Arabic Natural Language Processing (NLP): A Comprehensive Review of Challenges, Techniques, and Emerging Trends
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Determining the Research Questions
- RQ1: What are the main challenges and limitations in Arabic NLP for different fields?
- RQ2: What methods, tools, and models have been commonly applied in each Arabic NLP task?
- RQ3: What publicly available datasets exist for each Arabic NLP field?
- RQ4: What evaluation techniques have been applied to measure the performance and effectiveness of each trending methodologies?
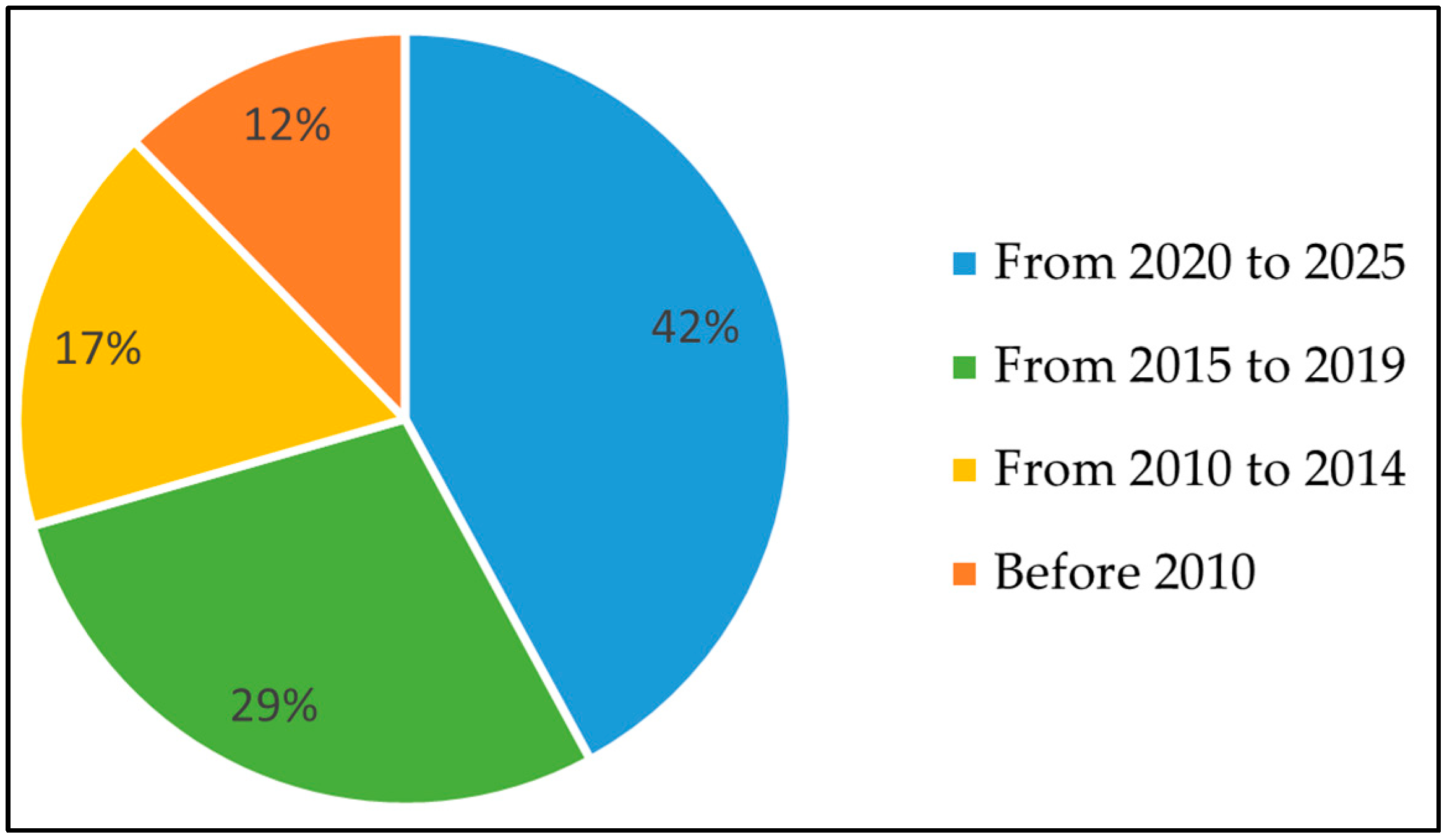
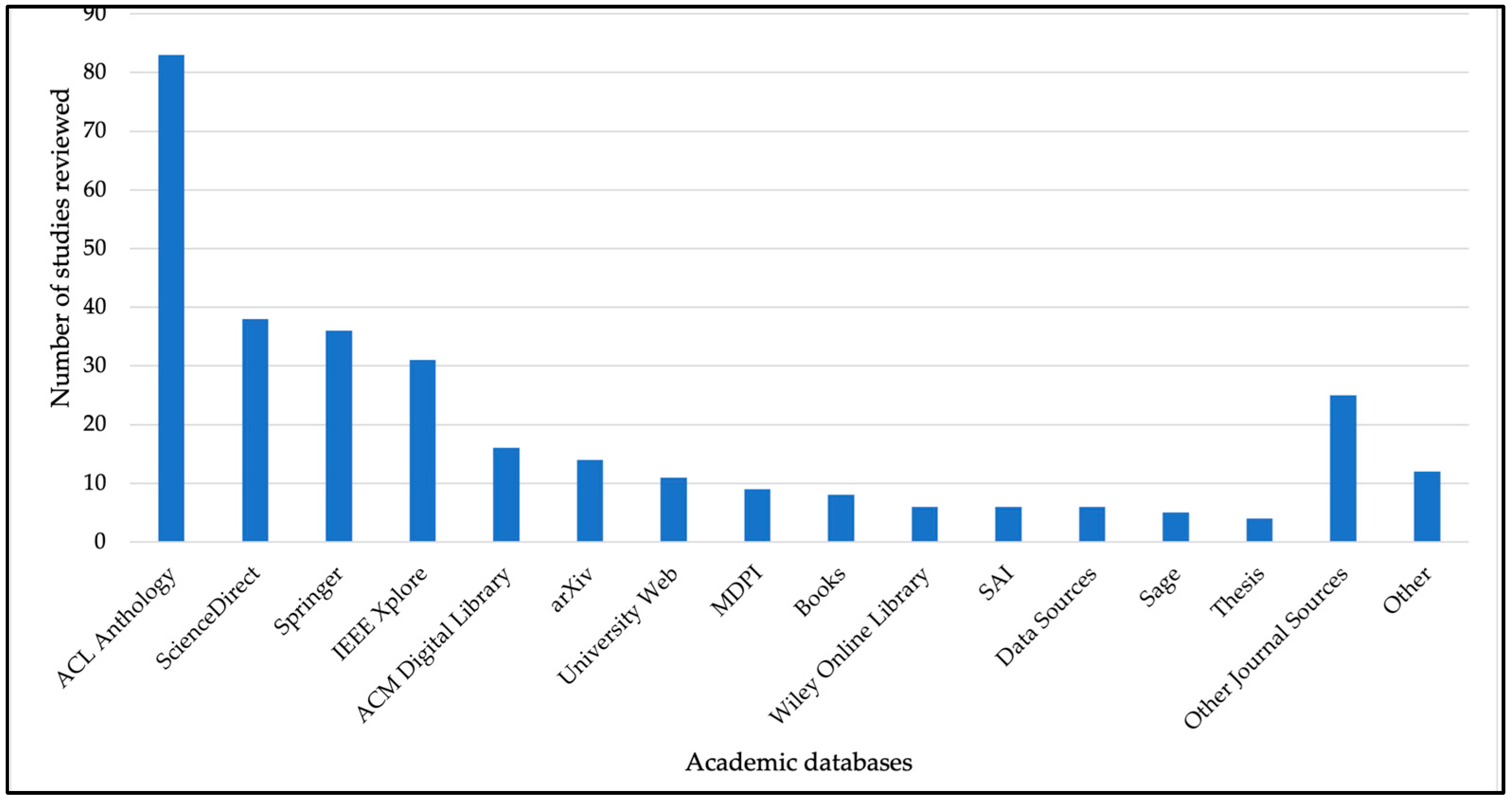
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Article Selection
2.4. Validation
3. Challenges in Arabic NLP
3.1. Complex Morphology
3.2. Diacritics and Orthography
3.3. Ambiguity and Polysemy
3.4. Challenges with Arabic NLP Datasets
4. Techniques in Arabic NLP
4.1. Text Tokenisation and Normalisation
4.2. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
4.3. Part-of-Speech (POS) Tagging
4.4. Lexicon
4.5. Sentiment Analysis
4.6. Text Classification
4.7. Text Summarisation
4.8. Question Answering
4.9. Machine Translation
4.10. Large Language Models (LLMs)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Works
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Future Works
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boudad, N.; Faizi, R.; Oulad Haj Thami, R.; Chiheb, R. Sentiment analysis in Arabic: A review of the literature. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 2479–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaliq, B.; Carroll, J. Unsupervised Induction of Arabic Root and Pattern Lexicons using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing RANLP 2013, Hissar, Bulgaria, 9–11 September 2013; pp. 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Huri, I. Arabic Language: Historic and Sociolinguistic Characteristics. Engl. Lit. Lang. Rev. 2015, 1, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarki, S.; Mourchid, M.; Silberztein, M. (Eds.) Formalizing Natural Languages with NooJ and Its Natural Language Processing Applications. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference, NooJ 2017, Kenitra and Rabat, Morocco, 18–20 May 2017; Revised Selected Papers; Communications in Computer and Information Science, 1st ed.. Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. ISBN 978-3-319-73420-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ryding, K.C. A Reference Grammar of Modern Standard Arabic, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-0-521-77771-1. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, J.J. A Prosodic Theory of Nonconcatenative Morphology. Linguist. Inq. 1981, 12, 373–418. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kabi, M.N.; Kazakzeh, S.A.; Abu Ata, B.M.; Al-Rababah, S.A.; Alsmadi, I.M. A novel root based Arabic stemmer. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2015, 27, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sughaiyer, I.A.; Al-Kharashi, I.A. Arabic morphological analysis techniques: A comprehensive survey. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 2004, 55, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J. (Ed.) The Oxford Handbook of Arabic Linguistics, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-0-19-976413-6. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, M.; Ghoneim, M.; Habash, N. Arabic diacritization in the context of statistical machine translation. In Proceedings of the Machine Translation Summit XI: Papers, Copenhagen, Denmark, 10 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Saiegh-Haddad, E.; Henkin-Roitfarb, R. The Structure of Arabic Language and Orthography. In Handbook of Arabic Literacy; Saiegh-Haddad, E., Joshi, R.M., Eds.; Literacy Studies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 9, pp. 3–28. ISBN 978-94-017-8544-0. [Google Scholar]
- Maroun, M.; Hanley, J.R. Diacritics improve comprehension of the Arabic script by providing access to the meanings of heterophonic homographs. Read. Writ. 2017, 30, 319–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aabed, M.A.; Awaideh, S.M.; Elshafei, A.-R.M.; Gutub, A.A. Arabic Diacritics based Steganography. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 24–27 November 2007; pp. 756–759. [Google Scholar]
- Midhwah, A.A.; Alhawary, M.T. Arabic Diacritics and Their Role in Facilitating Reading Speed, Accuracy, and Comprehension by English L2 Learners of Arabic. Mod. Lang. J. 2020, 104, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennoufi, A.; Mazroui, A. Morphological, syntactic and diacritics rules for automatic diacritization of Arabic sentences. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2017, 29, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaraf, A.; Bekal, S.; Macoir, J. The Orthographic Ambiguity of the Arabic Graphic System: Evidence from a Case of Central Agraphia Affecting the Two Routes of Spelling. Behav. Neurol. 2022, 2022, 8078607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazi, M.O.; Al-Dossari, Y.; Al-Yahy, A.; Al-Sumari, A.; Hilal, A. Preprocessing Arabic text on social media. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farghaly, A.; Shaalan, K. Arabic Natural Language Processing: Challenges and Solutions. ACM Trans. Asian Lang. Inf. Process. 2009, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Elhija, D. A new writing system? Developing orthographies for writing Arabic dialects in electronic media. Writ. Syst. Res. 2014, 6, 190–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadane, H.; Habash, N. A Conventional Orthography for Algerian Arabic. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Arabic Natural Language Processing, Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Cinta, F.; Irawan, B.; Hasan, N. Semantic study: Polysemi in Arabic form of verb and noun. AKSARA J. Bhs. Dan Sastra 2023, 24, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Abdul-Ghafour, A.-Q.K.; Mat Awal, N.; Zainudin, I.S.; Aladdin, A. The Interplay of Qur’ānic Synonymy and Polysemy with Special Reference to Al-asfār and Al-kutub (the Books) and their English Translations. 3L Southeast Asian J. Engl. Lang. Stud. 2019, 25, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lahham, Y.A. Index Term Selection Heuristics for Arabic Text Retrieval. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 3345–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-shameri, N.; Al-Khalifa, H. Arabic paraphrased parallel synthetic dataset. Data Brief 2024, 57, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boujou, E.; Chataoui, H.; Mekki, A.E.; Benjelloun, S.; Chairi, I.; Berrada, I. An open access NLP dataset for Arabic dialects: Data collection, labeling, and model construction. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.11000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, A.; Tuffaha, I.; Al-Ayyoub, M. Neural Arabic Text Diacritization: State-of-the-Art Results and a Novel Approach for Arabic NLP Downstream Tasks. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ayyoub, M.; Nuseir, A.; Alsmearat, K.; Jararweh, Y.; Gupta, B. Deep learning for Arabic NLP: A survey. J. Comput. Sci. 2018, 26, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladeemy, A.A.; Alzahrani, A.; Algarni, M.H.; Alsubari, S.N.; Aldhyani, T.H.H.; Deshmukh, S.N.; Khalaf, O.I.; Wong, W.-K.; Aqburi, S. Advancements and challenges in Arabic sentiment analysis: A decade of methodologies, applications, and resource development. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounhas, I. On the Usage of a Classical Arabic Corpus as a Language Resource: Related Research and Key Challenges. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B. A Theory of the Parts of Speech in Arabic (Noun, Verb and Particle): A Study in “ʿilm al-waḍʿ”. Arabica 1976, 23, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditters, W.E. A Formal Approach to Arabic Syntax: The Noun Phrase and the Verb Phrase. Ph.D. Thesis, Nijmegen University, Nijmegen Luxor, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- McOmber, M.L. Morpheme edges and Arabic infixation. In Current Issues in Linguistic Theory; Eid, M., Ed.; John Benjamins Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 130, p. 173. ISBN 978-90-272-3633-3. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, M.A. Arabic tokenization system. In Proceedings of the 2007 Workshop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Languages Common Issues and Resources-Semitic ’07, Prague, Czech Republic, 28 June 2007; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Qaroush, A.; Abu Farha, I.; Ghanem, W.; Washaha, M.; Maali, E. An efficient single document Arabic text summarization using a combination of statistical and semantic features. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 33, 677–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennoufi, A.; Mazroui, A. Impact of morphological analysis and a large training corpus on the performances of Arabic diacritization. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2016, 19, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.M.; Alnefaie, R.M.; Aboalsamh, H.A. Light Diacritic Restoration to Disambiguate Homographs in Modern Arabic Texts. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, Á. From stigmatization to predilection: Folk metalinguistic discourse on social media on the northwestern Moroccan Arabic variety. Int. J. Sociol. Lang. 2022, 2022, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennafi, M.E.; Bedlaoui, H.; Dahou, A.; Al-Qaness, M.A.A. Arabic Aspect-Based Sentiment Classification Using Seq2Seq Dialect Normalization and Transformers. Knowledge 2022, 2, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, Z.; Junaidi, A. Wamiliana Text Stemming and Lemmatization of Regional Languages in Indonesia: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Inf. Syst. Eng. Bus. Intell. 2024, 10, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, S.; Asif, M.; Rehman, M.; Ahmad, S. Machine learning based framework for fine-grained word segmentation and enhanced text normalization for low resourced language. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoja, S.; Garside, R. Stemming Arabic Text; Computing Department, Lancaster University: Lancaster, UK, 1999; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kabi, M.N. Towards improving Khoja rule-based Arabic stemmer. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Jordan Conference on Applied Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies (AEECT), Amman, Jordan, 3–5 December 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Larkey, L.S.; Ballesteros, L.; Connell, M.E. Light Stemming for Arabic Information Retrieval. In Arabic Computational Morphology; Soudi, A., Bosch, A.V.D., Neumann, G., Eds.; Text, Speech and Language Technology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 38, pp. 221–243. ISBN 978-1-4020-6045-8. [Google Scholar]
- Taghva, K.; Elkhoury, R.; Coombs, J. Arabic stemming without a root dictionary. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technology: Coding and Computing (ITCC’05)-Volume II, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–6 April 2005; Volume 1, pp. 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ghwanmeh, S.; Kanaan, G.; Al-Shalabi, R.; Rabab’ah, S. Enhanced Algorithm for Extracting the Root of Arabic Words. In Proceedings of the 2009 Sixth International Conference on Computer Graphics, Imaging and Visualization, Tianjin, China, 11–14 August 2009; pp. 388–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kanan, T.; Fox, E.A. Automated Arabic text classification with P-Stemmer, machine learning, and a tailored news article taxonomy. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Tech. 2016, 67, 2667–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, R.M.; Zerrouki, T.; Abu Shquier, M.M.; Balla, A. Tashaphyne0.4: A new Arabic light stemmer based on rhyzome modeling approach. Inf. Retr. J. 2023, 26, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habash, N.; Rambow, O.; Roth, R. MADA + TOKAN: A toolkit for Arabic tokenization, diacritization, morphological disambiguation, POS tagging, stemming and lemmatization. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Arabic Language Resources and Tools, Cairo, Egypt, 22–23 April 2009; Volume 41, p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Boudchiche, M.; Mazroui, A. A hybrid approach for Arabic lemmatization. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2019, 22, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiner, L.R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudlal, A.; Lakhouaja, A.; Mazroui, A.; Meziane, A.; Bebah, M.; Shoul, M. Alkhalil morpho sys1: A morphosyntactic analysis system for Arabic texts. In Proceedings of the International Arab Conference on Information Technology, New York, NY, USA, 14–16 December 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Boudchiche, M.; Mazroui, A.; Ould Abdallahi Ould Bebah, M.; Lakhouaja, A.; Boudlal, A. AlKhalil Morpho Sys 2: A robust Arabic morpho-syntactic analyzer. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2017, 29, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrar, M.; Akra, D.; Hammouda, T. Alma: Fast Lemmatizer and POS Tagger for Arabic. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 244, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrar, M.; Hammouda, T.H. Qabas: An Open-Source Arabic Lexicographic Database. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024, Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 13363–13370. [Google Scholar]
- Maamouri, M.; Bies, A.; Kulick, S.; Gaddeche, F.; Mekki, W.; Krouna, S.; Bouziri, B.; Zaghouani, W. Arabic Treebank: Part 2 V 3.1; Linguistic Data Consortium: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrar, M.; Malaysha, S.; Hammouda, T.; Khalilia, M. SALMA: Arabic Sense-Annotated Corpus and WSD Benchmarks. In Proceedings of the ArabicNLP 2023, Singapore (hybrid conference), 7 December 2023; pp. 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Emam, O.; Hassan, H. Language model based Arabic word segmentation. In Proceedings of the 41st Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics-ACL ’03, Sapporo, Japan, 7–12 July 2003; Volume 1, pp. 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- El Isbihani, A.; Khadivi, S.; Bender, O.; Ney, H. Morpho-syntactic Arabic Preprocessing for Arabic to English Statistical Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation, New York, NY, USA, 8–9 June 2006; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hammouda, N.G.; Haddar, K. Integration of a Segmentation Tool for Arabic Corpora in NooJ Platform to Build an Automatic Annotation Tool. In Proceedings of the Automatic Processing of Natural-Language Electronic Texts with NooJ, České Budějovice, Czech Republic, 9–11 June 2016; pp. 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Silberztein, M.; Váradi, T.; Tadić, M. Open source multi-platform NooJ for NLP. In Proceedings of the COLING 2012, Mumbai, India, 8–15 December 2012; pp. 401–408. [Google Scholar]
- Souri, A.; Al Achhab, M.; El Mouhajir, B.E. A Proposed Approach for Arabic Language Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 First International Conference on Arabic Computational Linguistics (ACLing), Cairo, Egypt, 17–20 April 2015; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Monroe, W.; Green, S.; Manning, C.D. Word Segmentation of Informal Arabic with Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–27 June 2014; pp. 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Eldesouki, M.; Samih, Y.; Abdelali, A.; Attia, M.; Mubarak, H.; Darwish, K.; Laura, K. Arabic Multi-Dialect Segmentation: Bi-LSTM-CRF vs. SVM. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.05891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheragui, M.A.; Hiri, E. Arabic Text Segmentation using Contextual Exploration and Morphological Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Mathematics and Information Technology (ICMIT), Adrar, Algeria, 18–19 February 2020; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Pasha, A.; Al-Badrashiny, M.; Diab, M.; El Kholy, A.; Eskander, R.; Habash, N.; Pooleery, M.; Rambow, O.; Roth, R. MADAMIRA: A Fast, Comprehensive Tool for Morphological Analysis and Disambiguation of Arabic. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’14), Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; pp. 1094–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, M. Second generation AMIRA tools for Arabic processing: Fast and robust tokenization, POS tagging, and base phrase chunking. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Arabic Language Resources and Tools, Cairo, Egypt, 22–23 April 2009; Volume 110, p. 198. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelali, A.; Darwish, K.; Durrani, N.; Mubarak, H. Farasa: A Fast and Furious Segmenter for Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Demonstrations, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, K.; Mubarak, H. Farasa: A New Fast and Accurate Arabic Word Segmenter. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 1070–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Obeid, O.; Zalmout, N.; Khalifa, S.; Taji, D.; Oudah, M.; Alhafni, B.; Inoue, G.; Eryani, F.; Erdmann, A.; Habash, N. CAMeL tools: An open source python toolkit for Arabic natural language processing. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 7022–7032. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, C.; Surdeanu, M.; Bauer, J.; Finkel, J.; Bethard, S.; McClosky, D. The Stanford CoreNLP Natural Language Processing Toolkit. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–27 June 2014; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Benajiba, Y.; Diab, M.; Rosso, P. Arabic Named Entity Recognition using Optimized Feature Sets. In Proceedings of the 2008 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–27 October 2008; pp. 284–293. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, K. Named Entity Recognition using Cross-lingual Resources: Arabic as an Example. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 1558–1567. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, R.E.; Binti Zakaria, L.Q. Building the Classical Arabic Named Entity Recognition Corpus (CANERCorpus). In Proceedings of the 2018 Fourth International Conference on Information Retrieval and Knowledge Management (CAMP), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 26–28 March 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qurishi, M.S.; Souissi, R. Arabic Named Entity Recognition Using Transformer-based-CRF Model. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Natural Language and Speech Processing (ICNLSP 2021), Trento, Italy, 12–13 November 2021; pp. 262–271. [Google Scholar]
