Knockout of p21-Activated Kinase 4 Stimulates MHC I Expression of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via an Autophagy-Independent Pathway
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
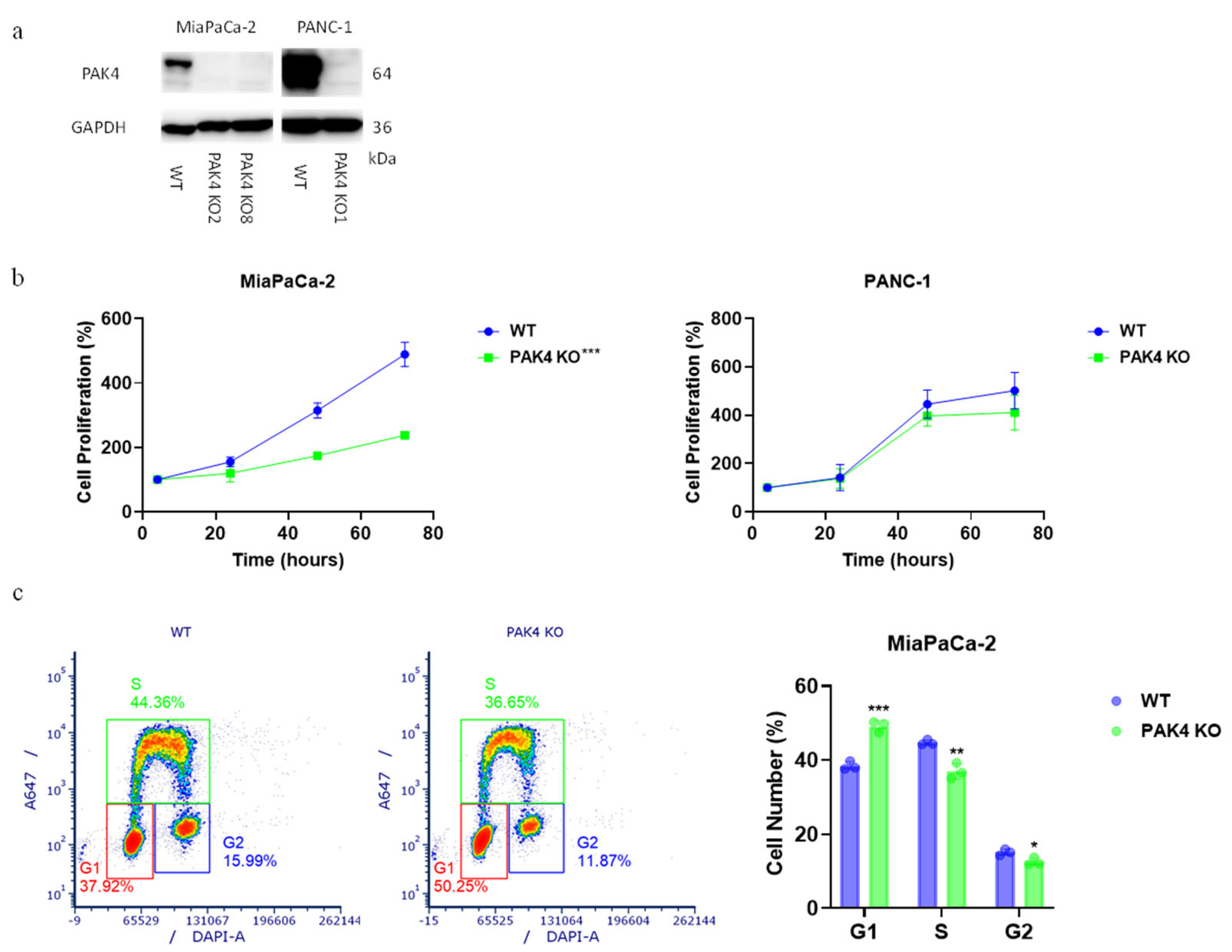
2.1. Generate PAK4 Knockout Cells
2.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.3. Immunoblot
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
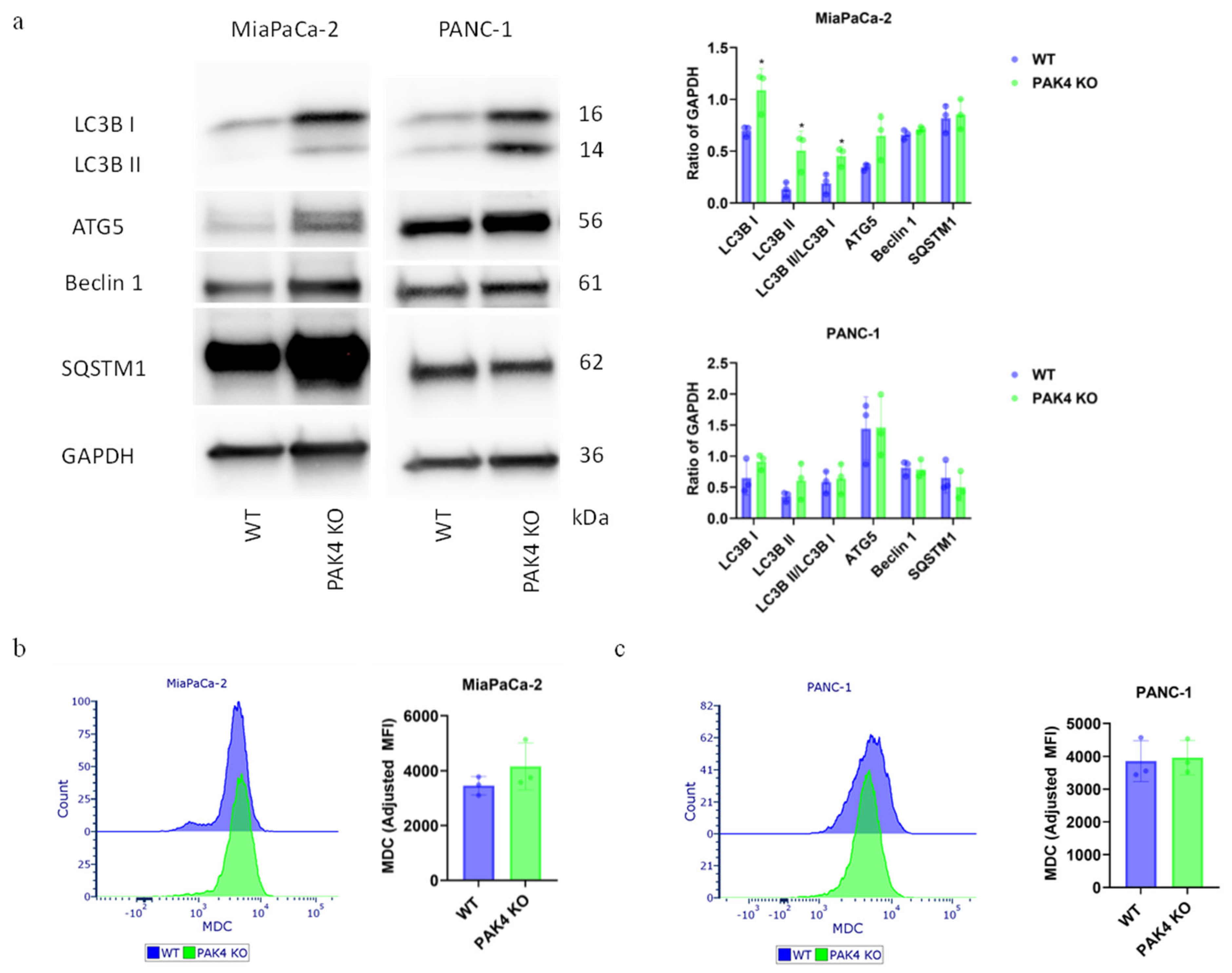
2.4.1. Monodansylcadaverine Staining
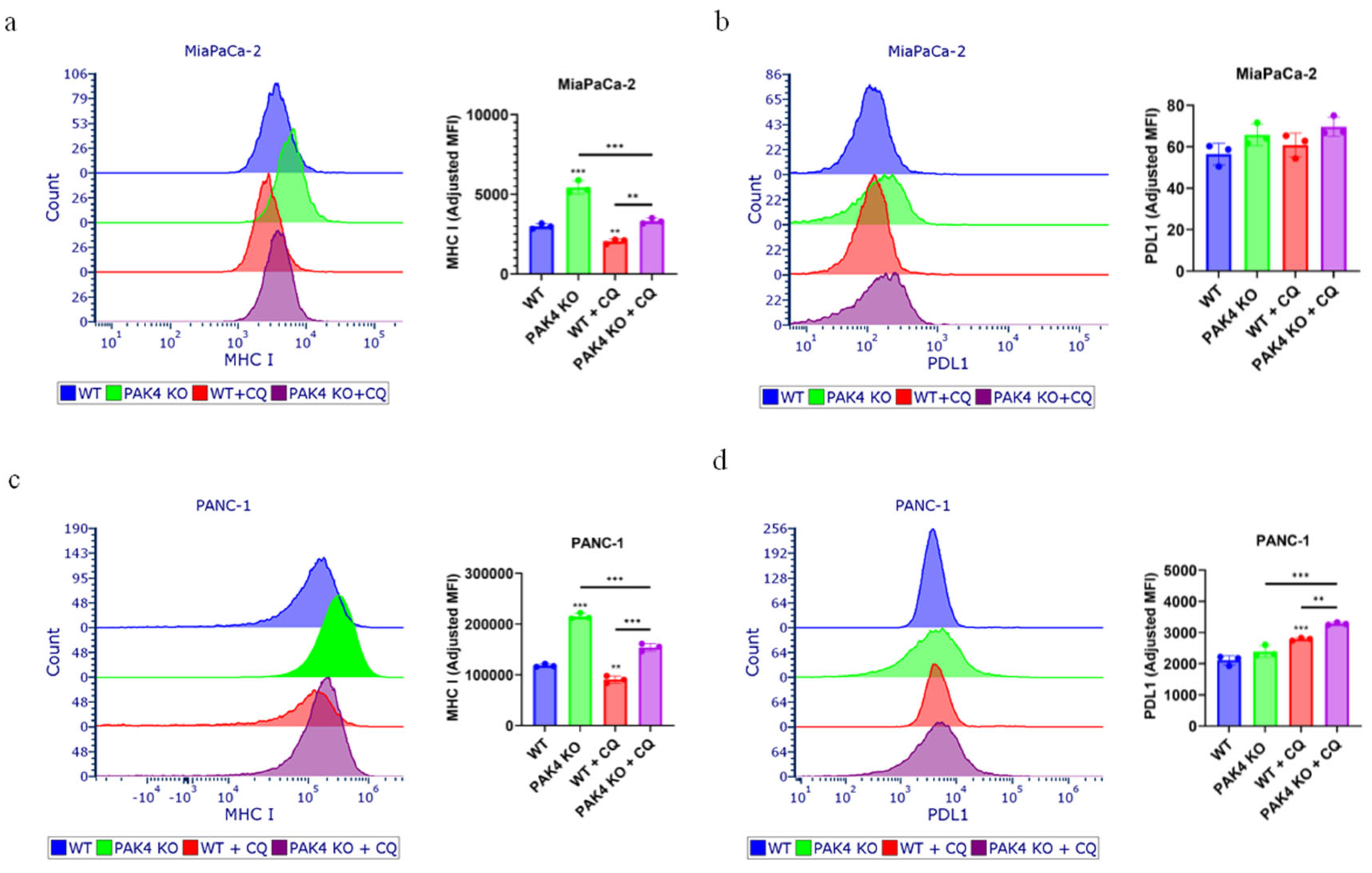
2.4.2. Determine the Expression of Cell Surface Immune Markers
2.5. Measure Apoptosis, Cell Death, and Cell Cycle Analysis
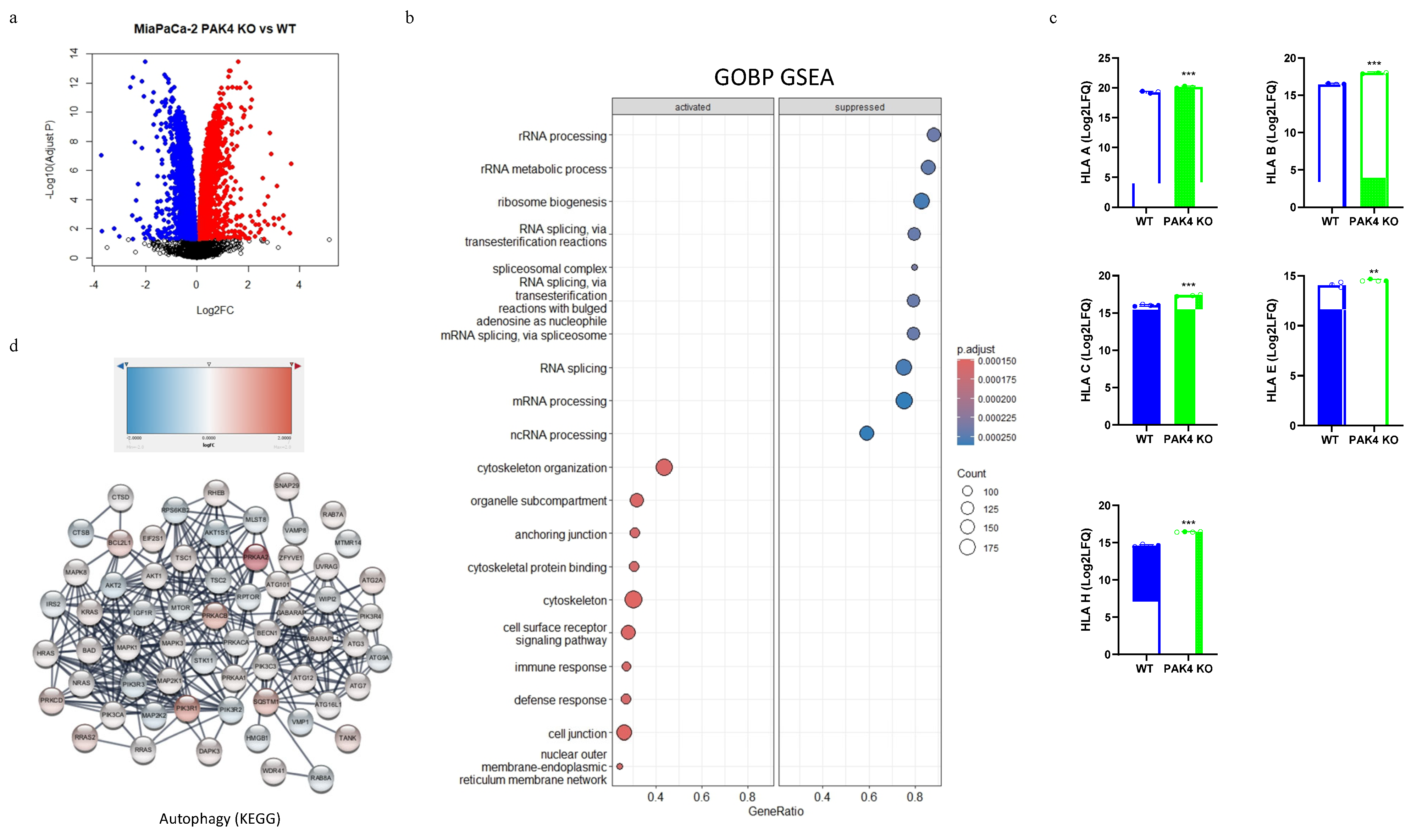
2.6. Proteomic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PAK4 Knockout Differentially Affected the Growth of Pancreatic Cancer Cells
3.2. PAK4 Knockout Stimulated the Expression of MHC I in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
3.3. PAK4 Knockout Differentially Regulated the Autophagy of Pancreatic Cancer Cells
3.4. Inhibition of Autophagy by Chloroquine Did Not Change the Effect of PAK4 KO on Cancer Cell Growth
3.5. Inhibition of Autophagy by Chloroquine Did Not Block the PAK4 KO-Stimulated Expression of MHC I in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Antigen-presenting cell |
| ATG | Autophagy-related gene |
| BAK | BCL2 homologous antagonist/Killer |
| BAX | BCL2-associated protein X |
| BCL2 | B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 protein |
| CAR | Chimeric antigen receptor |
| CAS | CRISPR-associated protein |
| CQ | Chloroquine |
| CRISPR | Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GABARAP | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| GOBP | Gene Ontology biological process |
| GSEA | Gene set enrichment analysis |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IQR | Interquantile range |
| KD | Knockdown |
| KO | Knockout |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma virus |
| LC3B | Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta |
| MDC | Monodansylcadaverine |
| MFI | Median fluorescence intensity |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MTT | Thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide |
| PAK | p21-activated kinase |
| PC | Pancreatic Cancer |
| PDA | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| PDL1 | Programmed death ligand 1 |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl-sulfate |
| SMAD | Suppressor of mothers against decapentaplegic |
| SQSTM1 | Sequestosome 1 |
| TP53 | Tumor protein p53 |
| WT | Wild-type |
References
- AIHW. Cancer in Australia 2019; Cancer Series; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2019; Volume 119, Cat. no. CAN 123. [Google Scholar]
- Burris, H.A., 3rd; Moore, M.J.; Andersen, J.; Green, M.R.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Modiano, M.R.; Cripps, M.C.; Portenoy, R.K.; Storniolo, A.M.; Tarassoff, P.; et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ma, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouche, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Becouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitra, A.; Hruban, R.H. Pancreatic cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2008, 3, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, A.P.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. p-21 activated kinase 4 promotes proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells through AKT- and ERK-dependent activation of NF-kappaB pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8778–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.M.; Li, Y.; Muqbil, I.; Aboukameel, A.; Senapedis, W.; Baloglu, E.; Landesman, Y.; Philip, P.A.; Azmi, A.S. Targeting Rho GTPase effector p21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) suppresses p-Bad-microRNA drug resistance axis leading to inhibition of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma proliferation. Small GTPases 2019, 10, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.; Thillai, K.; Whale, A.; Arumugam, P.; Eldaly, H.; Kocher, H.M.; Wells, C.M. PAK4 interacts with p85 alpha: Implications for pancreatic cancer cell migration. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.U.; Kim, J.W.; Sung, J.H.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, S.H.; Chang, H.; Lee, J.O.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; et al. p21-Activated Kinase 4 (PAK4) as a Predictive Marker of Gemcitabine Sensitivity in Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Marimuthu, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, A.P.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. p-21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) maintains stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamska, A.; Elaskalani, O.; Emmanouilidi, A.; Kim, M.; Abdol Razak, N.B.; Metharom, P.; Falasca, M. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2018, 68, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Torrejon, D.Y.; Karin, D.; Campbell, K.M.; Medina, E.; Saco, J.D.; Galvez, M.; Champhekar, A.S.; Perez-Garcilazo, I.; Baselga-Carretero, I.; et al. Remodeling of the tumor microenvironment through PAK4 inhibition sensitizes tumors to immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Torrejon, D.Y.; Liu, W.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Nowicki, T.S.; Tsoi, J.; Puig-Saus, C.; Baselga-Carretero, I.; Medina, E.; Quist, M.J.; et al. PAK4 inhibition improves PD-1 blockade immunotherapy. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; You, S.; Wang, Y.; Tamukong, P.; Quist, M.J.; Grasso, C.S.; Kim, H.L. PAK4 inhibition improves PD1 blockade immunotherapy in prostate cancer by increasing immune infiltration. Cancer Lett. 2023, 555, 216034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuka, D.; Tachinami, H.; Suzuki, N.; Yamazaki, M.; Yonesi, A.; Takaichi, M.; Imaue, S.; Yamada, S.I.; Tanuma, J.I.; Noguchi, M.; et al. PAK4 inhibition augments anti-tumour effect by immunomodulation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dumesny, C.; Dong, L.; Ang, C.S.; Asadi, K.; Zhan, Y.