Body Mass Index and Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Insights from a Large Series
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Anthropometric Data
2.3. Calcitonin (Ct) Assay
2.4. Histology
2.5. RET Somatic Mutation
2.6. Imaging Evaluation
2.7. Response to Treatment Definition
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Features
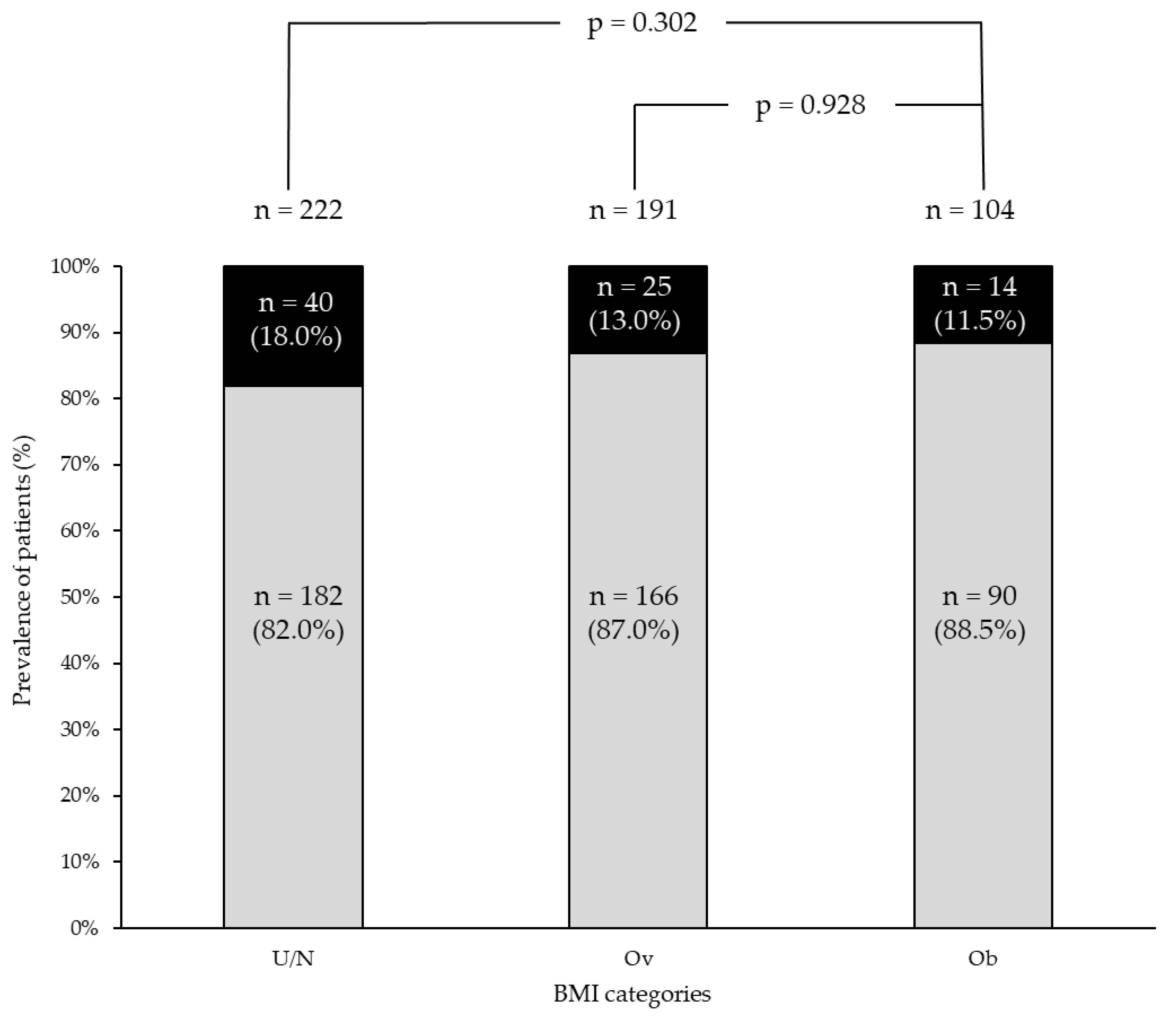
3.2. Epidemiological, Biochemical, and Pathological Data Across BMI Categories
3.3. Genetic Data Across BMI Categories
3.4. Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| ATC | Anaplastic thyroid cancer |
| BiR | Biochemical incomplete response |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| Ct | Calcitonin |
| DTC | Differentiated thyroid cancer |
| ER | Excellent response |
| FTC | Follicular thyroid cancer |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| mETE | Minimal extrathyroidal extension |
| MTC | Medullary thyroid cancer |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| Ob | Obesity group |
| Ov | Overweight group |
| PDTC | Poorly differentiated thyroid cancer |
| PTC | Papillary thyroid cancer |
| RET gene | Rearranged during transfection gene |
| SiR | Structural incomplete response |
| U/N | Under/normal weight group |
References
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. Body Fatness and Cancer—Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harborg, S.; A Kjærgaard, K.; Thomsen, R.W.; Borgquist, S.; Cronin-Fenton, D.; Hjorth, C.F. New Horizons: Epidemiology of Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, and Cancer Prognosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 109, 924–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Cortellini, A.; Indini, A.; Tomasello, G.; Ghidini, M.; Nigro, O.; Salati, M.; Dottorini, L.; Iaculli, A.; Varricchio, A.; et al. Association of Obesity with Survival Outcomes in Patients with Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e213520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seib, C.D.; Sosa, J.A. Evolving Understanding of the Epidemiology of Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 48, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, C.M.; McCullough, M.L.; Franceschi, S.; Rinaldi, S.; Wolk, A.; Neta, G.; Adami, H.O.; Anderson, K.; Andreotti, G.; Freeman, L.E.B.; et al. Anthropometric Factors and Thyroid Cancer Risk by Histological Subtype: Pooled Analysis of 22 Prospective Studies. Thyroid 2016, 26, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeland, A.; Tretli, S.; Akslen, L.A.; Bjørge, T. Body size and thyroid cancer in two million Norwegian men and women. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Port, M.; Landi, S.; Gemignani, F.; Cipollini, M.; Elisei, R.; Goudeva, L.; Müller, J.A.; Nerlich, K.; Pellegrini, G.; et al. Obesity and the Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Pooled Analysis of Three Case–Control Studies. Thyroid 2014, 24, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, Y.; Hou, X.; Peng, Z.; Yang, W.; Guan, L.; Hu, L.; Zhi, J.; Gao, M.; et al. Correlation between obesity and clinicopathological characteristics in patients with papillary thyroid cancer: A study of 1579 cases: A retrospective study. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, A.; Endo, B.; Nishimoto, S.; Ituarte, P.H.G.; Yeh, M.W. Risk of Advanced Papillary Thyroid Cancer in Obese Patients. Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grani, G.; Lamartina, L.; Montesano, T.; Ronga, G.; Maggisano, V.; Falcone, R.; Ramundo, V.; Giacomelli, L.; Durante, C.; Russo, D.; et al. Lack of association between obesity and aggressiveness of differentiated thyroid cancer. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 42, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, J.E.; Hua, K.; Nagy, R.; Kloos, R.T.; Jarjoura, D.; Ringel, M.D. The Relationship between Body Mass Index and Thyroid Cancer Pathology Features and Outcomes: A Clinicopathological Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trésallet, C.; Seman, M.; Tissier, F.; Buffet, C.; Lupinacci, R.M.; Vuarnesson, H.; Leenhardt, L.; Menegaux, F. The incidence of papillary thyroid carcinoma and outcomes in operative patients according to their body mass indices. Surgery 2014, 156, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gąsior-Perczak, D.; Pałyga, I.; Szymonek, M.; Kowalik, A.; Walczyk, A.; Kopczyński, J.; Lizis-Kolus, K.; Trybek, T.; Mikina, E.; Szyska-Skrobot, D.; et al. The impact of BMI on clinical progress, response to treatment, and disease course in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, M.; Choi, Y.M.; Jang, E.K.; Jeon, M.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Shong, Y.K.; Song, D.E.; Baek, J.H.; Hong, S.J.; et al. Lack of Associations between Body Mass Index and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 30, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, A.; Ceccarini, G.; Beghini, M.; Ferrari, F.; Gambale, C.; D’aqui, M.; Piaggi, P.; Torregrossa, L.; Molinaro, E.; Basolo, F.; et al. Potential Impact of BMI on the Aggressiveness of Presentation and Clinical Outcome of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 105, e1124–e1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, B.; Zheng, C. Clinical Characteristics, Surgical Management, and Prognostic Factors of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Retrospective, Single-Center Study. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 21, 15330338221078435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisei, R.; Alevizaki, M.; Conte-Devolx, B.; Frank-Raue, K.; Leite, V.; Williams, G. 2012 European Thyroid Association Guidelines for Genetic Testing and Its Clinical Consequences in Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Eur. Thyroid J. 2012, 1, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, R.; Romei, C.; Ramone, T.; Prete, A.; Tacito, A.; Cappagli, V.; Bottici, V.; Viola, D.; Torregrossa, L.; Ugolini, C.; et al. Genetic Landscape of Somatic Mutations in a Large Cohort of Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinomas Studied by Next-Generation Targeted Sequencing. iScience 2019, 20, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, A.; Gambale, C.; Torregrossa, L.; Ciampi, R.; Romei, C.; Ramone, T.; Agate, L.; Bottici, V.; Cappagli, V.; Molinaro, E.; et al. Clinical Evolution of Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma with Biochemical Incomplete Response After Initial Treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e613–e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapporto Osservasalute. 2022. Available online: https://osservatoriosullasalute.it/osservasalute/rapporto-osservasalute-2022 (accessed on 23 December 2024).
