Molecular Characterization of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using EGFR, CDKN2A, and HRAS Alterations
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples and Ethical Approval
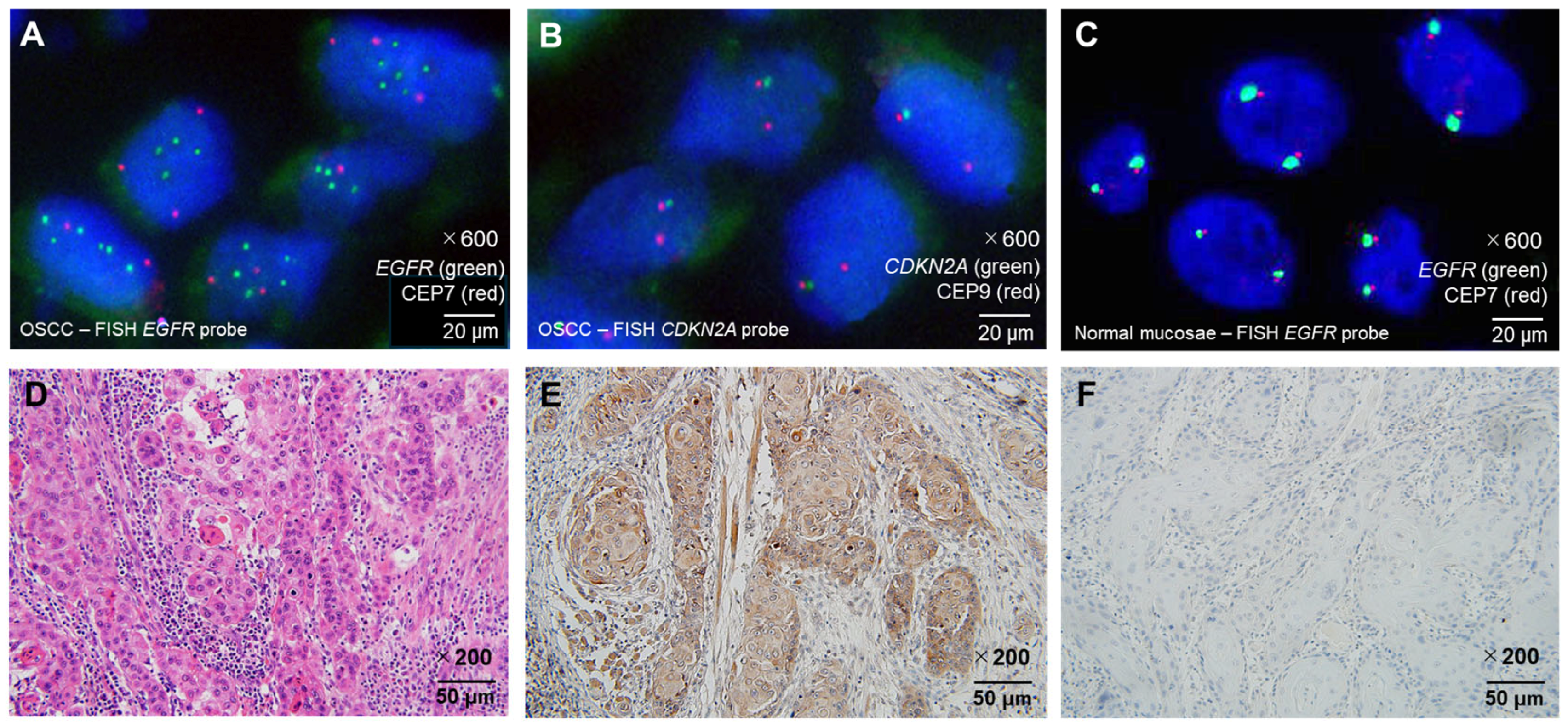
2.2. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
2.3. HRAS IHC in EGFR-Negative OSCC
2.4. Statistical Analysis
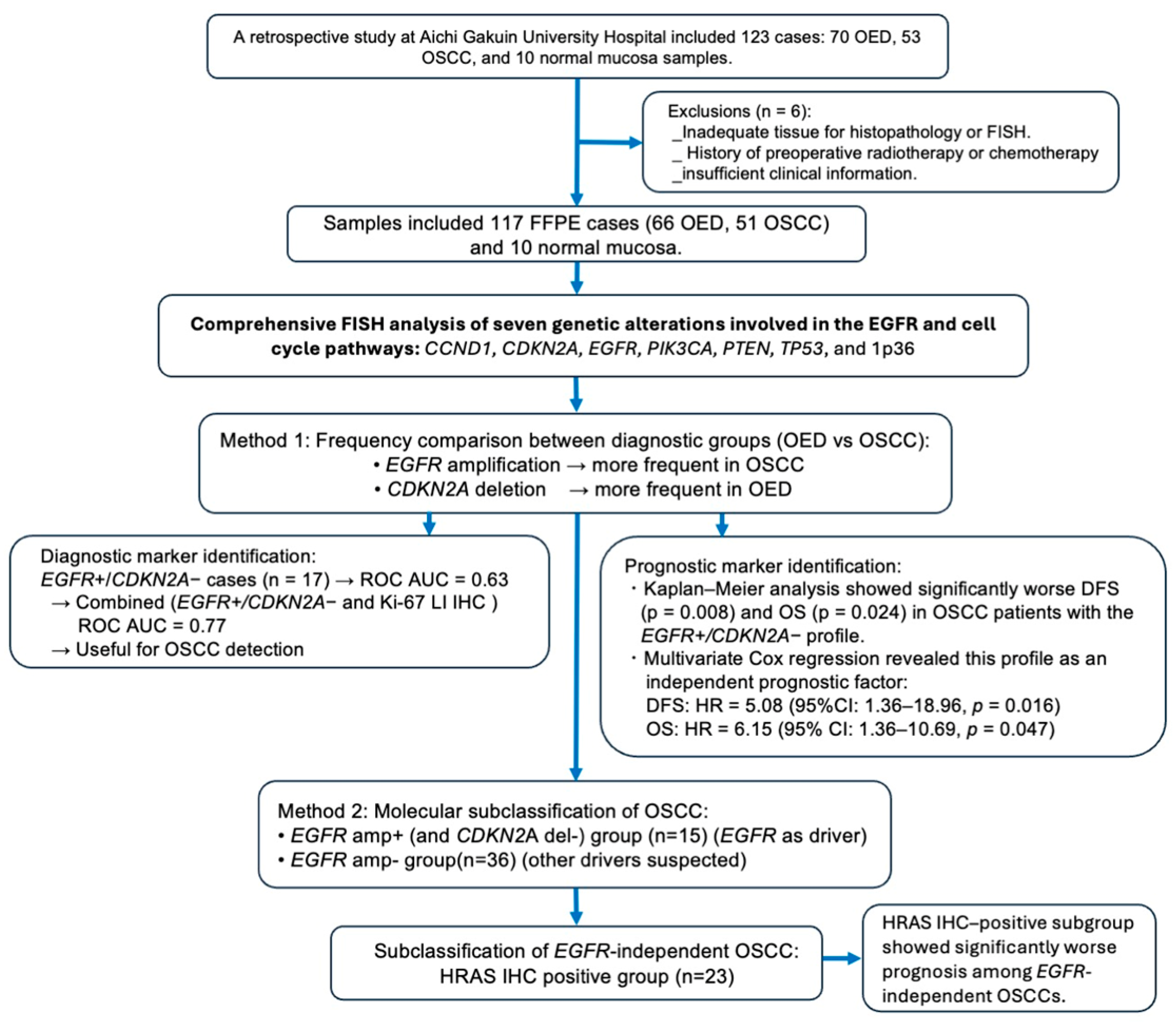
3. Results
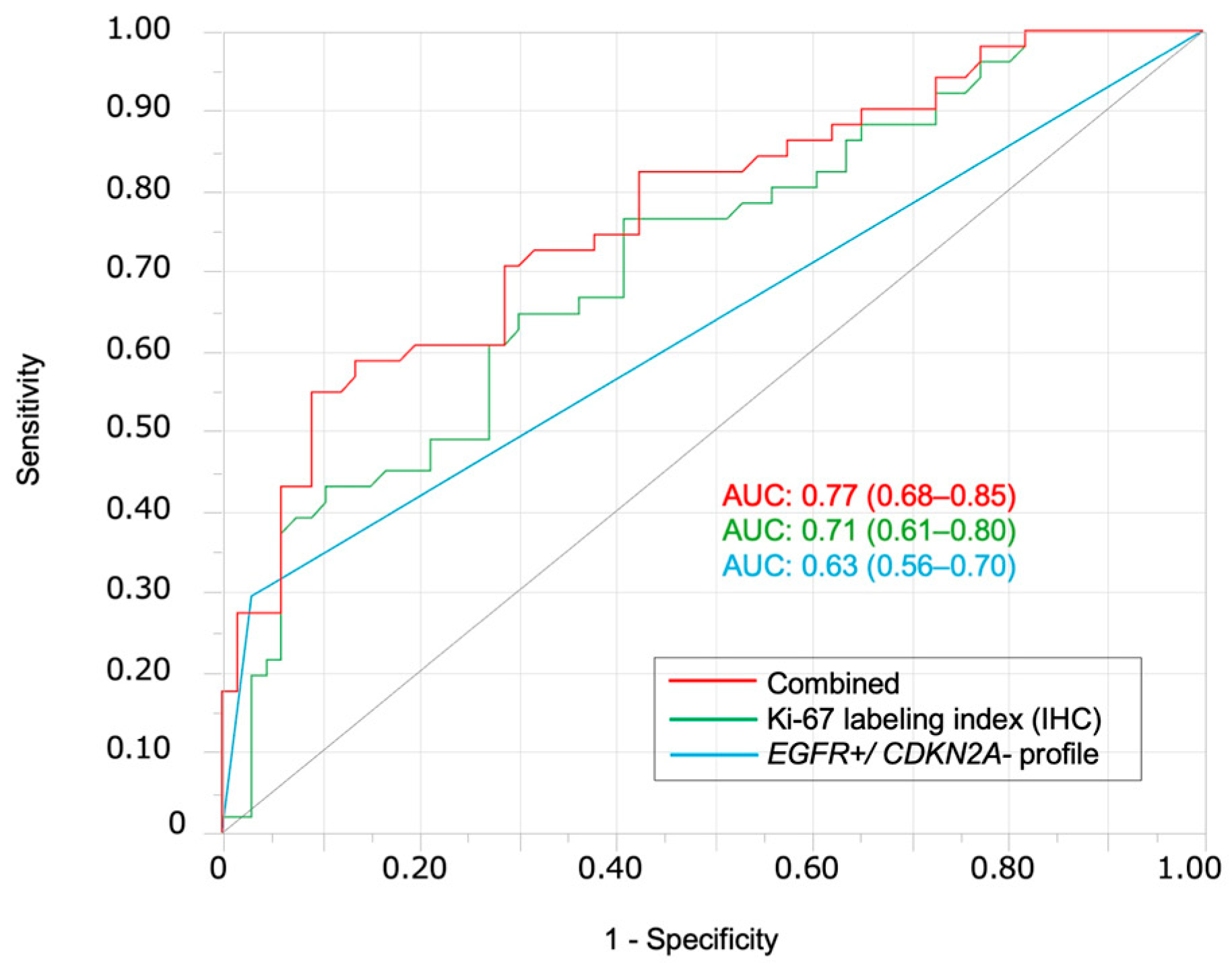
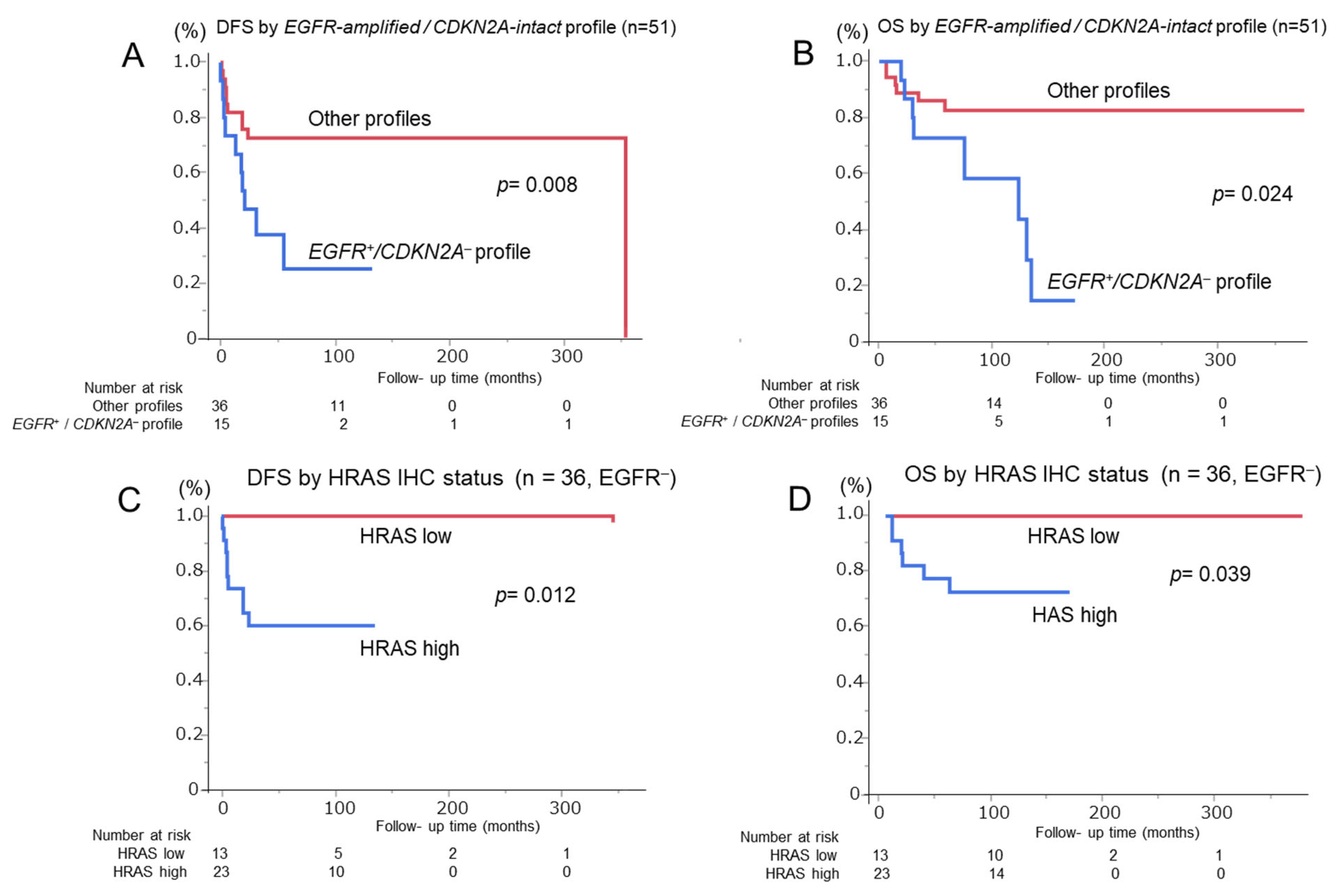
3.1. FISH Analysis of EGFR amp/CDKN2A Intact Profile for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Patients with OSCC
3.2. Prognostic Impact of HRAS Expression in EGFR-Negative OSCC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| HE | Hematoxylin–eosin |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| OED | Oral epithelial dysplasia |
| OS | Overall survival |
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
References
- Tan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, M.; Li, B.; Huang, Z.; Qin, S.; Nice, E.C.; Tang, J.; Huang, C. Oral squamous cell carcinomas: State of the field and emerging directions. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.S.; Li, H.P.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, Y.T.; Yi-Feng Chang, I.Y.K.; Chung, A.K.; Huang, Y.; Ueng, S.H.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Chien, K.Y.; et al. Integrated multi-omics analyses of oral squamous cell carcinoma reveal precision patient stratification and personalized treatment strategies. Cancer Lett. 2025, 614, 217482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davaatsend, O.; Altannamar, M.; Batbayar, B.; Jagdagsuren, U. Factors influencing the 5-year survival rate of oral cancer patients in the Mongolian population: A retrospective cohort study. Front. Oral Health 2023, 4, 1292720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hakami, H.A.; Al-Talhi, A.A.; AlRajhi, B.; Alshareef, M.A.; Awad, B.I.; Hussain, T.; Al-Garni, M. Oncological outcomes, survival analysis, and failure patterns in patients with resectable squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue treated with glossectomy. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2025, 41, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Lafuente-Ibáñez de Mendoza, I.