Abstract
Accurate speech recognition can provide a natural interface for human–computer interaction. Recognition rates of the modern speech recognition systems are highly dependent on background noise levels and a choice of acoustic feature extraction method can have a significant impact on system performance. This paper presents a robust speech recognition system based on a front-end motivated by human cochlear processing of audio signals. In the proposed front-end, cochlear behavior is first emulated by the filtering operations of the gammatone filterbank and subsequently by the Inner Hair cell (IHC) processing stage. Experimental results using a continuous density Hidden Markov Model (HMM) recognizer with the proposed Gammatone Hair Cell (GHC) coefficients are lower for clean speech conditions, but demonstrate significant improvement in performance in noisy conditions compared to standard Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCC) baseline.
1. Introduction
Speech is the most important means of human communication and enabling computers and other smart devices to communicate via speech would make significant progress in interaction with humans. Speech perception and recognition have intrigued scientists from the early works of Fletcher [1] and first speech recognition systems in Bell labs [2] to modern days, and yet machine recognition is still outperformed by humans.
In quiet environments, high recognition accuracy can be achieved. However, in noisy environments, performance of a typical speech recognizer degrades significantly, e.g., 50% in a cafeteria environment and 30% in a car traveling at 90 km/h [3]. Influence of environment and other factors on speech recognition are investigated in [4]. As the technology advances, speech recognition will be deployed on more devices which are used in everyday life where environmental factors play an important role, e.g., speech recognition applications for mobile phones [5], cars [6], automated access-control and information systems [7], emotion recognition systems [8], monitoring applications [9], assistance for handicapped people [10], and smart homes [11]. Besides speech, many applications of acoustics are also important in various engineering problems [12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. To improve the performance in real-world noisy environments, a noise reduction technique could be used [19,20,21,22].
Comparisons using many speech corpora demonstrate that word error rates of machines are often more than an order of magnitude greater than those of humans for quiet, wideband, read speech. Machine performance degrades further below that of humans in noise, with channel variability, and for spontaneous speech [23]. Until the performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR) surpasses human performance in accuracy and robustness, we stand to gain by understanding the basic principles behind human speech recognition (HSR) [24].
Despite the progress in understanding auditory processing mechanisms, only a few aspects of sound processing in the auditory periphery are modeled and simulated in common front-ends for ASR systems [25]. For example, popular parameterizations such as MFCC employ auditory features like variable bandwidth filter bank and magnitude compression. Perceptual Linear Prediction (PLP) coefficients are based on performing perceptual processing by employing critical-band resolution curves, equal loudness scaling and cube root power law of hearing to linear prediction coefficients (LPC) [26]. An example of auditory-motivated improvement of speech representation could include synaptic adaptation. In [27], a simplified model of synaptic adaptation was derived and integrated into conventional MFCC feature extraction. Results showed significant improvement in speech recognition performance.
In [28], new Power Normalized Cepstral Coeffients (PNCC) based on auditory processing were proposed. New features include the use of a power-law nonlinearity, a noise-suppression algorithm based on asymmetric filtering and temporal masking. Experimental results demonstrated improved recognition accuracy compared to MFCC and PLP processing. Another approach in feature extraction is based on deep neural networks (DNN)—noise robustness of DNN-based acoustic models was evaluated in [29]. In [30], Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) were introduced to clean distorted input features (MFCCs). The model was trained to predict clean features when presented with a noisy input. To handle highly non-stationary additive noise, the use of LSTM-RNNs was proposed in [31]. A detailed overview of deep learning for robust speech recognition can be found in [32].
In order to better simulate human auditory periphery, standard MFC or PLP coefficients could be replaced with coefficients based on some cochlear model. In [33], auditory front-ends based on the models of Seneff [34] and Ghitza [35] were evaluated in clean and noisy speech and compared with a control mel filter bank (MFB) based cepstral front-end. Results showed that front-ends based on the human auditory system perform comparably to, and can slightly reduce the error rate of, an MFB cepstral based speech recognition system for isolated words with noise and some spectral variability conditions.
