Recent Advances and Challenges in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: An Update on Completed and Ongoing Clinical Trials
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms Involved in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Progression
3. Challenges in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer
4. Ongoing and Completed Clinical Trials in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer
4.1. Monotherapy and Combinations with Standard Therapy
4.1.1. Cytotoxic Monotherapy or in Combination with Standard Therapy
4.1.2. Targeted Therapy as a Monotherapy or in Addition to Standard Therapy
4.1.3. Metabolic Inhibitors as a Monotherapy or in Addition to Standard Therapy
4.1.4. Immunotherapy Treatments as a Monotherapy or in Addition to Standard Therapy
4.1.5. Repurposed Drugs to Treat Advanced Pancreatic Cancer
4.2. Emerging Approaches in Pancreatic Cancer Management
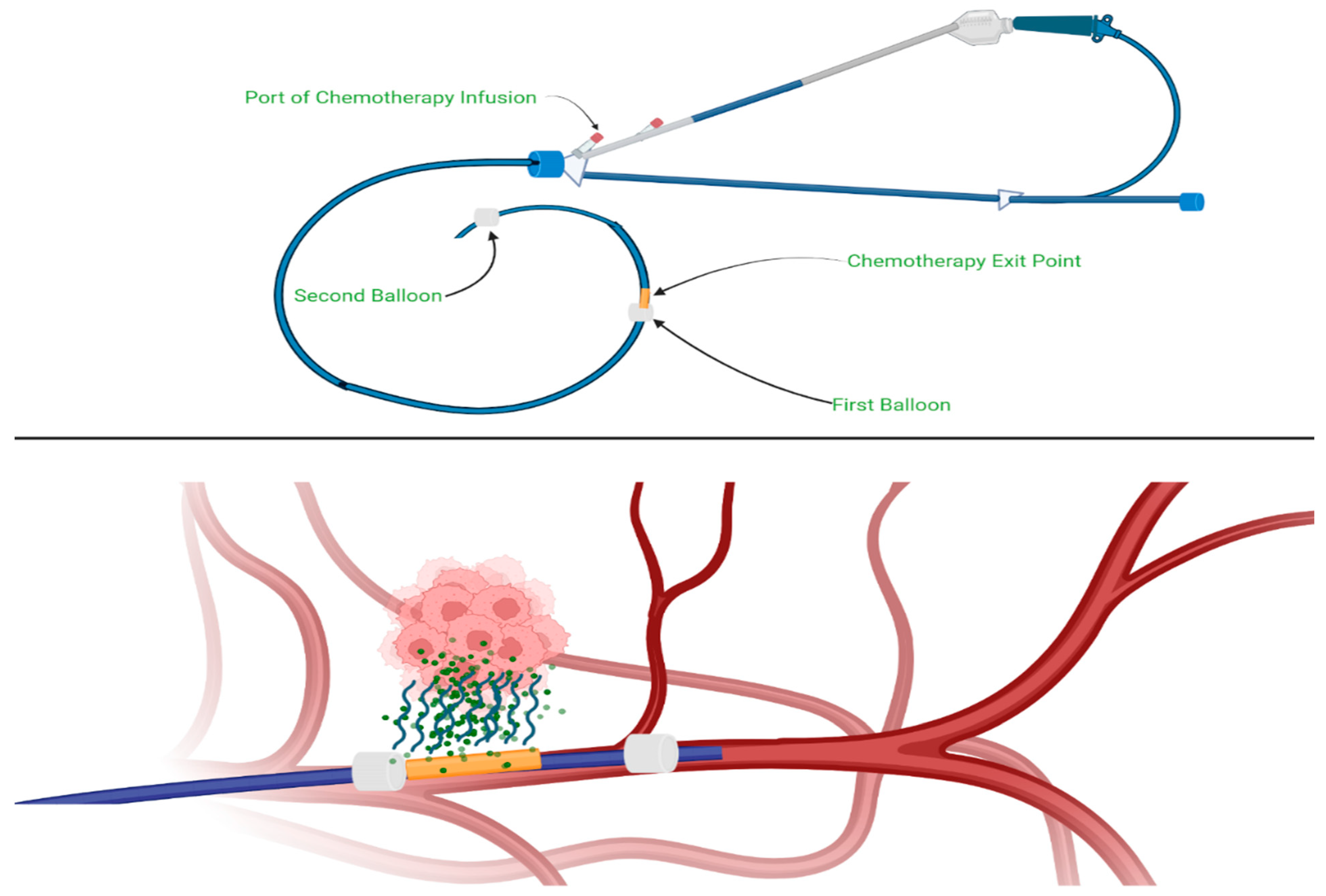
4.2.1. Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy
4.2.2. Nanoparticle and Liposomal Drug Delivery
4.2.3. Irreversible Electroporation and Electrochemotherapy
4.2.4. Ablation Procedures
Laparoscopic Microwave Ablation
Radiofrequency Ablation
High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
Robotic Whipple Procedure
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer of the Pancreas—Cancer Stat Facts. SEER. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- American Cancer Society. Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/pancreatic-cancer.html (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- Zhang, L.; Sanagapalli, S.; Stoita, A. Challenges in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCCN Pancreatic Cancer Guidelines. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Figures created with BioRender. Available online: https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 11 January 2025).
- ElSayed, S.A.; Mukherjee, S. Physiology, Pancreas. Nih.gov. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459261/ (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Pandol, S.J. Digestive Enzymes. Nih.gov. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK54127/ (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Mukund, A.; Afridi, M.A.; Karolak, A.; Park, M.A.; Permuth, J.B.; Rasool, G. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC): A Review of Recent Advancements Enabled by Artificial Intelligence. Cancers 2024, 16, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.A. Advanced pancreatic cancer: The standard of care and new opportunities. Oncol. Rev. 2018, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; MA, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Narang, A.; He, J.; Wolfgang, C.; Li, K.; Zheng, L. Consensus, debate, and prospective on pancreatic cancer treatments. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klein-Brill, A.; Amar-Farkash, S.; Lawrence, G.; Collisson, E.A.; Aran, D. Comparison of FOLFIRINOX vs Gemcitabine Plus Nab-Paclitaxel as First-Line Chemotherapy for Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2216199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.K.; Ko, A.H. Erlotinib in the treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. Biologics 2008, 2, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, T.; Yashiro, M. Molecular targets for the treatment of pancreatic cancer: Clinical and experimental studies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanoudakis, D.; Frountzas, M.; Schizas, D.; Michalopoulos, N.V.; Drakaki, A.; Toutouzas, K.G. Significance of TP53, CDKN2A, SMAD4 and KRAS in Pancreatic Cancer. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 2827–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, D.; Wang, L.; Zuo, X.; Maitra, A.; Bresalier, R.S. A Small Molecule with Big Impact: MRTX1133 Targets the KRASG12D Mutation in Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T. Impacts of activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in pancreatic cancer. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.N.; Goodwin, R.A.; Vickers, M.M. BRCA mutated pancreatic cancer: A change is coming. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grapa, C.M.; Mocan, T.; Gonciar, D.; Zdrehus, C.; Mosteanu, O.; Pop, T.; Mocan, L. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Its Role in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Mediated by Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9693–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makena, M.R.; Gatla, H.; Verlekar, D.; Sukhavasi, S.; Pandey, M.K.; Pramanik, K.C. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: The Culprit in Pancreatic Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, M.U.; Bansal, S.; Kaur, P.; Jain, S.K.; Altadil, T.; Hinzman, C.P.; Li, Y.; Moulton, J.; Singh, B.; Banasal, S.; et al. TGFβ Drives Metabolic Perturbations during Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Cancer: TGFβ Induced EMT in PDAC. Cancers 2021, 13, 6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Long, B.; Wang, Z. Role of Notch signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 173–186. [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo, A.; Forte, G.; Fasano, C.; Signorile, M.L.; Sanese, P.; Marco, K.D.; Nicola, E.D.; Latrofa, M.; Grossi, V.; Disciglio, V.; et al. Understanding the Genetic Landscape of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma to Support Personalized Medicine: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2023, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Voutsadakis, I.A.; Digklia, A. Pancreatic adenocarcinomas without KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A and SMAD4 mutations and CDKN2A/CDKN2B copy number alterations: A review of the genomic landscape to unveil therapeutic avenues. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Kohi, S.; Hirata, K.; Goggins, M. Role of hyaluronan in pancreatic cancer biology and therapy: Once again in the spotlight. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Cheng, X.B.; Kohi, S.; Koga, A.; Hirata, K. Targeting hyaluronan for the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulart, M.R.; Stasinos, K.; Fincham, R.E.A.; Delvecchio, F.R.; Kocher, H.M. T cells in pancreatic cancer stroma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7956–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucileanu, A.; Chira, R.; Mircea, P.A. PD-1/PD-L1 expression in pancreatic cancer and its implication in novel therapies. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2021, 94, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Saka, D.; Gökalp, M.; Piyade, B.; Cevik, N.C.; Sever, E.A.; Unutmaz, D.; Ceyhan, G.O.; Demir, I.E.; Asimgil, H. Mechanisms of T-Cell Exhaustion in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazeed, A.Y.; Day, C.M.; Garg, S. Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities in Locoregional Therapies. Cancers 2022, 14, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Li, T.; Du, Y.; Li, M. Pancreatic cancer: Challenges and opportunities. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Fagman, J.B.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Vihav, C.; Engstrom, C.; Liu, B.; Chen, C. A comprehensive review of pancreatic cancer and its therapeutic challenges. Aging 2022, 14, 7635–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheahan, A.V.; Biankin, A.V.; Parish, C.R.; Khachigian, L.M. Targeted therapies in the management of locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic cancer: A systematic review. