Salience Bias and Overwork
Abstract
1. Introduction
Related Literature
2. Model
2.1. Effort and Production
2.2. Information and Contracts
2.3. Sequence of Events
2.4. Preferences and Salience Bias
- (O)
- For all , if , then .
2.5. Benchmark 1: First-Best Effort
3. Analysis
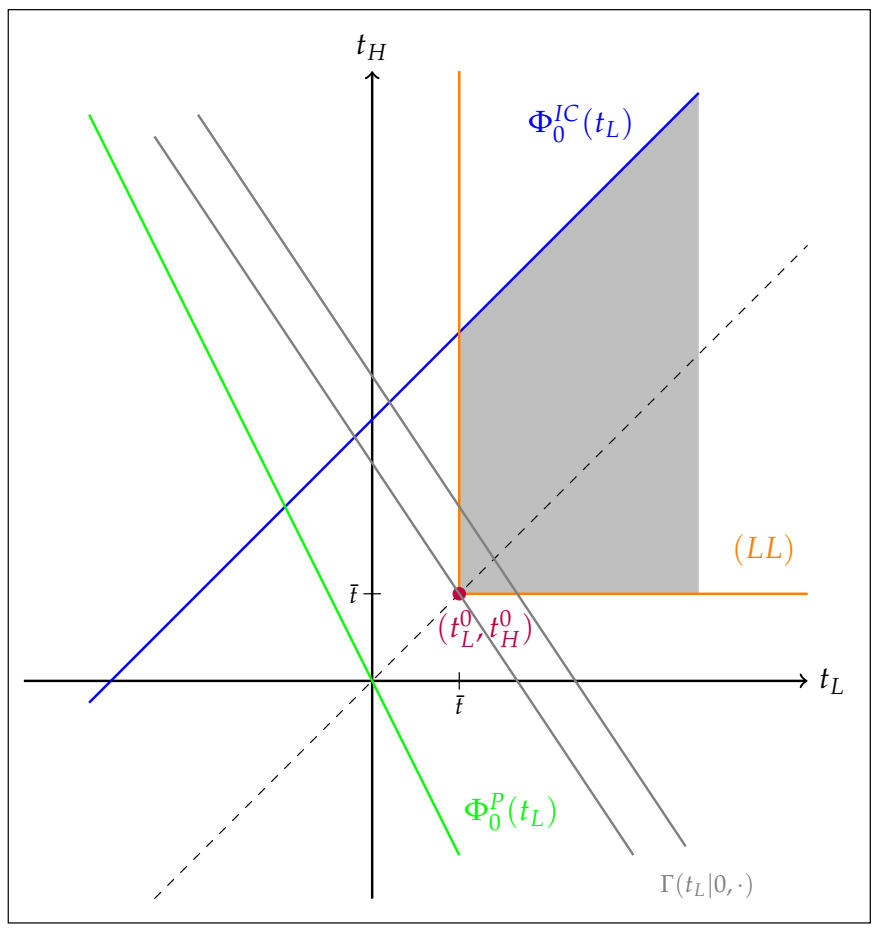
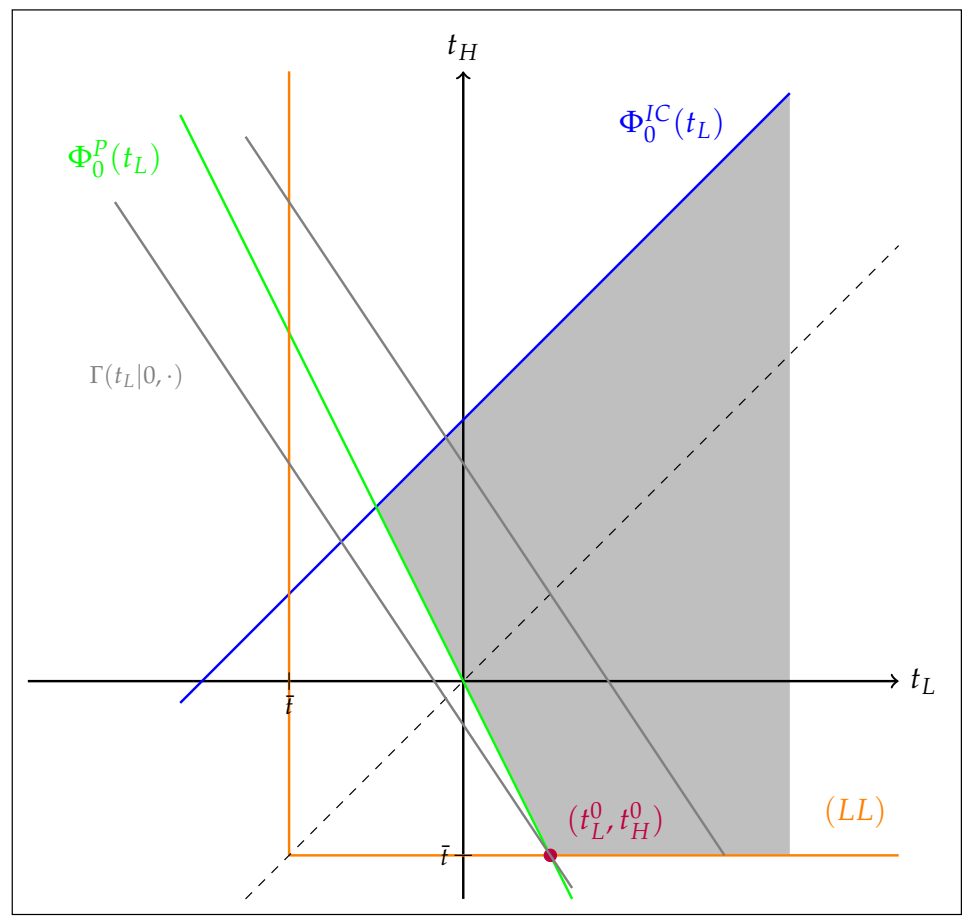
3.1. Benchmark 2: No Salience Bias
3.2. Cost-Minimizing Transfers with Salience Bias
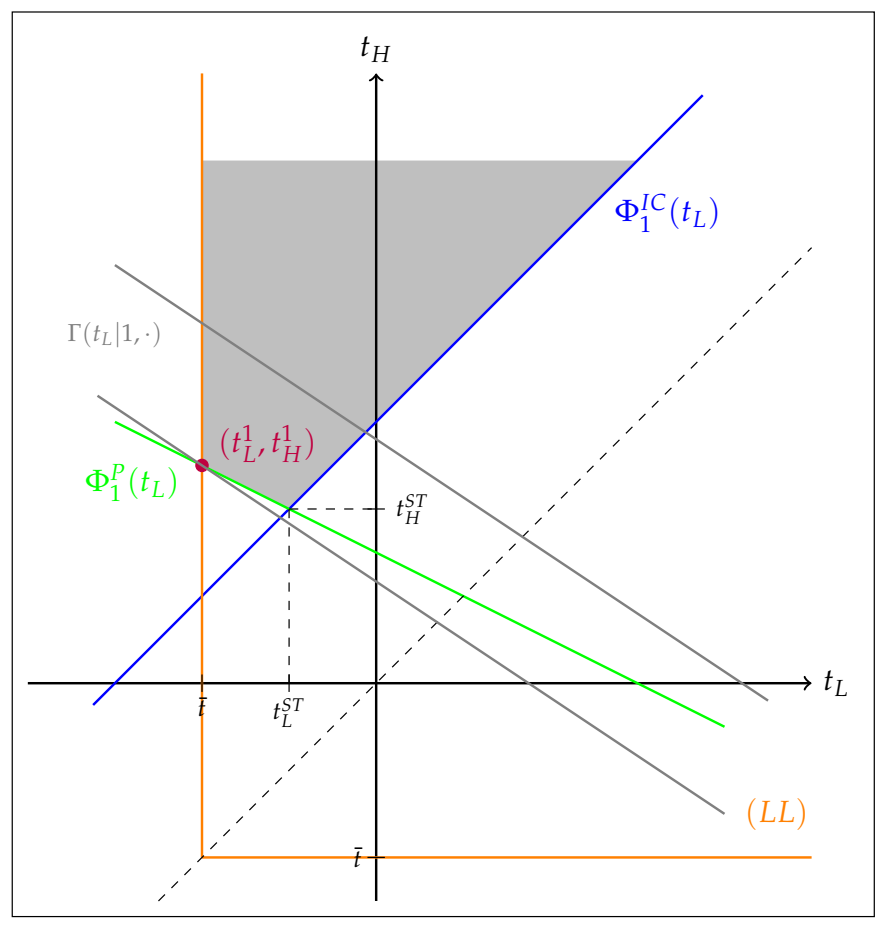
3.2.1. Implementation of High Effort ()
3.2.2. Implementation of Low Effort ()
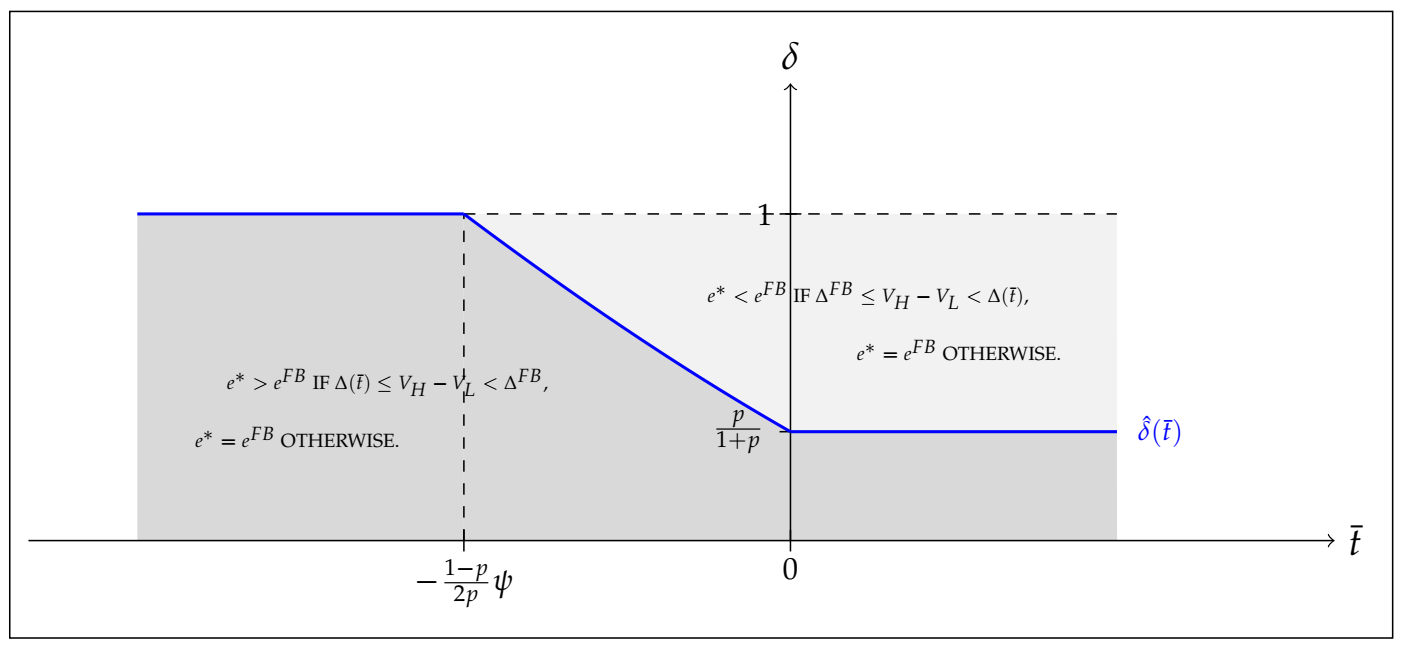
3.3. Second-Best Effort with Salience Bias
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 1 | In the taxonomy of Hart and Holmstrom [1], moral hazard refers to post-contractual private information, (in contrast to adverse selection, which refers to pre-contractual private information), and hidden action refers to a party’s private information regarding actions taken by this party (as opposed to hidden information, which refers to a party’s private information regarding its own type or some other payoff-relevant parameter). |
| 2 | The moral hazard model with hidden action, where both the principal and the wealth-constrained agent have linear utility functions for money, was applied to address questions of organization design [5,6], sales force compensation [7,8,9], job design [10,11,12,13,14], team compensation [15], delegation [16,17], lawyer compensation [18], human capital accumulation [8], and privacy protection at the workplace [19]. Experimental evidence for the predictions of the moral hazard model are provided by Hoppe and Kusterer [11], Nieken and Schmitz [20], and Hoppe and Schmitz [21]. |
| 3 | For example, Harnois and Gabriel [23] predicted that, by 2020, clinical depression would outrank cancer as the second greatest cause of death and disability worldwide. Similarly, conducting a representative study of how children felt about their employed parents, Galinsky [24] reports that most children wished for their parents to be less stressed and less tired from their respective work. |
| 4 | |
| 5 | In a dynamic setting where the same agent and the same principal interact over several periods, Ohlendorf and Schmitz [31] show that the usual finding of underwork prevails. |
| 6 | Complementary to our findings for post-contractual hidden action, Goldlücke and Schmitz [33] show that overwork can prevail in a model with post-contractual hidden information. |
