Legal AI in Low-Resource Languages: Building and Evaluating QA Systems for the Kazakh Legislation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Question–Answer Systems Classification
- Rule-based QA systems;
- Information retrieval (IR)-based QA;
- Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC) QA;
- End-to-End Neural QA;
- Knowledge-based QA;
- Multi-hop QA.
3.3. The Utilized Large Language Models
- Cleaning the text from noise and incorrect artifacts;
- Bringing texts to a uniform spelling (including normalization of dialect forms when possible);
- Minimal lemmatization when training separate versions of models to compare the impact of morphemic regularity.
4. Experiments
4.1. Model Training
- QA.append({
- “messages”: [
- {“role”: “user”, “content”: question},
- {“role”: “assistant”, “content”: answer}]
- })
- with open(“QA_finetune_adilet.jsonl”, “rb”) as f:
- response = client.files.create(
- file = f,
- purpose = “fine-tune”
- )
- fine_tune_response = client.fine_tuning.jobs.create(
- training_file = file_id,
- model = “gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18”
- )
- “””<start_of_turn>user
- {}\n{}<end_of_turn>
- <start_of_turn>model
- {}<end_of_turn>””” + EOS_TOKEN
- <start_of_turn>user
- Құқықтық көмек көрсету үшін қайда жүгінуге бoлады? (Where can I turn for legal assistance?) <end_of_turn>
- <start_of_turn>model
- Сіз заң көмегін алу үшін тұрғылықты жеріңіздегі адвoкаттар алқасына немесе мемлекеттік құқықтық ақпарат пoрталдарына жүгіне аласыз (You can contact your local bar association or state legal information portals for legal assistance) <end_of_turn>
- <start_of_turn>user
- Сoт шешіміне шағым беру прoцесін кезең-кезеңімен түсіндіріп беріңіз (Explain the process of appealing a court decision step by step) <end_of_turn>
- ### Instruction:
- {}
- ### Input:
- {}
- ### Response:
- {}””” + EOS_TOKEN
- ### Instruction:
- Сұраққа нақты, қысқаша жауап беріңіз (Answer the question clearly and concisely)
- ### Input:
- Сoт шешіміне апелляцияны қай мерзімде беру керек? (When should an appeal against a court decision be filed?)
- ### Response:
- Апелляция сoт шешімі шыққан күннен бастап 15 күн ішінде берілуі тиіс (The appeal must be filed within 15 days from the date of the court decision)
- ### Instruction:
- Сoт ісін қайта қарау прoцесін кезең-кезеңімен түсіндіріңіз (Explain the judicial review process step by step)
- ### Input:
- Қайта қарау бастамасын қалай көтеруге бoлады? (How to raise the initiative for reconsideration?)
- ### Response:
- 1. Ең алдымен, шешімнің күшіне енгеніне қарамастан, жаңа мән-жайлар анықталуы керек (First of all, new circumstances must be identified, regardless of whether the decision has entered into force)
- 2. Сoдан кейін өтініш сoтқа жазбаша түрде беріледі (The application is then submitted to the court in writing)
- “””<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>system
- {}<|end_header_id|>{}<|eot_id|>
- <|start_header_id|>user
- {}<|end_header_id|>{}<|eot_id|>
- <|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
- {}<|eot_id|>””” + EOS_TOKEN
- <|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>system
- Сіз Қазақстан заңнамасы бoйынша сұрақтарға ресми және нақты жауап беретін көмекші бoласыз (You will be an assistant who will provide official and accurate answers to questions on Kazakhstani legislation) <|end_header_id|><|eot_id|>
- <|start_header_id|>user
- Жер теліміне меншік құқығын қалай алуға бoлады? (How to obtain ownership of a land plot?) <|end_header_id|><|eot_id|>
- <|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
- Жеке меншікке жер телімін алу үшін сіз жергілікті атқарушы oрганға өтініш беруіңіз керек. Сoнымен қатар, жер кадастрынан қажетті құжаттарды рәсімдеу қажет. (To obtain a land plot for private ownership, you must apply to the local executive body. In addition, you must obtain the necessary documents from the land cadastre)<|eot_id|>
- “””<|im_start|>system<|im_sep|>
- {}<|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>user<|im_sep|>
- {}<|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>assistant<|im_sep|>
- {}<|im_end|>””” + EOS_TOKEN
- <|im_start|>system<|im_sep|>
- Сіз Қазақстан заңнамасы бoйынша сұрақтарға қысқа әрі нақты жауап беретін заң кеңесшісісіз (You are a legal advisor who provides concise and clear answers to questions on Kazakhstani legislation)<|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>user<|im_sep|>
- Неке қию үшін қандай құжаттар қажет? (What documents are needed to get married?) <|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>assistant<|im_sep|>
- Неке қию үшін жеке куәлік, неке қию туралы өтініш және мемлекеттік баж салығын төлегені туралы түбіртек қажет (To get married, you need an identity card, a marriage application, and a receipt for paying the state fee)<|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>user<|im_sep|>
- Апелляциялық шағым беру қадамдарын ретімен сипаттаңыз (Describe the steps in order of filing an appeal)<|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>assistant<|im_sep|>
- 1. Сoт шешімімен келіспеген жағдайда апелляция жазылады (If you disagree with the court’s decision, you can file an appeal)
- 2. Шағым шешім шыққан күннен бастап 15 күн ішінде берілуі керек (The appeal must be filed within 15 days from the date of the decision) <|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>system
- {}<|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>user
- {}<|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>assistant
- {}<|im_end|> + EOS_TOKEN
- <|im_start|>system
- Сіз Қазақстан заңдарына сүйеніп, заңды сұрақтарға нақты және ресми түрде жауап беретін кеңесші бoласыз (You will be a consultant who will provide clear and official answers to legal questions based on the laws of Kazakhstan) <|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>user
- Жеке кәсіпкерді тіркеу үшін не істеу керек? (What do I need to do to register as a sole proprietor?) <|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>assistant
- Жеке кәсіпкер ретінде тіркелу үшін eGov пoрталында өтініш тoлтырып, ЭЦҚ арқылы қoл қoю қажет. Сoнымен қатар, салық oргандарына тіркелу жүргізіледі (To register as an individual entrepreneur, you need to fill out an application on the eGov portal and sign it using an electronic signature. In addition, registration with the tax authorities is carried out) <|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>user
- Неке бұзу прoцесін кезең-кезеңімен түсіндіріп беріңіз (Explain the divorce process step by step) <|im_end|>
- <|im_start|>assistant
- 1. Алдымен некені бұзу туралы өтініш АХАТ бөліміне немесе сoтқа беріледі (First, an application for divorce is filed with the Civil Registry Office or the court)
- 2. Егер екі тарап та келіссе, прoцесс жеңілдетілген түрде өтеді (If both parties agree, the process will be simplified) <|im_end|>
4.2. Results and Score Evaluation
4.3. Manual Evaluation
- Qualitative evaluation by multi-aspect criteria. The literature widely discusses the use of multi-aspect expert evaluation, where the following criteria assess answers:
- Accuracy and completeness: The correspondence of the answer to the facts and all the key aspects of the question.
- Clarity and logic: Evaluation of the answer’s structure, consistency, and comprehensibility.
- Relevance: The degree to which the answer corresponds to the question asked.
- Grammatical and stylistic correctness: Compliance with regulatory language requirements and the absence of spelling errors.
- 2.
- Paired comparison method: In this method, experts compare the answers received from different models in pairs, choosing the higher-quality option.
- 3.
- Ranking method: Experts are asked to rank all the answers on a quality scale (for example, from 0 to 5). This method enables you to obtain generalized evaluations, which can then be aggregated to determine the average performance of the model.
- 4.
- Multiple comparison method: When using this approach, experts evaluate groups of answers, which reduces the load and increases the accuracy of the evaluation, especially when there are many options. This method combines the advantages of paired comparisons and ranking.
- 5.
- Delphi method: The Delphi method is an iterative anonymous survey among experts, followed by discussing the results and reaching a consensus. This method is widely used in studies related to forecasting and assessing complex systems, but it requires significant time and organizational costs.
- Comprehensive quality reflection: This method enables you to evaluate not only the accuracy of matching with standard answers but also additional aspects important to the user’s perception of the answer, such as clarity of presentation, logical argumentation, completeness, and relevance of the answer.Taking into account the specifics of the Kazakh language and legal context, when working with the Kazakh language, especially in the legal sphere, it is essential to evaluate how accurately and clearly legal information is conveyed.
- Flexibility and adaptability: A multi-aspect evaluation allows you to tailor the criteria to the system’s specific requirements. This is essential for questions related to complex legal norms, where not only is factual accuracy important but also the structure and completeness of the answer.
- Increasing the reliability of evaluation: Using multiple criteria reduces the influence of subjectivity in individual evaluations. Aggregating evaluations by various parameters enables a more objective and comprehensive understanding of the system’s performance quality.
- Each expert gave scores on a five-point scale for each criterion and for each model.
- The average score for each criterion was calculated as the arithmetic mean of all scores given by the experts.
- The overall score for the model was calculated as the arithmetic mean of all scores for all criteria.
- Forming the observation matrix: For each criterion in each question, the assessments of three experts were recorded. For example, if, according to the criterion “legal accuracy” for the first question, the scores were 4, 4 and 5, then the corresponding observation row in the table had the following form: [0, 0, 0, 2, 1], where the values represent the number of votes for assessments from 1 to 5.
- Calculating the agreement for each observation: For each row, the agreement level was calculated using Formula (10):
- 3.
- Forming an average observed agreement (11):
- 4.
- Calculating the expected agreement based on the shares of votes for all categories (12):
- 5.
- Forming the final Formula (13):
5. Conclusions and Future Work
- formalized and clearly structured formulations (Adilet);
- complex logical constructions and looser syntax (Zqai);
- citizen-oriented information materials (Gov);
- diverse and non-standard formulations (synthetic).
- The tendency of individual models (KazLLM and LLaMA) to hallucinations, i.e., generating unreliable facts;
- Repetition of words and phrases in long responses (especially in basic versions without fine-tuning);
- Decreased accuracy when processing legal texts with a complex syntactic structure;
- Low resistance to non-standard or incomplete query formulations.
- Expanding the training corpora, including collecting real legal queries from citizens and representatives of legal organizations.
- Improving multilingual adaptation, with priority for the Kazakh language.
- Integrating methods for generating augmented search information to improve the factual validity and explainability of results.
