Dynamic Model of Collaboration in Multi-Agent System Based on Evolutionary Game Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. Descriptions and Notes of the Parameters in a Multi-Agent System
2.2. Payoff Matrix of Agents
2.3. Replication Dynamic Equation of Agents
3. Equilibrium Point and Stability Analysis
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
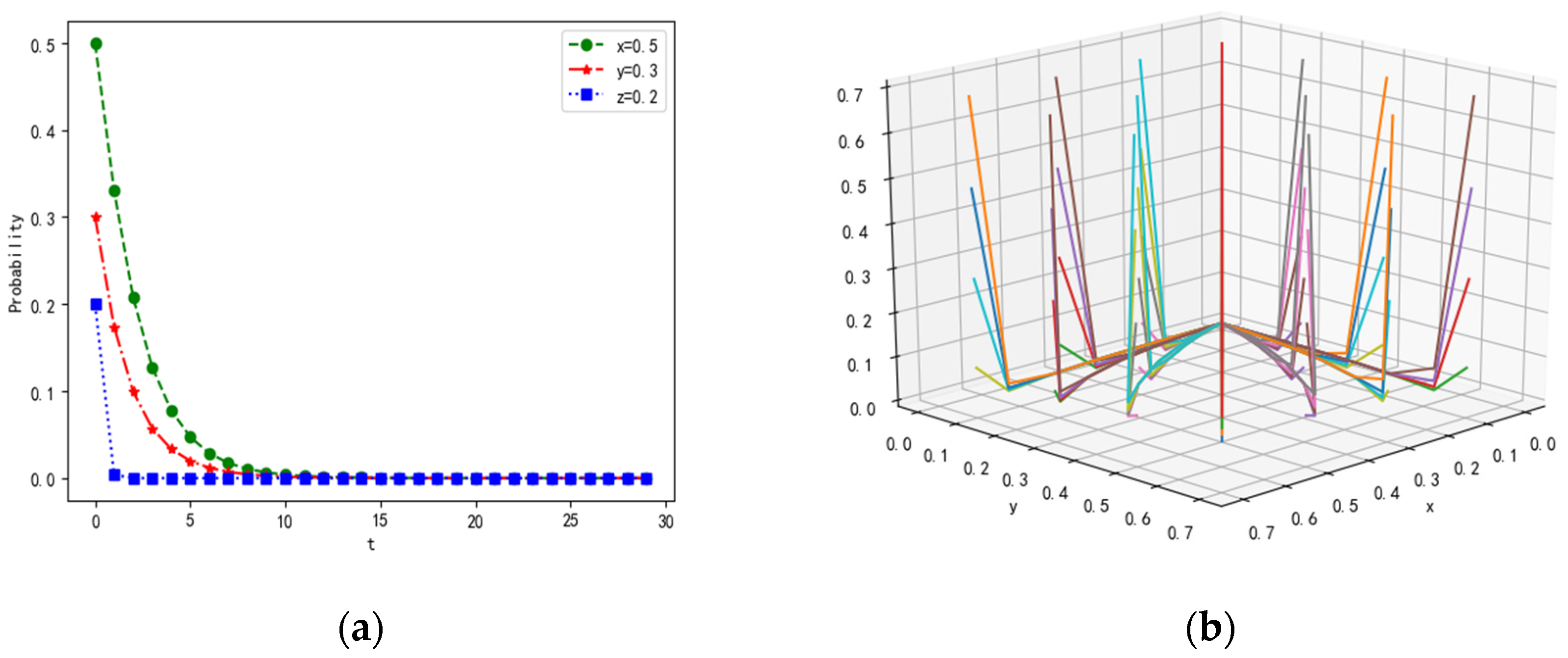
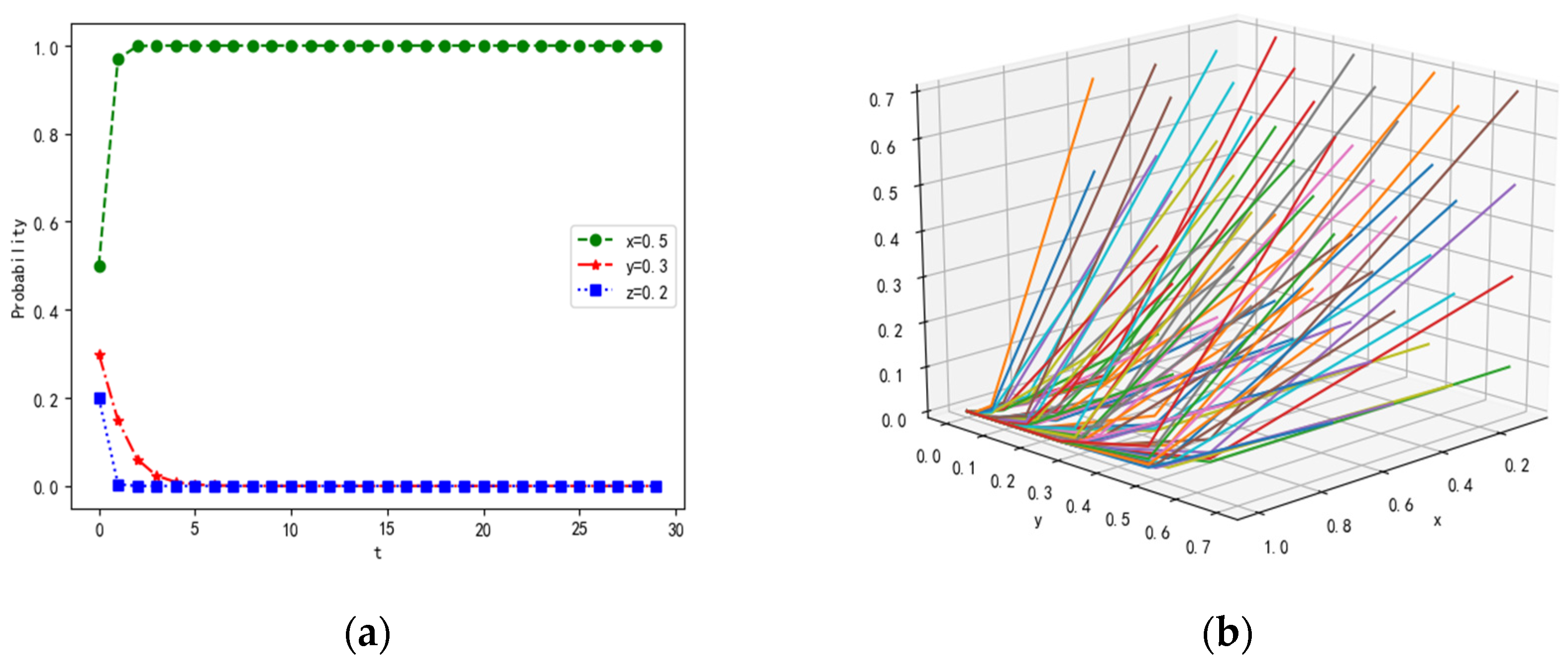
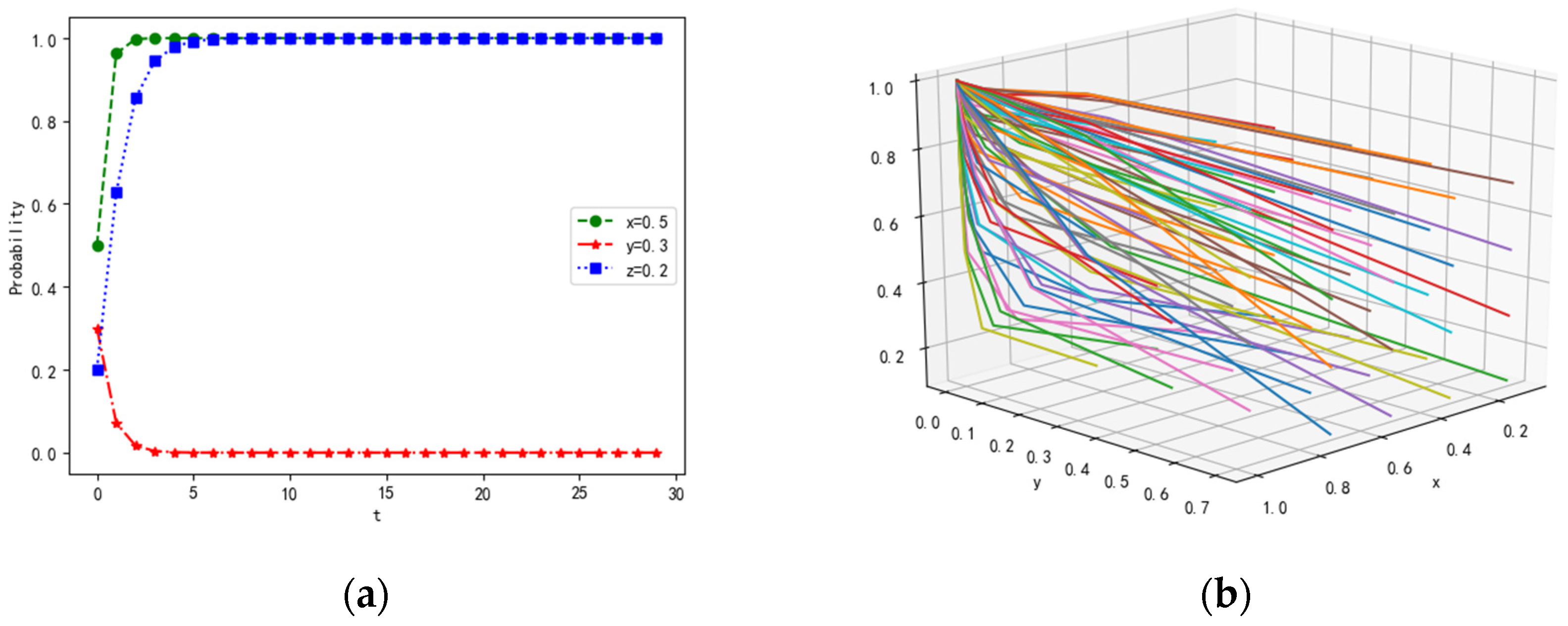
4.1. Scenarios of Different Parameters with Constraint Conditions in the Equilibrium Points
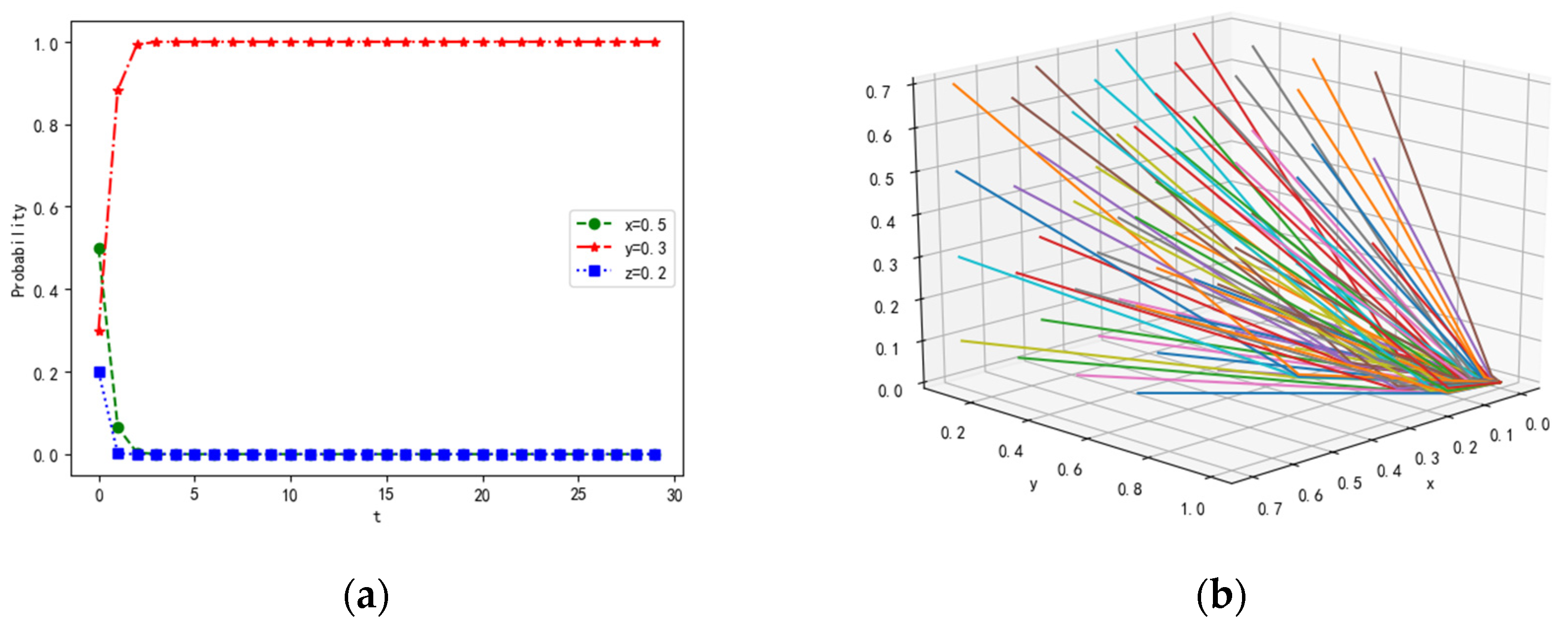
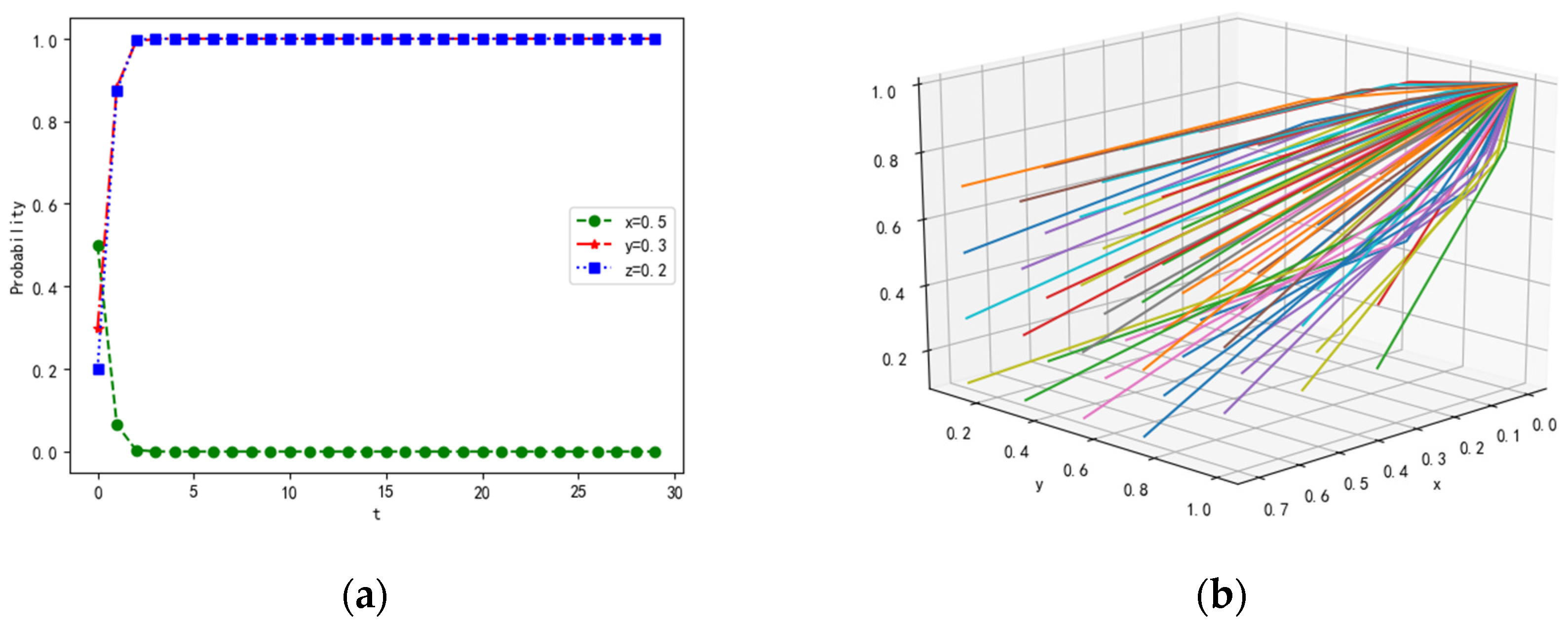
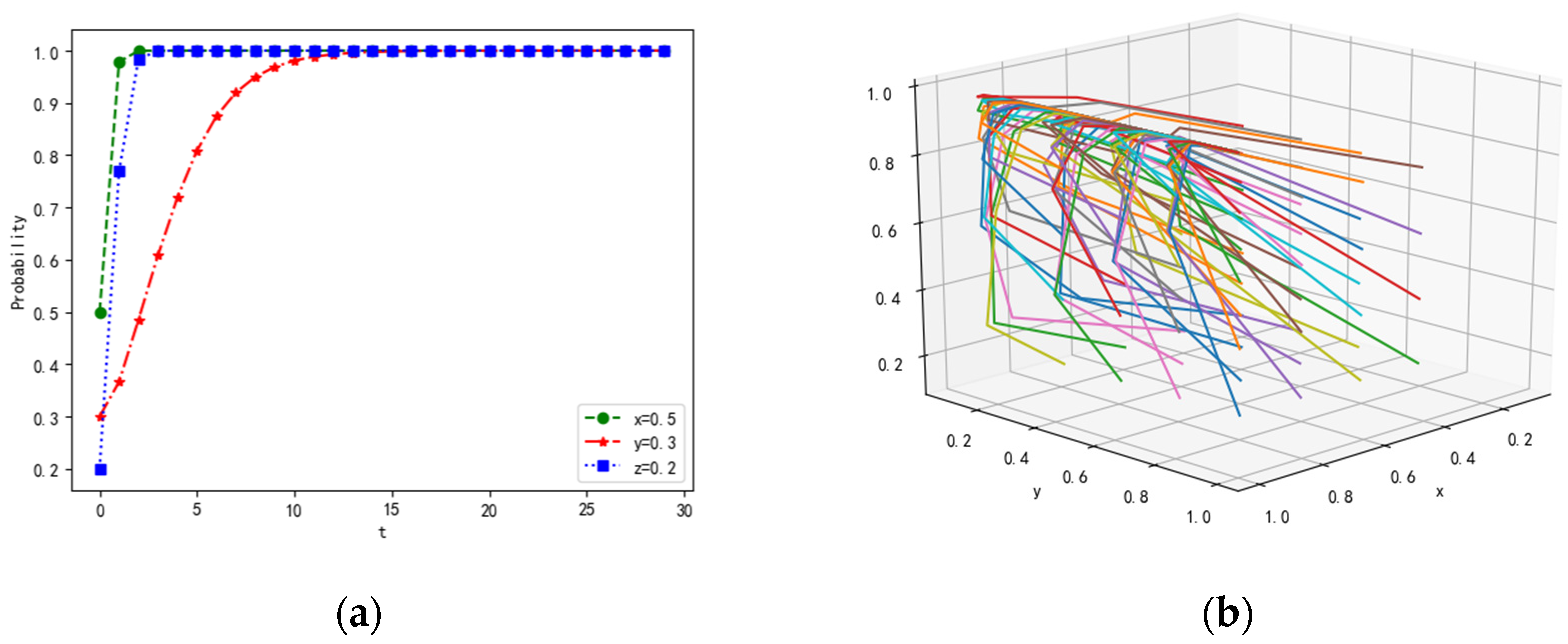
4.1.1. Scenario 1
4.1.2. Scenario 2
4.1.3. Scenario 3
4.1.4. Scenario 4
4.1.5. Scenario 5
4.1.6. Scenario 6
4.1.7. Scenario 7
4.1.8. Scenario 8
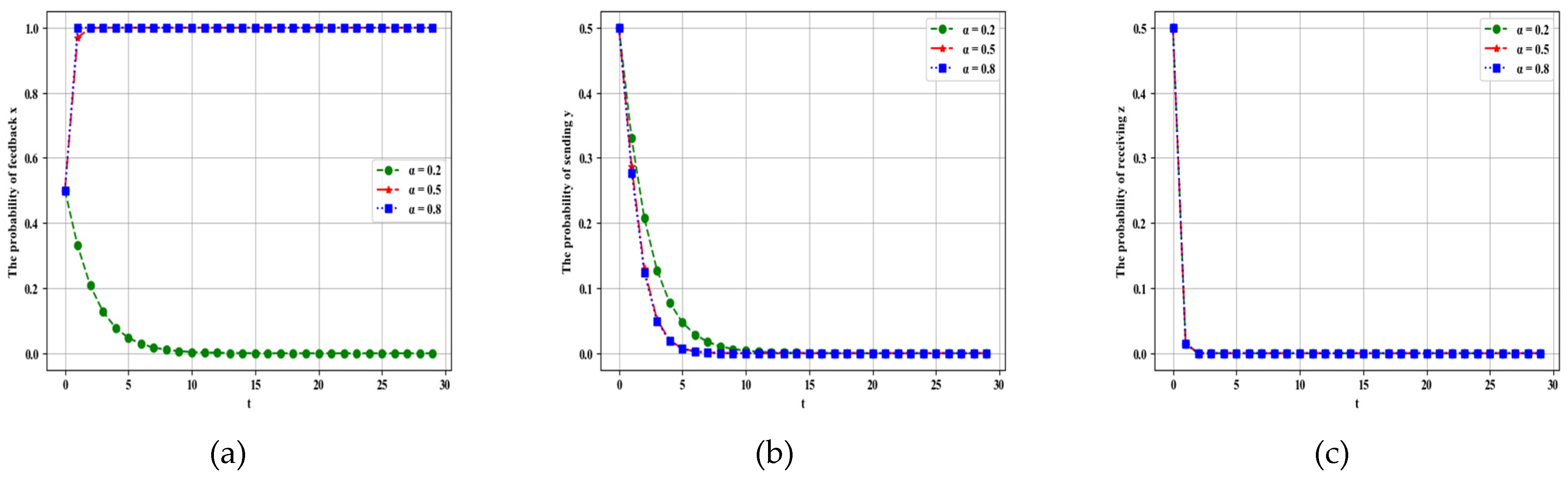
4.2. Impacts of Different Parameters on the Evolutionary Results
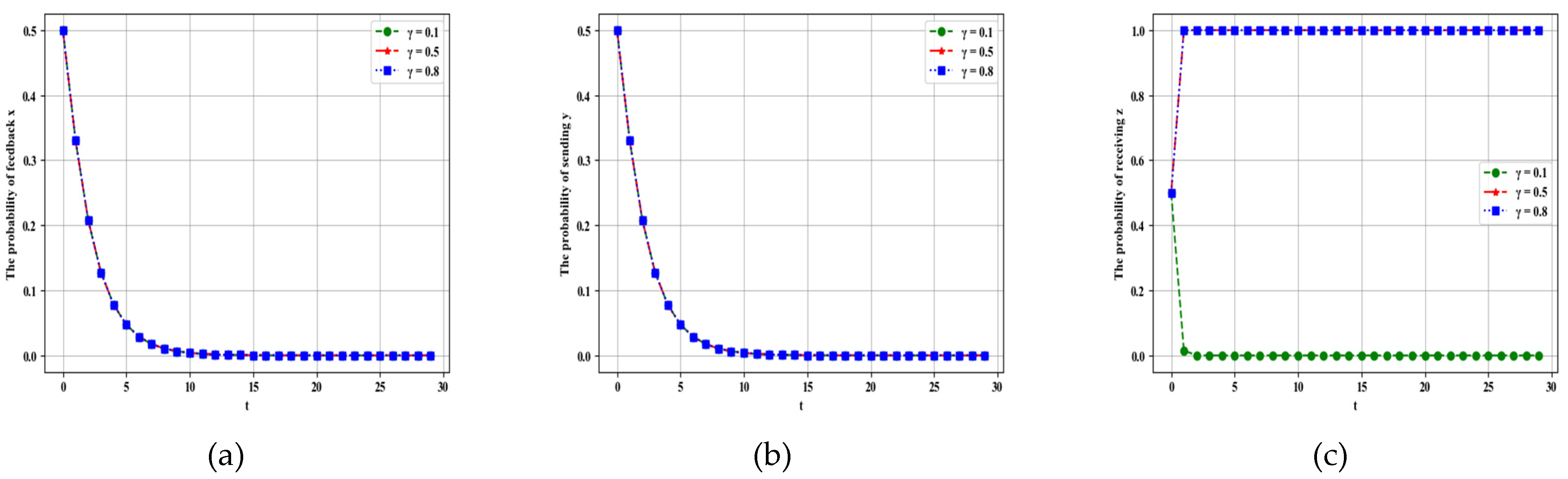
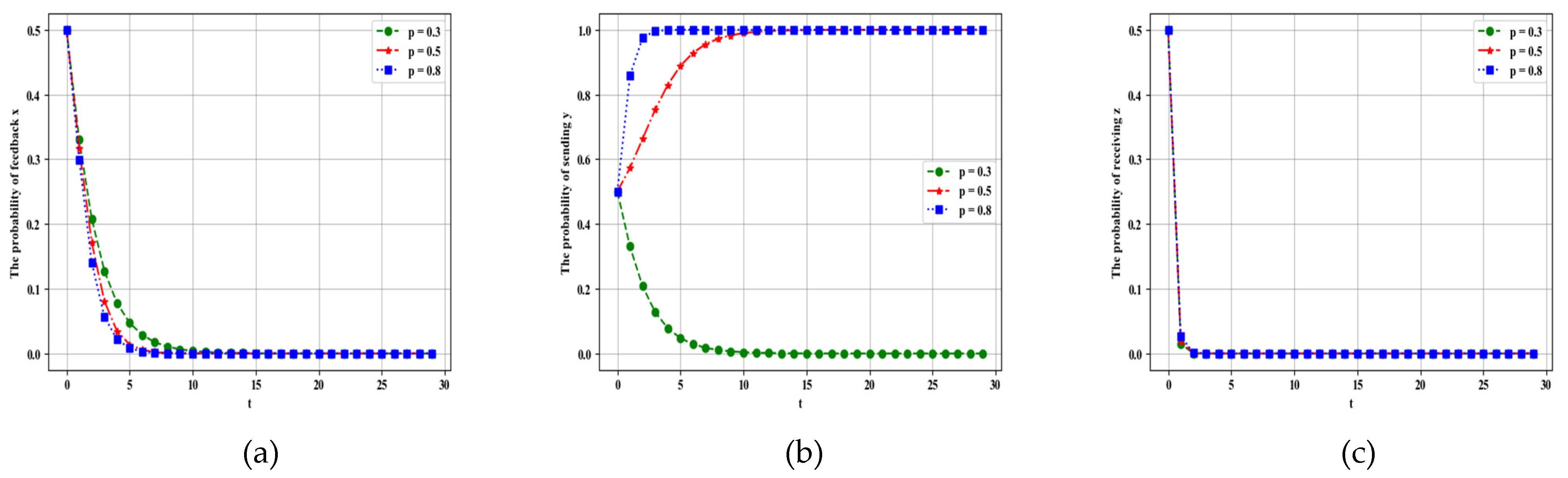
4.2.1. Influence of Parameter on Dynamic Evolution
4.2.2. Influence of Parameter on Dynamic Evolution
4.2.3. Influence of Parameter on Dynamic Evolution
4.2.4. Influence of Parameter on Dynamic Evolution
4.2.5. Influence of Parameter on Dynamic Evolution
5. Conclusions and Policy Enlightenment
