Harnessing Baseline Radiomic Features in Early-Stage NSCLC: What Role in Clinical Outcome Modeling for SBRT Candidates?
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Clinical Dataset
2.2. Tumor Delineation and RF Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- i.
- OS, defined as the time length from diagnosis to death from any cause or last contact at follow-up;
- ii.
- PFS, defined as the time length from diagnosis to any disease progression or death from any cause or to lost contact at follow-up;
- iii.
- LRPFS, defined as the time length from diagnosis to local disease progression or death.
2.4. Feature Selection and Radiomic Score Calculation
2.5. Comparison of Prognostic Models
3. Results
3.1. Patient- and Tumor Characteristics
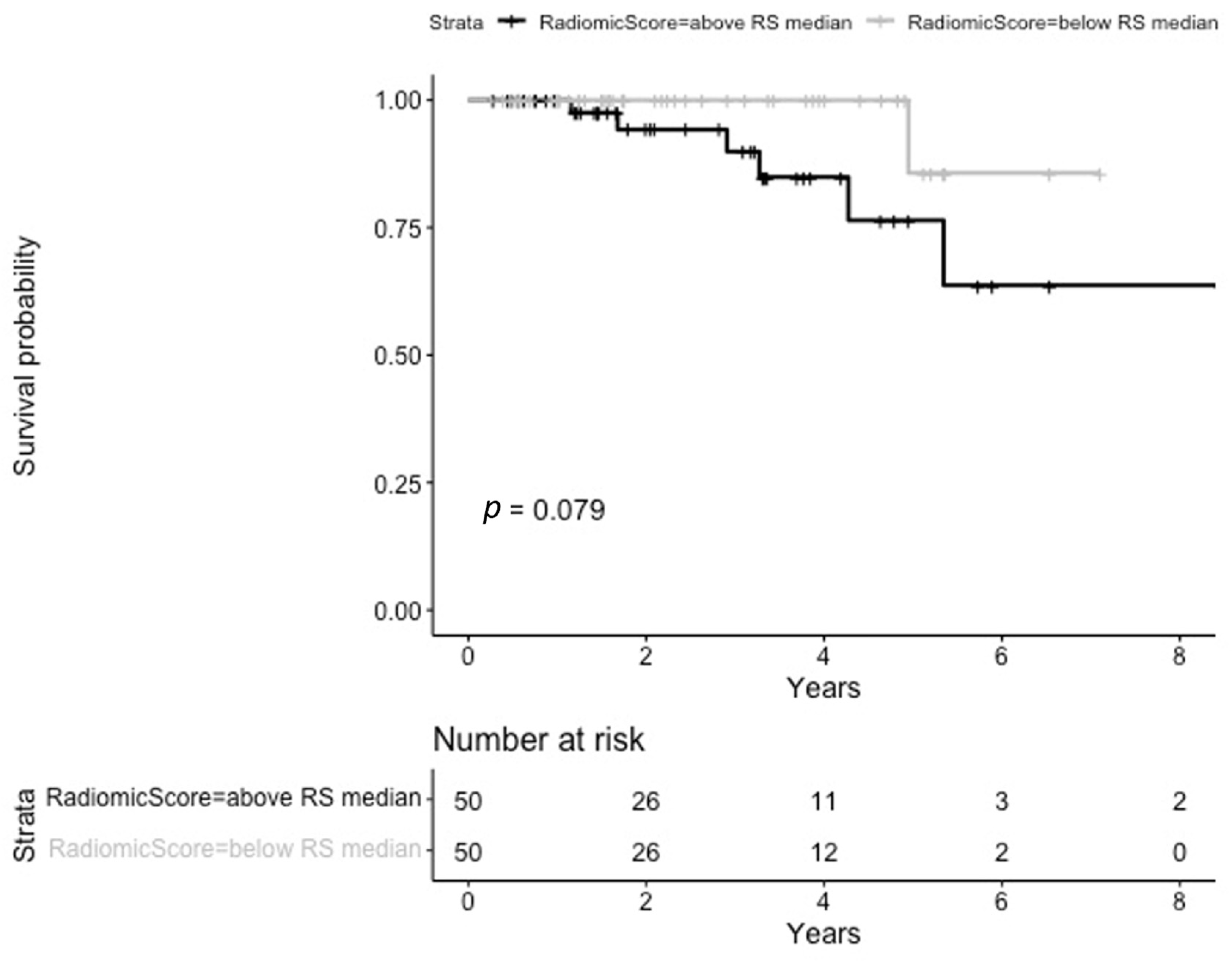
3.2. Overall Survival
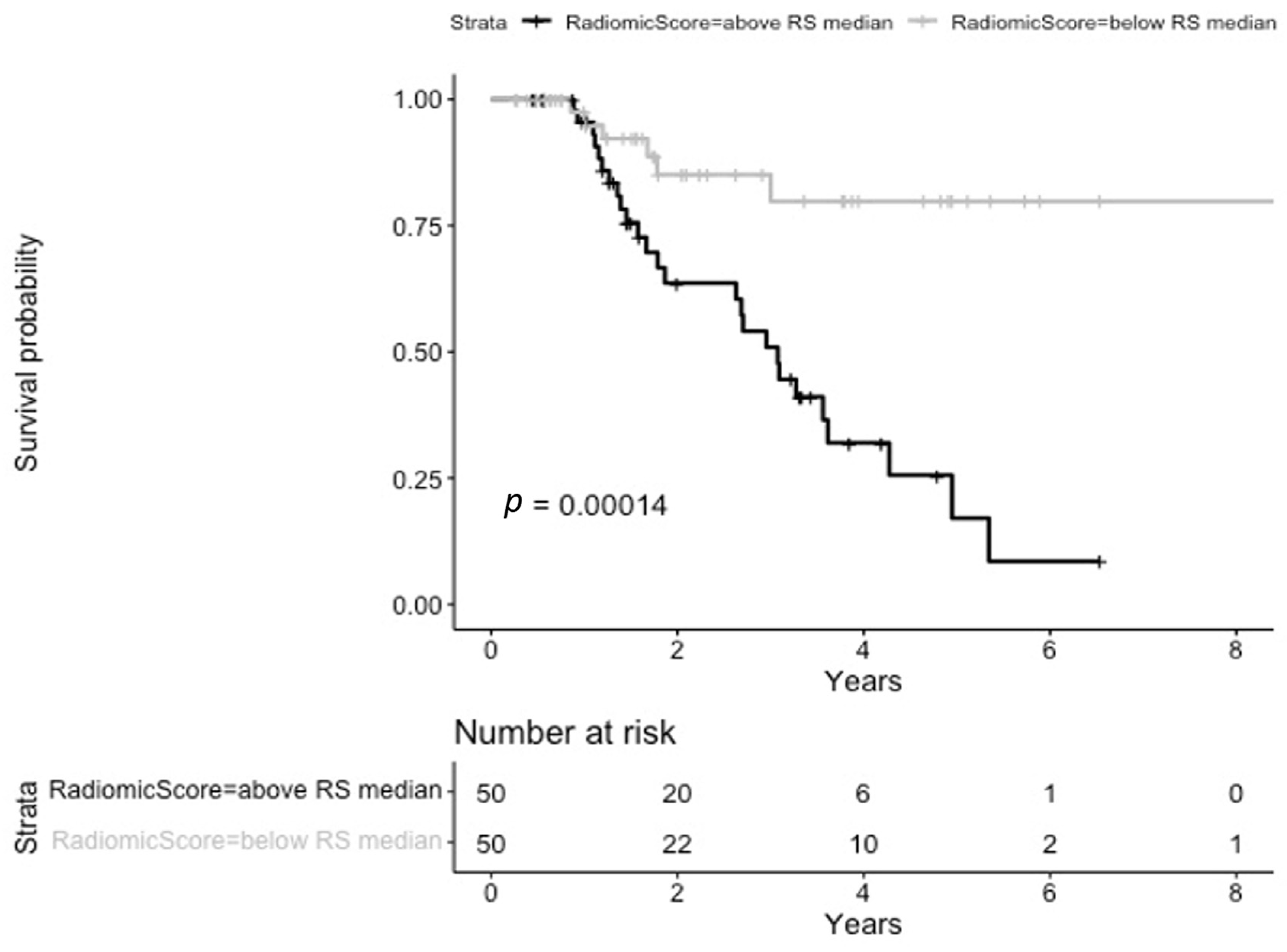
3.3. Progression-Free Survival
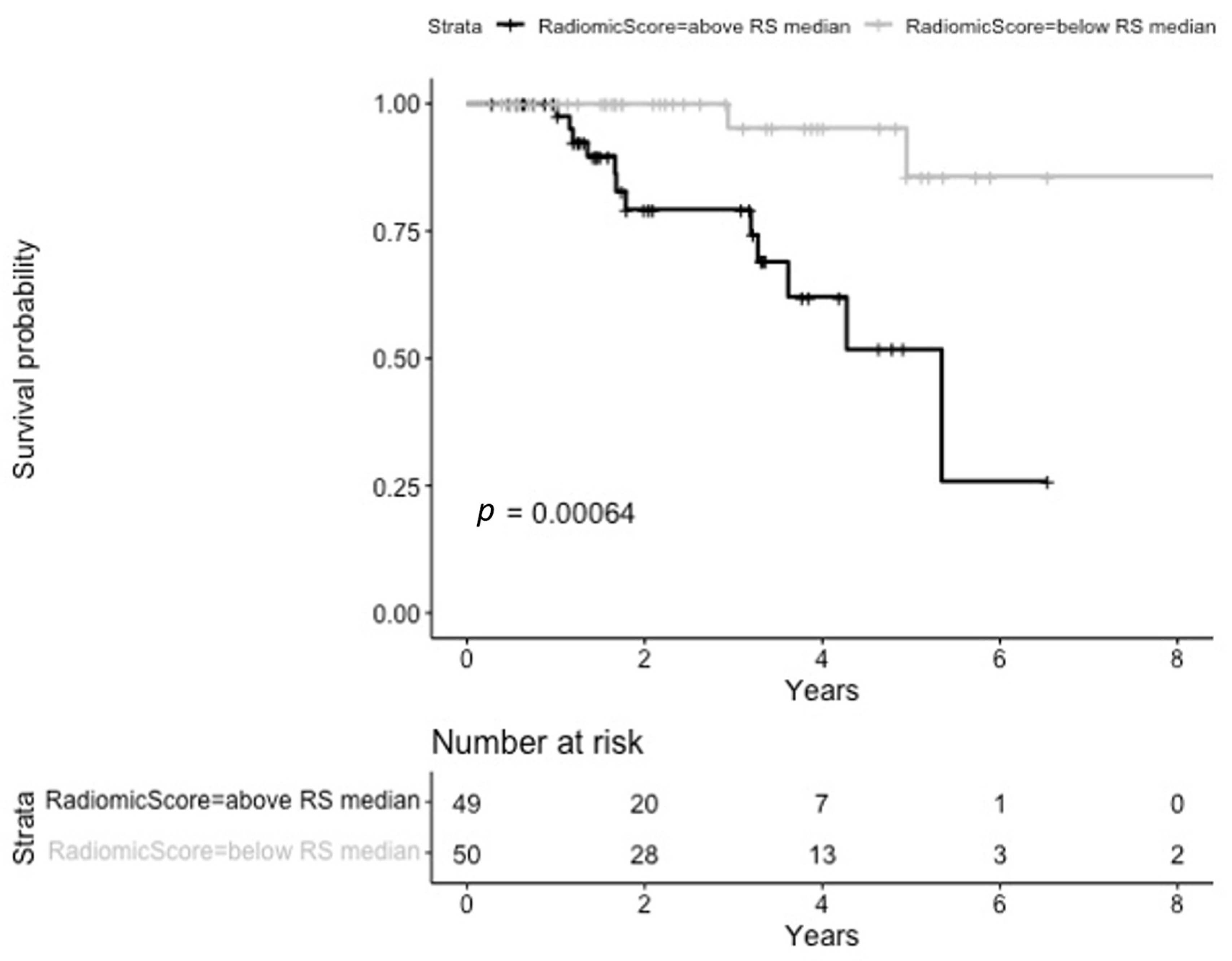
3.4. Loco Regional Progression-Free Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 4DCT | Four-Dimensional Computed Tomography |
| AJCC | American Joint Committee On Cancer |
| BED | Biologically Effective Dose |
| CCI | Charlson Comorbidity Index |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging And Communications In Medicine (DICOM) |
| ES-NSCLC | Early-Stage NSCLC |
| ES | Early Stage |
| FEV | Forced Expiratory Volume |
| GLCM | Grey Leve Co-Occurrence Matrix |
| GLDM | Grey Level Dependence Matrix |
| GLSZM | Grey Level Size Zone Matrix |
| H | High |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| L | Low |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage And Selection Operator |
| LRPFS | Local Progression Free-Survival |
| LRPFS | Loco-Regional Progression-Free Survival |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| OTT | Overall Treatment Time |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| PH | Proportional Hazard |
| RF | Radiomic Features |
| RT | Radiation Therapy |
| SBRT | Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy |
| TNM | Tumor, Node, Metastasis |
