The Mesothelioma Systemic Inflammation Score Is Independently Associated with Overall Survival and Predicts Benefit of Multimodality Treatment in Pleural Mesothelioma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Methods
2.2. Prognostic Scores
2.3. Validation Cohort
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Treatment Strategy
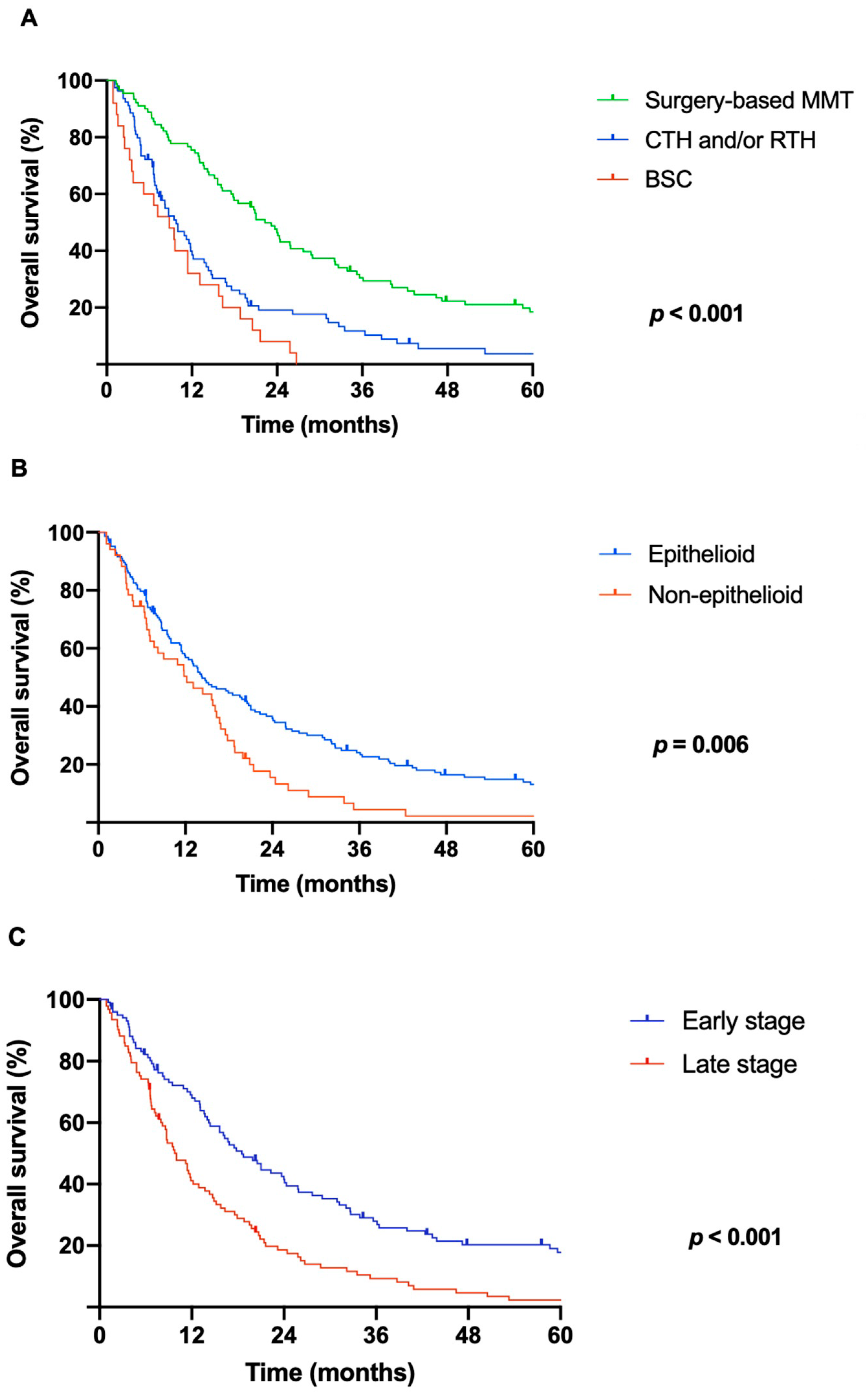
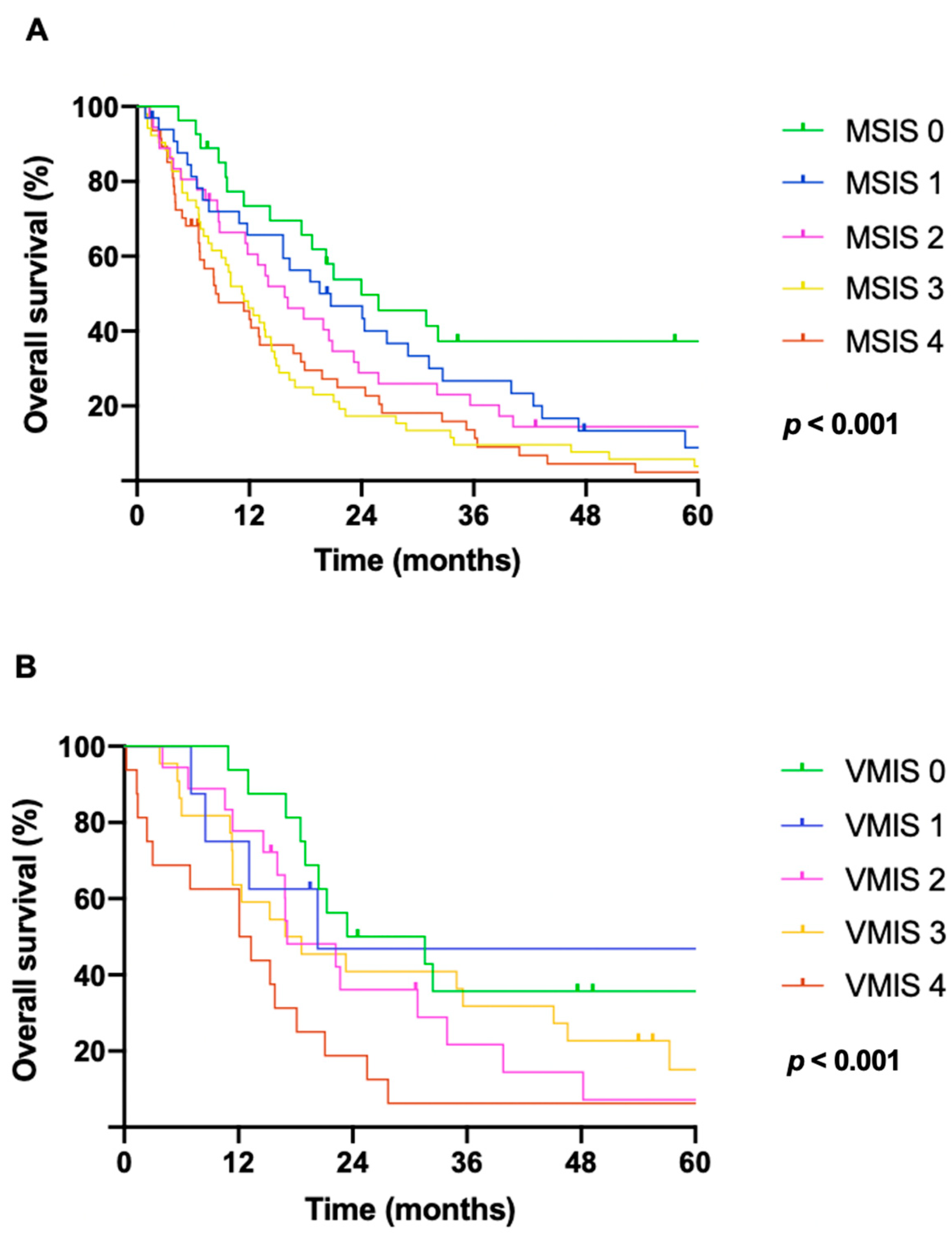
3.3. Survival and Prognostic Scores
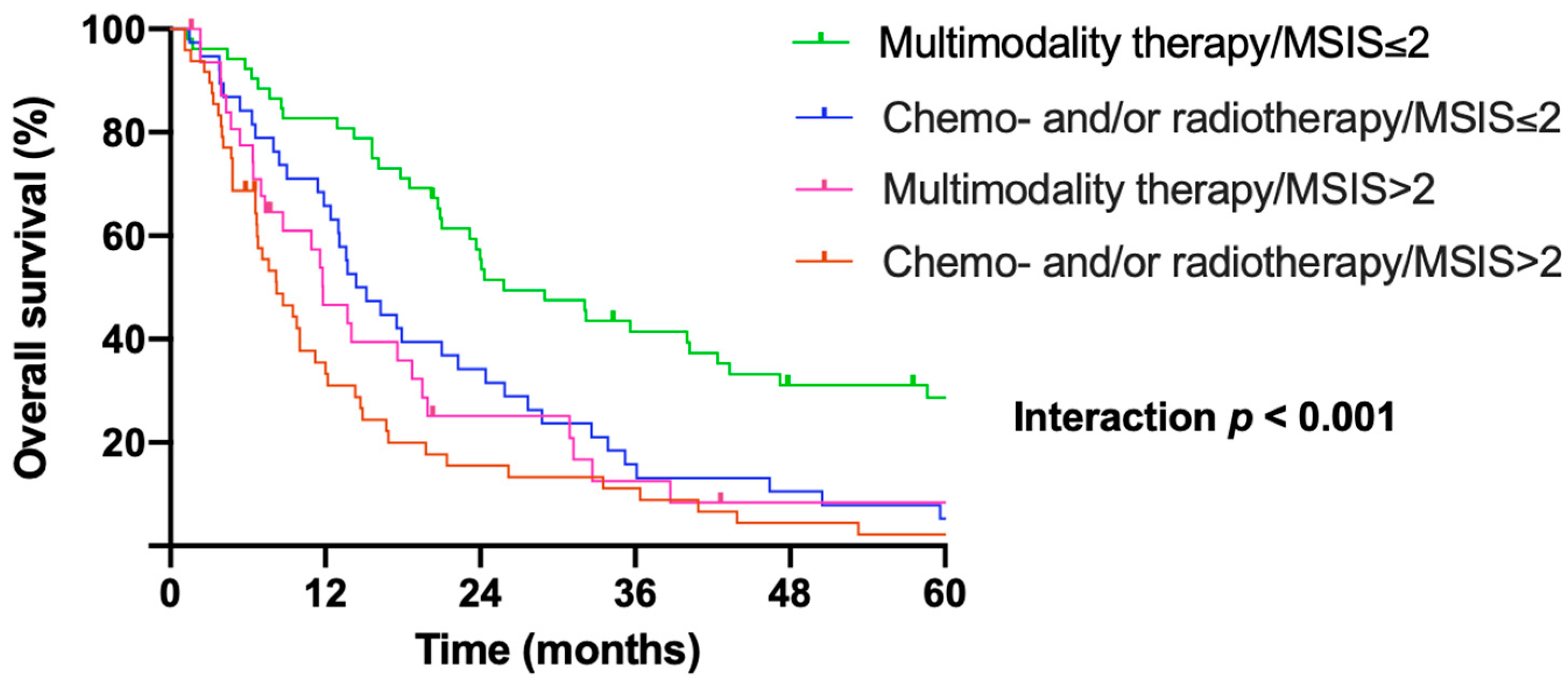
3.4. Pretreatment Msis Predicts Benefit of Surgery Within Multimodality Treatment Protocols
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, B.M. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: An epidemiological perspective. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 1, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brims, F. Epidemiology and Clinical Aspects of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, V.W.; Giroux, D.; Kennedy, C.; Ruffini, E.; Cangir, A.K.; Rice, D.; Pass, H.; Asamura, H.; Waller, D.; Edwards, J.; et al. Initial analysis of the international association for the study of lung cancer mesothelioma database. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, V.W.; Chansky, K.; Kindler, H.L.; Nowak, A.K.; Pass, H.I.; Rice, D.C.; Shemanski, L.; Galateau-Salle, F.; McCaughan, B.C.; Nakano, T.; et al. The IASLC Mesothelioma Staging Project: Proposals for the M Descriptors and for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2112–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gerwen, M.; Alpert, N.; Wolf, A.; Ohri, N.; Lewis, E.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; Flores, R.; Taioli, E. Prognostic factors of survival in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: An analysis of the National Cancer Database. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, A.; Pavlakis, N.; O’Connell, R.; Soeberg, M.; Kao, S.; Clarke, S.; Vardy, J.; van Zandwijk, N. Factors associated with survival in a large series of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma in New South Wales. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Gemba, K.; Aoe, K.; Kato, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sato, T.; Kubota, K.; Kishimoto, T. Survival and prognostic factors in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A retrospective study of 314 patients in the west part of Japan. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 41, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.G.; Abrams, K.R.; Leverment, J.N.; Spyt, T.J.; Waller, D.A.; O’Byrne, K.J. Prognostic factors for malignant mesothelioma in 142 patients: Validation of CALGB and EORTC prognostic scoring systems. Thorax 2000, 55, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.I. Biomarkers and prognostic factors for mesothelioma. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 1, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yu, N.; Wu, B. High systemic immune-inflammation index represents an unfavorable prognosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3973–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavelle, R.; Vavra-Musser, K.; Lee, J.; Brooks, J. Life Expectancy in Pleural and Peritoneal Mesothelioma. Lung Cancer Int. 2017, 2017, 2782590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, M.T.; Zhang, H. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: A population-based study of survival. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanaro, F.; Rosato, R.; Gangemi, M.; Roberti, S.; Ricceri, F.; Merler, E.; Gennaro, V.; Romanelli, A.; Chellini, E.; Pascucci, C.; et al. Survival of pleural malignant mesothelioma in Italy: A population-based study. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, V.; Mineo, T.C.; Multidisciplinary Tor Vergata University Study Group for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Clinical and biologic prognostic factors in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Thorac. Cancer 2012, 3, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, A.; Guerrera, F.; Roffinella, M.; Olivetti, S.; Costardi, L.; Oliaro, A.; Filosso, P.L.; Lausi, P.O.; Ruffini, E. Validation of EORTC and CALGB prognostic models in surgical patients submitted to diagnostic, palliative or curative surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Li, T.; Dai, Y.; Li, J. Preoperative systemic inflammation score (SIS) is superior to neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a predicting indicator in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanrikulu, A.C.; Abakay, A.; Komek, H.; Abakay, O. Prognostic value of the lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio and other inflammatory markers in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2016, 21, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Klikovits, T.; Winter, M.P.; Alimohammadi, A.; Grusch, M.; Dome, B.; Arns, M.; Schenk, P.; Jakopovic, M.; et al. Circulating fibrinogen is a prognostic and predictive biomarker in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneri, P.; Martorana, F.; Manzella, L.; Stella, S. Biomarkers and prognostic factors for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Future Oncol. 2015, 11 (Suppl. S24), 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, M.A.; Dong, Y.; Rozsas, A.; Klikovits, T.; Laszlo, V.; Ghanim, B.; Stockhammer, P.; Ozsvar, J.; Jakopovic, M.; Samarzija, M.; et al. Circulating activin A is a novel prognostic biomarker in malignant pleural mesothelioma–A multi-institutional study. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 63, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gaudino, G.; Pass, H.I.; Carbone, M.; Yang, H. Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for malignant mesothelioma: An update. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauk, O.; Hoda, M.A.; de Perrot, M.; Friess, M.; Klikovits, T.; Klepetko, W.; Keshavjee, S.; Weder, W.; Opitz, I. Extrapleural pneumonectomy after induction chemotherapy: Perioperative outcome in 251 mesothelioma patients from three high-volume institutions. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 98, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pass, H.I.; Levin, S.M.; Harbut, M.R.; Melamed, J.; Chiriboga, L.; Donington, J.; Huflejt, M.; Carbone, M.; Chia, D.; Goodglick, L.; et al. Fibulin-3 as a blood and effusion biomarker for pleural mesothelioma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, M.B.; Pulford, E.; Hoda, M.A.; Rozsas, A.; Griggs, K.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Edelman, J.J.; Kao, S.C.; Hyland, R.; Dong, Y.; et al. Fibulin-3 levels in malignant pleural mesothelioma are associated with prognosis but not diagnosis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanim, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Winter, M.P.; Klikovits, T.; Alimohammadi, A.; Hegedus, B.; Dome, B.; Grusch, M.; Arns, M.; Schenk, P.; et al. Pretreatment serum C-reactive protein levels predict benefit from multimodality treatment including radical surgery in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A retrospective multicenter analysis. Ann. Surg. 2012, 256, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banna, G.L.; Addeo, A.; Zygoura, P.; Tsourti, Z.; Popat, S.