- Oudah, M.; Shaalan, K. A Pipeline Arabic Named Entity Recognition using a Hybrid Approach. In Proceedings of the COLING 2012, Mumbai, India, 8–15 December 2012; pp. 2159–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; van der Goot, R.; Rehman, M.; Kruse, C.; Özsoy, Ö.; Mehler, A.; Roig, G. Tafsir Dataset: A Novel Multi-Task Benchmark for Named Entity Recognition and Topic Modeling in Classical Arabic Literature. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 12–17 October 2022; pp. 3753–3768. [Google Scholar]
- Albahli, S. An Advanced Natural Language Processing Framework for Arabic Named Entity Recognition: A Novel Approach to Handling Morphological Richness and Nested Entities. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahou, A.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Mohamed, H.; Dahou, A.H.; Al-Qaness, M.A.A.; Ghetas, M.; Ewess, A.; Zheng, Z. Linguistic feature fusion for Arabic fake news detection and named entity recognition using reinforcement learning and swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 2024, 598, 128078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hkiri, E.; Mallat, S.; Zrigui, M. Arabic-English Text Translation Leveraging Hybrid NER. In Proceedings of the 31st Pacific Asia Conference on Language, Information and Computation, Cebu City, Philippines, 16–18 November 2017; pp. 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Asbayou, O. Automatic Arabic Named Entity Extraction and Classification for Information Retrieval. In Proceedings of the International Journal on Natural Language Computing, Zurich, Switzerland, 21–22 November 2020; Volume 9, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sabty, C.; Elmahdy, M.; Abdennadher, S. Arabic Named Entity Recognition Using Clustered Word Embedding. In Proceedings of the Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing, La Rochelle, France, 7–13 April 2019; pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Abouenour, L.; Bouzoubaa, K.; Rosso, P. IDRAAQ: New Arabic Question Answering system based on Query Expansion and Passage Retrieval. In Proceedings of the CLEF 2012—QA4MRE Workshop, CEUR Workshop Proceedings. Rome, Italy, 17–20 September 2012; Volume 1178. [Google Scholar]
- Essa, N.; El-Gayar, M.M.; El-Daydamony, E.M. Enhanced model for abstractive Arabic text summarization using natural language generation and named entity recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 37, 7279–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, S.; Elarnaoty, M.; Magdy, M.; Fahmy, A. Integrated Machine Learning Techniques for Arabic Named Entity Recognition. Int. J. Sci. Innov. Eng. 2010, 7, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Shaalan, K.; Raza, H. Person Name Entity Recognition for Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2007 Workshop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Languages: Common Issues and Resources, Prague, Czech Republic, 28 June 2007; pp. 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Alkharashi, I. Person named entity generation and recognition for Arabic language. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Arabic Language Resources and Tools, Cairo, Egypt, 22–23 April 2009; pp. 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Shaalan, K.; Raza, H. NERA: Named Entity Recognition for Arabic. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 2009, 60, 1652–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habash, N.Y. Introduction to Arabic Natural Language Processing; Synthesis Lectures on Human Language Technologies; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2010; ISBN 978-3-031-01011-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zaraket, F.A.; Jaber, A. MATAr: Morphology-based Tagger for Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACS International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Ifrane, Morocco, 27–30 May 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Albared, M.; Omar, N.; Ab Aziz, M.J. Developing a Competitive HMM Arabic POS Tagger Using Small Training Corpora. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Information and Database Systems ACIIDS 2011, Daegu, Korea, 20–22 April 2011; pp. 288–296. [Google Scholar]
- AlGahtani, S.; Black, W.; McNaught, J. Arabic Part-Of-Speech Tagging Using Transformation-Based Learning; Citeseer: Cairo, Egypt, 2009; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- El Hadj, Y.; Al-Sughayeir, I.; Al-Ansari, A. Arabic Part-of-Speech Tagging Using the Sentence Structure; Citeseer: Cairo, Egypt, 2009; pp. 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, M.; Rashwan, M.A.A.; Al-Badrashiny, M.A.S.A.A. Fassieh, a Semi-Automatic Visual Interactive Tool for Morphological, PoS-Tags, Phonetic, and Semantic Annotation of Arabic Text Corpora. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2009, 17, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, A.; Nasr, A.; Habash, N.; Gala, N. POS-tagging of Tunisian Dialect Using Standard Arabic Resources and Tools. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Arabic Natural Language Processing, Association for Computational Linguistics. Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, K.M.O.; Al Eroud, A.F.; Barahoush, M.; Al-Akhras, A.M. SAP: Standard Arabic Profiling Toolset for Textual Analysis. Int. J. Mach. Learn. 2019, 9, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallas, O.; Inoue, G.; Habash, N. EMAD: A Bridge Tagset for Unifying Arabic POS Annotations. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 5637–5643. [Google Scholar]
- Himdi, H.T.; Assiri, F.Y. Tasaheel: An Arabic Automative Textual Analysis Tool—All in One. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 139979–139992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tnaji, K.; Bouzoubaa, K.; Aouragh, S.L. A Light Arabic POS Tagger Using a Hybrid Approach. In Digital Technologies and Applications; Motahhir, S., Bossoufi, B., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 211, pp. 199–208. ISBN 978-3-030-73881-5. [Google Scholar]
- Saidi, R.; Jarray, F.; Mansour, M. A BERT Based Approach for Arabic POS Tagging. In Advances in Computational Intelligence; Rojas, I., Joya, G., Català, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 12861, pp. 311–321. ISBN 978-3-030-85029-6. [Google Scholar]
- Al Shamsi, F.; Guessoum, A. A hidden Markov model-based POS tagger for Arabic. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on the Statistical Analysis of Textual Data, Besançon, France, 19–21 April 2006; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Ababou, N.; Mazroui, A. A hybrid Arabic POS tagging for simple and compound morphosyntactic tags. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2016, 19, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKhwiter, W.; Al-Twairesh, N. Part-of-speech tagging for Arabic tweets using CRF and Bi-LSTM. Comput. Speech Lang. 2021, 65, 101138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, Y.M.; Abdel-Galil, H.; El-Fatah Belal, M.A. Arabic ontology extraction model from unstructured text. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 6066–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, S.A.; Samawi, V.W.; Elkabani, I.; Zantout, R. The effect of combining different semantic relations on Arabic text classification. World Comput. Sci. Inform. Technol. J. 2015, 5, 12–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yousif, S.A.; Samawi, V.W.; Elkabani, I.; Zantout, R. Enhancement of Arabic text classification using semantic relations with part of speech tagger. W Trans. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2015, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Himdi, H.T. Classification of Arabic Real and Fake News Based on Arabic Textual Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alias, N.; Rahman, N.A.; Alias, M.N.; Nor, Z.M.; Ahmad, N.A.; Ismail, N.K. Tagging Algorithm and POS Tags for Narrator’s Name in Hadith Document. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Sciences (AiDAS), Ipoh, Malaysia, 6–7 September 2023; pp. 126–130. [Google Scholar]
- Nerabie, A.M.; AlKhatib, M.; Mathew, S.S.; Barachi, M.E.; Oroumchian, F. The Impact of Arabic Part of Speech Tagging on Sentiment Analysis: A New Corpus and Deep Learning Approach. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 184, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, K.; Mubarak, H.; Abdelali, A.; Eldesouki, M. Arabic POS Tagging: Don’t Abandon Feature Engineering Just Yet. In Proceedings of the Third Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Valencia, Spain, 3 April 2017; pp. 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Calzolari, N.; Gangemi, A.; Lenci, A.; Oltramari, A.; Prevot, L. (Eds.) Ontology and the Lexicon: A Natural Language Processing Perspective, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-521-88659-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pustejovsky, J.; Boguraev, B. Lexical knowledge representation and natural language processing. Artif. Intell. 1993, 63, 193–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaik, K.A.; Saad, M.; Chatzikyriakidis, S.; Dobnik, S. A Lexical Distance Study of Arabic Dialects. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 142, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, M.; Atwell, E.; Abushariah, M.A.M. SALMA: Standard Arabic Language Morphological Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 1st International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and their Applications (ICCSPA), Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 12–14 February 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Smrž, O. ElixirFM—Implementation of Functional Arabic Morphology. In Proceedings of the 2007 Workshop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Languages: Common Issues and Resources, Prague, Czech Republic, 28 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter, T. Buckwalter Arabic Morphological Analyzer Version 1.0; Linguistic Data Consortium: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwalter, T. Buckwalter Arabic Morphological Analyzer Version 2.0; Linguistic Data Consortium: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskenniemi, K. Two-Level Morphology: A General Computational Model for Word-Form Recognition and Production; Department of General Linguistics, University of Helsinki: Helsinki, Finland, 1983; ISBN 951-45-3201-5. [Google Scholar]
