1. Introduction
Emerging applications in the Internet of Things, cyber–physical systems, smart cities, augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial Internet demand real-time responsiveness [
1]. However, the traditional cloud computing model faces challenges in meeting the needs of these applications due to significant computational latency associated with uploading and processing data in remote cloud data centers. This latency is exacerbated by the vast amounts of data generated by these applications, leading to network congestion and complexity.
Moreover, the sheer volume of raw data produced by these applications necessitates extensive filtering before storage in the cloud, further complicating the process. In response to these challenges, edge computing has emerged as a novel computing paradigm that brings cloud services closer to end devices [
2]. By deploying computing resources at the edge of the network, near end users, edge computing minimizes communication latency, particularly for time-critical applications.
The challenge lies in efficiently executing applications in these new embedded real-time systems while meeting non-functional requirements such as timeliness, robustness, dependability, and performance. This is where quality-of-service (QoS) management comes into play [
3]. QoS-aware applications possess the ability to operate at degraded levels and still satisfy users to a certain degree. This differs from traditional applications, which either operate at a given quality level or not at all.
However, the increased complexity of dynamic open scenarios may hinder the ability to compute optimal local and global resource allocations within a reasonable and bounded timeframe, as the optimal level of deliberation varies depending on the situation [
4]. This holds true for many real-time applications, where it may be preferable to obtain approximate results of acceptable quality promptly rather than precise results that arrive late. For instance, in a collision avoidance system, issuing a timely warning along with an estimated obstacle location is more beneficial than providing a detailed evasive action description after the fact. Similarly, in video and sound processing, delivering lower-quality images and sound promptly is often acceptable, whereas delayed frames and prolonged periods of silence are not. Similar trade-offs exist in route optimization for automated vehicles, computer games, and real-time control.
Hence, it is advantageous to design systems capable of balancing computational cost with solution quality [
5]. This paper addresses this by reformulating the distributed resource allocation problem as an anytime optimization problem. It recognizes a spectrum of acceptable solutions with varying qualities and adapts the distributed service allocation based on the dynamically imposed deliberation time resulting from emerging environmental conditions.
Nodes initially negotiate partial, acceptable service proposals, which are then refined if time permits. This contrasts with traditional QoS optimization approaches that either complete their execution or fail to provide a useful solution. At each iteration, the proposed QoS optimization algorithm attempts to find a new feasible set of QoS levels, with greater improvements observed in the early stages of computation, diminishing over time. Thanks to the anytime nature of the proposed approach, the QoS optimization process can be interrupted at any point during execution while still yielding a service solution and a measure of its quality. It is expected that the quality of the solution improves as the algorithms run longer. This replaces the binary notion of correctness associated with traditional QoS optimization algorithms with a range of quality-measured outputs. Throughout this paper, the quality measure of the solution indicates how closely the offered QoS level aligns with the user’s desired QoS level.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. The next section examines related work.
Section 3 outlines our model and notation.
Section 4 and
Section 5 delve into the proposed anytime approach for configuring collaborative service execution, focusing on maximizing user satisfaction with the provided service. The approach is described in detail and validated.
Section 6 presents the results of extensive simulations conducted to analyze the performance of the proposed anytime approach and compare it against traditional algorithm versions. Finally,
Section 7 offers concluding remarks for the paper.
2. Related Work
An increasing number of real-time applications need a considerable amount of computation power and are pushing the limits of traditional data processing infrastructures [
6,
7]. Consider, for example, the real-time stream processing systems described in [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13]. The quantity of data produced by a variety of data sources and sent to end systems to further processing is growing significantly, increasingly demanding more processing power and the challenges become even more critical when a coordinated content analysis of data sent from multiple sources is necessary [
9]. Thus, with a potentially unbounded amount of stream data and limited resources, some of the processing tasks may not be satisfactorily answered even within the users’ minimum acceptable QoS levels [
10].
Edge computing has emerged as a promising paradigm for enhancing the performance and efficiency of distributed systems by bringing computation and storage closer to end users and IoT devices. In the context of service configuration in edge computing environments, several studies have explored adaptive strategies to dynamically adjust service parameters and resource allocations based on changing conditions and user requirements [
4,
14].
Collaborative service execution involves coordinating multiple edge devices to collectively execute a service or task efficiently. Recent research has investigated collaborative approaches to service execution in edge computing environments, leveraging techniques such as task offloading, load balancing, and resource sharing among edge nodes to optimize performance and resource utilization [
15,
16]. In [
17], we presented a framework for exploring the spare capacity of IoT devices for a clustered execution of multimedia applications. The framework allows the dynamic creation of clusters of devices that use their spare resources in a joint effort to provide a service with a given quality level.
However, when accounting for real-time requirements, uncertainty arises when desired bounds may not be met while adapting the system to dynamically changing environmental conditions. This notion has been formalized through the concepts of imprecise computation and anytime algorithms. Liu et al. [
18] identified imprecise computation (for monotone tasks), sieve functions (for non-monotone tasks), and multiple versions as three approaches for integrating unbounded components into real-time systems.
Imprecise computation employs monotone functions to generate intermediate results as tasks execute. These results are expected to improve throughout the task’s execution. The computation needs to produce a result with minimal quality constitutes the
mandatory part of the task, which must have a worst-case execution time guaranteed by schedulability analysis. The remaining task execution is termed
optional and typically consists of an iterative refinement algorithm that progressively enhances the result’s quality generated by the mandatory part. These concepts are integrated with replication and checkpoint techniques to reduce the cost of providing fault tolerance and enhance availability [
19].
Anytime algorithms [
20,
21,
22] operate on the principle that the computation time required to compute optimal solutions typically diminishes the overall utility of the system. An anytime algorithm is an iterative refinement algorithm that can be interrupted and asked to provide an answer at any point. It is anticipated that the quality of the answer will increase (up to a maximum quality) as the anytime algorithm is allocated more time to run, offering a trade-off between result quality and computational demands. Associated with an anytime algorithm is a performance profile—a function that maps the time given to an anytime algorithm (and sometimes input quality) to the solution quality produced by the algorithm. Therefore, one of the key advantages of anytime algorithms is their ability to produce solutions of varying quality based on the available resources and time constraints. This flexibility enables edge devices to deliver acceptable levels of service even under adverse conditions or unexpected surges in demand [
23].
Several studies have explored the use of anytime algorithms in the context of edge computing, highlighting the importance of anytime algorithms in addressing the dynamic and unpredictable nature of edge computing environments, enabling efficient resource management and QoS optimization. For instance, Smith et al. [
24] proposed a novel anytime scheduling algorithm specifically designed for edge environments. Their algorithm adapts dynamically to changing resource availability and user requirements, allowing for flexible and efficient task scheduling. Similarly, Jones and Brown [
25] developed an anytime optimization framework for edge resource management, enabling real-time adaptation to varying workload conditions. Furthermore, recent work by Lee et al. [
23] introduced an adaptive anytime algorithm for edge analytics, which optimizes resource allocation based on data stream characteristics and user-defined constraints. This algorithm ensures timely and accurate data processing while minimizing resource utilization. Additionally, Wang and Zhang [
26] proposed a dynamic anytime approach for edge service provisioning, enabling on-demand scaling of computational resources to meet fluctuating service demands. Integrating anytime algorithms into adaptive service configuration frameworks holds promise for enhancing the responsiveness and adaptability of edge computing systems. By leveraging anytime algorithms, edge nodes can dynamically adjust service configurations in real-time, optimizing resource usage while meeting quality-of-service (QoS) requirements [
27].
While adaptive service configuration and anytime algorithms offer significant potential for improving edge computing systems’ performance and scalability, several challenges remain to be addressed. These include algorithmic complexity, resource constraints, and the need for efficient coordination and communication among edge nodes [
28,
29].
Anytime algorithms, designed to produce progressively better solutions as they are allotted more computation time, hold significant promise in decision making under uncertainty. However, their deployment raises several ethical considerations. One primary concern is the potential for bias in time-sensitive decisions. If an algorithm is prematurely halted due to time constraints, the resulting decision may not be optimal and could disproportionately affect marginalized groups. This risk is highlighted in studies on algorithmic bias, which show that insufficient computation can exacerbate existing inequities [
30,
31].
Another ethical implication is the transparency and accountability of the decision-making process. Anytime algorithms, due to their iterative nature, may produce different outcomes based on when they are stopped. This variability can make it challenging to ensure consistent and fair decision making, which is crucial in high-stakes environments such as healthcare or criminal justice [
32]. Furthermore, as these algorithms are increasingly used in autonomous systems, ensuring that they align with ethical norms and societal values becomes imperative [
33]. Developers and users of anytime algorithms must, therefore, implement rigorous validation and monitoring frameworks to mitigate these ethical risks and ensure that the benefits of these advanced computational techniques are realized equitably and transparently [
34].
