Abstract
There is a strong correlation between the like/dislike responses to audio–visual stimuli and the emotional arousal and valence reactions of a person. In the present work, our attention is focused on the automated detection of dislike responses based on EEG activity when music videos are used as audio–visual stimuli. Specifically, we investigate the discriminative capacity of the Logarithmic Energy (LogE), Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (LFCC), Power Spectral Density (PSD) and Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT)-based EEG features, computed with and without segmentation of the EEG signal, on the dislike detection task. We carried out a comparative evaluation with eighteen modifications of the above-mentioned EEG features that cover different frequency bands and use different energy decomposition methods and spectral resolutions. For that purpose, we made use of Naïve Bayes classifier (NB), Classification and regression trees (CART), k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) classifier, and support vector machines (SVM) classifier with a radial basis function (RBF) kernel trained with the Sequential Minimal Optimization (SMO) method. The experimental evaluation was performed on the well-known and widely used DEAP dataset. A classification accuracy of up to 98.6% was observed for the best performing combination of pre-processing, EEG features and classifier. These results support that the automated detection of like/dislike reactions based on EEG activity is feasible in a personalized setup. This opens opportunities for the incorporation of such functionality in entertainment, healthcare and security applications.
Keywords:
physiological signals; electroencephalography (EEG); emotion recognition; detection of negative emotional states; Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (LFCC); Logarithmic Energy (LogE); Power Spectral Density (PSD); Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); Naïve Bayes classification (NB); classification and regression threes (CART); k-Nearest Neighbors classifier (kNN); Support Vector Machine (SVM) 1. Introduction
The vast abundance of video recordings imposes the need for appropriate content selection that is aligned with the preferences of individual users. This motivated research on automated recognition of video liking based on facial expressions, peripheral physiological signals and EEG activity captured from brain-computer interfaces (BCI). A brief summary of previous related work on EEG-based emotion classification is tabulated in Table 1. Considerable research on the topic was carried by Koelstra et al. [1,2,3,4], who have studied the relations between EEG signals, peripheral physiological signals and facial videos for classification of affective states. In these studies, different forms of fusion between features and modalities were examined; for example, the classification performance based on different criteria for measurement of affective states—arousal, valence and liking. These studies report significant correlation between like/dislike ratings and valence in EEG signals [3]. Correlation between liking and valence was also observed in [5]. Studies on automated recognition of liking based on EEG signals have demonstrated an average classification accuracy comparable to the one obtained for arousal and dominance [3] when peripheral modalities [1] and facial video [4] is concerned. Given these observations, it can be stated that like and dislike responses are indicative of emotional states [6] and their classification can be associated to the field of affective states classification. However, when compared to arousal and valence, liking is less studied and rarely used to define emotional states [7]. In the same time, like and dislike are traditionally employed in cases where reaction to media, such as music, movies or images, is being studied.

Table 1.
Related work on the automated classification of emotional states in different setups.
Several large-scale studies on the performance and relevance of features on tasks regarding the classification of affective states have been carried out. Jenke et al. [8] examined the relevance of a high number of time-domain, frequency-domain, time-frequency domain features, as well as features based on relations between different electrode measurement asymmetries (in total, 22,881 features). Results from feature selection with ReliefF, Min-Redundancy-Max-Relevance and Effect-Size showed that advanced feature extraction methods such as Higher Order Crossings (HOC), Higher Order Spectra (HOS), and Hilbert-Huang Spectrum (HHS) outperformed other commonly used spectral power bands. Although this study covered a wide range of features, other options such as LFCC and DWT with wavelet functions from the Symmlet and Coiflet families were not included. Another extensive study on emotion detection, reported by Zheng et al. [9], evaluated six features—PSD, differential entropy (DE), asymmetry (ASM), differential asymmetry (DASM), rational asymmetry (RASM) and differential causality (DCAU)—by using kNN, Linear regression, SVM classifier and a newly developed Graph regularized Extreme Learning Machine (GELM). The experimental evaluation of the models performed on the Database for Emotion Analysis using Physiological signal (DEAP) [1] and on the SJTU Emotion EEG Dataset (SEED) showed that features obtained from the beta and gamma frequency bands perform better than any other band. Thus, the authors concluded that beta and gamma oscillations are more strongly connected to the discrimination between negative and positive emotions, which is also supported by other studies on beta and gamma activity [10,11,12]. The higher classification results reported for frequency bands, associated to cognitive activity, can be attributed to the connection between cognition and the formation of emotions. Although traditional theories [13,14] consider emotions to be solely physiological phenomena, some definitions of emotions [15] and emotion theories [16,17,18] take the relation between cognition and emotion under consideration. The influence of cognitive activity on the formation of emotions is most notable in the cases where the evaluation of subjective work and media is considered. Often, the emotional impact of music and movies [19,20] is defined using conceptual terms, such as playful, meditative, aesthetic and others.
