Abstract
Cyberhate presents a multifaceted, context-sensitive challenge that existing detection methods often struggle to tackle effectively. Large language models (LLMs) exhibit considerable potential for improving cyberhate detection due to their advanced contextual understanding. However, detection alone is insufficient; it is crucial for software to also promote healthier user behaviors and empower individuals to actively confront the spread of cyberhate. This study investigates whether integrating large language models (LLMs) with persuasive technology (PT) can effectively detect cyberhate and encourage prosocial user behavior in digital spaces. Through an empirical study, we examine users’ perceptions of a self-monitoring persuasive strategy designed to reduce cyberhate. Specifically, the study introduces the Comment Analysis Feature to limit cyberhate spread, utilizing a prompt-based fine-tuning approach combined with LLMs. By framing users’ comments within the relevant context of cyberhate, the feature classifies input as either cyberhate or non-cyberhate and generates context-aware alternative statements when necessary to encourage more positive communication. A case study evaluated its real-world performance, examining user comments, detection accuracy, and the impact of alternative statements on user engagement and perception. The findings indicate that while most of the users (83%) found the suggestions clear and helpful, some resisted them, either because they felt the changes were irrelevant or misaligned with their intended expression (15%) or because they perceived them as a form of censorship (36%). However, a substantial number of users (40%) believed the interventions enhanced their language and overall commenting tone, with 68% suggesting they could have a positive long-term impact on reducing cyberhate. These insights highlight the potential of combining LLMs and PT to promote healthier online discourse while underscoring the need to address user concerns regarding relevance, intent, and freedom of expression.
1. Introduction
Social media platforms like Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), and WhatsApp are among the most popular venues for content creation and sharing. They provide users with a fast and efficient means to disseminate information, making them valuable sources of information [1,2]. However, these same platforms can also be exploited to spread harmful content, including cyberhate, misinformation, and cyberbullying. Such negative content not only degrades the quality of interactions but can also lead to adverse experiences for users and, in some cases, even spark criminal activities or violence [3,4].
Cyberhate—often referred to as online hate speech—encompasses expressions of hostility or incitements to hatred directed toward individuals or groups based on characteristics like ethnicity, religion, nationality, or sexual orientation [5,6,7]. Although there isn’t a universally accepted definition or legal framework for cyberhate, its rapid proliferation across social media has attracted significant attention from researchers, technology companies, and programmers over the last decade as they seek solutions.
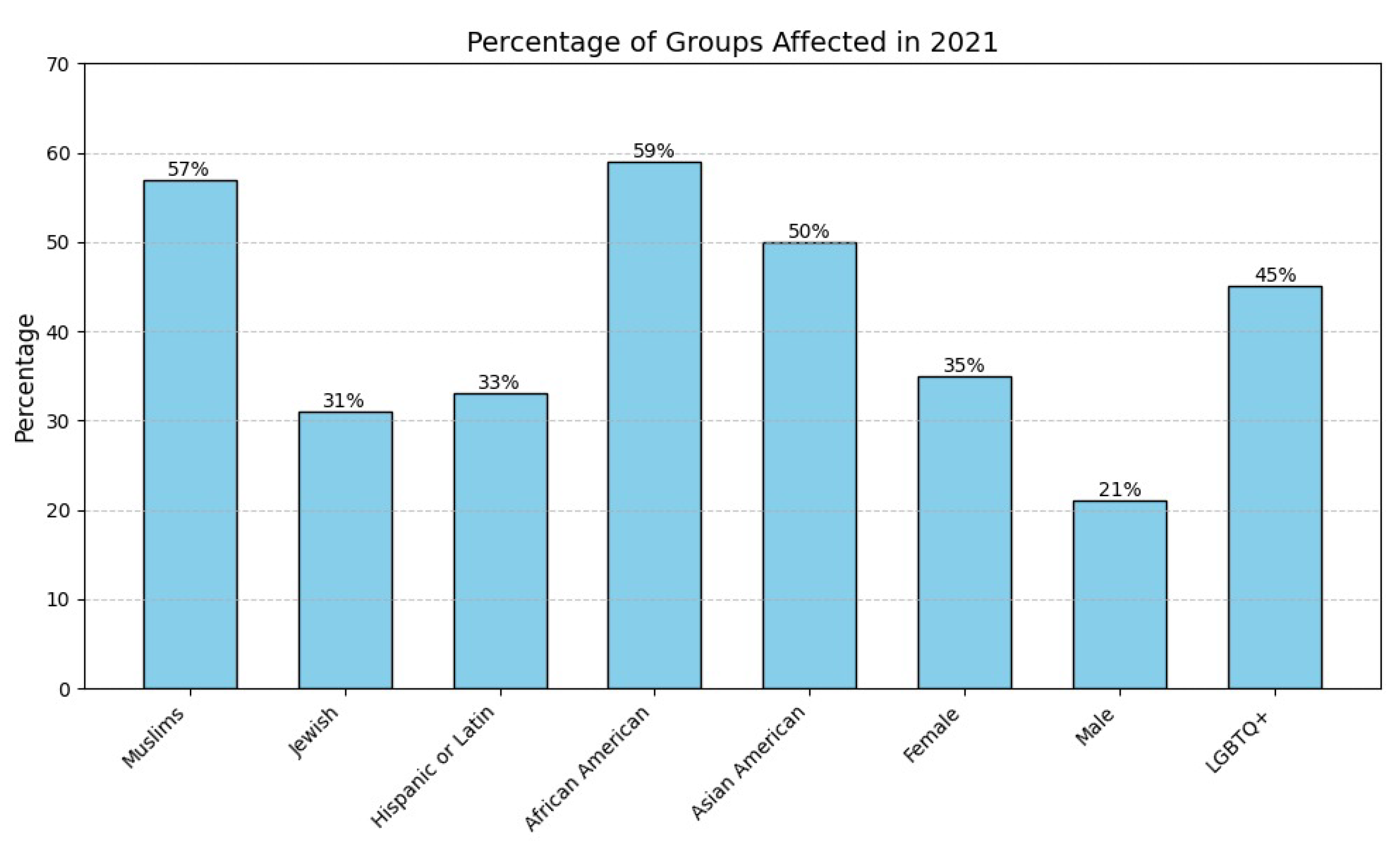
A recent Anti-Defamation League (ADL) report noted that 41% of Americans have encountered cyberhate or harassment [8,9]. Figure 1 displays the distribution of reported incidents based on individuals’ self-identified characteristics. Similarly, the European Union Kids Online Survey (2017–2019) documented an increase in cyberbullying and cyberhate [10,11]. In response, initiatives like the EU’s 2016 Code of Conduct mobilized companies such as Facebook, YouTube, and Microsoft to curb illegal cyberhate [12]. National laws with criminal penalties have also emerged to address this issue, yet cyberhate persists [13], often masked by coded language or seemingly innocuous phrases that evade traditional detection methods.
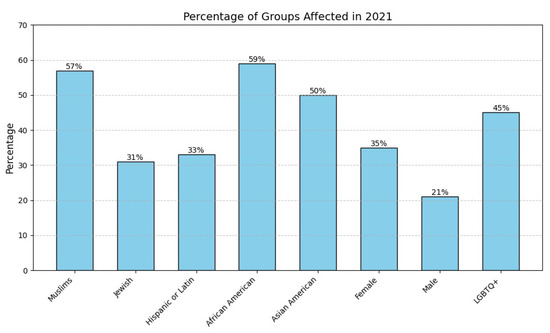
Figure 1.
Reported cyberhate and harassment instances based on respondents’ identities [8].
Recent advances in machine learning have produced models to identify cyberhate [14,15,16,17], but their real-world utility remains limited. Many perform well on specific datasets but falter when applied to new contexts [18,19,20], highlighting a critical need for generalizable solutions. Additional research has explored the dynamics and diffusion of cyberhate across social media [21], though relatively few studies have proposed methods to prevent its spread [12]. Other investigations have examined how users perceive and propagate cyberhate, along with their attitudes and behaviors related to the issue [22,23]. Notably, there is a gap in studies that aim to promote healthier online behavior as a means to counter the spread of cyberhate [24].
Fortunately, software can be a powerful tool for encouraging behavioral change among users, effectively motivating bystanders to actively counter cyberhate. Research indicates that bystanders play a critical role, as their inaction when witnessing cyberhate incidents can be perceived normalizing hostility [25,26]. Thus, fostering bystander intervention is vital for mitigating the negative impacts on targeted groups [27], particularly through visible counter-arguments in public comments [28,29,30].
To promote bystander action against cyberhate, it is essential to design social media platforms that effectively encourage their interventions. Information systems can be purposefully crafted to drive behavioral change and are commonly known as persuasive systems or persuasive technology (PT) [31,32,33]. PT refers to digital systems intentionally designed to influence user attitudes or behaviors in a non-coercive way. The success of PT in fields such as health, education, and wellness [34,35,36,37,38,39]—along with evidence that incorporating persuasive strategies increases engagement and behavior change [40,41]—suggests that similar techniques can be applied to motivate users to speak out against cyberhate, thereby lessening its prevalence and negative impact.
The recent emergence of large language models (LLMs), defined as AI systems trained on extensive text data to perform tasks like text classification and content moderation such as GPT-3 and Gemini, has also marked a significant advancement in Natural Language Processing (NLP) [42]. These models have proven highly effective in a range of NLP tasks, from text classification to sentiment analysis, due in part to their training on vast amounts of data, which enables them to acquire an extensive understanding of human language [43,44,45]. Furthermore, interest in using LLMs for cyberhate detection is growing. For example, one study found that GPT-3 could identify sexist and racist language with an accuracy of around 85% using few-shot learning [46]. Although that study was limited by its narrow focus and small dataset, further investigations, such as Li et al.’s evaluation of ChatGPT’s ability to classify harmful content, have shown comparable results to expert human annotations [47]. Another study by He et al. demonstrated that LLMs and prompt-based learning could slightly outperform existing baselines in detecting toxic content [48].
