Ionospheric Error Models for Satellite-Based Navigation—Paving the Road towards LEO-PNT Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction and Motivation
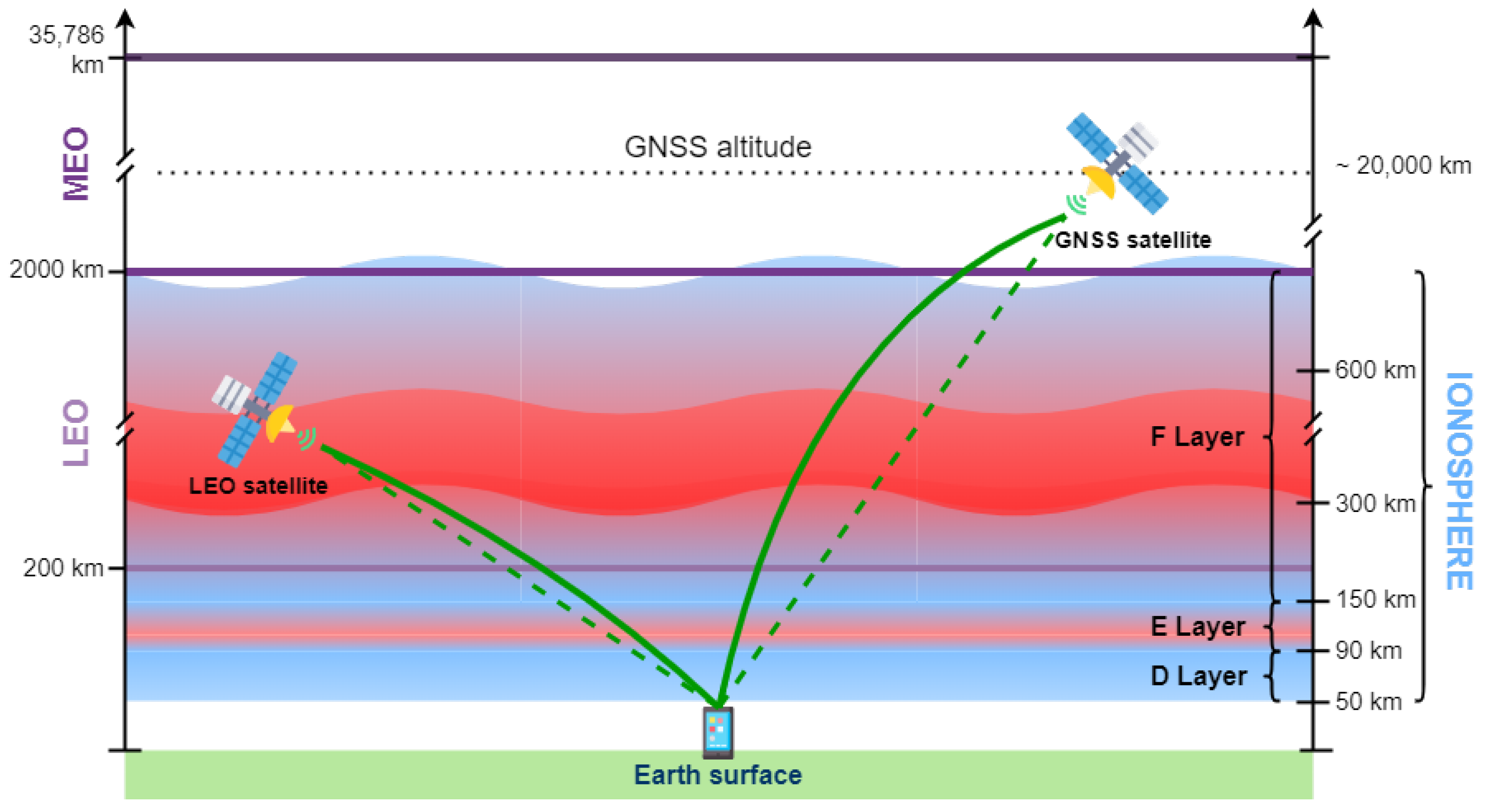
1.1. LEO-PNT versus GNSS
1.2. Sources of Errors in Satellite-Based Positioning
1.3. Paper Goals, Research Questions, and Main Contributions
- We propose a novel IAMM for ionospheric delay compensation at the receiver;
- We validate the IAMM model by comparing it with current state-of-the-art models used today using real observation data from a variety of GNSS reference stations, as well as from Android mobile receivers;
- We discuss the proposed model’s challenges and possible improvements to the LEO-PNT context.