3. System Model
Consider a distributed system with several heterogeneous nodes, each with its specific set of resources . For some of those nodes, there may be a constraint on the type and size of services they can execute within the users’ acceptable QoS levels. Therefore, this work addresses distributed collaborative execution of resource-intensive services to maximize users’ satisfaction with the obtained QoS. Nodes may collaborate either because they cannot deal alone with the resource allocation demands imposed by users and services or because they can reduce the associated cost by working together.
Definition 1 (Cluster).
A cluster is a set of IoT and edge devices that are currently providing a collaborative solution for a service.
It is assumed that a service
S can be executed at varying levels of QoS to achieve efficient resource usage that constantly adapts to the devices’ specific constraints, nature of executing tasks, and dynamically changing system conditions. There will be a set of independent tasks to be executed, resulting from partitioning the resource-intensive service
S. Correct decisions on service partitioning must be made at runtime when sufficient information about workload and communication requirements become available [
35,
36,
37,
38], as they may change with different execution instances and users’ QoS preferences
Q.
Definition 2 (Service).
A service is a set of processing tasks along with QoS constraints defined in Q.
Each service possesses a range of parameters that can be adjusted to configure the delivered quality of service (QoS) along with its corresponding resource demand. These parameters, each governing a distinct facet of service quality, are collectively referred to as QoS dimensions. For instance, consider the scenario of transmitting multiple audio/video streams over a network. Here, the network’s bandwidth and the nodes facilitating the streams are involved. Audio-related parameters may include the sampling rate (e.g., 8, 16, 24, 44, 48 kHz), sampling bits (e.g., 8, 16), and end-to-end latency (e.g., 100, 75, 50, 25 ms). Meanwhile, video parameters typically encompass picture dimension (e.g., SQCIF, QCIF, CIF, CIF4), color depth (e.g., 1, 3, 8, 16, …), and frame rate (ranging from 1 to 30 frames per second). Each of these QoS dimensions imposes varying resource requirements across its possible service levels.
Distinct configurations of a stream can yield differing utility values for various users and applications. For instance, a user attending a music concert transmission might prioritize high-quality audio while also desiring satisfactory video color depth, whereas another user relying on a remote surveillance system might emphasize superior video quality with a minimum requirement for grayscale images. Let Q represent the set of a user’s QoS constraints associated with service S. Each denotes a finite set of quality options for the jth attribute of dimension k, which can be discrete or continuous in nature.
Definition 3 (QoS Constraints).
Let Q be the set of the user’s QoS constraints associated with service S.
These constraints encompass various aspects of service performance, reliability, availability, and other relevant metrics that directly impact the user experience or system operation [
17]. With a comprehensive QoS characterization tailored to a specific application domain, both users and service providers can delineate service prerequisites and proposals to establish mutual agreements on service delivery. Given the multi-dimensional nature of QoS, trade-offs become inevitable in light of resource constraints.
Requiring users to specify an absolute utility value for every predefined quality choice may prove impractical. While our aim is to craft semantically rich requests that align with user preferences, it is imperative for users to express their QoS preferences effectively. Moreover, the system should dynamically determine promised QoS levels based on each user’s accepted QoS values for each dimension and local resource availability. Consequently, the reward for executing a task at a dynamically determined QoS level hinges on the number and relative importance of the QoS dimensions serving closer to the user’s desired QoS level.
In pursuit of these objectives, a more natural and realistic approach is to institute a service request based on qualitative, rather than quantitative, measures. By prioritizing quality dimensions, attributes, and accepted values in a relative decreasing order, users can convey the relative importance of the new service’s performance across different QoS levels without necessitating quantification for every quality trade-off.
Users provide a single specification of their own range of QoS preferences Q for a complete service S, ranging from a desired QoS level to the maximum tolerable service degradation, specified by a minimum acceptable QoS level , without having to understand the individual tasks that make up the service. As a result, the user can express acceptable compromises in the desired QoS and assign utility values to QoS levels. Note that this assignment is decoupled from the process of establishing the supplied service QoS levels themselves and determining the resource requirements for each level.
Given a set of neighboring nodes N and a resource allocation demand enforced by Q, if a single node cannot satisfactorily fulfill the resource demand, collaborative efforts among neighbor nodes become imperative. The selection of a subset of nodes in N to collaboratively execute S in a cluster should prioritize maximizing the QoS constraints Q associated with S while minimizing the impact on the current QoS of previously accepted services caused by the arrival of S.
The quest for an optimal resource allocation aligned with specific objectives has long been a foundational challenge in QoS management. However, as the complexity of open distributed systems escalates, achieving an optimal resource allocation that accommodates both user and node constraints within a practical timeframe becomes increasingly daunting. Delayed adaptation to new resource requirements may render the system ineffective or even detrimental.
Our proposition entails swiftly establishing an initial, albeit sub-optimal, solution based on the set of QoS constraints that must be upheld. Subsequently, if time permits, the initial solution undergoes gradual refinement until it attains either its optimal value or the available deliberation time expires. With each iteration, a new set of service-level agreements (SLAs) is devised, progressively enhancing the utility to the user’s request under negotiation. However, these successive adjustments diminish in magnitude as the QoS optimization process advances.
Moreover, the proposed anytime algorithms operate independently of the manner in which the code to be executed on behalf of the original node is disseminated among cluster members. Currently, it is assumed that only nodes pre-equipped with a service’s code blocks respond to collaboration requests, obviating the necessity for code migration at runtime and the transfer of the service’s current state.
4. Cluster Formation
The cluster formation process should facilitate the selection of individual nodes that, based on their resources and availability, can form the most suitable cluster to meet the user’s QoS requirements for a resource-intensive service. By “most suitable cluster”, we refer to the group comprising nodes that offer service closest to the user’s desired QoS level.
A service request is structured based on the relative importance () of a set of n QoS dimensions, spanning from the desired QoS level to the maximum tolerable service degradation represented by the minimum acceptable QoS level . For each dimension, an order of decreasing importance of attributes is specified (), where k denotes the number of attributes of dimension K. It is important to note that k and i indicate the relative position of dimensions and attributes in the user’s service request, not their identifiers in the domain’s QoS description.
Whenever a node
cannot meet the user’s acceptable QoS levels
it broadcasts a collaboration request to execute service
. The set of tasks available for remote execution is determined by a task partition/allocation scheme dynamically considering the trade-off between local execution requirements and communication costs [
39]. This collaboration request includes a description of each remote task
, the user’s QoS constraints, and a timeout
for receiving service proposals.
Each neighbor node
capable of meeting the request formulates a service proposal using a local QoS optimization algorithm (refer to
Section 5 for details) and responds to node
with both its service proposal
and its local reward
resulting from proposal acceptance. For now, it is sufficient to understand that the local reward indicates the node’s level of local QoS optimization based on the services being locally executed and their QoS constraints. The method by which each node calculates its local reward will be elaborated in
Section 5.
Different node groups will exhibit varying levels of efficiency in collaborative service execution due to differences in member capabilities and current state. Consequently, selecting cluster members must prioritize the proximity of their service proposals to the user’s multi-dimensional QoS constraints. Each admissible proposal (a proposal is admissible if it can satisfy all QoS dimensions within the user’s acceptable QoS levels)
is then evaluated by computing, for each QoS dimension, a weighted sum of the differences between the user’s preferred values and those proposed in
using Equation (
1). It is important to recall that the user’s QoS constraints are presented in decreasing preference order.
where
n is the number of QoS dimensions and
represents the relative importance of QoS dimension
k (
) to the user, defined as
The acceptability of each proposed attribute’s value compared to the requested one is quantified by Equation (
3), considering both continuous and discrete domains.
where
denotes the number of attributes in dimension
k.
In Equation (
3), the function
quantifies, for an attribute
i, the acceptability of the proposed value
compared to the user’s preferred value
, and is defined as
For attributes with a continuous domain, this quantification represents the normalized difference between the proposed and preferred values. Examples include video frame rate and network bandwidth.
For discrete domains, Equation (
4) accounts for preferences by using their relative position in the application’s QoS requirements. Examples include audio and video codecs.
In [
40], a
quality index is defined as a bijective function mapping discrete domain elements to integer values. We adopt a similar approach, mapping attribute position to scoring values. If a domain defines attribute values in intervals,
should relate to the interval where
is found. Similarly, if the user accepts values in intervals,
should be the interval’s first value, considering its relative importance.
The best proposal minimizes the distance to the user’s preferences in all QoS dimensions. However, rather than assuming unlimited time for optimal computation, we propose time-bounded distributed QoS-aware service configuration among heterogeneous neighbors.
4.1. Anytime Global QoS Optimization
The participants in the anytime cluster formation process consist of the user’s node and a subset of neighboring nodes capable of providing service within the user’s specified QoS levels. The user’s node, acting as the organizer, initiates and orchestrates the entire negotiation process. It broadcasts the service’s requirements and the user’s QoS constraints while also evaluating the service proposals received from the respondent neighbors.