- Dhurandhar, N.V. What is obesity? Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 1081–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islami, F.; Sauer, A.G.; Gapstur, S.M.; Jemal, A. Proportion of Cancer Cases Attributable to Excess Body Weight by US State, 2011–2015. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keum, N.; Greenwood, D.C.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, R.; Aune, D.; Ju, W.; Hu, F.B.; Giovannucci, E.L. Adult Weight Gain and Adiposity-Related Cancers: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, Obesity, and Mortality from Cancer in a Prospectively Studied Cohort of U.S. Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakimi, A.A.; Furberg, H.; Zabor, E.C.; Jacobsen, A.; Schultz, N.; Ciriello, G.; Mikklineni, N.; Fiegoli, B.; Kim, P.H.; Voss, M.H.; et al. An Epidemiologic and Genomic Investigation Into the Obesity Paradox in Renal Cell Carcinoma. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.M.; Lee, H.; Eom, K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S. Bioinformatic analysis of the obesity paradox and possible associated factors in colorectal cancer using TCGA cohorts. J. Cancer 2023, 14, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, G.; Xia, H.; Xia, J. Body mass index-associated molecular characteristics involved in tumor immune and metabolic pathways. Cancer Metab. 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-L.; Geukens, T.; Maetens, M.; Aparicio, S.; Bassez, A.; Borg, A.; Brock, J.; Broeks, A.; Caldas, C.; Cardoso, F.; et al. Obesity-associated changes in molecular biology of primary breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Castillon, V.J.; Waters, M.; Fong, C.; Park, T.; Boscenco, S.; Kim, S.; Pekala, K.; Carrot-Zhang, J.; Hakimi, A.A.; et al. Obesity-dependent selection of driver mutations in cancer. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 2318–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.R.; Ku, C.R.; Kang, S.-W.; Jeong, J.J.; Shin, D.Y.; Nam, K.-H.; Jung, S.G.; Lee, E.J.; Chung, W.Y.; et al. Association Between Obesity and BRAFV600E Mutation Status in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M. RET receptor signaling: Function in development, metabolic disease, and cancer. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2022, 98, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernichow, S.; Kengne, A.; Stamatakis, E.; Hamer, M.; Batty, G.D. Body mass index, waist circumference and waist–hip ratio: Which is the better discriminator of cardiovascular disease mortality risk? Evidence from an individual-participant meta-analysis of 82 864 participants from nine cohort studies. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, A.; Basolo, A.; Santini, F.; Elisei, R. Understanding the effect of obesity on papillary thyroid cancer: Is there a need for tailored diagnostic and therapeutic management? Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 17, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Epidemiologic Features | Total Cohort n = 529 (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | M | 241 (45.6) |