In this paper, we propose a front-end based on acoustic features obtained by the gammatone filterbank analysis followed by the IHC processing stage. Gammatone filtering models the cochlea by a bank of overlapping bandpass filters mimicking the structure of the peripheral auditory processing stage. Its performance as speech recognition front-end was investigated in several papers and improvement over MFC baseline was demonstrated [36,37,38,39]. Our idea is to further improve the model by adding the IHC processing stage. IHC modeling transforms the basilar membrane displacements into an auditory nerve firing pattern. We add the hair cell model to the back-end of a gammatone filterbank to further mimic the human auditory periphery and form a more complete cochlear model. Based on the model, new GHC coefficients are proposed. To evaluate the robustness of the proposed front-end, we have developed a continuous speech HMM recognizer for Croatian speech.
2. Cochlear-Based Processing for ASR
Incoming sound pressure is transformed by the cochlea into vibrations of the basilar membrane which are then transformed in a series of neural impulses. The cochlea can be seen as a system designed to analyze frequency components in complex sounds as it acts as a frequency analyzer where each position along the basilar membrane corresponds to a particular frequency.
The cochlea is shaped as a small tube, and is about 1 cm long and 3.5 cm wide. The main structural element within the cochlea is a flexible basilar membrane which varies in width and stiffness along the cochlea and separates two liquid-filled tubes. It contains the organ of Corti—a very sophisticated structure which responds to basilar membrane vibrations and allows for transduction into nerve impulses, Figure 1. Positioned along the organ of Corti are three rows of outer hair cells (OHCs) and one row of inner hair cells (IHCs). The IHCs are the actual sensory receptors; through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment and generate neural impulses.
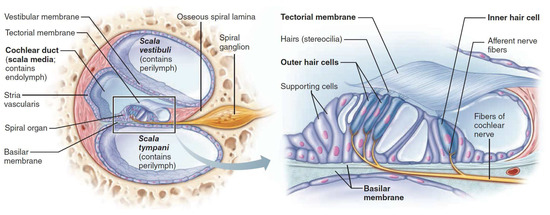
Figure 1.
Cross-section of the cochlea with enlarged organ of Corti [40].
At the limits of human hearing, hair cells can faithfully detect movements of atomic dimensions and respond in the tens of microseconds. Furthermore, hair cells can adapt rapidly to constant stimuli, thus allowing the listener to extract signals from a noisy background [41].
2.1. Gammatone Filterbank
In auditory modeling, filterbank is one of the most common concepts used to resemble the characteristics of the basilar membrane (BM). Since each position of the basilar membrane responds to a particular frequency contained in speech signal, each bandpass filter is modeled by particular frequency characteristics of the BM.
The gammatone filterbank contains non-uniform overlapping band pass filters, designed to mimic the basilar membrane characteristics. It was first introduced by Johanesma [42]. A gammatone filter impulse response is simply defined in time-domain as the product of a gamma distribution and a tone. The gammatone function is defined as
where n is the order of the filter (affects the slope of the filter skirts), b is the bandwidth of the filter (affects the duration of the impulse response, a defines the output gain, is the filter center frequency, is the phase.
For the filter order in the range 3–5, Patterson [43] showed that gammatone filter is very similar to that of the filter commonly used to represent the magnitude characteristic of the human auditory filter [44].
The equivalent rectangular bandwidth (ERB) of the filter is given with the equation [45]
When the order is 4, the bandwidth b of the gammatone filter is 1.019 ERB.
Figure 2a shows a gammatone impulse response we obtained from Equation (1) of a single filter centered at 1000 Hz. It can be regarded as a measure of the BM displacement at a particular position.
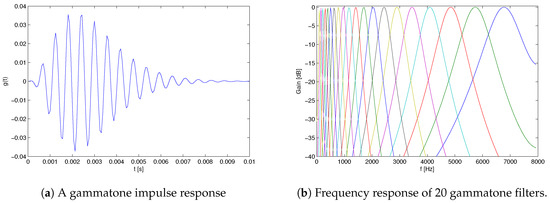
Figure 2.
