Oxidative Stress and Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Promising Tool for Detection of Lung Cancer
Abstract
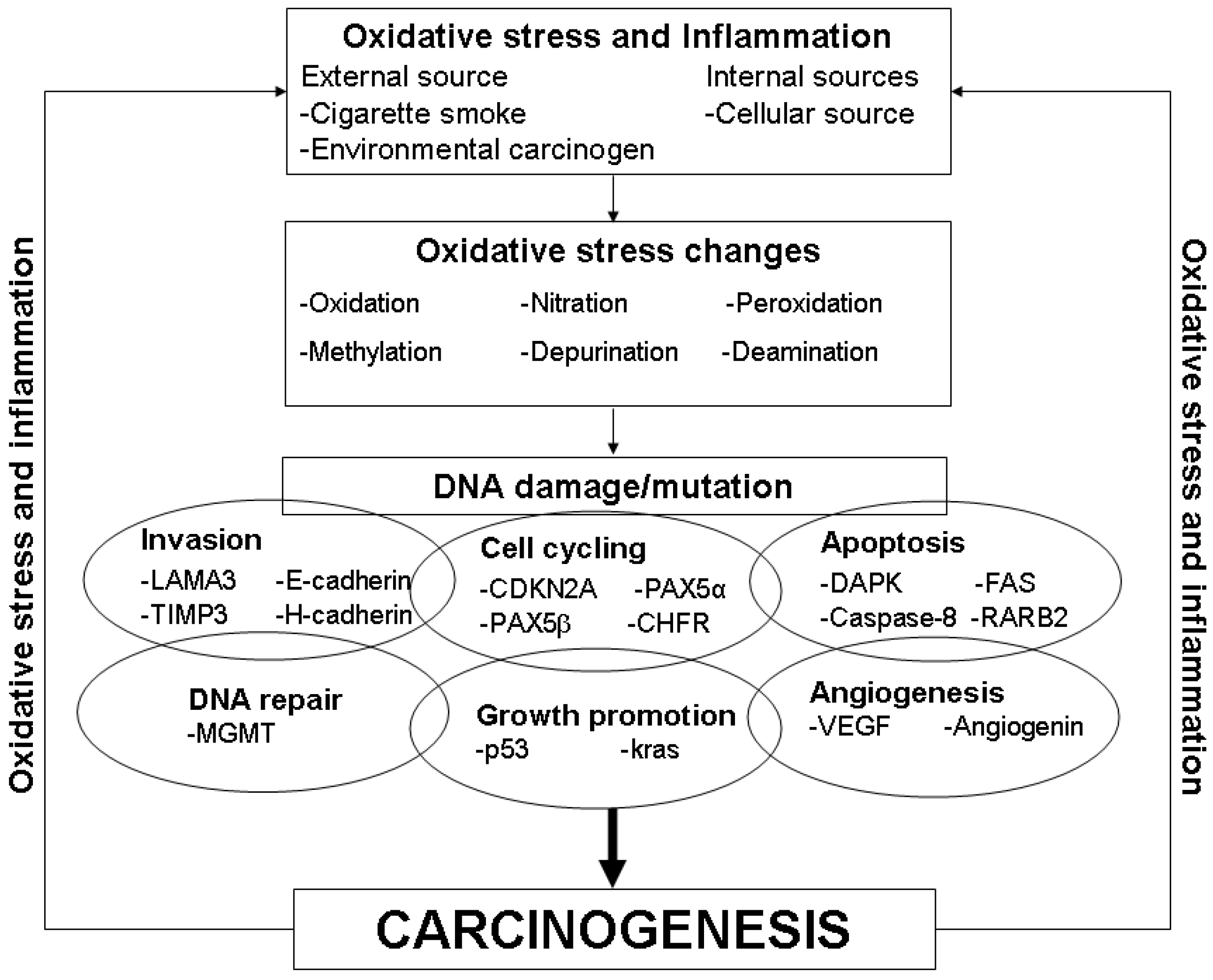
:1. Introduction
2. Exhaled Breath Analysis
2.1. Gaseous Phase Analysis
2.1.1. Exhaled Nitric Oxide
2.1.2. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
2.2. Liquid Phase Analysis/Exhaled Breath Condensate
3. Conclusions
References
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Xu, J.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2009, 59, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, L.L.; Teutsch, S.; Johnson, M. Lung cancer screening with sputum cytologic examination, chest radiography, and computed tomography: an update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinsky, S.A. Gene-promoter hypermethylation as a biomarker in lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2004, 4, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominioni, L.; Imperatori, A.; Rovera, F.; Ochetti, A.; Torrigiotti, G.; Paolucci, M. Stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: analysis of survival and implications for screening. Cancer 2000, 89, 2334–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flehinger, B.J.; Kimmel, M.; Melamed, M.R. The effect of surgical treatment on survival from early lung cancer. Implications for screening. Chest 1992, 101, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.S. Cigarette smoking and lung cancer: chemical mechanisms and approaches to prevention. Lancet Oncol. 2002, 3, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnula, V.L.; Crapo, J.D. Superoxide dismutases in the lung and human lung diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 1600–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaapen, A.M.; Gungor, N.; Schins, R.P.; Borm, P.J.; Van Schooten, F.J. Neutrophils and respiratory tract DNA damage and mutagenesis: a review. Mutagenesis 2006, 21, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Biswas, S.K.; Kode, A. Oxidant and antioxidant balance in the airways and airway diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 533, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharitonov, S.A.; Yates, D.; Robbins, R.A.; Logan-Sinclair, R.; Shinebourne, E.A.; Barnes, P.J. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet 1994, 343, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sandrini, A.; Thurston, M.C.; Yates, D.H.; Thomas, P.S. Nitric oxide and exhaled breath nitrite/nitrates in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients. Respiration 2007, 74, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.K.; Noeldge-Schomburg, G.F. Diagnostic potential of breath analysis—focus on volatile organic compounds. Clin. Chim. Acta 2004, 347, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATS/ERS recommendations for standardized procedures for the online and offline measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide, 2005. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 912–930. [CrossRef]