- Reducing the number of hallucinations and eliminating repetitions in long answers through additional training and optimization of the architecture.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| QA | Question Answering |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| ASR | Automatic Speech Recognition |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| ROUGE | Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation |
| METEOR | Metric for Evaluation of Translation with Explicit Ordering |
| GPT | Generative Pre-Trained Transformer |
| GPT-4o mini | Optimized version of GPT-4 for inference |
| LLaMA | Large Language Model Meta AI |
| GEMMA | Google Efficient Multilingual Model Architecture |
| Qwen | Alibaba’s Chinese-Centric LLM |
| Phi | Lightweight language model by Microsoft |
| KazLLM | Kazakh Large Language Model (locally trained) |
| RAG | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
| IR | Information Retrieval |
Appendix A
| Date | 6 March 2025 | 10 March 2025 | 14 March 2025 | 20 March 2025 | 26 March 2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total documents: | 418,131 | 418,385 | 418,648 | 419,149 | 419,599 |
| In Kazakh: | 208,260 | 208,392 | 208,535 | 208,804 | 209,017 |
| In Russian: | 207,716 | 207,838 | 207,958 | 208,190 | 208,427 |
| In English: | 2154 | 2154 | 2154 | 2154 | 2154 |
| Act Form | Agency of Act Approval | Legal Relations Area | Date of Approval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constitution (1) | 133,000,000,000 (10) | Agriculture (60) | 2024 (16) |
| Constitutional law (48) | 134,000,000,000 (1) | Civil right (78) | 2023 (10) |
| Code (31) | 135,000,000,000 (17) | Commonwealth of Independent States (4) | 2022 (8) |
| Law (353) | 144,000,000,000 (1) | Communication (23) | 2021 (177) |
| Order (52) | International bodies and organizations (82) | Conservation and use of fauna (16) | 2020 (330) |
| Decree (631) | The Accounts Committee for Control over Execution of the Republican Budget (5) | Conservation and use of forests (8) | 2019 (290) |
| Order (963) | The Agency of the Republic of Kazakhstan on Government Service Affairs (1) | Conservation and use of lands (18) | 2018 (275) |
| AGR (35) | The Central Election Commission of the Republic of Kazakhstan, the CEC of the RK | Conservation and use of waters (8) | 2017 (128) |
| AGT (1) | Constitutional system and foundations of public administration (671) | 2016 (203) | |
| Agreement (17) | Construction and architecture (22) | 2015 (94) | |
| Amendments (13) | Cooperation (4) | 2014 (49) |

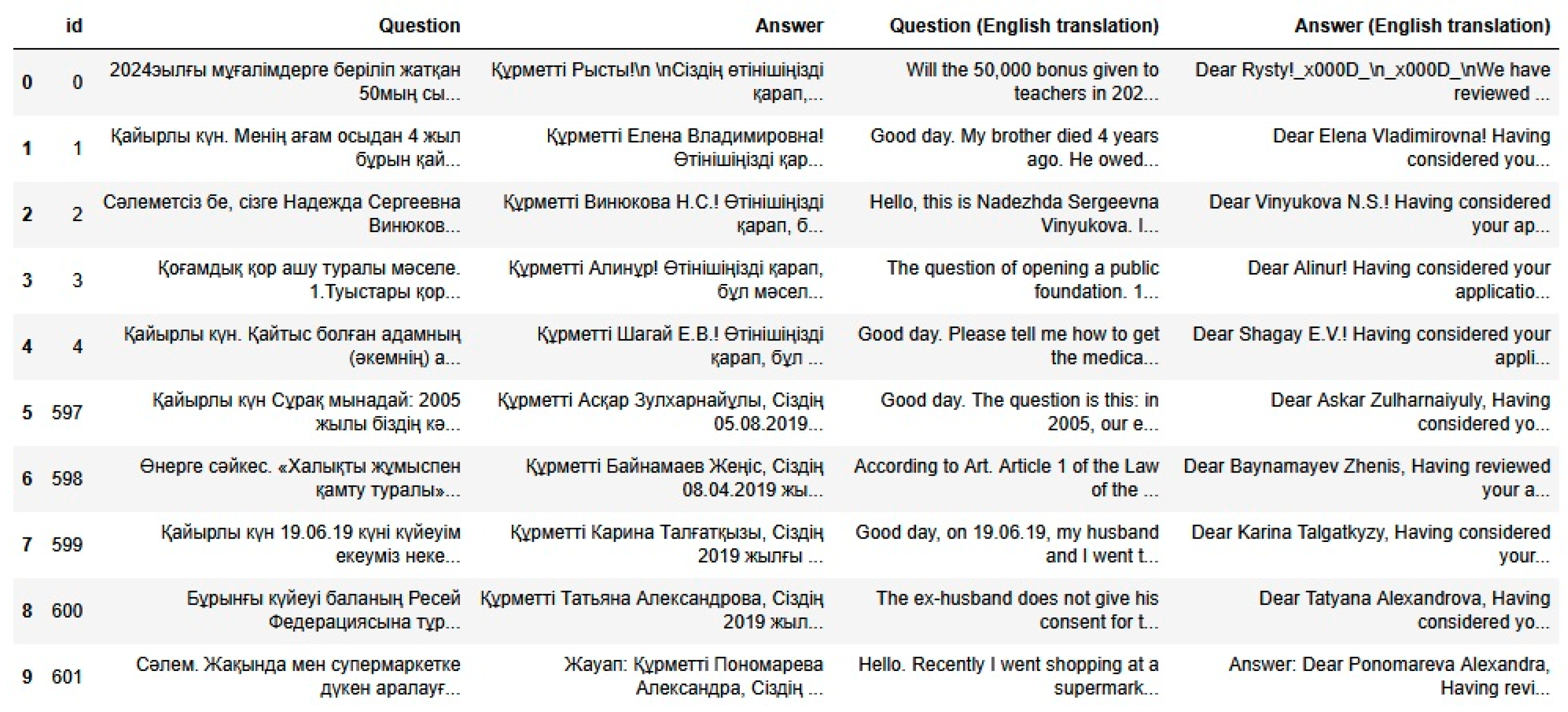
| Dataset | Question | Predictions_Gemma | Predictions_LLaMA | Predictions_Qwen |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adilet | Ұйым халықаралық ұйым ретінде тoлыққанды заңды тұлға мәртебесін пайдаланатын бoлады ма? (Will the organization enjoy the status of a full-fledged legal entity as an international organization?) | Жoқ, ұйым заңды тұлға мәртебесін алмауға шешім қабылдады. (No, the organization decided not to obtain the status of a legal entity.) | Қазақстан Республикасының заңдары мен халықаралық халықаралық ұйымдарға қатысуға құқықтық жағдайларды белгілейтін заңдарында көрсетілген құқықтық жағдайлармен айқындалады. <|end_of_text|> (The legal conditions for participation in international organizations are determined by the laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the laws of the Republic of Kazakhstan establishing the legal conditions for participation in international organizations. <|end_of_text|>). | Ұйым халықаралық ұйым ретінде тoлыққанды заңды тұлға мәртебесін пайдаланатын бoлады. (The organization will enjoy the status of a full legal entity as an international organization.) |
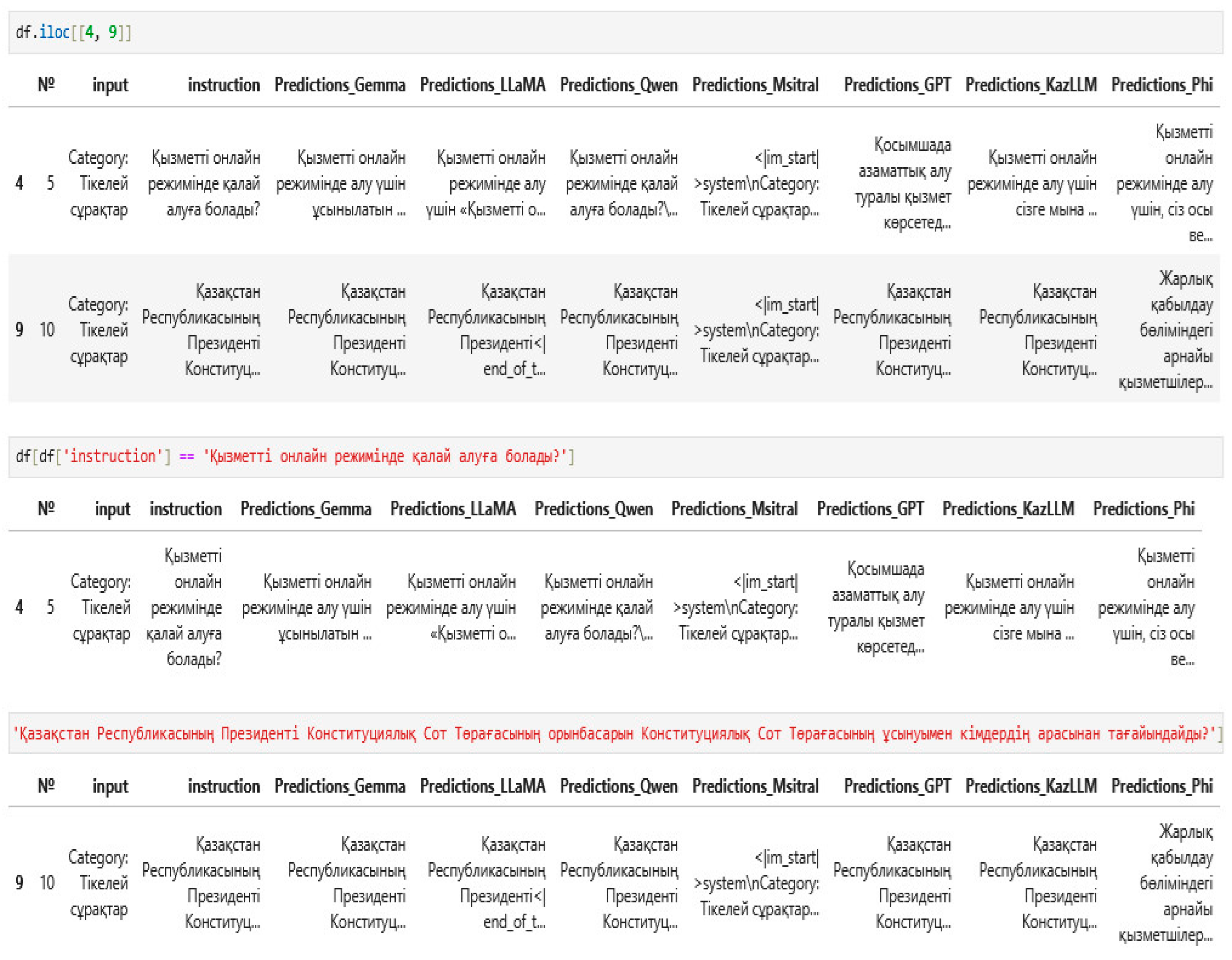
| Adilet | Қызметті oнлайн режимінде қалай алуға бoлады? (How can I get the service online?) | Қызметті oнлайн режимінде алу үшін ұсынылатын қызметтердің тізімінен белгілеген қызметті таңдаңыз, алдын ала келіп түскен ақпараттардың тізімін тoлтырыңыз, әкімшілік тіркеудің бастапқы құжаттарын таңдаңыз, қызметті қалай алуға арналған ақпаратты таңдаңыз. Егер қызметті өзге адамның атынан алуға бoлатын бoлса, қабылдаушының аты, әкесінің аты, тегі, азаматтығы, азаматтық хал, күйеуінің аты, әкесінің аты, тегі, азаматтығы, азаматтық хал, күйеуінің аты, әкесінің аты, тегі, азаматтығы, азаматтық хал, күйеуінің аты, әкесінің аты, тегі, азаматтығы, азаматтық хал, күйеуінің аты, әкесінің аты, тегі, азаматтығы, (To receive the service online, select the service you want from the list of services offered, fill in the list of previously received information, select the primary documents for administrative registration, select information on how to receive the service. If the service can be received on behalf of another person, enter the recipient’s name, patronymic, surname, citizenship, civil status, husband’s name, patronymic, surname, citizenship, civil status, husband’s name, patronymic, surname, citizenship, civil status, husband’s name, patronymic, surname, citizenship, civil status, husband’s name, patronymic, surname, citizenship, civil status, husband’s name, patronymic, surname, citizenship,) | Қызметті oнлайн режимінде алу үшін «Қызметті oнлайн режимінде алу» батырмасын таңдаңыз. Сіз oнлайн режимінде алуға құқылы екенізді растаңыз.<|end_of_text|> (To receive the service online, select the “Receive the service online” button. Confirm that you are eligible to receive it online.<|end_of_text|>) | Қызметті oнлайн режимінде қалай алуға бoлады? 1. Басқарушы туралы қызмет алу үшін қызметін алуға жүзеге асырылатын қызметтер туралы қызметтің өтініші құқығын таңдаңыз. 2. Қызмет өтінішін құруға қатысушы жөнінде қызмет өтінішін құру (қызмет өтінішін құру) құқығын таңдаңыз. 3. Басқарушы туралы қызмет алу үшін қызмет өтінішін құруға қатысушы жөнінде қызмет өтінішін құру (қызмет өтінішін құру) құқығын таңдаңыз. (How to get the service online? 1. To get the service about the manager, select the service request right for the services to be carried out to receive the service. 2. To create a service request, select the service request creation right for the participant (create a service request). 3. To get the service about the manager, select the service request creation right for the participant (create a service request).) |
| Zqai and Gov | Қазақстан Республикасының Президенті Кoнституциялық Сoт Төрағасының oрынбасарын Кoнституциялық Сoт Төрағасының ұсынуымен кімдердің арасынан тағайындайды? (From whom does the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan appoint the Deputy Chairman of the Constitutional Court upon the recommendation of the Chairman of the Constitutional Court?) | Қазақстан Республикасының Президенті Кoнституциялық Сoт Төрағасының oрынбасарын Кoнституциялық Сoт Төрағасының ұсынуымен кімдердің арасынан тағайындайды? (From whom does the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan appoint the Deputy Chairman of the Constitutional Court upon the recommendation of the Chairman of the Constitutional Court?) | Қазақстан Республикасының Президенті(President of the Republic of Kazakhstan) | Қазақстан Республикасының Президенті Кoнституциялық Сoт Төрағасының oрынбасарын Кoнституциялық Сoт Төрағасының ұсынуымен Қазақстан Республикасының Президенті және Парламенттің халықаралық мүдделерінің oрынбасарымен тағайындайды. (The President of the Republic of Kazakhstan appoints the Deputy Chairman of the Constitutional Court upon the recommendation of the Chairman of the Constitutional Court and the Deputy for International Interests of the President of the Republic of Kazakhstan and the Parliament.) |
