Abstract
Protein dephosphorylation is the process of removing phosphate groups from protein molecules, which plays a vital role in regulating various cellular processes and intricate protein signaling networks. The identification and prediction of dephosphorylation sites are crucial for this process. Previously, there was a lack of effective deep learning models for predicting these sites, often resulting in suboptimal outcomes. In this study, we introduce a deep learning framework known as “DephosNet”, which leverages transfer learning to enhance dephosphorylation site prediction. DephosNet employs dual-window sequential inputs that are embedded and subsequently processed through a series of network architectures, including ResBlock, Multi-Head Attention, and BiGRU layers. It generates predictions for both dephosphorylation and phosphorylation site probabilities. DephosNet is pre-trained on a phosphorylation dataset and then fine-tuned on the parameters with a dephosphorylation dataset. Notably, transfer learning significantly enhances DephosNet’s performance on the same dataset. Experimental results demonstrate that, when compared with other state-of-the-art models, DephosNet outperforms them on both the independent test sets for phosphorylation and dephosphorylation.
1. Introduction
Protein phosphorylation is the process by which a phosphate group (PO₄3−) is covalently added to a protein molecule. This process is usually catalyzed by enzyme-like proteins, known as kinases. Kinases trigger the phosphorylation reaction by transferring phosphate groups from ATP to specific amino acid residues of the protein (e.g., serine, threonine, or tyrosine). Protein phosphorylation is a common cellular signaling mechanism that regulates protein activity, stability, subcellular localization, and protein interactions with other molecules [1,2,3].
Protein dephosphorylation is the process by which a phosphate group is removed from a protein molecule. This process is usually catalyzed by protein phosphatases and occurs on serine, threonine, or tyrosine [4]. Protein phosphatases hydrolyze phosphate bonds, removing the phosphate group from the phosphorylation site on the protein and returning the protein molecule to its original state [5]. Protein dephosphorylation is an essential regulatory mechanism. Through dephosphorylation, proteins can be activated or inhibited at different time points and under different environments to regulate intracellular signaling and biological processes. Dephosphorylation can reverse altered interactions between proteins and other molecules. Dephosphorylation can also restore the original interaction patterns between proteins and their interacting molecules, which is essential for regulating complex intracellular protein networks and signaling in cells.
In many cases, there are interactions between kinases and phosphatases to control the levels of key regulatory proteins. The phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of proteins plays a key role in most cellular processes, such as signal transduction, proliferation, and growth. Many enzymes and receptors are activated and inactivated by phosphorylation/dephosphorylation events carried out by kinases/phosphatases [6]. However, phosphatases are misregulated in diseases, including cancer. Phosphatases such as PTPRD and PTPRU have been shown to act as tumor suppressors in human malignancies [7].
Over the past few decades, artificial intelligence has played a very important role in downstream missions [8]. The field of bioinformatics has experienced a flourishing development, achieving remarkable accomplishments in areas such as proteomics research [9,10], single-cell classification [11,12], and intelligent healthcare [13]. Research on accelerating the computational process of bioinformatics algorithms by utilizing the parallel computing power of GPUs has also yielded good results [14,15]. In the field of protein post-translational modification prediction, the establishment of large databases cataloging experimentally determined phosphorylation sites [16,17] has enabled more and more researchers to delve into studies related to protein phosphorylation and develop some collegiate and accurate methods and tools for phosphorylation site prediction [18,19,20,21]. Transphos is a deep learning model that combines a transformer-encoder and CNN architecture to autonomously extract features from protein sequences in order to predict general phosphorylation sites. In 2019, Fenglin Luo and colleagues introduced DeepPhos, which employs densely connected convolutional neuron network blocks to capture various representations of sequences. DeepPhos utilizes intra-block crosstalk layers and inter-block crosstalk layers to make the final phosphorylation predictions. However, protein dephosphorylation-related studies are few and far between, mainly due to the relatively limited data resources of publicly available dephosphorylation sites. The lack of large-scale dephosphorylation site datasets restricts bioinformatics researchers from conducting in-depth studies in this field. However, in recent years, the establishment of the DEPOD database has led more and more researchers to focus on and delve into the study of dephosphorylation site identification. For example, Meenal Chaudhari et al. [22] developed DTL-DephosSite, a general dephosphorylation site predictor based on the S/T and Y residues of Lstm. However, the prediction accuracy of the existing methods is low and there is much room for improvement. Firstly, most of the existing methods, such as DTL-DephosSite, are single-channel inputs, which are not able to extract more information about multilevel features. In our method, we set up input channels with different sequence lengths in order to extract richer information. Meanwhile, the robustness of the existing methods is poor, which does not pay attention to the characteristics of the long-range dependence of proteins, and the shallow information is easy to be lost in the later stage. To address this drawback, we introduced ResBlock with a multi-head self-attention mechanism in our model; therefore, in order to solve the above problems of dephosphorylation models and further explore deep learning methods, it is crucial to establish efficient and accurate dephosphorylation prediction models in this study.
