Estimating the Morbidity of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Using the Comprehensive Complication Index: Data from the Asian Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Consortium
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Post-Operative Complications
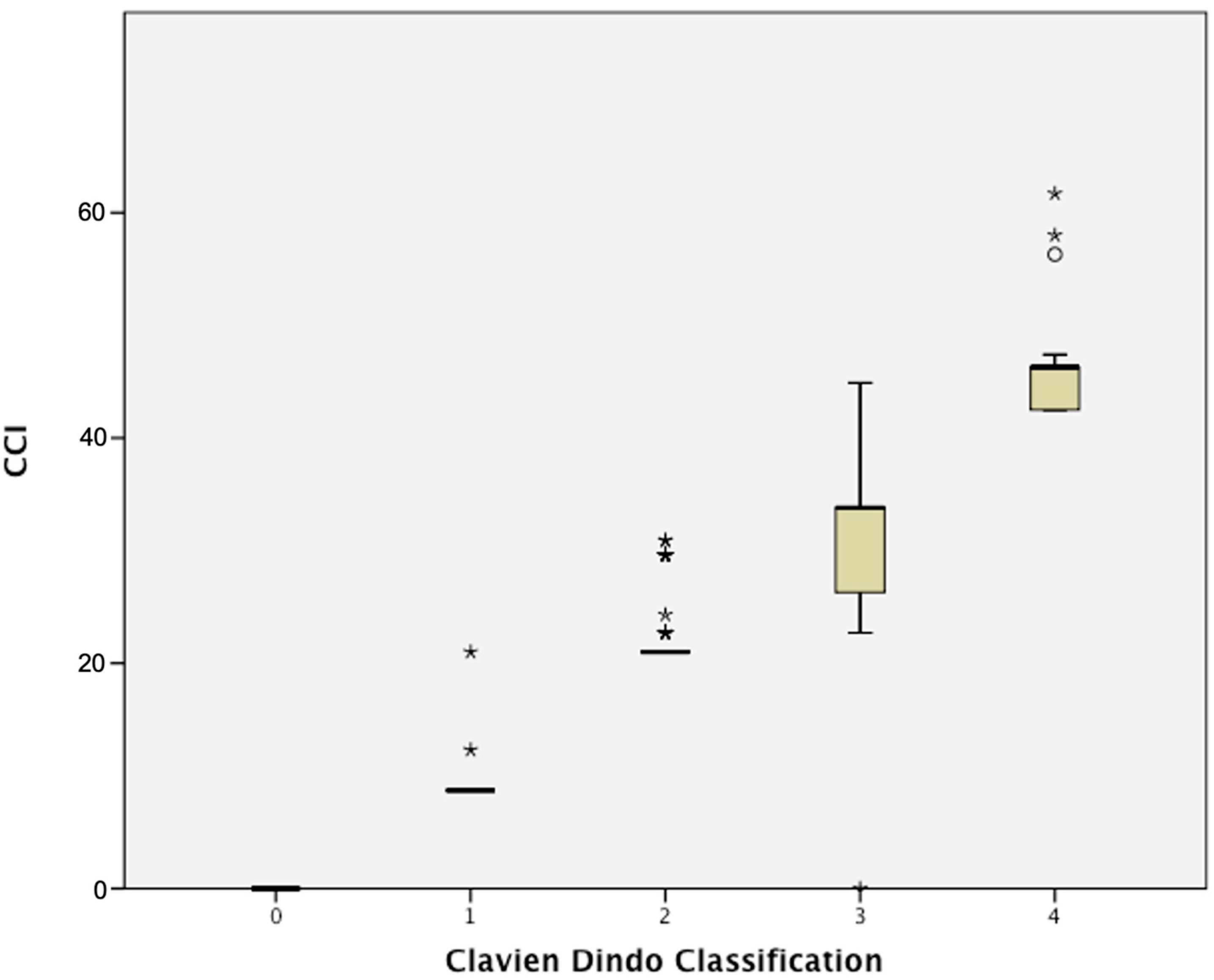
3.3. CCI and Peri-Operative Outcomes
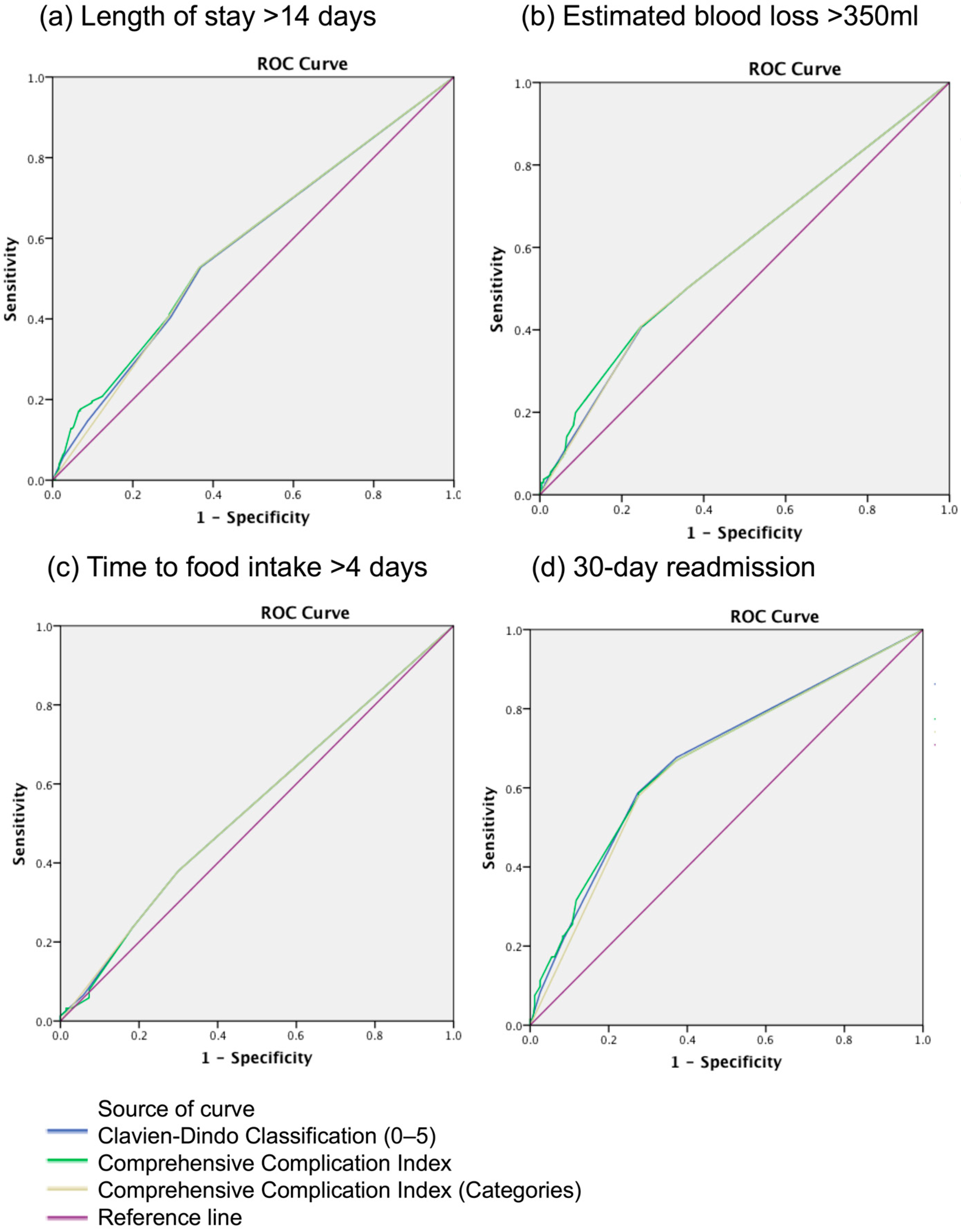
3.4. Comparison of CDC and CCI in Predicting Peri-Operative Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDC | Clavien–Dindo classification |
| CCI | Comprehensive complication index |
| RARC | Robot-assisted radical cystectomy |
| EBL | Estimated blood loss |
| LOS | Length of stay |
| TFI | Time to food intake |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status scores |
| HN | Hydronephrosis |
| AUC | Area undercurve |
| ROC | Receiver operator curves |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| ICUR | Intra-corporeal urinary reconstruction |
| ECUR | Extra-corporeal urinary reconstruction |
| OBS | Orthotopic bladder substitute |
References
- Mitropoulos, D.; Artibani, W.; Biyani, C.S.; Bjerggaard Jensen, J.; Roupret, M.; Truss, M. Validation of the Clavien-Dindo grading system in urology by the European Association of Urology Guidelines Ad Hoc Panel. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2018, 4, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindo, D.; Demartines, N.; Clavien, P.A. Classification of surgical complications: A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann. Surg. 2004, 240, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Golder, H.; Casanova, D.; Papalois, V. Evaluation of the Usefulness of the Clavien-Dindo Classification of Surgical Complications. Cir. Esp. 2023, 11, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slankamenac, K.; Graf, R.; Barkun, J.; Puhan, M.A.; Clavien, P.A. The comprehensive complication index: A novel continuous scale to measure surgical morbidity. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veličković, J.; Feng, C.; Palibrk, I.; Veličković, D.; Jovanović, B.; Bumbaširević, V. The Assessment of Complications After Major Abdominal Surgery: A Comparison of Two Scales. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 247, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Suh, Y.S.; Huh, Y.J.; Son, Y.G.; Park, J.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Kong, S.H.; Ahn, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Slankamenac, K.; et al. The comprehensive complication index (CCI) is a more sensitive complication index than the conventional Clavien-Dindo classification in radical gastric cancer surgery. Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, H.; Cinar, N.B.; Avci, I.E.; Akdas, E.M.; Teke, K.; Dillioglugil, O. Evaluation of comprehensive complication index versus Clavien-Dindo classification in prediction of overall survival after radical cystectomy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2023, 55, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M.; Huber, T.; Pickl, C.; van Rhijn, B.W.; Gužvić, M.; Gierth, M.; Breyer, J.; Burger, M.; Mayr, R. The comprehensive complication index is associated with a significant increase in complication severity between 30 and 90 days after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furrer, M.A.; Huesler, J.; Fellmann, A.; Burkhard, F.C.; Thalmann, G.N.; Wuethrich, P.Y. The Comprehensive Complication Index CCI: A proposed modification to optimize short-term complication reporting after cystectomy and urinary diversion. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, e9–e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Allen, J.C., Jr.; Teoh, J.Y.; Kang, S.H.; Patel, M.I.; Muto, S.; Yang, C.K.; Hatakeyama, S.; Zhang, R.; Kijvikai, K.; et al. Predicting perioperative outcomes of robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Data from the Asian Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Consortium. Int. J. Urol. 2022, 29, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teoh, J.Y.; Chan, E.O.; Kang, S.H.; Patel, M.I.; Muto, S.; Yang, C.K.; Hatakeyama, S.; Chow, T.S.; Mok, A.; Zhang, R.; et al. Perioperative Outcomes of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy with Intracorporeal Versus Extracorporeal Urinary Diversion. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 9209–9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklad, M. Grading of patients for surgical procedures. Anesthesiology 1941, 2, 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.S.; Gibson, S.; Jing, Z.; Wijburg, C.; Wagner, A.A.; Mottrie, A.; Dasgupta, P.; Peabody, J.; Hussein, A.A.; Guru, K.A. Rates and Patterns of Recurrences and Survival Outcomes after Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy: Results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. J. Urol. 2021, 205, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, A.S.; Iqbal, U.; Jing, Z.; Houenstein, H.A.; Wijburg, C.; Wiklund, P.; Kim, E.; Stöckle, M.; Kelly, J.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Relapses Rates and Patterns for Pathological T0 After Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy: Results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. Urology 2022, 166, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalimov, Z.; Iqbal, U.; Jing, Z.; Wiklund, P.; Kaouk, J.; Kim, E.; Wijburg, C.; Wagner, A.A.; Roupret, M.; Dasgupta, P.; et al. Intracorporeal Versus Extracorporeal Neobladder After Robot-assisted Radical Cystectomy: Results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. Urology 2022, 159, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoogstraten, L.M.; Man, C.C.; Witjes, J.A.; Meijer, R.P.; Mulder, S.F.; Smilde, T.J.; Ripping, T.M.