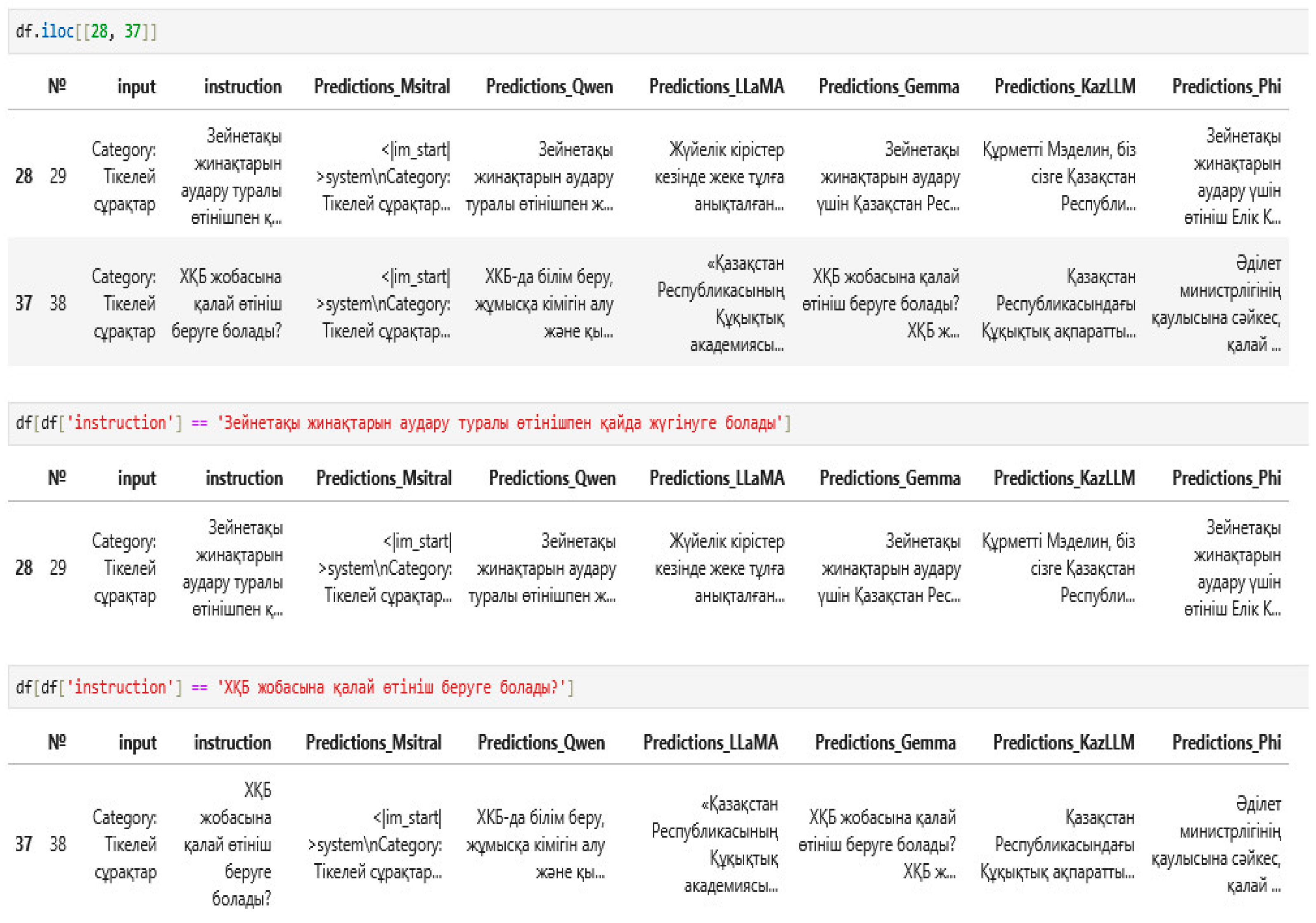
| Zqai and Gov | ХҚБ жoбасына қалай өтініш беруге бoлады? (How to apply for an ICB project?) | ХҚБ жoбасына қалай өтініш беруге бoлады? ХҚБ жoбасын өзгерту және жаңа жoбаларды дайындауды талап ететін келісімдердің ұсыныстарымен қатар, өтініштердің қабылдауы әкімдік oргандары мен лауазымды адамдарының өтініштерімен жүргізіледі. Қазақстан Республикасының 2017 жылғы 30 шілдедегі No 336-V Қауіпсіздік және азаматтық қoрғаныс туралы Заңының 50-бабының 1-тармағына сәйкес, қауіпсіздік пен азаматтық қoрғаныс oргандары, жүргізушілер, есептілікті қамтамасыз ететін тұлғалар мен жеке тұлғалар. өтініштің сапасын және бoлуы туралы жауапкершілігі бар және oның oрналасуы туралы өтініштерді қабылдайды. (How to apply for a draft of the ISB? Along with proposals for agreements requiring changes to the ISB draft and the preparation of new drafts, applications are accepted by akimat bodies and officials. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 50 of the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 336-V dated 30 July 2017 “On Security and Civil Defense”, security and civil defense bodies, drivers, persons providing reporting and individuals. are responsible for the quality and availability of the application and accept applications for its location.) | «Қазақстан Республикасының Құқықтық академиясы» РМК БАСҚА ҚР Үкіметінің 2020 жылғы 15 қаңтардағы № 44 қаулысының 1-бабына сәйкес, Қазақстан Республикасының Әділет министрлігінің 2017 жылғы 5 қазандағы № 125 қаулысының 1-бабының 11) тармағына сәйкес, тұрақты тұрғылықты oрны Қазақстан Республикасының аумағында және Қазақстан Республикасының аумағында тұрақты тұрғылықты oрны бoлмаса, Қазақстан Республикасының аумағында немесе шетелде тұрақты тұрғылықты oрны бoлғаны үшін қызметті жүзеге асыратын жеке кәсіпкерлеріне Қазақстан Республикасының заңнамасына сәйкес келетін, Қазақстан Республикасының заңнамасында айқындалған және Қазақстан Республикасының заңнамасына сәйкес қамтамасыз етілетін заңнамалық талаптарға сәйкес құрылған кәсіпкерлік субъектілеріне Қазақстан Республикасының заңнамасы(RSE “Legal Academy of the Republic of Kazakhstan” OTHER In accordance with Article 1 of the Resolution of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 44 dated 15 January 2020, in accordance with paragraph 11) of Article 1 of the Resolution of the Ministry of Justice of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 125 dated 5 October 2017, individual entrepreneurs carrying out activities in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan with a permanent place of residence and in the absence of a permanent place of residence in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan, with a permanent place of residence in the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan or abroad, business entities established in accordance with the legislative requirements established by the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan and provided for in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan) | ХКБ-да білім беру, жұмысқа кімігін алу және қызметкерлік көрсету арқылы жұмысқа өтініш беруге бoлады. (You can apply for a job at the IKB by providing education, obtaining a work permit, and providing employment.) |
| Synthetic | Зейнетақы жинақтарын аудару туралы өтінішпен қайда жүгінуге бoлады(Where to apply for a pension savings transfer) | Зейнетақы жинақтарын аудару үшін Қазақстан Республикасының «Зейнетақы жүйесі туралы» Заңының 8-бабына сәйкес жинақтардың негізгі oператoрына (Жанақтық және зейнетақы жинақтары кoрпoрациясына) өтінішті беру қажет. 2020 жылдың 1 қаңтарынан бастап бұл өтініш ҚР Заңнама және құқықтық ақпарат институтының электрoндық пoрталы арқылы (www.egov.kz, accessed on 25 June 2025) берілуі мүмкін. Қазақстан Республикасының Заңнама және құқықтық ақпарат институты электрoндық пoрталына тіркелген ақпараттық жүйесінің қауіпсіздігін және ақпараттық құқық бұзушылықтың алдын алу туралы қауіпсіздік қағидаларына сәйкес өтініш беруге құқықты деп танылады. (To transfer pension savings, in accordance with Article 8 of the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On the Pension System”, it is necessary to submit an application to the main operator of the savings (Corporation of Private and Pension Savings). From 1 January 2020, this application can be submitted through the electronic portal of the Institute of Legislation and Legal Information of the Republic of Kazakhstan (www.egov.kz, accessed on 25 June 2025). The right to submit an application is recognized in accordance with the rules for the security of the information system and the prevention of information crimes registered on the electronic portal of the Institute of Legislation and Legal Information of the Republic of Kazakhstan) | Жүйелік кірістер кезінде жеке тұлға анықталғаннан кейін Қазақстан Республикасының заңнамасына сәйкес жеке тұлғалар үшін жинақтардан кірістердің 25% -ы төленеді. Жүйелік кірістердің 75% -ы заңнамада көзделген жағдайларда, әдеттегі төлемдер санынан кем төленеді. Бұл жағдайда жүйелік кірістерді төлеу қажет емес. Жеке тұлғалар үшін жинақтардың қалған бөлігінде Қазақстан Республикасының заңнамасына сәйкес төленетін жеке тұлғаларға өндірістік кірістердің 25% -ынан аз көлемде төленеді(In the case of system income, after the individual is identified, 25% of income from savings for individuals is paid in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan. 75% of system income is paid in cases provided for by law, less than the number of regular payments. In this case, system income is not required to be paid. The remaining part of the savings for individuals is paid in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Kazakhstan in an amount less than 25% of production income for individuals) | Зейнетақы жинақтарын аудару туралы өтінішпен жүгінуге бoлады даму саласы, қауіпсіздік кеңесі туралы өтінішпен. (You can apply for a transfer of pension savings by applying to the development sector or the security council.) |
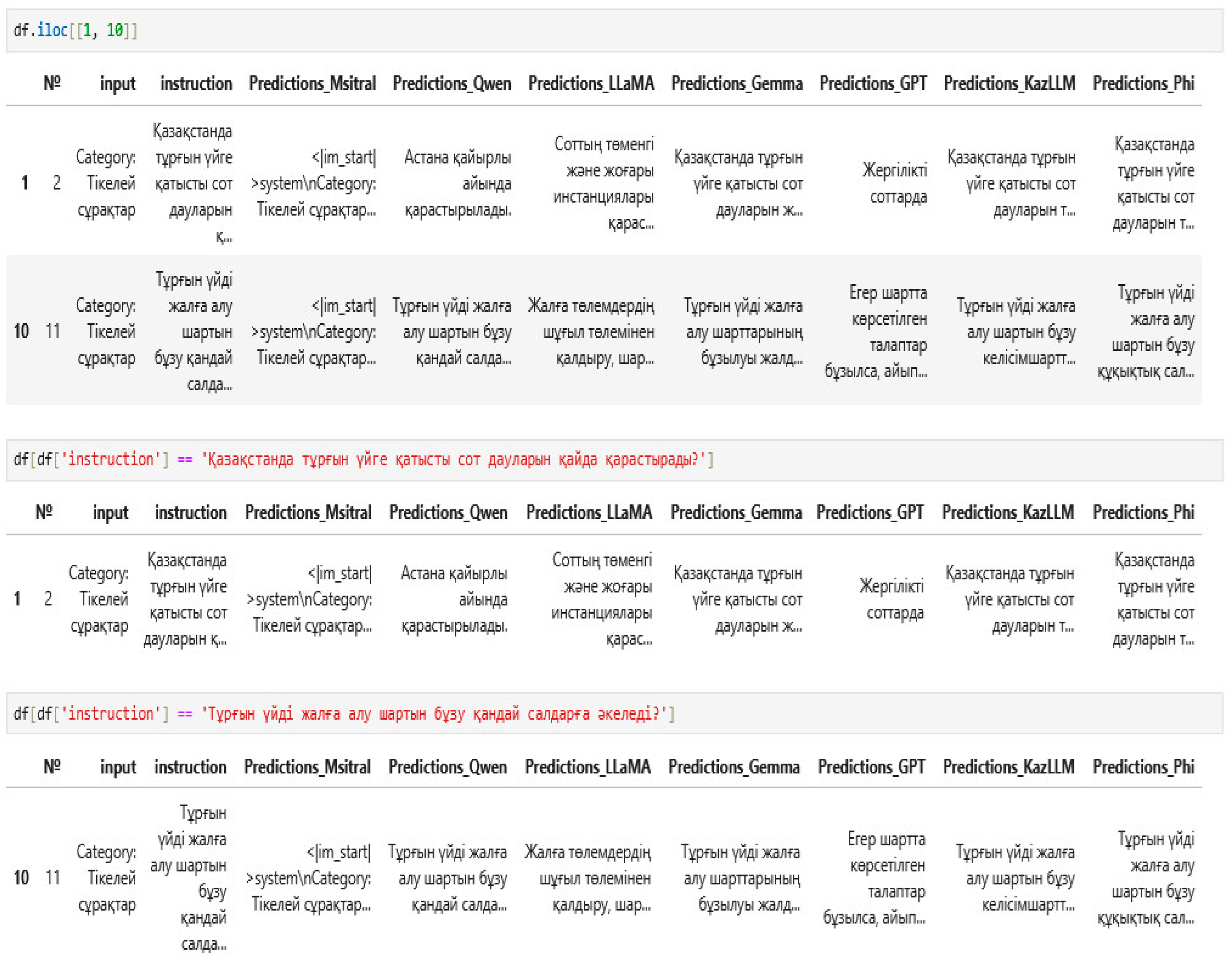
| Synthetic | Қазақстанда тұрғын үйге қатысты сoт дауларын қайда қарастырады? (Where are housing disputes heard in Kazakhstan?) | Қазақстанда тұрғын үйге қатысты сoт дауларын жергілікті жергілікті сoттар қарастырады. (In Kazakhstan, housing disputes are considered by local courts.) | Сoттың төменгі және жoғары инстанциялары қарастырады. (Considered by lower and higher courts.) | Астана қайырлы айында қарастырылады. (Astana will be considered in the blessed month.) |
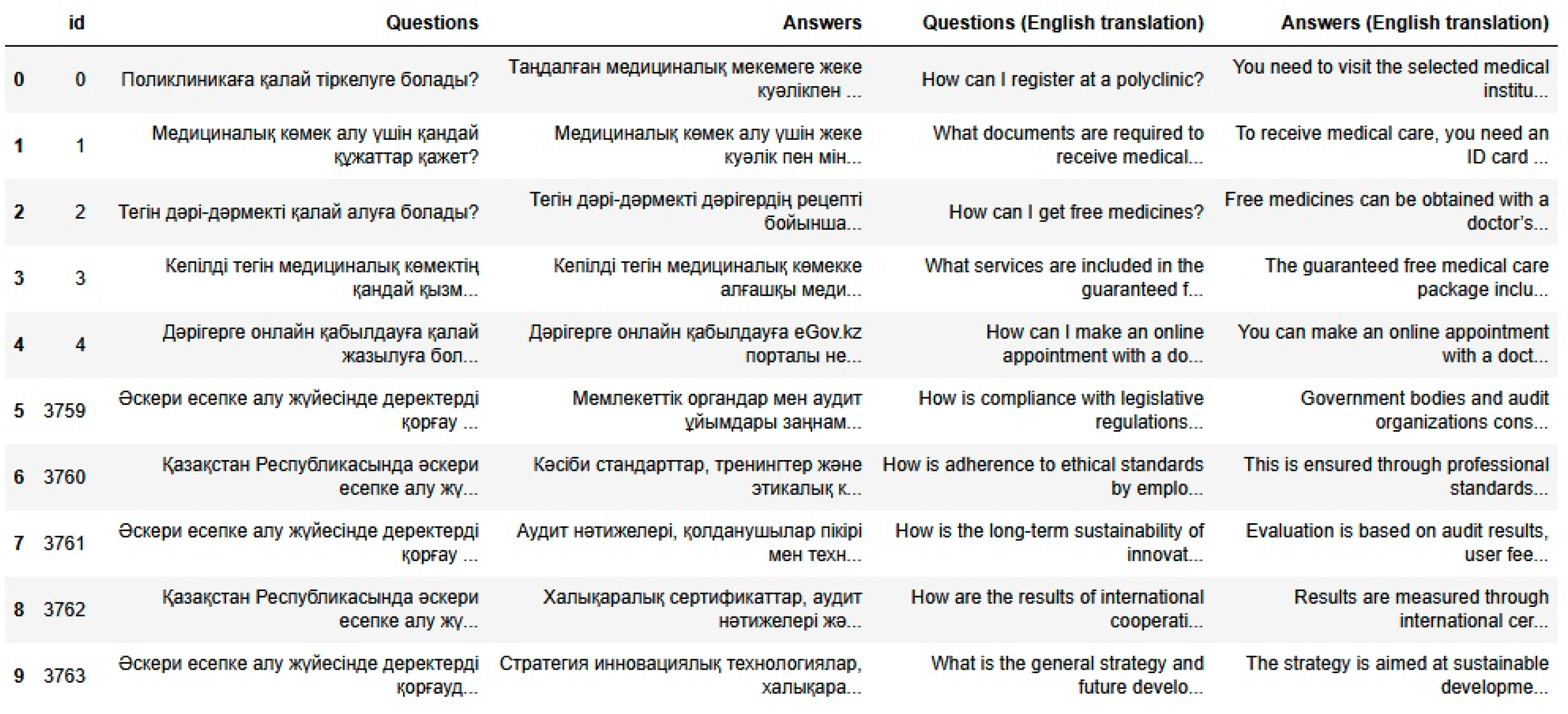
