A Pilot Study on the Potential of RNA-Associated to Urinary Vesicles as a Suitable Non-Invasive Source for Diagnostic Purposes in Bladder Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Human Samples
2.2. Isolation of EVs
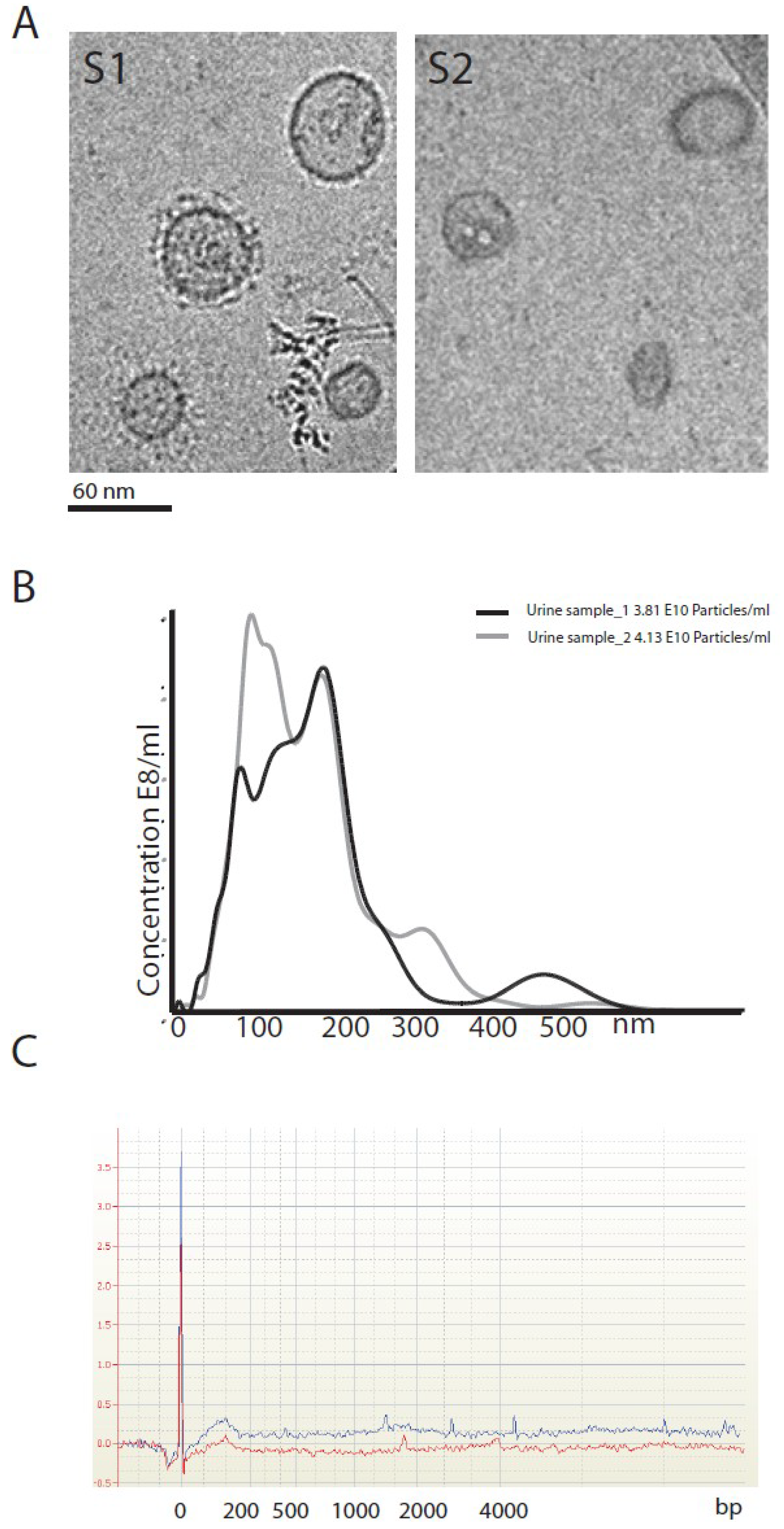
2.3. EVs Characterization
2.4. RNA Extraction
2.5. Microarray Gene Expression Data
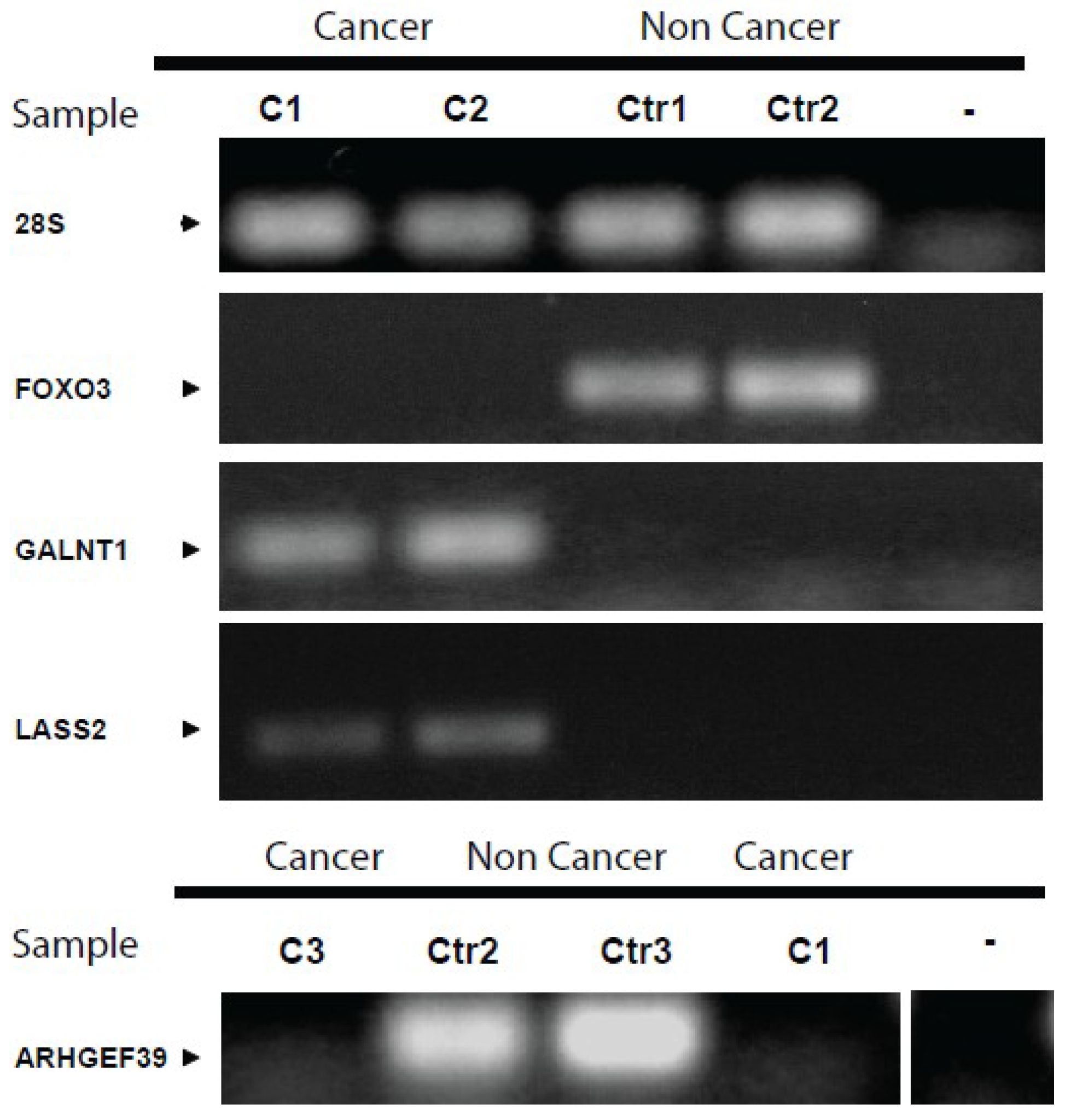
2.6. Reverse Transcriptase and PCR
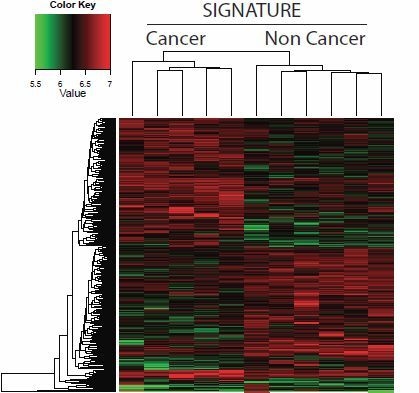
3. Results
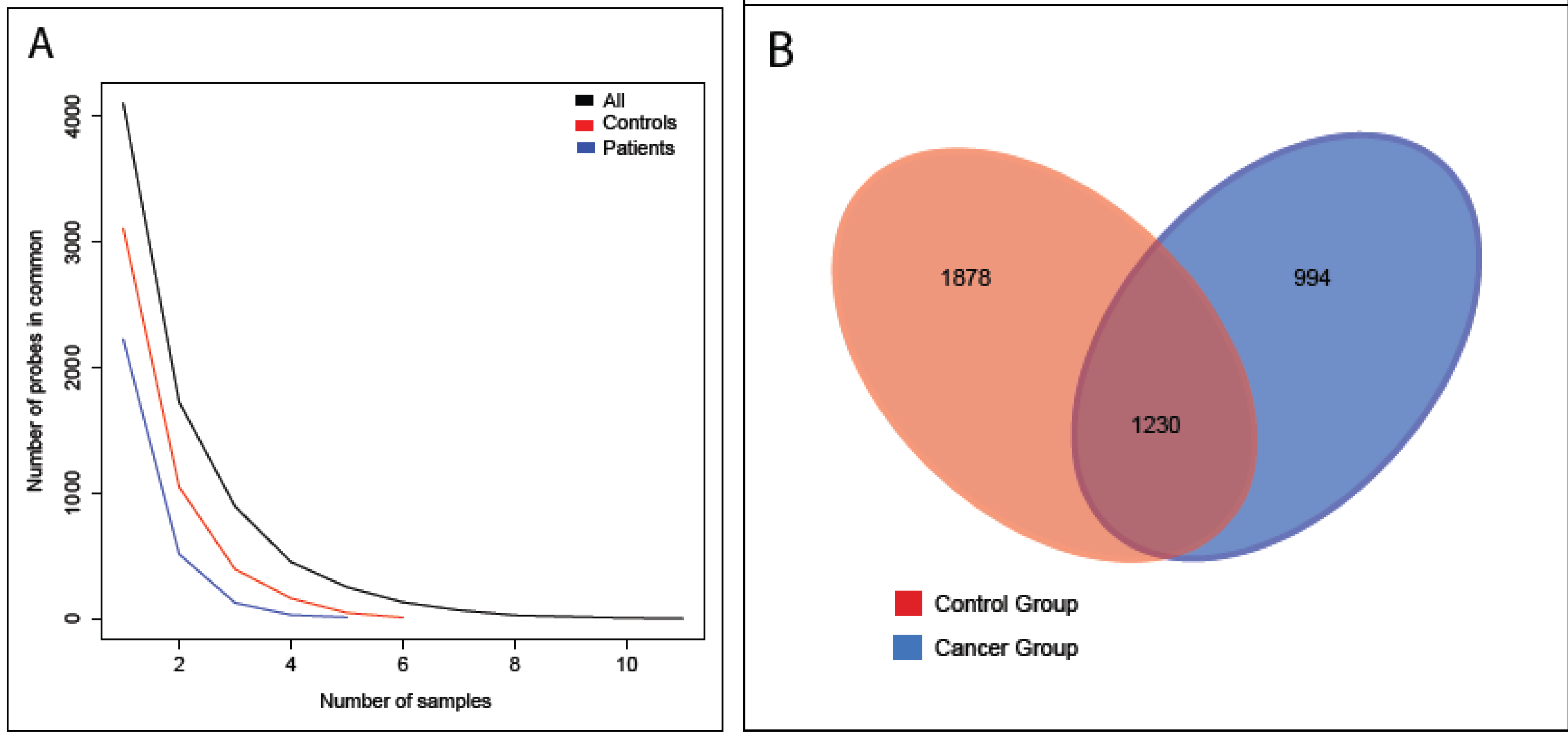
| Transcripts present in at least three cancer group samples, and absent in the control group | |
| Gene symbol | Gene name |
| LASS2 | Homo sapiens LAG1 homolog, ceramide synthase 2 (LASS2), transcript variant 1, mRNA. |
| CYB5B | Homo sapiens cytochrome b5 type B (outer mitochondrial membrane) (CYB5B), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, mRNA. |
| LOC90624 | Homo sapiens hypothetical protein LOC90624 (LOC90624), mRNA. |
| ST6GALNAC3 | Homo sapiens ST6 (alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminyl-2,3-beta-galactosyl-1, 3)-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 3 (ST6GALNAC3), mRNA. |
| HVCN1 | Homo sapiens hydrogen voltage-gated channel 1 (HVCN1), transcript variant 1, mRNA. |
| LOC653107 | PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to Annexin A8 (Annexin VIII) (Vascular anticoagulant-beta) (VAC-beta), transcript variant 2 (LOC653107), mRNA. |
| HS.581933 | DB298112 BRACE2 Homo sapiens cDNA clone BRACE2040248 3, mRNA sequence |
| Present genes in all the samples | |
| Gene symbol | Gene name |
| LOC100130701 | PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to hCG1657343 (LOC100130701), mRNA. |
| RHBDL3 | Homo sapiens rhomboid, veinlet-like 3 (Drosophila) (RHBDL3), mRNA. |
| HS.85445 | 603074330F1 NIH_MGC_119 Homo sapiens cDNA clone IMAGE:5166462 5, mRNA sequence |
| LOC100129952 | PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to mCG146274 (LOC100129952), mRNA. |
| Transcripts present in at least four control group samples, and absent from the cancer group | |
| Gene symbol | Gene name |
| ARHGEF39(C9ORF100) | Homo sapiens chromosome 9 open reading frame 100 (C9orf100), mRNA. |
| LOC730525 | PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical protein LOC730525 (LOC730525), mRNA. |
| FRAS1 | Homo sapiens Fraser syndrome 1 (FRAS1), transcript variant 3, mRNA. |
| HBBP1 | Homo sapiens hemoglobin, beta pseudogene 1 (HBBP1), non-coding RNA. |
| NUDT6 | Homo sapiens nudix (nucleoside diphosphate linked moiety X)-type motif 6 (NUDT6), transcript variant 1, mRNA. |