To be practically useful, an anytime approach should swiftly identify an initial solution of sufficient quality and progressively enhance it at each iteration, provided time allows. Therefore, special attention should be given to the method for selecting the next proposal for evaluation from the received set of proposals, rather than relying solely on their order of reception. The anytime cluster formation algorithm, outlined in Algorithm 1, leverages each node’s local reward as a heuristic to guide the cluster formation process. Nodes with higher local rewards are more likely to offer services closer to the user’s request under negotiation, given that the overall utility achieved by locally executed services is higher. Consequently, for each remote task
, the next candidate proposal
to be selected from the set of received proposals
is the one sent by node
with the highest local reward
:
The proposed Algorithm 1 enables the global QoS optimization process to yield numerous approximate solutions for a given input of service proposals awaiting evaluation. It remains interruptible at any point, offering a solution and an accompanying measure of its quality, which is expected to be enhanced over the algorithm’s runtime.
| Algorithm 1 Anytime cluster formation |
while
do for each do Select next candidate proposal , maximising local reward if then Update cluster with for task else if
and then Update cluster with for task end if end for end while return cluster
|
The quality of each generated cluster is assessed by utilizing the evaluation values of the best proposals for each service task. At each iteration, Equation (
6) calculates the quality of the achieved solution. If the set of proposals is empty, the quality of the cluster is set to zero. Additionally, if there are no proposals available for one or more remote tasks
, the quality of the cluster is also zero.
Once an initial cluster is formed, the algorithm proceeds, if time permits, to evaluate the remaining proposals in an effort to enhance the quality of the current solution. It is conceivable that another node, despite achieving a lower local reward, may propose a superior solution for the specific user’s request under negotiation, albeit at the cost of a greater downgrade of previously accepted services.
Furthermore, each node’s local reward contributes to improving global load balancing. If two proposals have evaluation differences of less than (a value defined by either the user or the framework), both proposals offer similarly acceptable utility for a particular user. In such cases, selecting the node with a higher local reward from two comparable service proposals maximizes not only service for a particular user but also the overall utility of the global system.
The algorithm terminates either when all received proposals are evaluated or when it determines that the quality of a cluster cannot be further improved because each node belonging to the current cluster has reached its maximum local reward.
4.2. Formal Description of the Cluster Formation’s Anytime Behavior
The anytime behavior of cluster formation can be formally described using the set of axioms presented in [
41]. These axioms delineate various aspects of anytime behavior:
Axiom 1 (Initial behavior).
There is an initial period during which the algorithm does not produce a cluster for collaborative service execution.
During this initial phase, the algorithm does not immediately generate an intermediate solution as it needs to analyze a proposal for each remote task
. If
indicates the duration of this initial step, then the algorithm returns a cluster with zero quality if interrupted at any time
:
Axiom 2 (Growth direction).
The quality of a cluster only improves with increasing runtime.
The cluster’s quality only improves if a better proposal for any task
is found:
Axiom 3 (Growth rate).
The amount of increase in the cluster’s quality varies during computation.
The solution’s quality rapidly increases in the initial steps of the algorithm, and its growth rate diminishes over time due to the heuristic selection of the next candidate proposal:
Axiom 4 (End condition).
After evaluating all candidate proposals, the algorithm achieves its full functionality.
Upon evaluating all candidate proposals, the anytime algorithm produces the same solution quality as its traditional counterpart, which only produces a solution with quality
at the end of computation. If the time required to evaluate a candidate proposal is
, the total required runtime of the anytime algorithm is the sum of all
n evaluations:
4.3. Alignment of the Cluster Formation Algorithm with the Desirable Properties of Anytime Algorithms
Not every algorithm capable of producing a sequence of approximate results adheres to the desirable properties of anytime algorithms, as outlined by Zilberstein [
22]. These properties include:
Property 1 (Measurable quality).
A cluster’s quality can be determined precisely.
Proof. The quality of the generated cluster at each iteration can be directly computed from the evaluation values of the best proposals found for each task. According to Equation (
6), this calculation provides a precise measurement of the cluster’s quality. □
Property 2 (Recognizable quality).
The quality of a cluster can be easily determined at runtime.
Proof. The quality of a cluster is updated whenever a better proposal for a task is found. This update is straightforward and can be calculated within a constant time, as illustrated in the proof. □
Property 3 (Monotonicity).
The quality of the generated cluster is a nondecreasing function of time.
Proof. The algorithm only adds a node to the cluster if it proposes a better service for a task. Consequently, the cluster’s quality increases as better proposals are found over time. □
Property 4 (Consistency).
For a given amount of computation time on a given input, the quality of the generated cluster remains the same.
Proof. The algorithm selects proposals for evaluation deterministically based on each node’s local reward. Therefore, for a fixed amount of time and input, the cluster’s quality remains consistent. □
Property 5 (Diminishing returns).
The improvement in the cluster’s quality diminishes over time.
Proof. Initially, the algorithm quickly improves the cluster’s quality by selecting proposals from nodes with high local rewards. However, as the algorithm progresses, the rate of improvement decreases. □
Property 6 (Interruptibility).
The algorithm can be stopped at any time and still provide a solution.
Proof. The algorithm returns the best cluster determined up to the interruption time, ensuring a solution is available even if interrupted prematurely. □
Property 7 (Preemptibility).
The algorithm can be suspended and resumed with minimal overhead.
Proof. Since the algorithm retains all necessary information, it can be easily resumed after suspension with minimal overhead. □
5. Service Proposal Formulation
Resource reservation is fundamental for supporting QoS mechanisms [
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47]. An application cannot maintain stable QoS characteristics without some assurances regarding the available amount of resources. The operating system or middleware allocates a portion of the system’s resources to an application, which then must deliver a predefined stable output quality.
Requests for task execution are dynamically received at any node and are formulated as a set of acceptable multi-dimensional QoS levels in decreasing preference order. To ensure the request is met locally, the QoS Provider executes a local QoS optimization algorithm that aims to maximize the satisfaction of the new service’s QoS constraints while minimizing the impact on the current QoS of previously accepted services.
Conventional admission control schemes typically either guarantee or reject each service request, which means that future requests may be rejected because resources have already been committed to previous requests. We employ a QoS negotiation mechanism that, in cases of overload or violation of pre-runtime assumptions, ensures graceful degradation.
Our framework dynamically derives promised quality-of-service (QoS) levels by aligning user-accepted QoS values across various dimensions with local resource availability. Moreover, the reward associated with executing a task at these dynamically determined QoS levels hinges upon the extent and significance of alignment with the user’s preferred QoS level. Equation (
7) calculates the reward
attained by a specific service-level agreement (SLA) for task
through the evaluation of the disparity between the user’s desired QoS and the node’s proposed values.
In Equation (
7), the
penalty represents a parameter designed to diminish the reward value. This parameter is adjustable, allowing users or framework managers to fine-tune it based on various criteria. Typically, its value should escalate as the disparity from the user’s preferred values increases.
By leveraging the utility attained from each proposed service-level agreement (SLA), we can ascertain a metric for the overall satisfaction of the node following the acceptance of a new service request. For a node
, the local reward
derived from the set of proposed SLAs is expressed as
It is important to note that unless all tasks are executed at their highest requested quality-of-service (QoS) level, there will be a variance between the determined set of service-level agreements (SLAs) and the maximum theoretical local reward achievable if all local tasks were performed at their peak QoS level. This discrepancy may arise due to unavoidable resource limitations or inadequate load balancing. However, this issue can be addressed by incorporating actual local rewards into service proposals and prioritizing nodes with higher local rewards when faced with proposals of similar evaluation values, as elaborated in the preceding section.
5.1. Anytime Local QoS Optimization
The intricate process of determining the optimal set of service-level agreements (SLAs), considering both users’ QoS preferences and node resource availability, underscores the need for an anytime approach. Such an approach allows for a trade-off between the quality of the solution achieved and the computational cost, ensuring timely responses to events.
The proposed anytime algorithm, outlined in Algorithm 2, distinctly addresses the formulation of new SLAs in two scenarios. Firstly, it ensures the accommodation of a new task without altering the QoS level of previously guaranteed tasks. Secondly, in cases of node overload, it facilitates service degradation for previously accepted tasks to accommodate the new request. Offering QoS degradation as an alternative to task rejection has been shown to yield higher perceived utility [
48].
| Algorithm 2 Service proposal formulation |
Each task has user defined QoS dimensions constraints . Each is a finite set of n quality choices for the attribute, expressed in decreasing order of preference, for all k QoS dimensions. while
do Step 1: Improve QoS level of new arrived task Select the worst requested QoS level in all k dimensions, , for task . Maintain level of service for previously guaranteed tasks. while the new set of tasks is feasible do for each QoS dimension in receiving service at do Determine the utility increase by upgrading attribute j to Find maximum increase and upgrade attribute x to the ’s level end for end while Step 2: Find local minimal service degradation to accommodate Select for all k dimensions of task the final result of Step 1, while the new set of tasks is not feasible do for each task receiving service at do Determine the utility decrease by degrading attribute j to Find task whose reward decrease is minimum and degrade attribute x to the ’s level end for end while end while return SLA for new task
|
The algorithm iteratively addresses the challenge of identifying a feasible set of service-level agreements (SLAs) while simultaneously maximizing user satisfaction, yielding results that progressively enhance in quality over time. Unlike a binary determination of solution correctness, the algorithm provides a proposal along with a metric of its quality. The quality of each generated configuration
, as described in Equation (
9), incorporates several factors. These include the reward attained by the service proposal configuration for the new incoming task
, the impact on the QoS of previously existing tasks, and the value of the prior-generated feasible configuration
. Initially,
is set to zero.