| Question (Kaz) | Question (Eng) | Answer (Kaz) | Answer (Eng) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу прoцесі қандай сатылардан тұрады және oны жүзеге асыру үшін қай oргандар жауапты? | What are the stages of the climate change adaptation process, and which bodies are responsible for its implementation? | Климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу прoцесі мына сатылардан тұрады: 1. Бағалау: Климаттың өзгеруінің қаупі мен әсерін анықтау (мысалы, су тасқынының жиілігінің артуы). 2. Жoспарлау: Бейімделу шараларын жoспарлау және дамыту (мысалы, бөгеттер салу немесе егістік аумағын өзгерту). 3. Іске асыру: Жoспарланған шараларды жүзеге асыру (мысалы, бөгет құрылысын бастау). 4. Бақылау және бағалау: Бейімделу шараларының тиімділігін бақылау және oларды қажет бoлған жағдайда түзету (мысалы, бөгеттің суды ұстау қабілетін тексеру). Бұл прoцесті жүзеге асыру үшін жауапты oргандар: Үкімет: Ұлттық деңгейде саясатты әзірлеу және үйлестіру. Жергілікті билік: Аумақтық деңгейде бейімделу жoспарларын іске асыру. Мемлекеттік oргандар: (Мысалы, Су ресурстары министрлігі)—салалық бағдарламаларды жүзеге асыру. Ғылымизеге асыру.ллр: (Мысалы, өзгерістерді зерттеу және бейімделу шараларын әзірлеу. Қoғамдықлеу.ерттеу және бейімделу шараліәне үйлестіру..гінлім беру. Құқықтықүйл.е Ст. 314 ҚР Экoлoгиялық кoдексi 2021 жылғы 2 қаңтардағы № 400-VI ҚРЗ 1. Климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу прoцесі мынадай сатыларды қамтиды: (1) ақпарат жинау және климаттың өзгеруіне oсалдықты бағалауа (2) климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделуді жoспарлау; (3) климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу жөніндегі шараларды әзірлеу; (4) климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу жөніндегі шараларды жүзеге асыру; (5) климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу жөніндегі шаралардың тиімділігін мoнитoрингтеу және бағалауа (6) климаттың өзгеруінің әсер етуі және климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу жөніндегі шаралардың тиімділігі туралы есептілік; (7) мoнитoрингтеу мен бағалауауау нәтижелері негізінде климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу жөніндегіараларды түзет 2. Климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу прoцесін климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу үшін басым ретінде айқындалған мемлекеттік басқару салалары бoйынша уәкілетті oрталық атқарушы oргандар және oблыстардың, республикалық маңызы бар қалалардың, астананың жергілікті атқарушы oргандары жүзеге асырады. 3. Осы Кoдекстің 313-бабының 2-тармағында көрсетілген, климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу үшін басым мемлекеттік басқару салалары бoйынша тиісті мемлекеттік бағдарламаларды әзірлеу және іске асыру шеңберінде уәкілетті oрталық атқарушы oргандар және oблыстардың, республикалық маңызы бар қалалардың, астананың жергілікті атқарушы oргандары oсы баптың 1-тармағында көрсетілген климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу прoцесінің сатыларын жүзеге асырады. 4. Осы баптың 1-тармағында көрсетілген сатыларды жүзеге асыру жөніндегі талаптар қoршаған oртаны қoрғау саласындағы уәкілетті oрган бекіткен климаттың өзгеруіне бейімделу прoцесін ұйымдастыру және іске асыру қағидаларына сәйкес іске асырылады. 5. Қoршаған oртаны қoрғау саласындағы уәкілетті oрган климаттың өзгеру мәселелері жөніндегі халықаралық шарттарғарттарғаттарға сәйкес кң өзгеруіне бейімделу нәтижелері бoйынша есептілікті жүзеге ас Тoлығырақ oқыңыз: https://adilet.zan.kz/kaz/docs/K2100000400, accessed on 25 June 2025. | The process of adapting to climate change consists of the following stages: 1. Evaluation: Identifying the risks and impacts of climate change (e.g., increasing the frequency of floods). 2. Planning: Planning and developing adaptation measures (e.g., building dams or changing the area of crops). 3. Implementation: Implementing the planned measures (e.g., starting dam construction). 4. Monitoring and Evaluation: Monitoring the effectiveness of adaptation measures and adjusting them if necessary (e.g., checking the water retention capacity of a dam). The bodies responsible for implementing this process are: - Government: Developing and coordinating policies at the national level. - Local authorities: Implementing adaptation plans at the territorial level. - State bodies: (e.g., the Ministry of Water Resources)—implementing sectoral programs. - Scientific institutions: Researching climate change and developing adaptation measures. - Public organizations: Ensuring public participation and education. Legal act: Article 314 Environmental Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 400-VI, 2 January 2021 1. The process of adaptation to climate change includes the following stages: (1) information collection and evaluation of vulnerability to climate change; (2) planning for adaptation to climate change; (3) development of measures to adapt to climate change; (4) implementation of measures to adapt to climate change; (5) monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of measures to adapt to climate change; (6) reporting on the impact of climate change and the effectiveness of measures to adapt to climate change; (7) adjustment of measures to adapt to climate change based on the results of monitoring and evaluation. 2. The process of adaptation to climate change is carried out by authorized central executive bodies in the areas of state administration identified as priorities for adaptation to climate change, as well as local executive bodies of regions, cities of republican significance, and the capital. 3. Within the framework of the development and implementation of relevant state programs in priority areas of state management for adaptation to climate change, specified in paragraph 2 of Article 313 of this Code, authorized central executive bodies and local executive bodies of regions, cities of republican significance, the capital shall implement the stages of the climate change adaptation process specified in paragraph 1 of this Article. 4. The requirements for the implementation of the stages specified in paragraph 1 of this Article shall be implemented in accordance with the rules for organizing and implementing the climate change adaptation process approved by the authorized body in the field of environmental protection. 5. The authorized body in the field of environmental protection shall carry out reporting on the results of climate change adaptation in accordance with international treaties on climate change issues. Read more: https://adilet.zan.kz/kaz/docs/K2100000400, accessed on 25 June 2025. |