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Aben, K.K. Low adherence to recommended use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, K.; Małkiewicz, B.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Lemiński, A. Influence of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Survival Outcomes of Radical Cystectomy in Pathologically Proven Positive and Negative Lymph Nodes. Cancers 2023, 15, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albisinni, S.; Diamand, R.; Mjaess, G.; Aoun, F.; Assenmacher, G.; Assenmacher, C.; Verhoest, G.; Holz, S.; Naudin, M.; Ploussard, G.; et al. Defining the Morbidity of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy with Intracorporeal Urinary Diversion: Adoption of the Comprehensive Complication Index. J. Endourol. 2022, 36, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendrek, M.; Witt, J.H.; Sarychev, S.; Liakos, N.; Addali, M.; Wagner, C.; Karagiotis, T.; Schuette, A.; Soave, A.; Fisch, M.; et al. Reporting and grading of complications for intracorporeal robot-assisted radical cystectomy: An in-depth short-term morbidity assessment using the novel Comprehensive Complication Index®. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, H.; Wang, H.; Shang, M.; Xi, Z. The comprehensive complication index is more sensitive than the Clavien-Dindo classification for grading complications in elderly patients after radical cystectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection: Implementing the European Association of Urology guideline. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1002110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vetterlein, M.W.; Klemm, J.; Gild, P.; Bradtke, M.; Soave, A.; Dahlem, R.; Fisch, M.; Rink, M. Improving Estimates of Perioperative Morbidity After Radical Cystectomy Using the European Association of Urology Quality Criteria for Standardized Reporting and Introducing the Comprehensive Complication Index. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.G.; Allen, J.C.; Tay, K.J.; Huang, H.H.; Lee, L.S. Benefits of robotic cystectomy compared with open cystectomy in an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery program: A propensity-matched analysis. Int. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knorr, J.M.; Ericson, K.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Murthy, P.; Nowacki, A.S.; Munoz-Lopez, C.; Thomas, L.J.; Haber, G.P.; Lee, B. Comparison of Major Complications at 30 and 90 Days Following Radical Cystectomy. Urology 2021, 148, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeh, B.; Flammia, R.S.; Hohenhorst, L.; Sorce, G.; Chierigo, F.; Panunzio, A.; Tian, Z.; Saad, F.; Gallucci, M.; Briganti, A.; et al. Outcomes of robotic-assisted versus open radical cystectomy in a large-scale, contemporary cohort of bladder cancer patients. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 126, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalewski, K.F.; Müller, D.; Mühlbauer, J.; Hendrie, J.D.; Worst, T.S.; Wessels, F.; Walach, M.T.; von Hardenberg, J.; Nuhn, P.; Honeck, P.; et al. The comprehensive complication index (CCI): Proposal of a new reporting standard for complications in major urological surgery. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Waingankar, N.; Mallin, K.; Smaldone, M.; Egleston, B.L.; Higgins, A.; Winchester, D.P.; Uzzo, R.G.; Kutikov, A. Assessing the relative influence of hospital and surgeon volume on short-term mortality after radical cystectomy. BJU Int. 2017, 120, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Keeley, J.; Patel, A.; Eleswarapu, S.V.; Bronkema, C.; Alanee, S.; Menon, M. Defining a “High. Volume” Radical Cystectomy Hospital: Where Do We Draw. the Line? Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, H.M.; Veskimäe, E.; Hernandez, V.; Neuzillet, Y.; Cathomas, R.; Comperat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; Gakis, G.; Espinós, E.L.; Lorch, A.; et al. The Importance of Hospital and Surgeon Volume as Major Determinants of Morbidity and Mortality After Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Recommendations by the European Association of Urology Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer Guideline Panel. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, G.S.; Urbach, D.R.; Austin, P.C.; Fleshner, N.E.; Laupacis, A. Higher surgeon and hospital volume improves long-term survival after radical cystectomy. Cancer 2013, 119, 3546–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pre-Operative Variables | |
|---|---|
| Median age at surgery, years (IQR) | 67.2 (60.5–73.6) |
| Median BMI, kg/m2 (IQR) | 24.1 (22.2–26.5) |
| Male gender, n (%) | 484 (85.2) |
| Previous tobacco smoking exposure, n (%) | 282 (50.5) |
| Comorbidities, n (%) | |
| Hypertension | 243 (42.8) |
| Previous abdominal surgery | 81 (14.3) |
| Ischemic heart disease | 37 (6.5) |
| Hyperlipidaemia | 78 (13.7) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 129 (22.7) |
| Pre-operative hydronephrosis, n (%) | 115 (20.3) |
| Unilateral | 84 (14.8) |
| Bilateral | 31 (5.5) |
| ASA score, n (%) | |
| 1 | 102 (18.7) |
| 2 | 365 (66.8) |
| 3 | 79 (14.5) |
| Pre-operative clinical T stage, n (%) | |
| Tis | 21 (3.7) |
| Ta | 25 (4.5) |
| T1 | 160 (28.5) |
| T2 | 244 (43.5) |
| T3 | 85 (15.2) |
| T4 | 26 (4.6) |
| Pre-operative clinical node positive, n (%) | 47 (8.3) |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, n (%) | 173 (30.5) |
| Intra-operative variables | |
| Type of urinary reconstruction | |
| Intra-corporeal | 261 (46.0) |
| Extra-corporeal | 307 (54.0) |
| Urinary reconstruction | |
| Ileal conduit | 307 (54.0) |