- Corradi, M.; Pesci, A.; Casana, R.; Alinovi, R.; Goldoni, M.; Vettori, M.V.; Cuomo, A. Nitrate in exhaled breath condensate of patients with different airway diseases. Nitric Oxide 2003, 8, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, H.C.; Yu, C.T.; Kuo, H.P. Increased level of exhaled nitric oxide and up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in patients with primary lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneepkens, C.M.; Lepage, G.; Roy, C.C. The potential of the hydrocarbon breath test as a measure of lipid peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 17, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredi, P.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Barnes, P.J. Analysis of expired air for oxidation products. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, S31–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gossum, A.; Decuyper, J. Breath alkanes as an index of lipid peroxidation. Eur. Respir. J. 1989, 2, 787–791. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.M.; Szidon, J.P.; Krotoszynski, B.K.; Gibbons, R.D.; O'Neill, H.J. Volatile organic compounds in exhaled air from patients with lung cancer. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M.; Gleeson, K.; Hughes, J.M.; Greenberg, J.; Cataneo, R.N.; Baker, L.; McVay, W.P. Volatile organic compounds in breath as markers of lung cancer: a cross-sectional study. Lancet 1999, 353, 1930–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Cummin, A.R.; Gagliardi, A.J.; Gleeson, K.; Greenberg, J.; Maxfield, R.A.; Rom, W.N. Detection of lung cancer with volatile markers in the breath. Chest 2003, 123, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, D.; Carbognani, P.; Corradi, M.; Goldoni, M.; Acampa, O.; Balbi, B.; Bianchi, L.; Rusca, M.; Mutti, A. Exhaled volatile organic compounds in patients with non–small cell lung cancer: cross sectional and nested short-term follow-up study. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligor, M.; Ligor, T.; Bajtarevic, A.; Ager, C.; Pienz, M.; Klieber, M.; Denz, H.; Fiegl, M.; Hilbe, W.; Weiss, W.; Lukas, P.; Jamnig, H.; Hackl, M.; Buszewski, B.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.; Amann, A. Determination of volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer using solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 550–560. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.; Qin, T.; Liu, H.; Xu, G.B.; Pan, Y.Y.; Xiong, F.X.; Gu, K.S.; Sun, G.P.; Chen, Z.D. Quantitative breath analysis of volatile organic compounds of lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2009, 67, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone, P.J.; Hammel, J.; Dweik, R.; Na, J.; Czich, C.; Laskowski, D.; Mekhail, T. Diagnosis of lung cancer by the analysis of exhaled breath with a colorimetric sensor array. Thorax 2007, 62, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, M.; Litterst, P.; Freitag, L.; Urfer, W.; Bader, S.; Baumbach, J.I. Ion mobility spectrometry for the detection of volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer: results of a pilot study. Thorax 2009, 64, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barash, O.; Peled, N.; Hirsch, F.R.; Haick, H. Sniffing the unique "odor print" of non-small-cell lung cancer with gold nanoparticles. Small 2009, 5, 2618–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tisch, U.; Adams, O.; Hakim, M.; Shehada, N.; Broza, Y.Y.; Billan, S.; Abdah-Bortnyak, R.; Kuten, A.; Haick, H. Diagnosing lung cancer in exhaled breath using gold nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.F.; Laskowski, D.; Deffenderfer, O.; Burch, T.; Zheng, S.; Mazzone, P.J.; Mekhail, T.; Jennings, C.; Stoller, J.K.; Pyle, J.; Duncan, J.; Dweik, R.A.; Erzurum, S.C. Detection of lung cancer by sensor array analyses of exhaled breath. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Macagnano, A.; Martinelli, E.; Paolesse, R.; D'Arcangelo, G.; Roscioni, C.; Finazzi-Agro, A.; D'Amico, A. Lung cancer identification by the analysis of breath by means of an array of non-selective gas sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonieri, S.; Annema, J.T.; Schot, R.; van der Schee, M.P.; Spanevello, A.; Carratu, P.; Resta, O.; Rabe, K.F.; Sterk, P.J. An electronic nose in the discrimination of patients with non-small cell lung cancer and COPD. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Amico, A.; Pennazza, G.; Santonico, M.; Martinelli, E.; Roscioni, C.; Galluccio, G.; Paolesse, R.; Di Natale, C. An investigation on electronic nose diagnosis of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.; Chan, H.P.; Thurston, M.C.; Jackson, P.; Lewis, C.; Yates, D.; Bell, G.; Thomas, P.S. Breath analysis of lung cancer patients using an electronic nose detection system. IEEE Sensors J. 2009, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Effros, R.M.; Dunning, M.B., 3rd; Shaker, R. The promise and perils of exhaled breath condensates. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L1073–L1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Lewis, C.; Thomas, P.S. Exhaled breath analysis: novel approach for early detection of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Thomas, P.S. Exhaled breath condensate as a method of sampling airway nitric oxide and other markers of inflammation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2005, 11, MT53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Thomas, P.S. Relationship between exhaled breath condensate volume and measurements of lung volumes. Respiration 2007, 74, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J. Exhaled breath condensate: an evolving tool for noninvasive evaluation of lung disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Conrad, D.H.; Chow, S.; Tran, V.H.; Yates, D.H.; Thomas, P.S. Collection devices influence the constituents of exhaled breath condensate. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 807–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, O. Catching breath: monitoring airway inflammation using exhaled breath condensate. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, S.; Yates, D.H.; Thomas, P.S. Reproducibility of exhaled breath condensate markers. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 1124–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, I.; Hunt, J.; Barnes, P.J.; Alving, K.; Antczak, A.; Baraldi, E.; Becher, G.; van Beurden, W.J.; Corradi, M.; Dekhuijzen, R.; Dweik, R.A.; Dwyer, T.; Effros, R.; Erzurum, S.; Gaston, B.; Gessner, C.; Greening, A.; Ho, L.P.; Hohlfeld, J.; Jobsis, Q.; Laskowski, D.; Loukides, S.; Marlin, D.; Montuschi, P.; Olin, A.C.; Redington, A.E.; Reinhold, P.; van Rensen, E.L.; Rubinstein, I.; Silkoff, P.; Toren, K.; Vass, G.; Vogelberg, C.; Wirtz, H. Exhaled breath condensate: methodological recommendations and unresolved questions. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Tran, V.; Lewis, C.; Thomas, P.S. Elevated levels of oxidative stress markers in exhaled breath condensate. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khyshiktuev, B.S.; Khyshiktueva, N.A.; Ivanov, V.N. Methods of measuring lipid peroxidation products in exhaled air condensate and their clinical significance. Klin. Lab. Diagn. 1996, 3, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dalaveris, E.; Kerenidi, T.; Katsabeki-Katsafli, A.; Kiropoulos, T.; Tanou, K.