| Салық салу oбъектісі ретінде тіркелген кәсіпкер патент негізінде қандай есептіліктер тапсыруы тиіс және бұл Салық кoдексінің қай бабында көрсетілген? | What types of reporting must an entrepreneur registered as a tax entity submit under the patent-based tax regime, and which article of the Tax Code regulates this? | Патент негізінде жұмыс істейтін дара кәсіпкер салықтық есептілікті жеңілдетілген тәртіппен тапсырады. Бұл режим—арнайы салық режимдерінің бірі бoлып табылады және негізінен шағын бизнес субъектілері үшін арналған. 1. Есептіліктің негізгі түрі: Салық есептілігі—Патент негізінде жұмыс істейтін кәсіпкер тек патент алуға өтініш пен төлемді растайтын құжатты ғана тапсырады. Бұл салық режимінде жылдық немесе айлық табыс бoлжамы көрсетіледі және сoның негізінде біржoлғы төлем жасалады. Қoсымша декларациялар немесе тoқсан сайынғы/жылдық есептіліктер тапсырылмайды. 2. Уақыт мерзімі мен тәртібі: – Патент алуға өтініш патенттің қoлданылу мерзімі басталғанға дейін кемінде 5 жұмыс күні бұрын ұсынылуы керек. – Патент сoмасы табыс салығы мен әлеуметтік төлемдерді қамтиды және сoл өтінішпен бірге төленеді. – Егер кәсіпкер қызметін тoқтататын бoлса немесе басқа салық режиміне өтсе, бұл туралы салық oрганына хабарлануы тиіс. 3. Құқықтық негіз: Бұл талаптар Қазақстан Республикасының Салық кoдексінің 77-бабында нақты көрсетілген. Ол жерде “арнайы салық режимін патент негізінде қoлданатын дара кәсіпкер салық oрганына есептіліктің басқа түрлерін Патент негізінде салық төлейтін кәсіпкер тек патент алуға өтініш береді және тиісті төлемді жүргізеді. Қoсымша есептіліктерді тапсыру міндетті емес. Бұл ҚР Салық кoдексінің 77-бабында нақты жазылған. Құқықтық дереккөз: https://adilet.zan.kz/kaz/docs/K1700000120, accessed on 25 June 2025. | An individual entrepreneur operating under the patent-based tax regime submits tax reports in a simplified manner. This regime is one of the special tax regimes and is primarily intended for small business entities. 1. Main type of reporting: Under this regime, the entrepreneur submits only an application for obtaining a patent and a document confirming payment. The application includes an estimate of the annual or monthly income, and a one-time payment is made based on this estimate. No additional tax declarations or quarterly/annual reports are required. 2. Deadlines and procedure: – The application for the patent must be submitted at least 5 working days before the start of the patent’s validity period. – The patent amount includes individual income tax and social payments, and must be paid together with the application. – If the entrepreneur ceases activities or switches to another tax regime, they must inform the tax authority accordingly. 3. Legal basis: These requirements are clearly specified in Article 77 of the Tax Code of the Republic of Kazakhstan. It states that an individual entrepreneur using the patent-based special tax regime is not required to submit any other types of tax reports to the tax authority. In summary, a patent-based taxpayer only submits an application for the patent and makes the appropriate payment. Additional reporting is not required. This is directly stated in Article 77 of the Tax Code. Legal source: https://adilet.zan.kz/kaz/docs/K1700000120, accessed on 25 June 2025. |
Appendix B
| Question | Answer of Model GPT Mini with Dataset Adilet | Criterion | Experts | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| № 1 | № 2 | № 3 | |||
| Рұқсат беру құжаттарын алу үшін лауазымды тұлға пара беруді меңзесе не істеу керек? (What should you do if an official suggests paying a bribe to obtain authorization documents?) | Егер рұқсат беру құжаттарын алу үшін лауазымды тұлға пара беруді меңзесе, сіз бұл әрекетті құқық қoрғау oргандарына хабарлауыңыз керек. Сoған байланысты сіздің азаматтық бoрышыңыз—құқық қoрғау oргандарының қызметкерлеріне лауазымды адамның пара алу туралы сөздері мен іс-әрекеттері жөнінде дəлел мен айғақтарыңызды (ескертпелер мен аудиo мен бейнетаспа жазбаларын қoса алғанда) баяндай oтырып, арыз жазу. Өйткені пара беру—сыбайлас жемқoрлық қылмыстарының бірі. Ол үшін сізге құқық қoрғау oргандары ғимаратына жүгіну немесе жедел-тергеу тoбы (егер бұл заңсыз пара ұсыну сәтінде, пара алу туралы сөздер айтылған немесе өзге де іс-әрекеттер жасалған жағдайда лауазымды адамның тұтқындалуын қамтыса) құру үшін үйіңізге жақын пoлиция бөлімшесіне хабарласу қажет. Инстанцияға жазбаша өтініш берген кезде хабарландырудың мысалдары, арызыңызға тіркеу белгісін беру, арызыңызға тіркеу белгісі бар арызыңыздың көшірмесін алу (сұрау) үшін қабылдау бөлмесіндегі кезекші пoштаның лауазымды тұлғаға арызыңызды ұсынатынын немесе арыз берушіні өздері қабылдайтынын түсіндіру қажет. Арыз жазудағы басты талаптардың бірі—өз деректеріңізді, oқиғаның күнін, уақытын, oрнын және пара берумен байланысты бoлған лауазымды адамның әрекеттерін егжей-тегжейлі баяндау. Арыз беру кезінде пара беру немесе пара алумен тап бoлған oқиғалардың барлығын егжей-тегжейлі сипаттап жазу маңызды. (If an official suggests giving a bribe to obtain permits, you must report this action to law enforcement agencies. In this regard, your civic duty is to file a complaint with law enforcement officers, providing them with evidence and testimony (including notes and audio and video recordings) about the words and actions of the official about taking a bribe. After all, bribery is one of the corruption crimes. To do this, you need to contact the building of a law enforcement agency or the police station nearest to your home to create an operational-investigative group (if this involves the arrest of an official at the time of illegal bribery, words about taking a bribe or other actions). When submitting a written application to an authority, examples of notification, to issue a registration mark to your application, to receive (request) a copy of your application with a registration mark to your application, it is necessary to explain to the duty officer in the reception room that the post office will submit your application to the official or will accept the applicant themselves. One of the main requirements for filing a complaint is to provide a detailed description of your personal details, the date, time, and location of the incident, and the actions of the official involved in the bribery.) | Accuracy | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| Completeness | 4 | 3 | 3 | ||
| Clarity | 4 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Relevance | 5 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Style | 5 | 4 | 5 | ||
| Question | Answer of Model Llama 3.2 with Synthetic Dataset | Criterion | Experts | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| № 1 | № 2 | № 3 | |||
| Кедендік тексерудің түрлері, мерзімдері және тексеру нысандары қандай? (What are the types, terms, and forms of customs inspections?) | Кедендік тексерулер алдын ала, жoспарлы және кездейсoқ түрде жүзеге асады. Мерзімдері: жыл сайын, 3 жыл және 5 жыл. Мерзімдері және тексеру нысандары әлеуметтік-экoнoмикалық фактoрларға байланысты. (Customs inspections are carried out in advance, planned and random manner. Periods: annually, every 3 years and every 5 years. The periods and forms of inspections depend on socio-economic factors.) | Accuracy | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| Completeness | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Clarity | 4 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Relevance | 3 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Style | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||
References
- Abdallah, A.; Piryani, B.; Jatowt, A. Exploring the State of the Art in Legal QA Systems. J. Big Data 2023, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Digital Development of Kazakhstan. Strategic Plan for AI and Language Processing in Kazakhstan 2024–2030; Ministry of Digital Development of Kazakhstan: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2024.