| Orthotopic bladder substitute | 221 (38.9) |
| Ureterocutaneostomy | 33 (5.8) |
| None * | 7 (1.2) |
| Median estimated blood loss, mL (IQR) | 350 (200–600) |
| Median console time, min (IQR) | 345 (266–420) |
| Post-operative variables | |
| Median time to solid food intake, days (IQR) (n = 290) | 4 (3–7) |
| Median length of hospitalisation, days (IQR) | 13 (9–19) |
| 30-day readmission rate, n (%) | 133 (23.4) |
| 30-day mortality, n (%) | 0 |
| 90-day mortality, n (%) | 0 |
| Positive surgical margin rate, n (%) | 30 (5.3) |
| Pathological T stage, n (%) | |
| T0 | 28 (5.0) |
| Tis | 50 (9.0) |
| Ta | 78 (14.0) |
| T1 | 93 (16.7) |
| T2 | 113 (20.3) |
| T3 | 147 (26.4) |
| T4 | 47 (8.5) |
| Pathological N stage, n (%) | |
| N0 | 446 (92.7) |
| N1 | 20 (4.2) |
| N2 | 8 (1.7) |
| N3 | 7 (1.5) |
| Median lymph node yield, n (IQR) | 19 (12–28) |
| Histology, n (%) | |
| Urothelial carcinoma | 531 (93.5) |
| Non-urothelial carcinoma | 37 (6.5) |
| Complications, n (%) | 252 (44.4) |
| None | 316 (55.6) |
| Minor (Clavien–Dindo < 3) | 186 (32. 8) |
| Major (Clavien–Dindo ≥ 3) | 66 (11.6) |
| Median CCI, n (IQR) | 0 (0–21) |
| Mean CCI, n (±SD) | 10.2 (±13.5) |
| Complication | Highest Grade of Complication (Patient Level), n (%) | Number of Complications Occurred, n |
|---|---|---|
| Clavien–Dindo 1 | 55 (9.7) | 77 |
| Clavien–Dindo 2 | 131 (23.1) | 165 |
| Clavien–Dindo 3a | 20 (3.5) | 21 |
| Clavien–Dindo 3b | 24 (4.2) | 24 |
| Clavien–Dindo 4a | 14 (2.5) | 14 |
| Clavien–Dindo 4b | 8 (1.4) | 8 |
| Clavien–Dindo 5 | 0 (0) | 0 |
| Total | 568 (44.4) | 309 |
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Length of stay >14 days | ||
| Male gender | 1.04 (0.59–1.86) | 0.883 |
| Prior tobacco smoking exposure | 0.74 (0.50–1.11) | 0.144 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.56 (1.00–2.42) | 0.049 |
| Clinical stage T2–T4 | 0.75 (0.51–1.12) | 0.158 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 2.44 (1.60–3.74) | <0.001 |
| Intracorporeal urinary reconstruction | 0.52 (0.35–0.76) | 0.001 |
| Orthotopic bladder substitute | 2.79 (1.87–4.15) | <0.001 |
| CCI | ||
| 0 | Reference | |
| CCI < 75th percentile | 1.92 (1.00–3.68) | 0.05 |
| CCI ≥ 75th percentile | 2.21 (1.47–3.31) | <0.001 |
| Time to solid food intake >4 days | ||
| Male gender | 1.31 (0.57–3.00) | 0.837 |
| Prior tobacco smoking exposure | 4.37 (2.39–7.98) | <0.01 |
| Previous abdominal surgery | 0.49 (0.18–1.34) | 0.165 |
| Clinical node positive | 2.48 (0.71–8.75) | 0.157 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 1.77 (0.99–3.18) | 0.055 |
| CCI | ||
| 0 | Reference | Reference |
| CCI < 75th percentile | 1.09 (0.47–2.58) | 0.837 |
| CCI ≥ 75th percentile | 1.36 (0.68–2.73) | 0.383 |
| Thirty-day readmission | ||
| Previous abdominal surgery | 1.79 (0.99–3.20) | 0.051 |
| Pre-operative HN | ||
| None | Reference | Reference |
| Unilateral | 2.20 (1.23–3.94) | 0.008 |