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Cancer Statistics for the Year. 2022. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today/en/fact-sheets-cancers (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Ganti, A.K.; Klein, A.B.; Cotarla, I.; Seal, B.; Chou, E. Update of Incidence, Prevalence, Survival, and Initial Treatment in Patients With Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer in the US. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Version 2.2024. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1450 (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Carvalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCague, C.; Ramlee, S.; Reinius, M.; Selby, I.; Hulse, D.; Piyatissa, P.; Bura, V.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Sala, E.; Woitek, R. Introduction to radiomics for a clinical audience. Clin. Radiol. 2023, 78, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, S.; Mastroleo, F.; Krengli, M.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A. Quo vadis Radiomics? Bibliometric analysis of 10-year Radiomics journey. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 6736–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, G.; Korte, J.; Lehrer, E.J.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Lazarakis, S.; Kron, T.; Hardcastle, N.; Siva, S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prognostic value of radiomics based models in non-small cell lung cancer treated with curative radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 155, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, B.M.F.; Lau, K.S.; Lee, V.H.F.; Leung, T.W.; Kong, F.-M.S.; Luk, M.Y.; Yuen, K.K. Computed tomography-based radiomic model predicts radiological response following stereotactic body radiation therapy in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer and pulmonary oligo-metastases. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2021, 39, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kim, J.; Balagurunathan, Y.; Qi, J.; Liu, Y.; Latifi, K.; Moros, E.G.; Schabath, M.B.; Ye, Z.; Gillies, R.J.; et al. CT imaging features associated with recurrence in non-small cell lung cancer patients after stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, E.; Coroller, T.P.; Narayan, V.; Agrawal, V.; Hou, Y.; Romano, J.; Franco, I.; Mak, R.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. CT-based radiomic analysis of stereotactic body radiation therapy patients with lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 120, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkov, P.; Aguilera, T.A.; Golden, D.I.; Shultz, D.B.; Trakul, N.; Maxim, P.G.; Le, Q.