Evaluating Pre-Interventional Administration of a Liver-Specific Contrast Agent During MRI-Guided Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Lesions
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
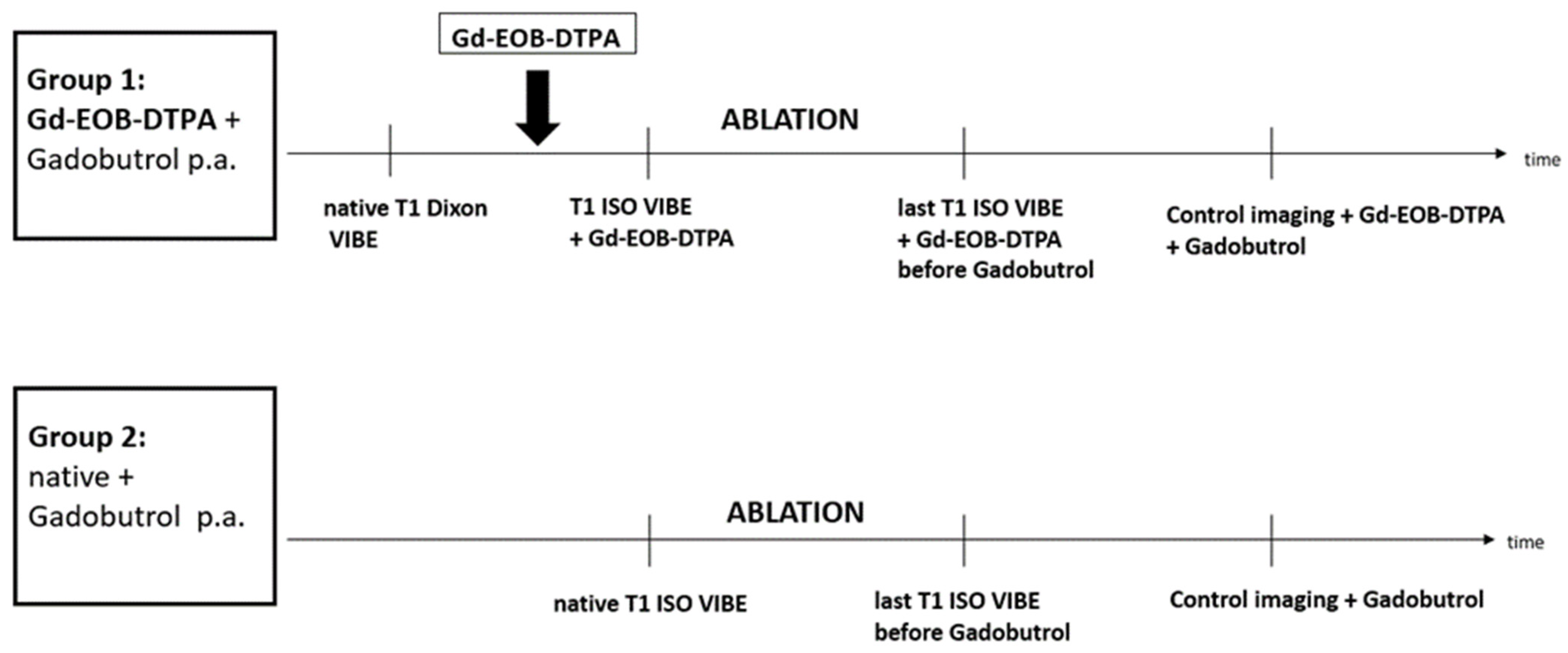
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Percutaneous Ablation Procedure
2.3. MR-Guided Interventional Imaging
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNR | Contrast-to-noise ratio |
| CT | Computer tomography |
| Gd-EOB-DTPA | Gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid |
| IR | Inversion recovery |
| LLC | Lesion liver contrast |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MWA | Microwave ablation |
| NSF | Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis |
| RFA | Radiofrequency ablation |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Solbiati, L.; Ahmed, M.; Cova, L.; Ierace, T.; Brioschi, M.; Goldberg, S.N. Small Liver Colorectal Metastases Treated with Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation: Local Response Rate and Long-term Survival with Up to 10-year Follow-up. Radiology 2012, 265, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, J.; Sellers, C.M.; Stein, S.M.; Kim, H.S. Radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: Contemporary treatment trends and outcomes from the United States National Cancer Database. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Vogl, T.J.; Chen, K.A.; Adwan, H. A Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of US-, CT-, and MR-Guided Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation for HCC: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltenbach, B.; Roman, A.; Eichler, K.; Nour-Eldin, N.E.; Vogl, T.J.; Zangos, S. Real-time qualitative MR monitoring of microwave ablation in ex vivo livers. Int. J. Hyperth. 2016, 32, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moche, M.; Trampel, R.; Kahn, T.; Busse, H. Navigation concepts for MR image-guided interventions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 27, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, S.; Rempp, H.; Hoffmann, R.; Graf, H.; Pereira, P.L.; Claussen, C.D. Image-guided radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Is MR guidance more effective than CT guidance? Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.L.; Siemou, P.; Rempp, H.J.; Hoffmann, R.; Hoffmann, R.T.; Kettenbach, J.; Clasen, S.; Helmberger, T. CT versus MR guidance for radiofrequency ablation in patients with colorectal liver metastases: A 10-year follow-up favors MR guidance. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.A.; Grove, J.J.; Van Der Spek, A.F.L.; Jarboe, M.D. Magnetic-resonance-guided biopsy of focal liver lesions. Pediatr. Radiol. 2017, 47, 750–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiao, D.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Han, X. Microwave Ablation of Small Hepatic Metastases Using MR Guidance and Monitoring: Clinical Safety and Efficacy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 3357–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrino, J.A.; Khurana, B.; Ready, J.E.; Silverman, S.G.; Winalski, C.S. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided percutaneous biopsy of musculoskeletal lesions. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempp, H.; Waibel, L.; Hoffmann, R.; Claussen, C.D.; Pereira, P.L.; Clasen, S. MR-guided radiofrequency ablation using a wide-bore 1.5-T MR system: Clinical results of 213 treated liver lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1972–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hou, B.