In addition to the above, Yazdani et al. [21] studied the affective states induced through music videos and used relative wavelet entropy as a feature on the emotion classification from EEG signals. By means of an SVM classifier with RBF kernel function, they obtained an average classification accuracy of 73.7% for a single trial, and 82% for single run classification. The average classification accuracy reported for liking recognition were 70.2% and 74%, respectively. Hadjidimitriu et al. [22] have used time-frequency processing of the EEG signal in order to compute the spectrogram, Zhao-Atlas-Marks distribution and HHS. These were used as features on the liking classification task. Using a kNN classifier, a classification accuracy of 86.52% ± 0.76% was reported.
In studies that use PSD as an EEG feature, traditionally all five—alpha, beta, gamma, delta and theta—frequency bands are considered [8,23,24]. In some cases, low frequency bands were omitted [25] or only specific bands (such as alpha and beta) were used [26,27]. The typical way of calculation for PSD-based features is through a short-time Discrete Fourier Transform (stDFT) (in fact, Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)) applied on non-overlapping frames of the segmented EEG signal [24,26]. STFT [8] and Welch’s method are common alternatives [23,27,28]. An alternative approach for decomposition of frequency bands is with DWT [29,30,31], where the DWT coefficients are used to calculate statistical parameters, power and entropy for the bands. Directly using the wavelet coefficients for classification was also evaluated in [32]. When compared to direct use of DFT and DWT coefficients, LFCC and Mel-Frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC) [33,34,35,36,37] provide a more compact representation of the energy in the frequency bands of a signal. Cepstral coefficients were computed from the spectrum of EEG signals with overlapping [33] or without overlapping [34] among subsequent frames.
These observations, as well as the previously discussed findings led us consider that PSD features extracted from higher frequency bands of EEG signals and cepstral coefficients could prove to be beneficial on the automated dislike detection task. Furthermore, DWT based features might also prove to be beneficial for the automated recognition of dislike responses. For that reason, in this study we evaluate the applicability of EEG features computed with different signal decomposition method, such as DFT and DWT, and compute features that cover different bands with different spectral resolution. Specifically, our study is focused on evaluating the performance of LogE, LFCC, DWT coefficients and PSD computed either for an entire EEG recording or after segmentation of the signal to frames and averaging of all frames.
2. Materials and Methods
We outline two different EEG preprocessing approaches (Section 2.1) and, in this context, we evaluate (Section 3) the discriminative capacity of various EEG features (Section 2.2), which were reported successful in previous related studies [23,24,25,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. These EEG features are based on the following:
- (i)
- frequency decomposition with DFT, such as the PSD (Section 2.2.1), Logarithmic Energy (LogE) (Section 2.2.2), and Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (LFCC) (Section 2.2.3),
- (ii)
- DWT-based decomposition with four different wavelet functions, such as Daubechies of order 4 and 32, Coiflets of order 5 and Symmlets of order 8 (Section 2.2.4).
Next, in Section 2.3 we outline the DEAP database, and in Section 2.4 the common experimental protocol used in all experiments.