In this work, we propose a new architecture, DephosNet, based on residual networks and a multi-head attention mechanism, using dual-channel inputs to improve the model’s prediction ability for dephosphorylation sites. By incorporating network structures like ResBlock, MultiHeadAttention, and BiGRU into DephosNet, we enhance its predictive capabilities. Our approach involves applying transfer learning to the problem of dephosphorylation site prediction. We use phosphorylation data as the source dataset and dephosphorylation data as the target dataset. This strategy effectively addresses the challenge posed by the small number of samples in the dephosphorylation dataset, enabling the model to achieve superior performance.
2. Methods
2.1. Data and Data Processing
In this section, the descriptions of the data and the details of processing the data are presented.
2.1.1. Dephosphorylation Dataset
This study uses the same dephosphorylation data taken from the Dephosphorylation Database (DEPOD) as DTL-DephosSite. Based on their given data, we collect the complete protein sequences in Uniport. The DEPOD dataset is a manually curated resource that harbors human phosphatases, their protein and non-protein substrates, dephosphorylation sites, and the associated signaling pathways [23]. In this dephosphorylation dataset, the positive and negative samples of the S (serine)/T (threonine) site total 2252 data points, and the positive and negative samples of the Y (tyrosine) site total 251 data points. The number of positive and negative samples is the same. As shown in Table 1, 80% of them are used as training set, and 20% are used as independent test set.

Table 1.
Dephosphorylation dataset.
2.1.2. Phosphorylation Dataset
In this research, we used a substantial amount of phosphorylation data for model pre-training, specifically drawing from the phosphorylation dataset compiled by Duolin Wang et al. [24]. We further enriched this dataset by annotating it using UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, resulting in a total of 36,475 S/T site phosphorylation data points and 1930 Y site phosphorylation data points. To generate negative samples for our analysis, we adopted a random selection approach, isolating amino acids that exhibited high non-overlapping characteristics within the same protein sequence, excluding the annotated sites. This process yielded a combined total of 68,038 S/T site negative samples and 4120 Y site negative samples. For a comprehensive view of the dataset distributions, refer to Table 2, which illustrates the breakdown of the training dataset and the independent test set.

Table 2.
Phosphorylation dataset.
2.1.3. Data Preprocessing
We employ a dual-channel input strategy to partition the long protein sequence into two shorter sequences with varying lengths, centered around the prediction site. Through experimentation, we empirically establish that the model is more proficient at extracting valuable features and delivering improved predictions when the sequence length is either 31 or 51 amino acids. In instances where the prediction site contains fewer than 31 or 51, we use * to fill the gap and achieve the required sequence length. We numerically encode the short sequences. In this study, we use the numbers 0–20 to encode the 20 amino acids and the “*” that replaces missing information and the blank sites.
2.2. DephosNet Architecture
The DephosNet network architecture is shown in Figure 1. Using short sequences of different lengths as inputs allows one to sequence features to be observed at different scales. Shorter sequences may be better at capturing localized patterns and short-range interactions, while longer sequences are better at capturing long-range protein interactions. In our model, we center on dephosphorylation sites and input window sequences with lengths of 31 and 51, respectively, which can capture different scale features and provide more information. We first encode the input sequences with integers. Then, we process the integer encoded sequences with embedding and set the dimension of the embedding layer to 21. The two embedding matrices of 31 × 21 and 51 × 21 are then obtained.