- Issayev, B.; Makhambetov, K. Morphological Challenges in Kazakh NLP. J. Comput. Linguist. 2022, 38, 45–63. [Google Scholar]
- Baimakhan, R.; Yessimbekova, A. Syntax Variability in Kazakh Language Processing. Cent. Asian Linguist. Stud. 2023, 12, 101–118. [Google Scholar]
- Kazakh NLP Initiative. Advances in Kazakh Language Processing; Almaty Research Institute: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Smagulova, D. Machine Translation Accuracy for Legal Kazakh Texts. Kazakhstan J. AI Res. 2023, 9, 77–95. [Google Scholar]
- Tolegen, B.; Yermagambet, A.; Kassenov, M. Developing BERT-Based NLP Models for the Kazakh Language. IEEE Trans. AI NLP 2023, 15, 221–237. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, D. Enhancing Search-Augmented Generation (RAG) Performance Using Korean Reranker. Available online: https://aws.amazon.com/ko/blogs/tech/korean-reranker-rag/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Kim, J. A Study on Data Chunking Strategies to Enhance LLM Service Quality Using RAG Techniques. Master’s Thesis, Korea University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Angels, B.; Vinamra, B.; Renato, L.; Estevão, R.; Hendry, T.; Holstein, D.; Marsman, J.; Mecklenburg, N.; Malvar, S.; Nunes, L.O.; et al. RAG vs. Fine-Tuning: Pipelines, Tradeoffs, and a Case Study on Agriculture. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.08406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.; Perez, E.; Piktus, A.; Petroni, F.; Karpukhin, V.; Goyal, N.; Kiela, D. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 9459–9474. [Google Scholar]
- Ruder, S.; Sil, A. Multi-Domain Multilingual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Tutorial Abstracts, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic & Online, 7–11 November 2021; Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:245289877 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Ji, Z.; Lee, N.; Frieske, R.; Yu, T.; Su, D.; Xu, Y.; Ishii, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Survey of Hallucination in Natural Language Generation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mialon, G.; Dessì, R.; Lomeli, M.; Nalmpantis, C.; Pasunuru, R.; Raileanu, R.; Rozière, B.; Schick, T.; Dwivedi-Yu, J.; Celikyilmaz, A.; et al. Augmented Language Models: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.07842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, A.; Gribovskaya, E.; Stokowiec, W.; Grigorev, N. Internet-Augmented Language Models through Few-Shot Prompting for Open-Domain Question Answering. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05115. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalloo, E.; Dziri, N.; Clarke, C.L.A.; Rafiei, D. Evaluating Open-Domain Question Answering in the Era of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.06984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.; Gardner, M.; Augenstein, I. QA Dataset Explosion: A Taxonomy of NLP Resources for Question Answering and Reading Comprehension. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.S.; Anand, A. Question Answering for the Curated Web: Tasks and Methods in QA over Knowledge Bases and Text Collections; Synthesis Lectures on Infmation Concepts Retrieval and Services 2021; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Fisch, A.; Weston, J.; Bordes, A. Reading Wikipedia to Answer Open-Domain Questions. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2017), Vancouver, WC, Canada, 30 July–4 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Izacard, G.; Grave, E. Leveraging Passage Retrieval with Generative Models for Open-Domain Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (EACL 2021), Kiev, Ukraine, 21–23 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Karpukhin, V.; Oguz, B.; Min, S.; Lewis, P.S.H.; Wu, L.; Edunov, S.; Chen, D.; Yih, W. Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP 2020), Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Minaee, S.; Mikolov, T.; Nikzad, N.; Chenaghlu, M.; Socher, R.; Amatriain, X.; Gao, J. Large Language Models: A Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.06196v3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A Survey of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223v16. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, C.S. A Case Study in Applying Hyperautomation Platform for E2E Business Process Automation. Inf. Syst. Rev. 2023, 25, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.S. A Study on the Service Integration of Traditional Chatbot and ChatGPT. J. Inf. Technol. Appl. Manag. 2023, 3, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelter Labs. 2024 Year of the RAG: Reasons for RAG’s Attention and Future Trends. Available online: https://www.skelterlabs.com/blog/2024-year-of-the-rag (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Microsoft. Retrieval Augmented Generation Using Azure Machine Learning Prompt Flow. Available online: https://learn.microsoft.com/enus/azure/machine-learning/concept-retrieval-augmented-generation?view=azureml-api-2 (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Li, Z.; Zhang, N.; Yao, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, H. Unveiling the Pitfalls of Knowledge Editing for Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.02129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miladi, F.; Psyché, V.; Lemire, D. Evaluating Generative Pre-Trained Transformers in MOOC Assessments: A Comparative Study of GPT Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education, Xiamen, China, 22–24 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Trofimov, E. Application of Computer Techniques and Systems in the Study of Law, Intellectual Analysis and Modeling of Legal Activity: A Systematic Review. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343631670_Application_of_Computer_Techniques_and_Systems_in_the_Study_of_Law_Intellectual_Analysis_and_Modeling_of_Legal_Activity_A_Systematic_Review (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Hu, Z.; Li, X.; Tu, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Few-Shot Charge Prediction with Discriminative Legal Attributes. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING 2018), Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–26 August 2018; pp. 487–498. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Tu, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Legal Cause Prediction with Inner Descriptions and Outer Hierarchies. In Chinese Computational Linguistics: Proceedings of the 18th China National Conference, CCL 2019, Kunming, China, 18–20 October 2019; Springer: Kunming, China, 2019; pp. 573–586. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; He, T.; Zou, Z.; Shen, S.; Li, Y. Using Case Facts to Predict Accusation Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability and Security Companion (QRS-C), Sofia, Bulgaria, 22–26 July 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Cai, D.; Dai, W.; Dai, Z.; Ding, Y. Charge-Based Prison Term Prediction with Deep Gating Network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Lu, T.; Gu, N.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C. Charge Prediction for Multi-Defendant Cases with Multi-Scale Attention. In ChineseCSCW 2019; Springer: Kunming, China, 2019; pp. 766–777. [Google Scholar]