To extend these efforts, the authors investigate the feasibility of combining the strengths of LLMs and Persuasive Technology to motivate users to take a prosocial role in addressing and limiting the spread of cyberhate. The study introduces the Comment Analysis Feature, which uses a prompt-based fine-tuning approach to classify user comments as cyberhate or non-cyberhate and generates context-aware alternative statements to encourage positive communication. A case study evaluated the feature’s real-world performance, exploring users’ perceptions of this self-monitoring strategy, assessing detection accuracy, and measuring the impact of alternative statements on user engagement and perceptions. The findings of this study are meant to guide software engineers in designing persuasive social media platforms that are cyberhate aware. The study’s primary contribution lies in its dual focus: leveraging LLMs’ contextual precision for cyberhate detection while employing a persuasive design to nudge behavioral change. This approach addresses a critical gap in existing research, which often prioritizes detection over prevention.
2. Related Work
Toxic content (e.g., cyberhate) is rapidly spreading on the internet in various forms such as racism on social media [49,50], bullying in online gaming, replies to posts on social media platforms [51,52], trolling [53], threats of violence, sexual harassment, and more [54]. These attacks constitute a subset of abusive behavior rooted in hate and harassment—part of a broader category of threats involving attempts to cause emotional harm to a target, such as stalking, doxxing, sextortion, and intimate partner violence [55].
The issue of combating cyberhate has garnered significant attention from researchers across various fields, including natural language processing (NLP), machine learning [56], psychology, and human-computer interaction. Traditional approaches to managing cyberhate primarily focused on rule-based systems and keyword filters, which are often rigid and prone to high false positive and negative rates due to the complexity and evolving nature of cyberhate. Additionally, recent advancements in NLP, particularly the development of large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and BERT, have significantly improved the ability to detect cyberhate with higher accuracy. LLMs are capable of understanding context, sarcasm, and nuanced language, which are critical in identifying subtle forms of cyberhate [57].
In addition, Zhou et al. [18] proposed a deep learning fusion approach combining CNNs and LSTMs to enhance context understanding for cyberhate detection. Furthermore, Swamy et al. [19] examined the challenge of generalizability across datasets, highlighting the issue of domain adaptation in cyberhate detection models. Caselli et al. [58] emphasized the mitigation of bias in training data and its impact on model fairness. Moreover, multilingual and cross-platform detection has gained traction, with Liu et al. [59] demonstrating how transformer-based models can adapt to varying linguistic contexts. These contributions collectively underscore the importance of building flexible, context-aware cyberhate detection models.
Almaliki et al. [9] introduce the Arabic BERT-Mini Model (ABMM) for the detection of cyberhate on social media. This study employs the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model to analyze Twitter data, classifying the content into three categories: normal, abuse, and cyberhate.To evaluate the effectiveness of the model, a series of experiments were conducted.
Liu et al. [59] demonstrated the effectiveness of LLMs in identifying cyberhate across various social media platforms, highlighting their ability to generalize across different contexts and languages. However, despite these advances, LLMs can still struggle with ambiguous or context-dependent content, where human interpretation plays a crucial role.
Elmezain et al. [11] propose a hybrid model that combines transformer architectures with SVM to classify images in a cyberbullying dataset. Initially, seven different CNN architectures are evaluated to identify the most effective ones. Feature extraction is then performed using the top four models—ResNet50, EfficientNetB0, MobileNet, and Xception. Then, the concatenated features are optimized and fed into the SVM classifier for the final classification.
Almars et al. [1] introduce a Hybrid Attention Neural Network (HANN) for rumor detection on social media. HANN is designed to capture the most relevant and distinguishing features across different classes while also offering interpretability of the model’s decisions. The proposed framework integrates two deep learning components: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) networks, both enhanced with attention mechanisms.
Studies like those conducted by Caselli et al. [58] have pointed out the biases inherent in training data, which can lead to biased outcomes in cyberhate detection. These models can sometimes reinforce stereotypes or overlook hate speech directed at minority groups. Furthermore, LLMs may be manipulated through adversarial attacks, where subtle changes in input can lead to incorrect classifications. These limitations indicate the need for supplementary approaches to enhance the robustness and fairness of cyberhate detection systems.
Persuasive technology, which involves the design of digital tools and interventions aimed at changing attitudes or behaviors, has been explored as a means to promote positive online interactions [60]. Oinas et al. [61] foundational work on the principles of persuasive technology has been widely applied in health, education, and environmental domains, demonstrating its potential to influence user behavior effectively. In the context of cyberhate, persuasive technology has been utilized to encourage empathy, reduce aggressive behavior, and promote respectful communication. For example, interventions like the “ReThink” software developed by Jain (2021) have shown success in reducing cyberbullying by prompting users to reconsider their messages before posting them [62,63,64].
Despite these advancements, several gaps remain in the current body of research. Most existing studies have focused on either detection (LLMs) or prevention (persuasive technology) of cyberhate [65], with few exploring the integration of both approaches. Additionally, Many models perform well on benchmark datasets but struggle to generalize across contexts, languages, or platforms, and often lack transparency in how decisions are made. In addition, these systems typically operate in isolation from the end user, limiting their potential to promote awareness or behavior change. Furthermore, there is a need for more research on the ethical implications of using AI and persuasive technology in this domain, particularly concerning user privacy, consent, and the potential for manipulation. Future work should also explore the development of standardized frameworks and metrics for evaluating the effectiveness of combined LLM and persuasive technology interventions, ensuring they are both scalable and adaptable to various online environments.
In contrast, our approach integrates real-time, context-aware suggestions with a self-monitoring strategy, combining detection and intervention within a single interface. This dual focus—classification and persuasion—aims to not only flag cyberhate content but also support users in adopting more prosocial communication practices, addressing a critical gap in the current literature.
3. Methodology
This paper presents an empirical investigation into the potential integration of persuasive technology and LLMs capabilities within the design process of social media platforms, with the goal of motivating users to actively combat the propagation of cyberhate. Particularly, the integration of a self-monitoring strategy in the form of a Comment analysis feature that employs LLMs to analyze and visually represent to users how their generated textual content (such as posts, replies, etc.) might be interpreted by others. As users draft their comments and right before they post them, LLM-based comment analyzer will analyze their input based on their choice of words, writing style, and punctuation, differentiating between tones such as hateful and natural, and subsequently generating appropriate recommendations. Users will then have the option to accept or reject these suggestions.
Self-monitoring is an effective persuasive technique [66], as it enables individuals to develop a clearer insight into their behavioral tendencies [67] and supports self-regulation [68]. In this context, the implementation of a comment analysis feature can play a valuable role by helping bystanders to improve their self-awareness regarding the tone and impression of their online comments to challenge cyberhate. To evaluate the effectiveness of this integration, a case study methodology was selected [69]. Case studies are often more appropriate than controlled experiments when assessing the broader implications of a tool or method. While they may not match the scientific rigor of formal experiments, case studies offer practical insights to determine whether a particular approach could be advantageous for an organization or project. Consequently, they are widely regarded as a fitting research strategy in software engineering contexts [70].
In the following sections, we will provide an overview of how the Comment Analysis Feature processes user comments, identifies instances of cyberhate, and generates appropriate responses. After that, we will discuss the case study design, development, and evaluation.
3.1. Comment Analysis Feature
This study introduces a feature capable of analyzing user input to detect instances of cyberhate, with the goal of motivating users to combat cyberhate by enhancing their self-awareness regarding the tone and impression of their online comments. Prompt engineering is consider essential factor for effectively guiding LLMs to deliver relevant, coherent, and high-quality responses [71]. In this context, a prompt refers to a natural language text that is provided to a language model (LLM) to generate specific output [72,73]. In related work, prompt-based techniques have been categorized into four main types: [71,74,75,76]: (1) Zero-shot prompts, where the LLM generates a response without being given any additional examples or information provided; (2) One-shot prompts, which provide the model with a single example to guide its response; (3) Few-shot prompts, where several examples are provided to help the model understand the expected pattern and generate similar types of responses; and (4) Template-based prompts, which use structured and consistent formats to deliver clear instructions and relevant context to the model.
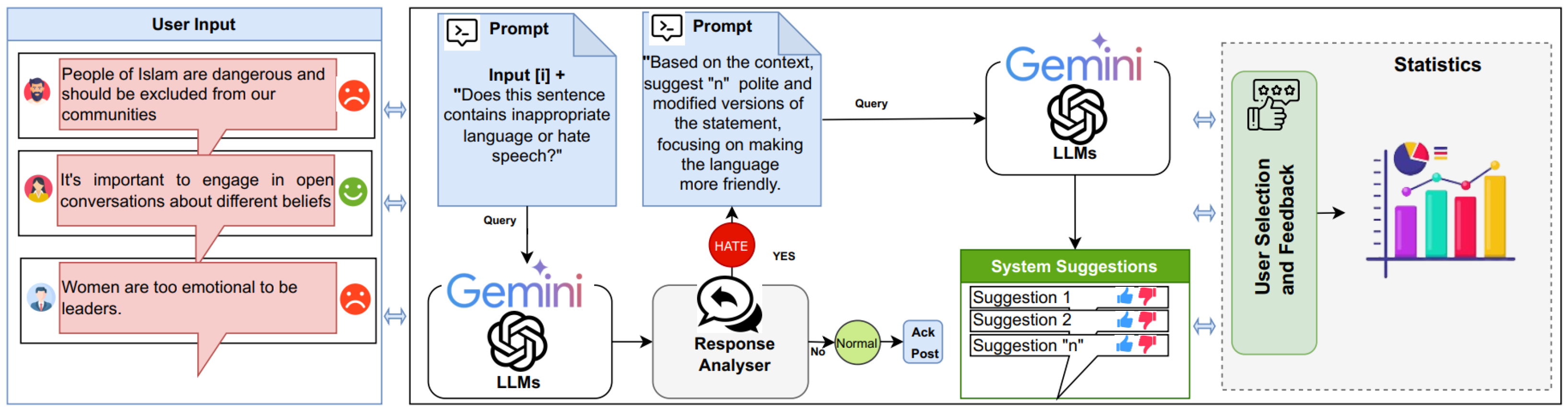
In this study, our proposed method utilizes a template-based prompts approach combined with large language model techniques to tailor the model for the specific task of cyberhate detection and recommendation. The prompt utilized in our feature was carefully crafted to frame the query within the relevant context of cyberhate, ensuring that the LLM could accurately process and classify the input based on this specific template and suggest several alternatives for hate speech. Additionally, prompts were iteratively tested and evaluated based on the quality of the model’s responses. Feedback from two experts was used to refine the prompt by adjusting its wording, structure, and level of detail. An overview of our proposed feature is illustrated in Figure 2. The gemini-1.5-pro-latest version is employed to generate responses using structured prompt templates (https://gemini.google.com/ (accessed on 20 November 2024)). Each prompt was sent to the model with the following parameter settings:
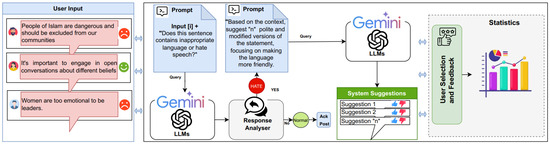
Figure 2.