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 21613–21627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeau, S.; Voutsadakis, I.A. FOLFIRINOX Chemotherapy in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Retrospective and Phase II Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoopathi, P.; Mannangatti, P.; Das, S.K.; Fisher, P.B.; Emdad, L. Chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Overcoming resistance to therapy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2023, 159, 285–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espona-Fiedler, M.; Patthey, C.; Lindblad, S.; Sarro, I.; Ohlund, D. Overcoming therapy resistance in pancreatic cancer: New insights and future directions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 229, 116492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Cutsem, E.V.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A. PARP inhibitors: Its role in treatment of cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2011, 30, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, J.; Chung, S.Y.; Prasad, S.; Saif, M.W. The Role of Olaparib in Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Med. J. 2021, 4, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann, V.; Quietzsch, D.; Gieseler, F.; Gonnermann, M.; Schonekas, H.; Rost, A.; Neuhaus, H.; Haag, C.; Clemens, M.; Heinrich, B.; et al. Randomized phase III trial of gemcitabine plus cisplatin compared with gemcitabine alone in advanced pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3946–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.G.; Seo, J.H.; Oh, S.C.; Choi, C.W.; Kim, J.S. A Phase II Trial of Gemcitabine plus Capecitabine for Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 44, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Jiang, C.; Yu, C.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, X. Capecitabine inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and proliferation of colorectal cancer cells by mediating the RANK/RANKL pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 23, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raedler, L.A. Lonsurf (Trifluridine plus Tipiracil): A New Oral Treatment Approved for Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2016, 9, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Feng, L.; Han, H.Q.; Yuan, J.; Qi, Z.K.; Lian, Y.F.; Kuang, B.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Deng, C.C.; Zhange, H.J.; et al. A novel Smac mimetic APG-1387 demonstrates potent antitumor activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by inducing apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court, O.R.; Shemilt, K. Lonsurf (trifluridine/tipiracil): Assessing the impact of dose related toxicities and progression free survival in (refractory) metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2022, 28, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. KRAS mutation in pancreatic cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2021, 48, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oya, Y.; Imaizumi, K.; Mitsudomi, T. The next-generation KRAS inhibitors…What comes after sotorasib and adagrasib? Lung Cancer 2024, 194, 107886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chour, A.; Toffart, A.C.; Berton, E.; Duruisseaux, M. Mechanisms of resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors in KRASG12C-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1328728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- KRYSTAL-1 Update: Adagrasib Yields Benefit in Variety of KRAS G12C–Mutated Tumors. Ascopost.com. Available online: https://ascopost.com/news/april-2023/krystal-1-update-adagrasib-yields-benefit-in-variety-of-kras-g12c-mutated-tumors/ (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Strickler, J.H.; Satake, H.; George, T.J.; Yaeger, R.; Hollebecque, A.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Schuler, M.; Burns, T.F.; Coveler, A.L.; Falchook, G.S.; et al. Sotorasib in KRAS p.G12C-Mutated Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saluja, A.K.; Dudeja, V.; Banerjee, S. Evolution of novel therapeutic options for pancreatic cancer. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 32, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosemurgy, A.; Harris, J.; Langleben, A.; Casper, E.; Goode, S.; Ramussen, H. Marimastat in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A dose-finding study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 22, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz-Praga, S.; Torri, J.; Johnson, M.; Steen, V.; Marshall, J.; Ness, E.; Dickson, R.; Sale, M.; Rasmussen, H.S.; Chiodo, T.A.; et al. Phase I trial of Marimastat, a novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, administered orally to patients with advanced lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.; Pelster, M.; Hong, D.S.; Strickler, J.H.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Aguirre, A.; Curran, D.; Woo, T.; Spira, A.I. A phase 1 trial evaluating the safety, tolerability, PK, and preliminary efficacy of QTX3034, an oral G12D-preferring multi-KRAS inhibitor, in patients with solid tumors with KRASG12D mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. 16), TPS3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendell, J.; Ulahannan, S.; Koczywas, M.; Brahmer, J.; Capasso, A.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Gordon, M.; McCoach, C.; Nagasaka, M.; Ng, K.; et al. 5 Oral—Intermittent dosing of RMC-4630, a potent, selective inhibitor of SHP2, combined with the MEK inhibitor cobimetinib, in a phase 1b/2 clinical trial for advanced solid tumors with activating mutations of RAS signaling. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 138, S8–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Okamoto, I.; Nishimura, Y.; Nakagawa, K. Nimotuzumab, a novel monoclonal antibody to the epidermal growth factor receptor, in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 2, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheis, B.; Reuter, D.; Ebert, M.P.; Siveke, J.; Kerkhoff, A.; Berdel, W.E.; Hofheinz, R.; Behringer, D.M.; Schmidt, W.E.; Goker, E.; et al. Gemcitabine combined with the monoclonal antibody nimotuzumab is an active first-line regimen in KRAS wildtype patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer: A multicenter, randomized phase IIb study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2429–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schram, A.M.; Goto, K.; Kim, D.W.; Macarulla, T.; Hollebecque, A.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Ou, S.H.I.; Rodon, J.; Rha, S.Y.; Nishino, K.; et al. Efficacy of Zenocutuzumab in NRG1 Fusion-Positive Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Subramani, R.; Lopez-Valdez, R.; Arumugam, A.; Nandy, S.; Boopalan, T.; Lakshmanaswamy, R. Targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibits pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abdel-Wahab, R.