| F | 288 (54.4) | |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | Median, IQR | 55 (45–66) |
| ≤55 years | 266 (50.3) | |
| >55 years | 263 (49.7) | |
| Biochemical features | ||
| Preoperative calcitonin (n = 427) | Median, IQR | 136 (31–730) |
| Histology | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | Median, IQR | 1.3 (0.7–2.4) |
| ≤1 | 208 (39.5) | |
| 1.1–4 | 283 (53.5) | |
| >4 | 38 (7.2) | |
| T stage according to AJCC 8th edition | T1a | 212 (40.1) |
| T1b | 148 (28.4) | |
| T2 | 104 (19.7) | |
| T3 | 38 (7.2) | |
| T4 | 24 (4.5) | |
| Tx | 1 (0.2) | |
| Tumor Multifocality | Yes | 76 (14.4) |
| No | 453 (85.6) | |
| Tumor mETE | Yes | 89 (16.8) |
| No | 440 (83.2) | |
| Lymph node metastasis | Yes | 216 (40.9) |
| No | 313 (59.1) | |
| Central compartment dissection | Yes | 465 (87.9) |
| No | 64 (12.1) | |
| N stage according to AJCC 8th edition | Nx | 47 (8.9) |
| N0 | 266 (50.2) | |
| N1a | 95 (18.0) | |
| N1b | 121 (22.9) | |
| M stage according to AJCC 8th edition | Mx/M0 | 493 (93.2) |
| M1 | 36 (6.8) | |
| Staging according to AJCC 8th edition | Stage I | 252 (47.6) |
| Stage II | 57 (10.8) | |
| Stage III | 91 (17.2) | |
| Stage IV | 129 (34.4) | |
| Follow-up data | ||
| Disease status at end of follow-up | ER | 313 (59.1) |
| BiR | 85 (16.1) | |
| SiR | 119 (22.5) | |
| Unknown | 12 (2.3) | |
| Follow-up (time, months) | Median, IQR | 75 (35–130) |
| Further treatments | Yes | 92 (17.5) |
| No | 437 (82.5) | |
| Death for disease | Yes | 39 (7.4) |
| No | 490 (92.6) | |
| Disease survival specific Time (time, months) | Median, IQR | 98 (57–152) |
| U/N Group n = 229 (%) | Ov Group n = 193 (%) | Ob Group n = 107 (%) | p-Value U/N vs. Ov Group | p-Value U/N vs. Ob Group | p-Value Ov vs. Ob Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epidemiologic features | |||||||
| Sex | Male | 89 (38.9) | 107 (55.4) | 45 (42.1) | 0.001 | 0.57 | 0.026 |
| Female | 140 (61.1) | 86 (44.6) | 62 (57.9) | ||||
| Age at diagnosis (years) | Median, IQR | 52 (43–63) | 58 (47–65) | 58 (48–69) | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.320 |
| ≤55 years | 138 (60.3) | 82 (42.5) | 46 (43.0) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.933 | |
| >55 years | 91 (39.7) | 111 (57.5) | 61 (57.0) | ||||
| Biochemical features | |||||||
| Preoperative calcitonin (n = 427) | Median, IQR | 167 (44–822) | 109 (30–766) | 69 (20–493) | 0.09 | 0.005 | 0.17 |
| Histology | |||||||
| Size (cm) | Median, IQR | 1.5 (0.8–2.5) | 1.3 (0.7–2.5) | 1.0 (0.5–2.0) | 0.48 | 0.002 | 0.018 |
| ≤1 | 80 (35.1) | 73 (38.0) | 55 (51.4) | 0.768 | 0.019 | 0.003 | |
| 1.1–4 | 127 (55.7) | 104 (54.2) | 50 (46.7) | ||||
| >4 | 21 (9.2) | 15 (7.8) | 2 (1.9) | ||||
| T stage according to AJCC 8th edition | T1a | 78 (34.1) | 78 (40.4) | 56 (52.3) | 0.19 | 0.002 | 0.128 |
| T1b | 72 (31.4) | 52 (26.9) | 26 (24.3) | ||||
| T2 | 41 (17.9) | 42 (21.7) | 19 (17.8) | ||||
| T3 | 25 (11.0) | 11 (5.7) | 2 (1.8) | ||||
| T4 | 12 (5.2) | 10 (5.2) | 2 (1.8) | ||||
| Tx | 1 (0.4) | 0 | 0 | ||||