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Nadal, E.; Shah, R.; Pope, A.; Fisher, P.; et al. A prognostic score for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) receiving second-line immunotherapy or chemotherapy in the ETOP 9–15 PROMISE-meso phase III trial. Lung Cancer 2022, 169, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tural Onur, S.; Sokucu, S.N.; Dalar, L.; Iliaz, S.; Kara, K.; Buyukkale, S.; Altin, S. Are neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and platelet/lymphocyte ratio reliable parameters as prognostic indicators in malignant mesothelioma? Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2016, 12, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Liu, S.; Huang, L.; Li, W.; Yang, W.; Cong, T.; Ding, L.; Qiu, M. Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 57460–57469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugada, D.; Allegri, M.; Lavand’homme, P.; De Kock, M.; Fanelli, G. Inflammation-based scores: A new method for patient-targeted strategies and improved perioperative outcome in cancer patients. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 142425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Q. Preoperative increased systemic immune-inflammation index predicts poor prognosis in patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 484, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shang, X.; Ren, P.; Gong, L.; Ahmed, A.; Ma, Z.; Ma, R.; Wu, X.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, H.; et al. The predictive value of a preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutritional index in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Cong, X.; Li, S.; Song, S.; Song, H.; Xue, Y. Systemic immune-inflammation index as a useful prognostic indicator predicts survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lolli, C.; Basso, U.; Derosa, L.; Scarpi, E.; Sava, T.; Santoni, M.; Crabb, S.J.; Massari, F.; Aieta, M.; Conteduca, V.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts the clinical outcome in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with sunitinib. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 54564–54571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajwa, P.; Schuettfort, V.M.; Quhal, F.; Mori, K.; Katayama, S.; Laukhtina, E.; Pradere, B.; Motlagh, R.S.; Mostafaei, H.; Grossmann, N.C.; et al. Role of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients treated with salvage radical prostatectomy. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 3771–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomrich, G.; Paireder, M.; Kristo, I.; Baierl, A.; Ilhan-Mutlu, A.; Preusser, M.; Asari, R.; Schoppmann, S.F. High Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index is an Adverse Prognostic Factor for Patients With Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L. Comparison of the Prognostic Value of Systemic Inflammation Response Markers in Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Yang, X. Systemic immune-inflammation index is a promising noninvasive marker to predict survival of lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e13788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, K.; Shi, B.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yue, D.; Zhang, B.; Wang, C. Prognostic Significance of Combination of Preoperative Platelet Count and Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (COP-NLR) in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Based on a Large Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, D.; Chansky, K.; Nowak, A.; Pass, H.; Kindler, H.; Shemanski, L.; Opitz, I.; Call, S.; Hasegawa, S.; Kernstine, K.; et al. The IASLC Mesothelioma Staging Project: Proposals for Revisions of the N Descriptors in the Forthcoming