- Beesley, K.R. Arabic finite-state morphological analysis and generation. In Proceedings of the 16th conference on Computational Linguistics, Copenhagen, Denmark, 5–9 August 1996; Association for Computational Linguistics: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1996; Volume 1, p. 89. [Google Scholar]
- Gridach, M.; Chenfour, N. Developing a new system for Arabic morphological analysis and generation. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on South Southeast Asian Natural Language Processing (WSSANLP), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 8–9 November 2011; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Manour, S.; Sima’an, K.; Winter, Y. Smoothing a lexicon-based pos tagger for Arabic and Hebrew. In Proceedings of the 2007 Workshop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Languages: Common Issues and Resources, Prague, Czech Republic, 28 June 2007; pp. 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sabbagh, R.; Girju, R. A supervised POS tagger for written Arabic social networking corpora. In Proceedings of the KONVENS2012—The 11th Conference on Natural Language Processing, Vienna, Austria, 19–21 September 2012; pp. 39–52. [Google Scholar]
- Attia, M.; Toral, A.; Tounsi, L.; Monachini, M.; van Genabith, J. An Automatically Built Named Entity Lexicon for Arabic; European Language Resources Association: Valletta, Malta, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, J. Lexicon-driven approach to the recognition of Arabic named entities. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Arabic Language Resources and Tools, Cairo, Egypt, 22–23 April 2009; pp. 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Hkiri, E.; Mallat, S.; Zrigui, M.; Mars, M. Constructing a Lexicon of Arabic-English Named Entity using SMT and Semantic Linked Data. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. (IAJIT) 2017, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Benajiba, Y.; Zitouni, I.; Diab, M.; Rosso, P. Arabic Named Entity Recognition: Using Features Extracted from Noisy Data. In Proceedings of the ACL 2010 Conference Short Papers, Uppsala, Sweden, 11–16 July 2010; pp. 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Badaro, G.; Baly, R.; Hajj, H.; Habash, N.; El-Hajj, W. A large scale Arabic sentiment lexicon for Arabic opinion mining. In Proceedings of the EMNLP 2014 Workshop on Arabic Natural Language Processing (ANLP), Doha, Qatar, 25 October 2014; pp. 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Hakami, S.A.A.; Hendley, R.; Smith, P. Arabic Emoji Sentiment Lexicon (Arab-ESL): A Comparison between Arabic and European Emoji Sentiment Lexicons. In Proceedings of the Sixth Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Kyiv, Ukraine, 19 April 2021; pp. 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Khabour, S.M.; Al-Radaideh, Q.A.; Mustafa, D. A New Ontology-Based Method for Arabic Sentiment Analysis. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, S.M.; Alamoodi, A.H. Lexicon annotation in sentiment analysis for dialectal Arabic: Consensus Expert Standardized Criteria. Appl. Data Sci. Anal. 2024, 2024, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfreihat, M.; Almousa, O.S.; Tashtoush, Y.; AlSobeh, A.; Mansour, K.; Migdady, H. Emo-SL Framework: Emoji Sentiment Lexicon Using Text-Based Features and Machine Learning for Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 81793–81812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M. Arabic sentiment analysis about online learning to mitigate COVID-19. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 30, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moslmi, T.; Albared, M.; Al-Shabi, A.; Omar, N.; Abdullah, S. Arabic senti-lexicon: Constructing publicly available language resources for Arabic sentiment analysis. J. Inf. Sci. 2018, 44, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.; Salameh, M.; Kiritchenko, S. Sentiment Lexicons for Arabic Social Media. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sallab, A.; Baly, R.; Hajj, H.; Shaban, K.B.; El-Hajj, W.; Badaro, G. AROMA: A Recursive Deep Learning Model for Opinion Mining in Arabic as a Low Resource Language. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukry, A.M. Arabic Sentence-Level Sentiment Analysis. Master’s Thesis, American University in Cairo, New Cairo, Egypt, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman, S.E.; Mobarz, H.; Farag, I.; Rashwan, M. Arabic Phrase-Level Contextual Polarity Recognition to Enhance Sentiment Arabic Lexical Semantic Database Generation. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Dabet, S.; Tedmori, S.; AL-Smadi, M. Enhancing Arabic aspect-based sentiment analysis using deep learning models. Comput. Speech Lang. 2021, 69, 101224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farra, N.; Challita, E.; Abou Assi, R.; Hajj, H. Sentence-level and document-level sentiment mining for Arabic texts. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 13 December 2010; pp. 1114–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Alayba, A.M.; Palade, V.; England, M.; Iqbal, R. A Combined CNN and LSTM Model for Arabic Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, Hamburg, Germany, 27–30 August 2018; pp. 179–191. [Google Scholar]
- El-Beltagy, S.R. NileULex: A Phrase and Word Level Sentiment Lexicon for Egyptian and Modern Standard Arabic. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 2900–2905. [Google Scholar]
- Alharbi, A.I.; Smith, P.; Lee, M. Integrating Character-level and Word-level Representation for Affect in Arabic Tweets. Data Knowl. Eng. 2022, 138, 101973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwairi, R.M.; Qarqaz, I. Arabic Sentiment Analysis Using Supervised Classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, Barcelona, Spain, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 579–583. [Google Scholar]
- Duwairi, R.; El-Orfali, M. A study of the effects of preprocessing strategies on sentiment analysis for Arabic text. J. Inf. Sci. 2014, 40, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwairi, R.M.; Marji, R.; Sha’ban, N.; Rushaidat, S. Sentiment Analysis in Arabic tweets. In Proceedings of the 2014 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), Irbid, Jordan, 1–3 April 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hamouda, A.E.-D.A.; El-taher, F.E. Sentiment analyzer for Arabic comments system. IJACSA. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Halees, A.M. Arabic text classification using maximum entropy. IUG J. Nat. Stud. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Alayba, A.M.; Palade, V.; England, M.; Iqbal, R. Arabic language sentiment analysis on health services. In Proceedings of the 2017 1st International Workshop on Arabic Script Analysis and Recognition (ASAR), Nancy, France, 3–5 April 2017; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kabi, M.N.; Gigieh, A.H.; Alsmadi, I.M.; Wahsheh, H.A.; Haidar, M.M. Opinion mining and analysis for Arabic language. IJACSA Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2014, 5, 181–195. [Google Scholar]
- Duwairi, R.M. Sentiment analysis for dialectical Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2015 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), Amman, Jordan, 7–9 April 2015; pp. 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, N.A.; Ahmed, N.A.; Shehab, M.A.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Al-Kabi, M.N.; Al-rifai, S. Towards Improving the Lexicon-Based Approach for Arabic Sentiment Analysis. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Web Eng. 2014, 9, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Posner, R.; Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Nabavi, S. Applying deep learning in digital breast tomosynthesis for automatic breast cancer detection: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 71, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusner, M.; Sun, Y.; Kolkin, N.; Weinberger, K. From Word Embeddings To Document Distances. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 957–966. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C. GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Joulin, A.; Grave, E.; Bojanowski, P.; Mikolov, T. Bag of Tricks for Efficient Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Volume 2, Short Papers. Valencia, Spain, 3–7 April 2017; pp. 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Al Sallab, A.; Hajj, H.; Badaro, G.; Baly, R.; El Hajj, W.; Bashir Shaban, K. Deep Learning Models for Sentiment Analysis in Arabic. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Arabic Natural Language Processing, Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Dahou, A.