathways by an analytic optimization approach. BioSystems 2011, 105, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, E. Evolutionary game theory: Theoretical concepts and applications to microbial communities. Physica A 2010, 389, 4265–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Rosenbloom, D.I.; Wang, L.; Nowak, M.A. Imitation dynamics of vaccination behaviour on social networks. Proc. R. Soc. B 2011, 278, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncela, J.; Gomez-Gardenes, J.; Moreno, Y.; Floria, L.M. Cooperation in the Prisoner’s Dilemma game in random scale-free graphs. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2010, 20, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Lazaro, C.; Gomez-Gardenes, J.; Floria, L.M.; Moreno, Y. Intergroup information exchange drives cooperation in the public goods game. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 94, 042808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Biodiversity in models of cyclic dominance is preserved by heterogeneity in site-specific invasion rates. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grujic, J.; Fosco, C.; Araujo, L.; Cuesta, A.J.; Sanchez, A. Social experiments in the mesoscale: Humans playing a spatial prisoner’s dilemma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklansky, D.; Malmuth, M. Hold’em Poker for Advanced Players; Two Plus Two Publications: Henderson, NV, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Reward and cooperation in the spatial public goods game. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2010, 92, 38003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gardenes, J.; Campillo, M.; Floria, L.M.; Moreno, Y. Dynamical Organization of Cooperation in Complex Topologies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perc, M.; Gomez-Gardenes, J.; Szolnoki, A.; Floria, L.M.; Moreno, Y. Evolutionary dynamics of group interactions on structured populations: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20120997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Fath, G. Evolutionary games on graphs. Phys. Rep. 2007, 446, 97–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, M.; Pestelacci, E.; Luthi, L. Social Dilemmas and Cooperation in Complex Networks Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2007, 18, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Varga, L.; Borsos, I. Evolutionary matching-pennies game on bipartite regular networks. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 042820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, C.Y.; Meloni, S.; Zhou, C.S.; Moreno, Y. Impact of social punishment on cooperative behavior in complex networks. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardillo, A.; Reyes-Suarez, C.; Naranjo, F.; Gomez-Gardenes, J. Evolutionary vaccination dilemma in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 032803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Lazaro, C.; Cuesta, A.J.; Sanchez, A.; Moreno, Y. Human behavior in Prisoner’s Dilemma experiments suppresses network reciprocity. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javarone, M.A.; Atzeni, A.E. The role of competitiveness in the Prisoner’s Dilemma. Comput. Soc. Netw. 2015, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javarone, M.A. Statistical Physics of the Spatial Prisoner’s Dilemma with Memory-Aware Agents. Eur. Phys. J. B 2016, 89, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Competition of tolerant strategies in the spatial public goods game. New J. Phys. 2016, 18, 083021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javarone, M.A.; Antonioni, A.; Caravelli, F. Conformity-driven agents support ordered phases in the spatial public goods game. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2016, 114, 38001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggett, T.M. Interacting Particle Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Javarone, M.A.; Battiston, F. The Role of Noise in the Spatial Public Goods Game. JSTAT 2016, 7, 073404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, A. The Mean Field Ising Model trough Interpolating Techniques. J. Stat. Phys. 2008, 132, 787–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).