Ketone Bodies Are Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL Trial
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Sample Preparation and Metabolomic Profiling
2.3. Endpoints
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients and Survival
3.2. Treatment Response Metabolomic Profile
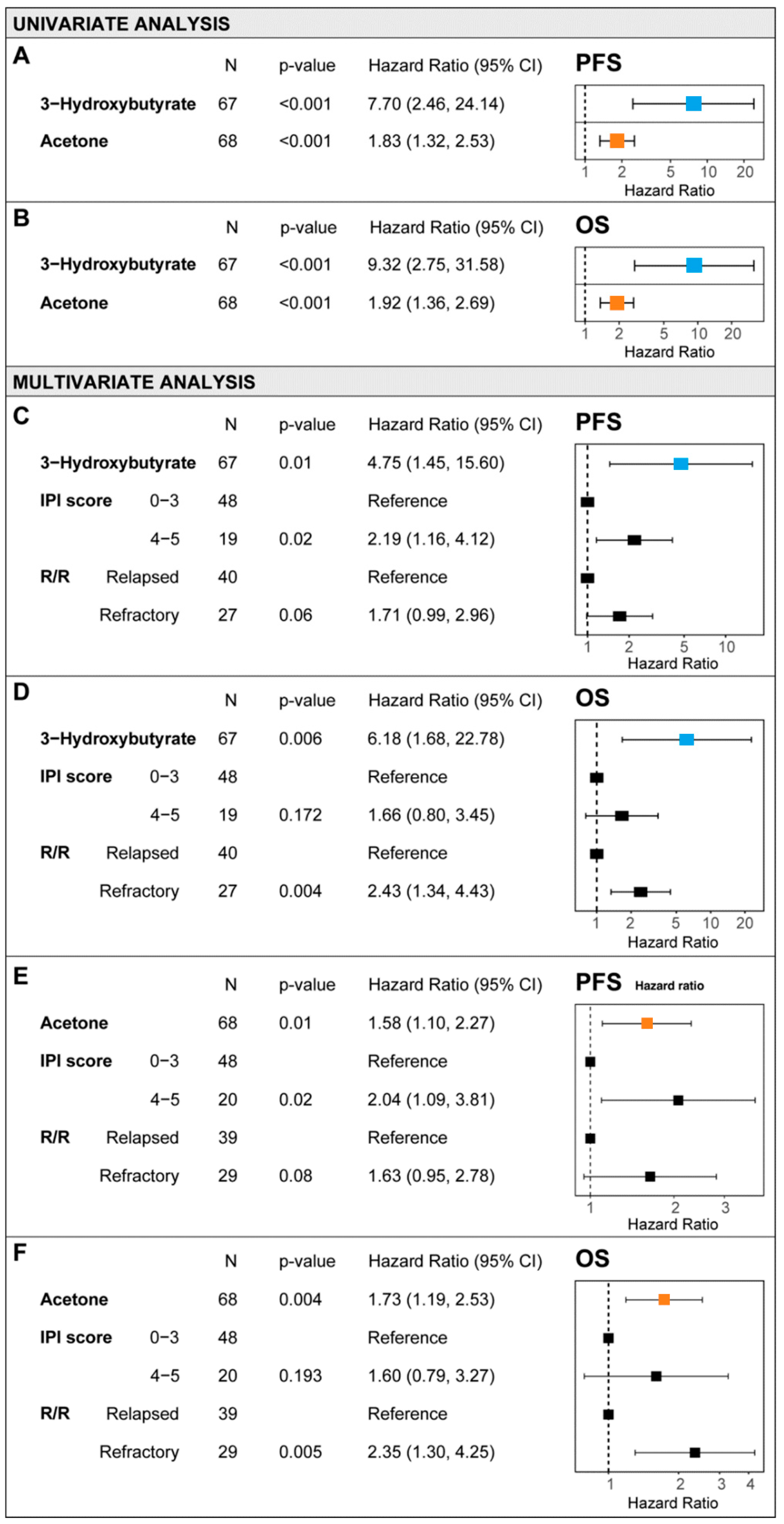
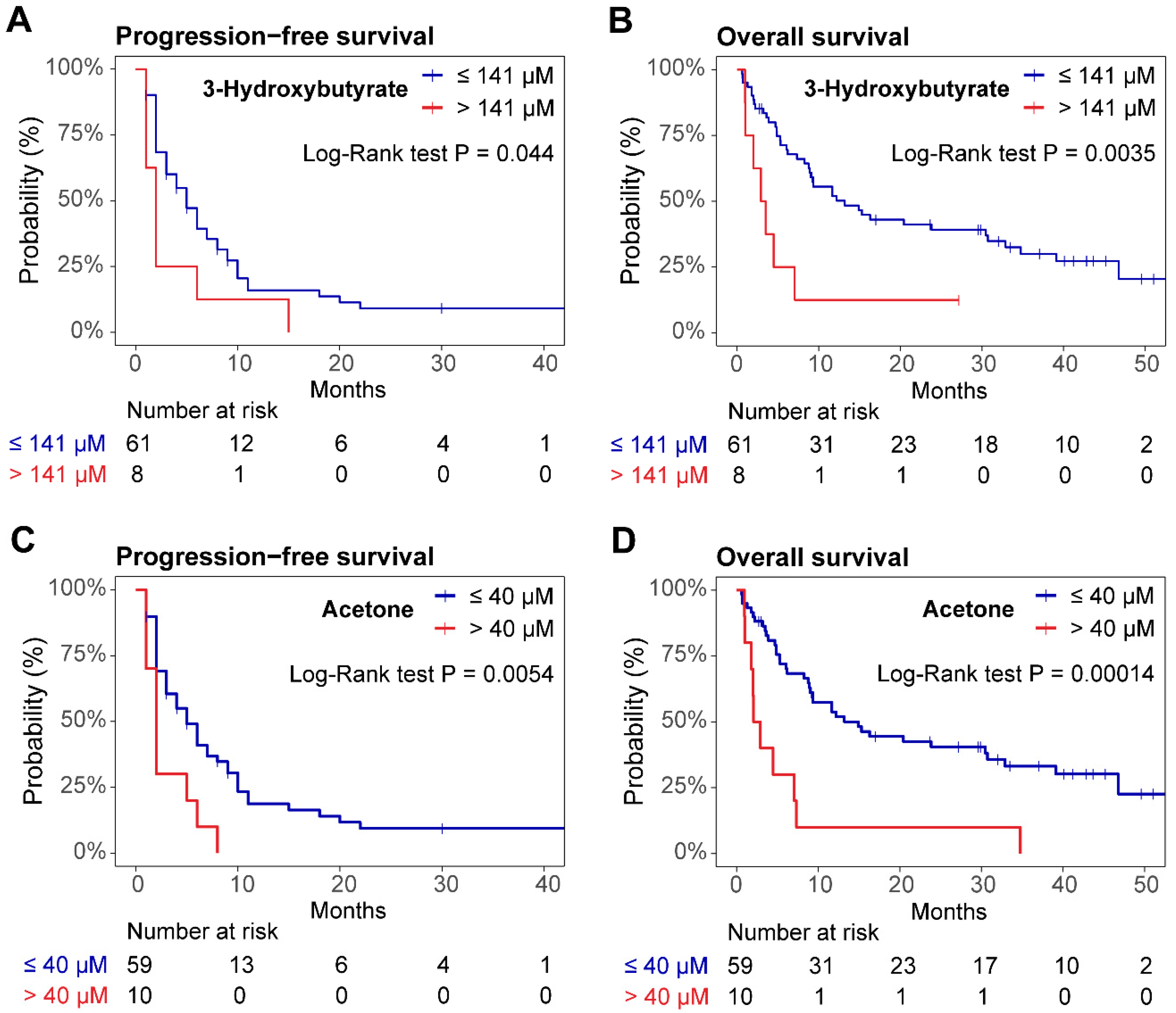
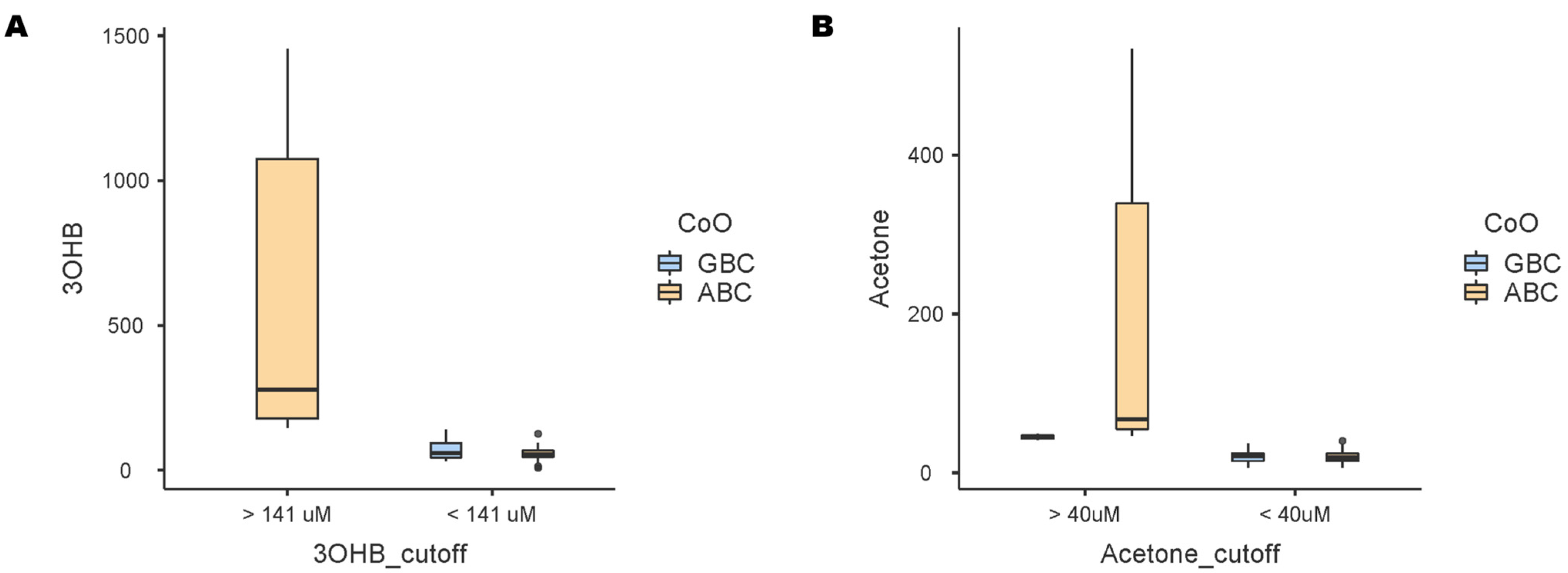
3.3. Survival Outcome and Metabolomic Profile
3.4. Nomogram for R/R DLBCL Risk Stratification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Medina-Cleghorn, D.; Bernal-Mizrachi, L.; Bracci, P.M.; Hubbard, A.; Conde, L.; Riby, J.; Nomura, D.K.; Skibola, C.F.; Skibola, C. The Potential Relevance of the Endocannabinoid, 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Oncoscience 2016, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medriano, C.A.D.; Na, J.; Lim, K.M.; Chung, J.H.; Park, Y.H. Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolite Pathway Analyses of Myeloma and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Patients. Cell J. 2017, 19, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberini, L.; Noto, A.; Fattuoni, C.; Satta, G.; Zucca, M.; Cabras, M.G.; Mura, E.; Cocco, P. The Metabolomic Profile of Lymphoma Subtypes: A Pilot Study. Molecules 2019, 24, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno Duarte, G.H.; de Piloto Fernandes, A.M.A.; Silva, A.A.R.; Zamora-Obando, H.R.; Amaral, A.G.; de Sousa Mesquita, A.; Schmidt-Filho, J.; Cordeiro de Lima, V.C.; D’Almeida Costa, F.; Andrade, V.P.; et al. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Untargeted Profiling of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Urinary Metabolite Markers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 7469–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, F.; Zheng, M.; Xu, Z.; Sun, R.; Chen, X.; Cao, B.; Li, J. Plasma Metabolites Forecast Occurrence and Prognosis for Patients With Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 894891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenson, M.; Pedersen, A.; Hasselblom, S.; Nilsson-Ehle, H.; Karlsson, B.G.; Pinto, R.; Andersson, P.O. Serum Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Based Metabolomics and Outcome in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients—A Pilot Study. Leuk Lymphoma 2016, 57, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, M.