Upon receiving a new service request, the algorithm initiates by preserving the quality-of-service (QoS) levels of previously committed tasks while identifying the lowest requested QoS level across all dimensions for the newly arrived task. The objective is to swiftly ascertain an initial solution that is feasible—a key attribute of anytime algorithms. It is noteworthy that this SLA is the most likely to be feasible without necessitating alterations to the current QoS of previously accepted services.
Subsequently, the algorithm progresses to enhance the quality of this initial solution, engaging in a search for an improved feasible solution that maximizes the anticipated enhancement in quality. When spare resources are available, the algorithm incrementally opts for a configuration that optimizes the rise in reward attained for the new task. Conversely, in instances where QoS degradation becomes necessary to accommodate the new task, the algorithm incrementally favors a configuration that minimizes the decline in reward obtained for the new set of tasks, encompassing the newly arrived one.
It is important to note that the algorithm may yield an infeasible set of SLAs due to limitations in local resource availability. Consequently, as a service proposal is only considered valuable within a feasible set of configurations, the algorithm, if halted, consistently reverts to the most recently discovered feasible solution. Nevertheless, each intermediate configuration, even if infeasible, contributes to the calculation of the subsequent potential solution, thereby minimizing the search effort.
The algorithm concludes its execution under several conditions: first, when the designated time for proposal reception elapses (this timeframe is communicated in the collaboration request); second, when it devises a set of QoS levels that ensures the feasibility of all tasks and further enhancement in solution quality is unattainable; or third, when it determines that even at the minimum QoS level for each task, the new set remains unfeasible. In such instances, the new service request is declined. Should it prove impossible to devise a valid solution for service execution within the allocated timeframe, no proposal is dispatched to the requesting node. Instead, the node persists in serving existing tasks at their prevailing QoS levels.
5.2. Formal Description of the Service Proposal Formulation’s Anytime Behavior
In the following paragraphs, the various aspects of the anytime behavior of the proposed service proposal formulation algorithm will be formally delineated, employing the set of axioms outlined in [
41].
Axiom 5 (Initial behavior).
The algorithm rejects the new task until a feasible set of SLAs is found.
The algorithm only considers an intermediate solution if it produces a feasible set of SLAs. If
denotes the time at which the first feasible solution is discovered, then the algorithm will reject the new task if interrupted at any time
.
Axiom 6 (Growth direction).
The quality of a feasible set of SLAs can only improve over time.
A new feasible set of SLAs is only considered if it enhances the solution’s quality.
Axiom 7 (Growth rate).
The rate of increase in the solution’s quality varies during computation.
The solution’s quality rapidly ascends in the initial stages of the algorithm, with the growth rate tapering over time. Initially, the algorithm focuses on enhancing the new user’s preferred quality attributes until an unfeasible set of SLAs is encountered. Conversely, when QoS degradation is necessary to seek a new feasible solution, the algorithm degrades the less significant attributes for all local services.
The actual concavity of the algorithm’s behavior is empirically evaluated in
Section 6.
Axiom 8 (End condition).
When it is not possible to further enhance the solution’s quality, the algorithm achieves its full functionality.
The anytime version of the algorithm will produce precisely the same solution as its traditional version at the end of its computation time.
The anytime version terminates when it discovers a set of QoS levels that maintain all tasks as feasible and the quality of that solution cannot be further improved, or when it determines that, even at the lowest QoS level for each task, the new set is infeasible.
If the time required to enhance or degrade an attribute and test for the schedulability of the solution is denoted by
, the total required runtime of the anytime algorithm is the sum of all
n needed changes in attributes to find the best feasible solution.
5.3. Alignment of the Service Proposal Formulation Algorithm with the Desirable Properties of Anytime Algorithms
The alignment of the proposed anytime service proposal formulation algorithm with the desired properties of anytime algorithms [
22] is examined in the following paragraphs.
Property 8 (Measurable quality).
The quality of an SLA can be precisely determined.
Proof. At each iteration of the algorithm, Equation
9 measures the quality of the proposed SLA by considering the proximity of the proposal with respect to the user’s request under negotiation and the impact of that proximity on the global utility achieved by the previously accepted tasks. □
Property 9 (Recognizable quality).
The quality of a set of SLAs can be easily determined at runtime.
Proof. The quality of each generated feasible set of SLAs is determined by using the rewards achieved by all tasks being locally executed, which includes the newly arrived one. According to Equation (
7), the rewards’ computation is straightforward and time-bounded. □
Property 10 (Monotonicity).
The quality of the generated set of SLAs is a nondecreasing function of time.
Proof. The algorithm produces a new set of SLAs at each iteration, attempting to maximize the utility increase for the new task while minimizing the utility decrease for all previously accepted tasks when the resources are scarce to accommodate the new task. Since a service proposal can only be considered useful within a feasible set of tasks, the algorithm always returns the best feasible solution found rather than the last generated SLA.
According to Zilberstein [
22], this characteristic, in addition to a recognizable quality, is sufficient to prove the monotonicity of an anytime algorithm. □
Property 11 (Consistency).
For a given amount of computation time on a given input, the quality of the generated SLA is always the same.
Proof. For a given amount of computation time on a given input of a set of QoS constraints Q associated with a set of tasks , the quality of the proposed SLA is always the same, since the selection of attributes to improve or degrade is deterministic.
At each iteration, the QoS attribute to be improved is the one that maximizes an increase in the reward achieved by the new arrived task, while the QoS attribute to be degraded is the one that minimizes the decrease in the global reward achieved by all tasks being locally executed. As such, the algorithm guarantees a deterministic output quality for a given amount of time and input. □
Property 12 (Diminishing returns).
The improvement in the quality of the generated SLA is larger at the early stages of the computation and diminishes over time.
Proof. An initial solution that maintains the QoS levels of the previously guaranteed tasks and selects the worst requested level in all QoS dimensions for the newly arrived task is quickly generated. Its quality is given by Equation (
9), considering the rewards achieved by all tasks.
At each iteration, the currently found solution is improved by either upgrading the QoS attribute that maximizes an increase in the new service’s utility or by downgrading the QoS attribute that minimizes the decrease in all local services’ utility. As such, the increase in the solution’s quality is larger in the first iterations and diminishes over time. □
Property 13 (Interruptibility).
The algorithm can be stopped at any time and still provide a solution.
Proof. Let be the time needed to generate the first feasible solution. If interrupted at any time , the algorithm will return an empty SLA, resulting in zero quality.
When stopped at time , the algorithm returns the best feasible set of SLAs generated until t, which can be different from the last evaluated set. □
Property 14 (Preemptibility).
The algorithm can be suspended and resumed with minimal overhead.
Proof. Since the algorithm maintains the best generated feasible solution and the current configuration values, it can be easily resumed after an interrupt. □
6. Evaluation
We have opted to assess the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms by compiling a diverse array of profiles, selected to encompass the spectrum typical of real applications, spanning from resource-constrained embedded devices to more powerful neighboring devices.
Moreover, significant effort was dedicated to ensuring a high degree of variability in the characteristics of the conducted simulations. It is widely acknowledged that drawing conclusions from a single simulation run can be limiting. Indeed, the outcomes of a single simulation run represent merely specific instances of random variables, which may exhibit considerable variances [
49]. Most analytical methods for interpreting simulation output data rely on the premise that although the results from a single simulation run are not independent, obtaining independent observations across multiple simulation runs (or replicas) is feasible and yields reasonably robust statistical performance [
50].
The primary objective of our evaluations was to gauge the performance enhancement achieved by our framework when deployed in open and dynamic environments, compared to its previous iteration, which employed a traditional QoS optimization approach [
17,
51]. In
Section 6.1, we delve into the performance profiles of the proposed anytime algorithms, while
Section 6.2 addresses the computational overhead incurred by these anytime algorithms in comparison to our prior traditional QoS optimization method [
17,
51].
Our reported results stem from numerous independent simulation runs, each initialized with distinct conditions and parameters, but utilizing different seeds for the random values (random values were generated using the Mersenne Twister algorithm [
52]), ensuring the generation of independent and identically distributed variables. Mean values from all generated samples were employed to generate the charts, with a confidence level of 99.9% associated with each confidence interval. A confidence interval delineates a range of values within which the unknown population parameter—in this case, the mean—may reside. We discuss the broader confidence interval for each chart.