2. Related Work
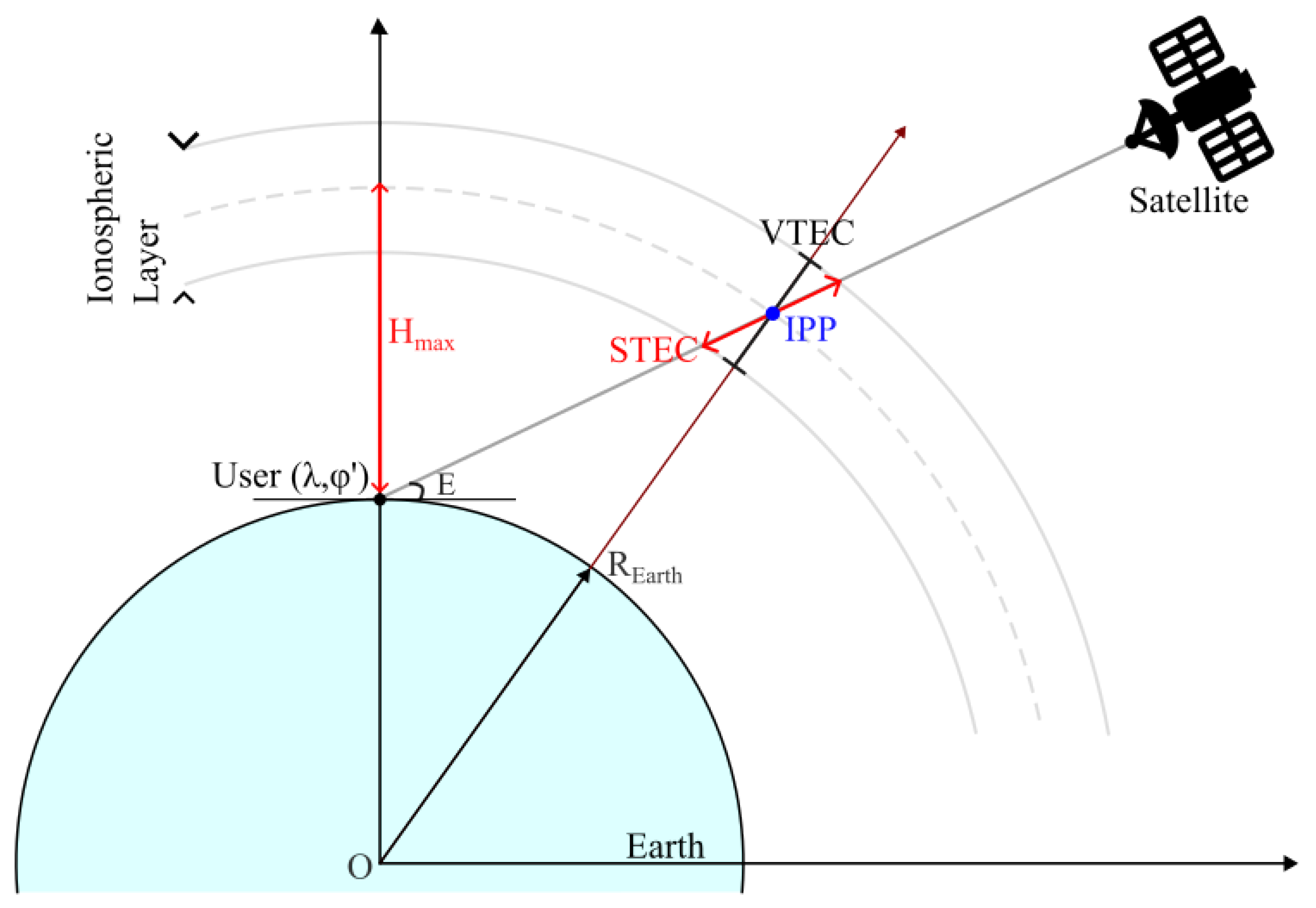
2.1. Overview of the Ionospheric Delay Concept
2.2. Klobuchar Model
2.3. NeQuick Model
2.4. Neural Network Models