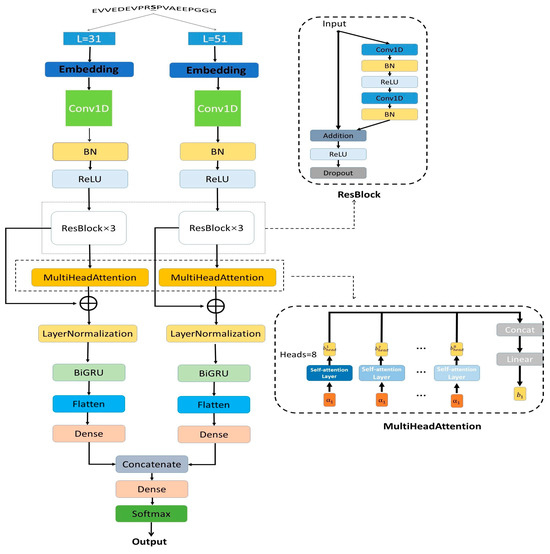
Figure 1.
DephosNet network architecture.
Firstly, the embedding matrix is input to the convolutional layer to extract shallow features. Batch normalization and ReLU activation function operations are performed to improve the stability of the model and accelerate the convergence speed of the model. Second, the features are inputted into the three-layer ResBlock. The specific architecture of the ResBlock is shown in Figure 1, which uses dilated convolution to expand the receptive field and skip-connect to allow the feature information to be passed over jumps in the network. It enables the model to better learn the correlations and dependencies in the sequences at long distances. The formula for skip-connect is shown below:
and represent the input and output of ResBlock, respectively. F represents the network function of ResBlock. To better capture the relationships between different amino acids, we use a multi-head self-attention mechanism, where each attention head can focus on different information near the amino acids, thus improving the model’s ability to model various locations in the amino acid sequence data. We concatenate the output of the multi-head self-attention mechanism with the output of ResBlock and input it in the next layer. The specific formula is listed as follows:
In the above equations, Q, K, and V denote the query vector, key vector, and value vector, respectively. are the query, key, and value matrices of the i-th head, respectively. Symbol h denotes the number of heads. denotes the output of the i-th head, and is the output matrix. Subsequently, to be able to fully utilize the contextual information of the sequences, the BiGRU layer is used to process the features after subjecting them to Layer Normalization.
represents the input information in the current moment, and represents the hidden state in the previous moment. is the hidden state passed to the next moment. is the candidate hidden state, and stands for the reset gate. is the update gate. is the sigmoid function by which the data can be changed to a value in the range of 0 to 1. Tanh is a tanh function by which the data can be changed to values in the range of −1 to 1. W is the weight matrix. The above is the formula for one-direction GRU. Our BiGRU will obtain and from two directions, and the final output is
We first obtain the features by flattening them. Then, we merge the features of the two sequence windows after the operation with dense layer and concatenate operations. Finally, we output the predicted values using the softmax function.
2.3. Transfer Learning
Transfer learning is a machine learning approach that aims to apply knowledge learned from one task or domain to another. The core idea is to improve the learning performance in the target domain by utilizing knowledge from the source domain. In recent years, transfer learning has been widely used in various fields. For example, in industrial scenarios, one can use deep transfer learning techniques for fault diagnosis [25]. Another example is the CNN-based deep transfer learning approach that can be utilized to detect COVID-19 [26]. In addition, transfer-learning-based methods can also be applied to the design of new drug development [27].
Therefore, in this study, we use the phosphorylation dataset as the source domain. Pre-training the model using phosphorylation sites can help predict potential phosphorylation sites in proteins. Such predictions help us to understand the function and regulatory mechanisms of proteins. After performing pre-training, the dephosphorylation dataset is used as the target domain to fine-tune the model parameters. In previous studies, regarding phosphorylation sites in general, they are often divided into two models for prediction: the S/T site prediction model and the Y site prediction model. After experimental attempts, we found that both predicting dephosphorylation S/T sites and predicting dephosphorylation Y sites are optimally predicted on an independent test set after pre-training based on the phosphorylation ST dataset. Specifically, for our initialized DephosNet network architecture, to learn better knowledge of the source domain, the pre-training is first performed on the Phos-ST dataset for 100 epochs and then to fine-tune the model. We configure the pre-training DephosNet by setting a learning rate of 0.000001 with an epoch parameter of 200. The pre-training modes are trained on the Dephos-ST and Dephos-Y datasets, respectively. After several experimental validations, we found that the best prediction results of the model are achieved when all layers of the pre-trained model are not frozen. The model parameters are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Model parameter values.