-T.; Loo, B.W.; Diehn, M.; Depeursinge, A.; et al. The use of texture-based radiomics CT analysis to predict outcomes in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, R.J.; Sonke, J.-J.; Allgäuer, M.; Andratschke, N.; Appold, S.; Belderbos, J.; Belka, C.; Dieckmann, K.; Eich, H.T.; Flentje, M.; et al. Estimation of the α/β ratio of non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 142, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, B.; Mangona, V.S.; Johnson, M.D.; Ye, H.; Grills, I.S. Changes in Pulmonary Function Following Image-Guided Stereotactic Lung Radiotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-L.; Shen, C.-I.; Chiang, C.-L.; Huang, H.-C.; Chou, K.-T.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-M.; Luo, Y.-H. Reduced FEV1 as Prognostic Factors in Patients With Advanced NSCLC Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 860733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, T.; Li, Y.; Brown, R.; Lanuti, M.; Gainor, J.F.; Christiani, D.C. Spirometry at diagnosis and overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 4796–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, Y.J.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, E.J. Pulmonary function is implicated in the prognosis of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer but not in extended disease small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 4562–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestle, U.; Adebahr, S.; Kaier, K.; Gkika, E.; Schimek-Jasch, T.; Hechtner, M.; Momm, F.; Gaertner, J.; Becker, G.; Grosu, A.-L. Quality of life after pulmonary stereotactic fractionated radiotherapy (SBRT): Results of the phase II STRIPE trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 148, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, D.A.; Bahig, H.; Hope, A.; Harrow, S.; Debenham, B.J.; Louie, A.V.; Vu, T.T.T.; Filion, E.; Bezjak, A.; Campeau, M.-P.; et al. Stereotactic Radiation Therapy in Early Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer and Interstitial Lung Disease: A Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, E.M.; Glatzel, E.; Bohnet, S.; Schild, S.E.; Rades, D. Prognostic Factors of Survival After Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer–The Impact of Smoking Pack Years. In Vivo 2022, 36, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawayanagi, S.; Yamashita, H.; Nozawa, Y.; Takenaka, R.; Miki, Y.; Morishima, K.; Ueno, H.; Ohta, T.; Katano, A. Establishment