Overview of the Proposed Model for the comment analysis feature.
- Max_output_tokens: This parameter controls the number of tokens (i.e., the length) generated by the model. We set it to maximum 100 tokens (words) to ensure concise responses, making it ideal for recommendations while avoiding long or irrelevant content.
- Temperature: This parameter defines the level of creativity and randomness in token selection. In this study, the temperature is set to 0.7, providing a balanced trade-off between logical coherence and creativity.
- Top_P and Top_K: These parameters determine how the model selects tokens during response generation. The Top_P parameter is set to 0.95, which means the model samples from the top 95% of the probability distribution. While, the Top_K parameter is set to 40, restricting selection to the top 40 most probable tokens within the Top_P range.
To effectively combat hate speech online, two prompt templates were implemented to identify hate speech behavior. The first prompt is designed to classify user comments as either hate speech or non-hate speech. Additionally, a second prompt template was integrated to assist the LLM suggest alternative statements for cyberhate, tailored to the context of the user’s original input. The process begins by analyzing user comments to determine whether they contain hateful language. Given a user input (comment) i, a predefined prompt (template) : “Does this sentence contain inappropriate language or hate speech?”, and another predefined prompt (template) : “Based on the context, suggest n polite and modified versions of the statement, focusing on making the language more friendly”. The objective is to classify a user input (comment) i into one of two predefined classes: , and subsequently generate a list of n recommendations tailored to i if the comment contains aggressive or hate speech.
To achieve this, the feature follows these steps to identify cyberhate:
- 1.
- Input Analysis: The feature first receives user input i
- 2.
- Hate Speech Classification: The feature then evaluates user input i by concatenating it with the prompt :where LLM is a function that processes prompt template and user input i, returning a response , which indicates whether i contains inappropriate language or cyberhate (hateful) or normal (not hateful). The configuration parameters here govern the model’s response generation behavior.
- 3.
- Contextual Recommendation: According to the output of :
- If : The feature generates n alternative sentences (suggestions) using template for user offensive input i:where , and each is an alternative suggestions for i. These suggestions aim to preserve the meaning while removing offensive or harmful words from user input.
- If : The feature acknowledges and posts the conversation:
Output Generation: Finally, the feature identifies the classification output and generates a list of suggested alternatives, if applicable.
3.2. Study Design
The aim of conducting this case study is to assess the impact of integrating a self-monitoring persuasive strategy and LLMs capability within the design process of social media platforms, with the goal of enhancing users’ behavior to limit the spread of cyberhate. To reach this aim, the authors developed an interactive news website that employs a self-monitoring strategy in the form of a real-time textual analysis and feedback using a comment analysis feature. The comment analysis feature is powered by Google Gemini AI model that analyzes user-generated textual comments and replies and then provides real-time feedback and suggestions to the users on the tone and potential impact of their comments to motivate them to reconsider their language choices, adopt more acceptable language to limit cyberhate spread. Users will then have the option to accept or reject these suggestions. An interactive news website was adopted to avoid platform-specific variables such as algorithms or user networks that are present on social media platforms (e.g., Facebook, X, etc.). This ensured ethical data collection but limits real-world replication (see Section 6). The design, development, and evaluation of the interactive news website are detailed in the following subsection:
3.2.1. News Website Development
The core elements of the website are as follows:
- Website Content:The website included news articles collected from trusted news sources, covering a wide range of tones and topics, from neutral subjects to more controversial and emotionally charged topics. The participants can post comments, reply to others, and engage in discussions related to news articles. Figure 3 shows the home page of the news website.
 Figure 3. News Website Homepage.
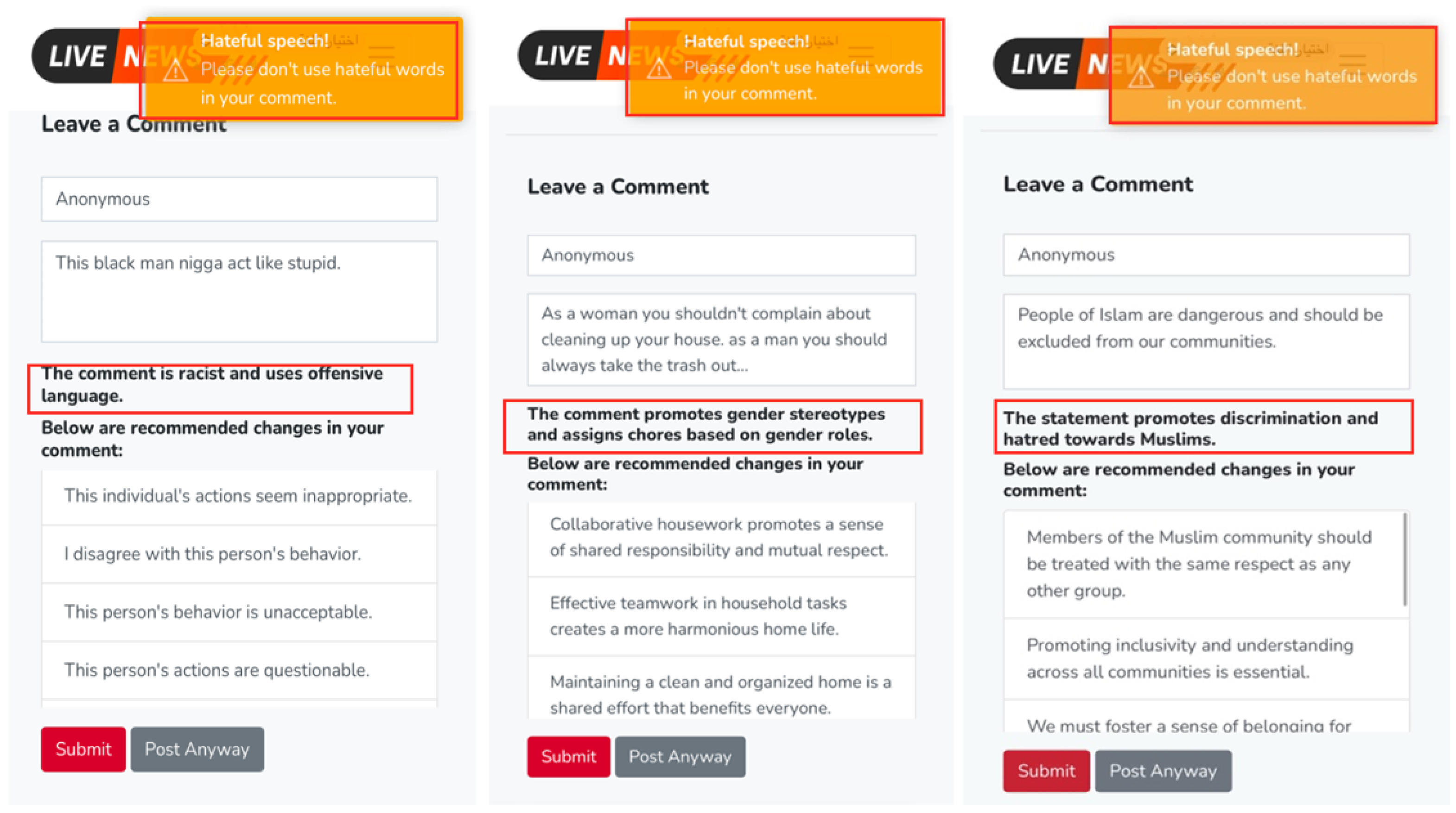
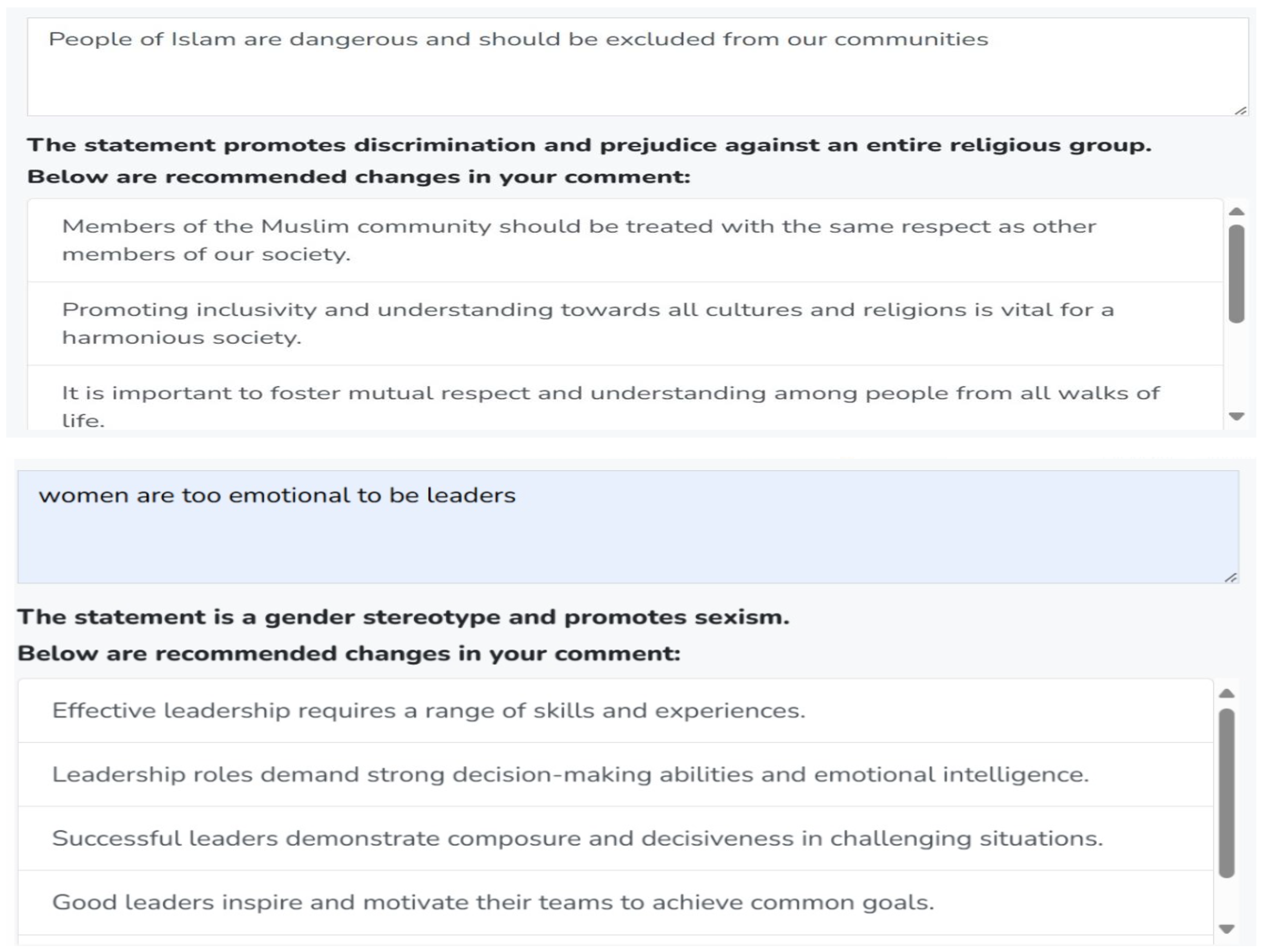
Figure 3. News Website Homepage. - LLM-Based Comment Analysis Feature:The website employs a comment analysis feature powered by Google Gemini AI model to analyze the participants’ comments before they post them to detect any cyberhate instances. Figure 4 presents examples of how LLM-Based Comment Analyzer detects and categorizes different types of hateful content in user comments.