| NEK10 | Homo sapiens NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)- related kinase 10 (NEK10), transcript variant 1, mRNA. |
| KLB | Homo sapiens klotho beta (KLB), mRNA. |
| LOC51152 | PREDICTED: Homo sapiens melanoma antigen (LOC51152), mRNA. |
| LCN2 | Homo sapiens lipocalin 2 (LCN2), mRNA. |
| LOC650961 | PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC650961 (LOC650961), mRNA. |
| Positive samples qPCR (%) | Positive samples in array (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GENE | Cancer | Control | Cancer | Control |
| AXL | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BCL2 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| BCL2L1 | 100 | 50 | 0 | 50 |
| ARHGEF39 (C9ORF100) | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
| CYB5B | 100 | 100 | 60 | 0 |
| DENR | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 |
| FOXO3 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 33 |
| GALNT1 | 100 | 0 | 20 | 0 |
| GPR103 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 83 |
| IL18 | 50 | 100 | 20 | 33 |
| LAIR1 | 50 | 100 | 60 | 67 |
| LASS2 | 100 | 0 | 60 | 0 |
| MSH3 | 100 | 100 | 40 | 33 |
| PTGS2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ROCK2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 83 |
4. Discussions and Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Authorship and Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Xu, J.; Ward, E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan-Rodriguez, F.; Chechile-Toniolo, G.; Salvador-Bayarri, J.; Palou, J.; Algaba, F.; Vicente-Rodriguez, J. Primary superficial bladder cancer risk groups according to progression, mortality and recurrence. J. Urol. 2000, 164, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Davison, D.D.; Adams, J.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Wang, L.; Montironi, R.; Zhang, S. Biomarkers in bladder cancer: Translational and clinical implications. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 89, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, B.P.; Hollander, M.P.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Witjes, J.A. Prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Difference between primary and progressive tumours and implications for therapy. Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, H.B.; Soloway, M.; Messing, E.; Katz, G.; Stein, B.; Kassabian, V.; Shen, Y. Surveillance for recurrent bladder cancer using a point-of-care proteomic assay. JAMA 2006, 295, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glas, A.S.; Roos, D.; Deutekom, M.