LFHP-1c Attenuates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability In Vitro Independent of PGAM5
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Small Molecule Inhibitor, and Culture Conditions
2.2. Cell Growth and Viability Quantification
2.3. Quantification of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.4. Immunoblots
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
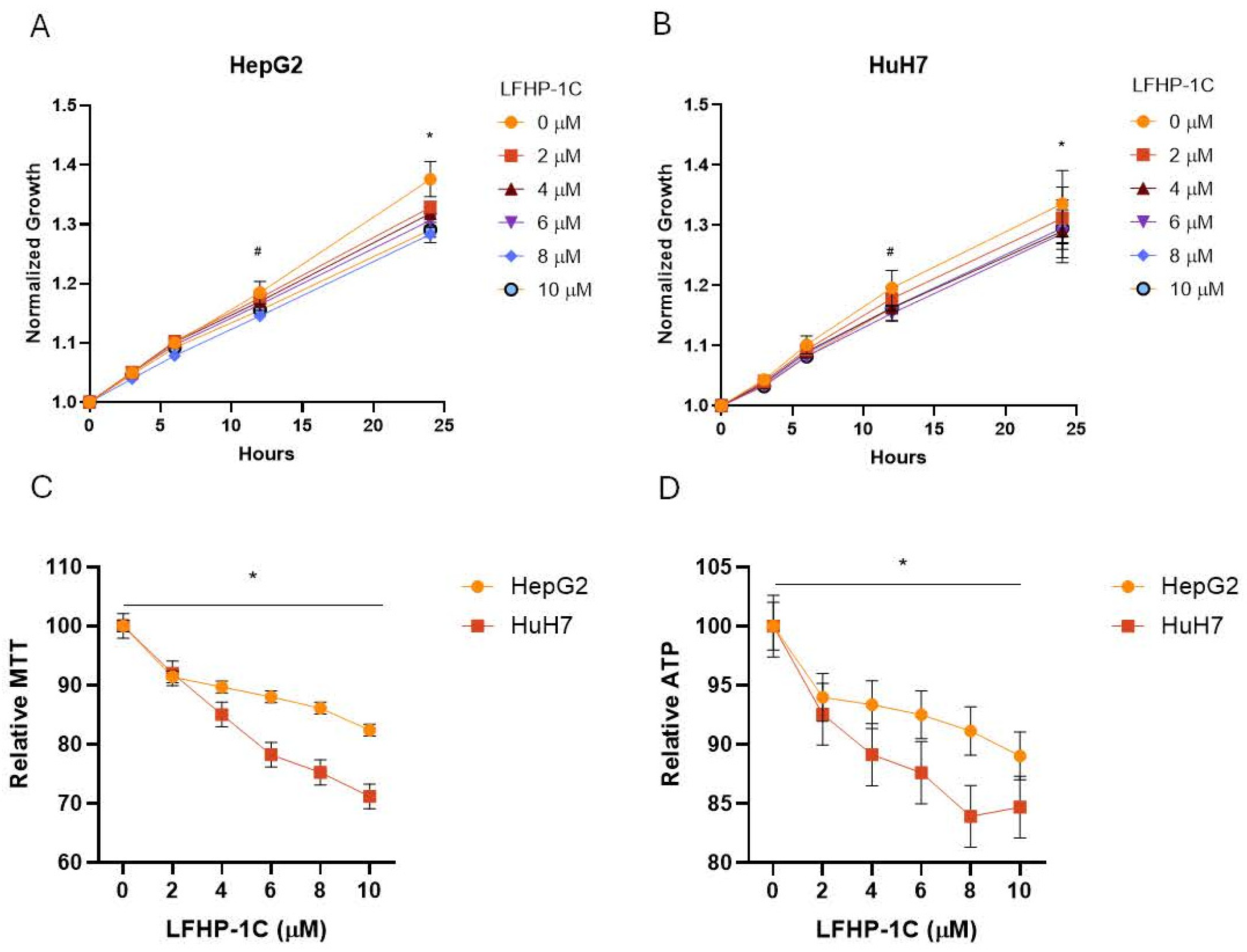
3.1. LFHP-1c Attenuates Cell Growth and Viability in Hepatoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Models
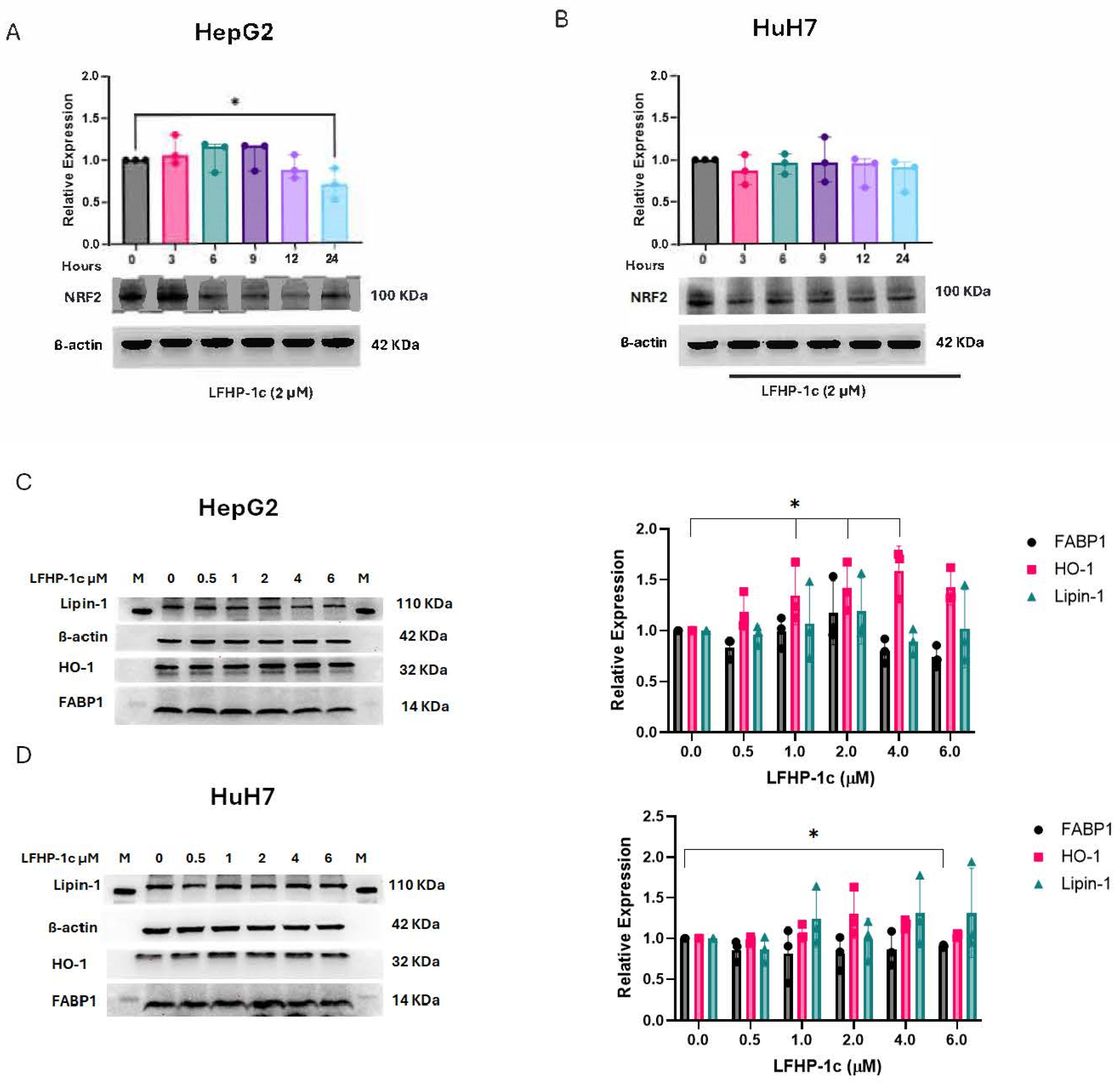
3.2. LFHP-1c Does Not Increase NRF2 Expression
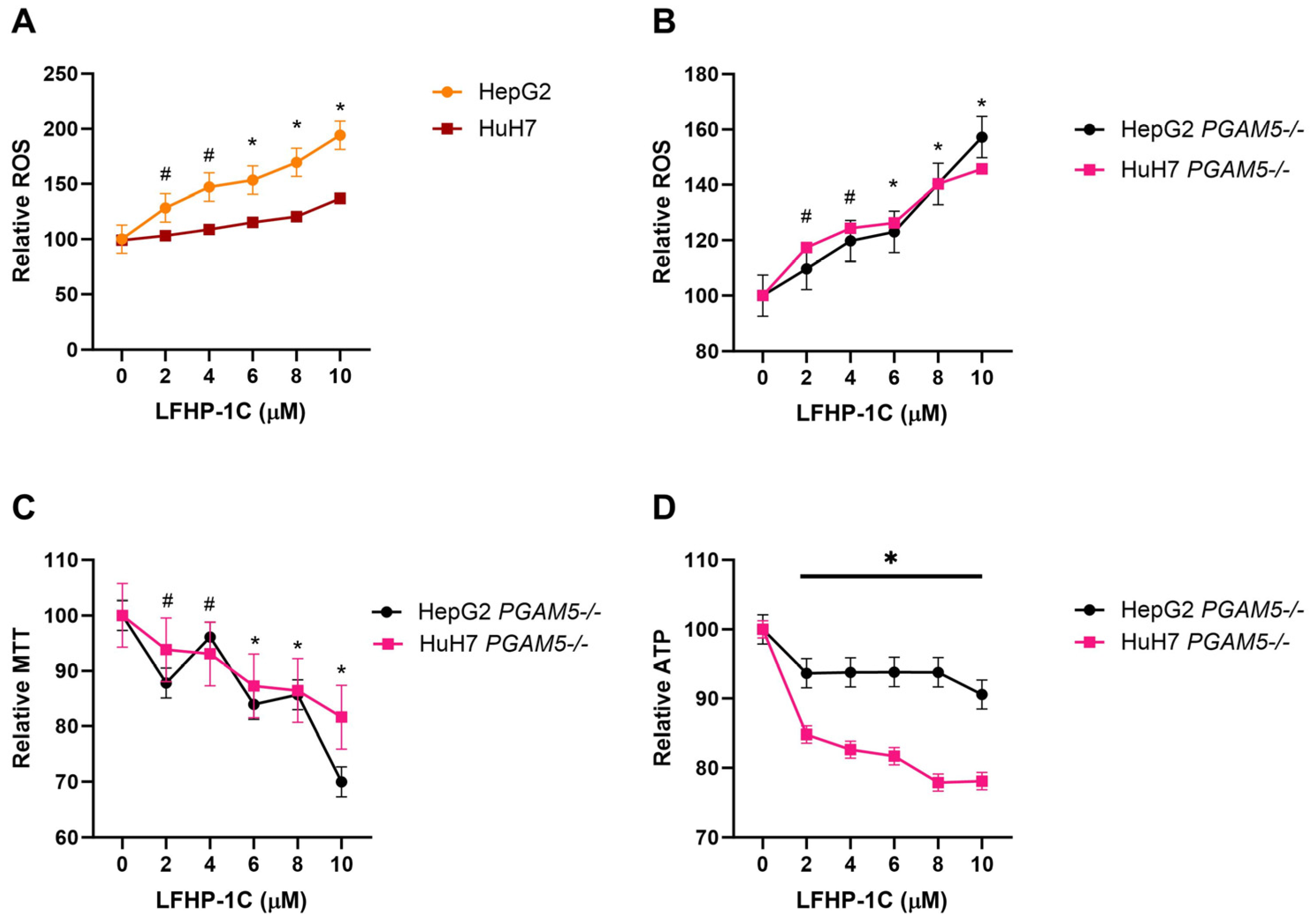
3.3. LFHP-1c Reduces Cell Viability and Promotes ROS Generation Independent of PGAM5
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMPK | 5′-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| KEAP | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NRF2/NFE2L2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2 |
| PAGE | Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PGAM5 | Phosphoglycerate mutase 5 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Qian, D.; Ding, X.; Song, T.; Cai, M.; Xie, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. High PGAM5 expression induces chemoresistance by enhancing Bcl-xL-mediated anti-apoptotic signaling and predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yin, M.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Weng, Z.; Xu, C. The prognostic value and clinical significance of mitophagy-related genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 917584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Yan, L.R.; Jiang, L.Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, B.G. Predicting Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Based on the Expression Signatures of Mitophagy Genes. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 4835826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhu, C.; Suo, C.; Wei, H.; Yu, Y.; Gu, X.; Chen, L.; Yuan, M.; Shen, S.; Li, S.; et al. Mitochondrion-Localized SND1 Promotes Mitophagy and Liver Cancer Progression Through PGAM5. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 857968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikuad, A.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Marcsisin, S.R.; Picaud, S.; Schroder, M.; Sekine, S.; Ichijo, H.; Engen, J.R.; Takeda, K.; Knapp, S. Structures of PGAM5 Provide Insight into Active Site Plasticity and Multimeric Assembly. Structure 2017, 25, 1089–1099.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, T.; Tanimura, S.; Yamaguchi, A.; Horikawa, K.; Yokozeki, M.; Hachiya, S.; Iemura, S.-I.; Natsume, T.; Matsuda, N.; Takeda, K. Cleaved PGAM5 dephosphorylates nuclear serine/arginine-rich proteins during mitophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, R.; Cheng, H.; Mu, C.; Zhao, T.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, Q.; Lin, J.; et al. Dynamic PGAM5 multimers dephosphorylate BCL-xL or FUNDC1 to regulate mitochondrial and cellular fate. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Choubey, V.; Gupta, R.; Kuum, M.; Safiulina, D.; Vaarmann, A.; Gogichaishvili, N.; Liiv, M.; Ilves, I.; Tämm, K.; et al. A novel role of KEAP1/PGAM5 complex: ROS sensor for inducing mitophagy. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Han, Z.; Feng, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Zhou, C.; Cai, X.; Fu, C.; et al. A regulatory signaling loop comprising the PGAM5 phosphatase and CK2 controls receptor-mediated mitophagy. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, G.; Liu, C.C.; Johnston, A.N. Deletion of PGAM5 Downregulates FABP1 and Attenuates Long-Chain Fatty Acid Uptake in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, H.; Okuzono, H.; Hayase, A.; Kumagai, F.; Tanii, S.; Hino, N.; Okada, Y.; Tachibana, K.; Doi, T.; Ishimoto, K. Lipin-1 is a novel substrate of protein phosphatase PGAM5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ruan, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Saavedra, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Pang, T. A Dual AMPK/Nrf2 Activator Reduces Brain Inflammation After Stroke by Enhancing Microglia M2 Polarization. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Xu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Ni, M.; Wu, D.; Huang, Z.; et al. A novel PGAM5 inhibitor LFHP-1c protects blood-brain barrier integrity in ischemic stroke. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1867–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Wang, J.J.; Niu, Z.H.; Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, C.C.; Hou, S.Q.; Zhou, D.R.; Zhang, C.; et al. LFHP-1c improves cognitive function after TBI in mice by reducing oxidative stress through the PGAM5-NRF2-KEAP1 ternary complex. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.K.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W. Enhanced expression of the transcription factor Nrf2 by cancer chemopreventive agents: Role of antioxidant response element-like sequences in the nrf2 promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Damulewicz, M.; Pyza, E.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3221–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, C.; Yu, Y.; Tie, L.; Lu, G.; Liu, F.; Han, X.; Ji, L.; Zou, X. Differential effects of PGAM5 knockout on high fat high fructose diet and methionine choline-deficient diet induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in mice. Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Li, S.T.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, Q.; Xiong, N.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H. PGAM5 deacetylation mediated by SIRT2 facilitates lipid metabolism and liver cancer proliferation. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2023, 55, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzhauser, S.; Wild, N.; Zupancic, M.; Ursu, R.G.; Bersani, C.; Näsman, A.; Kostopoulou, O.N.; Dalianis, T. Targeted Therapy With PI3K and FGFR Inhibitors on Human Papillomavirus Positive and Negative Tonsillar and Base of Tongue Cancer Lines With and Without Corresponding Mutations. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muthusamy, G.; Liu, C.-C.; Johnston, A.N. LFHP-1c Attenuates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability In Vitro Independent of PGAM5. Cancers 2025, 17, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091573
Muthusamy G, Liu C-C, Johnston AN. LFHP-1c Attenuates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability In Vitro Independent of PGAM5. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091573
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuthusamy, Ganesan, Chin-Chi Liu, and Andrea N. Johnston. 2025. "LFHP-1c Attenuates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability In Vitro Independent of PGAM5" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091573
APA StyleMuthusamy, G., Liu, C.-C., & Johnston, A. N. (2025). LFHP-1c Attenuates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Viability In Vitro Independent of PGAM5. Cancers, 17(9), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091573