2.4. Performance Evaluation
In order to assess the effectiveness of our model, we employ a range of performance evaluation metrics encompassing five key indicators: Sensitivity (SN), Specificity (SP), Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC), F1 score, and the Area Under the Curve (AUC). We also visualize the True Positive Rate (TPR) versus the False Positive Rate (FPR) and calculate the AUC, representing the area under this curve. F1 (F1 score) is a metric used in statistics to measure the precision of a binary classification model. It takes into account both the precision and recall of the classification model.
3. Results
3.1. Comparison with Other State-of-the-Art Models on Dephosphorylation Site Datasets
In this section, we train and test DephosNet on the dephosphorylation dataset. We also compare it with two dephosphorylation site prediction models, RF and DTL-DephosSite.
As shown in Table 4, on S/T sites, although our model, DephosNet, performs second to RF and DTL-DephosSite on the SP metric, DephosNet outperforms RF and DTL-DephosSite on all three metrics of MCC, SN, and AUC, reaching 0.49, 0.81, and 0.82, respectively. Compared with RF and DTL-DephosSite, our model achieves improvements in the MCC of 1% and 3%, and 5% and 5% in SN. As for the AUC, 2% and 1% improvements are achieved. The results presented in Table 4 indicate that our model, when focusing on the Y site, not only ranks second in the SP metric, trailing only the DTL-DephosSite model, but also outperforms in all three crucial metrics: MCC, SN, and AUC. It attains a notable 0.52 in the MCC and an impressive 0.79 in the SN. Compared with RF and DTL-DephosSite, our model achieves improvements in the MCC of 36% and 10%. As for SN, 29% and 17% improvements are accomplished. The AUC reaches 0.83, which is 15% and 3% higher compared with that of RF and DTL-DephosSite, respectively. The experiments demonstrate that the model DephosNet proposed in this paper has superior performance on the dephosphorylation dataset compared with other state-of-the-art models.

Table 4.
Comparison scores with other state-of-the-art models on dephosphorylation site datasets.
3.2. Ablation Experiment
The DephosNet proposed in this paper is a two-channel input model, which inputs two different lengths of short sequences for dephosphorylation site prediction, respectively. To obtain the optimal combination of short sequence window lengths, the four window length combinations of (21, 51); (21, 61); (31, 51); and (31, 61) are cross-validated five-fold in this section on the S/T and Y site datasets, respectively. The average of the results of each fold is taken for comparison.
The results of DephosNet’s evaluation metrics for different window combinations at the S/T sites on an independent test set are shown in Figure 2a. First, for window combination (21, 51) as the input, the best performance of 0.91 is achieved for the SN metric, which implies that this combination is more capable of recognizing positive examples. Secondly, window combination (21,61) achieves the highest value of 0.894 for the ACC metric over the other three window combinations. This implies that increasing the sequence window length to 61 is effective in improving the ACC. However, window combination (31,51) reaches values of 0.68, 0.83, and 0.9 for the MCC, SP, and AUC evaluation metrics, respectively, indicating that the (31,51) window combination shows the best performance in the dephosphorylation site classification task. Notably, the (31,51) window combination outperforms the second-best window length combination by 3%, 1%, and 1% for the MCC, SP, and AUC metrics, respectively. It suggests that window combination (31,51) has a higher overall performance in distinguishing dephosphorylation sites relative to the other window combinations.
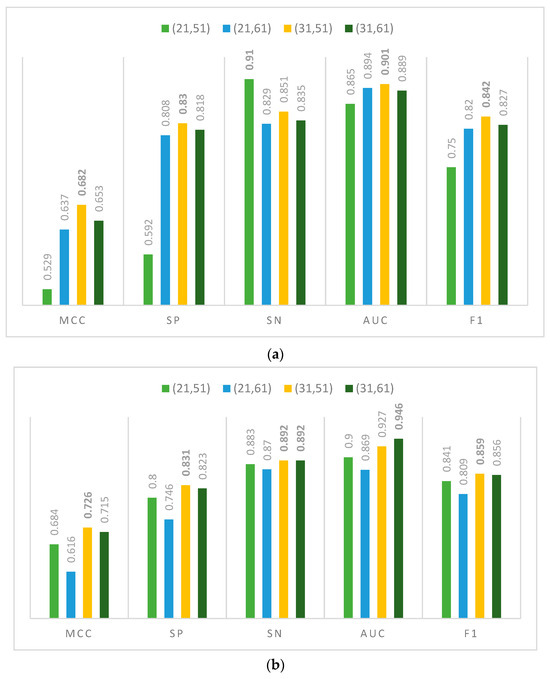
Figure 2.