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Kurth, K.H. Tumor markers in the diagnosis of primary bladder cancer. A systematic review. J. Urol. 2003, 169, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokeshwar, V.B.; Habuchi, T.; Grossman, H.B.; Murphy, W.M.; Hautmann, S.H.; Hemstreet, G.P., 3rd; Bono, A.V.; Getzenberg, R.H.; Goebell, P.; Schmitz-Drager, B.J.; et al. Bladder tumor markers beyond cytology: International Consensus Panel on bladder tumor markers. Urology 2005, 66, 35–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, P.; Sharples, K.; Dalphin, M.; Davidson, P.; Gilling, P.; Cambridge, L.; Harvey, J.; Toro, T.; Giles, N.; Luxmanan, C.; et al. A multigene urine test for the detection and stratification of bladder cancer in patients presenting with hematuria. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengual, L.; Ribal, M.J.; Lozano, J.J.; Ingelmo-Torres, M.; Burset, M.; Fernandez, P.L.; Alcaraz, A. Validation study of a non-invasive urine test for diagnosis and prognosis assessment of bladder cancer. Evidence for improved models. J. Urol. 2014, 191, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Welton, J.; Staffurth, J.; Court, J.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z.; Clayton, A. Can urinary exosomes act as treatment response markers in prostate cancer? J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, D.M.; Sheman, N.E.; Nelson, K.; Theodorescu, D. Isolation and identification of potential urinary microparticle biomarkers of bladder cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Lai, Y.F.; Tang, P.; Chien, K.Y.; Yu, J.S.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, H.W.; Wu, C.C.; Chung, T.; Hsu, C.W.; et al. Comparative and targeted proteomic analyses of urinary microparticles from bladder cancer and hernia patients. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 5611–5629. [Google Scholar]
- Welton, J.L.; Khanna, S.; Giles, P.J.; Brennan, P.; Brewis, I.A.; Staffurth, J.; Mason, M.D.; Clayton, A. Proteomics analysis of bladder cancer exosomes. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2010, 9, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, K.C.; Bond, D.T.; McKee, M.; Skog, J.; Paunescu, T.G.; da Silva, N.; Brown, D.; Russo, L.M. Nucleic acids within urinary exosomes/microvesicles are potential biomarkers for renal disease. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Duan, X.; Yao, Y.; Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Fan, Z.; Liu, X.; Qin, S.; et al. A translational study of urine miRNAs in acute myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Skog, J.; Nordstrand, A.; Baranov, V.