| 7 | For an extensive overview of these contributions, see Herweg et al. [35]. |
| 8 | This binary-effort specification, which is widely used in contract-theoretic contributions [6,7,15,40], is primarily made to ease exposition. First, a continuous effort specification would have required a rather technical discussion of the applicability of the first-order approach. Second, with more than two effort levels and, thus, more than two choice options, salience-theoretic preferences may exhibit intransitive choice behavior, which might complicate the analysis regarding incentive compatibility. See Laffont and Martimort [41] or Salanié [42] for a textbook treatment of the binary-effort model. |
| 9 | As usual, and also the case in our model set-up, the probability of a high-value being generated is strictly higher if A exerts high effort than if A exerts low effort . With the application of salience theory requiring a state-based description of the uncertainty that underlies the production process, we capture this aspect by assuming that the probability distribution over value realizations induced by is dominated state-wise by the probability distribution over value realizations induced by . While the assumption of state-wise dominance is not necessary to derive our results, it simplifies the exposition, as it allows the restriction of attention to only three potential states of the world. |
| 10 | By now several applications of salience theory for choice under risk exist [25] that rely on the specification of the decision weight in (4). For example, regarding investor choice and market equilibrium, Bordalo et al. [43] show that salience theory can account for several empirically well-documented puzzles in the finance literature, and Cosemans and Frehen [44] find strong empirical support for these predictions using cross-section data of US stocks. Königsheim et al. [45] empirically estimate the “local-thinking” parameter of salience theory and find substantial heterogeneity with regard to whether a lottery’s upside or downside is salient. By implementing manipulations of salience in both a choice study and an eye-tracking study, Alós-Ferrer and Ritschel [46] investigate to what extend the preference reversal phenomenon can be explained by salience theory for choice under risk. |
| 11 | Making the assumption that A’s outside option does not affect the misperception of probabilities seems particularly plausible if the associated reservation utility has a non-monetary origin such as the stigma or shame of being unemployed. If, on the other hand, A’s reservation utility has a monetary origin, such as a fixed wage at the next-best occupation or unemployment benefits, then A’s outside option might well affect salience. We comment on this below in Section 4. |