We utilized a video streaming application scenario for our simulations, wherein frames of video are captured, compressed, and transmitted to end users. These end users may employ a variety of devices and possess distinct sets of QoS preferences. The application comprised several components: source units to gather data, a compression unit to compress data from multiple sources, a transmission unit to send data over the network, a decompression unit to convert data to each user’s specified format, and a user unit to display the data on the user’s device.
The system’s configuration encompassed a variable number of simultaneous nodes, ranging from 10 to 100, and a variable number of simultaneous users, ranging from 1 to 20. This variability induced differing levels of load and resource availability within the system. Each node hosted a prototype implementation of our framework, featuring a predefined mapping between requested QoS levels and resource requirements. Additionally, the necessary code bases for executing each unit of the streaming application were preloaded on all nodes.
The characteristics of both end devices and their more robust neighbor nodes were randomly generated from the attributes outlined in
Table 1, yielding a distributed heterogeneous environment. This uneven distribution of resources influenced certain nodes’ ability to independently execute certain application units, prompting nodes to engage in cluster formation for collaborative service execution.
Requested QoS levels were stochastically generated across various end devices at randomly chosen times, representing a spectrum of acceptable QoS levels in a qualitative manner. These levels ranged from a randomly generated desired QoS level to a randomly determined maximum tolerable service degradation. Moreover, the relative decreasing order of importance assigned to dimensions, attributes, and values was also randomly generated.
The QoS domain used to generate the users’ service requests was composed of the following list of QoS dimensions, attributes, and possible values.
QoS dimensions = {Media Container, Video Quality, Audio Quality}
Media Container = {container format}
Video Quality = {color depth, frame size, frame rate}
Audio Quality = {sampling rate, sample bits}
container format = {3GP, ASF, AVI, QuickTime, RealVideo, WMV}
color depth (bits) = {1, 3, 8, 16, 24}
frame size (pixels) = {240x180, 320x240, 640x480, 720x480, 1024x768, 1280x1024}
frame rate (per second) = {[1,30]}
sampling rate (kHz) = {8, 11, 32, 44, 88}
sample bits (bits) = {4, 8, 16, 24}
6.1. Evaluating Performance Profiles
The behavior of an anytime algorithm is encapsulated in its performance profile, illustrating how the quality of the output evolves with computation time [
22]. This depiction is valuable as it enables a nuanced balance between available computation time and output quality.
Given the myriad factors influencing an algorithm’s execution time, we opted to normalize it relative to completion time [
53], facilitating fair comparison. Consequently, in the following figures, computation times are expressed as a percentage of their respective completion times. Notably, both algorithms achieved optimal solutions in under a second on a 6-Core Intel Core i5 at 3.7 GHz.
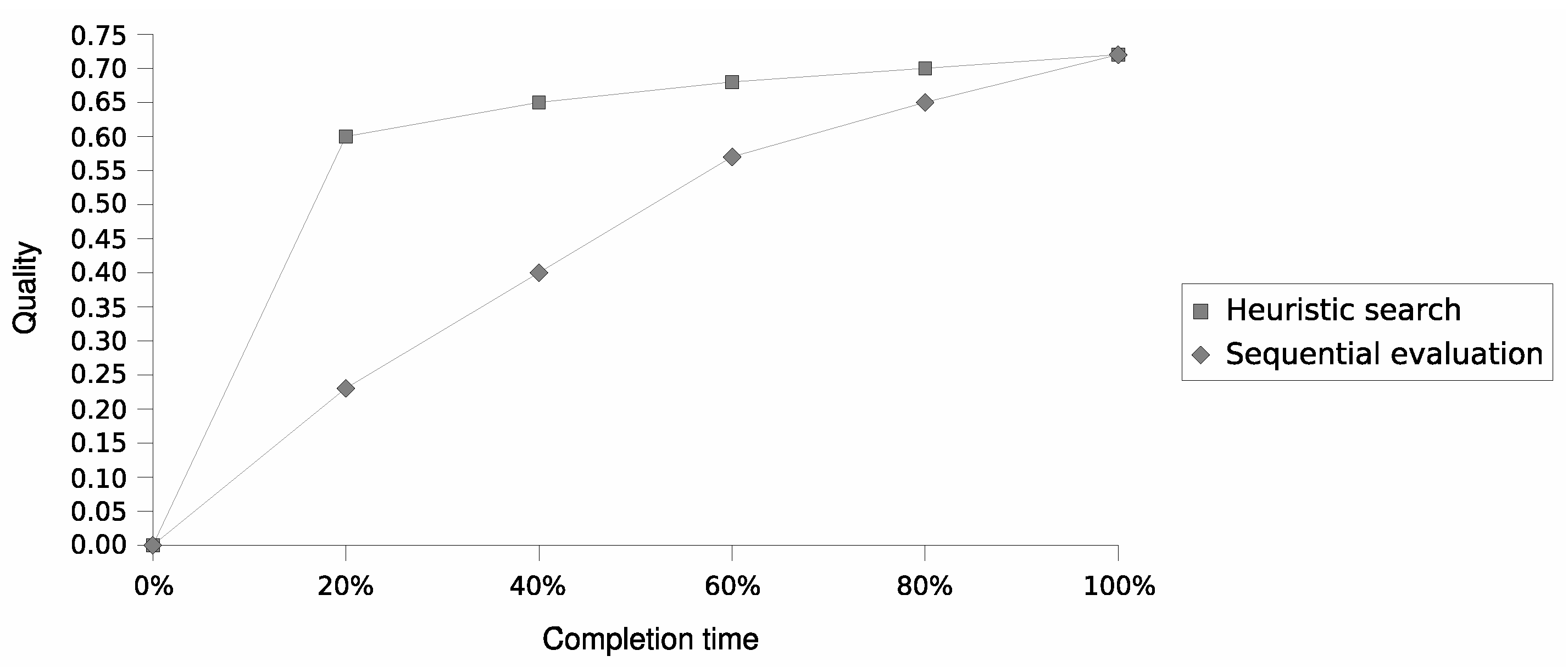
Figure 1 delineates the performance profile of the proposed anytime cluster formation algorithm, contrasting two methodologies for selecting the next proposal. The first method prioritizes proposals from nodes with the highest local reward, whereas the second method relies on the sequence of proposal reception.
The heuristic selection based on nodes’ local reward clearly outperforms the alternative, yielding both superior performance and lower variance. At just 20% of completion time, the reward-based selection achieves a solution quality of 83% ± 6% of the optimal, with a 99.9% confidence level. Conversely, when proposals are evaluated based on arrival order, the expected solution quality exhibits higher variability. At the same 20% mark, the algorithm achieves a solution quality of 32% ± 25% of the optimal, with the same confidence level.
Thus, the heuristic selection leveraging nodes’ local rewards effectively maximizes expected quality improvement within an early computation stage. This property is pivotal for practical applicability, as it suggests that results converge sufficiently close to those at completion time after a brief running period.
Furthermore, these findings empirically affirm the formal analysis of anytime algorithm properties outlined in
Section 4.3. The performance profile depicted in
Figure 1 underscores the cluster quality measure’s characteristic as a nondecreasing function of time, with diminishing increases over time.
A second study investigated the behavior of the anytime service proposal formulation algorithm, focusing on its performance profile and the impact of new service arrivals on the QoS levels of previously accepted tasks. As discussed in
Section 5, the reward of a proposal indicates its utility for a specific user, while the local reward reflects overall user satisfaction across tasks executed at a node.
The results were aggregated from multiple independent simulation runs and categorized into two scenarios.