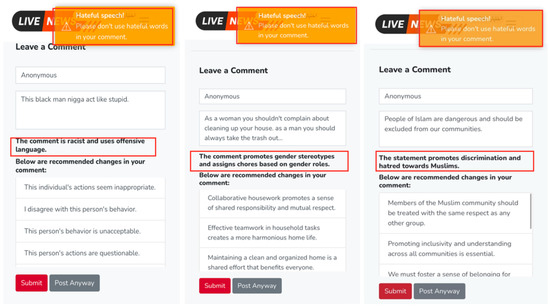 Figure 4. Examples of LLM-Based detection of different types of cyberhate.
Figure 4. Examples of LLM-Based detection of different types of cyberhate. - LLM-Based Feedback Feature:As shown in Figure 4, the comment analyzer not only identifies hateful instances in user comments but also suggests alternative, non-hateful revisions. If a comment includes hateful or aggressive input, the comment analyzer will provide the participants with suggestions of a none-hateful and more friendly form of their comments. It will offer textual recommendations to help the participants modify their input to sound more positive. For example, if a comment is detected as potentially harmful, the comment analyzer can suggest a rephrasing to make it less hateful and less aggressive. The participants will then have the option to accept or reject these suggestions. Figure 5 shows examples of some LLM-based suggestions to help the participants modify their comments.
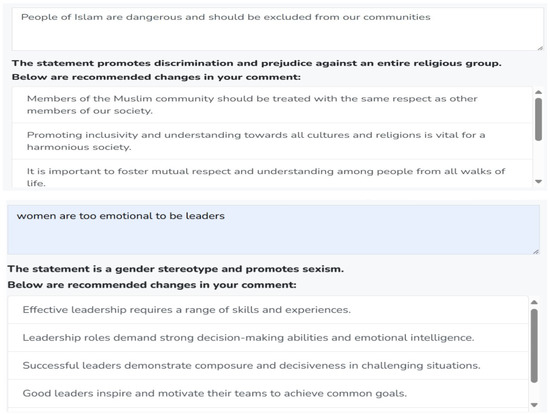 Figure 5. Examples of LLM-Based suggestions on different types of user comments.
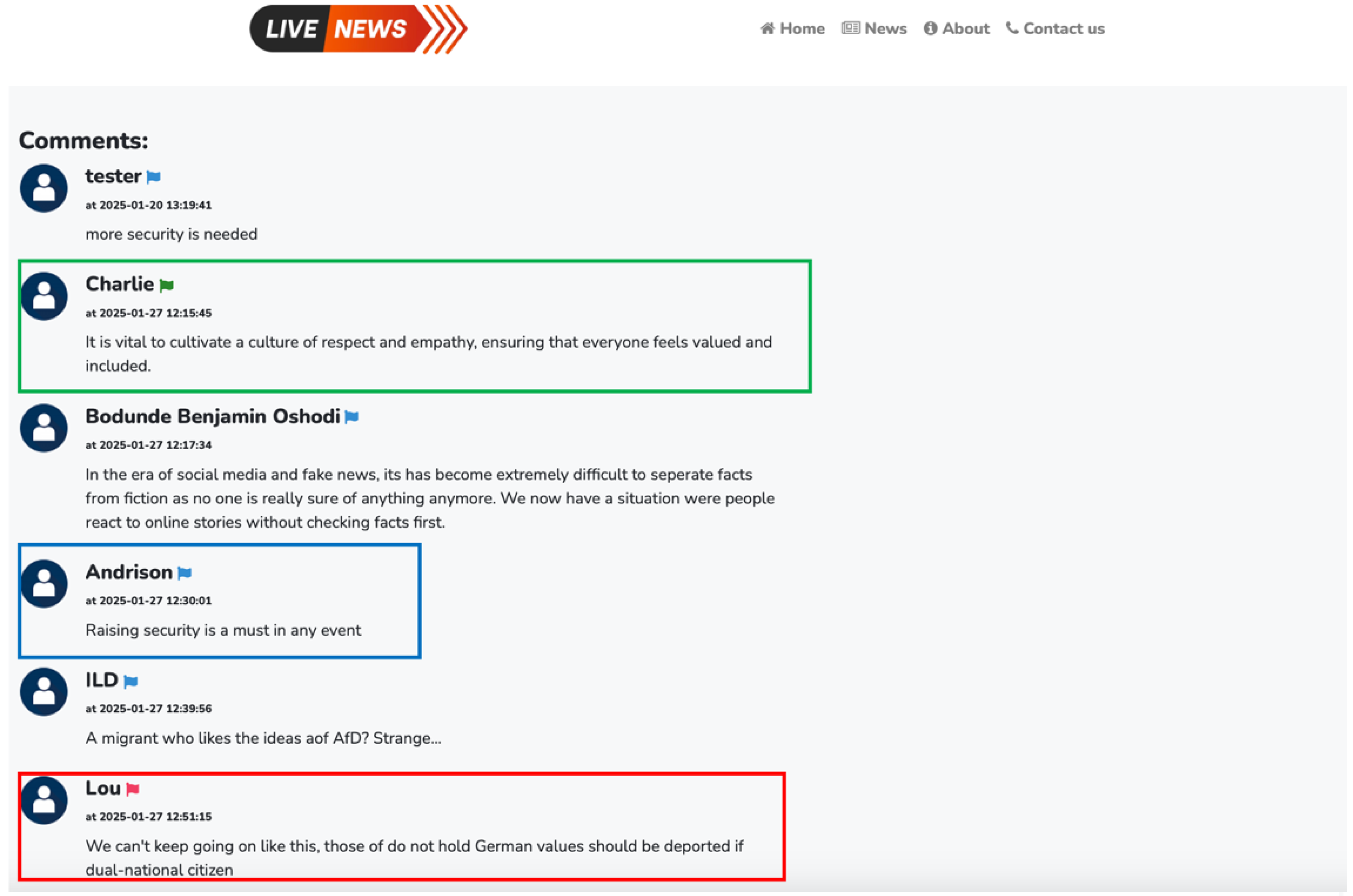
Figure 5. Examples of LLM-Based suggestions on different types of user comments. - Flagging on Comments: Three different flag indicators were assigned to the participants’ comments to measure their interactions with the proposed self-monitoring strategy (comment analysis feature) and the LLM-based suggestions. These flags were as follow: The Blue Flag was assigned to standard comments, where the participants posted their comment without requiring intervention from LLM. The Green Flag was used for comments that were detected by the comment analyzer as cyberhate and the participants accepted the suggested revisions by the LLM. Lastly, the Red Flag was assigned to hateful comments where the participants declined to adopt the LLM-based suggestions for modification. This classification enabled a structured analysis of user engagement with the proposed features and their willingness to adjust their language accordingly. Figure 6 presents examples of flagged comments.
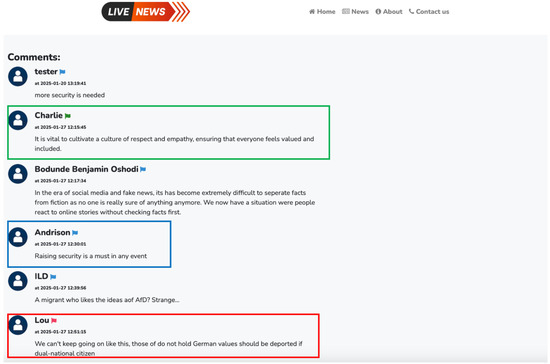 Figure 6. Examples of flagged comments.
