Outcomes of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery in Populations with Obesity and Their Risk of Developing Colorectal Cancer: Where Do We Stand? An Umbrella Review on Behalf of TROGSS—The Robotic Global Surgical Society
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Population: adult patients (>18 years); animal studies were excluded.
- Intervention: MBS (e.g., gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass).
- Comparison: CRC.
- Outcome: association with colorectal cancer, with effect sizes reported as odds ratio (OR), relative risk (RR), or hazard ratio (HR).
2.3. Data Extraction
- Study identifiers: author names, title, and publication year.
- Population characteristics: total number of participants and demographic details (if available).
- Outcomes: effect sizes (OR, RR, HR) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the following:
- CRC (overall).
- Colon and rectal cancer (separately).
- CRC stratified by sex (male and female).
- CRC associated with specific bariatric surgery types (gastric band, sleeve gastrectomy, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass).
2.4. Assessment of Methodological Quality
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
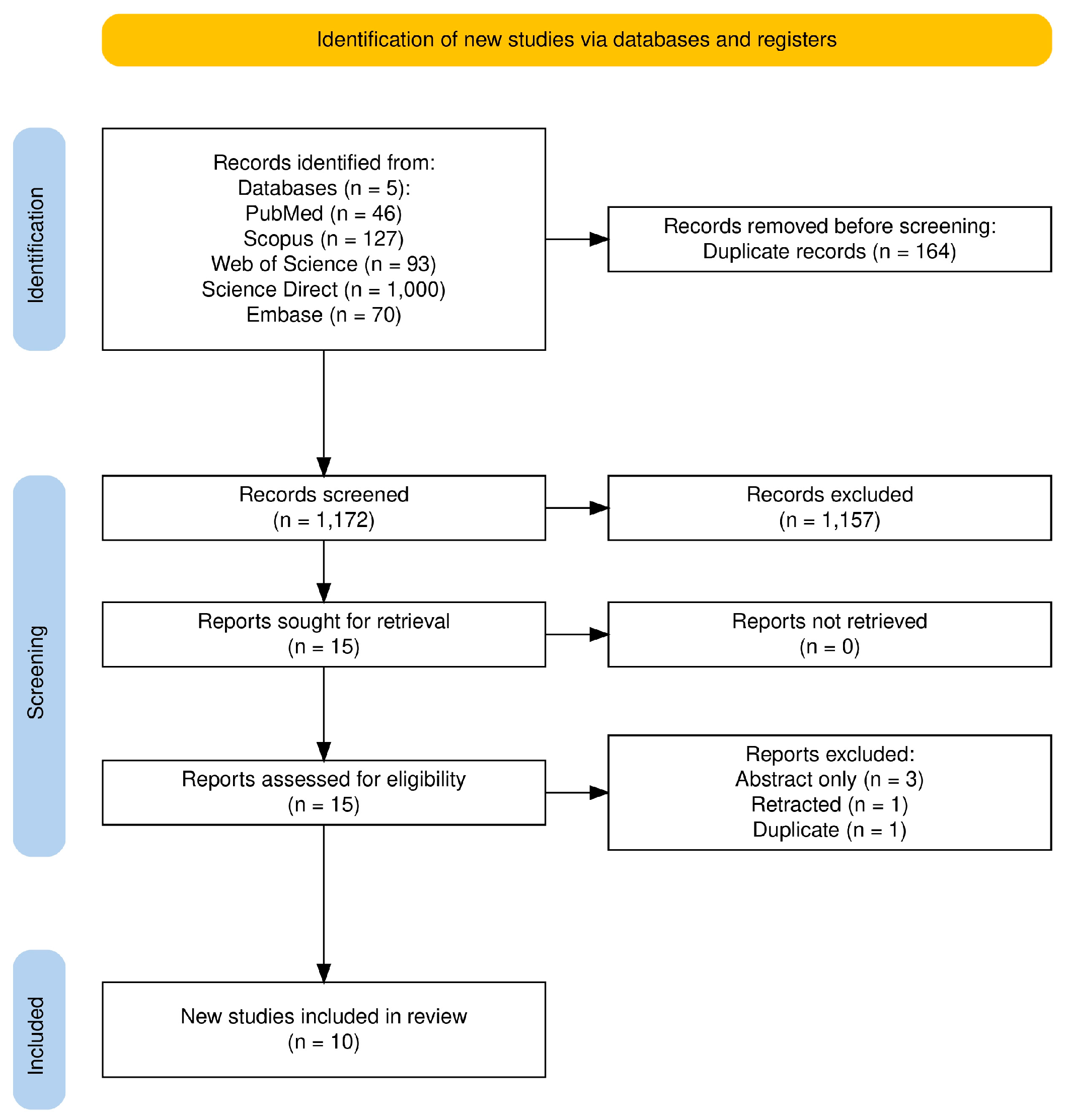
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
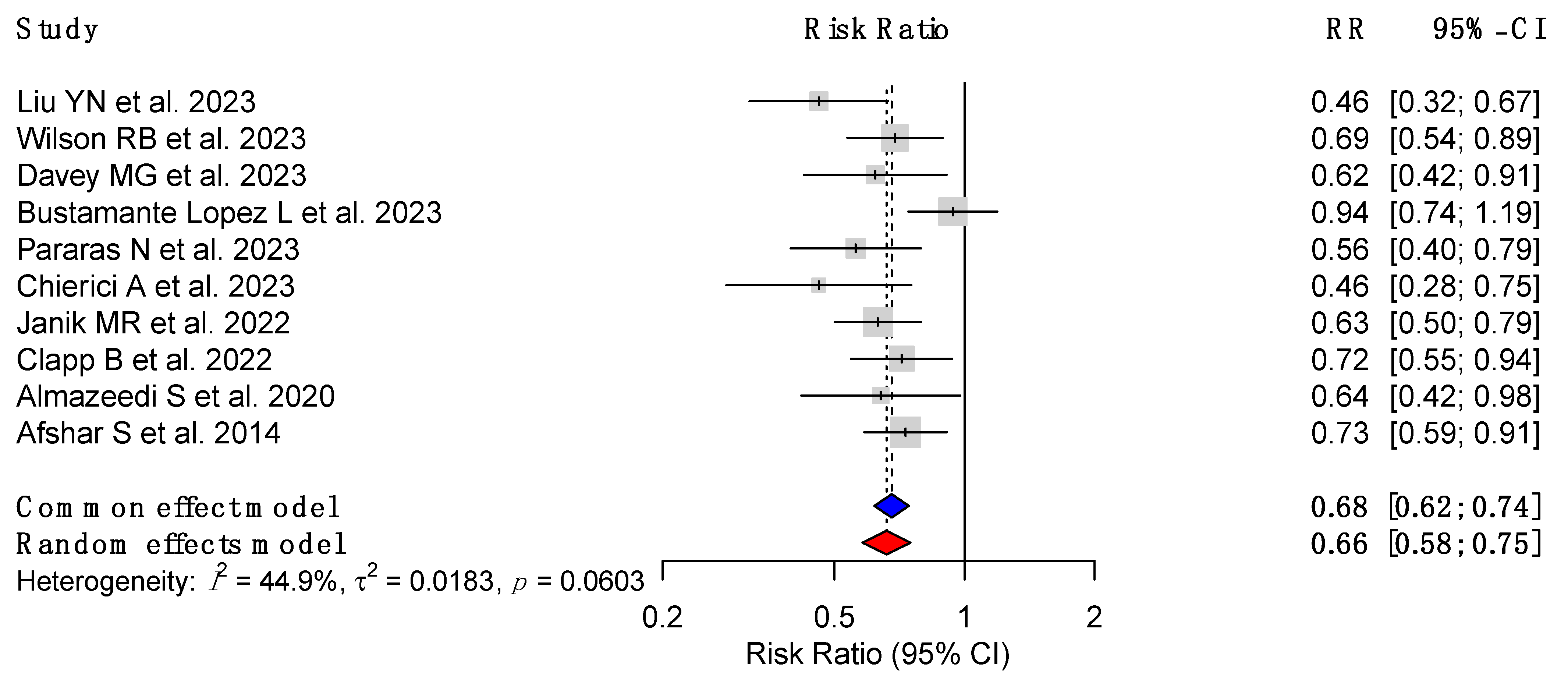
3.3. CRC Risk Reduction Following MBS
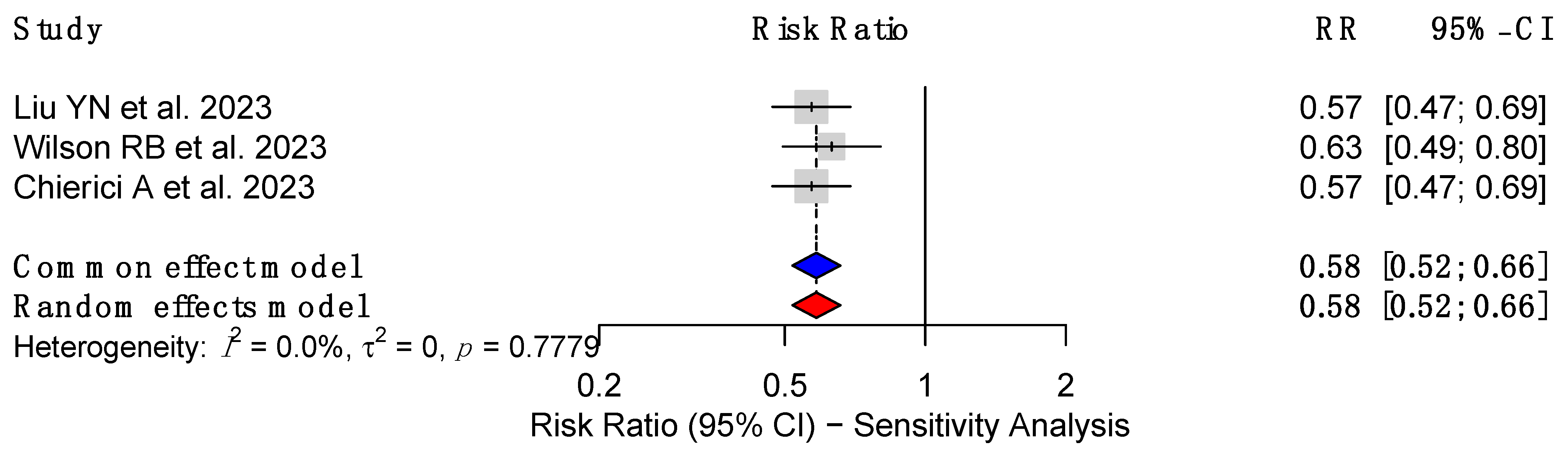
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis of CRC Risk in Patients with MBS
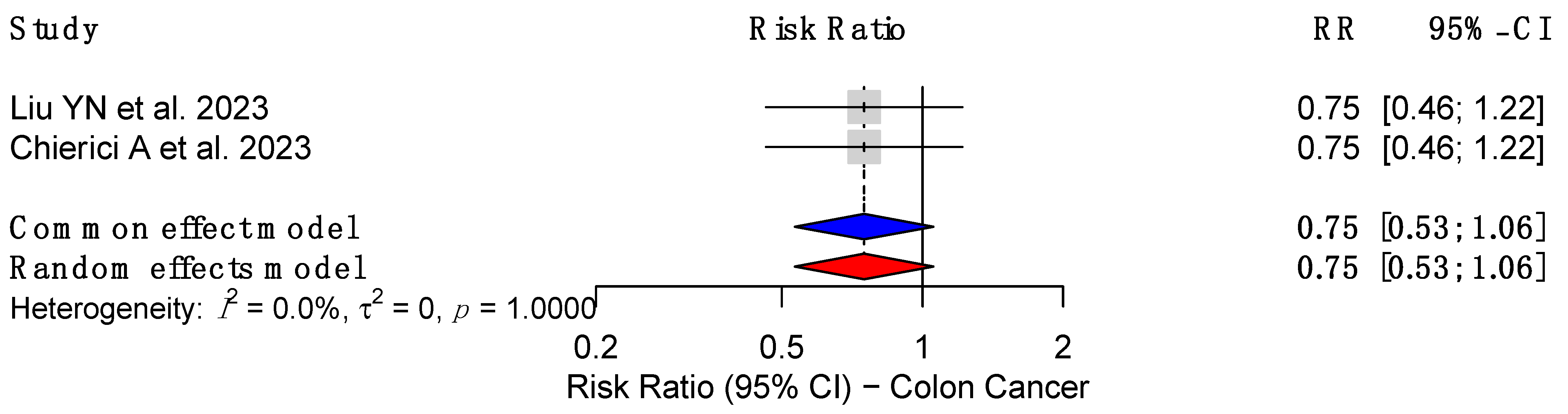
3.5. Effect of MBS on Colon and Rectal Cancer Risk
3.5.1. Effect on Colon Cancer Risk
3.5.2. Effect of MBS on Rectal Cancer Risk
3.6. Sex-Specific Analysis of CRC Risk Reduction Following MBS
3.7. Procedure-Specific Analysis of CRC Risk Reduction Following MBS
3.8. Publication Bias
3.9. AMSTAR 2 Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L. One in Eight People Globally Are Obese, with Rates in Children Increasing Fourfold in Three Decades. BMJ 2024, 384, q527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Balasundaram, P. Public Health Considerations Regarding Obesity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.W.; Seeley, R.J.; Zeltser, L.M.; Drewnowski, A.