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: Systematic review and meta-analysis of the last 5 years. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Ariyawardana, A. Malignant transformation of oral leukoplakia: A systematic review of observational studies. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellonen, R.; Suominen, A.; Kelppe, J.; Willberg, J.; Rautava, J.; Laine, H. Histopathological findings of oral epithelial dysplasias and their relation to malignant transformation. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2023, 34, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, M.R.; Hwang, J.T.K.; Dickson, B.J.; Cutz, J.C.; Salama, S.; McCord, C.; Pritzker, K.P.H.; Mock, D.; Thompson, L.D.R. Assessing oral epithelial dysplasia risk for transformation to cancer: Comparison between histologic grading systems versus S100A7 immunohistochemical signature-based grading. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2023, 31, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.; Rocha, E.; Ferreira, S.; Salazar, F.; Pacheco, J.J.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Tissue biomarkers for predicting the risk of oral cancer in patients diagnosed with oral leukoplakia: A systematic review of the past 4 years. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2025, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, K.; Feng, A.L.; Franco, R.A.; Varvares, M.A.; Faquin, W.C.; Naunheim, M.R.; Saladi, S.V. Molecular biomarkers of malignant transformation in head and neck dysplasia. Cancers 2022, 14, 5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Ye, J.; Dong, Z.; Hu, S.; Xiao, M. Novel genetic alterations and their impact on target therapy response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1321–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.Y.F.; Tseng, C.H.; Lu, P.H.; Wang, Y.P. Contemporary molecular analyses of malignant tumors for precision treatment and the implication in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Tie, Y.; Alu, A.; Ma, X.; Shi, H. Targeted therapy for head and neck cancer: Signaling pathways and clinical studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard-Sandu, C.; Tao, Y.G.; Sablin, M.P.; Dumitrescu, G.; Billard, D.; Deutsch, E. CDK4/6 inhibitors in P16/HPV16-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.J.; Ko, A.; Kil, S.H.; Mallen-St Clair, J.; Shin, D.S.; Wang, M.B.; Srivatsan, E.S. EGFR pathway targeting drugs in head and neck cancer in the era of immunotherapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2023, 1878, 188827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, L.G.S.; Martins, I.M.; Paulo, E.P.A.; Pomini, K.T.; Poyet, J.L.; Maria, D.A. Molecular mechanisms in the carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma: A literature review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barem Rabenhorst, S.H.; Lima Verde Osterne, R.; Weege Nonaka, C.F.; Montezuma Sales Rodrigues, A.; Luiz Maia Nogueira, R.; Mário Rodriguez Burbano, R.; Barroso Cavalcante, R. Detection of deletions in 1q25, 1p36 and 1pTEL and chromosome 17 aneuploidy in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Oral Oncol. 2021, 116, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lai, J.C.; Li, Y.; Tang, C.; Lu, J.; Han, M.; Ye, X.; Jia, L.; Cui, W.; Yang, J.; et al. Loss of CDKN2A enhances the efficacy of immunotherapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2025, 85, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, I.A.; Hood, F.E.; Hartley, J.L. The frequency of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, N.; Urata, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Ebata, R.; Matsumoto, H.; Hibi, H. Mutational landscape of Japanese patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma from comprehensive genomic profiling tests. Oral Oncol. 2024, 159, 107079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidavi Asl, A.; Shirkhoda, M.; Saffar, H.; Allameh, A. Analysis of H-ras mutations and immunohistochemistry in recurrence cases of high-grade oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck Pathol. 2023, 17, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Head and Neck Tumours. WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022.