Figure 6. Examples of flagged comments.
3.2.2. Study Procedure
The participants were asked to interact with the news website to read articles and participate in comment sections. As participants post comments, they interact with the LLM-Based comment analysis feature integrated into the website. When the LLM analysis identified potentially offensive or harmful language in a comment, it suggested alternative, more neutral phrasing. The participants could choose to accept or reject these suggestions. They were asked to comment on news articles that interest them as they normally do to let them express their opinions honestly and naturally. A post-study survey was then employed to gather their feedback, shedding light on the perceived effectiveness, user experience, and potential for broader application of such interventions in online environments. The participants were recruited to participate in the study through ClickWorkers (https://www.clickworker.com/ (accessed on 27 January 2025)), an online platform specializing in the recruitment of research participants. As an incentive, a payment of €1 was offered to each participant upon completing the study.
3.2.3. Study Evaluation
The evaluation of this study focuses on understanding the effectiveness of integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) and persuasive technology into a news website to reduce cyberhate. By tracking and analyzing the participants’ comments made before and after they receive the recommendations, the study measures whether they modify their comments to adopt less hateful or aggressive tones in their comments. The post-study survey gathers insights into how the participants perceive the LLM-based intervention and whether they find it useful for revising their comments and adopting more constructive language. Additionally, their feedback is gathered on the quality of the detection capability and the alternative suggestions received by the LLM and whether it provided appropriate and effective rephrasing for potentially harmful comments.
3.2.4. Survey Design
The survey designed for this study consisted of 20 diverse types. Initially, it was tested on a small group of 10 respondents who met the study’s sampling criteria. Feedback and responses from this initial group were used to improve and refine the questionnaire before distributing it to a larger audience. To ensure participants were familiar with the topic, a summary of the study was included at the beginning of the questionnaire. Additionally, respondents were briefed on the purpose of their participation and how their input would be used. The complete survey questionnaire used in this study is provided as Supplementary File S1 to enhance transparency and facilitate replication. A copy is also available at: https://shorturl.at/LUlcz (last accessed on 5 March 2025).
3.2.5. Sampling
A convenience sampling approach was employed to recruit 122 participants aged 18 or older, representing diverse cultural backgrounds. The characteristics of the participants were analyzed using cross-tabulation and frequency counts. Comparisons were made across variables such as age, gender, nationality, and educational level. The analysis revealed a high degree of diversity among the respondents, which strengthens the potential generalizability of the study’s findings. An overview of the participants’ characteristics is provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
An overview of participant demographics and characteristics.
3.2.6. Analysis
First, the frequencies of detected cyberhate comments and the accepted or rejected suggestions were quantified. The questionnaire responses were prepared and refined, removing 29 incomplete or inconsistent forms. To ensure a robust analysis, we calculated acceptance ratios (accepted suggestions/suggestions received) for participants and conducted correlation analyses using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient to explore relationships between variables such as willingness to express opinions and helpfulness of suggestions. An LLM classification performance and a post-hoc analysis of a random sample of flagged comments were performed to estimate the true-positive and false-positive rates of LLM detections, with results integrated into the findings. Descriptive analysis was also conducted to represent the collected responses [77].
4. Findings
4.1. LLM Intervention Clarity and Acceptance
The study’s findings suggest that the LLM-based suggestions to replace cyberhate comments were generally easy for people to understand. A total of 81% of participants indicated that the suggestions were easy to comprehend whereas only a very small proportion reported some difficulty (0.82%) in understanding those suggestions. This overall ease of understanding is encouraging, suggesting that the LLM communicates in a manner that is accessible to most users. Nevertheless, the minority who struggled with clarity signal an opportunity to further refine the simplicity and presentation of these suggestions, particularly for users with varying language proficiencies.
This finding is consistent with the work of Thomas Davidson et al. [78], who emphasize that clarity and interpretability are crucial in systems designed for cyberhate detection. In addition, ref. [79] highlights the importance of designing user-friendly interventions that can be seamlessly integrated into online interactions. However, the results show a moderate rate of acceptance for these LLM-based suggestions. To assess acceptance, we calculated individual acceptance ratios, revealing an average ratio of 0.35 across participants, with significant variation (SD = 0.21). Of the 80.3% participants who received at least one suggestion, 36% of participants accepted only one suggestion during the study and 17% accepted three suggestions, while 15% did not accept any suggestions. These findings suggest that although many users are open to modifying their comments based on the LLM’s feedback, a significant portion remain resistant. When participants chose to reject the LLM’s alternative phrasing, they cited several key reasons:
- The suggestion was not relevant to their opinions (51%)
- The suggestion was too different from what they wanted to express (38%)
- They did not think their comments were hateful (23%)
- They did not agree with the tone of the LLM suggestion (20%)
These observations align with insights from Gillespie [80], who examines how users often react to content moderation depending on their perceptions of fairness, transparency, and alignment with their own values. He emphasizes that effective moderation systems should be designed in a way that fosters user trust and engagement rather than creating a sense of imposed control.
These responses indicate that the LLM is often successful at flagging potentially harmful language but struggles to capture the nuanced intent behind a user’s original comment. Nearly a quarter of participants did not consider their comments hateful, suggesting that the system may misinterpret context and tone. This indeed aligns with [81] where it highlighted the issue of users rejecting interventions that they feel misrepresent their real intentions. Furthermore, Chandrasekharan et al. [82] underscore the difficulty of designing moderation systems that accurately interpret nuanced user intent. Future iterations of the LLM interventions should focus on improving the alignment between the LLM’s suggestions and the user’s original intent, as well as providing clearer explanations for why a particular suggestion is being offered.
4.2. LLM Frequency of Intervention
The frequency with which participants received LLM-based suggestions varied considerably. Among the 80.3% participants receiving suggestions, about 33.61% received suggestions once during the study, 20.49% received suggestions twice, and 15.57% received suggestions three times. Notably, 10.66% of the participants were presented with five or more suggestions, indicating that LLM was actively intervening when it detects language that may potentially include cyberhate instances. The minimum comment requirement was five per participant, but exact counts were not recorded, a limitation noted in Section 6.
This variability likely reflects differences in individual commenting behavior—some participants could be more prone to using language that triggered the LLM’s detection system. The fact that 10.66% of participants received five or more suggestions suggests that a subset of users may require more frequent interventions, which could be an area for further investigation taking into account that the effectiveness of moderation tools is often a function of their frequency of use; too many interventions can lead to fatigue, while too few may fail to curb harmful behavior.
In addition, to assess participant engagement patterns, we classified respondents into two groups based on their survey responses, those demonstrating constructive engagement (defined by high ratings for suggestion helpfulness and low rejection frequency) and those demonstrating resistant engagement (characterized by low suggestion helpfulness and high rejection frequency). The analysis revealed a statistically significant difference in suggestion acceptance ratios between the two groups (M = 0.45, SD = 0.18 for constructive engagers vs. M = 0.22, SD = 0.15 for resistant engagers), t(96) = 6.87, p < 0.001, indicating that constructive engagers were more receptive to the provided suggestions.
4.3. LLM Impact on Awareness and Behavior
The LLM’s-based suggestions appeared to have a varied impact on participants’ willingness to express their opinions. Focusing on the 80.3% participants who received suggestions, about 44% of them reported that the suggestions increased their willingness to express their opinions, while a similar percentage (45%) saw no change. However, 11% felt that the interventions decreased their willingness to speak freely. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was also used to assess the relationship between participants’ perceived helpfulness of LLM-generated suggestions and their willingness to express their opinions. The results revealed a positive correlation (, ), indicating that participants who found the suggestions more helpful were also more likely to report increased willingness to express their opinions.
This suggests that while the LLM’s interventions encouraged some participants to engage more openly, others felt constrained by the provided suggestions. The fact that a significant portion of participants felt that the suggestions decreased their willingness to express their opinions is a critical finding. It suggests that the LLM’s interventions may have inadvertently stifled some users’ freedom of expression, particularly if they felt that their comments were being unfairly flagged or altered.
This mixed outcome highlights the delicate balance between mitigating cyberhate and preserving free expression. Gillespie [80] discusses how moderation tools can sometimes have a chilling effect on free expression if users feel that their contributions are being unfairly moderated. Thus, ensuring transparency and fairness in automated interventions is critical.
In addition, a significant portion of participants 40.98% believed that the LLM’s interventions improved their language and commenting tone to some extent, and 23.77% reported significant improvements. However, 26.23% saw no effect, and a small percentage (2.46%) felt that their commenting tone worsened as a result. This suggests that the LLM’s suggestions actively contributed to a behavioral shift in how participants expressed themselves. This improvement is likely a result from the intervention prompting participants to rethink and adjust their language. By providing immediate feedback and constructive alternatives, the LLM served as a real-time nudge for self-regulation, aligning with the goal of adopting self-monitoring technique as a persuasive strategy. Additionally, this finding emphasizes the system’s role as a behavioral intervention tool, not merely a content moderation mechanism.
However, the fact that over a quarter of participants felt that the intervention had no effect indicates that the LLM’s impact may be limited in certain contexts or for certain types of comments. Additionally, the small percentage of participants who felt that the intervention worsened their tone suggests that there may be cases where the LLM’s suggestions inadvertently led to less effective or less authentic communication. Suler’s [83] discussion of the “online disinhibition effect” provides context here, as it explains how online interactions can become either more positive or negative, depending on various factors. In this case, the LLM’s interventions sometimes succeed in moderating the participants commenting tone, but there is still a room for improvement.