| Multifocality | Yes | 33 (14.4) | 25 (13.0) | 18 (16.8) | 0.665 | 0.566 | 0.360 |
| No | 196 (85.6) | 168 (87.0) | 89 (83.2) | ||||
| mETE | Yes | 42 (18.3) | 35 (18.1) | 12 (11.2) | 0.956 | 0.098 | 0.114 |
| No | 187 (81.7) | 158 (81.9) | 95 (88.8) | ||||
| Lymph node metastasis | Yes | 101 (44.1) | 81 (41.9) | 34 (31.8) | 0.659 | 0.032 | 0.082 |
| No | 128 (55.9) | 112 (58.1) | 73 (68.2) | ||||
| Central compartment dissection | Yes | 206 (90.0) | 170 (88.1) | 89 (83.2) | 0.538 | 0.077 | 0.236 |
| No | 23 (10.0) | 23 (11.9) | 18 (16.8) | ||||
| N stage according to AJCC 8th edition | Nx | 17 (7.4) | 13 (6.7) | 17 (15.9) | 0.641 | 0.028 | 0.013 |
| N0 | 111 (48.5) | 99 (51.4) | 56 (52.3) | ||||
| N1a | 46 (20.1) | 30 (15.5) | 19 (17.8) | ||||
| N1b | 55 (24.0) | 51 (26.4) | 15 (14.0) | ||||
| M stage according to AJCC 8th edition | Mx/M0 | 213 (93.0) | 180 (93.3) | 100 (93.5) | 0.919 | 0.935 | 0.859 |
| M1 | 16 (7.0) | 13 (6.7) | 7 (6.5) | ||||
| Staging according to AJCC 8th edition | Stage I | 102 (44.4) | 89 (46.2) | 61 (57.1) | 0.776 | 0.177 | 0.166 |
| Stage II | 26 (11.4) | 22 (11.4) | 9 (8.4) | ||||
| Stage III | 43 (18.8) | 29 (15.0) | 18 (16.8) | ||||
| Stage IV | 58 (25.4) | 53 (27.4) | 19 (17.7) |
| U/N Group n = 229 (%) | Ov Group n = 193 (%) | Ob Group n = 107 (%) | p-Value U/N vs. Ov Group | p-Value U/N vs. Ob Group | p-Value Ov vs. Ob Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Further therapies | |||||||
| Cervical surgical therapies | Yes | 10 (4.5) | 21 (11.0) | 4 (3.8) | 0.015 | 1.000 | 0.047 |
| No | 212 (95.5) | 170 (89.0) | 100 (96.2) | ||||
| Local therapies against distant metastases | Yes | 15 (6.8) | 19 (9.9) | 7 (6.7) | 0.283 | 1.000 | 0.398 |
| No | 207 (93.2) | 172 (90.1) | 97 (93.3) | ||||
| Systemic therapies | Yes | 29 (13.1) | 18 (9.4) | 8 (7.7) | 0.246 | 0.191 | 0.673 |
| No | 193 (86.9) | 173 (90.6) | 96 (92.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prete, A.; Gambale, C.; Bottici, V.; Cappagli, V.; Aringhieri, G.; Puccini, M.; Landi, S.; Torregrossa, L.; Santini, F.; Matrone, A.; et al. Body Mass Index and Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Insights from a Large Series. Cancers 2025, 17, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060950
Prete A, Gambale C, Bottici V, Cappagli V, Aringhieri G, Puccini M, Landi S, Torregrossa L, Santini F, Matrone A, et al. Body Mass Index and Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Insights from a Large Series. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060950
Chicago/Turabian StylePrete, Alessandro, Carla Gambale, Valeria Bottici, Virginia Cappagli, Giacomo Aringhieri, Marco Puccini, Stefano Landi, Liborio Torregrossa, Ferruccio Santini, Antonio Matrone, and et al. 2025. "Body Mass Index and Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Insights from a Large Series" Cancers 17, no. 6: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060950
APA StylePrete, A., Gambale, C., Bottici, V., Cappagli, V., Aringhieri, G., Puccini, M., Landi, S., Torregrossa, L., Santini, F., Matrone, A., & Elisei, R. (2025). Body Mass Index and Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Insights from a Large Series. Cancers, 17(6), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060950