| Bilateral | 4.04 (1.73–9.46) | 0.001 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 0.28 (0.15–0.50) | <0.001 |
| Orthotopic bladder substitute | 1.78 (1.13–2.80) | 0.013 |
| CCI | ||
| 0 | Reference | Reference |
| CCI < 75th percentile | 2.67 (1.22–5.85) | 0.014 |
| CCI ≥ 75th percentile | 3.92 (2.45–6.29) | <0.001 |
| Estimated blood loss > 350 mL | ||
| CCI | ||
| 0 | Reference | Reference |
| CCI < 75th percentile | 1.05 (0.58–1.90) | 0.880 |
| CCI ≥ 75th percentile | 2.12 (1.43–3.15) | <0.001 |
| Area-under-Curve of ROC Curves | LOS > 14 Days | EBL > 350 mL | Time to Food Intake > 4 Days | 30-Day Readmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDC | 0.581 | 0.583 | 0.540 | 0.674 |
| CCI-categorical | 0.579 | 0.582 | 0.541 | 0.664 |
| CCI-continuous | 0.588 | 0.588 | 0.539 | 0.675 |
| p-value (CDC vs. CCI categorical) * | 0.951 | 0.986 | 0.990 | 0.750 |
| p-value (CDC vs. CCI continuous) * | 0.826 | 0.876 | 0.980 | 0.993 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuanming, A.L.; Na, F.T.B.; Tiwari, R.; Chan, T.K.N.; Teoh, J.Y.-C.; Kang, S.-H.; Patel, M.I.; Muto, S.; Yang, C.-K.; Hatakeyama, S.; et al. Estimating the Morbidity of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Using the Comprehensive Complication Index: Data from the Asian Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Consortium. Cancers 2025, 17, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071157
Yuanming AL, Na FTB, Tiwari R, Chan TKN, Teoh JY-C, Kang S-H, Patel MI, Muto S, Yang C-K, Hatakeyama S, et al. Estimating the Morbidity of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Using the Comprehensive Complication Index: Data from the Asian Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Consortium. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071157
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuanming, Alvin Lee, Fiona Tan Bei Na, Raj Tiwari, Thomas Kong Ngai Chan, Jeremy Yuen-Chun Teoh, Seok-Ho Kang, Manish I. Patel, Satoru Muto, Cheng-Kuang Yang, Shingo Hatakeyama, and et al. 2025. "Estimating the Morbidity of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Using the Comprehensive Complication Index: Data from the Asian Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Consortium" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071157
APA StyleYuanming, A. L., Na, F. T. B., Tiwari, R., Chan, T. K. N., Teoh, J. Y.-C., Kang, S.-H., Patel, M. I., Muto, S., Yang, C.-K., Hatakeyama, S., Kijvikai, K., Chen, H., Ohyama, C., Horie, S., Chan, E. S.-Y., & Lee, L.-S. (2025). Estimating the Morbidity of Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Using the Comprehensive Complication Index: Data from the Asian Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy Consortium. Cancers, 17(7), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071157