Gammatone filter responses.
These filters are then combined to form an auditory filterbank used to simulate the motion of the basilar membrane. Output of each filter models the frequency response of the basilar membrane at a single place (Figure 2a). Filter center frequencies are equally distributed on the ERB scale [45].
Frequency domain responses of a gammatone filterbank with 20 filters whose center frequencies are equally spaced between 100 Hz and 8 kHz on the ERB scale are shown in Figure 2b. Unlike a traditional spectrogram, which has a constant bandwidth across all frequency channels, using the gammatone model, we obtained a representation similar to cochlea’s frequency subbands, which get wider for higher frequencies.
In this work, we used Slaney’s implementation of a gammatone filterbank [46], with default 64 filters spaced from 50 Hz to 8 kHz (speech is sampled at 16 kHz).
2.2. IHC Model
To further mimic the human auditory periphery and form a more complete auditory model, we add the IHC model to the back-end of the gammatone filterbank. Our proposed front-end for ASR is thus constructed by processing the output of each gammatone filter with the IHC model. We used the Meddis’ model of hair cell transduction [47].
Each gammatone filter output is converted by the hair cell model into a probabilistic representation of firing activity in the auditory nerve, incorporating well-known effects such as saturation and adaptation.
IHC function is characterized in the Meddis model by describing the dynamics of neurotransmitter at the hair cell synapse [48]. Transmitter is transferred between three reservoirs in a reuptake and re-synthesis process loop (see Figure 3 and Equations (3)–(7)).
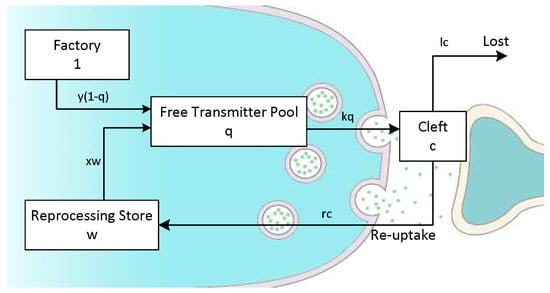
Figure 3.
The Meddis inner hair cell model.
The equations representing the model are
The permeability of the cell membrane is represented by , A, B, and g are the model constants, is the instantaneous amplitude, is the level of available transmitter in the pool, y is the replenishment rate factor (from the factory), is the transmitter content of the synaptic cleft, l is a loss factor, and r is a return factor from the cleft.
The probability of the afferent nerve firing (Equation (7)) is assumed proportional to the remaining level of transmitter in the cleft. The constant h is the proportionality factor used to scale the output for comparison with empirical data.
When we apply the IHC model to a sequence of 1 kHz tone bursts, each 0.25 s long and ranging in amplitude from 40 dB to 85 dB in 5 dB steps, the synaptic cleft contents resulting from a series of such pulses are shown in Figure 4. Using this model enables replication of many well-known nerve responses such as rectification, compression, spontaneous firing, and adaptation [49].
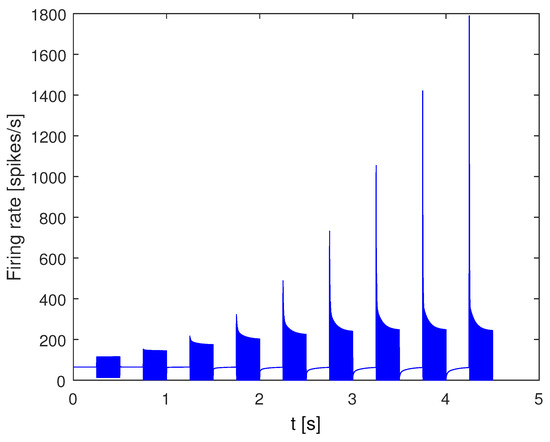
Figure 4.
IHC model response to 1-kHz tone bursts.