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harmati, I.; Skrzypczyk, K. Robot team coordination for target tracking using fuzzy logic controller in game theoretic framework. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2009, 57, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.H. Cooperative tracking a moving target using multiple fixed-wing uavs. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2016, 81, 505–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yu, D. Improved fast compressive tracking for low-altitude flying target tracking. Multi-Media Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 11239–11254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.A.; Yu, D. García-Martínez, Target tracking with dynamically adaptive correlation. Opt. Commun. 2016, 365, 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, J.E. Mix-valued logic-based formation control. Int. J. Control. 2013, 86, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S. Affine formation maneuver control of multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2018, 63, 4140–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, M.; Jiang, B.; Xu, D. Fault tolerant control scheme design for the formation control system of unmanned aerial vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control. Eng. 2013, 227, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H. Adaptive robust control of artificial swarm systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2010, 217, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Qu, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R. A novel distributed and self-organized swarm control framework for under-actuated unmanned marine vehicles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 112703–112712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y. Unmanned aerial vehicle swarm control using potential functions and sliding mode control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2008, 222, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, R.; Kim, J.; Luo, S.; Min, B.C. Multipoint rendezvous in multi-robot systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, C.; Peng, L. Distributed consensus strong tracking filter for wireless sensor networks with model mismatches. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13, 1550147717741576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.M.; Lin, T.E.; Lee, L.W. Group decision making using incomplete fuzzy preference relations based on the additive consistency and the order consistency. Inf. Sci. 2014, 259, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.Z.; Meng, H. Active power dispatch strategy of the wind farm based on improved multi-agent consistency algorithm. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2019, 13, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degroot, M.H. Reaching a consensus. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1974, 69, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkar, V.; Varaiya, P. Asymptotic agreement in distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1982, 27, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsitsiklis, J.; Athans, M. Convergence and asymptotic agreement in distributed decision problems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1984, 29, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicsek, T.; Czirók, A.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Cohen, I.; Shochet, O. Novel type of phase transition in a system of self-driven particles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadbabaie, A.; Lin, J.; Morse, A. Coordination of groups of mobile autonomous agents using nearest neighbor rules. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2003, 48, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olfati-Saber, R.; Murray, R. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2004, 49, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olfati-Saber, R.; Fax, J.A.; Murray, R.M. Consensus and cooperation in networked multi-agent systems. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, A. Consensus problems in discrete-time multiagent systems with fixed topology. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2006, 322, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Duan, Z.; Chen, G.; Huang, L. Consensus of multiagent systems and synchronization of complex networks: A unified viewpoint. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2010, 57, 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Mareels, I. Robustness analysis of leader-follower consensus. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2009, 22, 186–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, C.; Sun, D.; Yang, J.; Chen, H. Leader-Follower Formation Control of Multiple Non-holonomic Mobile Robots Incorporating a Receding-horizon Scheme. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Xie, G.; Wang, L. Leader-following formation control of multiple mobile vehicles. IET Control. Theory Appl. 2007, 1, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Song, Y.; Qin, R. Evaluation Methodology of Leader-Follower Autonomous Vehicle System for Work Zone Maintenance. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2021, 2675, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Ma, B. Adaptive practical leader-following formation control of multiple non-holonomic wheeled mobile robots. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2020, 30, 7216–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Cunha, R.; Hamel, T.; Silvestre, C. Formation control of a leader–follower structure in three dimensional space using bearing measurements. Automatica 2021, 128, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, R.; Murray, R. Consensus protocols for networks of dynamic agents. In Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 4–6 June 2003; Volume 2, pp. 951–956. [Google Scholar]