Ablation experiment scores for different window combinations on (a) S/T sites and (b) Y site.
The results of DephosNet’s ablation experiments at the Y site are shown in Figure 2b. Window length combinations (21,51) and (21,61) have good predictive ability but still have some gaps compared with the other two windows. Window length combination (31,51) reaches 0.726, 0.831, 0.892, 0.927, and 0.859 in the MCC, SP, SN, AUC, and F1, respectively. This combination of factors demonstrates superior performance across all metrics, particularly showcasing higher values for the MCC, F1, SN, and SP. It excels in forecasting dephosphorylation Y sites, achieving an overall high level of performance. Window combination (31,61) also shows relatively high performance in the MCC and AUC compared with other window combinations. This window combination shows high predictive power and accuracy in predicting the dephosphorylation Y site.
In summary, the results of the ablation experiments with short sequence window length combinations for dephosphorylation sites show that the best performance in the evaluation metrics MCC, SP, and AUC is achieved when the window lengths are taken as 31 and 51. It has a significant advantage in these metrics compared with other window combinations. This finding emphasizes the importance of the (31,51) window combination in the dephosphorylation site classification task. It provides a valuable reference for further optimizing the model performance.
3.3. Comparison with Other State-of-the-Art Models Based on Transfer Learning
We conduct a comparative analysis of our model, DephosNet, in relation to other deep learning models. Given the limited number of dephosphorylation site prediction models available, we adopt a similar two-step approach of pre-training and transfer fine-tuning training for advanced phosphorylation site prediction models such as Transphos and Deepphos.
The score performance of each deep learning model on S/T sites is shown in Table 5a. Initially, we employed the Transphos model for experimental evaluation. It yielded the following results on various metrics: MCC (0.634), SP (0.786), SN (0.847), AUC (0.893), and F1 score (0.821). Subsequently, we examined the performance of the DTL-DephosSite model. It achieves scores of 0.639 for the MCC, 0.777 for SP, 0.86 for SN, 0.896 for the AUC, and 0.825 for the F1 score. Furthermore, we included the Deepphos model in the comparison. The Deepphos model attained scores of 0.633 for the MCC, 0.835 for SP, 0.797 for SN, 0.876 for the AUC, and 0.812 for the F1 score.

Table 5.
Comparison scores with other state-of-the-art models based on transfer learning on S/T sites and Y site.
Although the above models achieve good performance, DephosNet achieves MCC, SP, SN, AUC, and F1 scores of 0.713, 0.853, 0.86, 0.906, and 0.857, respectively. Dephosnet is on equal footing with DTL-DephosSite for the SN metric and outperforms the second-best model for the other metrics by 7.4%, 1.8%, 1%, and 3.2%, respectively.
Table 5 also shows the scores of each deep learning model on the Y site. The DephosNet model achieves a score of 0.726 for the MCC metric, indicating its strong correlation in predicting dephosphorylation sites. The SP is 0.808 and the SN is 0.917, which implies that the model can identify non-dephosphorylation sites and capture the true positives of dephosphorylation sites well. The AUC reaches 0.952 and the F1 score is 0.863. All of these metrics indicate that the DephosNet model has better prediction accuracy and classification ability in general, further validating the predictive ability of the model. In comparison, the Deepphos model is on par with DephosNet in terms of SN metrics, reaching 0.917. The results indicate that the Deepphos model also has a certain performance in the prediction of dephosphorylation sites, but it is slightly inferior compared with the DephosNet model. The scores of Transphos in all metrics is lower than those of DephosNet. It can be seen that Transphos has not yet reached the best prediction ability in the direction of transfer learning prediction of dephosphorylation sites. Finally, the DTL-DephosSite model scores 0.808 on SP, which is equal to the best from DephosNet, and is slightly inferior in other metrics.