Eighth Edition of the TNM Classification for Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2100–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.K.; Chansky, K.; Rice, D.C.; Pass, H.I.; Kindler, H.L.; Shemanski, L.; Bille, A.; Rintoul, R.C.; Batirel, H.F.; Thomas, C.F.; et al. The IASLC Mesothelioma Staging Project: Proposals for Revisions of the T Descriptors in the Forthcoming Eighth Edition of the TNM Classification for Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.; Giroux, D.; Kennedy, C.; Ruffini, E.; Cangir, A.K.; Rice, D.; Asamura, H.; Waller, D.; Edwards, J.; Weder, W.; et al. The IASLC Mesothelioma Staging Project: Improving Staging of a Rare Disease Through International Participation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 2082–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Qian, Y.; Fang, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Gu, W. Prognostic Value of Plasma Fibrinogen in Lung Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3904–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meniawy, T.M.; Creaney, J.; Lake, R.A.; Nowak, A.K. Existing models, but not neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, are prognostic in malignant mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogl, M.; Rosenmayr, A.; Bohanes, T.; Scheed, A.; Brndiar, M.; Stubenberger, E.; Ghanim, B. Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma-A Novel View on Inflammation. Cancers 2021, 13, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Du, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xu, J.; Qiu, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhu, W.; Liu, P. Prognostic value of PLR in various cancers: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamamsy, M.; Ghali, R.R.; Saad, A.S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Salem, A.M. FAS and FASL genetic polymorphisms impact on clinical outcome of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 6857–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.H.; Vaynblat, A.; Pass, H.I. Diagnosis and prognosis-review of biomarkers for mesothelioma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panou, V.; Vyberg, M.; Weinreich, U.M.; Meristoudis, C.; Falkmer, U.G.; Roe, O.D. The established and future biomarkers of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paajanen, J.; Ilonen, I.; Lauri, H.; Jarvinen, T.; Sutinen, E.; Ollila, H.; Rouvinen, E.; Lemstrom, K.; Rasanen, J.; Ritvos, O.; et al. Elevated Circulating Activin A Levels in Patients With Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Are Related to Cancer Cachexia and Reduced Response to Platinum-based Chemotherapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, e142–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.M.; Zakowski, M.; Venkatraman, E.; Krug, L.; Rosenzweig, K.; Dycoco, J.; Lee, C.; Yeoh, C.; Bains, M.; Rusch, V. Prognostic factors in the treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma at a large tertiary referral center. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francart, J.; Vaes, E.; Henrard, S.; Legrand, C.; Baas, P.; Gaafar, R.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Sylvester, R.; Robert, A. A prognostic index for progression-free survival in malignant mesothelioma with application to the design of phase II trials: A combined analysis of 10 EORTC trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2304–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotecha, R.; Tonse, R.; Rubens, M.; Appel, H.; Albrecht, F.; Kaywin, P.; Alley, E.W.; Tom, M.C.; Mehta, M.P. Meta-Analysis of Survival and Development of a Prognostic Nomogram for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Treated with Systemic Chemotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, J.L.; Dacic, S.