4.4. Long-Term Impact on Cyberhate and Freedom of Speech
A substantial majority of the participants (68.03%) believed that the LLM-based interventions (using a self-monitoring strategy) could have a positive long-term impact on reducing cyberhate, while 13.11% were skeptical and 18.85% were unsure. This overall optimism suggests a willingness among users to embrace technological solutions for improving online discourse, despite some uncertainties about their implementation and potential overreach. Schmidt and Wiegand [84] provide further support for this optimism, arguing that automated moderation tools have the potential to reduce cyberhate—provided they are designed with both effectiveness and ethical considerations in mind. However, the skepticism and uncertainty expressed by a significant minority highlight the need for further research and development to address concerns about the effectiveness and ethical implications of LLM-based interventions to combat cyberhate.
Additionally, when the participants were asked about the impact of the LLM’s suggestions on their freedom of expression, 47.54% of participants felt that the interventions did not infringe on their ability to speak freely, describing them as “a helpful nudge to ensure respectful discourse”. However, 36.07% reported that the suggestions felt like censorship, and 16.39% were unsure. These responses underscore the tension between promoting respectful communication and protecting free speech.
The perception of the LLM’s interventions as censorship is a critical concern, as it suggests that some users may feel that their ability to express themselves freely is being curtailed. This underscores the importance of designing LLM-based intervention systems in a way that is transparent, user-controlled, and respectful of individual autonomy. Future research should explore ways to mitigate these concerns, such as by providing users with more control over the intervention process or by offering clearer explanations for why a particular suggestion is being made. As Crawford and Paglen [85] discuss, designing algorithmic systems involves complex ethical trade-offs, and ensuring that such systems respect users’ rights is essential.
4.5. LLM Classification Performance
To evaluate the classification performance of the comment analysis feature, we used the dataset from our previous work [9], which consists of approximately 9000 tweets categorized into three classes: normal, abusive, and hate speech. Due to the rate limit restrictions of the Gemini model, approximately 600 tweets were used in the evaluation. Furthermore, since our feature analysis task is a binary classification problem, we annotated normal tweets as 0, and both hate and abusive tweets as 1. Table 2 shows the number of tweets in each class.

Table 2.
Tweet Count by Class.
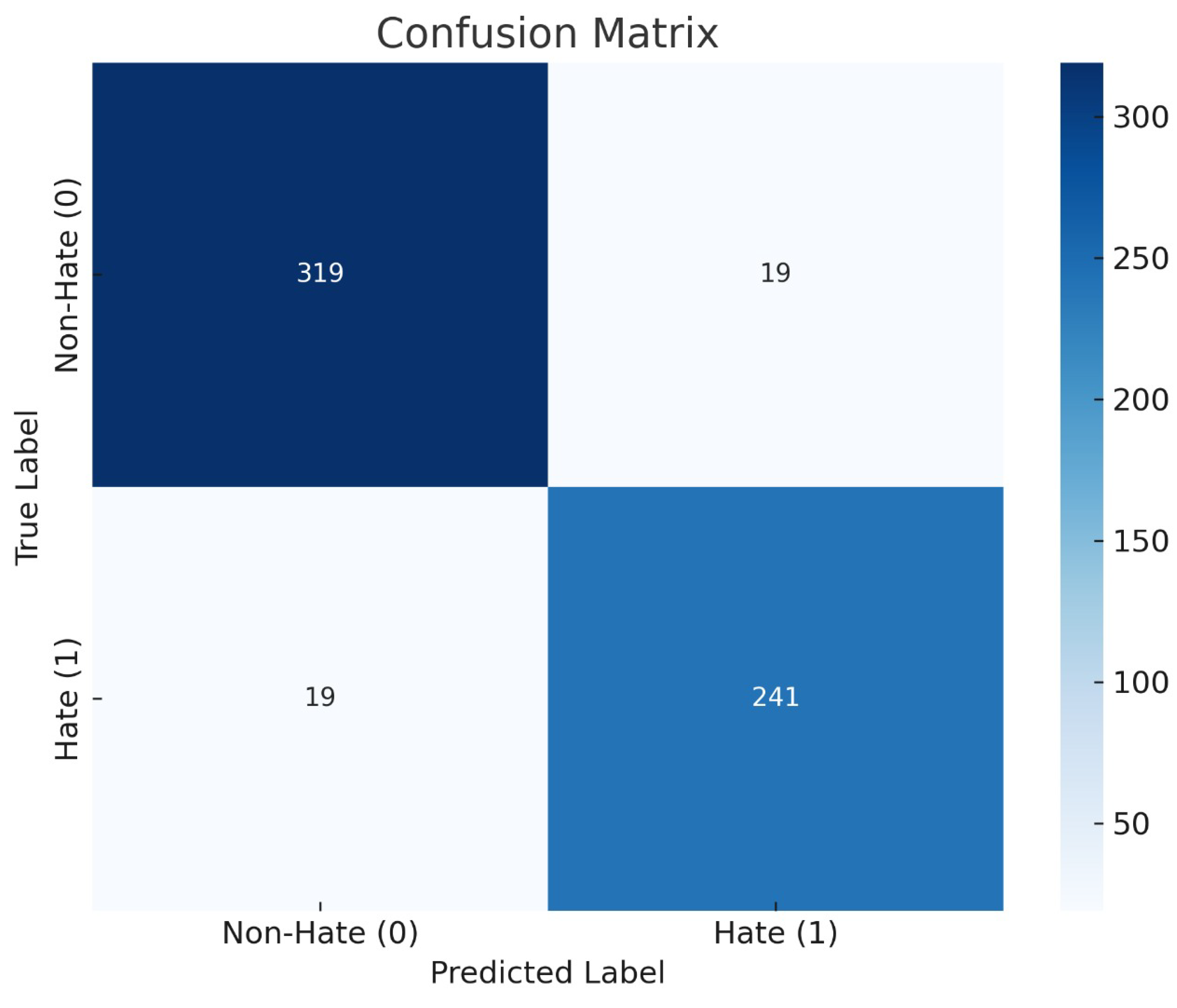
Each tweet was sent to the Gemini model without revealing its actual label, allowing us to assess the model’s performance based on its predictions. Figure 7 displays the confusion matrix for the LLM model, indicating its classification test performance. The matrix provides a detailed breakdown of the instances of each class that the model identified as hate and non-hate. According to the results, the model performs well across all classes. Moreover, the results demonstrates superior performance achieving a precision of 0.93, recall of 0.93, F-score of 0.93 and accuracy of 0.94. Furthermore, A manual expert post-hoc analysis of 50 flagged comments estimated a 92% true-positive rate and 8% false-positive rate for LLM detections, suggesting reasonable accuracy but room for improvement. In summary, these results indicate the potential of integrating a LLM into our feature analysis method to effectively identify and address instances of cyberhate. This integration improves the ability to analyze user behavior, classify harmful language, and provide constructive alternatives (suggestions).
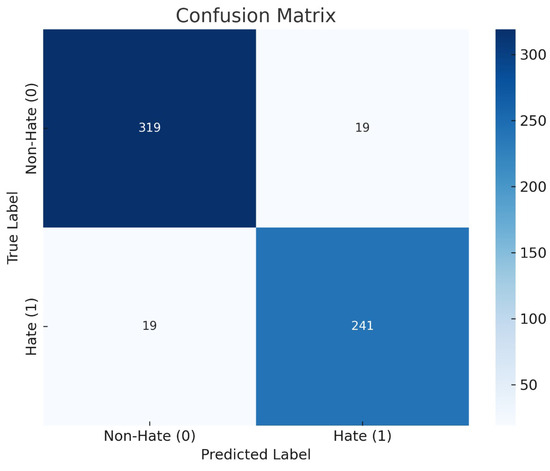
Figure 7.
Confusion matrix for the proposed framework.
5. Discussion
The discussed findings in Section 4 highlight several important insights into the effectiveness and challenges of using LLM-based interventions as a self-monitoring persuasive strategy to limit cyberhate spread. On the one hand, the overall ease of understanding and moderate acceptance rates suggest that many users can and do engage positively with LLM-based interventions. This supports the notion that well-designed interventions—those that prioritize clarity and relevance—can contribute to a more respectful online environment. However, the data also reveal persistent challenges.
A significant portion of users rejected the LLM-based suggestions due to perceived irrelevance or a mismatch with their intended tone. These findings underscore the importance of context in using LLM-based interventions to be finely tuned to distinguish between genuinely harmful language and benign expressions that might be misinterpreted as cyberhate. This nuance is critical, as misclassification can lead not only to user dissatisfaction but also to a perceived infringement on their freedom of expression.
The mixed impact on users’ willingness to express their opinions further complicates the picture. While some users appreciated the corrective LLM-based suggestions and felt encouraged to communicate more responsibly, others experienced a chilling effect, feeling that their autonomy was undermined. This duality reflects broader debates in the literature about the balance between moderation and free speech, with scholars such as Gillespie [80] and Roberts [86] emphasizing the need for moderation systems that are both effective and respectful of individual rights. In this study, the intervention was designed to be assistive rather than prescriptive, providing optional suggestions without enforcing censorship. Participants retained full control over whether to accept or reject language revisions. To address this, interventions should prioritize transparency, offer opt-out features, and clearly communicate why alternative suggestions are made. These steps can help build trust and mitigate perceptions of overreach while encouraging more respectful online discourse.
Additionally, the variability in the frequency of LLM-based suggestions points to the need for adaptive systems that can calibrate the level of intervention based on individual user behavior. Over-intervention can lead to fatigue and disengagement, whereas under- intervention might fail to curb cyberhate effectively. Future research should explore adaptive models that optimize intervention frequency based on real-time feedback and user context. Finally, the overall optimism regarding the long-term impact of LLM-based interventions as a self-monitoring persuasive strategy to limit cyberhate spread is tempered by significant concerns about potential overreach and censorship. This tension suggests that ongoing refinement, transparency, and user control will be critical components of any successful LLM-based intervention strategy moving forward.