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Bian, H.; Huo, Z. Microwave ablation of multifocal primary liver cancer guided by real-time 3.0T MRI. Int. J. Hyperth. 2023, 40, 2228519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincke, T.; Boll, D.; Zech, C. Bildgebung des hepatozellulären Karzinoms. Radiol. Up2date 2016, 16, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moche, M.; Heinig, S.; Garnov, N.; Fuchs, J.; Petersen, T.O.; Seider, D.; Brandmaier, P.; Kahn, T.; Busse, H. Navigated MRI-guided liver biopsies in a closed-bore scanner: Experience in 52 patients. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerstingl, R.; Huppertz, A.; Breuer, J.; Balzer, T.; Blakeborough, A.; Carter, R.; Fuste, L.C.; Heinz-Peer, G.; Judmaier, W.; Laniado, M.; et al. Diagnostic efficacy of gadoxetic acid (Primovist)-enhanced MRI and spiral CT for a therapeutic strategy: Comparison with intraoperative and histopathologic findings in focal liver lesions. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zou, L.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Song, B. Gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Ai, T.; Goerner, F.; Hu, X.; Runge, V.M.; Tweedle, M. MRI contrast agents: Basic chemistry and safety. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 36, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.Y.; Chen, Q.F.; Yang, Z.Q.; Wu, W.T.; Shi, H.B.; Liu, S. Early assessment of coagulation necrosis after hepatic microwave ablation: A comparison of non-enhanced and enhanced T1-weighted images. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kesen, S.; Liljeroth, M.; Nilsson, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sparrelid, E.; Brismar, T.B. Quantitative evaluation of liver function with gadoxetic acid enhanced MRI: Comparison among signal intensity-, T1-relaxometry-, and dynamic-hepatocyte-specific-contrast-enhanced MRI- derived parameters. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morana, G.; Salviato, E.; Guarise, A. Contrast agents for hepatic MRI. Cancer Imaging 2007, 7, S24–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, Q.F.; Yan, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.L. Feasibility and efficacy study of microwave ablation of recurrent small HCC guided by enhanced liver-specific magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zech, C.J.; Grazioli, L.; Jonas, E.; Ekman, M.; Niebecker, R.; Gschwend, S.; Breuer, J.; Jonsson, L.; Kienbaum, S. Health-economic evaluation of three imaging strategies in patients with suspected colorectal liver metastases: Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI vs. extracellular contrast media-enhanced MRI and 3-phase MDCT in Germany, Italy and Sweden. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19 (Suppl. S3), S753–S763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Winkelmann, M.T.; Gohla, G.; Kubler, J.; Clasen, S.; Nikolaou, K.; Hoffmann, R. MR-guided microwave ablation in hepatic malignancies: Clinical experiences from 50 procedures. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, F.; Lohfink, K.; Gaffke, G. Magnetic Resonance-Guided Freehand Radiofrequency Ablation of Malignant Liver Lesions. Investig. Radiol. 2013, 48, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.O.; Bae, K.; Choi, D.S.; Nickel, D. T1 mapping for liver function evaluation in gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging: Comparison of look-locker inversion recovery and B(1) inhomogeneity-corrected variable flip angle method. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3584–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Brunelli, S.M.; Williams, K.; Mitchell, M.D.; Feldman, H.I.; Umscheid, C.A. Gadolinium-based contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, K.; Baghdanian, A.H.; Baghdanian, A.A.; Sun, D.S.; Kolli, K.P.; Zagoria, R.J. Updated guidelines for intravenous contrast use for CT and MRI. Emerg. Radiol. 2020, 27, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, L.; Napolitano, A.; Visconti, E.; Longo, D.; Romano, A.; Toma, P.; Rossi Espagnet, M.C. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent-Related Toxicities. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubler, J.; Krumm, P.; Martirosian, P.; Winkelmann, M.T.; Gohla, G.; Nikolaou, K.; Hoffmann, R. Improved visualization of hepatic tumors in magnetic resonance-guided thermoablation using T1-inversion-recovery imaging with variable inversion time. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 7015–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nijm, G.M.; Sahakian, A.V.; Yang, G.Y.; Omary, R.A.; Larson, A.C. Irreversible electroporation in the liver: Contrast-enhanced inversion-recovery MR imaging approaches to differentiate reversibly electroporated penumbra from irreversibly electroporated ablation zones. Radiology 2011, 258, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, T.; Ito, K.; Sone, T.; Kanki, A.; Sato, T.; Higashi, H. Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MR imaging: Evaluation of biliary and renal excretion in normal and cirrhotic livers. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 80, e207–e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, F.A.; de Araujo, A.L.; Oliveira Neto, J.A.; Parente, D.B. Hepatobiliary contrast agents: Differential diagnosis of focal hepatic lesions, pitfalls and other indications. Radiol. Bras. 2014, 47, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Group 1 Gd-EOB-DTPA Before Ablation Gadobutrol After Ablation | Group 2 Gadobutrol After Ablation | p-Value (p < 0.05 *) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNR target lesion | native 2.5 | + Gd-EOB-DTPA 6.3 | p = 0.0006 * | |
| CNR of ablation zone during therapy monitoring | 2.14 | 7.85 | p < 0.0001 * | |
| CNR of ablation zone during control imaging | 2.0 | 7.65 | p < 0.0001 * | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashkar, A.; Kübler, J.; Nikolaou, K.; Hoffmann, R.; Winkelmann, M.T. Evaluating Pre-Interventional Administration of a Liver-Specific Contrast Agent During MRI-Guided Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Lesions. Cancers 2025, 17, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081264
Ashkar A, Kübler J, Nikolaou K, Hoffmann R, Winkelmann MT. Evaluating Pre-Interventional Administration of a Liver-Specific Contrast Agent During MRI-Guided Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Lesions. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081264
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshkar, Antonia, Jens Kübler, Konstantin Nikolaou, Rüdiger Hoffmann, and Moritz T. Winkelmann. 2025. "Evaluating Pre-Interventional Administration of a Liver-Specific Contrast Agent During MRI-Guided Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Lesions" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081264
APA StyleAshkar, A., Kübler, J., Nikolaou, K., Hoffmann, R., & Winkelmann, M. T. (2025). Evaluating Pre-Interventional Administration of a Liver-Specific Contrast Agent During MRI-Guided Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Lesions. Cancers, 17(8), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081264