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Attanoos, R.L.; Butnor, K.J.; Churg, A.; Husain, A.N.; Kadota, K.; Khoor, A.; Nicholson, A.G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Pleura: Advances Since the 2015 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromarino, M.G.; Lenzini, A.; Aprile, V.; Ali, G.; Bacchin, D.; Korasidis, S.; Ambrogi, M.C.; Lucchi, M. New Insights in Pleural Mesothelioma Classification Update: Diagnostic Traps and Prognostic Implications. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, G.; Papotti, M.; Righi, L.; Rossi, G.; Ferrero, S.; Bosari, S.; Calabrese, F.; Kern, I.; Maisonneuve, P.; Sonzogni, A.; et al. Pathologic Grading of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: An Evidence-Based Proposal. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, L.E.; Karrison, T.; Ananthanarayanan, V.; Gallan, A.J.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Alchami, F.S.; Attanoos, R.; Brcic, L.; Butnor, K.J.; Galateau-Salle, F.; et al. Nuclear grade and necrosis predict prognosis in malignant epithelioid pleural mesothelioma: A multi-institutional study. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Cao, S.; Jin, S.; Cao, J.; Shen, J.; Pan, B.; Zhu, R.; Yu, Y. Elevated aspartate aminotransferase and monocyte counts predict unfavorable prognosis in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Neoplasma 2017, 64, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Okita, R.; Saisho, S.; Maeda, A.; Nojima, Y.; Nakata, M. Preoperative neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and prognostic nutritional index predict survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nost, T.H.; Alcala, K.; Urbarova, I.; Byrne, K.S.; Guida, F.; Sandanger, T.M.; Johansson, M. Systemic inflammation markers and cancer incidence in the UK Biobank. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 36, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Liu, X.; Ji, W.; Lu, J.; Cui, J.; Li, W. The Efficacy of Different Inflammatory Markers for the Prognosis of Patients with Malignant Tumors. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 5769–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Pavlakis, N.; Harvie, R.; Vardy, J.L.; Boyer, M.J.; van Zandwijk, N.; Clarke, S.J. High blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is an indicator of poor prognosis in malignant mesothelioma patients undergoing systemic therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5805–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Mauri, F.A.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Wahab, L.; Lloyd, T.; Sharma, R. Inflammation-based prognostic indices in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihan, Y.B.; Ozturk, A.; Mutlu, H. Relationship between prognosis and neutrophil: Lymphocyte and platelet:lymphocyte ratios in patients with malignant pleural mesotheliomas. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 2061–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Klebe, S.; Henderson, D.W.; Reid, G.; Chatfield, M.; Armstrong, N.J.; Yan, T.D.; Vardy, J.; Clarke, S.; van Zandwijk, N.; et al. Low calretinin expression and high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio are poor prognostic factors in patients with malignant mesothelioma undergoing extrapleural pneumonectomy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.X.; Lin, J.P.; Xie, J.W.; Wang, J.B.