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Bhosale, P.R.; Wang, X.; Fogelman, D.R.; Shroff, R.T.; Overman, M.J.; Wolff, R.A.; Javle, M. Randomized, phase I/II study of gemcitabine plus IGF-1R antagonist (MK-0646) versus gemcitabine plus erlotinib with and without MK-0646 for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, G.; Palmer, D.H.; Greenhalf, W.; Ghaneh, P.; Jackson, R.; Cox, T.; Evans, A.; Shaw, V.E.; Wadsley, J.; Valle, J.W.; et al. Vandetanib plus gemcitabine versus placebo plus gemcitabine in locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic carcinoma (ViP): A prospective, randomised, double-blind, multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, J.P.; Chodkiewicz, C.; Maurel, J.; Wong, R.; Wasan, H.; Barone, C.; Letourneau, R.; Bajetta, E.; Pithavala, Y.; Bycott, P.; et al. Efficacy of gemcitabine plus axitinib compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: An open-label randomised phase II study. Lancet 2008, 371, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindler, H.L.; Ioka, T.; Richel, D.J.; Bennouna, J.; Letourneau, R.; Okusaka, T.; Funakoshi, A.; Furuse, J.; Park, Y.S.; Ohkawa, S.; et al. Axitinib plus gemcitabine versus placebo plus gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A double-blind randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Tempero, M.A.; Sigal, D.; Oh, D.Y.; Fazio, N.; Macrulla, T.; Hitre, E.; Hammel, P.; Hendifar, A.E.; Bates, S.E.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Pegvorhyaluronidase Alfa With Nab-Paclitaxel Plus Gemcitabine for Patients With Hyaluronan-High Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3185–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dhillon, S. Adagrasib: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.A.; Amparo, A.M.; Goodhart, G.; Ahmad, S.A.; Waters, A.M. Evaluation of KRAS inhibitor-directed therapies for pancreatic cancer treatment. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1402128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Holderfield, M.; Lee, B.J.; Jiang, J.; Tomlinson, A.; Seamon, K.J.; Mira, A.; Patrucco, E.; Goodhart, G.; Dilly, J.; Gindin, Y.; et al. Concurrent inhibition of oncogenic and wild-type RAS-GTP for cancer therapy. Nature 2024, 629, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jiang, J.; Jiang, L.; Maldonato, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Holderfield, M.; Aronchik, I.; Winters, I.P.; Salman, Z.; Blaj, C.; Menard, M.; et al. Translational and Therapeutic Evaluation of RAS-GTP Inhibition by RMC-6236 in RAS-Driven Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 994–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dilly, J.; Hoffman, M.T.; Abbassi, L.; Li, Z.; Paradiso, F.; Parent, B.D.; Hennessey, C.J.; Jordan, A.C.; Morgado, M.; Dasgupta, S.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to Oncogenic KRAS Inhibition in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 2135–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singhal, A.; Styers, H.C.; Rub, J.; Li, Z.; Torborg, S.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Grbovic-Huezo, O.; Feng, H.; Tarcan, Z.C.; Ozkan, H.S.; et al. A Classical Epithelial State Drives Acute Resistance to KRAS Inhibition in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 2122–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tapia Contreras, C.; Falke, J.D.; Seifert, D.M.; Schneider, C.; Kraub, L.; Fang, X.; Muller, D.; Demirdizen, E.; Spitzner, M.; Oliveira, T.D.; et al. KRASG12C-inhibitor-based combination therapies for pancreatic cancer: Insights from drug screening. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goodwin, C.M.; Waters, A.M.; Klomp, J.E.; Javaid, S.; Bryant, K.L.; Stalnecker, C.A.; Drizyte-Miller, K.; Papke, B.; Yang, R.; Amparo, A.M.; et al. Combination Therapies with CDK4/6 Inhibitors to Treat KRAS-Mutant Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thatikonda, V.; Lyu, H.; Jurado, S.; Kostyrko, K.; Bristow, C.A.; Albrecht, C.; Alpar, D.; Arnhof, H.; Bergner, O.; Bosch, K.; et al. Co-targeting SOS1 enhances the antitumor effects of KRASG12C inhibitors by addressing intrinsic and acquired resistance. Nat. Cancer 2024, 5, 1352–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thatikonda, V.; Lu, H.; Jurado, S.; Kostyrko, K.; Bristow, C.A.; Bosch, K.; Feng, N.; Gao, S.; Gerlach, D.; Gmachl, M.; et al. Combined KRASG12C and SOS1 inhibition enhances and extends the anti-tumor response in KRASG12C-driven cancers by addressing intrinsic and acquired resistance. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chugh, R.; Sangwan, V.; Patil, S.P.; Dudeja, V.; Dawra, R.K.; Banerjee, S.; Schumaker, R.J.; Blazar, B.R.; Georg, G.I.; Vickers, S.M.; et al. A preclinical evaluation of Minnelide as a therapeutic agent against pancreatic cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 156ra139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Saida, Y.; Kishimoto, S.; Lee, J.; Otowa, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Chandramouli, G.V.; Devasahayam, N.; Mitchell, J.B.; Krishna, M.C.; et al. PEGPH20, a PEGylated human hyaluronidase, induces radiosensitization by reoxygenation in pancreatic cancer xenografts. A molecular imaging study. Neoplasia 2022, 30, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stanciu, S.; Ionita-Radu, F.; Stefani, C.; Miricescu, D.; Stanescu-Spinu, I.I.; Greabu, M.; Totan, A.R.; Jinga, M. Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: From Molecular to Clinical Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Blagosklonny, M.V. Cancer prevention with rapamycin. Oncotarget 2023, 14, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani Reddy, R.; Arumugam, A.; Nandy, S.B.; Gonzalez, E.; Gonzalez, V.; Bonkoungou, S.; Ortega, A.; Lakshmanaswamy, R. Abstract 5055: Role of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75 (Suppl. 15), 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalnecker, C.A.; Grover, K.R.; Edwards, A.C.; Coleman, M.F.; Yang, R.; DeLiberty, J.M.; Papke, B.; Goodwin, C.M.; Pierobon, M.; Petricoin, E.F.; et al. Concurrent Inhibition of IGF1R and ERK Increases Pancreatic Cancer Sensitivity to Autophagy Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Faller, B.A.; Burtness, B. Treatment of pancreatic cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy. Biologics 2009, 3, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; Capasso, A.; Morgillo, F.; Orditura, M.; Vita, F.D.; Ciardiello, F. Targeting EGFR in pancreatic cancer treatment. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, Y.; Concepción, M.L.; Amador, Y.; Piriz, A.; Rabassa, R.; Leyva, A.; Arguelles, O.; Leblanach, L.; Moret, S.; Rivero, G.; et al. Nimotuzumab Concurrent with Gemcitabine as First-Line Treatment of Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 1496072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xu, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Nimotuzumab Plus Gemcitabine for K-Ras Wild-Type Locally Advanced or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5163–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, D.W.; Schram, A.M.; Hollebecque, A.; Nishino, K.; Macarulla, T.; Rha, S.Y.; Duruisseaux, M.; Liu, S.V.; Hallak, M.N.A.; Umemoto, K.; et al. The phase I/II eNRGy trial: Zenocutuzumab in patients with cancers harboring NRG1 gene fusions. Future Oncol. 2024, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Zenocutuzumab-Zbco for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-zenocutuzumab-zbco-non-small-cell-lung-cancer-and-pancreatic (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, C. RET rearrangement-positive pancreatic cancer has remarkable response to pralsetinib: A case report. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1078076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Regua, A.T.; Najjar, M.; Lo, H.W. RET signaling pathway and RET inhibitors in human cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 932353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gupta, S.; El-Rayes, B.F. Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors in pancreatic cancer. Biologics 2008, 2, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioka, T.; Okusaka, T.; Ohkawa, S.; Boku, N.; Sawaki, A.; Fujii, Y.; Kamei, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Namazu, K.; Umeyama, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of axitinib in combination with gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic cancer: Subgroup analyses by region, including Japan, from the global randomized Phase III trial. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 45, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Cancer metabolism: Looking forward. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemberg, K.M.; Gori, S.S.; Tsukamoto, T.; Rais, R.; Slusher, B.S. Clinical development of metabolic inhibitors for oncology. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e148550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, H.; Fu, M.; Wu, M.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z. Emerging mechanisms and promising approaches in pancreatic cancer metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Suzuki, T.; Otsuka, M.; Seimiya, T.; Iwata, T.; Kishikawa, T.; Koike, K. The biological role of metabolic reprogramming in pancreatic cancer. MedComm 2020, 1, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, D.; Fu, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, B.; Yu, M.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, Q.; Gao, W.; et al. Inhibition of glutamine metabolism counteracts pancreatic cancer stem cell features and sensitizes cells to radiotherapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31151–31163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Encarnación-Rosado, J.; Sohn, A.S.W.; Biancur, D.E.; Lin, E.Y.; Osorio-Vasquez, V.; Rodrick, T.; Gonzalez-Baerga, D.; Zhao, E.; Yokoyama, Y.; Simeone, D.M.; et al. Targeting pancreatic cancer metabolic dependencies through glutamine antagonism. Nat. Cancer 2024, 5, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Goswami, D.; Adiseshaiah, P.P.; Burgan, W.; Yi, M.; Guerin, T.M.; Kozlov, S.V.; Nissley, D.V.; McCormick, F. Undermining Glutaminolysis Bolsters Chemotherapy While NRF2 Promotes Chemoresistance in KRAS-Driven Pancreatic Cancers. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1630–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Harding, J.J.; Telli, M.; Munster, P.; Voss, M.H.; Infante, J.R.; Demichele, A.; Dunphy, M.; Le, M.H.; Molineaux, C.; Orford, K.; et al. A Phase I Dose-Escalation and Expansion Study of Telaglenastat in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4994–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alistar, A.; Morris, B.B.; Desnoyer, R.; Klepin, H.D.; Hosseinzadeh, K.; Clark, C.; Cameron, A.; Leyendecker, J.; D’Agostino, R.; Topaloglu, U.; et al. Safety and tolerability of the first-in-class agent CPI-613 in combination with modified FOLFIRINOX in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer: A single-centre, open-label, dose-escalation, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Philip, P.A.; Buyse, M.E.; Alistar, A.T.; Lima, C.M.R.; Luther, S.; Pardee, T.S.; Cutsem, E.V. A Phase III open-label trial to evaluate efficacy and safety of CPI-613 plus modified FOLFIRINOX (mFFX) versus FOLFIRINOX (FFX) in patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 3189–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Konteatis, Z.; Travins, J.; Gross, S.; Marjon, K.; Barnett, A.; Mandley, E.; Nicolay, B.; Nagaraja, R.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Discovery of AG-270, a First-in-Class Oral MAT2A Inhibitor for the Treatment of Tumors with Homozygous MTAP Deletion. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 4430–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derle, A.; De Santis, M.C.; Gozzelino, L.; Ratto, E.; Martini, M. The role of metabolic adaptation to nutrient stress in pancreatic cancer. Cell Stress 2018, 2, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vaziri-Gohar, A.; Zarei, M.; Brody, J.R.; Winter, J.M. Metabolic Dependencies in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 617, Erratum in: Front. Oncol. 2019, 8, 672. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khan, H.Y.; Kamgar, M.; Aboukameel, A.; Bannoura, S.; Chung, B.Y.; Li, Y.; Hallak, M.N.A.; Philip, P.A.; Tsai, S.; Luther, S.; et al. Targeting Cellular Metabolism With CPI-613 Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Radiation Therapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 8, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tomasi, M.L.; Cossu, C.; Spissu, Y.; Floris, A.; Ryoo, M.; Iglesias-Ara, A.; Wang, Q.; Pandol, S.J.; Bhowmick, N.A.; Seki, E.; et al. S-adenosylmethionine and methylthioadenosine inhibit cancer metastasis by targeting microRNA 34a/b-methionine adenosyltransferase 2A/2B axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 78851–78869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Picozzi, V.J.; Duliege, A.M.; Collisson, E.A.; Maitra, A.; Hidalgo, M.; Hendifar, A.E.; Beatty, G.L.; Goss, S.; Matrisian, L.M.; Herena, P.S.; et al. Precision Promise (PrP): An adaptive, multi-arm registration trial in metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. 16), TPS4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, C.; Liu, Y. The role of metabolic reprogramming in pancreatic cancer chemoresistance. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 13, 1108776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shimu, A.S.; Wei, H.X.; Li, Q.; Zheng, X.; Li, B. The new progress in cancer immunotherapy. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, G.; Yau, T.C.C.; Chiu, J.W.; Tse, E.; Kwong, Y.L. Pembrolizumab (Keytruda). Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2016, 12, 2777–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, M.; Tang, F.; Zhang, P.; Ai, C.; Fields, J.K.; Sundberg, E.J.; Latinovic, O.S.; Davenport, M.; et al. Hijacking antibody-induced CTLA-4 lysosomal degradation for safer and more effective cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 609–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Tang, F.; Liu, M.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Devenport, M.; Lazarski, C.A.; Zhange, P.; Wange, X.; et al. A reappraisal of CTLA-4 checkpoint blockade in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Liu, M.; Su, J.; Zhang, P.; Tang, F.; Ye, P.; Devenport, M.; Wang, X.; Zhange, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Uncoupling therapeutic from immunotherapy-related adverse effects for safer and effective anti-CTLA-4 antibodies in CTLA4 humanized mice. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, K.F., Jr.; Roychowdhury, S.; Bhatt, D.; Kocak, E.; Bai, X.F.; Liu, J.Q.; Ferketich, A.K.; Martin, E.W.