- Fukumura, M.; Ishibashi, K.; Nakaguro, M.; Nagao, T.; Saida, K.; Urano, M.; Tanigawa, M.; Hirai, H.; Yagyuu, T.; Kikuchi, K.; et al. Salivary gland polymorphous adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathological features and gene alterations in 36 Japanese patients. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, H.; Bradburn, M.; Rajpoot, N.; Islam, N.M.; Kujan, O.; Khurram, S.A. Prediction of malignant transformation and recurrence of oral epithelial dysplasia using architectural and cytological feature specific prognostic models. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Histological grading of oral epithelial dysplasia: Revisited. J. Pathol. 2001, 194, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäwert, F.; Fehr, A.; Öhman, J.; Stenman, G.; Kjeller, G. Recurrent copy number alterations involving EGFR, CDKN2A, and CCND1 in oral premalignant lesions. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2022, 51, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.J.C.; Hua, C.H.; Wan, L.; Lin, Y.J.; Lai, M.T.; Tseng, H.C.; Jinawath, N.; Tsai, M.H.; Chang, N.W.; Lin, C.F.; et al. Functional genomic analysis identified epidermal growth factor receptor activation as the most common genetic event in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2568–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnavaz, S.A.; Bradley, G.; Regezi, J.A.; Thakker, N.; Gao, L.; Hogg, D.; Jordan, R.C. Patterns of CDKN2A gene loss in sequential oral epithelial dysplasias and carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2371–2375. [Google Scholar]
- Fiala, C.; Diamandis, E.P. Mutations in normal tissues—Some diagnostic and clinical implications. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Risques, R.A. Cancer-associated mutations but no cancer: Insights into the early steps of carcinogenesis and implications for early cancer detection. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, L.; Delgado, L.; Amaral, B.; Ricardo, S.; Fraga, M.; Lopes, C.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Occludin and claudin-1 are potential prognostic biomarkers in patients with oral squamous cell carcinomas: An observational study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2022, 134, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyo, M.; Li, R.J.; Bettegowda, C.; Pickering, C.R.; Frederick, M.J.; Myers, J.N.; Agrawal, N. Lessons