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Widmark, A. Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: A novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Greenhaw, J.; Shi, Q.; Su, Z.; Qian, F.; Davis, K.; Mendrick, D.L.; Salminen, W.F. Identification of urinary microRNA profiles in rats that may diagnose hepatotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 125, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovic, R.A.; Gardiner, C.; Brooks, A.S.; Tannetta, D.S.; Ferguson, D.J.; Hole, P.; Carr, B.; Redman, C.W.; Harris, A.L.; Dobson, P.J.; et al. Sizing and phenotyping of cellular vesicles using Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis. Nanomedicine 2011, 7, 780–788. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.; Kibbe, W.A.; Lin, S.M. lumi: A pipeline for processing Illumina microarray. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, G. Limma: Linear Models for Microarray Data. In Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor; Gentleman, R., Carey, V., Dudoit, S., Irizarry, R., Huber, W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 397–420. [Google Scholar]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.K.; Kang, T.W.; Baek, S.J.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.S. CaGe: A web-based cancer gene annotation system for cancer genomics. Genomics Inform. 2012, 10, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldh, M.; Lotvall, J.; Malmhall, C.; Ekstrom, K. Importance of RNA isolation methods for analysis of exosomal RNA: Evaluation of different methods. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 50, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.L.; Khosroheidari, M.; Kanchi Ravi, R.; DiStefano, J.K. Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisitkun, T.; Johnstone, R.; Knepper, M.A. Discovery of urinary biomarkers. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2006, 5, 1760–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Llama, P.; Khositseth, S.; Gonzales, P.A.; Star, R.A.; Pisitkun, T.; Knepper, M.A. Tamm-Horsfall protein and urinary exosome isolation. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 736–742. [Google Scholar]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brems-Eskildsen, A.S.; Zieger, K.; Toldbod, H.; Holcomb, C.; Higuchi, R.; Mansilla, F.; Munksgaard, P.P.; Borre, M.; Orntoft, T.F.; Dyrskjot, L. Prediction and diagnosis of bladder cancer recurrence based on urinary content of hTERT, SENP1, PPP1CA, and MCM5 transcripts. BMC Cancer 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, C.J.