2.5. IRI Model
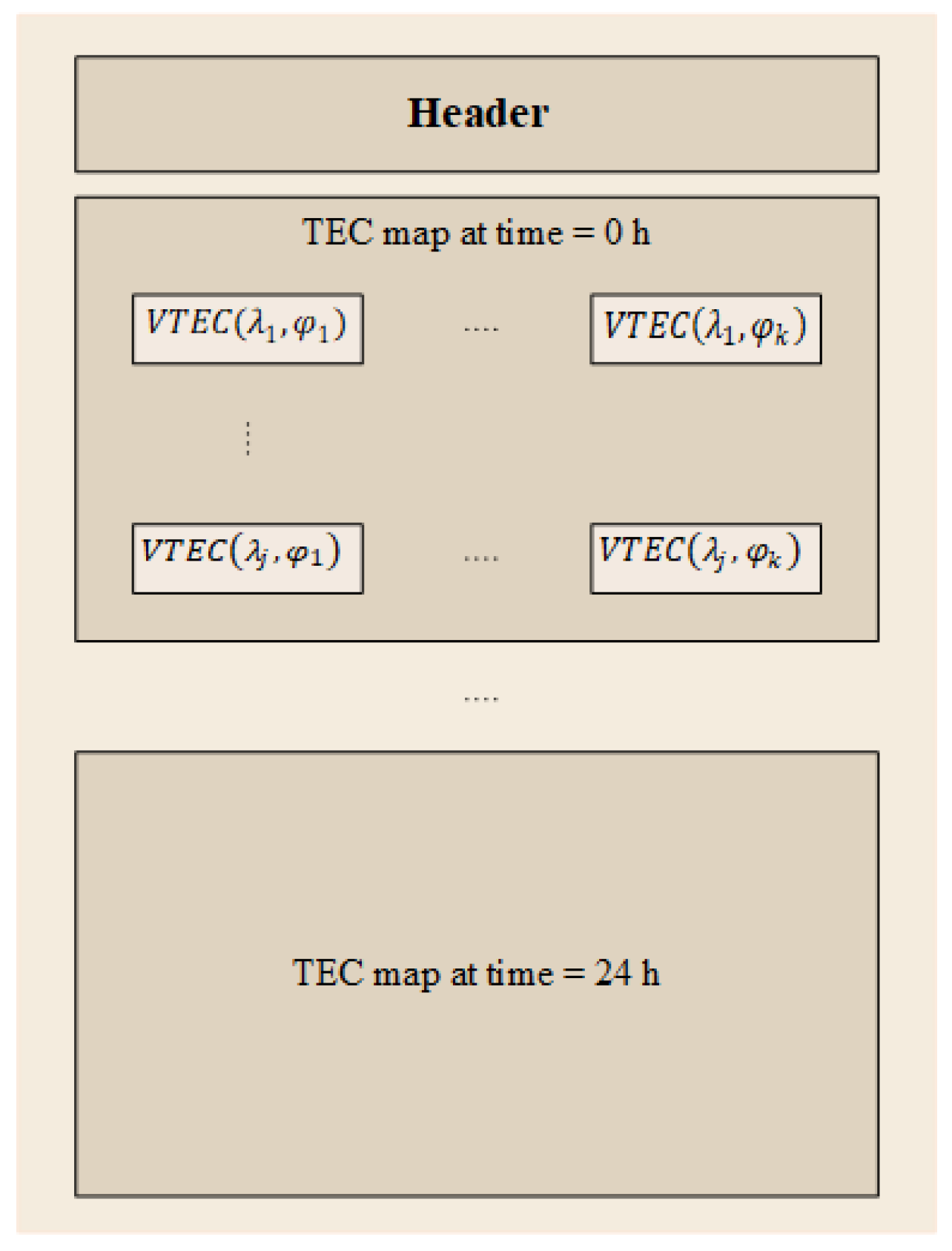
2.6. IGS Model and Database
- Final GIMs (11 days);
- A predicted solution (available 1–2 days in advance).