| 12 | In addition to the ordering property, Bordalo et al. [25] require the function to be continuous and bounded and to satisfy two further properties called diminishing sensitivity and reflection. Neither of these assumptions is of relevance for our analysis. |
| 13 | |
| 14 | Notably, without salience bias there is a continuum of optimal contracts in the case where the participation constraint is binding. More specifically, all transfer combinations that satisfy the participation constraint with equality, which also satisfy limited liability and the incentive compatibility constraint, are part of an optimal contract. Graphically, this follows from the fact that, without salience bias, the slope of the isocost curves and the slope of the -curve are identical. For , the optimal contract for a salience-biased agent converges to one particular element of the continuum of contracts that are optimal in the absence of salience bias—the contract where is set as low as possible and is specified such that the participation constraint binds. |
| 15 | Notable alternative theories are regret theory (e.g., Loomes and Sugden [54]) and theories of additive differences (e.g., Kőszegi and Szeidl [55]). For a comprehensive overview and qualitative comparison of such theories see Bhatia et al. [56]. According to their classification of key properties, we applied a theory with (i) between-option interactions and (ii) weight transformations that are based on (iii) similarity and dissimilarity. While models of value transformations may lead to similar findings, their welfare implications might be rather different ([56], p. 1352). |
| 16 | Note that the necessary minimum wage might well be strictly positive if A’s reservation utility is strictly positive, or exerting low effort is associated with a strictly positive effort cost. |
References
- Hart, O.; Holmstrom, B. The Theory of Contracts. In Advances in Economics and Econometrics, Econometric Society Monographs, Fifth World Congress; Bewely, T., Ed.; Camebridge University Press: Camebridge, UK, 1987; pp. 71–155. [Google Scholar]