2.1. Preprocessing of the EEG Signal
Here, we assume that each EEG channel is processed independently from the others. A convenient way to preprocess the EEG signal is to remove artifacts and interferences due to other activity, detrend and filter the signal, and then use the entire duration of the EEG recording in the feature computation process. The entire recording would contain brain activity for the duration of the stimuli or longer, which provides the basis for higher frequency resolution in the analysis of content in the subbands of interest. However, when the recording is very long the temporal localization of events is worsened, as the time localization ambiguity is proportional to the recording length.
A trade-off, which could improve the temporal localization resolution, would be to segment the EEG signal into frames. The frame duration could be from one to several seconds, i.e., time which is far smaller than the usual length of an EEG recording and, thus, temporal ambiguity decreases. However, processing each frame separately and computing EEG features on frame level would mean large number of EEG features with lower resolution in the frequency domain. Thus, we experiment with an averaged EEG frame, computed as the mean of the corresponding samples of all frames. The averaged frame is considered as a representation of the general EEG activity during the recording. Here, we evaluate whether the averaged frame is useful in the detection of dislike responses.
Let us assume that si(n) corresponds to the i-th channel in a multichannel EEG signal. We can either make use of the entire signal si(n) in order to compute the DFT or segment the signal to P short frames xip(n), with 1 ≤ p ≤ P, which are processed one-by-one. The last will permit better temporal resolution of the event localization in time and will reduce the risk of smearing short-living events. However, frame-by-frame processing will bring higher complexity and higher computational demand. In contrast, processing the entire signal si(n) at ones will provide better frequency resolution at the cost of loss of temporal localization of events.
In brief, each channel of the EEG signal can be segmented into short frames using a sliding window with overlap between two successive frames. The total number of frames per channel, obtained in such a way is calculated as:
where N is the total number of samples in si(n), Nw is the frame size in samples, L is the step size of sliding in samples, and the operator denotes that the result is rounded toward the smaller integer number. In order to reduce the complexity, we make use of averaged frames, which are computed as the average value of samples among all P frames, i.e.,
Here, corresponds to the value of n-th sample in the frame with index p and is the n-th sample of the resulting averaged frame. In this way, the N values of the signal si(n) are represented with only Nw values of the averaged frame, , where Nw << N usually holds true in the case of EEG recordings.
2.2. Feature Extraction
In the EEG feature computation process, we assume that each channel of the EEG signal is processed independently of the others. Furthermore, we denote the signal that is subject to feature extraction with s(n), regardless of whether segmentation and averaging is used, i.e., s(n) ≅ , or entire signal is used, i.e., s(n) ≅ si(n).
2.2.1. Power Spectral Density
We compute the PSD following Stoika and Moses [38]. Specifically, after preprocessing, DFT is performed on the time domain signal s(n) in order to compute the spectral coefficients S(k):
Once the spectrum S(k) is computed, we can calculate the average power spectrum density (PSDAll) for the entire bandwidth of interest [1 Hz, 45 Hz], excluding only the DC offset:
or we can estimate the average PSD within a specific frequency range PSDHigh, such as
with . In our case, PSDHigh corresponds to frequency range [20 Hz, 40 Hz].
2.2.2. Logarithmic Energy
The logarithmic energy (LogE) of the signal represents the sum of log-power spectrum coefficients in specific set of spectral subbands. These frequency subbands are obtained after applying a filterbank containing M triangular filters (6) on the power spectrum |S(k)|2, computed from the DFT (3). Each of the filters, Hm, in the filterbank is defined as:
where m, with 1 ≤ m ≤ M, is the filter index, k, with 0 ≤ k ≤ N/2-1, is the frequency bin index in the N-point DFT, fbm defines the boundaries of the m-th filter in terms of frequency bin index. The filters are used for acquiring frequency subbands of the power spectrum from which the logarithmic energy is calculated as
where Sm is the output of the m-th filter, |S(k)|2 is the power spectrum value of the frequency bin k, N is the DFT size, Hm denotes the m-th filter of the filter bank and M is the total number of filters. For convenience, in the following discussion we refer to Sm as the LogE with suffix F10, F15, F20, F30, F45, F60, depending on the number of filters in (6).