3. Speech Recognition Experiments
Our speech recognition system is based on continuous density HMM models, and is developed using the HTK toolkit [50]. In order to evaluate the proposed cochlear based front-end, we have constructed a system based on standard MFCC front-end and a system based on the cochlear based front-end (including gammatone filtering and IHC processing).
Our speech database is based on the texts of short weather forecasts for the Adriatic coast. It was recorded in a quiet office by 12 male speakers and contains 673 sentences in Croatian (5731 words) sampled at 16 kHz with 16 bits. Vocabulary size is 362 words. The data and the speakers were divided in two sets: one for training and one for testing.
Acoustical modeling was started with simple monophone continuous Gaussian density HMMs with three states (left-right topology) and diagonal covariance matrix for each of the 30 Croatian phonemes. Models were trained with feature vectors of 39 elements (13 static + 13 velocity + 13 acceleration coefficients) representing 25 ms segments of speech, every 10 ms. We used a bigram language model.
In the next step, context-dependent triphone models were constructed from monophone HMMs. Context dependent models provide a better modeling accuracy, but there is a significant increase in the number of models and the problem of insufficient training data arises. To handle this problem, state tying strategy was applied, according to Croatian phonetic rules. Not only does this procedure ensure enough acoustic material to train all context-dependent HMMs, but it also enables modeling of acoustic units not present in the training data (simply by passing them down the phonetic decision tree). The system was further refined by the conversion from single Gaussian HMMs to multiple mixture components. We used six mixture components per state.
Besides standard MFCC based front-end, we have also developed a cochlear based front-end where the speech signal is first processed by the gammatone filterbank and then the output of each gammatone filter is processed by the IHC model. In order to obtain standard speech recognition segmentation, output of the model is temporally integrated on 25 ms segments (every 10 ms) and discrete cosine transform (DCT) is applied. Similarly, the DCT is applied during MFCCs calculation on the “auditory” spectrum obtained after mel-warping of the frequency axis and logarithm calculation. The number of coefficients used is chosen to be 13—the same as for the standard MFCC baseline. We will refer to these new feature vectors as Gammatone Hair Cell (GHC) coefficients. Besides these static spectral feature vectors, standard practice is to also use dynamic feature vectors (velocity and acceleration) to better model the spectral dynamics. These vectors are concatenated with the static vector and a combined feature vector is constructed.
Block diagram of the ASR system with the proposed cochlear based front-end is given in Figure 5.
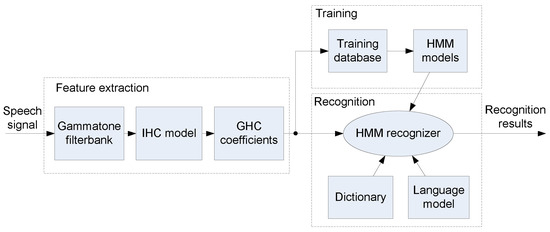
Figure 5.
HMM recognizer based on the GHC front-end. First, gammatone filtering is applied to the speech signal; then, the output of each gammatone filter is processed by the IHC model resulting in auditory representation of a speech signal from which GHC coefficients are constructed and used in the HMM recognizer.
Depending on the number of coefficients used, the auditory spectrum will be approximated with more or less detail. Although a higher number of coefficients means better approximation, it doesn’t necessarily mean a better speech recognition performance. In fact, coefficients should be as different as possible for different phonemes, but, at the same time, as similar as possible for the same phonemes uttered in different words, at different intonations, from different speakers, and in different recording conditions (noise). Figure 6 shows the effect of white noise on standard MFC and our GHC based speech representations. It is clearly visible that GHC coefficients are more robust to noise than standard MFCCs.
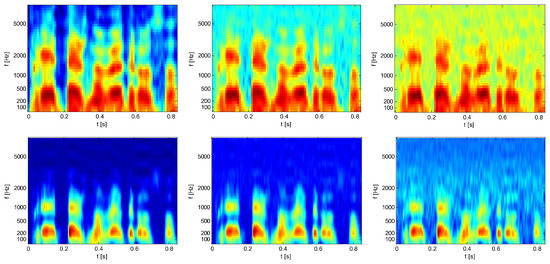
Figure 6.