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, J.; Haddoud, M.H.; Duan, P. Word Embeddings and Convolutional Neural Network for Arabic Sentiment Classification. In Proceedings of the COLING 2016, the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers, Osaka, Japan, 11–17 December 2016; pp. 2418–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Alhumoud, S.O.; Al Wazrah, A.A. Arabic sentiment analysis using recurrent neural networks: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 707–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazrah, A.A.; Alhumoud, S. Sentiment Analysis Using Stacked Gated Recurrent Unit for Arabic Tweets. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 137176–137187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smadi, M.; Talafha, B.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Jararweh, Y. Using long short-term memory deep neural networks for aspect-based sentiment analysis of Arabic reviews. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cyber. 2019, 10, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoun, W.; Baly, F.; Hajj, H. AraBERT: Transformer-based Model for Arabic Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Open-Source Arabic Corpora and Processing Tools, with a Shared Task on Offensive Language Detection, Marseille, France, 12 May 2020; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, O.; Kassem, A.M.; Ashraf, A.; Jamal, S.; Mohamed, E.H. An ensemble transformer-based model for Arabic sentiment analysis. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrey, L.; Shavlik, J. Transfer Learning. In Handbook of Research on Machine Learning Applications and Trends; Olivas, E.S., Guerrero, J.D.M., Martinez-Sober, M., Magdalena-Benedito, J.R., Serrano López, A.J., Eds.; IGI Global: Palmdale, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 242–264. ISBN 978-1-60566-766-9. [Google Scholar]
- Bensoltane, R.; Zaki, T. Towards Arabic aspect-based sentiment analysis: A transfer learning-based approach. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2022, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayba, A.M.; Palade, V. Leveraging Arabic sentiment classification using an enhanced CNN-LSTM approach and effective Arabic text preparation. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 9710–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, O. A deep learning approach combining CNN and Bi-LSTM with SVM classifier for Arabic sentiment analysis. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldayel, H.K.; Azmi, A.M. Arabic tweets sentiment analysis—A hybrid scheme. J. Inf. Sci. 2016, 42, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabil, M.; Aly, M.; Atiya, A. ASTD: Arabic Sentiment Tweets Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; pp. 2515–2519. [Google Scholar]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S.; AL-Smadi, M.; Al-Ayyoub, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, B.; De Clercq, O.; et al. SemEval-2016 Task 5: Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2016), San Diego, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2016; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, S.; Farra, N.; Nakov, P. SemEval-2017 Task 4: Sentiment Analysis in Twitter. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2017), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–4 August 2017; pp. 502–518. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, N.A.; Ahmed, N.A.; Shehab, M.A.; Al-Ayyoub, M. Arabic sentiment analysis: Lexicon-based and corpus-based. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Jordan Conference on Applied Electrical Engineering and Computing Technologies (AEECT), Amman, Jordan, 3–5 December 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nabil, M.; Aly, M.; Atiya, A. LABR: A Large Scale Arabic Sentiment Analysis Benchmark. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagar, A.; Khalifa, Y.S.; Einea, A. Hotel Arabic-Reviews Dataset Construction for Sentiment Analysis Applications. In Intelligent Natural Language Processing: Trends and Applications; Shaalan, K., Hassanien, A.E., Tolba, F., Eds.; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 740, pp. 35–52. ISBN 978-3-319-67055-3. [Google Scholar]
- Alayba, A.M.; Palade, V.; England, M.; Iqbal, R. Improving Sentiment Analysis in Arabic Using Word Representation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Workshop on Arabic and Derived Script Analysis and Recognition (ASAR), London, UK, 12–14 March 2018; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gamal, D.; Alfonse, M.; El-Horbaty, E.-S.M.; Salem, A.-B.M. Twitter benchmark dataset for Arabic sentiment analysis. Int. J. Mod. Educ. Comput. Sci. 2019, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Twairesh, N.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Al-Salman, A.; Al-Ohali, Y. AraSenTi-Tweet: A Corpus for Arabic Sentiment Analysis of Saudi Tweets. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 117, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnawas, A.; Arıcı, N. The corpus based approach to sentiment analysis in modern standard Arabic and Arabic dialects: A literature review. Politek. Derg. 2018, 21, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhamed, M.; Sutcliffe, R.; Quteineh, H.; Sun, X.; Almekhlafi, E.; Retta, E.A.; Feng, J. A deep CNN architecture with novel pooling layer applied to two Sudanese Arabic sentiment data sets. J. Inf. Sci. 2023, 01655515231188341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnawas, A.; Arici, N. Sentiment analysis of Iraqi Arabic dialect on Facebook based on distributed representations of documents. ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. (TALLIP) 2019, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussous, A.; Benjelloun, F.-Z.; Lahcen, A.A.; Belfkih, S. ASA: A framework for Arabic sentiment analysis. J. Inf. Sci. 2020, 46, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, T.M.; Sharef, B.T.; Grosan, C.; Li, Y. Transfer learning and sentiment analysis of Bahraini dialects sequential text data using multilingual deep learning approach. Data Knowl. Eng. 2023, 143, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelli, A.; Guerrouf, F.; Tibermacine, O.; Abdelli, B. Sentiment Analysis of Arabic Algerian Dialect Using a Supervised Method. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Advanced Computing Sciences (ISACS), Taza, Morocco, 26–27 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shoukry, A.S.; Rafea, A. A Hybrid Approach for Sentiment Classification of Egyptian Dialect Tweets. In Proceedings of the 2015 First International Conference on Arabic Computational Linguistics (ACLing), Cairo, Egypt, 17–20 April 2015; pp. 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Al Shamsi, A.; Abdallah, S. Sentiment Analysis of Emirati Dialect. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atoum, J.O.; Nouman, M. Sentiment analysis of Arabic Jordanian dialect tweets. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraty, R.; Chehade, M. Transfer learning and sentiment analysis of lebanese dialect data using a multilingual deep learning approach. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2025, 28, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroub, M.K.; Maghari, A.Y.; Alashqar, A.M. Sentiment Analysis of Palestinian Arabic Dialect Using Lexicon-Based Approach. Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst. 2024, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medhaffar, S.; Bougares, F.; Estève, Y.; Hadrich-Belguith, L. Sentiment Analysis of Tunisian Dialects: Linguistic Ressources and Experiments. In Proceedings of the Third Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Valencia, Spain, 03 April 2017; pp. 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Najar, D.; Mesfar, S. Opinion mining and sentiment analysis for Arabic on-line texts: Application on the political domain. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2017, 20, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, S.M.; Alotaibi, F.M. A comparative analysis for Arabic sentiment analysis models in e-marketing using deep learning techniques. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2023, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaqtari, H.; Zeng, F.; Mohammed, A. Enhancing Arabic Sentiment Analysis of Consumer Reviews: Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methods Based on NLP. Algorithms 2024, 17, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayba, A. Twitter Sentiment Analysis on Health Services in Arabic. Ph.D. Thesis, Coventry University, Coventry, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alzahrani, M.; AlGhamdi, F. Social Media Sentiment Analysis for Sustainable Rural Event Planning: A Case Study of Agricultural Festivals in Al-Baha, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomari, E.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I. Sentiment analysis of Arabic tweets for road traffic congestion and event detection. In Smart Infrastructure and Applications: Foundations for Smarter Cities and Societies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Basabain, S.; Al-Dubai, A.; Cambria, E.; Alomar, K.; Hussain, A. Arabic Short-Text Dataset for Sentiment Analysis of Tourism and Leisure Events. Expert Syst. 2025, 42, e70030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishac, W.; Javani, V.; Youssef, D. Leveraging sentiment analysis of Arabic tweets for the 2022 FIFA world cup insights, incorporating the gulf region. Manag. Sport Leis. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Smaili, K. Comparison of topic identification methods for arabic language. In Proceedings of the International Conference RANLP-2005 (Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing), Borovets, Bulgaria, 21–23 September 2005; pp. 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Moh’d A Mesleh, A. Chi square feature extraction based svms Arabic text categorization system. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Software and Data Technologies-PL/DPS/KE/WsMUSE, Barcelona, Spain, 22–25 July 2007; Volume 2, pp. 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, M.K.; Ashour, W. Osac: Open source Arabic corpora. In Proceedings of the 6th ArchEng International Symposiums, EEECS’10, Lefke, North Cyprus, 25–26 November 2010; Volume 10, p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, M.; Smaïli, K.; Berkani, D. Evaluation of topic identification methods on Arabic corpora. J. Digit. Inf. Manag. 2011, 9, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Selab, E.; Guessoum, A. Building TALAA, a Free General and Categorized Arabic Corpus. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence-Volume 1, Setubal, Portugal, 10–12 January 2015; pp. 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Chouigui, A.; Khiroun, O.B.; Elayeb, B. ANT Corpus: An Arabic News Text Collection for Textual Classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACS 14th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Hammamet, Tunisia, 30 October–3 November 2017; pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Boukil, S.; Biniz, M.; Adnani, F.E.; Cherrat, L.; Moutaouakkil, A.E.E. Arabic Text Classification Using Deep Learning Technics. Int. J. Grid Distrib. Comput. 2018, 11, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal, M.; Madbouly, M.M.; El-Zoghby, A. Classifying Arabic text using deep learning. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2019, 97, 3412–3422. [Google Scholar]
- Einea, O.; Elnagar, A.; Al Debsi, R. SANAD: Single-label Arabic News Articles Dataset for Automatic Text Categorization. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Salemi, B.; Ayob, M.; Kendall, G.; Noah, S.A.M. Multi-label Arabic text categorization: A benchmark and baseline comparison of multi-label learning algorithms. Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Debsi, R.; Elnagar, A.; Einea, O. NADiA: News Articles Dataset in Arabic for Multi-Label Text Categorization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuzaini, H.A.; Azmi, A.M. Impact of Stemming and Word Embedding on Deep Learning-Based Arabic Text Categorization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 127913–127928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdeir, A.M.; Ibrahim, F. A Framework for Arabic Tweets Multi-label Classification Using Word Embedding and Neural Networks Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd International Conference on Big Data Engineering, New York, NY, USA, 29–31 May 2020; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Altamimi, M.; Alayba, A.M. ANAD: Arabic news article dataset. Data Brief 2023, 50, 109460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchiha, D.; Bouziane, A.; Doumi, N.; Berbouchi, F.O.; Kebir, A.A.; Mebarki, N.; Benameur, B.A. WiHArD: Wikipedia Based Hierarchical Arabic Dataset for Text Classification. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Embedded & Distributed Systems (EDiS), Bechar, Algeria, 3–5 November 2024; pp. 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Farha, I.A.; Magdy, W. From Arabic Sentiment Analysis to Sarcasm Detection: The ArSarcasm Dataset. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Open-Source Arabic Corpora and Processing Tools, Paris, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Alayba, A.M.; Altamimi, M. Optimization of Arabic text classification using SVM integrated with word embedding models on a novel dataset. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2025, 12, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayba, A. ANACD-Arabic-News-Article-Classification-Dataset; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanfouri, I.; Tlik, G.; Jarray, F. An automatic arabic text summarization system based on genetic algorithms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 189, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, Y.; Bouzoubaa, K. Towards a New Hybrid Approach for Abstractive Summarization. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 142, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarelis, N.; Mastrokostas, C.; Karacapilidis, N. Abstractive vs. Extractive Summarization: An Experimental Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.; Al-Shaar, M. Method for Arabic text Summarization using statistical features and word2vector approach. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Computer Technology Applications, Vienna, Austria, 20 August 2023; pp. 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Khassawneh, Y.A.; Hanandeh, E.S. Extractive Arabic Text Summarization-Graph-Based Approach. Electronics 2023, 12, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazery, Y.M.; Saleh, M.E.; Alharbi, A.; Ali, A.A. Abstractive Arabic Text Summarization Based on Deep Learning. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1566890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etaiwi, W.; Awajan, A. SemG-TS: Abstractive Arabic Text Summarization Using Semantic Graph Embedding. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Qassem, L.; Wang, D.; Barada, H.; Al-Rubaie, A.; Almoosa, N. Automatic Arabic text summarization based on fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Natural Language and Speech Processing, Trento, Italy, 12–13 September 2019; pp. 42–48. [Google Scholar]
- Belkebir, R.; Guessoum, A. A Supervised Approach to Arabic Text Summarization Using AdaBoost. In New Contributions in Information Systems and Technologies; Rocha, A., Correia, A.M., Costanzo, S., Reis, L.P., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 353, pp. 227–236. ISBN 978-3-319-16485-4. [Google Scholar]
- Alshemaimri, B.; Alrayes, I.; Alothman, T.; Almalik, F.; Almotlaq, M. Summarizing Arabic Articles using Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Advanced Natural Language Processing, May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bani-Almarjeh, M.; Kurdy, M.-B. Arabic abstractive text summarization using RNN-based and transformer-based architectures. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Reda, A.; Salah, N.; Adel, J.; Ehab, M.; Ahmed, I.; Magdy, M.; Khoriba, G.; Mohamed, E.H. A Hybrid Arabic Text Summarization Approach based on Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Mobile, Intelligent, and Ubiquitous Computing Conference (MIUCC), Cairo, Egypt, 8–9 May 2022; pp. 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- El-Haj, M.; Kruschwitz, U.; Fox, C. Creating language resources for under-resourced languages: Methodologies, and experiments with Arabic. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2015, 49, 549–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamadani, A.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Khatri, A.; Lu, C.-T. LANS: Large-scale Arabic News Summarization Corpus. In Proceedings of the ArabicNLP 2023, Singapore (hybrid conference), 7 December 2023; pp. 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Almarjeh, M.B. SumArabic; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahla, M.; Yang, Z.G.; Novák, A. Cross-lingual Fine-tuning for Abstractive Arabic Text Summarization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing (RANLP 2021), Online, 1–3 September 2021; pp. 655–663. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Maleh, M.; Desouki, S. Arabic text summarization using deep learning approach. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Gao, M.; Wan, X. Is Summary Useful or Not? An Extrinsic Human Evaluation of Text Summaries on Downstream Tasks. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 9389–9404. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-Y. ROUGE: A Package for Automatic Evaluation of Summaries. In Proceedings of the Text Summarization Branches Out, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 July 2004; pp. 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Alahmadi, D.; Wali, A.; Alzahrani, S. TAAM: Topic-aware abstractive Arabic text summarisation using deep recurrent neural networks. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 2651–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Numai, A.; Azmi, A. LEMMA-ROUGE: An Evaluation Metric for Arabic Abstractive Text Summarization. Indones. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 12, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khawaldeh, F.; Samawi, V. Lexical cohesion and entailment based segmentation for Arabic text summarization (lceas). World Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. J. (WSCIT) 2015, 5, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Azmi, A.M.; Al-Thanyyan, S. A text summarizer for Arabic. Comput. Speech Lang. 2012, 26, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elayeb, B.; Chouigui, A.; Bounhas, M.; Khiroun, O.B. Automatic Arabic Text Summarization Using Analogical Proportions. Cogn. Comput. 