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wen, Q.; Zhu, F.; Li, J.; Mungur, I.D.; Zhang, L. Serum Metabolomic Profiling Based on GC/MS Helped to Discriminate Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients with Different Prognosis. Leuk Res. 2021, 111, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazón-Carrión, N.; García-Sancho, A.M.; Nogales-Fernández, E.; Jiménez-Cortegana, C.; Carnicero-González, F.; Ríos-Herranz, E.; de la Cruz-Vicente, F.; Rodríguez-García, G.; Fernández-Álvarez, R.; Martínez-Banaclocha, N.; et al. Lenalidomide plus R-GDP (R2-GDP) in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Final Results of the R2-GDP-GOTEL Trial and Immune Biomarker Subanalysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3658–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckonert, O.; Keun, H.C.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Bundy, J.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic Profiling, Metabolomic and Metabonomic Procedures for NMR Spectroscopy of Urine, Plasma, Serum and Tissue Extracts. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallol, R.; Amigó, N.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Heras, M.; Vinaixa, M.; Plana, N.; Rock, E.; Ribalta, J.; Yanes, O.; Masana, L.; et al. Liposcale: A Novel Advanced Lipoprotein Test Based on 2D Diffusion-Ordered 1H NMR Spectroscopy. J. Lipid. Res. 2015, 56, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfgren, L.; Ståhlman, M.; Forsberg, G.B.; Saarinen, S.; Nilsson, R.; Hansson, G.I. The BUME Method: A Novel Automated Chloroform-Free 96-Well Total Lipid Extraction Method for Blood Plasma. J. Lipid. Res. 2012, 53, 1690–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrilero, R.; Gil, M.; Amigó, N.; Dias, C.B.; Wood, L.G.; Garg, M.L.; Ribalta, J.; Heras, M.; Vinaixa, M.; Correig, X. LipSpin: A New Bioinformatics Tool for Quantitative 1H NMR Lipid Profiling. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2031–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Pfistner, B.; Juweid, M.E.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Specht, L.; Horning, S.J.; Coiffier, B.; Fisher, R.I.; Hagenbeek, A.; Zucca, E.; et al. Revised Response Criteria for Malignant Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project A Predictive Model for Aggressive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 987–994. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monferrer, E.; Vieco-Martí, I.; López-Carrasco, A.; Fariñas, F.; Abanades, S.; de la Cruz-Merino, L.; Noguera, R.; Naranjo, T.