- Innes, R.D. Limited Liability and Incentive Contracting with Ex-Ante Action Choices. J. Econ. Theory 1990, 52, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, S.; Sjöström, T. Decentralization and Collusion. J. Econ. Theory 1998, 83, 196–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, R. Moral Hazard and Limited Liability: The Real Effects of Contract Bargaining. Econ. Lett. 1998, 61, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berkovitch, E.; Israel, R.; Spiegel, Y. A Double Moral Hazard Model of Organization Design. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2010, 19, 55–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.; Vereshchagina, G. Partnerships versus Corporations: Moral Hazard, Sorting, and Ownership Structure. Am. Econ. Rev. 2001, 104, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Jerath, K. Salesforce Compensation with Inventory Considerations. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 2490–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräkel, M.; Schöttner, A. Optimal Sales Force Compensation. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2016, 126, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöttner, A. Optimal Sales Force Compensation in Dynamic Settings: Commissions vs. Bonuses. Manag. Sci. 2017, 63, 1529–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, P.W. Allocating Control in Agency Problems with Limited Liability and Sequential Hidden Actions. RAND J. Econ. 2005, 36, 318–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe, E.I.; Kusterer, D.J. Conflicting Tasks and Moral Hazard: Theory and Experimental Evidence. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2011, 55, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragl, J.; Schöttner, A. Wage Floors, Imperfect Performance Measures, and Optimal Job Design. Int. Econ. Rev. 2014, 55, 525–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J. Job Design with Sequential Tasks and Outcome Externalities Revisited. Econ. Lett. 2014, 125, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J. Another Look at Job Design with Conflicting Tasks. Aust. Econ. Pap. 2018, 57, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.K.; Yoo, S.W. Optimal Incentives for Teams. Am. Econ. Rev. 2001, 93, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, Y.; Tsai, T.S. Delegating the Decision-Making Authority to Terminate a Sequential Project. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2014, 99, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräkel, M.; Schöttner, A. Delegating Pricing Authority to Sales Agents: The Impact of Kickbacks. Manag. Sci. 2019, 66, 2686–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- At, C.; Friehe, T.; Gabuthy, Y. On Lawyer Compensation when Appeals are Possible. BE J. Econ. Anal. Policy 2019, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, P.W. Workplace Surveillance, Privacy Protection, and Efficiency Wages. Labour Econ. 2005, 12, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nieken, P.; Schmitz, P.W. Repeated Moral Hazard and Contracts with Memory: A Laboratory Experiment. Games Econ. Behav. 2012, 75, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, E.I.; Schmitz, P.W. Hidden Action and Outcome Contractibility: An Experimental Test of Moral Hazard Theory. Games Econ. Behav. 2018, 109, 544–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinsky, E.; Bond, J.T.; Kim, S.; Backon, L.; Brownfield, E.; Sakai, K. Overwork in America: When the Way We Work Becomes Too Much; Families and Work Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Harnois, G.; Gabriel, P. Mental Health and Work: Impact, Issues and Good Practices; World Health Organization and International Labour Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; WHO/MSD/MPS/00.2. [Google Scholar]
- Galinsky, E. Ask the Children: What America’s Children Really Think about Working Parents; William Morrow and Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bordalo, P.; Gennaioli, N.; Shleifer, A. Salience Theory for Choice under Risk. Q. J. Econ. 2012, 127, 1243–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontek, K. A Critical Note on Salience Theory of Choice under Risk. Econ. Lett. 2016, 143, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bako, B.; Neszveda, G. The Achilles’ Heel of Salience Theory and How to Fix It. Econ. Lett. 2020, 193, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, B. Moral Hazard and Observability. Bell J. Econ. 1979, 10, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, S.J.; Hart, O.D. An Analysis of the principal–agent Problem. Econometrica 1983, 51, 7–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kräkel, M.; Schöttner, A. Minimum Wages and Excessive Labor Supply. Econ. Lett. 2010, 108, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ohlendorf, S.; Schmitz, P.W. Repeated Moral Hazard and Contracts with Memory: The Case of Risk-Neutrality. Int. Econ. Rev. 2012, 53, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englmaier, F.; Fahn, M.; Schwarz, M.A. Long-Term Employment Relations When Agents Are Present Biased; CEPR Discussion Paper No. DP13227; 2018; Available online: https://econpapers.repec.org/paper/cprceprdp/13227.htm (accessed on 6 December 2021).