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. Inhibition of P21-activated kinases 1 and 4 synergistically suppresses the growth of pancreatic cancer by stimulating anti-tumour immunity. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Dorsey, J.F.; Binder, Z.A.; O’Rourke, D.M.; et al. Targeting PAK4 to reprogram the vascular microenvironment and improve CAR-T immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Nature Cancer 2021, 2, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Qiu, Y.; Fitzsimonds, Z.R.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Lei, Y.L. Immune escape of head and neck cancer mediated by the impaired MHC-I antigen presentation pathway. Oncogene 2024, 43, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Venida, A.; Yano, J.; Biancur, D.E.; Kakiuchi, M.; Gupta, S.; Sohn, A.S.W.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Lin, E.Y.; Parker, S.J.; et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I. Nature 2020, 581, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauthe, M.; Orhon, I.; Rocchi, C.; Zhou, X.; Luhr, M.; Hijlkema, K.J.; Coppes, R.P.; Engedal, N.; Mari, M.; Reggiori, F. Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1435–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, W.J.; Ye, Y.C.; Ling, Y.Q.; Dai, Y.F. PAK4-relevant proliferation reduced by cell autophagy via p53/mTOR/p-AKT signaling. Transl. Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. The trilogy of P21 activated kinase, autophagy and immune evasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2022, 548, 215868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Dumesny, C.; Ang, C.S.; Dong, L.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, J.; Nikfarjam, M. A novel PAK4 inhibitor suppresses pancreatic cancer growth and enhances the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 16, 101329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewirtz, D.A. The four faces of autophagy: Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Vaux, D.L. Glucocorticoids can induce BIM to trigger apoptosis in the absence of BAX and BAK1. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Gorodkin, J.; Jensen, L.J. Cytoscape StringApp: Network Analysis and Visualization of Proteomics Data. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stifter, K.; Krieger, J.; Ruths, L.; Gout, J.; Mulaw, M.; Lechel, A.; Kleger, A.; Seufferlein, T.; Wagner, M.; Schirmbeck, R. IFN-gamma treatment protocol for MHC-I(lo)/PD-L1(+) pancreatic tumor cells selectively restores their TAP-mediated presentation competence and CD8 T-cell priming potential. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdel-Aziz, A.K.; Abdelfatah, S.; Abdellatif, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abel, S.; Abeliovich, H.; Abildgaard, M.H.; Abudu, Y.P.; Acevedo-Arozena, A.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition). Autophagy 2021, 17, 1–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugan, S.; Amaravadi, R.K. Methods for Studying Autophagy Within the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 899, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munafo, D.B.; Colombo, M.I. A novel assay to study autophagy: Regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino acid deprivation. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3619–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Shukla, N.; Singh, S.S.; Kushwaha, S.; Shrivastava, R. Mechanism of interaction between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Gruta, N.L.; Gras, S.; Daley, S.R.; Thomas, P.G.; Rossjohn, J. Understanding the drivers of MHC restriction of T cell receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleeiro, R.B.; Bouwens, C.J.; Liu, P.; Di Gioia, C.; Dunmall, L.S.C.; Nagano, A.; Gangeswaran, R.; Chelala, C.; Kocher, H.M.; Lemoine, N.R.; et al. MHC class II molecules on pancreatic cancer cells indicate a potential for neo-antigen-based immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2080329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamarsheh, S.; Gross, O.; Brummer, T.; Zeiser, R. Immune