6. Validity Threats
Despite the authors’ careful adherence to the principles of conducting empirical studies, there are still several potential threats to the validity of this study as follows:
- The persuasive suggestions generated by the LLM may implicitly assume a universal standard of politeness, potentially overlooking cultural, contextual, and rhetorical variations in communication. As a result, individual participants may interpret these suggestions differently based on their personal beliefs, language proficiency, or communication norms. Future work should prioritize fairness by incorporating diverse datasets, multi-perspective evaluations, and explainability features to ensure that interventions are culturally sensitive and do not disproportionately moderate marginalized voices. To improve interpretability and reduce unintended variation in user responses, future studies will also include standardized participant training and calibration sessions prior to interaction, along with behavioral analytics (e.g., tracking changes in commenting patterns) to supplement self-reported perceptions with objective measures of intervention impact.
- Participants may have provided socially desirable responses rather than their true opinions, particularly regarding sensitive topics like cyberhate. To minimize this threat, the author ensured anonymity in responses and emphasized that there were no right or wrong answers, encouraging honesty.
- While the news website allowed for testing of the LLM-based intervention, we acknowledge that it does not fully replicate real-world social media dynamics. Key features such as user networks, content algorithms, and evolving community standards were beyond the scope of this study. However, this study environment enabled a focused evaluation of user responses to self-monitoring strategies. Future research will explore integration with real-world social platforms to validate and extend these findings in more dynamic and socially nuanced contexts.
- Conducting the study on a custom-built news website may limit the generalizability of findings to other social media platforms with different dynamics and policies. To mitigate this, future experiments will replicate the study across multiple platforms with varying user interfaces and community guidelines. Cross-platform comparisons will help determine the consistency of LLM-based intervention effects.
- While the adopted methodology successfully identified and described users’ perceptions regarding our proposed approach, it is possible that certain significant aspects that could impact their behaviors in this context were not fully captured.
- A common concern when using questionnaires is whether respondents interpreted and understood the questions as intended. To address this, a pilot study was conducted with 10 participants who met the study’s inclusion criteria. Based on their feedback, some questions were reviewed and improved to ensure a shared understanding among all respondents.
- The sample size of the study, consisting of 122 respondents, can be considered medium-sized. A larger sample would enable the findings to be more generalizable to larger population groups. Further investigation of the study’s results on a larger population will be conducted in future research.
- The study utilized a convenience sampling method, which may not fully represent the broader population. To mitigate this issue, the author recruited participants from diverse cultural backgrounds and demographics to enhance the generalizability of the findings.
- The exact number of comments posted per participant was not recorded, limiting our ability to fully decouple the effects of the comments volume. In future work will track this precisely.
- Resource constraints prevented human labeling of all suggestions, though our sample analysis (92% true-positive) provides an initial estimate.
7. Conclusions
This study presented a novel approach that integrates the advanced contextual capabilities of LLMs with PT to address the persistent challenge of cyberhate. By employing a self-monitoring strategy (i.e., comment analysis feature) that is designed to enhance user self-awareness and encourage prosocial language choices. The empirical evaluation of users perceptions regarding our proposed approach revealed that a significant majority of participants found the LLM-based suggestions clear and beneficial, and many adjusted their language accordingly, demonstrating the potential effectiveness of this intervention. However, our findings also highlight important challenges, particularly in striking a balance between effective moderation and preserving freedom of expression, as well as ensuring high accuracy in the detection of cyberhate. These challenges underscore the need for further refinement of both the underlying models and the intervention strategies. The study’s primary contribution lies in its dual focus: leveraging LLMs’ contextual precision for cyberhate detection while employing persuasive design to nudge behavioral change. This approach addresses a critical gap in existing research, which often prioritizes detection over prevention. However, the mixed outcomes underscore the complexity of designing interventions that respect user autonomy while mitigating harm.
Moving forward, this work advocates for three key directions: (1) longitudinal studies to assess sustained behavioral impact and user fatigue, (2) refinement of LLM accuracy and contextual sensitivity to reduce mismatches between user intent and algorithmic interpretation, and (3) ethical frameworks to guide the deployment of persuasive technologies without compromising free speech. By centering user agency and fostering collaborative design, such tools could empower communities to self-regulate harmful content while preserving the open discourse vital to digital platforms. Ultimately, this research underscores the transformative potential of combining AI-driven analysis with human-centered persuasive strategies—a synergy that could redefine how social media platforms address cyberhate, not as mere moderators but as facilitators of healthier digital ecosystems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/computers14050173/s1, File S1: Hate Speech on News Websites Survey.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A. and A.M.A.; methodology, M.A., A.M.A. and K.O.A.; software, K.O.A.; validation, M.A., A.M.A. and E.-S.A.; formal analysis, M.A., A.M.A., K.O.A. and E.-S.A.; investigation, M.A. and A.M.A.; data curation, M.A., A.M.A. and E.-S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A., A.M.A., K.O.A. and E.-S.A.; writing—review and editing, M.A., A.M.A., K.O.A. and E.-S.A.; visualization, M.A., A.M.A., K.O.A. and E.-S.A.; supervision, M.A. and E.-S.A.; project administration, M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data is available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Almars, A.M.; Almaliki, M.; Noor, T.H.; Alwateer, M.M.; Atlam, E. Hann: Hybrid attention neural network for detecting COVID-19 related rumors. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 12334–12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Schwarz, C. Fanning the flames of hate: Social media and hate crime. J. Eur. Econ. Assoc. 2021, 19, 2131–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobata, C.; Tetreault, J.; Thomas, A.; Mehdad, Y.; Chang, Y. Abusive language detection in online user content. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–15 April 2016; pp. 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, T.H.; Almars, A.M.; Alwateer, M.; Almaliki, M.; Gad, I.; Atlam, E.S. Sarima: A seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average model for crime analysis in Saudi Arabia. Electronics 2022, 11, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaya, C. Cyberhaine: Les Jeunes et la Violence sur Internet; Nouveau Monde: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Machackova, H.; Blaya, C.; Bedrosova, M.; Smahel, D.; Staksrud, E. Children’s Experiences with Cyberhate. 2020. Available online: https://eprints.lse.ac.uk/106730/1/EUkidsonline_childrens_experiences_wth_cyberhate.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Wachs, S.; Wright, M.F. Associations between bystanders and perpetrators of online hate: The moderating role of toxic online disinhibition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- League, A.D. Online Hate and Harassment. The American Experience 2021; Center for Technology and Society: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Almaliki, M.; Almars, A.M.; Gad, I.; Atlam, E.S. Abmm: Arabic bert-mini model for hate-speech detection on social media. Electronics 2023, 12, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, C.; Batista, S. EU kids online Portugal. Usos, competências, riscos e mediações da internet reportados por crianças e jovens (9-17 anos). EU Kids Online e NOVA FCSH. 2019. Available online: https://fabricadesites.fcsh.unl.pt/eukidsonline/wp-content/uploads/sites/36/2019/03/RELATO%CC%81RIO-FINAL-EU-KIDS-ONLINE.docx.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Elmezain, M.; Malki, A.; Gad, I.; Atlam, E.S. Hybrid deep learning model-based prediction of images related to cyberbullying. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2022, 32, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.; Mendes da Silva, B.; Tavares, M. Video games and gamification against online hate speech? In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Digital and Interactive Arts, Aveiro, Portugal, 13–15 October 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Citron, D.K.; Norton, H. Intermediaries and hate speech: Fostering digital citizenship for our information age. BUL Rev. 2011, 91, 1435. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Lee, R.K.W.; Hoang, T.A. DeepHate: Hate speech detection via multi-faceted text representations. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM Conference on Web Science, Southampton, UK, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Almars, A.M.; Atlam, E.S.; Noor, T.H.; ELmarhomy, G.; Alagamy, R.; Gad, I. Users opinion and emotion understanding in social media regarding COVID-19 vaccine. Computing 2022, 104, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, K.; Noersasongko, E.; Fanani, A.Z.; Basuki, R.S. Improving random forest method to detect hatespeech and offensive word. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information and Communications Technology (ICOIACT), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 24–25 July 2019; pp. 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Arango, A.; Pérez, J.; Poblete, B. Hate speech detection is not as easy as you may think: A closer look at model validation. In Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM Sigir Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Paris, France, 21–25 July 2019; pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Savage, N. Deep learning based fusion approach for hate speech detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 128923–128929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, S.D.; Jamatia, A.; Gambäck, B. Studying generalisability across abusive language detection datasets. In Proceedings of the 23rd Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL), Hong Kong, China, 3–4 November 2019; pp. 940–950. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Zubiaga, A. Towards generalisable hate speech detection: A review on obstacles and solutions. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Dutt, R.; Goyal, P.; Mukherjee, A. Spread of hate speech in online social media. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Web Science, Boston, MA, USA, 30 June–3 July 2019; pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Bedrosova, M.; Machackova, H.; Šerek, J.; Smahel, D.; Blaya, C. The relation between the cyberhate and cyberbullying experiences of adolescents in the Czech Republic, Poland, and Slovakia. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 126, 107013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Illendula, A.; Saha, P.; Sarkar, S.; Goyal, P.; Mukherjee, A. Hate begets hate: A temporal study of hate speech. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2020, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaliki, M. Cyberhate Dissemination: A Systematic Literature Map. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 117385–117392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhard, L.; Rueß, C.; Obermaier, M.; Reinemann, C. Perceiving threat and feeling responsible. How severity of hate speech, number of bystanders, and prior reactions of others affect bystanders’ intention to counterargue against hate speech on Facebook. SCM Stud. Commun. Media 2018, 7, 555–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieb, C.; Preuss, M. Governing hate speech by means of counterspeech on Facebook. In Proceedings of the 66th ICA Annual Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 9–13 June 2016; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Preuß, M.; Tetzlaff, F.; Zick, A. Publizieren wird zur Mutprobe. In Studie zur Wahrnehmung von und Erfahrungen mit Angriffen unter JournalistInnen [Publishing Is Becoming a Test of Courage: A Study on Perceptions and Experiences Concerning Aggression Among Journalists]. Report; Mediendienst Integration: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, J.; Krasodomski-Jones, A. Counter-Speech Examining Content That Challenges Extremism Online. DEMOS. October 2015. Available online: https://demos.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Counter-speech.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Delgado, R.; Stefancic, J. Hate speech in cyberspace. Wake Forest L. Rev. 2014, 49, 319. [Google Scholar]