Comparison of auditory spectrograms obtained from 13 MFCCs (top panels) and 13 GHCs (bottom panels) for the same test sentence in clean (left column) and white noise conditions (middle column signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) = 10 dB and right column SNR = 0 dB).
Table 1 shows the recognition results of the baseline MFCC, PLP and PNCC based front-ends and our cochlear model (GHC coefficients) based front-end in clean and white noise conditions in terms of correctness () and accuracy (), where S, D, I represent the number of substitution, deletion and insertion errors and N is the total number of words. Maximum recognition rates for each condition are shown in bold. Besides comparison to standard MFCCs and PLP coefficients, we also included PNC coefficients which are based on auditory processing and include the use of a power-law nonlinearity, a noise-suppression algorithm based on asymmetric filtering and temporal masking [28,51]. In addition, we also evaluated the average performance across all conditions. Statistical significance of performance improvement over MFC baseline was assessed using the difference of proportions significance test [52]. Accuracy comparison is also given in Figure 7.

Table 1.
Recognition rates (%) with significance levels p (in parentheses) against the MFC baseline.
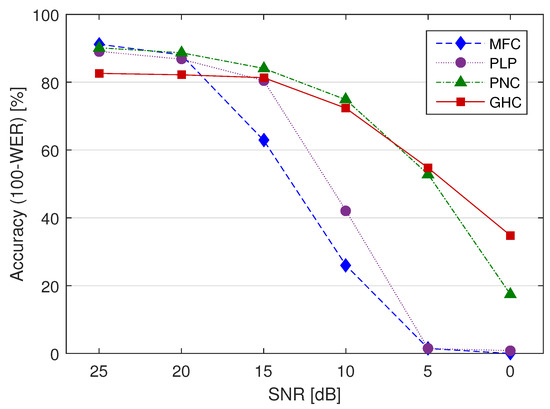
Figure 7.
Comparison of recognition accuracy.
It can be observed that, in clean speech conditions, recognition performance of the GHC based system is lower than for the other approaches. It should be noted here that the same number of coefficients was used in GHC based system as in MFC based system, and it is possible that some other number of coefficients would better fit the GHC based system. As the noise level increases, the recognition rates of the cochlear model based front-end become higher than the standard MFCC based front-end as well as the PLP front-end. The difference is statistically significant for all conditions (p < 0.05). Our results are comparable with the state-of-the-art PNCC front-end which is also based on auditory processing. Significance test between their average performances shows no statistically significant difference (p > 0.05). When SNR is below 10 dB, recognition rates are close to 0% for MFC and PLP, and around 50% for a GHC based system. Average GHC based performance is ≈20 percentage points higher than standard MFC baseline (p < 0.05).
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we have proposed a speech recognition front-end motivated by cochlear processing of audio signals. Cochlear behavior is first emulated by the filtering operations of the gammatone filterbank and subsequently by the IHC processing stage. Experimental results using a continuous density HMM recognizer clearly demonstrate the robustness of the proposed system, compared to standard MFC and PLP front-ends. Although the recognition rates are lower for clean speech, they are greatly improved in noisy conditions. We have also compared our system with the PNCC front-end which is also based on auditory processing and we have achieved comparable results. Our future work will include a more detailed analysis of the proposed approach with possible new improvements (especially in clean speech conditions) and will include analysis in various types of additive noise on a well-known database, other state-of-the-art front-ends and computational efficiency analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R. and M.S. (Maja Stella); Methodology, M.R. and M.S. (Maja Stella); Software, M.S. (Marjan Sikora); Validation, M.R., M.S. (Maja Stella) and M.S. (Marjan Sikora); Formal Analysis, M.R. and M.S. (Maja Stella); Investigation, M.R. and M.S. (Maja Stella); Resources, M.R, M.S. (Maja Stella) and V.P.; Data Curation, V.P.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.R. and M.S. (Maja Stella); Writing—Review and Editing, M.R., M.S. (Maja Stella), M.S. (Marjan Sikora), V.P.; Visualization, V.P.; Supervision, M.R. and M.S. (Maja Stella); Project Administration, M.R.; Funding Acquisition, M.R.