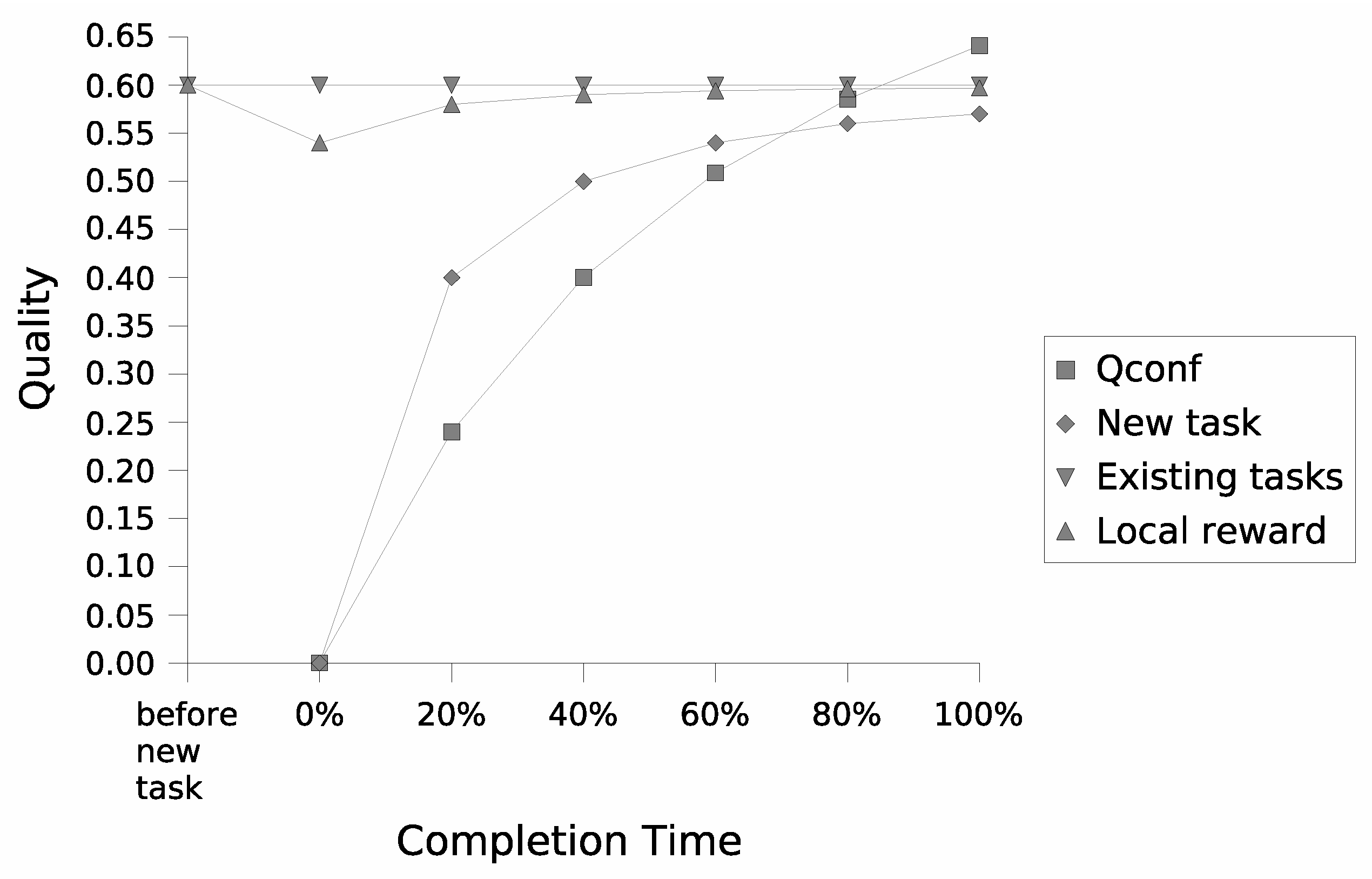
Figure 2 illustrates a scenario where the average available resources per node exceed the average resource demands of executed services. Conversely,
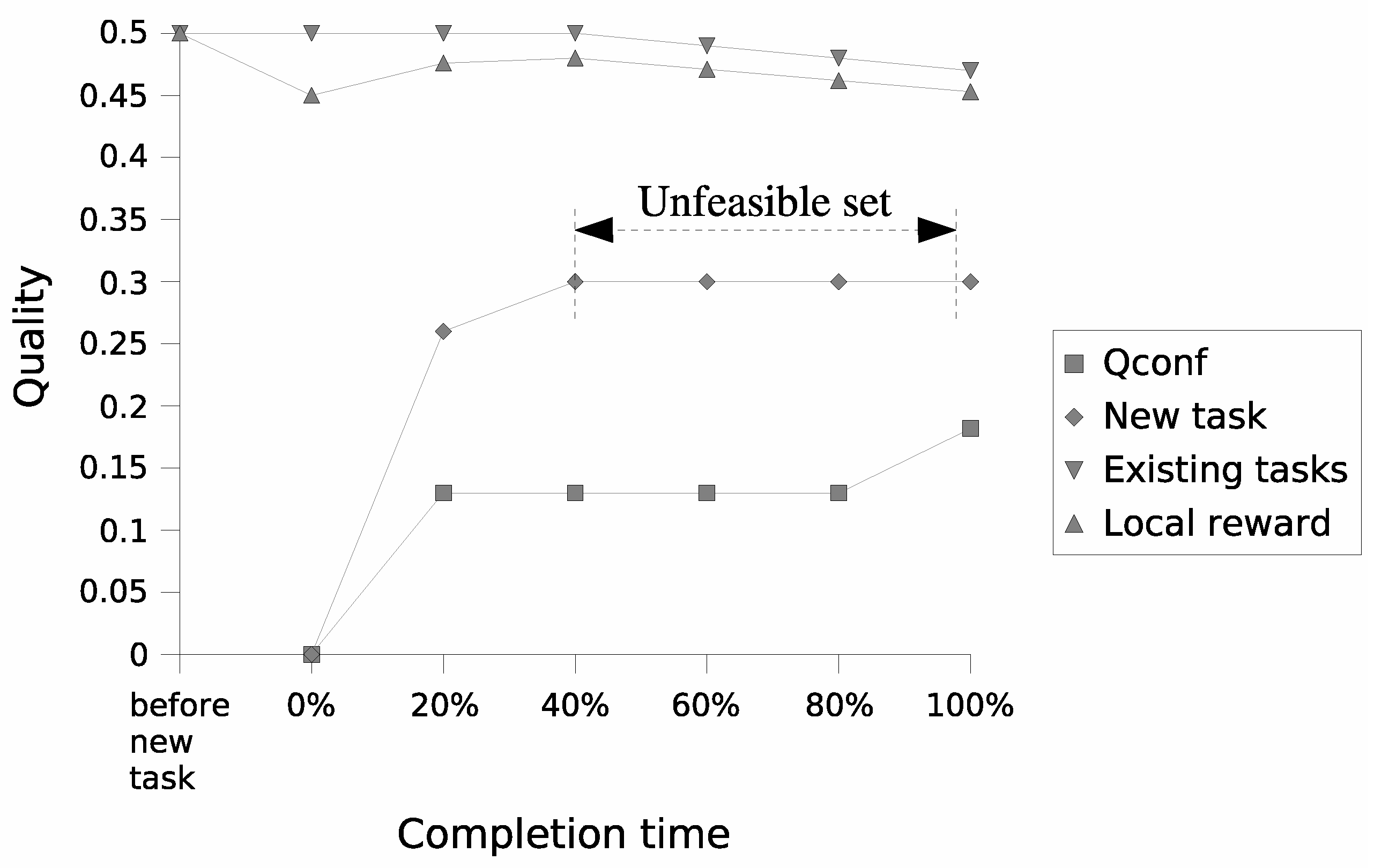
Figure 3 depicts a scenario where the average available resources per node fall short of the average resource demands.
In
Figure 2, the enhancement in the solution’s quality,
, stems from the augmented reward of the new task (step 1 of the algorithm). Notably, with surplus resources, the QoS levels of previously accepted tasks remain unaltered. Consequently, this elevation in the reward attained by the new service also bolsters the node’s local reward, initially influenced by the proposal to serve the newly arrived service at the minimum requested QoS level. However, in scenarios constrained by resources (depicted in
Figure 3), endeavors to elevate the reward obtained by the new service might yield an infeasible set of SLAs. This prompts the execution of step 2 of the service formulation algorithm, aimed at seeking a new feasible solution that enhances satisfaction for the service request under negotiation. As detailed in
Section 4, the cluster formation algorithm shoulders the responsibility of selecting nodes with higher local rewards from proposals with comparable evaluation values for the new user, thereby fostering load balancing.
Note that in both scenarios, the proposed heuristics optimize the rate at which the quality of the determined solution for the new task improves over time. With spare resources (
Figure 2), at only 20% of the computation time, the solution’s quality for the newly arrived task reaches approximately 70% ± 5% of the achieved quality at completion time. Conversely, when QoS degradation is necessary to accommodate the new task (
Figure 3), its service proposal attains around 87% ± 4% of its final quality at 20% of computation time.
Additionally, observe that the quality of the node’s global service solution, identified by
in both figures, rapidly approaches its maximum value at an early stage of the computation. This validates the diminishing returns property of the anytime service proposal formulation, as empirically verified following its formal analysis in
Section 5.3. The same trend holds for the quality measure of a service proposal, which serves as a nondecreasing function of time, as the best feasible configuration is replaced only if another feasible solution is found with higher quality for the user’s request under negotiation (
Figure 3).
Both studies unmistakably demonstrate the utility of the proposed anytime algorithms, even when there is insufficient time to compute an optimal local and global resource allocation. While the solution’s quality can indeed be further improved with additional runtime, it rapidly approaches its optimal value during the initial stages of computation time. For complex and dynamic real-time systems, the ability to determine a collaborative service configuration at any moment represents a substantial enhancement to our framework.
