Deploying Serious Games for Cognitive Rehabilitation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. The System Architecture
3.1. Use of IoT Devices and Edge Computing
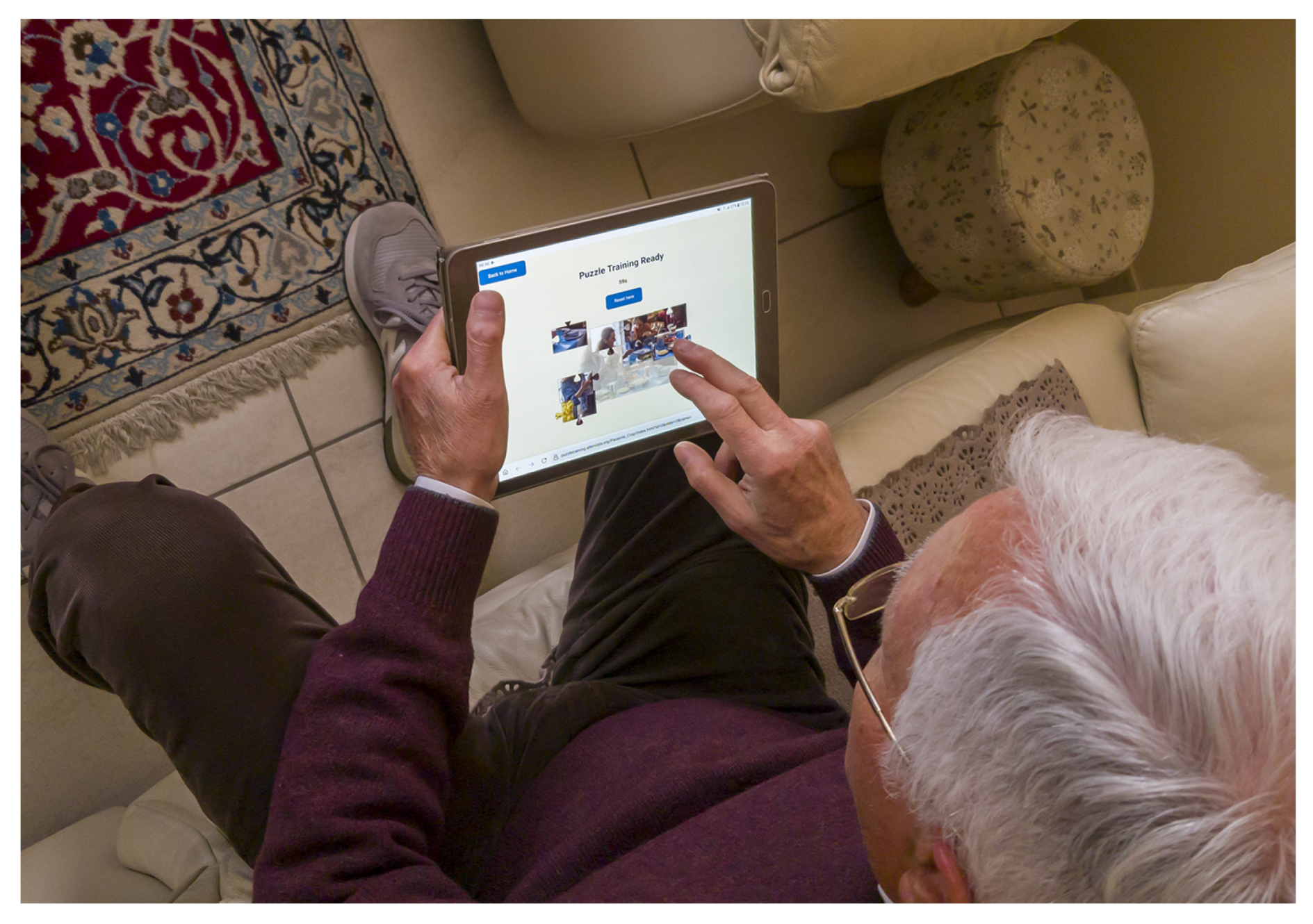
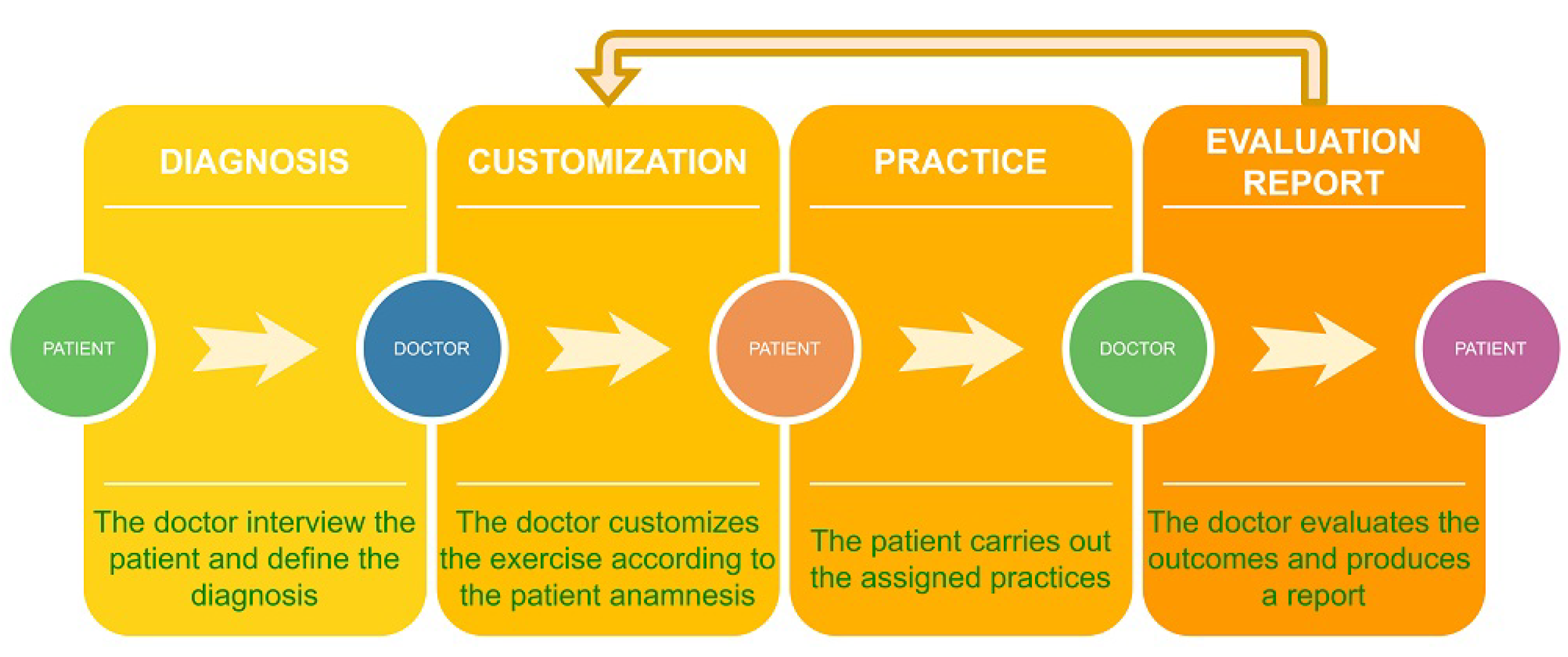
3.2. The Web App
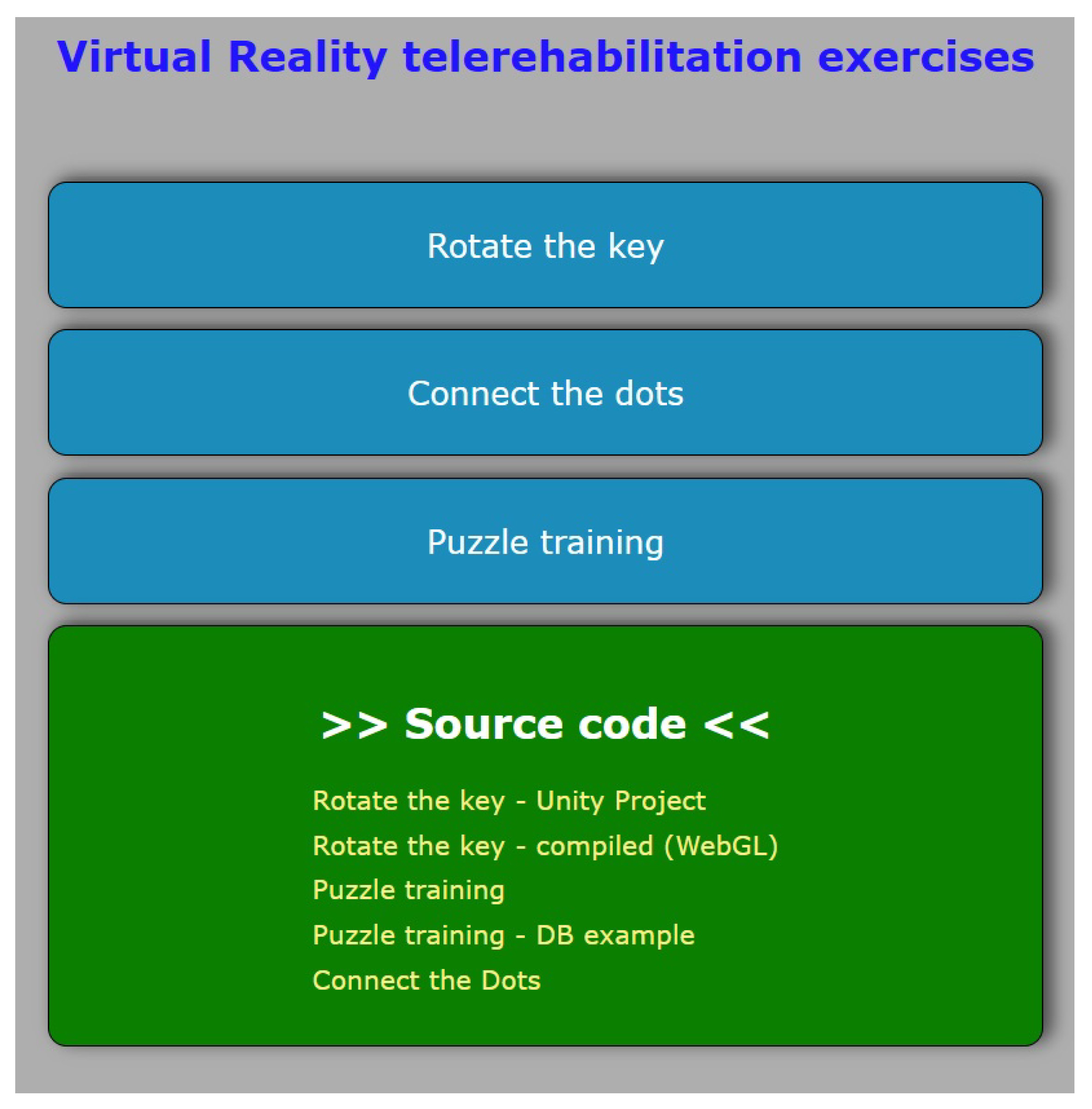
3.3. The Exercises
4. Implementing the Case Studies
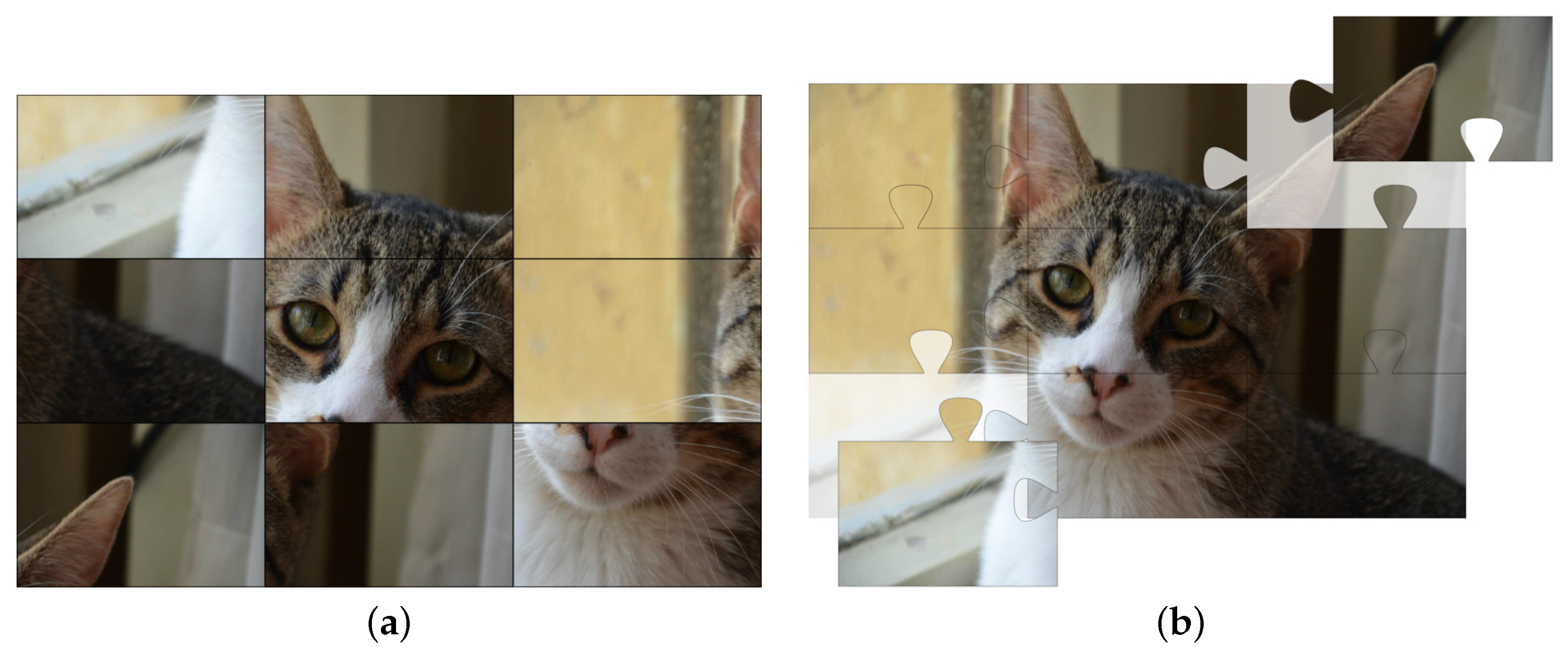
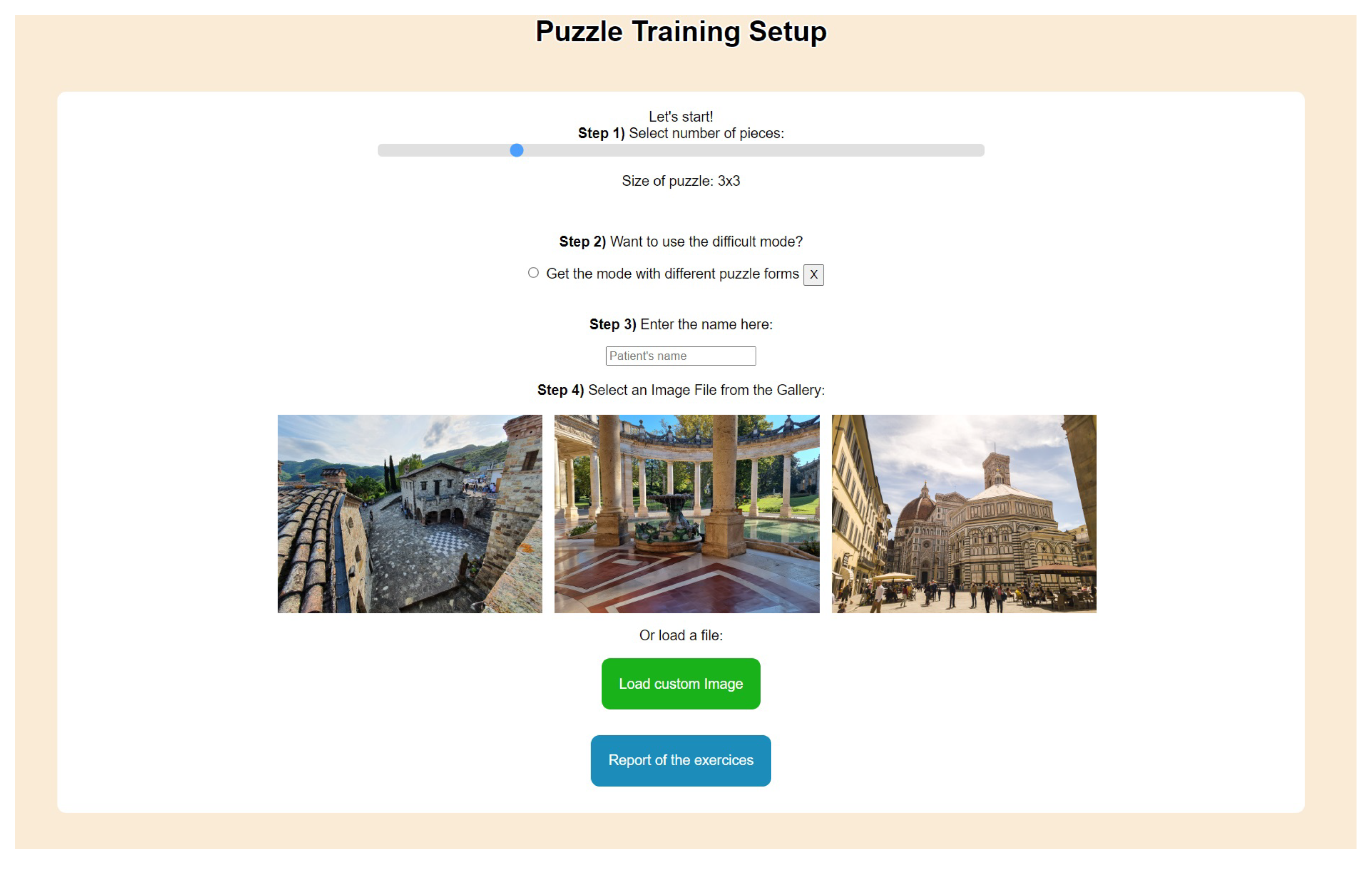
4.1. Solving a Puzzle
4.2. Connect the Dots
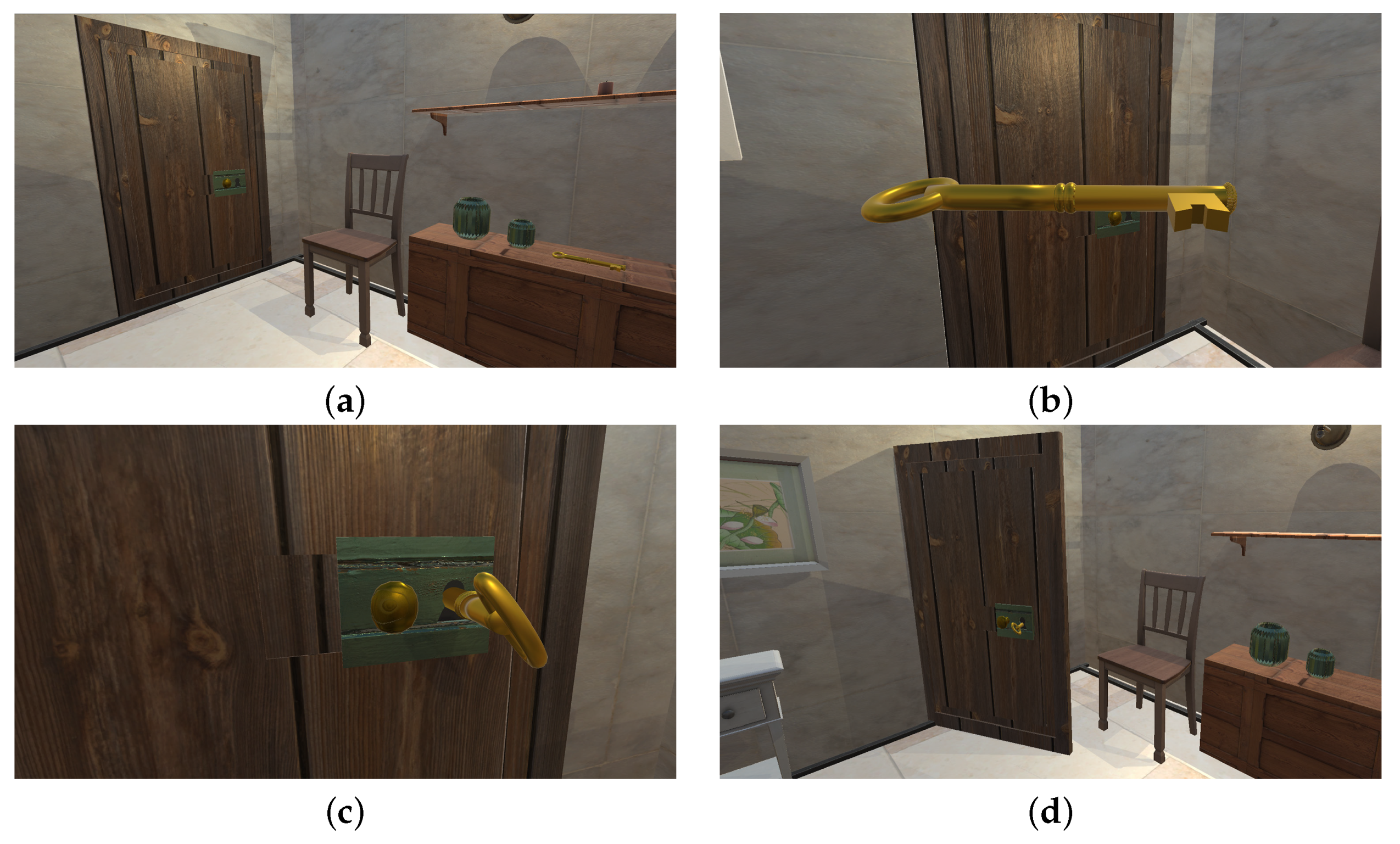
4.3. Key Turning in a Lock
5. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aFib | Atrial Fibrillation |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CSS | Cascading Style Sheets |
| HTML | HyperText Markup Language |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| JPEG | Joint Photographic Experts Group |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| OpenCV | Open Source Computer Vision Library |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
References
- Rizzolatti, G.; Craighero, L. The mirror-neuron system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 27, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calabrò, R.S.; Naro, A.; Russo, M.; Leo, A.; De Luca, R.; Balletta, T.; Buda, A.; La Rosa, G.; Bramanti, A.; Bramanti, P. The role of virtual reality in improving motor performance as revealed by EEG: A randomized clinical trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritterfeld, U.; Cody, M.; Vorderer, P. Serious Games: Mechanisms and Effects; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, J.; Bente, G. Why so serious? On the relation of serious games and learning. J. Comput. Game Cult. 2010, 4, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, M.G.; Latella, D.; Maresca, G.; Sciarrone, F.; Manuli, A.; Naro, A.; De Luca, R.; Calabrò, R.S. Virtual reality and cognitive rehabilitation in people with stroke: An overview. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2019, 51, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, E.; Zucchella, C.; Bottiroli, S.; Federico, A.; Giugno, R.; Sandrini, G.; Chiamulera, C.; Tamburin, S. Telemedicine and virtual reality for cognitive rehabilitation: A roadmap for the COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peretti, A.; Amenta, F.; Tayebati, S.K.; Nittari, G.; Mahdi, S.S. Telerehabilitation: Review of the state-of-the-art and areas of application. JMIR Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2017, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, C.C. Serious Games; University Press of America: Lanham, MA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bellotti, F.; Kapralos, B.; Lee, K.; Moreno-Ger, P.; Berta, R. Assessment in and of serious games: An overview. Adv. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2013, 2013, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Gloria, A.; Bellotti, F.; Berta, R. Serious Games for education and training. Int. J. Serious Games 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, F.; Ott, M.; Arnab, S.; Berta, R.; de Freitas, S.; Kiili, K.; De Gloria, A. Designing serious games for education: From pedagogical principles to game mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Games Based Learning, Athens, Greece, 20–21 October 2011; University of Athens Greece: Athens, Greece, 2011; pp. 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ritterfeld, U.; Shen, C.; Wang, H.; Nocera, L.; Wong, W.L. Multimodality and interactivity: Connecting properties of serious games with educational outcomes. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2009, 12, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meehan, M.; Insko, B.; Whitton, M.; Brooks, F.P., Jr. Physiological measures of presence in stressful virtual environments. ACM Trans. Graph. (tog) 2002, 21, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giessen, H.W. Serious games effects: An overview. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 174, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhonggen, Y. A meta-analysis of use of serious games in education over a decade. Int. J. Comput. Games Technol. 2019, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonetti, M.; Perri, D.; Amato, N.; Gervasi, O. Teaching Math with the Help of Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2020—20th International Conference, Cagliari, Italy, 1–4 July 2020; Proceedings, Part VII; Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Misra, S., Garau, C., Blecic, I., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O., Rocha, A.M.A.C., Tarantino, E., Torre, C.M., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 12255, pp. 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, C.; McGrath, D.; McIntyre, T.; Wegener, M.; Williamson, M. Teaching physics using virtual reality. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: University Park, MD, USA, 2010; Volume 1263, pp. 