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Zheng, P.; et al. Anti-human CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody promotes T-cell expansion and immunity in a hu-PBL-SCID model: A new method for preclinical screening of costimulatory monoclonal antibodies. Blood 2005, 105, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lute, K.D.; May, K.F., Jr.; Lu, P.; Zhang, H.; Kocak, E.; Mosinger, B.; Wolford, C.; Phillips, G.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Zheng, P.; et al.; et al. Human CTLA4 knock-in mice unravel the quantitative link between tumor immunity and autoimmunity induced by anti-CTLA-4 antibodies. Blood 2005, 106, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, P. Preserving the CTLA-4 Checkpoint for Safer and More Effective Cancer Immunotherapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salama, Z.T. Durvalumab: A Review in Extensive-Stage SCLC. Target. Oncol. 2021, 16, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feins, S.; Kong, W.; Williams, E.F.; Milone, M.C.; Fraietta, J.A. An introduction to chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; Melhem, R.; Blum-Murphy, M.A.; Ramos, C.; Petrosyan, L.; Li, J.; Perer, J.K.; Zou, H.; Wang, M.; Wright, H.M. A phase I, first-in-human, open-label, dose escalation and expansion study of PT886 in adult patients with advanced gastric, gastroesophageal junction, and pancreatic adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. 4), TPS765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, E.; FDA Grants Fast Track Designation to PT886 for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Pharmacy Times. Available online: https://www.pharmacytimes.com/view/fda-grants-fast-track-designation-to-pt886-for-the-treatment-of-pancreatic-cancer (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Zheng, R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, S.; Jin, X.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Frontiers and future of immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer: From molecular mechanisms to clinical application. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1383978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ota, S.; Miyashita, M.; Yamagishi, Y.; Ogasawara, M. Baseline immunity predicts prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients treated with WT1 and/or MUC1 peptide-loaded dendritic cell vaccination and a standard chemotherapy. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2021, 17, 5563–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chick, R.C.; Gunderson, A.J.; Rahman, S.; Cloyd, J.M. Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy for Localized Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Early Results. Cancers 2023, 15, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, A.A.; Bever, K.M.; Ho, W.J.; Fertig, E.J.; Niu, N.; Zheng, L.; Parkinson, R.M.; Durham, J.N.; Onners, B.; Ferguson, A.K.; et al. A Phase II Study of Allogeneic GM-CSF-Transfected Pancreatic Tumor Vaccine (GVAX) with Ipilimumab as Maintenance Treatment for Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5129–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Han, N.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Y.; Ma, D.; Lu, L.; Guo, X.; Qiu, M.; Huang, Q.; et al. A Neoantigen-Based Peptide Vaccine for Patients With Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Refractory to Standard Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 691605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rojas, L.A.; Sethna, Z.; Soares, K.C.; Olcese, C.; Pang, N.; Patterson, E.; Lihm, J.; Ceglia, N.; Guasp, P.; Chu, A.; et al. Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2023, 618, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, S.H.; Yu, J.; Creeden, J.F.; Sutton, J.M.; Marokowiak, S.; Sanchez, R.; Nemunaitis, J.; Kalinoski, A.; Zhang, J.T.; Damoiseaux, R.; et al. Repurposing metformin, simvastatin and digoxin as a combination for targeted therapy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 491, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, P.M.V.; Roife, D.; Dai, B.; Pratt, M.; Dobrowolski, R.; Kang, Y.; Li, X.; Augustine, J.J.; Zielinski, R.; Priebe, W.; et al. Antineoplastic effects of auranofin in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma preclinical models. Surg. Open Sci. 2019, 1, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lellis, L.; Veschi, S.; Tinari, N.; Mokini, Z.; Carradori, S.; Brocco, D.; Florio, R.; Grassadonia, A.; Cama, A. Drug Repurposing, an Attractive Strategy in Pancreatic Cancer Treatment: Preclinical and Clinical Updates. Cancers 2021, 13, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, R.; Veschi, S.; di Giacomo, V.; Pagotto, S.; Carradori, S.; Verginelli, F.; Cirilli, R.; Casulli, A.; Grassadonia, A.; Tinari, N.; et al. The Benzimidazole-Based Anthelmintic Parbendazole: A Repurposed Drug Candidate That Synergizes with Gemcitabine in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passero, F.C., Jr.; Grapsa, D.; Syrigos, K.N.; Saif, M.W. The safety and efficacy of Onivyde (irinotecan liposome injection) for the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer following gemcitabine-based therapy. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2016, 16, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang-Gillam, A.; Hubner, R.A.; Siveke, J.T.; Hoff, D.D.V.; Belanger, B.; Jong, F.A.D.; Mirakhur, B.; Chen, L.T. NAPOLI-1 phase 3 study of liposomal irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Final overall survival analysis and characteristics of long-term survivors. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 108, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Qin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.; Cui, J.; Fang, W.; Gu, K.; Li, Z.; et al. Irinotecan hydrochloride liposome HR070803 in combination with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma following prior gemcitabine-based therapy (PAN-HEROIC-1): A phase 3 trial. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Narayanan, G.; Bilimoria, M.M.; Hosein, P.J.; Su, Z.; Mortimer, K.M.; Martin, R.C.G. Multicenter randomized controlled trial and registry study to assess the safety and efficacy of the NanoKnife® system for the ablation of stage 3 pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Overview of study protocols. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Martin, R.C.G., 2nd; White, R.R.; Bilimoria, M.M.; Kluger, M.D.; Iannitti, D.A.; Polanco, P.M.; Hammil, C.W.; Cleary, S.P.; Heithaus, R.E.; Welling, T.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Irreversible Electroporation When Used for the Ablation of Stage 3 Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Initial Results from the DIRECT Registry Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- White, R.R.; Miller, A.; Messer, K.; Schoenberger, S.P.; Ambarkhane, S.V.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Berman, Z. Intra-tumoral CD40 antibody with irreversible electroporation (IRE) in locally advanced pancreas cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43 (Suppl. 4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, M.; Khouri, D.A.; Küppers, J.; Ramig, O.; Strunk, H.M.; Breuers, J.; Fazaal, J.; Fuhrmann, C.; Coenen, M.; Mohring, C.; et al. Study Protocol of a Randomized, Two-Arm, Phase I/II Trial Investigating the Feasibility, Safety, and Efficacy of Local Treatment with US-Guided High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound in Combination with Palliative Chemotherapy in Inoperable Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, K.; Strunk, H.; Dimitrov, D.; Vidal-Jove, J.