2020, 12, 1043–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammo, B.; Abu-Salem, H.; Lytinen, S. QARAB: A question answering system to support the Arabic language. In Proceedings of the ACL-02 workshop on Computational Approaches to Semitic Languages, Philadelphia, PA, USA, July 2002; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Maraoui, H.; Haddar, K.; Romary, L. Arabic factoid Question-Answering system for Islamic sciences using normalized corpora. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 192, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadaoui, Z.; Tlig, G.; Jarray, F. LLMs Based Approach for Quranic Question Answering. 2024. Available online: https://www.scitepress.org/Papers/2024/130129/130129.pdf (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Al-Smadi, M.; Al-Dalabih, I.; Jararweh, Y.; Juola, P. Leveraging Linked Open Data to Automatically Answer Arabic Questions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 177122–177136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdour, W.N.; Gharaibeh, N.K. Development of Yes/No Arabic Question Answering System. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2013, 4, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, A.M.; Alshenaifi, N.A. Answering Arabic Why-Questions: Baseline vs. RST-Based Approach. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2017, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozannar, H.; Maamary, E.; El Hajal, K.; Hajj, H. Neural Arabic Question Answering. In Proceedings of the Fourth Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Florence, Italy, 1 August 2019; pp. 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, W.S.; Homsi, M.N. DAWQAS: A Dataset for Arabic Why Question Answering System. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 142, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleid, H.A.; Azmi, A.M. Hajj-FQA: A benchmark Arabic dataset for developing question-answering systems on Hajj fatwas. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2025, 37, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouenour, L.; Bouzouba, K.; Rosso, P. An evaluated semantic query expansion and structure-based approach for enhancing Arabic question/answering. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2010, 3, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Atef, A.; Mattar, B.; Sherif, S.; Elrefai, E.; Torki, M. AQAD: 17,000+ Arabic Questions for Machine Comprehension of Text. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACS 17th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Antalya, Turkey, 2–5 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alami, H.; El Mahdaouy, A.; Benlahbib, A.; En-Nahnahi, N.; Berrada, I.; Ouatik, S.E.A. DAQAS: Deep Arabic Question Answering System based on duplicate question detection and machine reading comprehension. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.M.; Hassan, S.I.; Elrefaei, L. VAQA: Visual Arabic Question Answering. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 10803–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadla, L.S.; Hailat, T.M.; Al-Kabi, M.N. Evaluating Arabic to English machine translation. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2014, 5, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrat, S.; Meftouh, K.; Smaili, K. Machine translation for Arabic dialects (survey). Inf. Process. Manag. 2019, 56, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfardy, H.; Al-Badrashiny, M.; Diab, M. AIDA: Identifying Code Switching in Informal Arabic Text. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Computational Approaches to Code Switching, Doha, Qatar, 25 October 2014; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Husin, M.Z.; Saad, S.; Noah, S.A.M. Syntactic rule-based approach for extracting concepts from quranic translation text. In Proceedings of the 2017 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI), Langkawi, Malaysia, 25–27 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hatem, A.; Omar, N.; Shaker, K. Morphological analysis for rule based machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Semantic Technology and Information Retrieval, Putrajaya, Malaysia, 28–29 June 2011; pp. 260–263. [Google Scholar]
- Alqudsi, A.; Omar, N.; Shaker, K. Arabic machine translation: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2014, 42, 549–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, I.; Zbib, R.; Glass, J. Segmentation for English-to-Arabic Statistical Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the ACL-08: HLT, Short Papers. Columbus, OH, USA, 16–17 June 2008; pp. 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, P.; Duh, K. Morphological Word Embeddings for Arabic Neural Machine Translation in Low-Resource Settings. In Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Subword/Character LEvel Models, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6 June 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bari, M.S.; Alnumay, Y.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Alotaibi, N.M.; Alyahya, H.A.; AlRashed, S.; Mirza, F.A.; Alsubaie, S.Z.; Alahmed, H.A.; Alabduljabbar, G.; et al. ALLaM: Large Language Models for Arabic and English. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.15390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, A.A.A.; Elneima, A.H.; Darwish, K. LLM-based MT Data Creation: Dialectal to MSA Translation Shared Task. In Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Open-Source Arabic Corpora and Processing Tools (OSACT) with Shared Tasks on Arabic LLMs Hallucination and Dialect to MSA Machine Translation @ LREC-COLING 2024, Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Alqudsi, A.; Omar, N.; Shaker, K. A Hybrid Rules and Statistical Method for Arabic to English Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1–3 May 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ziemski, M.; Junczys-Dowmunt, M.; Pouliquen, B. The United Nations Parallel Corpus v1. In 0. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 3530–3534. [Google Scholar]
- Zaghouani, W.; Habash, N.; Mohit, B. The Qatar Arabic Language Bank Guidelines; Technical Report CMU-CS-QTR-124; School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bouamor, H.; Habash, N.; Salameh, M.; Zaghouani, W.; Rambow, O.; Abdulrahim, D.; Obeid, O.; Khalifa, S.; Eryani, F.; Erdmann, A.; et al. The MADAR Arabic Dialect Corpus and Lexicon. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Miyazaki, Japan, 7–12 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alzamzami, F.; Saddik, A.E. OSN-MDAD: Machine Translation Dataset for Arabic Multi-Dialectal Conversations on Online Social Media. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khered, A.; Benkhedda, Y.; Batista-Navarro, R. Dial2MSA-Verified: A Multi-Dialect Arabic Social Media Dataset for Neural Machine Translation to Modern Standard Arabic. In Proceedings of the 4th Workshop on Arabic Corpus Linguistics (WACL-4), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 20 January 2025; pp. 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shirko, O.; Omar, N.; Arshad, H.; Albared, M. Machine translation of noun phrases from Arabic to English using transfer-based approach. J. Comput. Sci. 2010, 6, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almahasees, Z.M. Assessment of Google and Microsoft Bing Translation of Journalistic Texts. Int. J. Lang. Lit. Linguist. 2018, 4, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouamor, H.; Alshikhabobakr, H.; Mohit, B.; Oflazer, K. A Human Judgement Corpus and a Metric for Arabic MT Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Condon, S.; Parvaz, D.; Aberdeen, J.; Doran, C.; Freeman, A.; Awad, M. Evaluation of Machine Translation Errors in English and Iraqi Arabic; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Al Amer, S.A.; Lee, M.G.; Smith, P. Comparative Evaluation of Machine Translation Models Using Human-Translated Social Media Posts as References: Human-Translated Datasets. In Proceedings of the Eighth Workshop on Technologies for Machine Translation of Low-Resource Languages (LoResMT 2025), Albuquerque, NM, USA, 3–4 May 2025; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Alabdullah, A.; Han, L.; Lin, C. Advancing Dialectal Arabic to Modern Standard Arabic Machine Translation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.20301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-Mageed, M.; Elmadany, A.; Nagoudi, E.M.B. ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Arabic. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), Online, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 7088–7105. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, G.; Alhafni, B.; Baimukan, N.; Bouamor, H.; Habash, N. The Interplay of Variant, Size, and Task Type in Arabic Pre-trained Language Models. In Proceedings of the Sixth Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Kyiv, Ukraine, 19 April 2021; pp. 92–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.P. ChatGPT: A comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 121–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoun, W.; Baly, F.; Hajj, H. AraGPT2: Pre-Trained Transformer for Arabic Language Generation. In Proceedings of the Sixth Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop, Kyiv, Ukraine, 19 April 2021; pp. 196–207. [Google Scholar]