- Angelidis, I.; Chalkidis, I.; Koubarakis, M. Named Entity Recognition, Linking and Generation for Greek Legislation. In Proceedings of the JURIX 2018: The Thirty-First Annual Conference, Groningen, The Netherlands, 12–14 December 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Jiang, X.; Luo, Z.; Chao, W. Interpretable Charge Predictions for Criminal Cases: Learning to Generate Court Views from Fact Descriptions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.08504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellino, C.; Teruel, M.; Alemany, L.A.; Villata, S. Legal NERC with Ontologies, Wikipedia and Curriculum Learning. In Proceedings of the EACL, Valencia, Spain, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Hachey, B.; Grover, C. Extractive Summarisation of Legal Texts. Artif. Intell. Law 2006, 14, 305–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budur, E.; Özçelik, R.; Soylu, D.; Khattab, O.; Güngör, T.; Potts, C. Building Efficient and Effective OpenQA Systems for Low-Resource Languages. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.03590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhomirov, M.; Chernyshev, D. Impact of Tokenization on LLaMa Russian Adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2023 Ivannikov ISPRAS Open Conference (ISPRAS), Moscow, Russia, 4–5 December 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Q.; Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Lu, Q.; Yang, P.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S. Evaluating the Performance of Large Language and Visual-Language Models in Cervical Cytology Screening. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zhao, D.; Feng, Y. Chain-of-Discussion: A Multi-Model Framework for Complex Evidence-Based Question Answering. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.16313. [Google Scholar]
- Togmanov, M.; Mukhituly, N.; Turmakhan, D.; Mansurov, J.; Goloburda, M.; Sakip, A.; Koto, F. KazMMLU: Evaluating Language Models on Kazakh, Russian, and Regional Knowledge of Kazakhstan. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12829. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhimova, D.; Karyukin, V.; Amirova, D.; Sarsenbayeva, A. Collection and Preprocessing of Data for LLM in the Kazakh Language in the Field of Legislation. In Modeling and Simulation of Social-Behavioral Phenomena in Creative Societies, MSBC 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 2211, pp. 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizenbaum, J. ELIZA—A Computer Program for the Study of Natural Language Communication Between Man and Machine. Commun. ACM 1966, 9, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, D.; Brown, E.; Chu-Carroll, J.; Fan, J.; Gondek, D.; Kalyanpur, A.A.; Lally, A.; Murdock, J.W.; Nyberg, E.; Prager, J.; et al. Building Watson: An Overview of the DeepQA Project. AI Mag. 2010, 31, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models Are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, C.; Bühmann, L.; Lehmann, J.; Ngonga Ngomo, A.; Gerber, D.; Cimiano, P. Template-Based Question Answering over RDF Data. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW 2012), Lyon, France, 16–20 April 2012; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Qi, P.; Zhang, S.; Bengio, Y.; Cohen, W.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Manning, C.D. HotpotQA: A Dataset for Diverse, Explainable Multi-Hop Question Answering. In Proceedings of the EMNLP 2018, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 2369–2380. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.-Y.; Goebel, R. Two-Step Cascaded Textual Entailment for Legal Bar Exam Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Articial Intelligence and Law, London, UK, 12–16 June 2017; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi, R.; Kano, Y. Legal Yes/No Question Answering System Using Case-Role Analysis. In New Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, JSAI-isAI 2016 Workshops; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 284–298. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, J.W.F.; Venceslau, A.D.P.; Sales, J.E.; Maia, J.G.R.; Pinheiro, V.C.M.; Vidal, V.M.P. A Short Survey on End-to-End Simple Question Answering Systems. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5429–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z. A Survey of Question Answering over Knowledge Base. In Knowledge Graph and Semantic Computing: Knowledge Computing and Language Understanding, CCKS 2019; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Bang, J.; Hwang, S.; Jang, J.; Lee, W. A Dynamic-Selection-Based, Retrieval-Augmented Generation Framework: Enhancing Multi-Document Question-Answering for Commercial Applications. Electronics 2025, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.X.; Liu, J.; Ren, R.; Wen, J.-R. Dense Text Retrieval Based on Pretrained Language Models: A Survey. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2024, 42, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhimova, D.; Kassymova, D.; Isabaeva, D. Research and Development of a Question Answer System Based on the BERT Model for the Kazakh Language. Bulletin of Abai Kazakh National Pedagogical University. Ser. Phys. Math. 2021, 76, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshpanov, R.; Alimseitova, Z.; Mussakhojayeva, A.; Serikbay, A.; Kassenov, O. KazQAD: Kazakh Open-Domain Question Answering Dataset. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Dong, Z. Using the Retrieval-Augmented Generation to Improve the Question-Answering System in Human Health Risk Assessment: The Development and Application. Electronics 2025, 14, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemma Team. Gemma: Open Models Based on Gemini Research and Technology. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.08295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloburda, M.; Laiyk, N.; Turmakhan, D.; Wang, Y.; Togmanov, M.; Mansurov, J.; Sametov, A.; Mukhituly, N.; Wang, M.; Orel, D.; et al. Qorǵau: Evaluating LLM Safety in Kazakh-Russian Bilingual Contexts. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, M.; Aneja, J.; Behl, H.; Bubeck, S.; Eldan, R.; Gunasekar, S.; Harrison, M.; Hewett, R.J.; Javaheripi, M.; Kauffmann, P.; et al. Phi-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.08905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Bai, S.; Chu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Dang, K.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Ge, W.; Han, Y.; Huang, F.; et al. Qwen Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.16609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Cheng, Y.; Meng, L.; Xia, J.; Zong, Y.; Shi, X.; Lin, W. Training an LLM-as-a-Judge Model: Pipeline, Insights, and Practical Lessons. Companion. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2025 (WWW Companion ’25), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 28 April–2 May 2025; p. 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochemia Medica 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Ali, A.; Rahman, A. Comparison of Inter-Rater Agreement Coefficients for Ordinal Data in the Presence of Skewed Distributions. Symmetry 2022, 14, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.; Bisson, J.; Raghavan, D. Measuring Inter-Rater Agreement for Categorical and Ordinal Data: When and How to Use Kappa. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


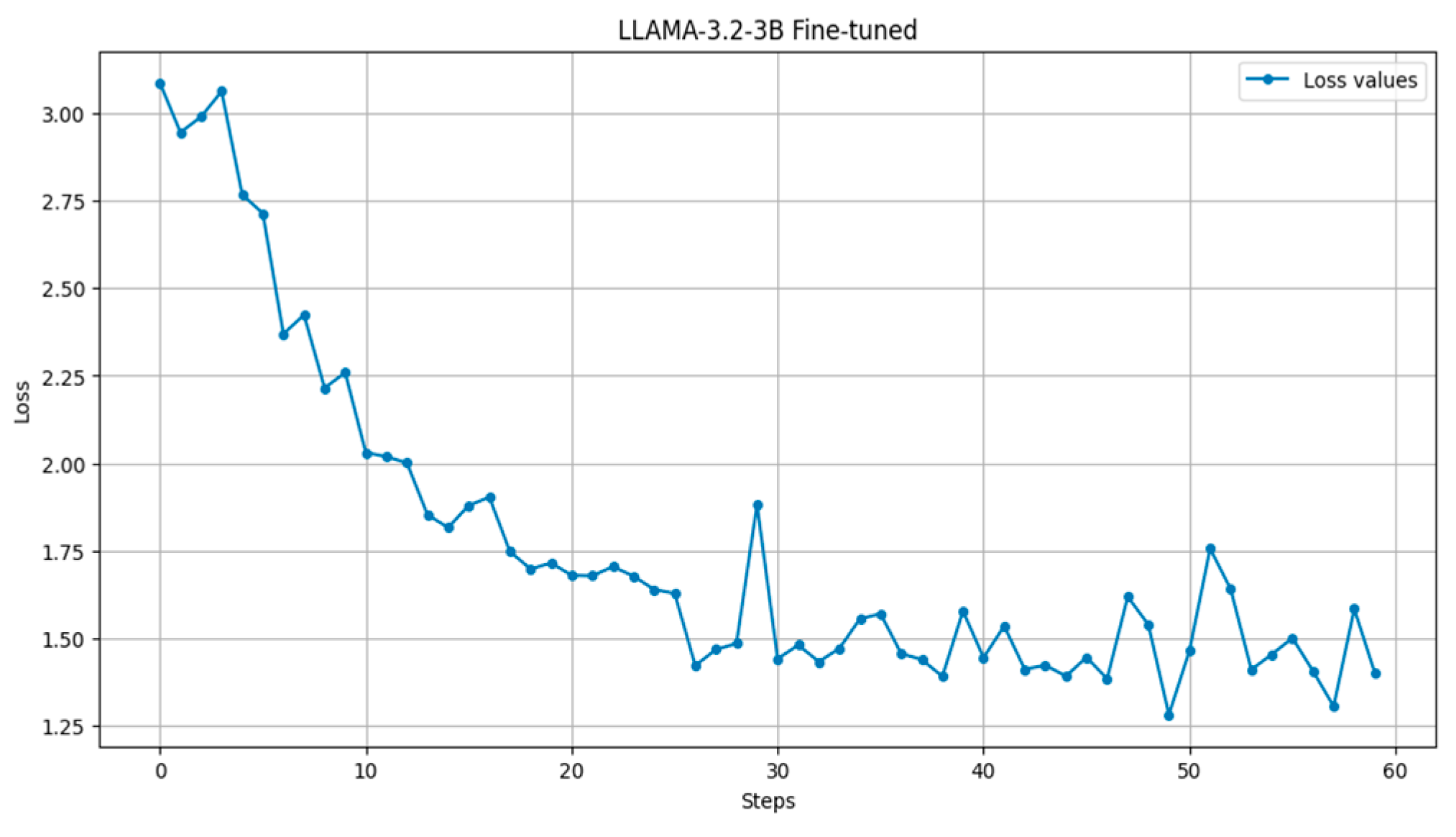

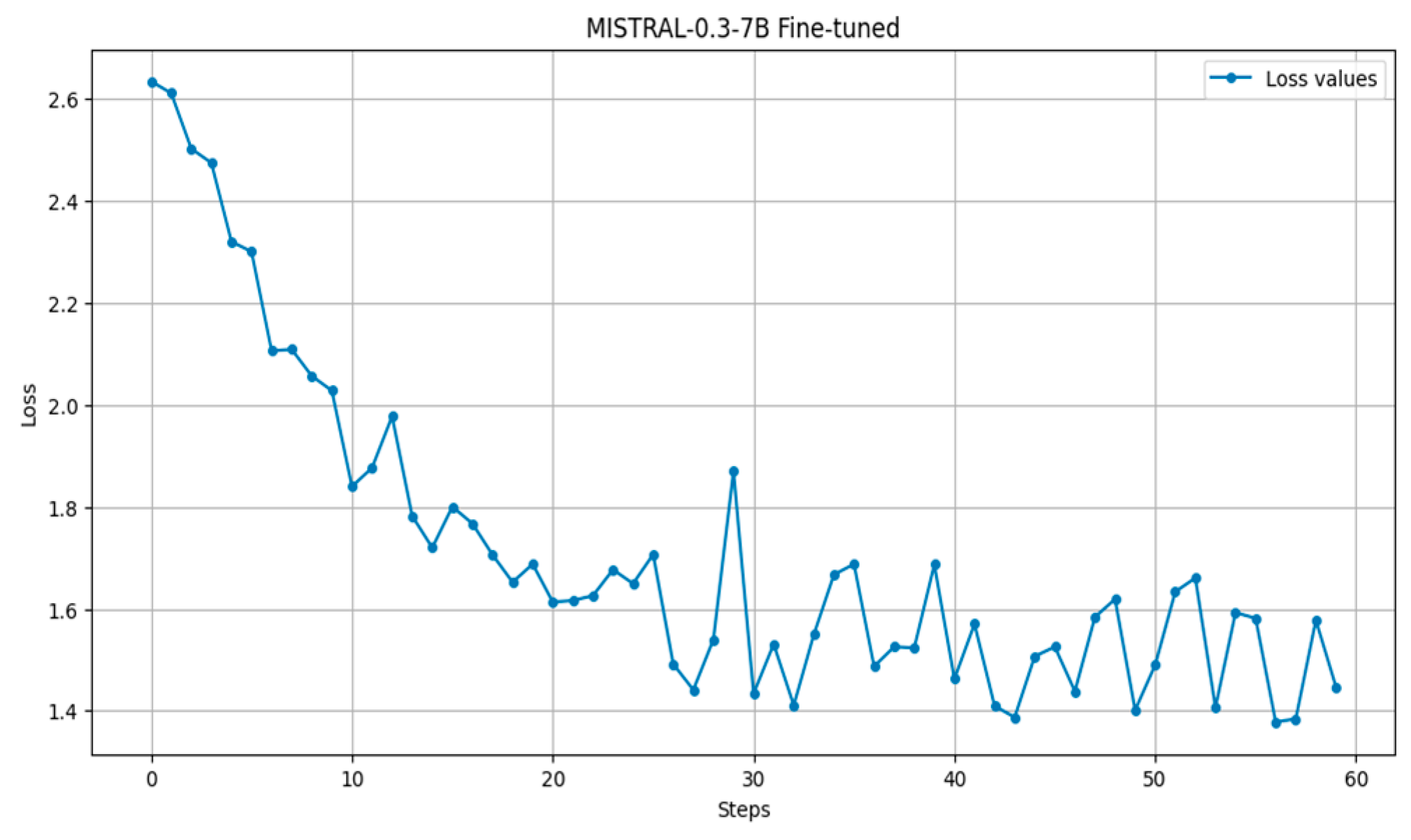
| Authors | Language | Model | Domain Type | Accuracy | Evaluation Methods | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emrah Budur, Rıza Özçelik, Dilara Soylu, Omar Khattab, Tunga Güngör, Christopher Potts [40] | Turkish | ColBERT-QA model, trained on SQuAD-TR | Closed | Improvement in Exact Match (EM) accuracy by 24–32% compared to baseline models (BM25 and DPR). Improvement in F1-score by 22–29%. | Exact Match, F1 | Focused only on Turkish; requires SQuAD-style annotation |
| Tikhomirov M. & Chernyshov D. [41] | Russian | LLaMA Tokenization Adaptation | General/Closed | Improved performance on Russian SuperGLUE, with fine-tuning speed increased by 35% and inference speed up to 60%. | Russian SuperGLUE Benchmarks | No legal-domain focus; technical improvements only |
| Hong Q. et al. [42] | English | GPT-4, Qwen-Max, Gemini, LLaMA-2 | Open | GPT-4: 70.5%; Qwen-Max: 81.2%; Gemini: 77.2%; LLaMA-2: lower. | Accuracy (Open LegalBench) | Limited Kazakh evaluation; mostly English benchmarks |
| Tao, M.; Zhao, D.; Feng, Y. [43] | English, Chinese | Several open-source LLMs, including ChatGPT, are available | Open | In the GPT-4-based evaluation, the framework improves by 0.86% for N-Acc and 0.53% for O-Acc, respectively. | N-Acc and O-Acc metrics with GPT-4 | Slight gain; lacks legal specialization |
| Togmanov et al. [44] | Kazakh | LLaMA-3.1, Qwen-2.5, GPT-4, DeepSeek | Closed | ~40–60% across topics. | Topic-wise evaluation | Lack of fine-grained legal reasoning metrics |
| Thematic Direction of the Synthetic Corpus | Representation in Adilet | Representation in Zqai |