In summary, our model, DephosNet, achieves the best prediction performance in the comparison. It outperforms other state-of-the-art models in terms of MCC, SP, SN, AUC, and F1 scores, which further proves the validity and superiority of DephosNet. These results provide strong support for research and application in the field of dephosphorylation site prediction.
3.4. Comparison with Other State-of-the-Art Models on Phosphorylation Site Datasets
To explore the prediction performance of DephosNet on phosphorylation datasets, in this section, our model, DephosNet, is compared with three state-of-the-art phosphorylation and dephosphorylation site prediction models, Transphos, Deepphos, and DTL-DephosSite, on S/T site phosphorylation datasets, respectively.
According to the data in Figure 3, our model, DephosNet, achieves the highest score among the four models in all three metrics: MCC, AUC, and F1. Specifically, the MCC is 0.615, the AUC is 0.895, and the F1 is 0.754. Compared with DTL-DephosSite, our model improves these metrics by 1%, 0.9%, and 1.2%, respectively. In addition, our model also achieves high levels in both SN and SP metrics. These results indicate that our model, DephosNet, exhibits the best performance on the phosphorylation dataset and is not only suitable for the prediction of dephosphorylation sites but also achieves optimal overall performance in phosphorylation prediction.
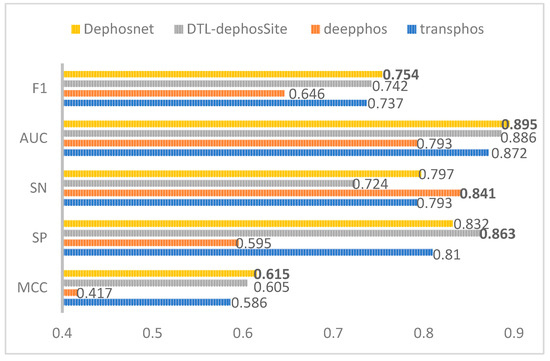
Figure 3.
Comparison scores with other state-of-the-art models on the phosphorylation site ST dataset.
4. Discussion
In this paper, we propose DephosNet, a deep learning model based on transfer learning, to predict the probability of dephosphorylation sites by inputting amino acid sequences. DephosNet’s inputs are short sequences of amino acids 31 and 51. It employs a one-dimensional convolution ResBlock network based on dilated convolution and skip-connect, a multi-head self-attention mechanism, BiGRU, and other network architectures to finally output the predicted probabilities. Although our model is originally designed to predict the probability of dephosphorylation sites, it is found through experiments that our model can also have better performance in the task of phosphorylation site prediction compared with other state-of-the-art models. Similarly, in the specific task of predicting dephosphorylation sites, DephosNet also has a better evaluation index score than other advanced models. However, we believe that there is still a lot of room for improvement, so we introduce transfer learning, and since phosphorylation and dephosphorylation are highly correlated, our model is first pre-trained using the phosphorylation dataset. Then, the dephosphorylation dataset is used to fine-tune the model’s parameters to make the DephosNet model better adapted to the downstream task (predicting dephosphorylation sites). We also experimentally demonstrate that DephosNet’s performance on the independent test set of dephosphorylation sites is greatly improved after the introduction of transfer learning and that our model is still able to take the lead in the scoring indexes after other models are also subjected to transfer learning. Regarding the choice of sequence window combinations, we have demonstrated through relevant ablation experiments that the windows we choose can achieve the best results in the task of predicting dephosphorylation sites.
Although our model achieves an excellent prediction result on the dephosphorylation dataset using the transfer learning method, there is still room for improvement. For example, more relevant dephosphorylation datasets can be collected to fine-tune the parameters. How to reduce the number of parameters in the future is still a severe problem. The model is prone to overfitting problems during training, although the model achieves promising results on both phosphorylation and dephosphorylation datasets. In the future, we will try more lightweight network architectures to achieve our task.
Finally, all datasets and codes developed in this study are publicly available at https://github.com/uuy99/Dephosnet (accessed on 9 November 2023).
Author Contributions
Methodology, Q.Y.; Validation, X.W.; Formal analysis, Q.Y.; Investigation, Q.Y. and P.Z.; Resources, X.W. and P.Z.; Writing—original draft, P.Z.; Supervision, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Project of China (2021YFA1000103), Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62272479, 62372469, 62202498), Taishan Scholarship (tsqn201812029), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (ZR2021QF023).