2.2.3. Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients
Using the LogE values, Sm, (7), computed for the individual frequency subbands defined via (6), we compute the LFCC by performing decorrelation by means of the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT):
where r is the LFCC index, and R ≤ M is the total number of unique LFCC that can be computed.
2.2.4. Discrete Wavelet Transform Based Features
These EEG features are computed following the DWT implementation in [39]. On each level of decomposition, we obtain the approximation (9) and details (10),
where W[j,k] is the j-th wavelet coefficients from the k-th level of decomposition of the EEG signal s(n), and and are the orthogonal basis functions used to separate each frequency band to approximation and details.
We computed four variants of the EEG features based on the DWT decomposition. These were implemented with four different wavelet functions, such as, Daubechies of order 4 and 32, Coiflets of order 5 and Symmlets of order 8, which were used in previous related work on emotion recognition [29,30,31,32]. We are interested to evaluate their performance on the dislikes detection task and compare it with better-studied EEG features.
2.3. Dataset
The experimental evaluation was performed using EEG recordings from the DEAP dataset [1], which consists of 32 subjects, each presented with 40 audio–visual stimuli. Specifically, musical videos of songs, varying in style and genre, were used to induce affective reactions and each of the trial recordings is rated by each subject based on his/her emotional response to the shown video clips. The data is tagged in five dimensions, namely valance, arousal, dominance, liking and familiarity [40], based on self-graded ranks by the subjects on a scale from one to nine, where rank one is the lowest and nine is the highest. The familiarity rating provides the only exception to this ranking system, with the range in this case being from one to five, with one being the lowest and five being the highest.
2.4. Experimental Protocol
The data split used for the purpose of our study is based on the liking ratings, where we consider two categories—negative (dislikes) and other. Specifically, recordings with liking ratings lower than four were tagged as dislikes, while recordings with liking rating higher than four were tagged as other. Subjects, for which less than 20% of the total amount of data was tagged as negative, were excluded, in order to avoid great misbalance between categories dislikes and other. Due to this pruning, the number of subjects in our study was reduced to 24 [33,41]. These 24 subjects are shown in Table 2, where the column subject ID value, Pn, with 1 ≤ n ≤ 32, corresponds to the n-th participant in the DEAP dataset. The column dislikes in (%) shows the percentage of dislike responses for the corresponding subject.

Table 2.
Percentages of recordings tagged with dislike for the selected subjects of the DEAP dataset.
A subject-dependent classification setup with a 10-fold cross validation was considered. Each feature type described in Section 2.2 was computed for 60 sc. recordings with or without segmentation (Section 2.1). For LFCC and LogE, we experimented with filterbanks consisting of 10, 15, 20, 30, 45 or 60 filters. For the DWT-based features, we experimented with four wavelet functions. Thus, a total of 18 sets of EEG feature types were calculated in each of the two preprocessing setups.
The experimental evaluation was carried out using the WEKA [42] implementations of four classification algorithms, which have frequently been used in previous related studies. These are the Naïve Bayes (NB), Classification and regression threes (REP), k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN), and SVM classifier with a RBF kernel trained with the Sequential Minimal Optimization (SMO) method. In all experiments, the default settings of the classifiers were used and 10-fold cross-validation was performed. In Section 3, we report the average classification accuracy and standard deviation across all 24 subjects.
3. Evaluation Results
Based on the common experimental protocol outlined in Section 2.4, we evaluated eighteen EEG feature sets, computed in two signal pre-processing setups (Section 2.1). In Figure 1 and Figure 2, we present the average dislikes detection accuracy and the standard deviation in percentages, computed for all 24 subjects. Each feature set was evaluated with four classification methods: NB, REP, kNN, and SMO (Section 2.4). Specifically, in Figure 1 we present the accuracy obtained for the EEG features computed for averaged frames, and in Figure 2 the results obtained for features computed for an entire EEG recording. As shown in the figures, the average classification accuracy varies in a wide range depending on the specific combination of EEG features and classification method—between 53.8% and 98.6%. The lowest accuracy, 53.8%, is observed for the NB classifier with PSDAll features calculated for the entire signal. The highest average classification accuracy, 98.6%, was observed for the kNN classifier with WPT-db4 features computed for the entire signal. We observed identical average detection accuracy, 98.5%, for the other three wavelet functions: db32, coif5, and sym8. The classification accuracy of the REP tree is much lower because in the specific EEG feature sets, there are no highly discriminative features that can provide adequate split on the top levels of the tree. The NB classifier does not perform well due to the limited amount of training data.