- Goldlücke, S.; Schmitz, P.W. Pollution Claim Settlements Reconsidered: Hidden Information and Bounded Payments. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2018, 110, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordalo, P.; Gennaioli, N.; Shleifer, A. Salience and Consumer Choice. J. Political Econ. 2013, 127, 803–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweg, F.; Müller, D.; Weinschenk, P. Salience in Markets. In Handbook of Behavioral Industrial Organization; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, N. Price Discrimination and Salience-Driven Consumer Preferences; Technical Report, Discussion Papers; University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Friehe, T.; Pham, C.L. Settling with Salience-biased Defendants. Econ. Lett. 2020, 192, 109235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mungan, M.C. Salience and the Severity versus the Certainty of Punishment. Int. Rev. Law Econ. 2019, 57, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rosa, L.E. Overconfidence and Moral Hazard. Games Econ. Behav. 2011, 73, 429–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.; Schmitz, P.W. The Right to Quit Work: An Efficiency Rationale for Restricting the Freedom of Contract. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2021, 184, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffont, J.J.; Martimort, D. The Theory of Incentives: The Principal–Agent Model; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Salanié, B. The Economics of Contracts: A Primer; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bordalo, P.; Gennaioli, N.; Shleifer, A. Salience and Asset Prices. Am. Econ. Rev. Pap. Proc. 2013, 103, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosemans, M.; Frehen, R. Salience Theory and Stock Prices: Empirical Evidence. J. Financ. Econ. 2021, 140, 460–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Königsheim, C.; Lukas, M.; Nöth, M. Salience Theory: Calibration and Heterogeneity in Probability Distortion. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2019, 157, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alós-Ferrer, C.; Ritschel, A. Attention and Salience in Preference Reversals. Exp. Econ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, A.; Squintani, F. Overconfidence, Insurance, and Paternalism. Am. Econ. Rev. 2007, 97, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubb, M. Selling to Overconfident Consumers. Am. Econ. Rev. 2009, 99, 1770–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweg, F.; Müller, D. Overconfidence in the Markets for Lemons. Scand. J. Econ. 2016, 118, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, K.; Spiegler, R. Contracting with Diversely Naive Agents. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2006, 73, 689–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, K.; Spiegler, R. Consumer Optimism and Price Discrimination. Theor. Econ. 2008, 3, 459–497. [Google Scholar]
- Luce, R.D. Individual Choice Behavior: A Theoretical Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Tversky, A. Features of Similarity. Psychol. Rev. 1977, 84, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomes, G.; Sugden, R. Regret Theory: An Alternative Theory of Rational Choice under Uncertainty. Econ. J. 1982, 92, 805–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kőszegi, B.; Szeidl, A. A Model of Focusing in Economic Choice. Q. J. Econ. 2013, 128, 53–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Loomes, G.; Read, D. Establishing the Laws of Preferential Choice Behavior. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2021, 16, 1324–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Kahneman, D.; Tversky, A. On the Study of Statistical Intuitions. Cognition 1982, 11, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Römeis, F.; Herweg, F.; Müller, D. Salience Bias and Overwork. Games 2022, 13, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/g13010015
Römeis F, Herweg F, Müller D. Salience Bias and Overwork. Games. 2022; 13(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/g13010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRömeis, Fabio, Fabian Herweg, and Daniel Müller. 2022. "Salience Bias and Overwork" Games 13, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/g13010015
APA StyleRömeis, F., Herweg, F., & Müller, D. (2022). Salience Bias and Overwork. Games, 13(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/g13010015