learned from next-generation sequencing in head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2013, 35, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S.; Kuribayashi, N.; Goda, H.; Nakashiro, K.I.; Uchida, D. Oral cancer driver gene mutations in oral potentially malignant disorders: Clinical significance and diagnostic implications. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, J.; van der Riet, P.; Westra, W.; Nawroz, H.; Clayman, G.; Piantadosi, S.; Corio, R.; Lee, D.; Greenberg, B.; Koch, W.; et al. Genetic progression model for head and neck cancer: Implications for field cancerization. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2488–2492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rane, J.K.; Frankell, A.M.; Weeden, C.E.; Swanton, C. Clonal evolution in healthy and premalignant tissues: Implications for early cancer interception strategies. Cancer Prev. Res. 2023, 16, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.; Lesluyes, T.; Baker, T.M.; Tarabichi, M.; Gillenwater, A.; Wang, J.R.; Van Loo, P.; Zhao, X. Reconstructing oral cavity tumor evolution through brush biopsy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorno-Farias, D.; Santos, J.N.D.; González-Arriagada, W.; Tarquinio, S.; Santibáñez Palominos, R.A.; Martín Martín, A.J.M.; Fernandez-Ramires, R. Whole-exome sequencing of oral epithelial dysplasia samples reveals an association with new genes. Braz. Oral Res. 2023, 37, e016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H.; Li, J.; Steuer, C.E.; Bhateja, P.; Johnson, M.; Masannat, J.; Poole, M.I.; Song, F.; Hernandez-Prera, J.C.; Molina, H.; et al. Phase II multi-institutional clinical trial result of concurrent cetuximab and nivolumab in recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.F.; Cheng, S.D.; Chien, H.T.; Liao, C.T.; Chen, I.H.; Wang, H.M.; Chuang, W.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Hsieh, L.L. Relationship between epidermal growth factor receptor gene copy number and protein expression in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranath, D.; Chang, S.E.; Bhoite, L.T.; Panchal, R.G.; Kerr, I.B.; Mehta, A.R.; Johnson, N.W.; Deo, M.G. High frequency mutation in codons 12 and 61 of H-ras oncogene in chewing tobacco-related human oral carcinoma in India. Br. J. Cancer 1991, 63, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Dwivedi, R.; Sankar, R.; Jain, A.