Funding
This work has been fully supported by the Croatian Science Foundation under the project number UIP-2014-09-3875.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fletcher, H. The nature of speech and its interpretation. J. Franklin Inst. 1922, 193, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Biddulph, R.; Balashek, S. Automatic recognition of spoken digits. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1952, 24, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.F. Speech recognition in noisy environments—A survey. Speech Comm. 1995, 16, 261–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceidaite, G.; Telksnys, L. Analysis of factors influencing accuracy of speech recognition. Elektron. Ir Elektrotech. 2010, 9, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.H.; Lindberg, B. Mobile Multimedia Processing; Springer: New York, UY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Takeda, K.; Itakura, F. Robust in-car speech recognition based on nonlinear multiple regressions. EURASIP J. Adv. Sig. Process. 2007, 2007, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Gao, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q. Application of keywords speech recognition in agricultural voice information system. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Natural Computing, Wuhan, China, 13–14 September 2010; pp. 197–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W. Emotion recognition from chinese speech for smart affective services using a combination of SVM and DBN. Sensors 2017, 17, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriega-Linares, J.E.; Navarro Ruiz, J.M. On the application of the raspberry Pi as an advanced acoustic sensor network for noise monitoring. Electronics 2016, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rousan, M.; Assaleh, K. A wavelet-and neural network-based voice system for a smart wheelchair control. J. Franklin Inst. 2011, 348, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, I.; Sharifzadeh, H.R. Speech Recognition, Technologies and Applications; I-Tech Education and Publishing: Vienna, Austria, 2008; pp. 477–494. [Google Scholar]
- Glowacz, A. Diagnostics of rotor damages of three-phase induction motors using acoustic signals and SMOFS-20-EXPANDED. Arch. Acoust. 2016, 41, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowacz, A. Fault diagnosis of single-phase induction motor based on acoustic signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 117, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunicki, M.; Cichoń, A. Application of a Phase Resolved Partial Discharge Pattern Analysis for Acoustic Emission Method in High Voltage Insulation Systems Diagnostics. Arch. Acoust. 2018, 43, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Mika, D.; Józwik, J. Advanced time-frequency representation in voice signal analysis. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K. Review on structural health evaluation with acoustic emission. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, T. A method of abnormal states detection based on adaptive extraction of transformer vibro-acoustic signals. Energies 2017, 10, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wen, G.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Dai, L. Experimental investigation on influence factors of acoustic emission activity in coal failure process. Energies 2018, 11, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarpour, L.; Hassanpour, H. A self-tuning hybrid active noise control system. J. Franklin Inst. 2012, 349, 1904–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Wang, J.F.; Chen, M.H. Threshold-based noise detection and reduction for automatic speech recognition system in human-robot interactions. Sensors 2018, 18, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.M.; Peng, W.M. Principle and applications of asymmetric crosstalk-resistant adaptive noise canceler. J. Franklin Inst. 2000, 337, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.W.; Lin, J.S.; Wu, P.J. Employing Robust Principal Component Analysis for Noise-Robust Speech Feature Extraction in Automatic Speech Recognition with the Structure of a Deep Neural Network. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2018, 1, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, R.P. Speech recognition by machines and humans. Speech Commun. 1997, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.B. How do humans process and recognize speech? IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1994, 2, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.; Togneri, R.; Zaknich, A. Perceptual features for automatic speech recognition in noisy environments. Speech Commun. 2009, 51, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansky, H. Perceptual linear predictive (PLP) analysis of speech. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 1738–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmberg, M.; Gelbart, D.; Hemmert, W. Automatic speech recognition with an adaptation model motivated by auditory processing. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang Process. 