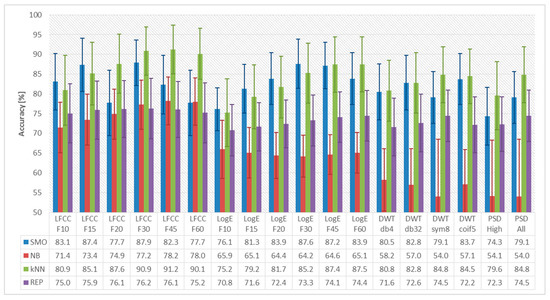
Figure 1.
The average detection accuracy for dislikes detection, shown in percentages, when the EEG features were calculated after segmentation of the EEG signal to frames with duration 1 s and subsequently averaged into a single averaged frame.
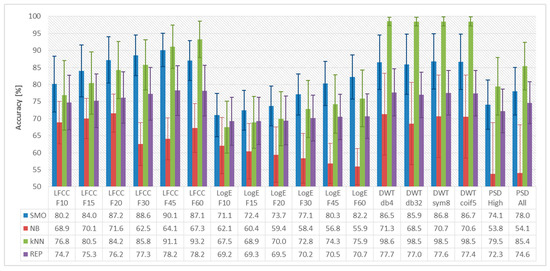
Figure 2.
The average detection accuracy for dislikes detection, shown in percentages, when the EEG features were calculated from the entire recording, without segmentation.
Summarizing the results presented in Figure 1 and Figure 2, the highest average classification accuracy is observed for the kNN classifier, followed by SMO. We explain this observation with the ability of these two classifiers to build robust models when the amount of training data is small. Because in the present study we assume subject-specific dislikes detection, the amount of training data is small—classifiers are trained with just 1152 feature vectors, distributed in the two categories according to Table 2.
Analyzing the average classification accuracy observed for the various EEG features, we point out that LFCC perform well (accuracy above 90%) both when computed for an entire recording and for an averaged frame. Due to the use of filterbank, the increased frequency resolution, which using an entire EEG recording brings, does not lead to some advantage. For the LogE features, it is observed that LogE leads to a higher accuracy when calculated for the averaged frames, 87.5%, which is much better than the one obtained for the entire signal, 75.9%. Using only the higher band of the spectrum, i.e., PSDHigh decreases the accuracy, when compared to the entire bandwidth, PSDAll, regardless of whether these are computed for an entire recording or for averaged frames.
The computation of DWT-based features for an entire recording, in our case 60 s, provides the opportunity to observe the signal on larger time scales. The DWT decomposition of the signal provides a mechanism for flexible time-scale localization of the components in an EEG recording, which clearly benefits the detection of dislike reactions. Specifically, for the combination of kNN classifier and DWT features, we observed classification accuracy in the range of 98.5% to 98.6%, regardless of the particular wavelet function. These results are in good conformance with the accuracy, 95.6% reported in Rached et al. [31], for WPT-based features. The accuracy reported here is higher than the accuracy reported in Murugappan [29], 82.9%, on a different experimental setup using the DWT with db4, db8, sym8, coif5 wavelet functions to calculate features such as the standard deviation, power and entropy of different frequency bands. The advantageous results obtained with the EEG features studied here is due to their higher time-scale resolution and number of coefficients, when compared to previous related work.
4. Conclusions
In the present study, we evaluated four types of EEG features in different modifications, which led to eighteen EEG feature sets. These were evaluated in two different pre-processing setups, on the task of automated detection of dislikes responses. A mean classification accuracy of up to 98.6% is reported for the best performing classifier (kNN) and feature set (DWT-db4). The results reported in Section 3 are in good agreement with the accuracy reported in previous related work [29,31,32,33,34,35] on the DEAP dataset, summarized in Section 1. Our experimental evaluation has shown an average classification accuracy of 1–3% higher than the results reported in previous related work for the best performing classifiers (kNN and SVM). These performed better than the other classification methods evaluated here because as it is widely known kNN and SMO cope well (although in different manner) when the amount of training data is small.