- Darley, J.M. The Unresponsive Bystander: Why Doesn’t He Help? Appleton-Century Crofts: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Oinas-Kukkonen, H. A foundation for the study of behavior change support systems. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2013, 17, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oinas-Kukkonen, H.; Harjumaa, M. Towards deeper understanding of persuasion in software and information systems. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Advances in Computer-Human Interaction, Sainte Luce, France, 10–15 February 2008; pp. 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Fogg, B.J. Creating persuasive technologies: An eight-step design process. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Persuasive Technology, Claremont, CA, USA, 26–29 April 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alhasani, M.; Mulchandani, D.; Oyebode, O.; Orji, R. A Systematic Review of Persuasive Strategies in Stress Management Apps. BCSS@ PERSUASIVE 2020. Available online: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2662/BCSS2020_paper4.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Orji, R.; Moffatt, K. Persuasive technology for health and wellness: State-of-the-art and emerging trends. Health Inform. J. 2018, 24, 66–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyasari, Y.D.L.; Nugroho, L.E.; Permanasari, A.E. Persuasive technology for enhanced learning behavior in higher education. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2019, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, K.T.; Mullan, J.; Howard, S.K.; Oinas-Kukkonen, H. Persuasive Systems Design Features in Promoting Medication Management for Consumers. 2017. Available online: https://scholarspace.manoa.hawaii.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/e876d59d-2ae4-4089-a482-40881f39d75d/content (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Atlam, E.S.; Ewis, A.; Abd El-Raouf, M.; Ghoneim, O.; Gad, I. A new approach in identifying the psychological impact of COVID-19 on university student’s academic performance. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 5223–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Z.; Arafa, A.; Atlam, E.S.; El-Qerafi, N.; El-Shazly, M.; Al-Hazazi, O.; Ewis, A. Psychological problems among the university students in Saudi Arabia during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaheebocus, S.M.R.A.; Weal, M.; Morrison, L.; Yardley, L. Peer-based social media features in behavior change interventions: Systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiafe, I.; Koranteng, F.N.; Owusu, E.; Ekpezu, A.O.; Gyamfi, S.A. Persuasive social features that promote knowledge sharing among tertiary students on social networking sites: An empirical study. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2020, 36, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Introducing ChatGPT. Available online: https://openai.com/index/chatgpt/ (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Bang, Y.; Cahyawijaya, S.; Lee, N.; Dai, W.; Su, D.; Wilie, B.; Lovenia, H.; Ji, Z.; Yu, T.; Chung, W.; et al. A multitask, multilingual, multimodal evaluation of chatgpt on reasoning, hallucination, and interactivity. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.04023. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Nie, J.; Ding, Y.; Yue, J.; Wu, Y. How close is chatgpt to human experts? comparison corpus, evaluation, and detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.07597. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A survey of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, K.L.; Collins, A.; Alexander, R. Detecting hate speech with gpt-3. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.12407. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Fan, L.; Atreja, S.; Hemphill, L. “HOT” ChatGPT: The promise of ChatGPT in detecting and discriminating hateful, offensive, and toxic comments on social media. ACM Trans. Web 2024, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zannettou, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y. You only prompt once: On the capabilities of prompt learning on large language models to tackle toxic content. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–22 May 2024; pp. 770–787. [Google Scholar]
- Zannettou, S.; Finkelstein, J.; Bradlyn, B.; Blackburn, J. A quantitative approach to understanding online antisemitism. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Buffalo, NY, USA, 3–6 June 2020; Volume 14, pp. 786–797. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, W.; Hirschberg, J. Detecting hate speech on the world wide web. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Language in Social Media, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7 June 2012; pp. 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Sambasivan, N.; Batool, A.; Ahmed, N.; Matthews, T.; Thomas, K.; Gaytán-Lugo, L.S.; Nemer, D.; Bursztein, E.; Churchill, E.; Consolvo, S. “They Don’t Leave Us Alone Anywhere We Go” Gender and Digital Abuse in South Asia. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, Scotland, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, H.; Blackburn, J.; Han, S. Exploring cyberbullying and other toxic behavior in team competition online games. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 18–23 April 2015; pp. 3739–3748. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Danescu-Niculescu-Mizil, C.; Leskovec, J. Antisocial behavior in online discussion communities. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Oxford, UK, 26–29 May 2015; Volume 9, pp. 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.; Akhawe, D.; Bailey, M.; Boneh, D.; Bursztein, E.; Consolvo, S.; Dell, N.; Durumeric, Z.; Kelley, P.G.; Kumar, D.; et al. Sok: Hate, harassment, and the changing landscape of online abuse. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–27 May 2021; pp. 247–267. [Google Scholar]
- Citron, D.K. Addressing cyber harassment: An overview of hate crimes in cyberspace. Case W. Res. JL Tech. Internet 2014, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khali, L. Identifying cyber hate: Overview of online hate speech policies &finding possible measures to counter hate speech on internet. J. Media Stud. 2019, 31. Available online: http://111.68.103.26//journals/index.php/jms/article/view/1925 (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Alorainy, W.; Burnap, P.; Liu, H.; Williams, M.L. “The enemy among us” detecting cyber hate speech with threats-based othering language embeddings. ACM Trans. Web (TWEB) 2019, 13, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, C.; Tonelli, S. Generation-Based Data Augmentation for Offensive Language Detection: Is It Worth It? In Proceedings of the 17th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2–6 May 2023; pp. 3359–3377. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, D.; Tian, F.; Zheng, Y. When MOE Meets LLMs: Parameter Efficient Fine-tuning for Multi-task Medical Applications. In Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 1104–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Adaji, I.; Adisa, M. A review of the use of persuasive technologies to influence sustainable behaviour. In Proceedings of the Adjunct Proceedings of the 30th ACM Conference on User Modeling, Adaptation and Personalization, Barcelona, Spain, 4–7 July 2022; pp. 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Oinas-Kukkonen, H.; Harjumaa, M. Persuasive systems design: Key issues, process model and system features 1. In Routledge Handbook of Policy Design; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 87–105. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, A. Impact of Digitalization and Artificial Intelligence as Causes and Enablers of Organizational Change; Nottingham University Business School: Nottingham, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, W.N.W.; Salim, M.H.M.; Rodzuan, A.R.A. An Inspection of Learning Management Systems on Persuasiveness of Interfaces and Persuasive Design: A Case in a Higher Learning Institution. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergram, K.; Djokovic, M.; Bezençon, V.; Holzer, A. The digital landscape of nudging: A systematic literature review of empirical research on digital nudges. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 29 April–5 May 2022; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Shu, K. Combating misinformation in the age of llms: Opportunities and challenges. AI Mag. 2023, 45, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyebode, O.; Alqahtani, F.; Orji, R. Exploring for possible effect of persuasive strategy implementation choices: Towards tailoring persuasive technologies. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Persuasive Technology, Virtual Event, 29–31 March 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 145–163. [Google Scholar]
- Halttu, K.; Oinas-Kukkonen, H. Need for cognition among users of self-monitoring systems for physical activity: Survey study. JMIR Form. Res. 2021, 5, e23968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandura, A. Social Cognitive Theory of Self-Regulation. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Processes 1991, 50, 248–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B.; Pickard, L.; Pfleeger, S.L. Case studies for method and tool evaluation. IEEE Softw. 1995, 12, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlin, C.; Runeson, P.; Höst, M.; Ohlsson, M.C.; Regnell, B.; Wesslén, A. Experimentation in Software Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; Volume 236. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Yang, W.; Wei, F.; He, L. Prompt for extraction: Multiple templates choice model for event extraction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 289, 111544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.; Berryman, J. A developer’s guide to prompt engineering and LLMs. GitHub Blog. 2023, 17. Available online: https://github.blog/ai-and-ml/generative-ai/prompt-engineering-guide-generative-ai-llms/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. A practical survey on zero-shot prompt design for in-context learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.13205. [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil, S.; Tran, A.; Kim, J.; Huang, Z.; Bernstein, S.; Mogil, D. Prompt middleware: Mapping prompts for large language models to UI affordances. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.01142. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Li, L.; Xiang, Y.; Qin, X. PromptCL: Improving event representation via prompt template and contrastive learning. In Proceedings of the CCF International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Chinese Computing, Foshan, China, 12–15 October 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A. How to… Write and analyse a questionnaire. J. Orthod. 2003, 30, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, T.; Warmsley, D.; Macy, M.; Weber, I. Automated hate speech detection and the problem of offensive language. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Montreal, QC, Canada, 15–18 May 2017; Volume 11, pp. 512–515. [Google Scholar]
- Sandvig, C.; Hamilton, K.; Karahalios, K.; Langbort, C. Auditing algorithms: Research methods for detecting discrimination on internet platforms. Data Discrim. Convert. Crit. Concerns Into Product. Inq. 2014, 22, 4349–4357. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, T. Custodians of the Internet: Platforms, Content Moder Ation, and the Hidden Decisions That Shape Social Media; Yale University Press: Dunmore, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why should i trust you?” Explaining the predictions of any classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekharan, E.; Pavalanathan, U.; Srinivasan, A.; Glynn, A.; Eisenstein, J.; Gilbert, E. You can’t stay here: The efficacy of reddit’s 2015 ban examined through hate speech. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2017, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suler, J. The online disinhibition effect. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2004, 7, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Wiegand, M. A survey on hate speech detection using natural language processing. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Natural Language Processing for Social Media, Valencia, Spain, 3–4 April 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, K.; Paglen, T. Excavating AI: The politics of images in machine learning training sets. Ai Soc. 2021, 36, 1105–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.T. Behind the Screen: Content Moderation in the Shadows of Social Media; Yale University Press: Dunmore, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).