Á. Metabolic Classification and Intervention Opportunities for Tumor Energy Dysfunction. Metabolites 2021, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Peiris-Pagés, M.; Pestell, R.G.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Cancer Metabolism: A Therapeutic Perspective. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 14, 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardinis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. Fundamentals of Cancer Metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600200. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, J.E.; Chiche, J. Metabolic Reprogramming of Non-Hodgkin’s B-Cell Lymphomas and Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 426970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, K.; Jaber, S.; Nahid, N.M.; Underwood, K.; Beheshti, A.; Landon, A.; Bhandary, B.; Bastain, P.; Evens, A.M.; Haley, J.; et al. Role of Hypoxia in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Metabolic Repression and Selective Translation of HK2 Facilitates Development of DLBCL. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiden, M.G.V.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg Effect: The Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation. Science (1979) 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, C.; Pinto, A.; Martherus, R.; Santiago de Jesus, J.P.; Polet, F.; Feron, O. Acidosis Drives the Reprogramming of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Cancer Cells through Changes in Mitochondrial and Histone Acetylation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbet, C.; Draoui, N.; Polet, F.; Pinto, A.; Drozak, X.; Riant, O.; Feron, O. The SIRT1/HIF2α Axis Drives Reductive Glutamine Metabolism under Chronic Acidosis and Alters Tumor Response to Therapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5507–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiche, J.; Reverso-Meinietti, J.; Mouchotte, A.; Rubio-Patiño, C.; Mhaidly, R.; Villa, E.; Bossowski, J.P.; Proics, E.; Grima-Reyes, M.; Paquet, A.; et al. GAPDH Expression Predicts the Response to R-CHOP, the Tumor Metabolic Status, and the Response of DLBCL Patients to Metabolic Inhibitors. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1243–1257.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, B.; Krumsiek, J.; Assouline, S.E.; Marullo, R.; Patel, J.; Phillip, J.M.; Román, L.; Mann, K.K.; Cerchietti, L. Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Cellular Reprogramming of B-Cell Lymphoma by a Lysine Deacetylase Inhibitor through the Choline Pathway. EBioMedicine 2018, 28, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensah, A.A.; Spriano, F.; Sartori, G.; Priebe, V.; Cascione, L.; Gaudio, E.; Tarantelli, C.; Civanelli, E.; Aresu, L.; Rinaldi, A.; et al. Study of the Antilymphoma Activity of Pracinostat Reveals Different Sensitivities of DLBCL Cells to HDAC Inhibitors. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2467–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, R.A.; Thomas, H.; Zhao, Y.; Herendi, L.; Howarth, R.; Dragoni, I.; Keun, H.C.; Vellano, C.P.; Marszalek, J.R.; Wedge, S.R. Simultaneous Targeting of Glycolysis and Oxidative Phosphorylation as a Therapeutic Strategy to Treat Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, N. Ketone Body, 3-Hydroxybutyrate: Minor Metabolite—Major Medical Manifestations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; AA, J.; Zhou, F.; Wang, G. Multi-Dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Cancer Biology: Opportunities for Cancer Therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Yan, R.; Li, K.; Xing, S.; Wu, G.; Hu, L.; Jia, W.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Redirects to Ketolysis for Progression under Nutrition Deprivation Stress. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 1112–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, M.; Fan, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Jin, J. The Prognostic Value of Hydroxybutyrate Dehydrogenase in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. iScience 2024, 27, 110905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro, P.; Kishan, A.U.; Norberg, E.; Stanley, I.; Chapuy, B.; Ficarro, S.B.; Polak, K.; Tondera, D.; Gounarides, J.; Yin, H.; et al. Metabolic signatures uncover distinct targets in molecular subsets of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penning, T.M.; Jonnalagadda, S.; Trippier, P.C.; Rižner, T.L.; Gottesman, M. Aldo-Keto Reductases and Cancer Drug Resistance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 1150–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedkova, E.N.; Blatter, L.A. Role of β-Hydroxybutyrate, Its Polymer Poly-β-Hydroxybutyrate and Inorganic Polyphosphate in Mammalian Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.K.; Chang, P.H.; Kuo, W.H.; Chen, C.L.; Jeng, Y.M.; Chang, K.J.; Shew, J.Y.; Hu, C.M.; Lee, W.H. Adipocytes Promote Malignant Growth of Breast Tumours with Monocarboxylate Transporter 2 Expression via β-Hydroxybutyrate. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skorupa, A.; Poński, M.; Ciszek, M.; Cichoń, B.; Klimek, M.; Witek, A.; Pakuło, S.; Boguszewicz, Ł.; Sokół, M. Grading of Endometrial Cancer Using 1H HR-MAS NMR-Based Metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranovicova, E.; Racay, P.; Zubor, P.; Smolar, M.; Kudelova, E.; Halasova, E.; Dvorska, D.; Dankova, Z. Circulating Metabolites in the Early Stage of Breast Cancer Were Not Related to Cancer Stage or Subtypes but Associated with Ki67 Level. Promising Statistical Discrimination from Controls. Mol. Cell Probes 2022, 66, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouirand, V.; Gicquel, T.; Lien, E.C.; Jaune-Pons, E.; Da Costa, Q.; Finetti, P.; Metay, E.; Duluc, C.; Mayers, J.R.; Audebert, S.; et al. Ketogenic HMG-CoA Lyase and Its Product Β-hydroxybutyrate Promote Pancreatic Cancer Progression. EMBO J. 2022, 41, e110466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Xie, G.; Jia, W. Metabonomics of Human Colorectal Cancer: New Approaches for Early Diagnosis and Biomarker Discovery. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3857–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Tang, S.; Mo, P.; Wu, K.; Nie, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Distinguishing Pancreatic Cancer from Chronic Pancreatitis and Healthy Individuals by 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance-Based Metabonomic Profiles. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.O.; Xu, J.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z. Metabolomic Profiling of Serum from Human Pancreatic Cancer Patients Using 1H NMR Spectroscopy and Principal Component Analysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaifi, A.; Bahashwan, S.; Alsaadi, M.; Malhan, H.; Aqeel, A.; Al-Kahiry, W.; Almehdar, H.; Qadri, I. Metabolic Biomarkers in B-Cell Lymphomas for Early Diagnosis and Prediction, as Well as Their Influence on Prognosis and Treatment. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaifi, A.; Refai, M.Y.; Alsaadi, M.; Bahashwan, S.; Malhan, H.; Al-Kahiry, W.; Dammag, E.; Ageel, A.; Mahzary, A.; Albiheyri, R.; et al. Metabolomics: A New Era in the Diagnosis or Prognosis of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaita-esteruelas, S.; Saavedra-Garcíagarcía, P.; Bosquet, A.; Borr, J.; Girona, J.; Amiliano, K.; Rodríguezrodríguez-Balada, M.; Heras, M.; Masana, L.; Gum, J. Adipose-Derived Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins Plasma Concentrations Are Increased in Breast Cancer Patients. Oncologist 2017, 22, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Gumà, J.; Masana, L.; Borràs, J. The Peritumoural Adipose Tissue Microenvironment and Cancer. The Roles of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 and Fatty Acid Binding Protein 5. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 462, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Bosquet, A.; Saavedra, P.; Gumà, J.; Girona, J.; Lam, E.W.F.; Amillano, K.; Borràs, J.; Masana, L. Exogenous FABP4 Increases Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Activates the Expression of Fatty Acid Transport Proteins. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonuccelli, G.; Tsirigos, A.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Pavlides, S.; Pestell, R.G.; Chiavarina, B.; Frank, P.G.; Flomenberg, N.; Howell, A.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; et al. Ketones and Lactate “Fuel” Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3506–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables 1 | Total Patients (n = 69) |
|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Men | 35 (50.7%) |
| Women | 34 (49.3%) |
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 70.1 (61.7–74.5) |
| Body mass index (BMI), kg/m2, median (IQR) | 27.0 (23.9–30.2) |
| Cell-of-origin (CoO), n (%) [n = 65] | |
| Germinal center B-cell-like | 27 (41%) |
| Activated B-cell-like | 39 (59%) |
| Refractoriness, n (%) | |
| Relapsed | 40 (58.0%) |
| Chemorefractory | 29 (42.0%) |
| International Prognostic Index (IPI) score, n (%) | |
| Low risk (0–1) | 12 (17.4%) |
| Low/High-intermediate risk (2–3) | 37 (53.6%) |
| High risk (4–5) | 20 (29.0%) |
| Response, n (%) | |
| Responders | 41 (59.4%) |
| Non-responders | 28 (40.6%) |
| Metabolites 1 | Responders (n = 41) | Non-Responders (n = 28) | p Value | Fold Change 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low molecular weight | ||||
| Creatinine, µM, mean (SD) | 73.0 (43.3) | 48.7 (17.6) | 0.030 | 1.50 |
| Lactate, µM, mean (SD) | 1174.2 (989.7) | 2023.5 (1655.6) | 0.034 | 0.58 |
| Glycoproteins | ||||
| Glycoprotein A, µmol/L, mean (SD) | 846.0 (165.3) | 915.5 (161.0) | 0.028 | 0.92 |
| Glycoprotein A, H/W ratio, mean (SD) | 24.7 (4.3) | 27.04 (4.7) | 0.024 | 0.92 |
| Cholesterol | ||||
| Free cholesterol, mmol/L, mean (SD) | 2.36 (0.71) | 2.84 (0.83) | 0.016 | 0.83 |
| Esterified cholesterol, mmol/L, mean (SD) | 4.76 (1.20) | 5.36 (1.40) | 0.043 | 0.89 |