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Weiskopf, D.; Borchers, M.; Ertl, T.; Falk, M.; Fechtig, O.; Frank, R.; Grave, F.; King, A.; Kraus, U.; Muller, T.; et al. Visualization in the einstein year 2005: A case study on explanatory and illustrative visualization of relativity and astrophysics. In Proceedings of the VIS 05. IEEE Visualization, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 23–28 October 2005; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 583–590. [Google Scholar]
- Perri, D.; Fortunelli, M.; Simonetti, M.; Magni, R.; Carloni, J.; Gervasi, O. Rapid Prototyping of Virtual Reality Cognitive Exercises in a Tele–Rehabilitation Context. Electronics 2021, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCue, M.; Fairman, A.; Pramuka, M. Enhancing quality of life through telerehabilitation. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. 2010, 21, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogante, M.; Grigioni, M.; Cordella, D.; Giacomozzi, C. Ten years of telerehabilitation: A literature overview of technologies and clinical applications. NeuroRehabilitation 2010, 27, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerone, K.D.; Goldin, Y.; Ganci, K.; Rosenbaum, A.; Wethe, J.V.; Langenbahn, D.M.; Malec, J.F.; Bergquist, T.F.; Kingsley, K.; Nagele, D.; et al. Evidence-based cognitive rehabilitation: Systematic review of the literature from 2009 through 2014. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019, 100, 1515–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maggio, M.G.; Maresca, G.; De Luca, R.; Stagnitti, M.C.; Porcari, B.; Ferrera, M.C.; Galletti, F.; Casella, C.; Manuli, A.; Calabrò, R.S. The growing use of virtual reality in cognitive rehabilitation: Fact, fake or vision? A scoping review. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2019, 111, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Chiaravalloti, N.D.; DeLuca, J. Neurological update: Cognitive rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4908–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi-Sisakht, F.; Farhoudi, M.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Mahmoudi, J.; Mohaddes, G. Cognitive rehabilitation improves ischemic stroke-induced cognitive impairment: Role of growth factors. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 104299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, M.G.; De Luca, R.; Molonia, F.; Porcari, B.; Destro, M.; Casella, C.; Salvati, R.; Bramanti, P.; Calabro, R.S. Cognitive rehabilitation in patients with traumatic brain injury: A narrative review on the emerging use of virtual reality. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 61, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalik, L.; Dosbaba, F.; Hartman, M.; Batalikova, K.; Spinar, J. Benefits and effectiveness of using a wrist heart rate monitor as a telerehabilitation device in cardiac patients: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2020, 99, e19556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, P.; Podsiadły, B.; Zych, M.; Kamiński, M.; Skalski, A.; Raczyński, T.; Janczak, D.; Jakubowska, M. CNT/Graphite/SBS Conductive Fibers for Strain Sensing in Wearable Telerehabilitation Devices. Sensors 2022, 22, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozevink, S.G.; van der Sluis, C.K.; Garzo, A.; Keller, T.; Hijmans, J.M. HoMEcare aRm rehabiLItatioN (MERLIN): Telerehabilitation using an unactuated device based on serious games improves