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Essler, M.; Jin, C.; Mei, Z.; Zhu, H.; Marinova, M. US-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound in pancreatic cancer treatment: A consensus initiative between Chinese and European HIFU centers. Int. J. Hyperth. 2024, 41, 2295812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laface, C.; Laforgia, M.; Molinari, P.; Foti, C.; Ambrogio, F.; Gadaleta, C.D.; Ranieri, G. Intra-Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy in Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Kamimura, H.; Tsuchiya, A.; Togashi, T.; Watanabe, K.; Seki, K.I.; Ohta, H.; Yoshida, T.; Takeda, K.; Kamimura, T. Clinical efficacy of intra-arterial pharmacokinetic chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil, CDDP, gemcitabine, and angiotensin-II in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2007, 54, 2378–2382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.; Dutta, D.; Haque, I.; Nair, G.; Mohammed, J.; Parmer, M.; Kale, N.; Orr, M.; Jain, P.; Banerjee, S.; et al. pH-Sensitive Nanodrug Carriers for Codelivery of ERK Inhibitor and Gemcitabine Enhance the Inhibition of Tumor Growth in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, Z.L.; Feakins, R.; Pallett, L.J.; Manas, D.; Davidson, B.R. Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Review of Current Clinical Outcomes, Mechanism of Action and Opportunities for Synergistic Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Casadei, R.; Ricci, C.; Ingaldi, C.; Alberici, L.; Marco, M.D.; Guido, A.; Minni, F.; Serra, C. Intraoperative electrochemotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Indications, techniques and results-a single-center experience. Updates Surg. 2020, 72, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyftopoulos, A.; Ziogas, I.A.; Barbas, A.S.; Moris, D. The Synergistic Role of Irreversible Electroporation and Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 843769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Girelli, R.; Prejanò, S.; Cataldo, I.; Corbo, V.; Martini, L.; Scarpa, A.; Claudio, B. Feasibility and safety of electrochemotherapy (ECT) in the pancreas: A pre-clinical investigation. Radiol. Oncol. 2015, 49, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, J.; Wen, X.; Tian, L.; Li, T.; Xu, C.; Wen, X.; Melancon, M.P.; Gupta, S.; Shen, B.; Peng, W.; et al. Melancon MP, Gupta S, Shen B, Peng W, Li C. Irreversible electroporation reverses resistance to immune checkpoint blockade in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lv, Y. Irreversible Electroporation: An Emerging Immunomodulatory Therapy on Solid Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 811726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xi, P.; Zeng, D.; Chen, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, D.; Yao, Z.; He, C. Enhancing pancreatic cancer treatment: The role of H101 oncolytic virus in irreversible electroporation. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1546242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irenaeus, S.M.M.; Nielsen, D.; Ellmark, P.; Yachnin, J.; Deronic, A.; Nilsson, A.; Norlen, P.; Veitonmaki, N.; Wennersten, C.S.; Ullenhag, G.J. First-in-human study with intratumoral administration of a CD40 agonistic antibody, ADC-1013, in advanced solid malignancies. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankara Narayanan, J.S.; Hayashi, T.; Erdem, S.; McArdle, S.; Tiriac, H.; Ray, P.; Pu, M.; Milkulski, Z.; Miller, A.; Messer, K.; et al. Treatment of pancreatic cancer with irreversible electroporation and intratumoral CD40 antibody stimulates systemic immune responses that inhibit liver metastasis in an orthotopic model. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tian, G.; Guan, J.; Chu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, T. Immunomodulatory Effect of Irreversible Electroporation Alone and Its Cooperating With Immunotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 712042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ardeshna, D.R.; Leupold, M.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Pawlik, T.M.; Cloyd, J.M.; Ejaz, A.; Shah, H.; Burlen, J.; Krishna, S.G. Advancements in Microwave Ablation Techniques for Managing Pancreatic Lesions. Life 2023, 13, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lygidakis, N.J.; Sharma, S.K.; Papastratis, P.; Zinanovic, V.; Kefalourous, H.; Koshariya, M.; Lintzeris, I.; Porfiris, T.; Koutsiouroumba, D. Microwave ablation in locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma--a new look. Hepatogastroenterology 2007, 54, 1305–1310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carrafiello, G.; Ierardi, A.M.; Fontana, F.; Petrillo, M.; Floridi, C.; Lucchina, N.; Cuffari, S.; Dionigi, G.; Rotondo, A.; Fugazzola, C. Microwave ablation of pancreatic head cancer: Safety and efficacy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merchant, A.A.; Goebel, A.M.; Willingham, F.F. Radiofrequency ablation for the management of pancreatic mass lesions. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 39, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moond, V.; Maniyar, B.; Harne, P.S.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M.; Thosani, N.C. Harnessing endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation to reshape the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma microenvironment and elicit systemic immunomodulation. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2024, 5, 1056–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Iancu, I.; Bartoș, A.; Cioltean, C.L.; Breazu, C.; Iancu, C.; Bartos, D. Role of radio-ablative technique for optimizing the survival of patients with locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yousaf, M.N.; Ehsan, H.; Muneeb, A.; Wahab, A.; Sana, M.K.; Neupane, K.; Chaudhary, F.S. Role of Radiofrequency Ablation in the Management of Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 624997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tieranu, C.G.; Balaban, D.V.; Tabacelia, D.; Klimko, A.; Gheorghe, C.; Pereira, S.P.; Jinga, M.; Saftoiu, A. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Scoping Review with Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thosani, N.; Cen, P.; Rowe, J.; Guha, S.; Bailey-Lundberg, J.M.; Bhakta, D.; Patil, P.; Wray, C.J. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation (EUS-RFA) for advanced pancreatic and periampullary adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oh, D.; Seo, D.W.; Song, T.J.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, M.H. Clinical outcomes of EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation for unresectable pancreatic cancer: A prospective observational study. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gollapudi, L.A.; Tyberg, A. EUS-RFA of the pancreas: Where are we and future directions. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, F. High intensity focused ultrasound: A noninvasive therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16480–16488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marinova, M.; Feradova, H.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.A.; Conrad, R.; Tonguc, T.; Thudium, M.; Becher, M.U.; Kun, Z.; Gorchev, G.; Tomov, S.; et al. Improving quality of life in pancreatic cancer patients following high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in two European centers. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5818–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, O.M.; Mullinax, J.E.; Pimiento, J.M.; Meredith, K.L.; Malafa, M.P. Robotic Whipple Procedure for Pancreatic Cancer: The Moffitt Cancer Center Pathway. Cancer Control. 2015, 22, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, Z.V.; Lwin, T.M.; Aliaj, A.; Wang, J.; Clancy, T.E. Four-Day Robotic Whipple: Early Discharge after Robotic Pancreatoduodenectomy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2023, 236, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, J.P.; Kelsey, C.R.; Palta, M.; Cabrera, A.R.; Salama, J.K.; Patel, P.; Perez, B.A.; Lee, J.; Yin, F.F. Stereotactic body radiotherapy: A critical review for nonradiation oncologists. Cancer 2014, 120, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for pancreatic cancer: A potential ally in the era of immunotherapy? Radiat. Oncol. J. 2022, 40, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Burkoň, P.; Trna, J.; Slávik, M.; Nemecek, R.; Kazda, T.; Pospisil, P.; Dastych, M.; Eid, M.; Novotny, I.; Prochazka, T.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) of Pancreatic Cancer-A Critical Review and Practical Consideration. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rudra, S.; Jiang, N.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Olsen, J.R.; Roach, M.C.; Wan, L.; Portelance, L.; Mellon, E.A.; Bruynzeel, A.; Lagerwaard, F.; et al. Using adaptive magnetic resonance image-guided radiation therapy for treatment of inoperable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Reddy, A.V.; Hill, C.S.; Sehgal, S.; Zheng, L.; He, J.; Laheru, D.A.; Jesus-Acosta, A.D.; Herman, J.M.; Meyer, J.; Narang, A.K. Post-radiation neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic marker in patients with localized pancreatic adenocarcinoma treated with anti-PD-1 antibody and stereotactic body radiation therapy. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2022, 40, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ghaly, M.; Gogineni, E.; Herman, J.; Saif, M.W. New Potential Options for SBRT in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Med. J. 2021, 4 (Suppl. 3), 41–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
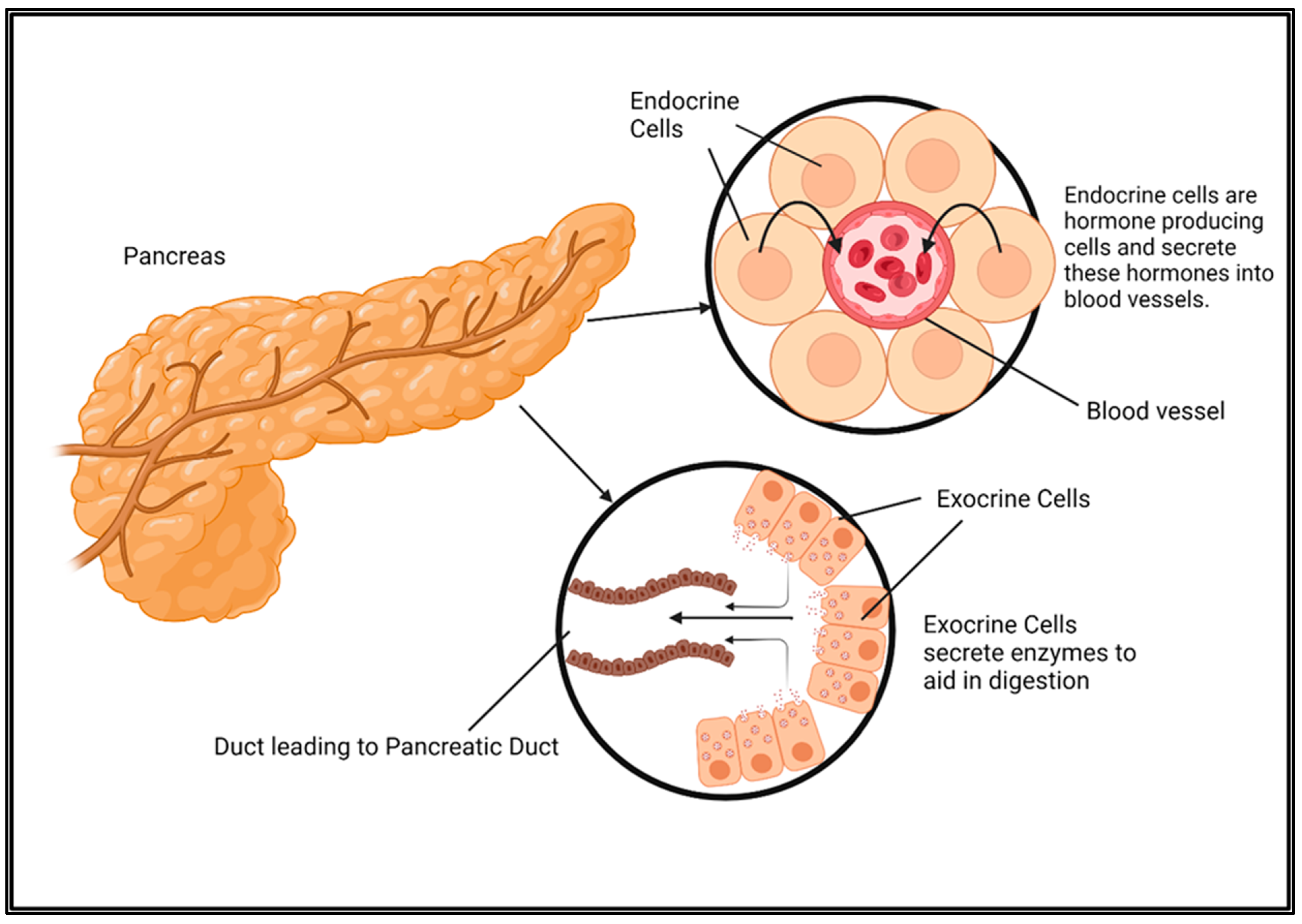

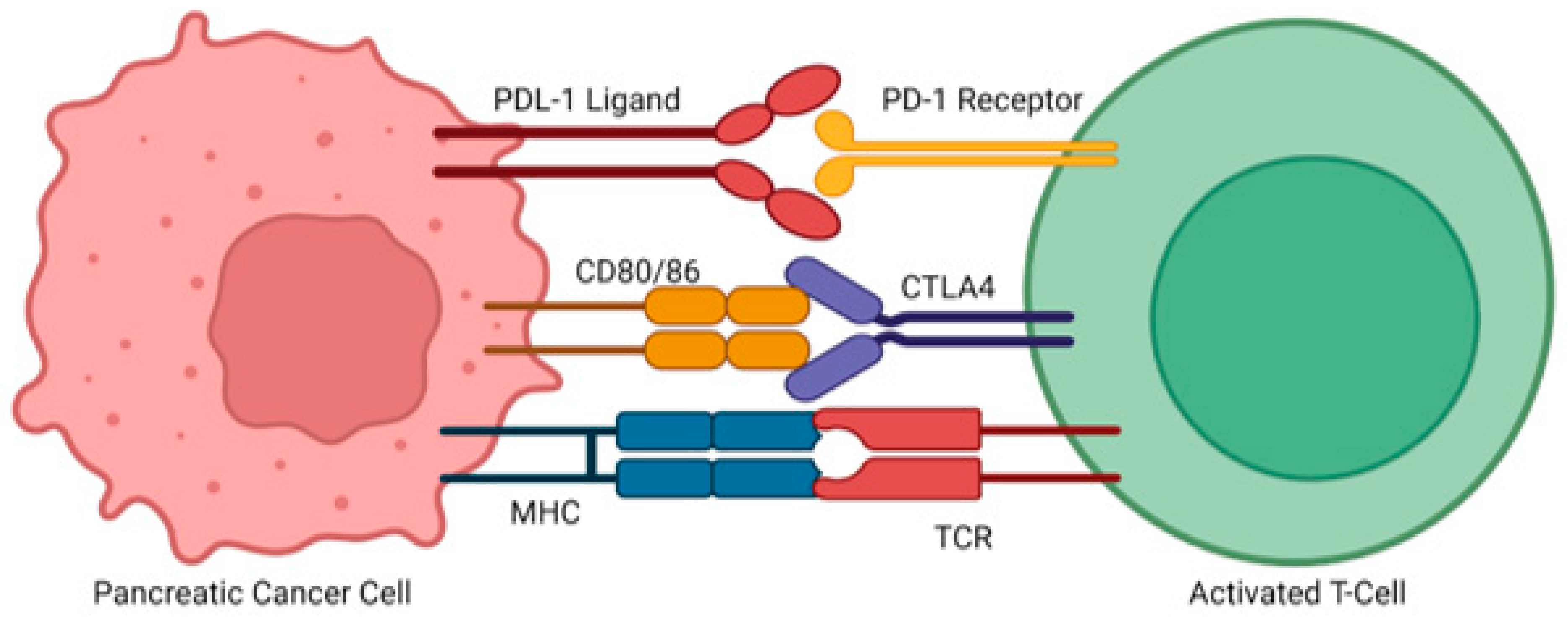
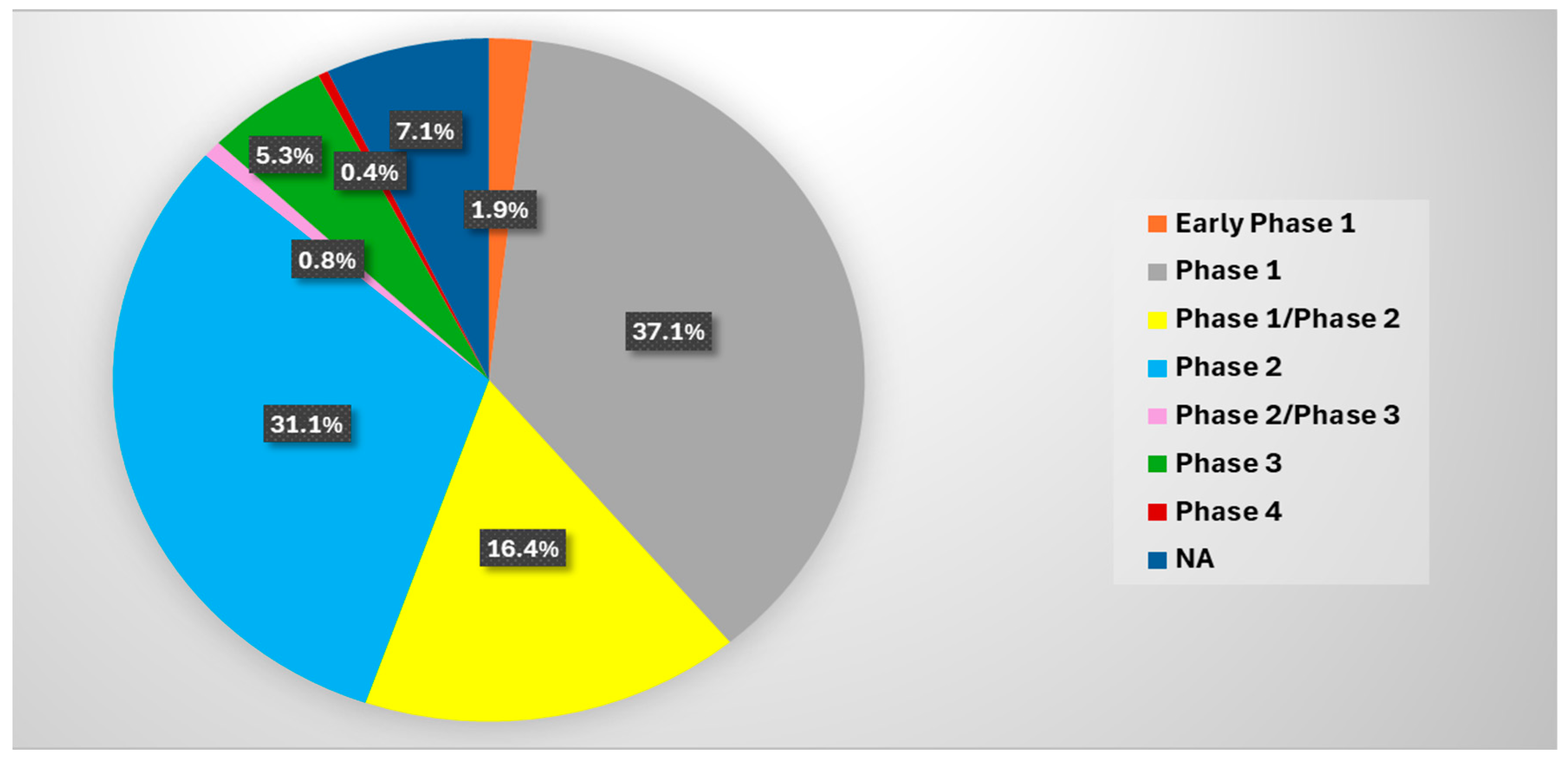
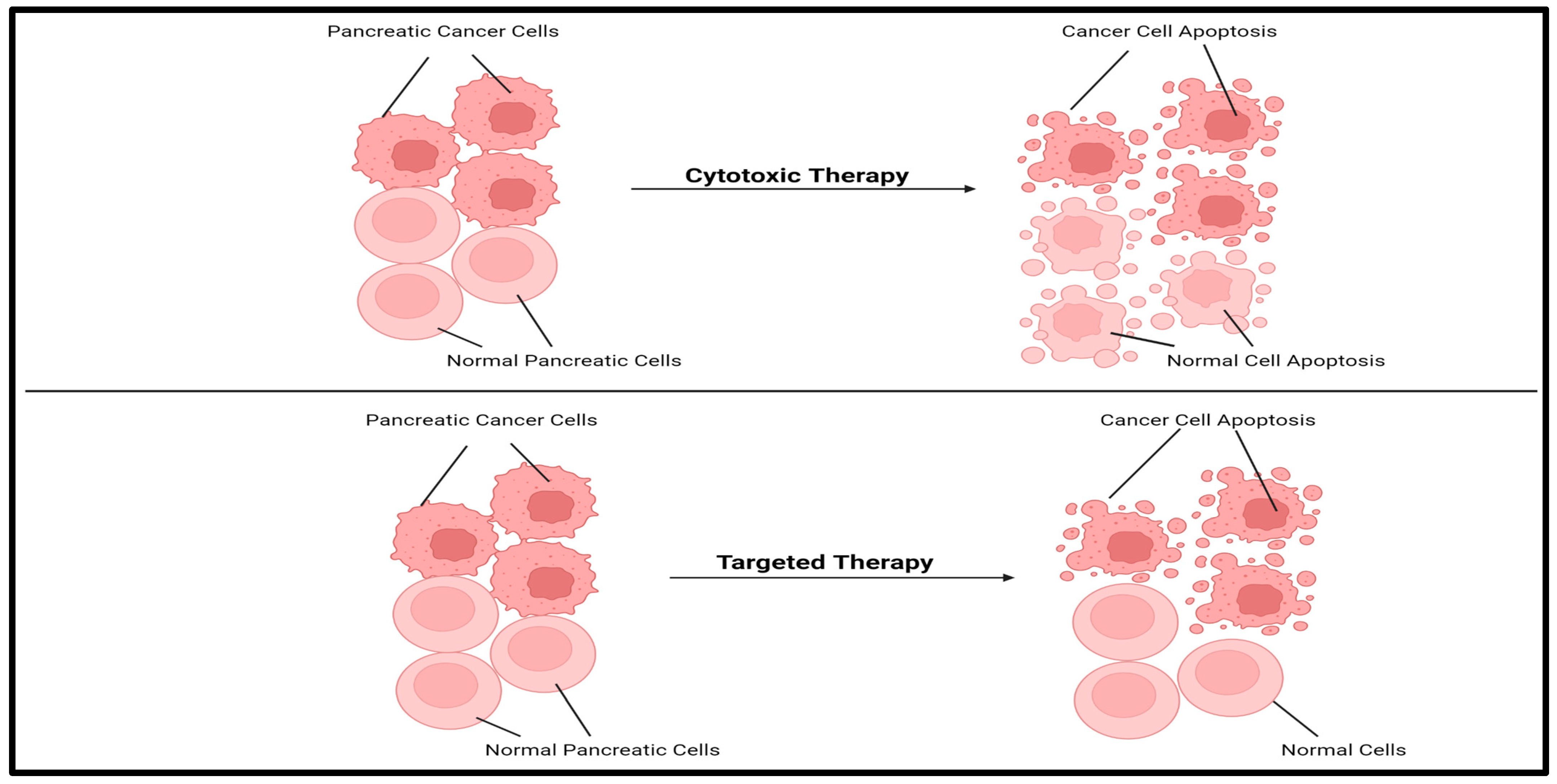

| Drug | Action of Drug Used as Monotherapy or with Standard Care | Clinical Status | Phase | Clinical Studies and References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olaparib | PARP inhibitor | Completed in 2019 | Phase 3 | NCT02184195 [38] |
| Lonsurf | Inhibits Thymidine Phosphorylase | Terminated in 2020 | Phase 2 | NCT02921737 |
| Cisplatin + Gemcitabine | Inhibits DNA replication | Completed in 2002 | Phase 3 | (No clinical trial number; trial done outside the United States.) [41] |
| Capecitabine + Gemcitabine | Inhibits Expression of RANK/RANKL pathway proteins in HT29 Cell Line | Completed in 2009 | Phase 2 | (No clinical trial number; trial done outside the United States.) [42,43] |
| APG-1387 + Gemcitabine + Nab-paclitaxel | Inhibits apoptosis regulator proteins, IAPs | Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT04643405 [42] |
| Lonsurf + Gemcitabine + Nab-paclitaxel | Inhibits Thymidine Phosphorylase and interferes with DNA Synthesis | Completed in 2021 | Phase 1 | NCT04046887 [44] |
| Drug | Action of Drug Used as Monotherapy or with Standard Care | Clinical Status | Phase | Clinical Studies and References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adagrasib | KRAS inhibitor | Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT03785249 [50] |
| Adagrasib | KRAS inhibitor | Recruiting | Phase 1b | NCT05634525 |
| Sotorasib | KRAS inhibitor | Active, Not Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT03600883 [51] |
| RMC-6236 | Pan-RAS inhibitor | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT05379985 |
| Minnelide | Interferes with Hyaluronan Synthesis | Completed in 2019 | Phase 2 | NCT03117920 [52] |
| Marimastat | A novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor | Completed in 2001 | Phase 2 | (No clinical trial number; trial done outside the United States.) [53,54] |
| Sirolimus | mTOR inhibitor | Unknown | Phase 2 | NCT03662412 |
| QTX3034 or QTX3034 + Cetuximab | KRAS inhibitor or KRAS inhibitor + Anti-EGFR antibody | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT06227377 [55] |
| HRS-4642 + Adebelimab | KRAS inhibitor + PD-L1 inhibitor | Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT06427239 |
| HRS-4642 + ADC | KRAS inhibitor | Not yet recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT06547736 |
| HRS-4642 + Nimotuzumab | KRAS inhibitor + EGFR inhibitor | Not yet recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT06773130 |
| HRS-4642 + Nimotuzumab + Gemcitabine + Nab-paclitaxel | KRAS inhibitor + EGFR inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Not yet recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT06770452 |
| BI 1823911 or BI 1823911 + BI 1701963 | SOS1 inhibitor or SOS1 inhibitor + SHP2 inhibitor | Active, not recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT04973163 [56] |
| Nimotuzumab + Gemcitabine | EGFR inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Completed in 2013 | Phase 2/Phase 3 | NCT00561990 [57] |
| Nimotuzumab + Gemcitabine | EGFR inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Completed in 2021 | Phase 3 | NCT02395016 [58] |
| Nimotuzumab + NALIRIFOX | EGFR inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Active, not recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT06429904 |
| Nimotuzumab + gemcitabine + nab-paclitaxel | EGFR inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT06404840 |
| Zenocutuzumab (MCLA-128) | Her 2 and Her 3 bispecific antibody | Active, not recruiting | NCT02912949 [59] | |
| MK-0646 + gemcitabine or MK-0646 + gemcitabine + Erlotinib | Anti-IGF-1R antibody + Chemotherapy or Anti-IGF-1R antibody + Chemotherapy + EGFR inhibitor | Completed 2020 | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT00769483 [60,61] |
| Vandetanib + Gemcitabine | RET inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Completed in 2017 | Phase 2 | (No clinical trial number; trial done outside the United States.) [62] |
| Axitinib + Gemcitabine | VEGFR inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Completed in 2008 | Phase 2 | NCT00219557 [63] |
| Axitinib + Gemcitabine | VEGFR inhibitor+ Chemotherapy | Completed in 2009 | Phase 3 | NCT00471146 [64] |
| PEGPH20 + Gemcitabine + Nab-paclitaxel | Targets and breaks down hyaluronan + Chemotherapy | Terminated | Phase 3 | NCT02715804 [65] |
| PEGPH20 + Gemcitabine + Nab-paclitaxel | Targets and breaks down hyaluronan + Chemotherapy | Active, not recruiting | Not applicable | NCT02921022 |
| Drug | Action of Drug Used as Monotherapy or with Standard Care | Clinical Status | Phase | Clinical Studies and References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telaglenastat hydrochloride (CB-839 HCl) | Glutaminase inhibitor | Completed 2019 | Phase 1 | NCT02071862 [99] |
| Telaglenastat hydrochloride (CB-839 HCl) | Glutaminase inhibitor | Active, not recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT03872427 |