In conclusion, it is pointed out that the two signal preprocessing approaches considered here serve as different representations of the EEG activity. Specifically, the averaged frames provide a compressed representation of the EEG signal, which contains information about the entire recording. The features based on the entire signal convey information about the activity during the period, which the DFT-based features cannot capture. In contrast, the DWT-based features possess temporal localization capability, and this is expressed in the much higher detection accuracy. Although experimental evaluation has shown that EEG feature sets calculated using the entire signal show the highest mean classification accuracy it might not be the ultimate choice in all application scenarios. Computing the EEG features from an averaged frame allows for a substantial reduction of data size, memory demand and computational complexity, which could make these a convenient trade-off choice in practical applications that make use of automated detection of dislike responses.
Author Contributions
The research reported in this study was carried out by F.F., I.M. and T.G. Conceptualization, I.M. and T.G.; methodology, I.M.; software, F.F.; validation, F.F.; formal analysis, F.F., I.M.; investigation, F.F., I.M.; resources, F.F.; data curation, F.F.; writing—original draft preparation, F.F.; writing—review and editing, I.M. and T.G.; visualization, F.F.; supervision, I.M.; project administration, T.G.; funding acquisition, T.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Bulgarian National Science Fund (BNSF), grant number FNI № KP-06-PN37/18, entitled “Investigation on intelligent human-machine interaction interfaces, capable to recognize high-risk emotional and cognitive conditions”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. DEAP: A database for emotion analysis using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Mühl, C.; Patras, I. EEG analysis for implicit tagging of video data. In Proceedings of the 2009 3rd International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction and Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 10–12 September 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Koelstra, S.; Yazdani, A.; Soleymani, M.; Mühl, C.; Lee, J.S.; Nijholt, A.; Pun, T.; Ebrahimi, T.; Patras, I. Single trial classification of EEG and peripheral physiological signals for recognition of emotions induced by music videos. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Brain Informatics, Toronto, ON, Canada, 28–30 August 2010; pp. 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Koelstra, S.; Patras, I. Fusion of facial expressions and EEG for implicit affective tagging. Image Vis. Comput. 2013, 31, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupi, E.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T. EEG correlates of different emotional states elicited during watching music videos. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Memphis, TN, USA, 9–12 October 2011; pp. 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Berridge, K.; Winkielman, P. What is an unconscious emotion? (The case for unconscious “liking”). Cognit. Emotion 2003, 17, 181–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabian, A. Basic Dimensions for a General Psychological Theory: Implications for Personality, Social, Environmental, and Developmental Studies; Oelgeschlager, Gunn & Hain: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Jenke, R.; Peer, A.; Buss, M. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2014, 5, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Lu, B.L. Identifying stable patterns over time for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, B.L. Emotion classification based on gamma-band EEG. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–6 September 2009; pp. 1223–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Güntekin, B.; Başar, E. Event-related beta oscillations are affected by emotional eliciting stimuli. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 483, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, N.; Menicucci, D.; Sebastiani, L.; Bedini, R.; Pingitore, A.; Vanello, N.; Milanesi, M.; Landini, L.; Gemignani, A. The dynamics of EEG gamma responses to unpleasant visual stimuli: From local activity to functional connectivity. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, C.G.; James, W. The Emotions; Williams & Wilkins Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1922. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, W.B. The James-Lange theory of emotions: A critical examination and an alternative theory. Am. J. Psychol. 1927, 39, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, R.J. Psychology: In Search of the Human Mind; Wadsworth Publishing: Belmont, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Schachter, S. The interaction of cognitive and physiological determinants of emotional state. In Advances in Experimental Social Psychology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1964; pp. 49–80. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Fu, X. The interaction between cognition and emotion. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, R.S. Progress on a cognitive-motivational-relational theory of emotion. Am. Psychol. 