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M.; Leibel, R.L. Obesity Pathogenesis: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2017, 38, 267–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pati, S.; Irfan, W.; Jameel, A.; Ahmed, S.; Shahid, R.K. Obesity and Cancer: A Current Overview of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Outcomes, and Management. Cancers 2023, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. Body Fatness and Cancer—Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, B.; Portela, R.; Sharma, I.; Nakanishi, H.; Marrero, K.; Schauer, P.; Halfdanarson, T.R.; Abu Dayyeh, B.; Kendrick, M.; Ghanem, O.M. Risk of Non-Hormonal Cancer after Bariatric Surgery: Meta-Analysis of Retrospective Observational Studies. Br. J. Surg. 2022, 110, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D.; Sen, A.; Prasad, M.; Norat, T.; Janszky, I.; Tonstad, S.; Romundstad, P.; Vatten, L.J. BMI and All Cause Mortality: Systematic Review and Non-Linear Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of 230 Cohort Studies with 3.74 Million Deaths among 30.3 Million Participants. BMJ 2016, 353, i2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, M.; Mansoor, E.; Panhwar, M.; Parasa, S.; Cooper, G.S. Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancer in Average Risk Adults 20–39 Years of Age: A Population-Based National Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 3602–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshandel, G.; Ghasemi-Kebria, F.; Malekzadeh, R. Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention. Cancers 2024, 16, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Hayes, R.B.; Bray, F.; Weber, T.K.; Jemal, A. Global Patterns and Trends in Colorectal Cancer Incidence in Young Adults. Gut 2019, 68, 2179–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Shikora, S.A.; Aarts, E.; Aminian, A.; Angrisani, L.; Cohen, R.V.; De Luca, M.; Faria, S.L.; Goodpaster, K.P.S.; Haddad, A.; et al. 2022 American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) and International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity and Metabolic Disorders (IFSO): Indications for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2022, 18, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakis, A.; Wall-Wieler, E.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, F.; Sharaiha, R.Z. Type 2 Diabetes Remission After Bariatric Surgery and Its Impact on Healthcare Costs. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 3806–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, D.P.; Liu, L.; Arterburn, D.; Coleman, K.J.; Courcoulas, A.; Haneuse, S.; Johnson, E.; Li, R.A.; Theis, M.K.; Taylor, B.; et al. Remission and Relapse of Hypertension After Bariatric Surgery: A Retrospective Study on Long-Term Outcomes. Ann. Surg. Open 2022, 3, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A Critical Appraisal Tool for Systematic Reviews That Include Randomised or Non-Randomised Studies of Healthcare Interventions, or Both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-N.; Gu, J.-F.; Zhang, J.; Xing, D.-Y.; Wang, G.-Q. Bariatric Surgery Reduces Colorectal Cancer Incidence in Obese Individuals: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2023, 15, 2331–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.B.; Lathigara, D.; Kaushal, D. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Future Cancer Risk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.G.; Ryan, O.K.; Ryan, É.J.; Donlon, N.E.; Reynolds, I.S.; Fearon, N.M.; Martin, S.T.; Heneghan, H.M. The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on the Incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Patients with Obesity—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Registry Data. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Lopez, L.; Sulbaran, M.; Changoor, N.R.; Tilahun, Y.; Garcia-Henriquez, N.; Albert, M.; Soliman, M.; Monson, J.R.T.; Pepe, J. Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Updates Surg. 2023, 75, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pararas, N.; Pikouli, A.; Dellaportas, D.; Nastos, C.; Charalampopoulos, A.; Muqresh, M.A.; Bagias, G.; Pikoulis, E.; Papaconstantinou, D. The Protective Effect of Bariatric Surgery on the Development of Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierici, A.; Amoretti, P.; Drai, C.; De Fatico, S.; Barriere, J.; Schiavo, L.; Iannelli, A. Does Bariatric Surgery Reduce the Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Individuals with Morbid Obesity? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janik, M.R.; Clapp, B.; Sroczyński, P.; Ghanem, O. The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Reducing the Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of 3,233,044 Patients. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2023, 19, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazeedi, S.; El-Abd, R.; Al-Khamis, A.; Albatineh, A.N.; Al-Sabah, S. Role of Bariatric Surgery in Reducing the Risk of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar, S.; Kelly, S.B.; Seymour, K.; Lara, J.; Woodcock, S.; Mathers, J.C. The Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Colorectal Cancer Risk: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 1793–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, N.H.; Singleton, R.K.; Zhou, B.; Heap, R.A.; Mishra, A.; Bennett, J.E.; Paciorek, C.J.; Lhoste, V.P.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Stevens, G.A.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Underweight and Obesity from 1990 to 2022: A Pooled Analysis of 3663 Population-Representative Studies with 222 Million Children, Adolescents, and Adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, S.A.; Co, E.L.; Kanagala, S.G.; Padda, I.; Sethi, Y.; Johal, G. Metabolic Surgery in Improving Arterial Health in Obese Individuals. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.C.; Akinde, Y.M.; Schauer, P.R.; Le Roux, C.W.; Brennan, D.; Jernigan, A.M.; Bueter, M.; Albaugh, V.L. The Role of Bariatric and Metabolic Surgery in the Development, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Endometrial Cancer. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 943544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrgiou, M.; Kalliala, I.; Markozannes, G.; Gunter, M.J.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Gabra, H.; Martin-Hirsch, P.; Tsilidis, K.K. Adiposity and Cancer at Major Anatomical Sites: Umbrella Review of the Literature. BMJ 2017, 356, j477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinicrope, F.A. Increasing Incidence of Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, E.; O’Reilly, D.A.; Sherlock, D.J.; Manoharan, P.; Renehan, A.G. Excess Adiposity and Survival in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 434–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doleman, B.; Mills, K.T.; Lim, S.; Zelhart, M.D.; Gagliardi, G. Body Mass Index and Colorectal Cancer Prognosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Tech. Coloproctology 2016, 20, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Giovannucci, E.; Jeon, J.Y. Association Between Body Mass Index and Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, E.R. Obesity, Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, and Cancer Prevention: What Do We Need to Learn and How Do We Get There? Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2023, 19, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Artama, M.; Von Euler-Chelpin, M.; Hull, M.; Ljung, R.; Lynge, E.; Ólafsdóttir, G.H.; Pukkala, E.; Romundstad, P.; Talbäck, M.; et al. Colon and Rectal Cancer Risk after Bariatric Surgery in a Multicountry Nordic Cohort Study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussan, H.; Akinyeye, S.; Mihaylova, M.; McLaughlin, E.; Chiang, C.; Clinton, S.K.; Lieberman, D. Colorectal Cancer Risk Is Impacted by Sex and Type of Surgery After Bariatric Surgery. Obes. Surg. 2022, 32, 2880–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, D.; Park, S.B.; Li, T.; Timmins, H.C.; Trinh, T.; Au, K.; Battaglini, E.; Wyld, D.; Henderson, R.D.; Grimison, P.; et al. Hemoglobin, Body Mass Index, and Age as Risk Factors for Paclitaxel- and Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2036695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaiano, A.; Nappi, A.; Tafuto, S.; Nasti, G.; De Divitiis, C.; Romano, C.; Cassata, A.; Casaretti, R.; Silvestro, L.; Avallone, A.; et al. Diabetes and Body Mass Index Are Associated with Neuropathy and Prognosis in Colon Cancer Patients Treated with Capecitabine and Oxaliplatin Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Oncology 2016, 90, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenancia, C.; Lefebvre, A.; Cardinale, D.; Yu, A.F.; Ladoire, S.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Zeller, M.; Rochette, L.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Anthracyclines and Trastuzumab Cardiotoxicity in Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3157–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboré, E.G.; Guenancia, C.; Vaz-Luis, I.; Di Meglio, A.; Pistilli, B.; Coutant, C.; Cottu, P.; Lesur, A.; Petit, T.; Dalenc, F.; et al. Association of Body Mass Index and Cardiotoxicity Related to Anthracyclines and Trastuzumab in Early Breast Cancer: French CANTO Cohort Study. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
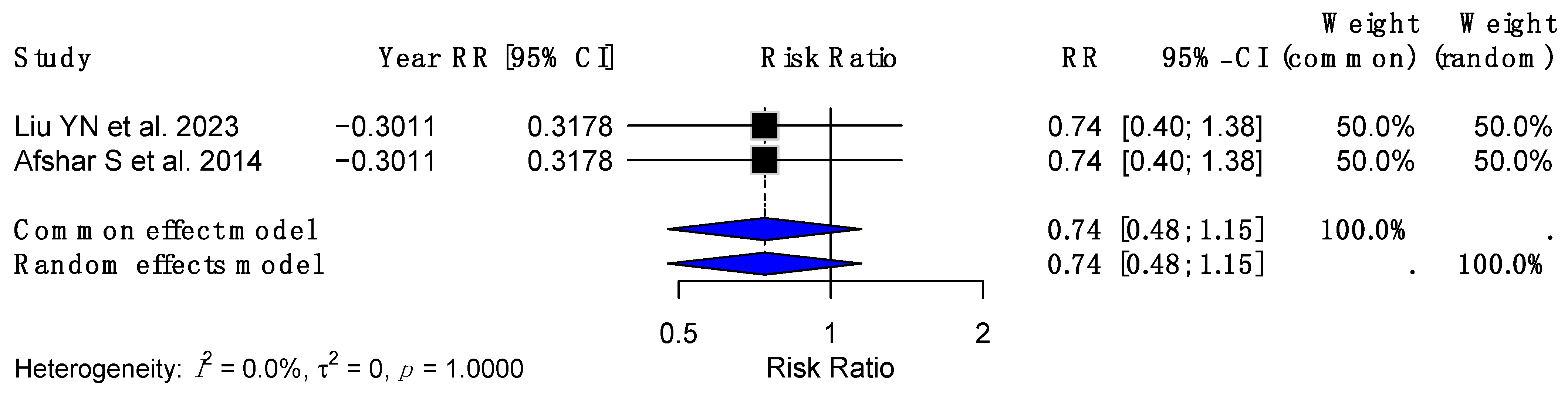
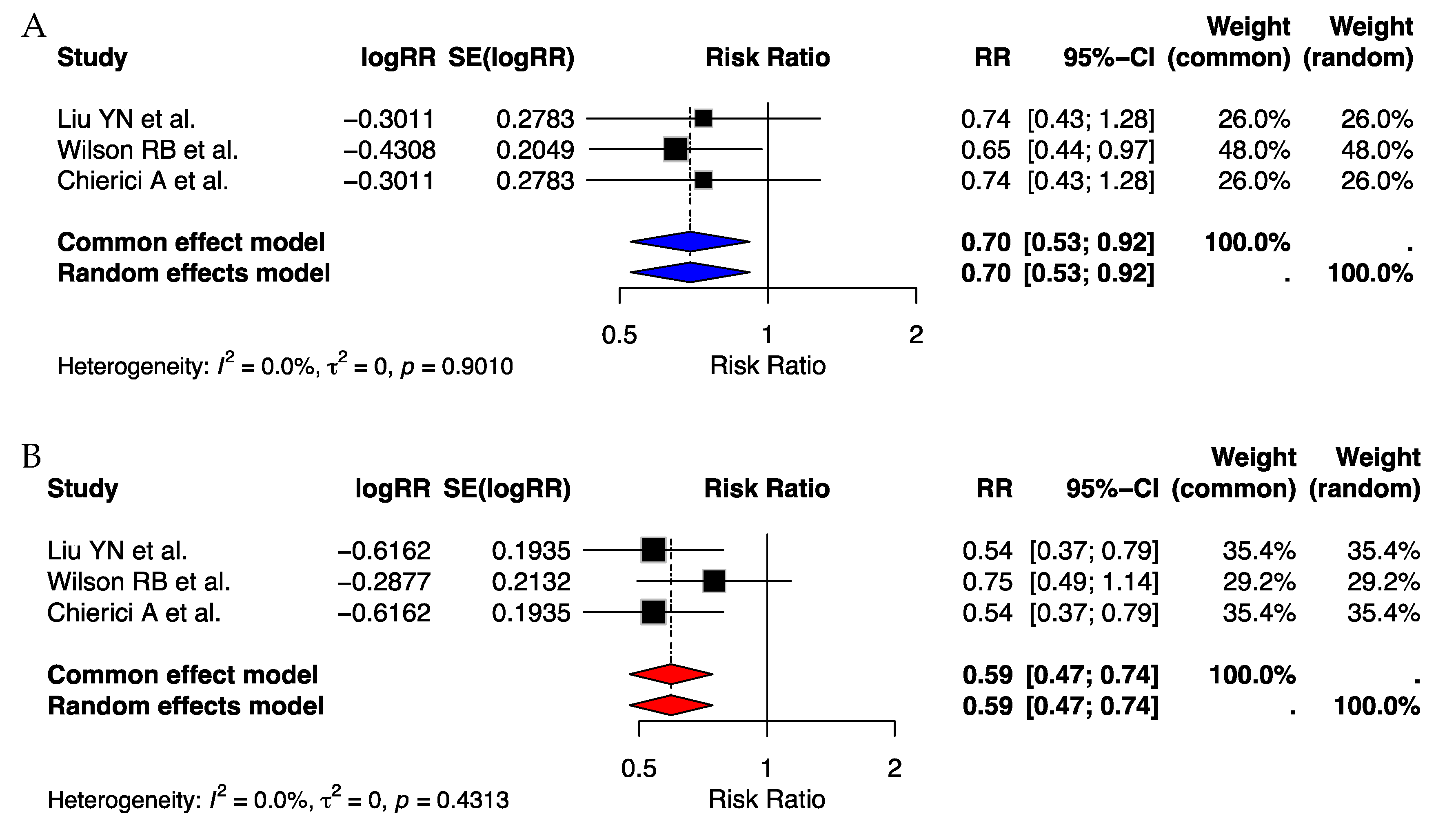

| Authors | Journal | Year of Publication | Country of Publication | Total Number of Studies Included | Total Number of Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu YN et al. [18] | World Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery | 2023 | China | 17 | 12,497,322 |