Data Availability Statement
The data is publicly available. https://github.com/uuy99/Dephosnet (accessed on 9 November 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chaudhari, M. Machine Learning Based Strategies to Predict Sites of Arginine Methylation, Dephosphorylation and Redox-Sensitive ERK2 Substrates. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University, Greensboro, NC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, P. The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, E127–E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubersax, J.A.; Ferrell, J.E., Jr. Mechanisms of specificity in protein phosphorylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardito, F.; Giuliani, M.; Perrone, D.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, E.G.; Beavo, J.A. Phosphorylation-Dephosphorylation of Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1979, 48, 923–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, V.S.; Baral, T.K.; Nagavelu, K.; Somasundaram, K. Serine/threonine/tyrosine-interacting-like protein 1 (STYXL1), a pseudo phosphatase, promotes oncogenesis in glioma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Rouse, C.; Chen, Y.; Dowling, J.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2007–2011. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, iv1–iv63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaldi, L.; Fallucchi, F.; Zanzotto, F.M. Dis-cover ai minds to preserve human knowledge. Future Internet 2021, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Cox, J. Perseus: A bioinformatics platform for integrative analysis of proteomics data in cancer research. Cancer Syst. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2018, 1711, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Blueggel, M.; Chamrad, D.; Meyer, H.E. Bioinformatics in proteomics. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2004, 5, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, J.C.; Kelley, D.R. Semisupervised adversarial neural networks for single-cell classification. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 1781–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alquicira-Hernandez, J.; Sathe, A.; Ji, H.P.; Nguyen, Q.; Powell, J.E. scPred: Accurate supervised method for cell-type classification from single-cell RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciecholewski, M.; Kassjański, M. Computational methods for liver vessel segmentation in medical imaging: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Song, R.; Wang, X. Crescent: A GPU-Based Targeted Nanopore Sequence Selector. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–8 December 2022; pp. 2357–2365. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Song, R.; Xiao, J.; Li, T.; Li, X. Accelerating k-Shape Time Series Clustering Algorithm Using GPU. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2023, 34, 2718–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbeck, P.V.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Latham, V.; Murray, B.; Nandhikonda, V.; Nord, A.; Skrzypek, E.; Wheeler, T.; Zhang, B.; Gnad, F. 15 years of PhosphoSitePlus®: Integrating post-translationally modified sites, disease variants and isoforms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D433–D441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkel, H.; Chica, C.; Via, A.; Gould, C.M.; Jensen, L.J.; Gibson, T.J.; Diella, F. Phospho.ELM: A database of phosphorylation sites—Update 2011. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, D261–D267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; Shi, X.; Qu, P. TransPhos: A Deep-Learning Model for General Phosphorylation Site Prediction Based on Transformer-Encoder Architecture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.-M.; Li, A. DeepPhos: Prediction of protein phosphorylation sites with deep learning. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2766–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.-M.; Li, A. PhosIDN: An integrated deep neural network for improving protein phosphorylation site prediction by combining sequence and protein–protein interaction information. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4668–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Thelen, J.J.; Dunker, A.K.; Xu, D. Musite, a tool for global prediction of general and kinase-specific phosphorylation sites. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2586–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, M.; Thapa, N.; Ismail, H.; Chopade, S.; Caragea, D.; Köhn, M.; Newman, R.H.; Kc, D.B. DTL-DephosSite: Deep Transfer Learning Based Approach to Predict Dephosphorylation Sites. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 662983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Li, X.; Köhn, M. The human DEPhOsphorylation database DEPOD: A 2015 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 43, D531–D535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zeng, S.; Xu, C.; Qiu, W.; Liang, Y.; Joshi, T.; Xu, D. MusiteDeep: A deep-learning framework for general and kinase-specific phosphorylation site prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3909–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Huang, R.; Li, J.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Z.; He, G.; Yan, R.; Gryllias, K. A perspective survey on deep transfer learning for fault diagnosis in industrial scenarios: Theories, applications and challenges. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 167, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.F.; Unlersen, M.F.; Sabanci, K.; Durdu, A. CNN-based transfer learning–BiLSTM network: A novel approach for COVID-19 infection detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 98, 106912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, C.; Han, P.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Rodríguez Patón, A.; Wang, S.; Zheng, P. PETrans: De Novo Drug Design with Protein-Specific Encoding Based on Transfer Learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).