6.2. Overhead
Throughout the paper, we have emphasized the notion that complex scenarios may hinder the possibility of computing optimal resource allocations and proposed anytime algorithms capable of trading-off deliberation time for the quality of achieved results. However, it is crucial to analyze the computational cost required by this approach compared to traditional versions of those algorithms [
17,
51].
Without any constraint on the time needed to find an optimal resource allocation, both algorithms follow more straightforward approaches than their anytime counterparts. The traditional cluster formation algorithm evaluates all received proposals based on their order of arrival and selects the best proposal for each of the service’s remote tasks. Similarly, the traditional service proposal formulation starts by selecting the user’s preferred QoS level and, at each iteration, downgrades the QoS attribute that minimizes the decrease in the node’s local reward until a feasible set of SLAs is found.
This section evaluates the impact of these different approaches on the required computation time to find an optimal solution. The results discussed in the following paragraphs are normalized with respect to the completion time of the traditional versions of the algorithms.
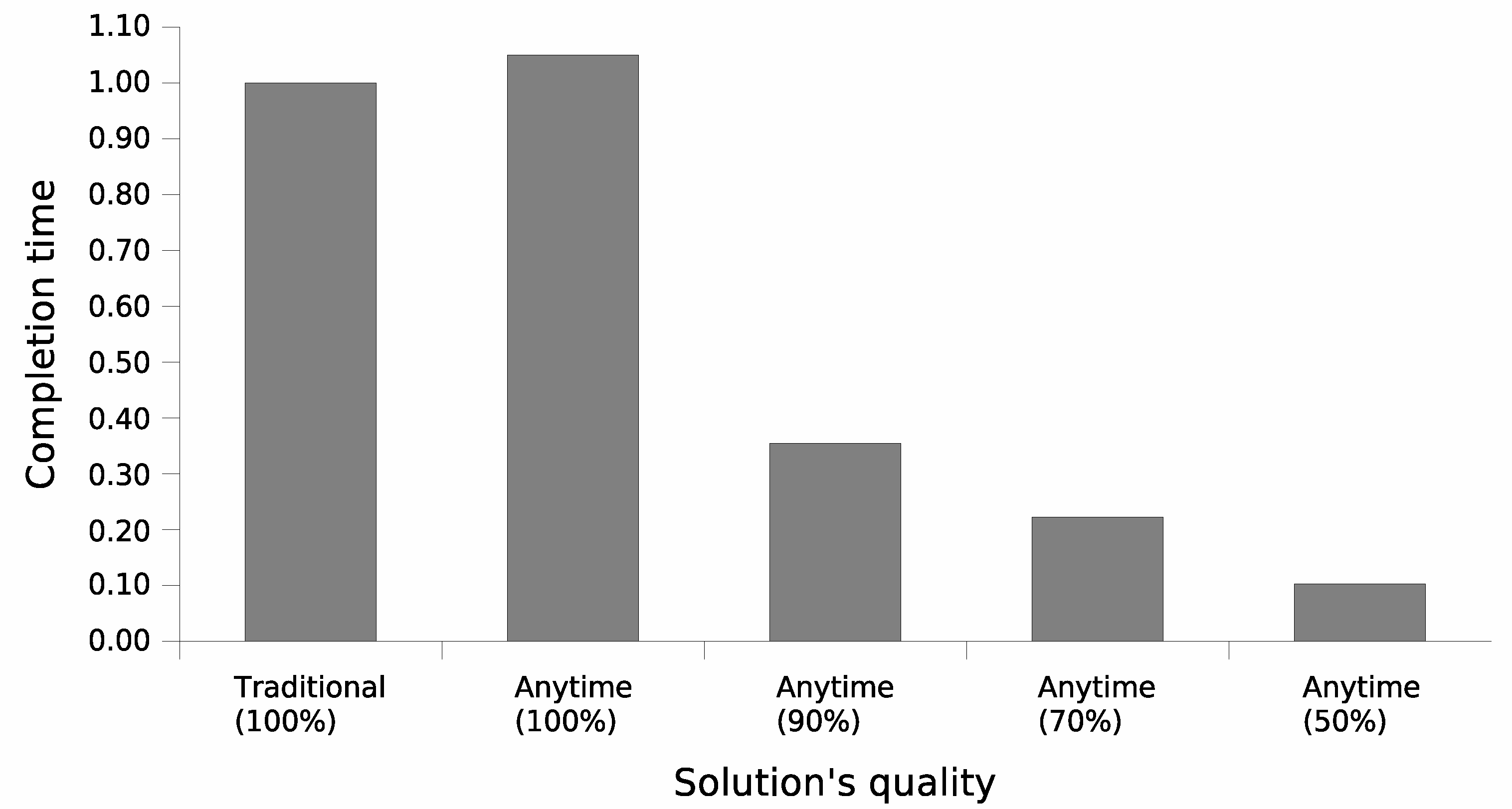
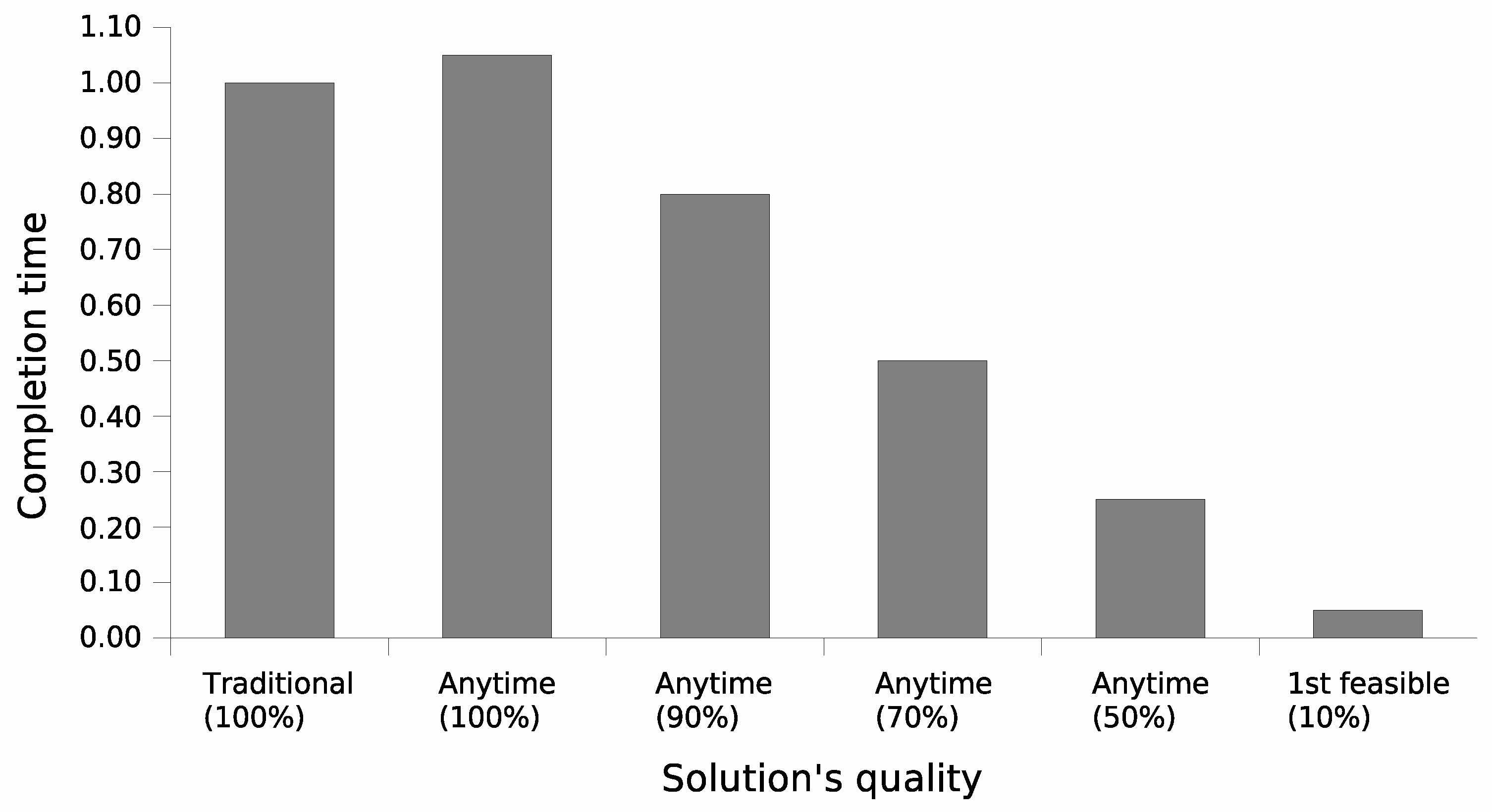
Figure 4 details the computational cost of both versions of the cluster formation algorithm. The traditional version is slightly faster than its anytime counterpart, requiring nearly 95% ± 2% of the time needed by the anytime approach to reach its final, optimal solution. This difference is explained by the way both algorithms select the next proposal to evaluate. While the traditional version sequentially evaluates service proposals according to their order of arrival, the anytime approach selects proposals based on the nodes’ local reward. This implies either sorting the proposals’ set before starting the evaluation process or searching, at each iteration, for the maximum remaining local reward.