| Wilson RB et al. [19] | International Journal of Molecular Science | 2023 | Australia | 32 | 3,526,338 |
| Davey MG et al. [20] | Obesity Surgery The Journal of Metabolic Surgery and Allied Care | 2023 | Ireland | 11 | 6,214,682 |
| Bustamante-Lopez L et al. [21] | Updates in Surgery | 2023 | USA | 5 | 48,916 |
| Pararas N et al. [22] | International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health | 2023 | Greece | 13 | 6,279,722 |
| Chierici A et al. [23] | Nutrients | 2023 | France | 18 | 12,517,893 |
| Janik MR et al. [24] | Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases | 2022 | Poland | 13 | 3,233,044 |
| Clapp B et al. [7] | British Journal of Surgery | 2022 | USA | 15 | 947,787 |
| Almazeedi S et al. [25] | British Journal of Surgery | 2020 | Kuwait | 7 | 1,213,727 |
| Afshar S et al. [27] | Obesity Surgery The Journal of Metabolic Surgery and Allied Care | 2014 | UK | 4 | 105,187 |
| Authors | Effect Size of Gastric Band | Effect Size of Sleeve Gastrectomy | Effect Size of RYGB | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p-value | I2 (%) | RR | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p-value | I2 (%) | RR | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p-value | I2 (%) | |
| Davey MG et al. [20] | 0.513 | 0.336 | 0.818 | - | - | 0.484 | 0.307 | 0.763 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pararas N et al. [22] | 0.77 | 0.48 | 1.22 | 0.27 | - | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.83 | <0.001 | - | 0.64 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 0.05 | - |
| Clapp B et al. [7] | 1.34 | 0.28 | 7.12 | - | 99.08 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.83 | - | 77.81 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 0.61 | - | 64.22 |
| AMSTAR 2 Item | Liu YN et al. [18] | Wilson RB et al. [19] | Davey MG et al. [20] | Bustamante-Lopez et al. [21] | Pararas N et al. [22] | Chierici A et al. [23] | Janik MR et al. [24] | Clapp B et al. [7] | Almazeedi S et al. [25] | Afshar S et al. [27] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Did the research questions and inclusion criteria for the review include the components of PICO? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 2. Did the report of the review contain an explicit statement that the review methods were established prior to the conduct of the review and did the report justify any significant deviations from the protocol? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 3. Did the review authors explain their selection of the study designs for inclusion in the review? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 4. Did the review authors use a comprehensive literature search strategy? | PARTIAL YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | YES | YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | YES |
| 5. Did the review authors perform study selection in duplicate? | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 6. Did the review authors perform data extraction in duplicate? | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 7. Did the review authors provide a list of excluded studies and justify the exclusions? | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | PARTIAL YES | PARTIAL YES | NO | NO |
| 8. Did the review authors describe the included studies in adequate detail? | YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | PARTIAL YES |
| 9. Did the review authors use a satisfactory technique for assessing the risk of bias (RoB) in individual studies that were included in the review? | YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | PARTIAL YES | YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | YES | PARTIAL YES | YES |
| 10. Did the review authors report on the sources of funding for the studies included in the review? | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO |
| 11. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors use appropriate methods for statistical combination of results? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 12. If meta-analysis was performed, did the review authors assess the potential impact of RoB in individual studies on the results of the meta-analysis or other evidence synthesis? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 13. Did the review authors account for RoB in individual studies when interpreting/discussing the results of the review? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 14. Did the review authors provide a satisfactory explanation for, and discussion of, any heterogeneity observed in the results of the review? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 15. If they performed quantitative synthesis, did the review authors carry out an adequate investigation of publication bias (small study bias) and discuss its likely impact on the results of the review? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| 16. Did the review authors report any potential sources of conflict of interest, including any funding they received for conducting the review? | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Final Rating | CRITICAL LOW | LOW QUALITY | CRITICAL LOW | LOW QUALITY | LOW QUALITY | LOW QUALITY | MODERATE | HIGH | LOW QUALITY | LOW QUALITY |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goyal, A.; Macias, C.A.; Corzo, M.P.; Tomey, D.; Shetty, S.; Peña, V.; Bulut, H.; Abou-Mrad, A.; Marano, L.; Oviedo, R.J. Outcomes of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery in Populations with Obesity and Their Risk of Developing Colorectal Cancer: Where Do We Stand? An Umbrella Review on Behalf of TROGSS—The Robotic Global Surgical Society. Cancers 2025, 17, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040670
Goyal A, Macias CA, Corzo MP, Tomey D, Shetty S, Peña V, Bulut H, Abou-Mrad A, Marano L, Oviedo RJ. Outcomes of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery in Populations with Obesity and Their Risk of Developing Colorectal Cancer: Where Do We Stand? An Umbrella Review on Behalf of TROGSS—The Robotic Global Surgical Society. Cancers. 2025; 17(4):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040670
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoyal, Aman, Christian Adrian Macias, Maria Paula Corzo, Daniel Tomey, Sachin Shetty, Victor Peña, Halil Bulut, Adel Abou-Mrad, Luigi Marano, and Rodolfo J. Oviedo. 2025. "Outcomes of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery in Populations with Obesity and Their Risk of Developing Colorectal Cancer: Where Do We Stand? An Umbrella Review on Behalf of TROGSS—The Robotic Global Surgical Society" Cancers 17, no. 4: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040670
APA StyleGoyal, A., Macias, C. A., Corzo, M. P., Tomey, D., Shetty, S., Peña, V., Bulut, H., Abou-Mrad, A., Marano, L., & Oviedo, R. J. (2025). Outcomes of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery in Populations with Obesity and Their Risk of Developing Colorectal Cancer: Where Do We Stand? An Umbrella Review on Behalf of TROGSS—The Robotic Global Surgical Society. Cancers, 17(4), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040670