2.7. Ionospheric Models for LEO Satellites
2.8. Summary of State-of-the-Art and Our Proposed Model at a Glance
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. IAMM Calculation Strategy
4. Results
4.1. TEC Results
4.2. Ionospheric Delay Results
- Method 1: No ionospheric correction;
- Method 2: Klobuchar ionospheric correction;
- Method 3: IRI ionospheric correction;
- Method 4: IAMM ionospheric correction.
4.2.1. Data from Reference Stations—Static Conditions
4.2.2. Data from Android Devices—Dynamic Conditions
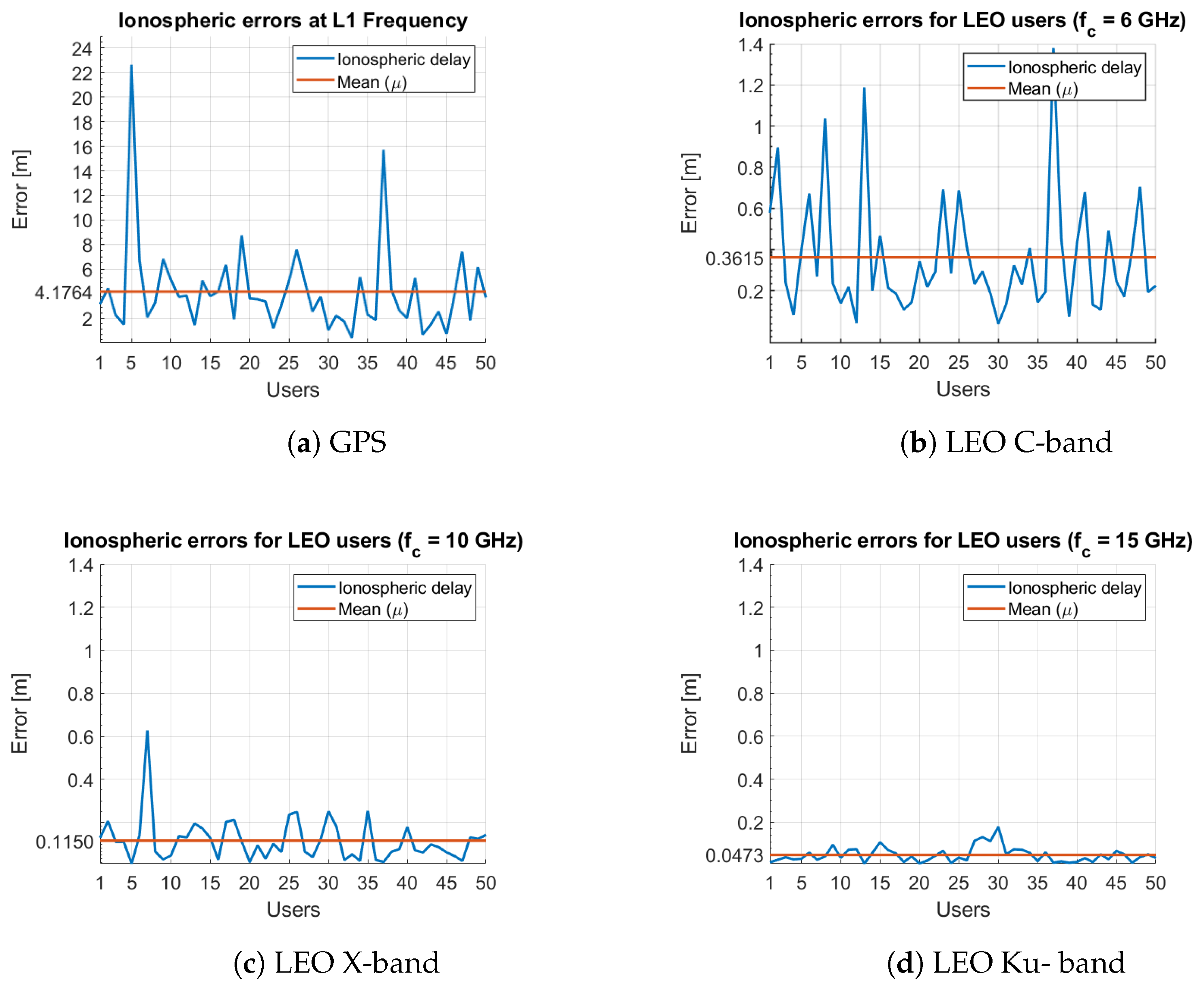
4.3. Results Extended to an LEO-PNT System
5. Discussion and Future Works
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| AWGN | Additive white Gaussian noise |
| BDGIM | BeiDou Global Broadcast Ionospheric Delay Correction Model |
| CDDIS | Crustal Dynamics Data Information System |
| CMEs | Coronal mass ejections |
| COSPAR | Committee on Space Research |
| DFRs | Dual-frequency receivers |
| ED | Electron density |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform |
| GEO | Geo-stationary orbit |
| GIMs | Global ionospheric maps |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite Systems |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IAMM | Interpolated and Averaged Memory Model |
| ID | Ionopsheric delay |
| IGS | International GNSS Service |
| IONEX | IONosphere map EXchange format |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IRI | International Reference Ionosphere |
| ISR | Incoherent scattered radar |
| IWG | Ionosphere Working Group |
| LEO | Low Earth orbit |
| LOS | Line of sight |
| MEO | Medium Earth orbit |
| ML | Machine learning |
| NASA | National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| NLOS | Non-line-of-sight |
| NLS | National Land Survey of Finland |
| NMEA | National Marine Electronics Association |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| PNT | Position, Navigation, and Timing |
| PPP | Precise point positioning |
| QZSS | Quasi-Zenith Satellite System |
| Q4DIM | Quasi-4-Dimension Ionospheric Modeling |
| RF | Radio frequency |
| RIM | Regional ionospheric map |
| RINEX | Receiver-independent exchange format |
| RMS | Root mean square |
| RSS | Received signal strength |
| RT-GIMs | Real-time global ionospheric maps |
| SLM-MF | Single-layer model mapping function |
| SFRs | Single-frequency receivers |
| SPP | Single-point positioning |
| STEC | Slant total electron content |
| TDL | Tapped delay line |
| TEC | Total electron content |
| TECU | TEC units |
| ToA | Time of arrival |
| URSI | Union of Radio Science |
| VTEC | Vertical total electron content |
| WLS | Weighted least squares |
References
- Reid, T.G.; Neish, A.M.; Walter, T.; Enge, P.K. Broadband LEO Constellations for Navigation. Navigation 2018, 65, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Revisiting Doppler positioning performance with LEO satellites. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassas, Z.Z.M. Navigation from Low-Earth Orbit. In Position, Navigation, and Timing Technologies in the 21st Century; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Chapter 43; pp. 1381–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prol, F.S.; Ferre, R.M.; Saleem, Z.; Välisuo, P.; Pinell, C.; Lohan, E.S.; Elsanhoury, M.; Elmusrati, M.; Islam, S.; Çelikbilek, K.; et al. Position, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) Through Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites: A Survey on Current Status, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 83971–84002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ferre, R.; Lohan, E.S.; Falco, G.; Falletti, E. GDOP-based analysis of suitability of LEO constellations for future satellite-based positioning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Wireless for Space and Extreme Environments (WiSEE), Virtual, 12–14 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, G.; Riddell, A.; Hausler, G. The International GNSS Service. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 967–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.; Montenbruck, O. Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems, 1st ed.; Springer Handbooks; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Ferre, R.; Richter, P.; Falletti, E.; de la Fuente, A.; Lohan, E.S. A Survey on Coping With Intentional Interference in Satellite Navigation for Manned and Unmanned Aircraft. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22, 249–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzione, F.; Paonni, M. LEO-PNT Mega-Constellations: A New Design Driver for the Next Generation MEO GNSS Space Service Volume and Spaceborne Receivers. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Monterey, CA, USA, 24–27 April 2023; pp. 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, P. ESA LEO PNT Program Getting Underway. Inside GNSS Journal. 2023. Available online: https://insidegnss.com/esa-leo-pnt-program-getting-underway/ (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Industry Invited to Bid for Ow-Earth Orbit Satnav Demo. Newsletters. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Navigation/Industry_invited_to_bid_for_low-Earth_orbit_satnav_demo (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Janssen, T.; Koppert, A.; Berkvens, R.; Weyn, M. A Survey on IoT Positioning Leveraging LPWAN, GNSS, and LEO-PNT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 11135–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PNT from and for Space: What Are the Steps Necessary to Make LEO Positioning a Eality? Novatel Webinar. 2023. Available online: https://novatel.com/tech-talk/webinars/pnt-from-and-for-space-leo-positioning (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Joerger, M.; Gratton, L.; Pervan, B.; Cohen, C.E. Analysis of Iridium-Augmented GPS for Floating Carrier Phase Positioning. Navigation 2010, 57, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Su, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. BeiDou Augmented Navigation from Low Earth Orbit Satellites. Sensors 2019, 19, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Xu, T.; Gao, F.; Nie, W.; Yang, H. Optimal Walker Constellation Design of LEO-Based Global Navigation and Augmentation System. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Fu, W.; Han, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, R. Bottomside ionospheric snapshot modeling using the LEO navigation augmentation signal from the Luojia-1A satellite. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeek, A. Ionosphere delay remote sensing during geomagnetic storms over Egypt using GPS phase observations. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.M. Space Weather Telecommunications; Springer Science & Business Media: Cham, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilitza, D.; Altadill, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mertens, C.; Truhlik, V.; Richards, P.; McKinnell, L.A.; Reinisch, B. The International Reference Ionosphere 2012—A model of international collaboration. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2014, 4, A07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K. Ionospheric Radio Propagation. 1965. Available online: https://digital.library.unt.edu/ark:/67531/metadc13264/ (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Jakowski, N.; Mayer, C.; Hoque, M.M.; Wilken, V. Total electron content models and their use in ionosphere monitoring. Radio Sci. 2011, 46, RS0D18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasyukevich, Y.V.; Zatolokin, D.; Padokhin, A.; Wang, N.; Nava, B.