1991, 46, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, L.B. Emotion and Meaning in Music; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, M.B.; Hartmann, T. Exploring the role of meaningful experiences in users’ appreciation of “good movies”. Projections 2010, 4, 128–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, A.; Lee, J.S.; Vesin, J.M.; Ebrahimi, T. Affect recognition based on physiological changes during the watching of music videos. ACM Trans. Interact. Intell. Syst. 2012, 2, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjidimitriou, S.K.; Hadjileontiadis, L.J. Toward an EEG-based recognition of music liking using time-frequency analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3498–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos-Filho, T.F.; Ferreira, A.; Atencio, A.C.; Arjunan, S.; Kumar, D. Evaluation of feature extraction techniques in emotional state recognition. In Proceedings of the 2012 4th International Conference on Intelligent Human Computer Interaction (IHCI), Kharagpur, India, 27–29 December 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, D.; Wang, X.W.; Shi, L.C.; Lu, B.L. EEG-based emotion recognition during watching movies. In Proceedings of the 2011 5th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering, Cancun, Mexico, 27 April–1 May 2011; pp. 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nafjan, A.; Hosny, M.; Al-Wabil, A.; Al-Ohali, Y. Classification of human emotions from electroencephalogram (EEG) signal using deep neural network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, D.O. EEG-based emotion recognition. Influ. Visual Audit. Stimuli. 2006, 56, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.; Grundlehner, B.; Penders, J. Towards wireless emotional valence detection from EEG. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 2188–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Song, D.; Yu, G.; Hou, Y.; Hu, B. EEG based emotion identification using unsupervised deep feature learning. In Proceedings of the SIGIR2015 Workshop on Neuro-Physiological Methods in IR Research, Santiago, Chile, 13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Murugappan, M.; Juhari, M.R.; Nagarajan, R.; Yaacob, S. An Investigation on visual and audiovisual stimulus based emotion recognition using EEG. Int. J. Med. Eng. Inform. 2009, 1, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, M. Human emotion classification using wavelet transform and KNN. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Pattern Analysis and Intelligence Robotics, Kuala Lump, Malaysia, 28–29 June 2011; pp. 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Rached, T.S.; Perkusich, A. Emotion recognition based on brain-computer interface systems. In Brain-Computer Interface Systems-Recent Progress and Future Prospects; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 253–270. [Google Scholar]
- Yohanes, R.E.; Ser, W.; Huang, G.B. Discrete Wavelet Transform coefficients for emotion recognition from EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 2251–2254. [Google Scholar]
- Feradov, F. Study of the Quality of Linear Frequency Cepstral Coefficients for Automated Recognition of Negative Emotional States from EEG Signals; Volume G: Medicine, Pharmacy and Dental Medicine; Researcher’s Union: Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Fang, Y.; Li, L.; Hou, L.; Yang, F.; Guo, Y. Multiple feature fusion for automatic emotion recognition using EEG signals. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 896–900. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, A.; Kamaruddin, N.; Palaniappan, L.K.; Li, M.; Khosrowabadi, R. EEG signals for emotion recognition. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2010, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.; Wahab, A.; Karim, I.; Dzulkifli, M.A.; Alshaikli, I.F.T. EEG emotion recognition based on the dimensional models of emotions. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 97, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, M.; Wahab, A.; Khosrowabadi, R. MFCC for robust emotion detection using EEG. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 9th Malaysia International Conference on Communications (MICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 14–17 December 2009; pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, P.; Moses, R.L. Spectral Analysis of Signals; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.-L. A Tutorial of the Wavelet Transform; NTUEE: Taipei, Taiwan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring emotion: The self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 1994, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feradov, F.; Mporas, I.; Ganchev, T. Evaluation of Cepstral Coefficients as Features in EEG-based Recognition of Emotional States. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Information Technologies for Industry, Varna, Bulgaria, 14–16 September 2017; pp. 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data mining: Practical machine learning tools and techniques with Java implementations. ACM Sigmod Record 2002, 31, 76–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).