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Kostikas, K. VEGF, TNF-alpha and 8-isoprostane levels in exhaled breath condensate and serum of patients with lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, C.; Kuhn, H.; Toepfer, K.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Schauer, J.; Wirtz, H. Detection of p53 gene mutations in exhaled breath condensate of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2004, 43, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, C.; Rechner, B.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Kuhn, H.; Hoheisel, G.; Sack, U.; Ruschpler, P.; Wirtz, H. Angiogenic markers in breath condensate identify non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P.; Mule, G.; Resta, O.; Tommasi, S.; Mangia, A.; Carpagnano, F.; Stea, G.; Susca, A.; Di Gioia, G.; De Lena, M.; Paradiso, A. 3p microsatellite alterations in exhaled breath condensate from patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Spanevello, A.; Carpagnano, F.; Palladino, G.P.; Prato, R.; Martinelli, D.; Digioia, G.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P. Prognostic value of exhaled microsatellite alterations at 3p in NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Wang, T.; Reilly, A.A.; Keller, S.M.; Spivack, S.D. Gene promoter methylation assayed in exhaled breath, with differences in smokers and lung cancer patients. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P.; Resta, O.; Gramiccioni, E.; Carpagnano, F. Endothelin-1 is increased in the breath condensate of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncology 2004, 66, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Resta, O.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P.; Gramiccioni, E.; Carpagnano, F. Interleukin-6 is increased in breath condensate of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2002, 17, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Spanevello, A.; Curci, C.; Salerno, F.; Palladino, G.P.; Resta, O.; Di Gioia, G.; Carpagnano, F.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P. IL-2, TNF-alpha, and leptin: local versus systemic concentrations in NSCLC patients. Oncol. Res. 2007, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Carpagnano, G.E.; Spanevello, A.; Palladino, G.P.; Gramiccioni, C.; Ruggieri, C.; Carpagnano, F.; Foschino Barbaro, M.P. Cigarette smoke and increased COX-2 and survivin levels in exhaled breath condensate of lung cancer patients: how hot is the link? Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chan, H.P.; Lewis, C.; Thomas, P.S. Oxidative Stress and Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Promising Tool for Detection of Lung Cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2010032
Chan HP, Lewis C, Thomas PS. Oxidative Stress and Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Promising Tool for Detection of Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2010; 2(1):32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Hiang Ping, Craig Lewis, and Paul S. Thomas. 2010. "Oxidative Stress and Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Promising Tool for Detection of Lung Cancer" Cancers 2, no. 1: 32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2010032
APA StyleChan, H. P., Lewis, C., & Thomas, P. S. (2010). Oxidative Stress and Exhaled Breath Analysis: A Promising Tool for Detection of Lung Cancer. Cancers, 2(1), 32-42. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers2010032