- Moreau, L. Stability of multiagent systems with time-dependent communication links. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2005, 50, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, H.G.; Jadbabaie, A.; Pappas, G.J. Flocking in fixed and switching networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2007, 52, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Chen, G.; Huang, L. Disconnected synchronized regions of complex dynamical networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2009, 54, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porfiri, M.; Stilwell, D.J.; Bollt, E.M. Synchronization in random weighted directed networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2008, 55, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, W.; Chen, T. Cluster synchronization of linearly coupled complex networks under pinning control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2009, 56, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristodoulou, A.; Jadbabaie, A.; Münz, U. Effects of delay in multi-agent consensus and oscillator synchronization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 2010, 55, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, L. Finite-time information consensus for multi-agent systems with fixed and switching topologies. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2009, 238, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xie, L.; Lewis, F.L. Synchronization of multi-agent systems with delayed control input information from neighbors. Automatica 2011, 47, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D. Evolutionary game in economics. Econometrica 1991, 59, 637–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, D. On economic application of evolutionary game theory. J. Evol. Econ. 1998, 8, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
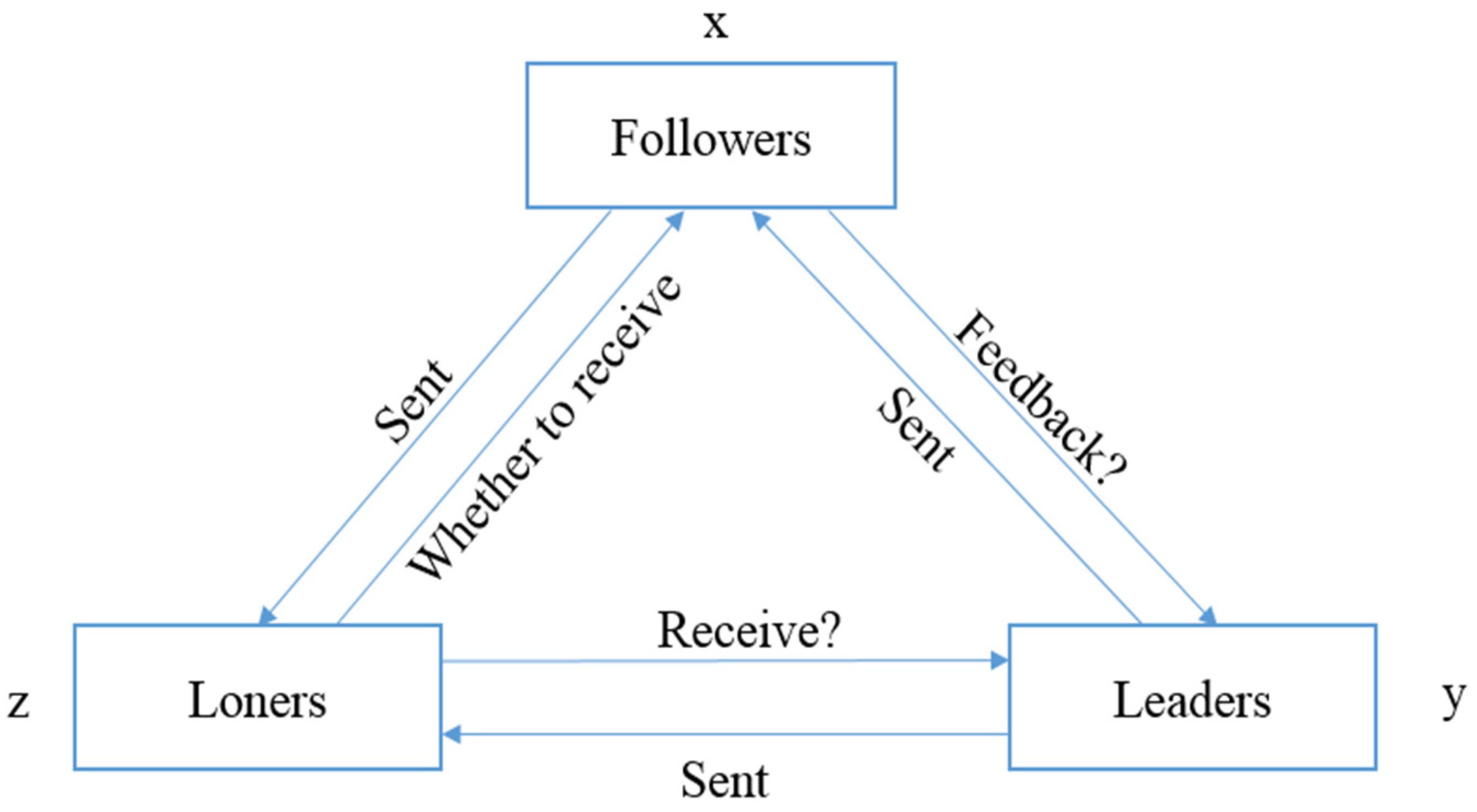




| Parameters | Descriptions | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Profits and costs of followers receiving messages, respectively. | ||
| Profits and costs of sending messages to loners, respectively. | ||
| Rewards and costs of followers sending feedback messages to leaders. | ||
| Positive degree of feedback to leaders. | ||
| Positive degree of reception. | ||
| Profits and costs of leaders sending all messages, respectively. | ||
| Profits and costs of leaders sending partial messages, respectively. | ||
| Rewards and costs of receiving messages from followers, respectively. | ||
| Probability of sending messages successfully. | ||
| indicates all messages, represents partial messages. | ||
| Profits and costs of loners receiving messages from followers. | ||
| Profits and costs of receiving messages from leaders, respectively. | ||
| Profits of receiving messages unsuccessfully. | ||
| Possibility of interaction when loners receive messages successfully. | ||
| Rewards of interacting with followers and leaders respectively. |
| Feedback () | ||||
| Not feedback () | ||||
| Equilibrium Points | Stability Condition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | ||||
| unstable | ||||
| unstable |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, Z.; Deng, Y. Dynamic Model of Collaboration in Multi-Agent System Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. Games 2021, 12, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/g12040075
Gou Z, Deng Y. Dynamic Model of Collaboration in Multi-Agent System Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. Games. 2021; 12(4):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/g12040075
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Zhuozhuo, and Yansong Deng. 2021. "Dynamic Model of Collaboration in Multi-Agent System Based on Evolutionary Game Theory" Games 12, no. 4: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/g12040075
APA StyleGou, Z., & Deng, Y. (2021). Dynamic Model of Collaboration in Multi-Agent System Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. Games, 12(4), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/g12040075