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Villicana, P.; McCullers, M.; Porvasnik, S.; Young, P.R.; Parker, A.S.; Goodison, S. Bladder cancer-associated gene expression signatures identified by profiling of exfoliated urothelia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borras, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Hall, A. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho GTPases: Turning on the switch. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1587–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, K.M.; Little, A.F.; Swart, J.M.; Kastrinakis, W.V.; Fitzgerald, J.M.; Hess, D.T.; Libertino, J.A.; Summerhayes, I.C. Human bladder carcinoma cell lines as indicators of oncogenic change relevant to urothelial neoplastic progression. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fei, M.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M.; Cheng, C.; Shen, A. Expression of Foxo3a in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas is correlated with cell cycle inhibitor p27. Eur. J. Haematol. 2008, 81, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, W.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, K.; et al. The tumor-suppressor gene Nkx2.8 suppresses bladder cancer proliferation through upregulation of FOXO3a and inhibition of the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrskjot, L.; Ostenfeld, M.S.; Bramsen, J.B.; Silahtaroglu, A.N.; Lamy, P.; Ramanathan, R.; Fristrup, N.; Jensen, J.L.; Andersen, C.L.; Zieger, K.; et al. Genomic profiling of microRNAs in bladder cancer: miR-129 is associated with poor outcome and promotes cell death in vitro. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4851–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Ding, M.; Yan, R.; Yang, D.; Ke, C. Expression and prognostic significance of a new tumor metastasis suppressor gene LASS2 in human bladder carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, P.; Korniychuk, G.; Yamamoto, Y.; Grubisic, K.; Oelgeschlager, M. Regulation of TGF-(beta) signalling by N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-like 1. Development 2008, 135, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.X.; Wang, H.F.; Wang, J.S.; Zhan, H.; Zuo, Y.G.; Yang, D.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, W.; Ke, C.X.; Yan, R.P. ppGalNAc T1 as a potential novel marker for human bladder cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 5653–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffmann, S.; Sandner, J.; Birod, K.; Wobst, I.; Angioni, C.; Ruckhaberle, E.; Kaufmann, M.; Ackermann, H.; Lotsch, J.; Schmidt, H.; et al. Ceramide synthases and ceramide levels are increased in breast cancer tissue. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesicek, J.; Lee, H.; Feldman, T.; Jiang, X.; Skobeleva, A.; Berdyshev, E.V.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Fuks, Z.; Kolesnick, R. Ceramide synthases 2, 5, and 6 confer distinct roles in radiation-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrskjot, L.; Zieger, K.; Real, F.X.; Malats, N.; Carrato, A.; Hurst, C.; Kotwal, S.; Knowles, M.; Malmstrom, P.U.; de la Torre, M.; et al. Gene expression signatures predict outcome in non-muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma: A multicenter validation study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3545–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez, A.; Loizaga, A.; Arceo, R.; Lacasa, I.; Rabade, A.; Zorroza, K.; Mosen-Ansorena, D.; Gonzalez, E.; Aransay, A.M.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; et al. A Pilot Study on the Potential of RNA-Associated to Urinary Vesicles as a Suitable Non-Invasive Source for Diagnostic Purposes in Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2014, 6, 179-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6010179
Perez A, Loizaga A, Arceo R, Lacasa I, Rabade A, Zorroza K, Mosen-Ansorena D, Gonzalez E, Aransay AM, Falcon-Perez JM, et al. A Pilot Study on the Potential of RNA-Associated to Urinary Vesicles as a Suitable Non-Invasive Source for Diagnostic Purposes in Bladder Cancer. Cancers. 2014; 6(1):179-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6010179
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez, Amparo, Ana Loizaga, Raquel Arceo, Isabel Lacasa, Ainara Rabade, Kerman Zorroza, David Mosen-Ansorena, Esperanza Gonzalez, Ana M. Aransay, Juan M. Falcon-Perez, and et al. 2014. "A Pilot Study on the Potential of RNA-Associated to Urinary Vesicles as a Suitable Non-Invasive Source for Diagnostic Purposes in Bladder Cancer" Cancers 6, no. 1: 179-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6010179
APA StylePerez, A., Loizaga, A., Arceo, R., Lacasa, I., Rabade, A., Zorroza, K., Mosen-Ansorena, D., Gonzalez, E., Aransay, A. M., Falcon-Perez, J. M., Unda-Urzaiz, M., & Royo, F. (2014). A Pilot Study on the Potential of RNA-Associated to Urinary Vesicles as a Suitable Non-Invasive Source for Diagnostic Purposes in Bladder Cancer. Cancers, 6(1), 179-192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers6010179