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.Y.; Cao, L.L.; Lin, M.; Tu, R.; Zheng, C.H.; et al. Prognostic importance of the preoperative modified systemic inflammation score for patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2019, 22, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamori, S.; Toyokawa, G.; Shimokawa, M.; Kinoshita, F.; Kozuma, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Haratake, N.; Akamine, T.; Hirai, F.; Seto, T.; et al. The C-Reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio is a Novel Significant Prognostic Factor in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Retrospective Multi-institutional Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoshi, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Kaku, S.; Iki, R.; Hirabayashi, M. Prognostic Impact of Inflammation-related Biomarkers on Overall Survival of Patients with Inoperable Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. In Vivo 2018, 32, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, R.; Okada, M.; Inokawa, H.; Murakami, T.; Ikeda, E. Prognostic values of preoperative C-reactive protein, albumin, and neutrophil ratios in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma who underwent extrapleural pneumonectomy. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 43, 101813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greb, D.; Hebeisen, M.; Matter, A.; Opitz, I.; Lauk, O. Prospective validation and extension of the Multimodality Prognostic Score for the treatment allocation of pleural mesothelioma patients. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2022, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I.; Friess, M.; Kestenholz, P.; Schneiter, D.; Frauenfelder, T.; Nguyen-Kim, T.D.; Seifert, B.; Hoda, M.A.; Klepetko, W.; Stahel, R.A.; et al. A New Prognostic Score Supporting Treatment Allocation for Multimodality Therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Review of 12 Years’ Experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillebeeckx, E.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Lamote, K. Clinical utility of diagnostic biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.J.; Donahoe, L.; Bradbury, P.A.; Leighl, N.; Keshavjee, S.; Hope, A.; Pal, P.; Cabanero, M.; Czarnecka, K.; McRae, K.; et al. Surgery for malignant pleural mesothelioma after radiotherapy (SMART): Final results from a single-centre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treasure, T.; Lang-Lazdunski, L.; Waller, D.; Bliss, J.M.; Tan, C.; Entwisle, J.; Snee, M.; O’Brien, M.; Thomas, G.; Senan, S.; et al. Extra-pleural pneumonectomy versus no extra-pleural pneumonectomy for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: Clinical outcomes of the Mesothelioma and Radical Surgery (MARS) randomised feasibility study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Darlison, L.; Edwards, J.; Elliott, D.; Fennell, D.A.; Popat, S.; Rintoul, R.C.; Waller, D.; Ali, C.; Bille, A.; et al. Mesothelioma and Radical Surgery 2 (MARS 2): Protocol for a multicentre randomised trial comparing (extended) pleurectomy decortication versus no (extended) pleurectomy decortication for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bondt, C.; Psallidas, I.; Van Schil, P.E.Y.; van Meerbeeck, J.P. Combined modality treatment in mesothelioma: A systemic literature review with treatment recommendations. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strbac, D.; Dolzan, V. Novel and Future Treatment Options in Mesothelioma: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, A.; Opitz, I.; Berghmans, T.; Psallidas, I.; Glatzer, M.; Rigau, D.; Astoul, P.; Bolukbas, S.; Boyd, J.; Coolen, J.; et al. ERS/ESTS/EACTS/ESTRO guidelines for the management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantini, L.; Hassan, R.; Sterman, D.H.; Aerts, J. Emerging Treatments for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Where Are We Heading? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.I.; Alimi, M.; Carbone, M.; Yang, H.; Goparaju, C.M. Mesothelioma Biomarkers: A Review Highlighting Contributions from the Early Detection Research Network. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2020, 29, 2524–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MSIS (Score 0–4) | 0 Point Each | 1 Point Each |