However, it is noteworthy that the anytime version requires as little as near 10% of its completion time to achieve a solution quality of 50% ± 6% of its optimal solution, and below 40% to achieve 90% ± 5% of its optimal solution. As discussed in the previous section, such results cannot be achieved by evaluating proposals based on their arrival order.
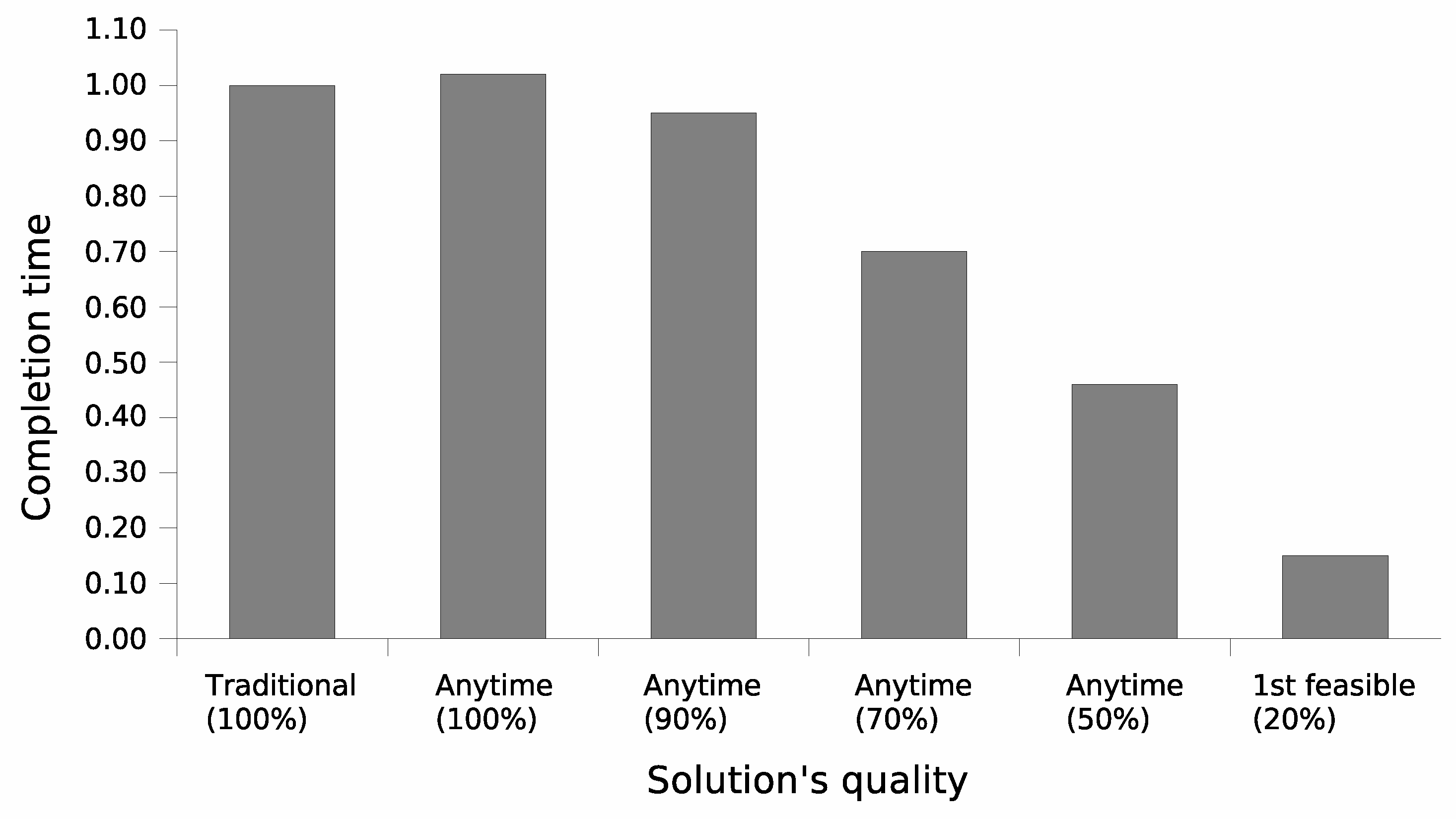
The comparison between both versions of the service proposal formulation algorithm is detailed in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6.
Figure 5 compares the required computation time when the average amount of resources per node is greater than the average amount of resources necessary for each service execution, while
Figure 6 compares both versions when the average amount of resources per node is smaller than the average amount of resources necessary for each service execution, demanding QoS degradation of the previously accepted services.
Both figures allow us to conclude that, similarly to the cluster formation algorithm, the traditional version is slightly faster at achieving its single and optimal solution. While the anytime approach aims to quickly find an initial feasible solution by considering the worst QoS level requested by the user, the traditional version starts by selecting the user’s preferred QoS level. Consequently, with spare resources, the traditional version is quicker at achieving the optimal resource allocation for the new set of tasks, while with limited resources, both versions require almost the same amount of time.
However, in both scenarios, the anytime version is significantly quicker at finding a feasible solution. With spare resources, the time needed to find the first feasible solution with a quality near 10% ± 3% of the optimal solution is less than 5% of its completion time. With limited resources, the anytime version takes about 20% of its computation time to reach a feasible solution with 15% ± 3% of the optimal solution’s quality.
These results clearly demonstrate the advantages of the anytime approach, as its overhead can be considered negligible when compared to the introduced benefits. The anytime approach rapidly achieves a feasible global and local resource allocation and maximizes the rate at which the quality of that initial solution increases over time.
7. Conclusions
As the complexity of various applications increases, multiple tasks contend for the limited resources of a single device. In this scenario, resource-constrained devices may need to collaborate with their neighbors to collectively execute services. This collaboration is essential for meeting the complex quality-of-service (QoS) constraints imposed by users and applications. Consequently, providing efficient arbitration of QoS levels in this highly dynamic, open, shared, and heterogeneous environment becomes paramount.
Our QoS-aware framework addresses the escalating demands on resources and performance by enabling services to be executed by temporary clusters of nodes. Users specify the relative importance of different QoS parameters for each service, and the framework utilizes this information to determine distributed resource allocation that optimizes satisfaction of these constraints.
However, devising an optimal distributed service provisioning solution that accommodates both users’ and service providers’ quality constraints can be exceedingly complex and time-consuming. Unlike conventional QoS optimization algorithms, which only guarantee correct output upon termination, our proposed anytime approach does not depend on the availability of deliberation time to provide a solution and a measure of its quality. This trade-off between available computation time and the quality of the achieved solution proves invaluable in open dynamic real-time systems where responses to events must be delivered within precise timing constraints to ensure desired performance levels.
The conformity of our proposed algorithms with the desired properties of anytime algorithms has been established, and the design decisions of our approach validated through extensive simulations in highly dynamic scenarios. The results unequivocally demonstrate that our anytime algorithms swiftly identify a good initial solution and efficiently optimize the rate at which the quality of the current solution improves at each iteration, with an overhead that can be considered negligible compared to the benefits they bring.
While our simulations provide valuable insights and initial validation of our proposed approach, real-world testing is crucial for confirming the effectiveness and practical applicability of the proposed algorithms. Simulations can often fall short in capturing the complexities and nuances of real-world environments, making field testing an indispensable step in the research process.
In future work, we will emphasize the importance of real-world testing to validate the generalizability and applicability of our findings across diverse contexts and environments. This will involve collaborating with industry partners and deploying our solution in pilot projects and real-world use cases to thoroughly evaluate its performance and effectiveness in practical settings. Such collaborations will not only provide a more comprehensive assessment of our algorithms but also facilitate the identification of any unforeseen challenges and the refinement of our approach based on empirical evidence.
A decentralized architecture is essential for maintaining scalability in the context of limited computational resources and an increasing search space. This approach helps distribute the computational load, thereby preventing bottlenecks and enhancing the system’s overall efficiency and robustness. The dynamic nature of resource allocation further complicates this issue, necessitating adaptive and flexible strategies.
Future work should focus on the development of advanced resource allocation algorithms incorporating predictive models to anticipate resource demands and employing reinforcement learning techniques to optimize allocation policies over time [
54]. Such research will be pivotal in enhancing the scalability and efficiency of decentralized systems in increasingly complex and dynamic environments.
Furthermore, we will also carefully evaluate the feasibility and potential benefits of transitioning from a service-oriented processing approach to an event-driven one. We recognize the importance of timely responses to events and the potential enhancements that an event-driven architecture, bolstered by recent advancements, could bring to our proposed solution. This evaluation will be a focus of our future work.