2006, 14, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Stern, R.M. Power-normalized cepstral coefficients (PNCC) for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 4101–4104. [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer, M.L.; Yu, D.; Wang, Y. An investigation of deep neural networks for noise robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Vancouver, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 7398–7402. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.L.; Le, Q.V.; O’Neil, T.M.; Vinyals, O.; Nguyen, P.; Ng, A.Y. Recurrent neural networks for noise reduction in robust ASR. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Oregon, Poland, 9–13 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wollmer, M.; Schuller, B.; Eyben, F.; Rigoll, G. Combining long short-term memory and dynamic bayesian networks for incremental emotion-sensitive artificial listening. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Sign. Process. 2010, 4, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Geiger, J.; Pohjalainen, J.; Mousa, A.E.D.; Jin, W.; Schuller, B. Deep learning for environmentally robust speech recognition: An overview of recent developments. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2018, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, C.R., Jr.; Vo, H.D.H.; Lippmann, R.P. A comparison of signal processing front ends for automatic word recognition. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1995, 3, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneff, S. A computational model for the peripheral auditory system: Application of speech recognition research. In Proceedings of the ICASSP ’86. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Tokyo, Japan, 7–11 April 1986; pp. 1983–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ghitza, O. Auditory models and human performance in tasks related to speech coding and speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1994, 2, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, R. Auditory features based on gammatone filters for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Beijing, China, 19–23 May 2013; pp. 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Hohmann, V.; Nadeu, C. Acoustic features for speech recognition based on Gammatone filterbank and instantaneous frequency. Speech Commun. 2011, 53, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Jin, Z.; Wang, D.; Srinivasan, S. An auditory-based feature for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 4625–4628. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, A.; Kim, C.; Stern, R.M. Robust Speech Recognition Based on Binaural Auditory Processing. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 3872–3876. [Google Scholar]
- Marieb, E.N.; Hoehn, K. Human anatomy & physiology; Benjamin Cummings: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Hall, W.C.; LaMantia, A.S.; McNamara, J.O.; Williams, S.M. Neuroscience; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Johannesma, P.I. The pre-response stimulus ensemble of neurons in the cochlear nucleus. In Proceedings of the Symposium of Hearing Theory, Eindhoven, The Netherland, 22–23 June 1972; pp. 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, R.D.; Robinson, K.; Holdsworth, J.; McKeown, D.; Zhang, C.; Allerhand, M. Complex sounds and auditory images. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Hearing, Carcens, France, 9–14 June 1991; pp. 429–446. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, R.D. Frequency Selectivity in Hearing; Auditory Filters and Excitation Patterns as Representations of Fre-Quency Resolution; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1986; pp. 123–177. [Google Scholar]
- Glasberg, B.R.; Moore, B.C. Derivation of auditory filter shapes from notched-noise data. Hear. Res. 1990, 47, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaney, M. An Efficient Implementation of the Patterson-Holdsworth Auditory Filter Bank. 1993. Available online: https://engineering.purdue.edu/~malcolm/apple/tr35/PattersonsEar.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2018).
- Meddis, R. Simulation of mechanical to neural transduction in the auditory receptor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1986, 79, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwan, A.; Van Schaik, A. A silicon representation of the Meddis inner hair cell model. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Intelligent Systems and Applications (ISA’2000), Sydney, Australia, 12–15 December 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Brown, G.J. Computational Auditory Scene Analysis: Principles, Algorithms, and Applications; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Young, S.J.; Evermann, G.; Gales, M.J.F.; Hain, T.; Kershaw, D.; Moore, G.; Odell, J.; Ollason, D.; Povey, D.; Valtchev, V.; Woodland, P.C. The HTK Book, Edition 3.4 ed; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Stern, R.M. Power-normalized cepstral coefficients (PNCC) for robust speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 24, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Gauvreau, K. Principles of Biostatistics; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).