|---|---|---|
| NLR | <5 | ≥5 |
| PLR | <160 | ≥160 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | <537.5 | ≥537.5 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | <1 | ≥1 |
| Demographics | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, y, median | 67 (IQR 58–74) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 147 (75) |
| Female | 48 (25) |
| Histological subtype | |
| Epithelioid | 144 (74) |
| Non-epithelioid | 51 (26) |
| ECOG PS | |
| 0 | 118 (60) |
| 1 | 54 (28) |
| 2 | 14 (7) |
| 3 | 9 (5) |
| Stage | |
| Early (I–II) Late (III–IV) | 96 (49) 99 (51) |
| Diagnostic method | |
| VATS Open thoracotomy | 160 (82) 35 (18) |
| Treatment | |
| Surgery-based multimodality treatment | 90 (46) |
| Chemo-and/or radiotherapy | 80 (41) |
| Best supportive care | 25 (13) |
| Symptoms | |
| Dyspnea Chest pain Cough | 121 (62) 76 (39) 36 (19) |
| Pleural effusion | 137 (70) |
| Site | |
| Left | 106 (54) |
| Right | 89 (46) |
| MSIS 0 | MSIS 1 | MSIS 2 | MSIS 3 | MSIS 4 | Total | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | p-Value | n% | |
| Age | |||||||||||||
| <65 | 16 | 59 | 14 | 42 | 16 | 44 | 21 | 40 | 18 | 38 | 0.484 | 85 | 44 |
| >65 | 11 | 41 | 19 | 58 | 20 | 56 | 31 | 60 | 29 | 62 | 110 | 56 | |
| Sex | |||||||||||||
| Male | 21 | 78 | 24 | 73 | 22 | 61 | 39 | 75 | 41 | 87 | 0.104 | 147 | 75 |
| Female | 6 | 22 | 9 | 27 | 14 | 39 | 13 | 25 | 6 | 13 | 48 | 25 | |
| ECOG PS | |||||||||||||
| 0 | 20 | 74 | 17 | 52 | 24 | 67 | 32 | 61 | 23 | 50 | 0.174 | 116 | 59 |
| 1 | 6 | 22 | 12 | 36 | 8 | 22 | 16 | 31 | 18 | 38 | 60 | 31 | |
| 2 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 13 | 7 | |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 3 | |
| Histology | |||||||||||||
| Epithelioid | 25 | 93 | 23 | 70 | 28 | 78 | 36 | 69 | 32 | 68 | 0.145 | 144 | 74 |
| Non-epithelioid | 2 | 7 | 10 | 30 | 8 | 22 | 16 | 31 | 15 | 32 | 51 | 26 | |
| Stage | |||||||||||||
| I | 16 | 59 | 19 | 58 | 13 | 36 | 18 | 35 | 15 | 32 | 0.001 | 81 | 41 |
| II | 4 | 15 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 15 | 8 | |
| III | 7 | 26 | 11 | 33 | 19 | 53 | 28 | 54 | 21 | 45 | 86 | 44 | |
| IV | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 17 | 13 | 7 | |
| Treatment | |||||||||||||
| Surgery-based MMT | 19 | 70 | 17 | 52 | 16 | 44 | 25 | 48 | 13 | 28 | 0.047 | 90 | 46 |
| CTH and/or RTH | 4 | 15 | 13 | 39 | 15 | 42 | 21 | 40 | 27 | 59 | 80 | 41 | |
| BSC | 4 | 15 | 3 | 9 | 5 | 14 | 6 | 12 | 6 | 13 | 25 | 13 | |
| Patients Treated with Surgery Within Multimodality Protocols | Patients Treated with Chemo- and/or Radiotherapy | Patients Received Best Supportive Care | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 90 | n = 80 | n = 25 | |
| Scores | Median OS in months (95% CI) | ||
| MSIS 0 | 73.4 (0.0–163.4) | 18.7 (16.9–20.6) | 16.3 (0.0–41.1) |
| MSIS 1 | 29.0 (7.6–50.4) | 7.0 (0.0–14.8) | 9.6 (7.7–11.5) |
| MSIS 2 | 23.2 (17.7–28.7) | 11.8 (6.4–17.2) | 8.8 (0.0–20.2) |
| MSIS 3 | 14.4 (11.9–16.9) | 7.6 (3.6–11.7) | 6.6 (0.0–15.8) |
| MSIS 4 | 11.5 (8.9–14.2) | 6.7 (2.0–12.4) | 3.2 (1.4–5.1) |
| Variables | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | OS (95% CI) | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Age | 0.019 | 1.4 | 1.1–1.9 | 0.780 | ||