of a Prediction Model for Overall Survival after Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Primary Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Radiomics Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Leger, S.; Vallières, M.; Löck, S. Image biomarker standardisation initiative. Radiology 2020, 295, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafata, K.J.; Hong, J.C.; Geng, R.; Ackerson, B.G.; Liu, J.-G.; Zhou, Z.; Torok, J.; Kelsey, C.R.; Yin, F.-F. Association of pre-treatment radiomic features with lung cancer recurrence following stereotactic body radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, S.; Gaeta, A.; Colombo, F.; Zaffaroni, M.; Mastroleo, F.; Vincini, M.G.; Pepa, M.; Isaksson, L.J.; Turturici, I.; Marvaso, G.; et al. Blood- and Imaging-Derived Biomarkers for Oncological Outcome Modelling in Oropharyngeal Cancer: Exploring the Low-Hanging Fruit. Cancers 2023, 15, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.; Liu, J.; Masterson, L.; Fenton, T.R. HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer: Epidemiology, molecular biology and clinical management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depeursinge, A.; Andrearczyk, V.; Whybra, P.; van Griethuysen, J.; Müller, H.; Schaer, R.; Vallières, M.; Zwanenburg, A. Standardised convolutional filtering for radiomics. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.05470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, S.; Zaffaroni, M.; Piperno, G.; Vincini, M.G.; Zerella, M.A.; Mastroleo, F.; Cattani, F.; Fodor, C.I.; Bellerba, F.; Bonaldi, T.; et al. Multi-omics integrative modelling for stereotactic body radiotherapy in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical trial protocol of the MONDRIAN study. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | N = 100 |
|---|---|
| Median age at diagnosis, IQR | 76, 70–82 |
| Comorbidities | |
| Yes | 92 |
| No | 8 |
| CCI | |
| CCI Median, IQR | 7 (6, 8) |
| CCI range | 2, 11 |
| Hypertension | |
| Yes | 61 |
| No | 39 |
| Heart disease | |
| Yes | 46 |
| No | 54 |
| Diabetes | |
| Yes | 19 |
| No | 81 |
| COPD | |
| Yes | 48 |
| No | 52 |
| Tobacco smoke | |
| Never smoked | 21 |
| Active smoker | 41 |
| Former smoker | 30 |
| Unknown | 8 |
| Baseline spirometry | |
| Available | 84 |
| Not available | 16 |
| Vital Capacity Median, IQR | 2.74, 2.00–3.28 |
| Unknown | 23 |