- Koubaa, A.; Ammar, A.; Ghouti, L.; Najar, O.; Sibaee, S. ArabianGPT: Native Arabic GPT-based Large Language Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.15313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Nagoudi, E.M.B.; Elmadany, A.; Abdul-Mageed, M. AraT5: Text-to-Text Transformers for Arabic Language Generation. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 628–647. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.; Duan, X.; Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Rezagholizadeh, M.; Huai, B.; et al. AraMUS: Pushing the Limits of Data and Model Scale for Arabic Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 2883–2894. [Google Scholar]
- Qachfar, F.Z.; Verma, R. ReDASPersuasion at ArAIEval Shared Task: Multilingual and Monolingual Models For Arabic Persuasion Detection. In Proceedings of the ArabicNLP 2023, Singapore (hybrid conference), 7 December 2023; pp. 549–557. [Google Scholar]
- Billah Nagoudi, E.M.; Abdul-Mageed, M.; Elmadany, A.; Inciarte, A.; Islam Khondaker, M.T. JASMINE: Arabic GPT Models for Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 16721–16744. [Google Scholar]
- AlYami, R.; Al-Zaidy, R. Weakly and Semi-Supervised Learning for Arabic Text Classification using Monodialectal Language Models. In Proceedings of the Seventh Arabic Natural Language Processing Workshop (WANLP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 8 December 2022; pp. 260–272. [Google Scholar]
- Qarah, F. SaudiBERT: A Large Language Model Pretrained on Saudi Dialect Corpora. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgezouli, M.; Elmadani, K.N.; Saeed, M. SudaBERT: A Pre-trained Encoder Representation For Sudanese Arabic Dialect. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer, Control, Electrical, and Electronics Engineering (ICCCEEE), Khartoum, Sudan, 26 February–1 March 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdaoui, A.; Berrimi, M.; Oussalah, M.; Moussaoui, A. DziriBERT: A Pre-trained Language Model for the Algerian Dialect. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.12346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, O.; El Younnoussi, Y. Pre-training Two BERT-Like Models for Moroccan Dialect: MorRoBERTa and MorrBERT. Mendel 2023, 29, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaanoun, K.; Naira, A.M.; Allak, A.; Benelallam, I. DarijaBERT: A step forward in NLP for the written Moroccan dialect. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2025, 20, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Abdine, H.; Khoubrane, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Abbahaddou, Y.; Ennadir, S.; Momayiz, I.; Ren, X.; Moulines, E.; Nakov, P.; et al. Atlas-Chat: Adapting Large Language Models for Low-Resource Moroccan Arabic Dialect. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Language Models for Low-Resource Languages, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 20 January 2025; pp. 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, H.; Rouhou, A.C.; Messaoudi, A.; Korched, A.; Fourati, C.; Sellami, A.; Ben HajHmida, M.; Ghriss, F. TunBERT: Pretraining BERT for Tunisian Dialect Understanding. SN Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qarah, F. EgyBERT: A Large Language Model Pretrained on Egyptian Dialect Corpora. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.03524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Alfasly, S.; Wen, B.; Addeen, J.; Ahmed, M.; Liu, Y. AlclaM: Arabic Dialect Language Model. In Proceedings of the Second Arabic Natural Language Processing Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 16 August 2024; pp. 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Alkaoud, M. A bilingual benchmark for evaluating large language models. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2024, 10, e1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Ritter, A. An Empirical Study of Pre-trained Transformers for Arabic Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 4727–4734. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, N.; Sahu, S.K.; Jia, B.; Katipomu, S.; Li, H.; Koto, F.; Marshall, W.; Gosal, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; et al. Jais and Jais-chat: Arabic-Centric Foundation and Instruction-Tuned Open Generative Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yu, F.; Zhu, J.; Sun, X.; Cheng, H.; Dingjie, S.; Chen, Z.; Alharthi, M.; An, B.; He, J.; et al. AceGPT, Localizing Large Language Models in Arabic. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers), Mexico City, Mexico, 16–21 June 2024; pp. 8139–8163. [Google Scholar]
- Alwajih, F.; Nagoudi, E.M.B.; Bhatia, G.; Mohamed, A.; Abdul-Mageed, M. Peacock: A Family of Arabic Multimodal Large Language Models and Benchmarks. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; pp. 12753–12776. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, U.; Ahmad, M.S.; Alam, F.; Altinisik, E.; Asgari, E.; Boshmaf, Y.; Boughorbel, S.; Chawla, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Dalvi, F.; et al. Fanar: An Arabic-Centric Multimodal Generative AI Platform. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourahouat, G.; Abourezq, M.; Daoudi, N. Toward an efficient extractive Arabic text summarisation system based on Arabic large language models. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2025, 20, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Mageed, M.; Keleg, A.; Elmadany, A.; Zhang, C.; Hamed, I.; Magdy, W.; Bouamor, H.; Habash, N. NADI 2024: The Fifth Nuanced Arabic Dialect Identification Shared Task. In Proceedings of the Second Arabic Natural Language Processing Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 16 August 2024; pp. 709–728. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, N.R.; Abdelmoneim, S.; Marchisio, K.; Ruder, S. AL-QASIDA: Analyzing LLM Quality and Accuracy Systematically in Dialectal Arabic. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2025, Vienna, Austria, 27 July–1 August 2025; pp. 22048–22065. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Matham, R.; Darwish, K.; Al-Rasheed, R.; Alshammari, W.; Alhoshan, M.; Almazrua, A.; Wazrah, A.A.; Alheraki, M.; Alam, F.; Nakov, P.; et al. BALSAM: A Platform for Benchmarking Arabic Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.22603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, B.; Nakov, P.; Baldwin, T. Arabic Dataset for LLM Safeguard Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2025 Conference of the Nations of the Americas Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers), Albuquerque, NM, USA, 29 April–4 May 2025; pp. 5529–5546. [Google Scholar]
- Nacar, O.; Sibaee, S.T.; Ahmed, S.; Ben Atitallah, S.; Ammar, A.; Alhabashi, Y.; Al-Batati, A.S.; Alsehibani, A.; Qandos, N.; Elshehy, O.; et al. Towards Inclusive Arabic LLMs: A Culturally Aligned Benchmark in Arabic Large Language Model Evaluation. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Language Models for Low-Resource Languages, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 20 January 2025; pp. 387–401. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, E.A.; Masoud, R.; Alnuhait, D.; Alomairi, A.Y.; Ashraf, A.; Zaytoon, M. AraTrust: An Evaluation of Trustworthiness for LLMs in Arabic. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 19–24 January 2025; pp. 8664–8679. [Google Scholar]
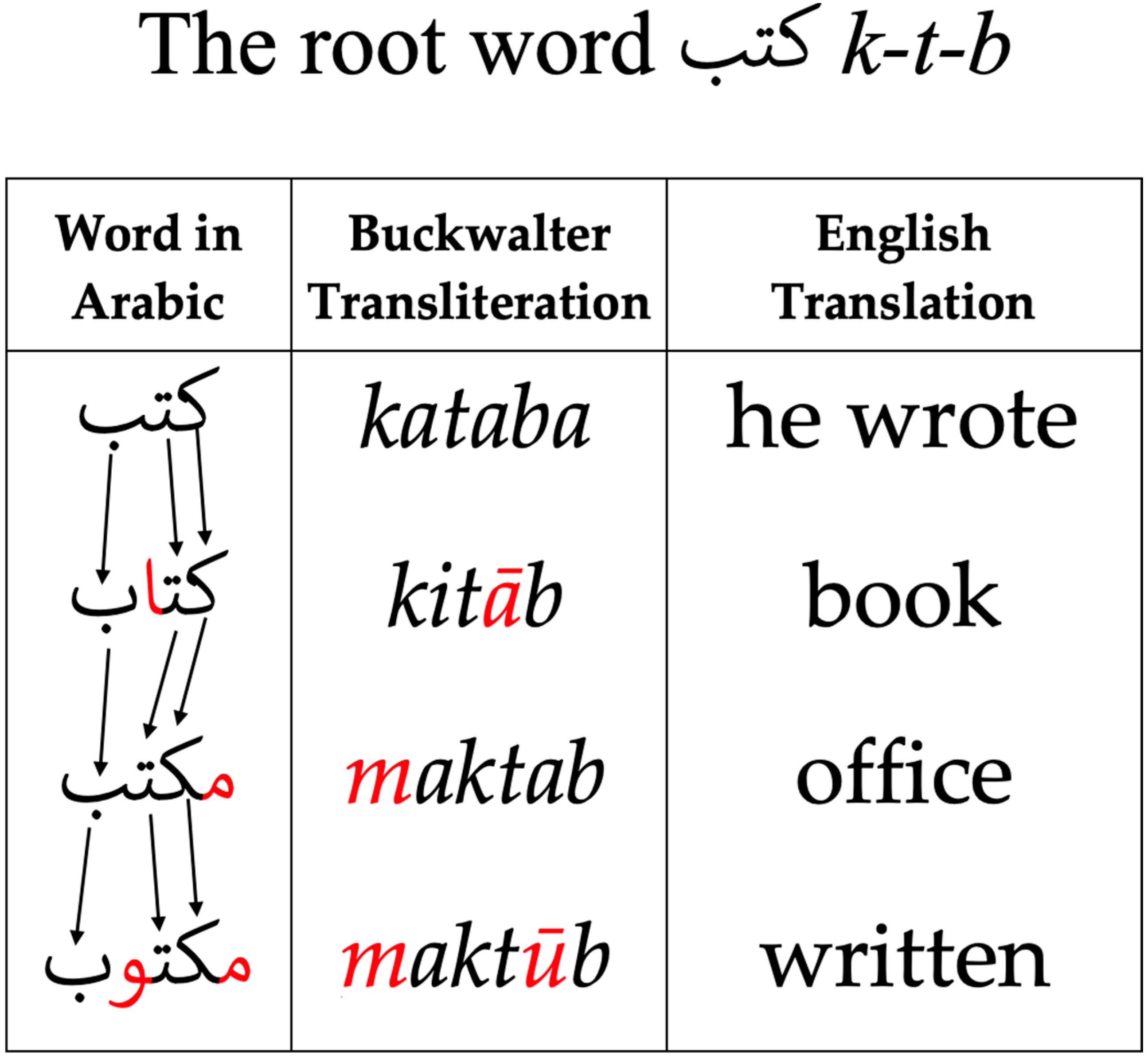
| Normalisation Technique | Tool | Type/Approach |
|---|---|---|
| stemming | Khoja stemmer [42] | List of Root-based and Pattern based |
| Larkey’s light stemmer [44] | Simplified root-based | |
| (ISRI)stemmer [45] | Light common affix stripping | |
| Enhanced algorithm for Arabic stemmer [46] | Enhanced root-based algorithm affix stripping | |
| Light and heavy Arabic stemmer [8] | Enhanced light and heavy root-based algorithm | |
| P-Stemmer [47] | Light prefixes only stemmer | |
| Tashaphyne 0.4 stemmer [48] | light stemming algorithm based on the Rhyzome model | |
| lemmatisation | MADA + TOKAN [49] | Rule-based morphological analyzer |
| AlKhalil Morpho Sys [52,53] | Extensive morphological rules and linguistic datasets | |
| Alma [54] | A frequency-based morphological dictionary and Qabas lexicographic database [55] | |
| segmentation | Morpho-syntactic [59] | Hybrid supervised learning, frequency-based, and finite-state automaton approaches |
| Integration of a segmentation [60] | Based on punctuation signs extracted from a study corpus | |
| The linguistic and graphic segmentation approach [62] | Based on linguistic and graphic connectors | |
| SVM-based and Bi-LSTM-CRF segmentation [64] | SVM ranking and Bi-LSTM-CRF sequence labeling | |
| DJAZI segmentation [65] | Hybrid contextual text exploration with word-level morphological segmentation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alayba, A.M. Arabic Natural Language Processing (NLP): A Comprehensive Review of Challenges, Techniques, and Emerging Trends. Computers 2025, 14, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14110497
Alayba AM. Arabic Natural Language Processing (NLP): A Comprehensive Review of Challenges, Techniques, and Emerging Trends. Computers. 2025; 14(11):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14110497
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlayba, Abdulaziz M. 2025. "Arabic Natural Language Processing (NLP): A Comprehensive Review of Challenges, Techniques, and Emerging Trends" Computers 14, no. 11: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14110497
APA StyleAlayba, A. M. (2025). Arabic Natural Language Processing (NLP): A Comprehensive Review of Challenges, Techniques, and Emerging Trends. Computers, 14(11), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14110497