| Lipoproteins | ||||
| IDL cholesterol, mg/dL, mean (SD) | 14.14 (5.84) | 17.39 (5.61) | 0.015 | 0.86 |
| IDL triglycerides, mg/dL, mean (SD) | 13.38 (4.59) | 15.64 (4.07) | 0.018 | 0.81 |
| LDL triglycerides, mg/dL, mean (SD) | 18.94 (6.40) | 22.90 (6.08) | 0.005 | 0.83 |
| Medium LDL-P, nmol/L, mean (SD) | 340.83 (134.98) | 424.09 (157.02) | 0.008 | 0.80 |
| Large LDL-P, nmol/L, mean (SD) | 180.15 (44.78) | 201.32 (51.39) | 0.043 | 0.89 |
| Medium HDL-P, µmol/L, mean (SD) | 10.18 (1.68) | 11.27 (1.72) | 0.006 | 0.90 |
| Large HDL-P, µmol/L, mean (SD) | 0.30 (0.05) | 0.33 (0.05) | 0.005 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Castillejo, S.; Badia, J.; de la Cruz-Merino, L.; Martín Garcia-Sáncho, A.; Carnicero-González, F.; Palazón-Carrión, N.; Ríos-Herranz, E.; de la Cruz-Vicente, F.; Rueda-Domínguez, A.; Martínez-Banaclocha, N.; et al. Ketone Bodies Are Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL Trial. Cancers 2025, 17, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030532
Fernández-Castillejo S, Badia J, de la Cruz-Merino L, Martín Garcia-Sáncho A, Carnicero-González F, Palazón-Carrión N, Ríos-Herranz E, de la Cruz-Vicente F, Rueda-Domínguez A, Martínez-Banaclocha N, et al. Ketone Bodies Are Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL Trial. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030532
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Castillejo, Sara, Joan Badia, Luís de la Cruz-Merino, Alejandro Martín Garcia-Sáncho, Fernando Carnicero-González, Natalia Palazón-Carrión, Eduardo Ríos-Herranz, Fátima de la Cruz-Vicente, Antonio Rueda-Domínguez, Natividad Martínez-Banaclocha, and et al. 2025. "Ketone Bodies Are Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL Trial" Cancers 17, no. 3: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030532
APA StyleFernández-Castillejo, S., Badia, J., de la Cruz-Merino, L., Martín Garcia-Sáncho, A., Carnicero-González, F., Palazón-Carrión, N., Ríos-Herranz, E., de la Cruz-Vicente, F., Rueda-Domínguez, A., Martínez-Banaclocha, N., Gómez-Codina, J., Labrador, J., Martínez-Madueño, F., Amigó, N., Salar-Silvestre, A., Rodríguez-Abreu, D., Gálvez-Carvajal, L., Sánchez-Beato, M., Provencio-Pulla, M., ... Gumà, J., on behalf of the Spanish Lymphoma Oncology Group (GOTEL). (2025). Ketone Bodies Are Potential Prognostic Biomarkers in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the R2-GDP-GOTEL Trial. Cancers, 17(3), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030532