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yasyukevich, A.; Chen, C.; Vesnin, A. Klobuchar, NeQuickG, BDGIM, GLONASS, IRI-2016, IRI-2012, IRI-Plas, NeQuick2, and GEMTEC Ionospheric Models: A Comparison in Total Electron Content and Positioning Domains. Sensors 2023, 23, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, E.D.; Hegarty, C.J. Understanding GPS, Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Artech House: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grunwald, G.; Ciećko, A.; Kozakiewicz, T.; Krasuski, K. Analysis of GPS/EGNOS Positioning Quality Using Different Ionospheric Models in UAV Navigation. Sensors 2023, 23, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Haralambous, H.; Kavutarapu, V. Global Longitudinal Behavior of IRI Bottomside Profile Parameters From FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC Ionospheric Occultations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 7011–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Shprits, Y.; Prol, F.; Lühr, H.; Berrendorf, M.; Zhelavskaya, I.; Xiong, C. A novel neural network model of Earth’s topside ionosphere. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, W.; Burns, A.G.; Zhao, B.; Luan, X.; Zhong, J.; Dou, X. Response of the topside and bottomside ionosphere at low and middle latitudes to the October 2003 superstorms. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 6974–6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmołowski, W.; Ren, X.; Wielgosz, P.; Krypiak-Gregorczyk, A. On the advantage of stochastic methods in the modeling of ionospheric total electron content: Southeast Asia case study. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 044008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, M.M.; Schuh, H.; Schmidt, M. Ray tracing technique for global 3-D modeling of ionospheric electron density using GNSS measurements. Radio Sci. 2015, 50, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natras, R.; Goss, A.; Halilovic, D.; Magnet, N.; Mulic, M.; Schmidt, M.; Weber, R. Regional Ionosphere Delay Models Based on CORS Data and Machine Learning. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2023, 70, navi.577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, S.; Forootan, E. Reconstructing Regional Ionospheric Electron Density: A Combined Spherical Slepian Function and Empirical Orthogonal Function Approach. Surv. Geophys. 2017, 39, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhi, N.; Fu, H. A Data-Driven Forecast Model of Ionospheric Slant Total Electron Content Based on Decision Trees. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES), Monterey/Seaside, CA, USA, 26–30 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, L.; Fortunato, M.; Gioia, C. Assessment of Real-time Multipath Detection with Android Raw GNSS Measurements by Using a Xiaomi Mi 8 Smartphone. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohan, E.S.; Bierwirth, K.; Kodom, T.; Ganciu, M.; Lebik, H.; Elhadi, R.; Cramariuc, O.; Mocanu, I. Standalone Solutions for Clean and Sustainable Water Access in Africa Through Smart UV/LED Disinfection, Solar Energy Utilization, and Wireless Positioning Support. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 81882–81899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohan, E.S.; Kodom, T.; Lebik, H.; Grenier, A.; Zhang, X.; Cramariuc, O.; Mocanu, I.; Bierwirth, K.; Nurmi, J. Raw GNSS Data Analysis for the LEDSOL Project—Preliminary Results and Way Ahead. In Proceedings of the WiP in Hardware and Software for Location Computation (WIPHAL 2023), Castellon, Spain, 6–8 June 2023; 3434. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, V.; Stopar, B.; Sterle, O.; Pavlovčič-Prešeren, P. Low-Cost Dual-Frequency GNSS Receivers and Antennas for Surveying in Urban Areas. Sensors 2023, 23, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, C.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Shang, R. Smartphone Positioning and Accuracy Analysis Based on Real-Time Regional Ionospheric Correction Model. Sensors 2021, 21, 3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda a, S.K.; Harikaa, B.; Vineetha, P.; Kumar Dabbakutib, J.R.K.; Akhila, S.; Srujanaa, G. Validity of Different Global Ionospheric TEC Maps over Indian Region. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking (ICAC3N), Greater Noida, India, 17–18 December 2021; pp. 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobuchar, J. Ionospheric Time-Delay Algorithm for Single-Frequency GPS Users. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1987, AES-23, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M.K.K. Comparison and Development of Ionospheric Correction Methods in GNSS. Master’s Thesis, Tampere University, Tampere, Finland, 2016. Available online: https://trepo.tuni.fi/handle/123456789/24484 (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- European GNSS Open Service. Ionospheric Correction Algorithm for Galileo Single Frequency Users. 2016. Available online: https://www.gsc-europa.eu/sites/default/files/sites/all/files/Galileo_Ionospheric_Model.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Sanz Subirana, J.; Juan Zornoza, J.M.; Hernández-Pajares, M. NeQuick Ionospheric Model—Navipedia. 2017. Available online: https://gssc.esa.int/navipedia/index.php?title=NeQuick_Ionospheric_Model (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Mallika, I.L.; Ratnam, D.V.; Ostuka, Y.; Sivavaraprasad, G.; Raman, S. Implementation of Hybrid Ionospheric TEC Forecasting Algorithm Using PCA-NN Method. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisits, J.; Glaner, M.; Weber, R. Regiomontan: A Regional High Precision Ionosphere Delay Model and Its Application in Precise Point Positioning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froń, A.; Galkin, I.; Krankowski, A.; Bilitza, D.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Reinisch, B.; Li, Z.; Kotulak, K.; Zakharenkova, I.; Cherniak, I.; et al. Towards Cooperative Global Mapping of the Ionosphere: Fusion Feasibility for IGS and IRI with Global Climate VTEC Maps. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hernández-Pajares, M.; Yang, H.; Monte-Moreno, E.; Roma-Dollase, D.; García-Rigo, A.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Laurichesse, D.; Blot, A.; et al. The cooperative IGS RT-GIMs: A reliable estimation of the global ionospheric electron content distribution in real time. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4567–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, S.; Gurtner, W.; Feltens, J. IONEX: The IONosphere Map EXchange Format Version 1.1. 1998. Available online: https://www.aiub.unibe.ch/download/ionex/ionex1.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Kim, J.; Kim, M. Determination of Ionospheric Delay Scale Factor for Low Earth Orbit using the International Reference Ionosphere Model. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2014, 30, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M. NeQuick G model based scale factor determination for using SBAS ionosphere corrections at low earth orbit. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Liu, C. Modeling the effects of ionospheric scintillations on LEO Satellite communications. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2004, 8, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilitza, D.; Pezzopane, M.; Truhlik, V.; Altadill, D.; Reinisch, B.W.; Pignalberi, A. The International Reference Ionosphere Model: A Review and Description of an Ionospheric Benchmark. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2022RG000792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Song, S. Near real-time global ionospheric total electron content modeling and nowcasting based on GNSS observations. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, A. Introduction To Modeling and Simulation. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference Proceedings, Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–10 December 1997; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pajares, M.; Juan, J.M.; Sanz, J.; Orus, R.; Garcia-Rigo, A.; Feltens, J.; Komjathy, A.; Schaer, S.C.; Krankowski, A. The IGS VTEC maps: A reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, Y. Establishment of polynomial regional ionospheric delay model by using GNSS dual-frequency combined observations. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1550, 042057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Plumb, R.A. Introduction to Ionospheric Physics; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Solar and Geophysical Event Reports. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Space Weather Prediction Center. 2023. Available online: ftp://ftp.swpc.noaa.gov/pub/indices/events/20230805events.txt (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Grenier, A. Development of a GNSS Positioning Application under Android OS Using GALILEO Signals. Master’s Thesis, Ecole Nationale de Sciences Geographiques, Champs-sur-Marne, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]




| Ref. | Model | Type | Broadcast | Input Data | Direct Output Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40] | Klobuchar | Empirical | Yes | Atmospheric coef., approx. receiver position | ID |
| [42] | NeQuick | Empirical | Yes | Atmospheric coef., approx. user position | ED, ID |
| [31,33,44,45] | Neural networks | Data-driven | No | Data from other models/stations | TEC, ID |
| [52] | IRI | Empirical | No | Ionosondes, ISRs, in situ data (satellites) | ED, ID, ionosphere detailed composition (see Section 2.5) |
| [53] | IGS (GIMs) | Mathematical | No | Dual-frequency measurements from GNSS stations | IONEX files |
| This work | IAMM | Data-driven | No | Approx. receiver position, Y matrix (see Section 3.2) | TEC, ID |
| R | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Solar Year | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Number of Points Used in Statistics | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|
| 5183 | 0.9283 |
| 15,549 | 0.9574 |
| 31,098 | 0.9589 |
| AVG [m] | No Correction | Klobuchar | IRI | IAMM (Proposed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 5.390 | 3.244 | 3.159 | 1.976 |
| – | (−39.7%) | (−41.4%) | (−63.3%) | |
| StD (1-) | 1.277 | 1.051 | 1.0682 | 0.848 |
| – | (−17.7%) | (−16.4%) | (−33.6%) | |
| a Using observations from Tampere University (high-grade) | ||||
| AVG [m] | No Correction | Klobuchar | IRI | IAMM (Proposed) |
| Mean | 6.209 | 4.252 | 4.397 | 4.1708 |
| – | (−31.5%) | (−29.2%) | (−32.8%) | |
| StD (1-) | 3.470 | 3.219 | 3.141 | 3.164 |
| – | (−7.2%) | (−9.5%) | (−8.8%) | |
| b Using observations from the FinnRef network (high-grade) | ||||
| AVG [m] | No Correction | Klobuchar | IRI | IAMM (Proposed) |
| Mean | 42.815 | 34.052 | 38.884 | 36.388 |
| – | (−20.5%) | (−9.2%) | (−15%) | |
| StD (1-) | 18.710 | 18.103 | 18.397 | 18.211 |
| – | (−3.2%) | (−1.7%) | (−2.7%) | |
| c Using observations from Android smartphones (low-power) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imad, M.; Grenier, A.; Zhang, X.; Nurmi, J.; Lohan, E.S. Ionospheric Error Models for Satellite-Based Navigation—Paving the Road towards LEO-PNT Solutions. Computers 2024, 13, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13010004
Imad M, Grenier A, Zhang X, Nurmi J, Lohan ES. Ionospheric Error Models for Satellite-Based Navigation—Paving the Road towards LEO-PNT Solutions. Computers. 2024; 13(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleImad, Majed, Antoine Grenier, Xiaolong Zhang, Jari Nurmi, and Elena Simona Lohan. 2024. "Ionospheric Error Models for Satellite-Based Navigation—Paving the Road towards LEO-PNT Solutions" Computers 13, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13010004
APA StyleImad, M., Grenier, A., Zhang, X., Nurmi, J., & Lohan, E. S. (2024). Ionospheric Error Models for Satellite-Based Navigation—Paving the Road towards LEO-PNT Solutions. Computers, 13(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers13010004