modulatory effects of oncogenic KRAS in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Gradiz, R.; Silva, H.C.; Carvalho, L.; Botelho, M.F.; Mota-Pinto, A. MIA PaCa-2 and PANC-1—Pancreas ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines with neuroendocrine differentiation and somatostatin receptors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, B.; Jian, Y.; Yao, C.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Feng, X.; An, J.; et al. Development of a PAK4-targeting PROTAC for renal carcinoma therapy: Concurrent inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and enhancement of immune cell response. EBioMedicine 2024, 104, 105162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Dumesny, C.; Dong, L.; Ang, C.-S.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. Knockout of p21-Activated Kinase 4 Stimulates MHC I Expression of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via an Autophagy-Independent Pathway. Cancers 2025, 17, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030511
Ma Y, Dumesny C, Dong L, Ang C-S, Nikfarjam M, He H. Knockout of p21-Activated Kinase 4 Stimulates MHC I Expression of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via an Autophagy-Independent Pathway. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030511
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yi, Chelsea Dumesny, Li Dong, Ching-Seng Ang, Mehrdad Nikfarjam, and Hong He. 2025. "Knockout of p21-Activated Kinase 4 Stimulates MHC I Expression of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via an Autophagy-Independent Pathway" Cancers 17, no. 3: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030511
APA StyleMa, Y., Dumesny, C., Dong, L., Ang, C.-S., Nikfarjam, M., & He, H. (2025). Knockout of p21-Activated Kinase 4 Stimulates MHC I Expression of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via an Autophagy-Independent Pathway. Cancers, 17(3), 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030511