the upper limb function in chronic stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Lee, G. Virtual Reality-Based Cognitive–Motor Rehabilitation in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Study on Motivation and Cognitive Function. Healthcare 2020, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santucci, F.; Frenguelli, F.; Angelis, A.D.; Cuccaro, I.; Perri, D.; Simonetti, M. An immersive Open Source environment using Godot. In Proceedings of the Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2020—20th International Conference, ICCSA 2020, Online, 1–4 July 2019; Volume 12255, pp. 784–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, C.; Bordegoni, M.; Ferrise, F. A Multimodal Virtual Environment Based on Haptic Interfaces for Upper-Limb Rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 2–5 August 2015; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 57052, p. V01BT02A023. [Google Scholar]
- Vitali, A.; Regazzoni, D.; Rizzi, C.; Spajani, A. Vr serious games for neuro-cognitive rehabilitation of patients with severe memory loss. Comput. Des. Appl. 2021, 18, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postolache, O.; Hemanth, D.J.; Alexandre, R.; Gupta, D.; Geman, O.; Khanna, A. Remote monitoring of physical rehabilitation of stroke patients using IoT and virtual reality. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 39, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.J.; Yin, Y.H.; Da Xu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, F. IoT-based smart rehabilitation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Gradim, L.C.C.; José, M.A.; da Cruz, D.M.C.; de Deus Lopes, R. IoT services and applications in rehabilitation: An interdisciplinary and meta-analysis review. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perri, D.; Simonetti, M.; Bordini, A.; Cimarelli, S.; Gervasi, O. IoT to Monitor People Flow in Areas of Public Interest. In Proceedings of the Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2021—21st International Conference, Cagliari, Italy, 13–16 September 2021; Proceedings, Part X, Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Misra, S., Garau, C., Blecic, I., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O., Rocha, A.M.A.C., Tarantino, E., Torre, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 12958, pp. 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaswamy, T.M.; Pradhan, G.N.; Chakka, K.; Khargonkar, N.; Borresen, A.; Prabhakaran, B. Using Biometric Technology for Telehealth and Telerehabilitation. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. 2021, 32, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, H.; Joshi, R.; Guzman, V.; Kilger, M.; Desai, K. Multimodal Data Streaming using Visual IoTs and Wearables for Telerehabilitation and Teletreatment. In Proceedings of the 2021 World Automation Congress (WAC), Taipei, Taiwan, 1–5 August 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 233–238. [Google Scholar]
- Gervasi, O.; Fortunelli, M.; Magni, R.; Perri, D.; Simonetti, M. Mobile Localization Techniques Oriented to Tangible Web. In Proceedings of the Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2019—19th International Conference, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1–4 July 2019; Proceedings, Part I, Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Misra, S., Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., Stankova, E.N., Korkhov, V., Torre, C.M., Rocha, A.M.A.C., Taniar, D., Apduhan, B.O., Tarantino, E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11619, pp. 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Deng, J.; Pang, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Deng, B.; Pang, Z.; Xu, J.; Jiang, M.; Liljeberg, P.; et al. An IoT-enabled stroke rehabilitation system based on smart wearable armband and machine learning. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2018, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohlberg, M.M.; Mateer, C.A. Cognitive Rehabilitation: An Integrative Neuropsychological Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Meng, G.; Sun, Q. An Overview on Edge Computing Research. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85714–85728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perri, D.; Simonetti, M.; Gervasi, O. Deploying Serious Games for Cognitive Rehabilitation. Computers 2022, 11, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers11070103
Perri D, Simonetti M, Gervasi O. Deploying Serious Games for Cognitive Rehabilitation. Computers. 2022; 11(7):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers11070103
Chicago/Turabian StylePerri, Damiano, Marco Simonetti, and Osvaldo Gervasi. 2022. "Deploying Serious Games for Cognitive Rehabilitation" Computers 11, no. 7: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers11070103
APA StylePerri, D., Simonetti, M., & Gervasi, O. (2022). Deploying Serious Games for Cognitive Rehabilitation. Computers, 11(7), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers11070103