| >65 | 110 | 11.8 (8.0–15.6) | ||||
| <65 | 85 | 17.9 (12.5–23.3) | ||||
| Sex | 0.078 | 0.7 | 0.5–1.0 | |||
| Female | 48 | 15.6 (12.4–18.8) | ||||
| Male | 147 | 13.6 (10.7–16.5) | ||||
| ECOG PS | <0.001 | 1.5 | 1.2–1.9 | 0.129 | ||
| 0 | 116 | 16.1 (12.7–19.5) | ||||
| 1 | 60 | 14.0 (9.6–18.5) | ||||
| 2 | 13 | 8.8 (2.8–14.9) | ||||
| 3 | 6 | 1.4 (0.5–2.2) | ||||
| Histology | 0.006 | 0.6 | 0.4–0.9 | 0.141 | ||
| Epithelioid | 144 | 14.3 (10.5–18.1) | ||||
| Non-epithelioid | 51 | 12.2 (6.1–18.3) | ||||
| Stage | <0.001 | 1.6 | 1.3–1.8 | 0.001 | ||
| I | 81 | 21.4 (15.2–27.6) | ||||
| II | 15 | 19.9 (13.0–26.8) | ||||
| III | 86 | 11.4 (9.2–13.6) | ||||
| IV | 13 | 3.0 (1.3–4.8) | ||||
| Treatment | <0.001 | 1.9 | 1.5–2.3 | 0.004 | ||
| Surgery-based MMT | 90 | 22.3 (18.6–26.0) | ||||
| CTH and/or RTH | 80 | 9.8 (6.7–12.8) | ||||
| BSC | 25 | 8.8 (4.2–13.5) | ||||
| mGPS | 0.008 | 1.3 | 1.1–1.6 | 0.945 | ||
| 0 | 62 | 20.7 (15.4–26.1) | ||||
| 1 | 92 | 12.9 (11.2–14.6) | ||||
| 2 | 41 | 6.7 (2.6–10.8) | ||||
| NLR | 0.006 | 1.5 | 1.1–2.1 | 0.272 | ||
| High (≥5) | 70 | 11.4 (6.7–16.1) | ||||
| Low (<5) | 125 | 16.1 (12.4–19.9) | ||||
| PLR | 0.009 | 1.6 | 1.1–2.2 | 0.139 | ||
| High (≥160) | 53 | 12.9 (10.9–14.9) | ||||
| Low (<160) | 142 | 20.2 (14.3–26.1) | ||||
| LMR | 0.053 | 0.7 | 0.5–1.0 | |||
| High (≥2.6) | 66 | 15.6 (10.2–21.0) | ||||
| Low (<2.6) | 129 | 13.6 (10.8–16.4) | ||||
| Fibrinogen | <0.001 | 1.7 | 1.3–2.4 | 0.125 | ||
| High (≥537.5 mg/dL) | 107 | 10.0 (7.2–12.8) | ||||
| Low (<537.5 mg/dL) | 88 | 20.5 (13.8–27.3) | ||||
| CRP | 0.004 | 1.6 | 1.2–2.2 | 0.164 | ||
| High (≥1 mg/dL) | 134 | 11.9 (9.4–14.3) | ||||
| Low (<1 mg/dL) | 61 | 20.5 (15.7–25.3) | ||||
| MSIS | <0.001 | 1.2 | 1.1–1.4 | <0.001 | ||
| 0 | 27 | 24.0 (11.4–36.5) | ||||
| 1 | 33 | 20.7 (10.3–31.1) | ||||
| 2 | 36 | 15.8 (10.1–21.4) | ||||
| 3 4 | 52 47 | 11.2 (8.1–14.3) 8.4 (3.2–13.6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosleh, B.; Sinn, K.; Cho, A.; Reiner, A.; Steindl, A.; Lang, C.; Zöchbauer-Müller, S.; Dieckmann, K.; Widder, J.; Prosch, H.; et al. The Mesothelioma Systemic Inflammation Score Is Independently Associated with Overall Survival and Predicts Benefit of Multimodality Treatment in Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2025, 17, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081371
Mosleh B, Sinn K, Cho A, Reiner A, Steindl A, Lang C, Zöchbauer-Müller S, Dieckmann K, Widder J, Prosch H, et al. The Mesothelioma Systemic Inflammation Score Is Independently Associated with Overall Survival and Predicts Benefit of Multimodality Treatment in Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081371
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosleh, Berta, Katharina Sinn, Anna Cho, Anton Reiner, Ariane Steindl, Christian Lang, Sabine Zöchbauer-Müller, Karin Dieckmann, Joachim Widder, Helmut Prosch, and et al. 2025. "The Mesothelioma Systemic Inflammation Score Is Independently Associated with Overall Survival and Predicts Benefit of Multimodality Treatment in Pleural Mesothelioma" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081371
APA StyleMosleh, B., Sinn, K., Cho, A., Reiner, A., Steindl, A., Lang, C., Zöchbauer-Müller, S., Dieckmann, K., Widder, J., Prosch, H., Dome, B., Schelch, K., Aigner, C., Klikovits, T., Benej, M., Watzka, S., Filipits, M., Bölükbas, S., Sarova, P., ... Hoda, M. A. (2025). The Mesothelioma Systemic Inflammation Score Is Independently Associated with Overall Survival and Predicts Benefit of Multimodality Treatment in Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers, 17(8), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081371