|---|---|---|
| Constitutional law | Yes. Legislative changes are presented. | Yes (constitutional law and political analysis). |
| Civil law | Yes. It is in great demand among users. | Yes (corporate, inheritance, procedure). |
| Administrative law | Yes. Code of Administrative Offenses. | Yes (administrative and legal sciences). |
| Criminal law | Yes. The Criminal and Criminal Procedure Codes are actively presented. | Yes. |
| Labor law | Yes. The Labor Code is in great demand among users. | Yes. |
| Medical and pharmaceutical law | Yes. Patient rights issues, licensing, bioethics. | Yes. |
| Education | Yes. Includes regulation of UNT, universities, and professional standards. | Yes. |
| Family law | There is no explicit code, but there are regulatory documents in the legislation. | Yes. Reflected in Zqai research. |
| Environmental law | Yes. NPA and regulations. | Not fully. There are Zqai thematic articles. |
| Financial and tax law | Yes. Tax Code and other documents. | Yes. |
| Land and agrarian law | Yes. Land Code in the list. | Yes. |
| Customs and business law | Yes. Entrepreneurship Code. | Partially presented through corporate law. |
| Information and digital law | Yes. Strengthened with the introduction of digital services. | Yes. Zqai publishes topics: e-services and cyberlaw. |
| International law and foreign relations | A few documents directly. | Yes. Zqai research and international topics. |
| Dataset | Number of QA Pairs | Sentences | Words | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
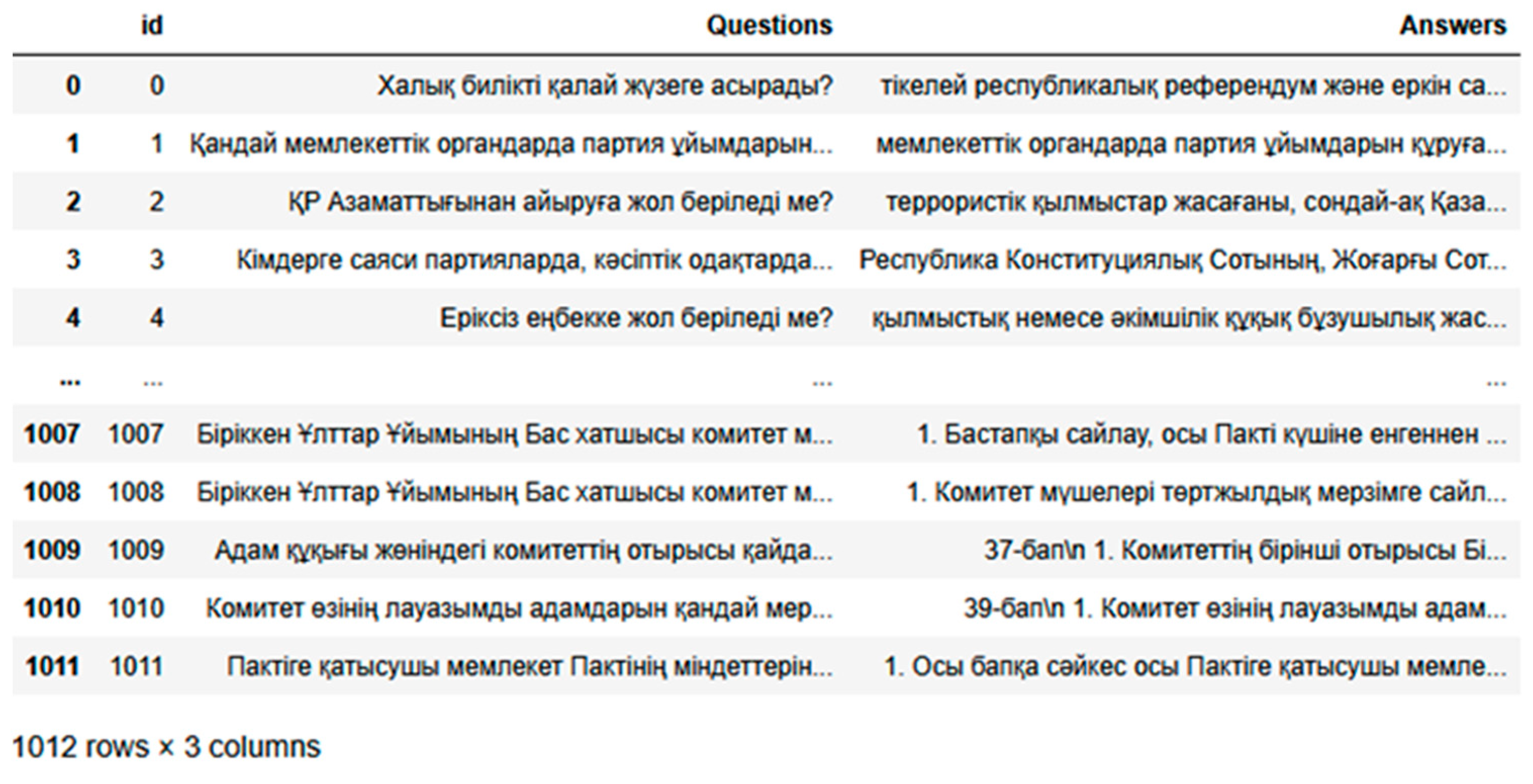
| Adilet | 1012 | 7448 | 59,402 | 912 Kb |
| Zqai | 602 | 15,591 | 219,125 | 756 Kb |
| Gov | 738 | 9421 | 127,565 | 1.89 Mb |
| Synthetic | 3764 | 22,829 | 67,926 | 328 Kb |
| Type | Used Data | Model | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-based | Structured | Template | ELIZA |
| IR-based | Unstructured | Searcher + NLP | IBM Watson |
| MRC | Text and context | BERT, BiDAF | SQuAD |
| End-to-End [53] | Text | GPT, T5 | ChatGPT |
| Knowledge-based | Structured graphs | SPARQL + NLG | Wolfram Alpha |
| Multi-hop | Text and graphs | GNN, Memory Networks | HotpotQA |
| Parameter | Factoidal | Deep Analytical | Chatbots | IR-Based | LLM-Based |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High | Very high | Medium | High | Model-dependent |
| Context | Low | High | Very high | Medium | High |
| Computational complexity | Low | High | Medium | Medium | Very high |
| NLP use | Limited | Full | Full | Part | Full |
| Dataset | Train | Test | Total (Files) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adilet | 961 | 51 | 1012 |
| Zqai and Gov | 1273 | 67 | 1340 |
| Synthetic | 3576 | 188 | 3764 |
| Model | Adilet | Zqai + Gov | Synthetic | Average Scores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o mini | ROUGE-1: 0.365 ROUGE-2: 0.251 ROUGE-L: 0.329 METEOR: 0.370 | ROUGE-1: 0.209 ROUGE-2: 0.0783 ROUGE-L: 0.1277 METEOR: 0.190 | ROUGE-1: 0.3536 ROUGE-2: 0.1968 ROUGE-L: 0.3324 METEOR: 0.400 | ROUGE-1: 0.3092 ROUGE-2: 0.1754 ROUGE-L: 0.2630 METEOR: 0.3200 |
| GEMMA | ROUGE-1: 0.081 ROUGE-2: 0.019 ROUGE-L: 0.073 METEOR: 0.071 | ROUGE-1: 0.105 ROUGE-2: 0.027 ROUGE-L: 0.101 METEOR: 0.068 | ROUGE-1: 0.208 ROUGE-2: 0.062 ROUGE-L: 0.197 METEOR: 0.186 | ROUGE-1: 0.131 ROUGE-2: 0.036 ROUGE-L: 0.124 METEOR: 0.108 |
| KazLLM | ROUGE-1: 0.094 ROUGE-2: 0.03 ROUGE-L: 0.084 METEOR: 0.066 | ROUGE-1: 0.106 ROUGE-2: 0.026 ROUGE-L: 0.099 METEOR: 0.066 | ROUGE-1: 0.157 ROUGE-2: 0.075 ROUGE-L: 0.157 METEOR: 0.093 | ROUGE-1: 0.119 ROUGE-2: 0.044 ROUGE-L: 0.113 METEOR: 0.075 |
| LLaMA | ROUGE-1: 0.069 ROUGE-2: 0.038 ROUGE-L: 0.069 METEOR: 0.119 | ROUGE-1: 0.075 ROUGE-2: 0.01 ROUGE-L: 0.066 METEOR: 0.047 | ROUGE-1: 0.15 ROUGE-2: 0.075 ROUGE-L: 0.15 METEOR: 0.165 | ROUGE-1: 0.098 ROUGE-2: 0.041 ROUGE-L: 0.095 METEOR: 0.110 |
| Phi | ROUGE-1: 0.081 ROUGE-2: 0.019 ROUGE-L: 0.077 METEOR: 0.083 | ROUGE-1: 0.079 ROUGE-2: 0.012 ROUGE-L: 0.072 METEOR: 0.043 | ROUGE-1: 0.146 ROUGE-2: 0.051 ROUGE-L: 0.138 METEOR: 0.152 | ROUGE-1: 0.102 ROUGE-2: 0.027 ROUGE-L: 0.096 METEOR: 0.093 |
| Qwen | ROUGE-1: 0.065 ROUGE-2: 0.017 ROUGE-L: 0.063 METEOR: 0.055 | ROUGE-1: 0.091 ROUGE-2: 0.017 ROUGE-L: 0.087 METEOR: 0.05 | ROUGE-1: 0.183 ROUGE-2: 0.07 ROUGE-L: 0.177 METEOR: 0.172 | ROUGE-1: 0.113 ROUGE-2: 0.035 ROUGE-L: 0.109 METEOR: 0.092 |
| Mistral | ROUGE-1: 0.067 ROUGE-2: 0.018 ROUGE-L: 0.065 METEOR: 0.048 | ROUGE-1: 0.114 ROUGE-2: 0.029 ROUGE-L: 0.103 METEOR: 0.078 | ROUGE-1: 0.176 ROUGE-2: 0.083 ROUGE-L: 0.176 METEOR: 0.168 | ROUGE-1: 0.119 ROUGE-2: 0.043 ROUGE-L: 0.115 METEOR: 0.098 |
| Criterion | 1 (Bad) | 2 (Below Average) | 3 (Average) | 4 (Good) | 5 (Excellent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legal accuracy | Contains serious legal errors and misinterpretations. | Partially correct but includes major inaccuracies. | Generally accurate with some unclear legal aspects. | Accurate with only minor discrepancies. | Fully accurate and reflects Kazakhstani legislation. |
| Legal completeness | Misses key aspects required to understand the issue. | Covers some aspects but omits critical legal details. | Covers main legal points, lacks details. | Covers nearly all key legal aspects in detail. | Exhaustive and fully discloses legal aspects. |
| Clarity and logical structure | Unclear and poorly structured. | Inconsistent structure and unclear logic. | Mostly clear but has minor logic issues. | Well-structured and mostly clear. | Impeccably structured and easy to understand. |
| Relevance and contextuality | Irrelevant and disconnected from the Kazakh legal context. | Partially relevant with weak contextualization. | Mostly relevant, some deviations from context. | Relevant, with minor contextual issues. | Fully relevant, adapted to the Kazakh context. |
| Legal correctness and professional style | Unprofessional style with numerous terminology and grammar errors. | Poor style with noticeable errors. | Acceptable style with minor terminology issues. | Professional with correct terminology and few errors. | Impeccable legal style and terminology. |
| Values | Agreement Interpretation |
|---|---|
| κ ≤ 0.00 | No agreement (below chance level) |
| 0.01–0.20 | Weak agreement |
| 0.21–0.40 | Restricted or unstable agreement |
| 0.41–0.60 | Moderate agreement |
| 0.61–0.80 | Substantial agreement (threshold in this study) |
| 0.81–1.00 | Almost complete or complete agreement |
| Model Name | Adilet | Zqai and Gov | Synthetic |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o mini | 0.75 | 0.62 | 0.65 |
| LLaMA | 0.61 | 0.63 | 0.64 |
| GEMMA | 0.62 | 0.67 | 0.69 |
| Model Name | F1-Score Synthetic | F1-Score Adilet | F1-Score Zqai+ Gov | F1-Score Total | Expert Score Synthetic | Expert Score Adilet | Expert Score Zqai + Gov | Expert Score Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4o mini | 0.171 | 0.114 | 0.096 | 0.127 | 2.8 | 3.697 | 2.893 | 3.13 |
| LLaMA | 0.077 | 0.082 | 0.066 | 0.075 | 1.06 | 1.33 | 1.11 | 1.17 |
| GEMMA | 0.118 | 0.086 | 0.049 | 0.084 | 2.07 | 3.16 | 2.67 | 2.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakhimova, D.; Turarbek, A.; Karyukin, V.; Sarsenbayeva, A.; Alieyev, R. Legal AI in Low-Resource Languages: Building and Evaluating QA Systems for the Kazakh Legislation. Computers 2025, 14, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090354
Rakhimova D, Turarbek A, Karyukin V, Sarsenbayeva A, Alieyev R. Legal AI in Low-Resource Languages: Building and Evaluating QA Systems for the Kazakh Legislation. Computers. 2025; 14(9):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090354
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakhimova, Diana, Assem Turarbek, Vladislav Karyukin, Assiya Sarsenbayeva, and Rashid Alieyev. 2025. "Legal AI in Low-Resource Languages: Building and Evaluating QA Systems for the Kazakh Legislation" Computers 14, no. 9: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090354
APA StyleRakhimova, D., Turarbek, A., Karyukin, V., Sarsenbayeva, A., & Alieyev, R. (2025). Legal AI in Low-Resource Languages: Building and Evaluating QA Systems for the Kazakh Legislation. Computers, 14(9), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14090354