| FEV1 Median, IQR | 1.64, 1.21–2.18 |
| Unknown | 21 |
| PEF Median, IQR | 64.00, 46.00–83.00 |
| Unknown | 23 |
| DLCO Median, IQR | 55.00, 40.00–71.00 |
| Unknown | 25 |
| Vital Capacity % Median, IQR | 84.00, 71.00–93.00 |
| Unknown | 24 |
| FEV1% Median, IQR | 79.00, 55.00–92.00 |
| Unknown | 24 |
| Clinical Staging | |
| IA1 | 12 |
| IA2 | 46 |
| IA3 | 16 |
| IB | 21 |
| IIB | 5 |
| Lesion side | |
| Right | 56 |
| Left | 44 |
| Central vs. Peripheral | |
| Central | 27 |
| Peripheral | 73 |
| Shape | |
| Round | 33 |
| Oval | 23 |
| Complex | 44 |
| Margins | |
| Smooth | 24 |
| Lobulated | 17 |
| Spiculate/Irregular | 59 |
| Peripheral GGO | |
| Yes | 42 |
| No | 58 |
| Density | |
| Partially solid | 30 |
| Solid | 70 |
| Internal air bronchogram | |
| Yes | 29 |
| No | 71 |
| Emphysema | |
| Yes | 35 |
| No | 65 |
| Periscissural location | |
| Yes | 23 |
| No | 77 |
| Pleuric contact | |
| Yes | 62 |
| No | 38 |
| OVERALL SURVIVAL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Clinical Model | Radiomic Model | Clinico-Radiomic Model | ||||||
| N | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value |
| BED_value | |||||||||
| <med 124.8 Gy | — | — | — | — | |||||
| >=med 124.8 Gy | 0.08 | 0.01, 0.69 | 0.022 | 0.15 | 0.01, 3.11 | 0.221 | |||
| radiomic_score_os | 1.47 | 1.17, 1.86 | 0.001 | 1.46 | 1.12, 1.90 | 0.006 | |||
| n = 96.0; N events = 6.00; | |||||||||
| PROGRESSION-FREE SURVIVAL | |||||||||
| Characteristic | Clinical Model | Radiomic Model | Clinico-Radiomic Model | ||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| FEV1% | 0.98 | 0.97, 1.00 | 0.020 | 0.99 | 0.98, 1.00 | 0.181 | |||
| Shape | |||||||||
| Round | — | — | — | — | |||||
| Complex | 0.30 | 0.13, 0.71 | 0.006 | 0.40 | 0.17, 0.96 | 0.039 | |||
| Oval | 0.21 | 0.06, 0.75 | 0.016 | 0.27 | 0.07, 0.97 | 0.046 | |||
| radiomic_score*10 | 1.45 | 1.25, 1.68 | <0.001 | 1.35 | 1.13, 1.61 | <0.001 | |||
| n = 76.0; N events = 26.0; | |||||||||
| LOCAL PROGRESSION-FREE SURVIVAL | |||||||||
| Characteristic | Clinical Model | Radiomic Model | Clinico-Radiomic Model | ||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| FEV1% | 0.97 | 0.95, 1.00 | 0.019 | 0.98 | 0.95, 1.00 | 0.096 | |||
| radiomic_score_local | 7.15 | 3.07, 16.7 | <0.001 | 6.31 | 2.32, 17.1 | <0.001 | |||
| n = 76.0; N events = 12.0; | |||||||||
| OVERALL SURVIVAL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Model | Radiomic Model | Clinico-Radiomic Model | |||
| Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test |
| 0.88 (0.85–0.91) | 0.87 (0.86–0.88) | 0.91 (0.90–0.92) | 0.95 (0.93–0.97) | 0.97 (0.95–0.98) | 0.92 (0.91–0.93) |
| PROGRESSION-FREE SURVIVAL | |||||
| Clinical Model | Radiomic Model | Clinico-Radiomic Model | |||
| Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test |
| 0.70 (0.69–0.71) | 0.68 (0.66–0.71) | 0.68 (0.66–0.70) | 0.67 (0.66–0.68) | 0.76 (0.75–0.79) | 0.73 (0.70–0.76) |
| LOCAL PROGRESSION-FREE SURVIVAL | |||||
| Clinical Model | Radiomic Model | Clinico-Radiomic Model | |||
| Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test |
| 0.79 (0.74–0.84) | 0.71 (0.70–0.73) | 0.78 (0.75–0.80) | 0.77 (0.76–0.78) | 0.86 (0.85–0.87) | 0.84 (0.80–0.87) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volpe, S.; Vincini, M.G.; Zaffaroni, M.; Gaeta, A.; Raimondi, S.; Piperno, G.; Franzetti, J.; Colombo, F.; Camarda, A.M.; Mastroleo, F.; et al. Harnessing Baseline Radiomic Features in Early-Stage NSCLC: What Role in Clinical Outcome Modeling for SBRT Candidates? Cancers 2025, 17, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050908
Volpe S, Vincini MG, Zaffaroni M, Gaeta A, Raimondi S, Piperno G, Franzetti J, Colombo F, Camarda AM, Mastroleo F, et al. Harnessing Baseline Radiomic Features in Early-Stage NSCLC: What Role in Clinical Outcome Modeling for SBRT Candidates? Cancers. 2025; 17(5):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050908
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolpe, Stefania, Maria Giulia Vincini, Mattia Zaffaroni, Aurora Gaeta, Sara Raimondi, Gaia Piperno, Jessica Franzetti, Francesca Colombo, Anna Maria Camarda, Federico Mastroleo, and et al. 2025. "Harnessing Baseline Radiomic Features in Early-Stage NSCLC: What Role in Clinical Outcome Modeling for SBRT Candidates?" Cancers 17, no. 5: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050908
APA StyleVolpe, S., Vincini, M. G., Zaffaroni, M., Gaeta, A., Raimondi, S., Piperno, G., Franzetti, J., Colombo, F., Camarda, A. M., Mastroleo, F., Botta, F., Spaggiari, L., Gandini, S., Guckenberger, M., Orecchia, R., Casiraghi, M., & Jereczek-Fossa, B. A. (2025). Harnessing Baseline Radiomic Features in Early-Stage NSCLC: What Role in Clinical Outcome Modeling for SBRT Candidates? Cancers, 17(5), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17050908