| Devimistat (CPI-613) + mFOLFIRINOX | Mitochondrial metabolism inhibitor targeting both PDH and α-KGDH | Completed 2023 | Phase 1 | NCT01835041 [100] |
| Devimistat (CPI-613) + mFOLFIRINOX | Mitochondrial metabolism inhibitor targeting both PDH and α-KGDH | Completed 2022 | Phase 3 | NCT03504423 [101] |
| Devimistat (CPI-613) + chemoradiation | Mitochondrial metabolism inhibitor targeting both PDH and α-KGDH | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT05325281 |
| Devimistat (CPI-613) + Hydroxychloroquine + 5-fluorouracil or Gemcitabine | Mitochondrial metabolism inhibitor targeting both PDH and α-KGDH + Antimalarial + Chemotherapy | Active | Phase 2 | NCT05733000 |
| Devimistat (CPI-613) + Modified FOLFIRINOX | Mitochondrial metabolism inhibitor targeting both PDH and α-KGDH + Chemotherapy | Withdrawn | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT05926206 |
| AG-270 | MAT2A inhibitor | Terminated | Phase 1 | NCT03435250 [102] |
| Racemetyrosine (SM-88) + methoxsalen, phenytoin, and sirolimus (MPS) | Disrupts tyrosine-mediated metabolic pathways + Other agents | Terminated | Phase 2/Phase 3 | NCT03512756 |
| Racemetyrosine (SM-88) + mFOLFIRINOX + pamrevlumab + gemcitabine + nab-paclitaxel + canakinumab + spartalizumab | Disrupts tyrosine-mediated metabolic pathways + Chemotherapy + Other targeted agents | Active, Not Recruiting | Phase 3 | NCT04229004 |
| Drug | Action of Drug Used as Monotherapy or with Standard Care | Clinical Status | Phase | Clinical Studies and References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pembrolizumab + XL888 | PD-1 Inhibitor + Blocks enzymes needed for tumor growth | Completed in 2021 | Phase 1 | NCT03095781 |
| Pembrolizumab + BCA101 | PD-1 Inhibitor + Targets EGFR and TGFβ | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT04429542 |
| Pembrolizumab + NGM831 | PD-1 Inhibitor + ILT3 antagonist antibody | Active, Not Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT05215574 |
| Pembrolizumab + Lenvatinib | PD-1 Inhibitor + VEGFR inhibitor | Active, Not Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT05273554 |
| Pembrolizumab + SD-101 | PD-1 Inhibitor + TLR 9 agonist | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT05607953 |
| Pembrolizumab + NT-17 | PD-1 Inhibitor + Promotes T-cell development | Active, Not Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT04332653 |
| Pembrolizumab + ONC-392 | PD-1 Inhibitor + A humanized anti-CTLA4 IgG1 monoclonal antibody | Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT04140526 [111,112,113,114,115,116] |
| Durvalumab + Tazemetostat | PDL-1 Inhibitor + EZH2 inhibitor | Recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT04705818 |
| Pembrolizumab + Durvalumab + Ipilimumab | PD-1 Inhibitor + PDL-1 Inhibitor + CTLA4 Inhibitor | Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT05187338 |
| U87 CART-T cells | Engineered receptors that bind to tumor antigens | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT05605197 |
| IM92 CAR-T cells | Engineered receptors that bind to tumor antigens | Unknown | Early Phase 1 | NCT05275062 |
| IM96 CAR-T cells | Engineered receptors that bind to tumor antigens | Unknown | Early Phase 1 | NCT05287165 |
| Spevatamig (PT886) | Antibody targeting Claudin 18.2 (CLDN18.2) and CD47 | Unknown | Phase 1 | [119] |
| Spevatamig (PT886) | Antibody targeting Claudin 18.2 (CLDN18.2) and CD47 | Active | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT05482893 |
| GVAX vaccine + Ipilimumab + FOLFIRINOX | Stimulates anti-tumor immune responses + Blocks T-cell inhibitory signals + Chemotherapy | Completed 2019 | Phase 2 | NCT01896869 |
| GVAX vaccine + Pembrolizumab + Cyclophosphamide + Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) | Stimulates anti-tumor immune responses + Blocks T-cell negative signals + chemotherapy + radiation | Completed 2022 | Phase 2 | NCT02648282 |
| GV1001 vaccine + Gemcitabine + Capecitabine | Telomerase peptide vaccine aiding in an immune system response + Chemotherapy | Completed 2013 | Phase 3 | NCT00425360 |
| iNeo-Vac-P01 | Peptide noeoantigen vaccine | Completed 2021 | Phase 1 | NCT03645148 |
| Autogene Cevumeran + Atezolizumab + mFOLFIRINOX | mRNA Vaccine + PD-L1 inhibitor + Chemotherapy | Recruiting | Phase 2 | NCT05968326 |
| Drug | Action of Drug Used as Monotherapy or with Standard Care | Clinical Status | Phase | Clinical Studies and References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin + Digoxin + Simvastatin | Targets PDX1 and BIRC5 | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT03889795 |
| Auranofin | Inhibits Txnrd1 and HIF-1α | Not Applicable (in-vivo study) | Not Applicable | (Preclinical) [128] |
| Parbendazole | Fosters apoptosis | Not Applicable (in-vitro study) | Not Applicable | (Preclinical) [130] |
| Delivery Method/Procedure | Device Used/Vehicle Used or with Standard Care | Clinical Status | Phase | Clinical Studies and References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraarterial chemotherapy with gemcitabine | RenovoCath | Recruiting | Phase 3 | NCT03257033 |
| Nanoliposomal irinotecan (Onyvide) + 5-FU/leucovorin | Nanoparticle + Chemotherapy | Completed 2015 | Phase 3 | NCT01494506 [131,132] |
| Nanoliposomal irinotecan + oxaliplatin + 5-FU/leucovorin (NALIRIFOX) | Nanoparticle + Chemotherapy | Completed 2025 | Phase 3 | NCT04083235 |
| Irinotecan liposomal hydrochloride (HR070803) + 5-FU/leucovorin | Liposome + Chemotherapy | Completed 2022 | Phase 3 | NCT05074589 [133] |
| IRE +SOC | IRE | Active, not recruiting | Observational | NCT03899649 [134,135] |
| 1IRE+ Intra-tumoral mitazalimab, a CD40 agonistic antibody | IRE | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT06205849 [136] |
| IRE + Pembrolizumab | IRE | Recruiting | Phase 1 | NCT06378047 |
| HIFU + Standard chemotherapy | HIFU | Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | DRKS00012367 [137] |
| US-guided HIFU | HIFU | Ongoing | No information available | [138] |
| HIFU | HIFU | Recruiting | Phase 1/Phase 2 | NCT06211933 |
| Robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy | Robotic Whipple Therapy | Unknown Status | Not applicable | NCT04400357 |
| Miniinvasive pancreaticoduodenectomy | Robotic Whipple Therapy | Active, not recruiting | Not applicable | NCT04763642 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shenoy, A.; Yousif, A.; Hussain, M.D. Recent Advances and Challenges in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: An Update on Completed and Ongoing Clinical Trials. Cancers 2025, 17, 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081319
Shenoy A, Yousif A, Hussain MD. Recent Advances and Challenges in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: An Update on Completed and Ongoing Clinical Trials. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081319
Chicago/Turabian StyleShenoy, Abhinav, Amar Yousif, and Muhammad Delwar Hussain. 2025. "Recent Advances and Challenges in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: An Update on Completed and Ongoing Clinical Trials" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081319
APA StyleShenoy, A., Yousif, A., & Hussain, M. D. (2025). Recent Advances and Challenges in the Treatment of Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: An Update on Completed and Ongoing Clinical Trials. Cancers, 17(8), 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081319