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, S. Unraveling the genetic web: H-Ras expression and mutation in oral squamous cell carcinoma—A systematic review. Head Neck Pathol. 2024, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, P.; Cristea, S.; Beerenwinkel, N. Clonal evolution driven by superdriver mutations. BMC Evol. Biol. 2020, 20, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Xi, Y.; Lu, M.; Zou, X.; Chen, W. A novel molecular classification system for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Predicting treatment response and metastatic potential through multi-omics analysis. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhosale, P.G.; Cristea, S.; Ambatipudi, S.; Desai, R.S.; Kumar, R.; Patil, A.; Kane, S.; Borges, A.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Beerenwinkel, N.; et al. Chromosomal alterations and gene expression changes associated with the progression of leukoplakia to advanced gingivobuccal cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.; Kaigala, G.V. Rapid micro fluorescence in situ hybridization in tissue sections. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 042212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelhűbel, G.A.; Cserepes, M.; Szabó, B.; Türk, D.; Kárpáti, A.; Kenessey, I.; Rásó, E.; Barbai, T.; Hegedűs, Z.; László, V.; et al. EGFR alterations influence the cetuximab treatment response and c-MET tyrosine-kinase inhibitor sensitivity in experimental head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 620256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, B.S. Immunohistochemistry as a practical tool in molecular pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.; Ofek, E.; Fridrich, D.E.; Molchanov, Y.; Yacobi, R.; Gazy, I.; Hayun, I.; Zalach, J.; Paz-Yaacov, N.; Barshack, I. Direct identification of ALK and ROS1 fusions in non-small cell lung cancer from hematoxylin and eosin-stained slides using deep learning algorithms. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
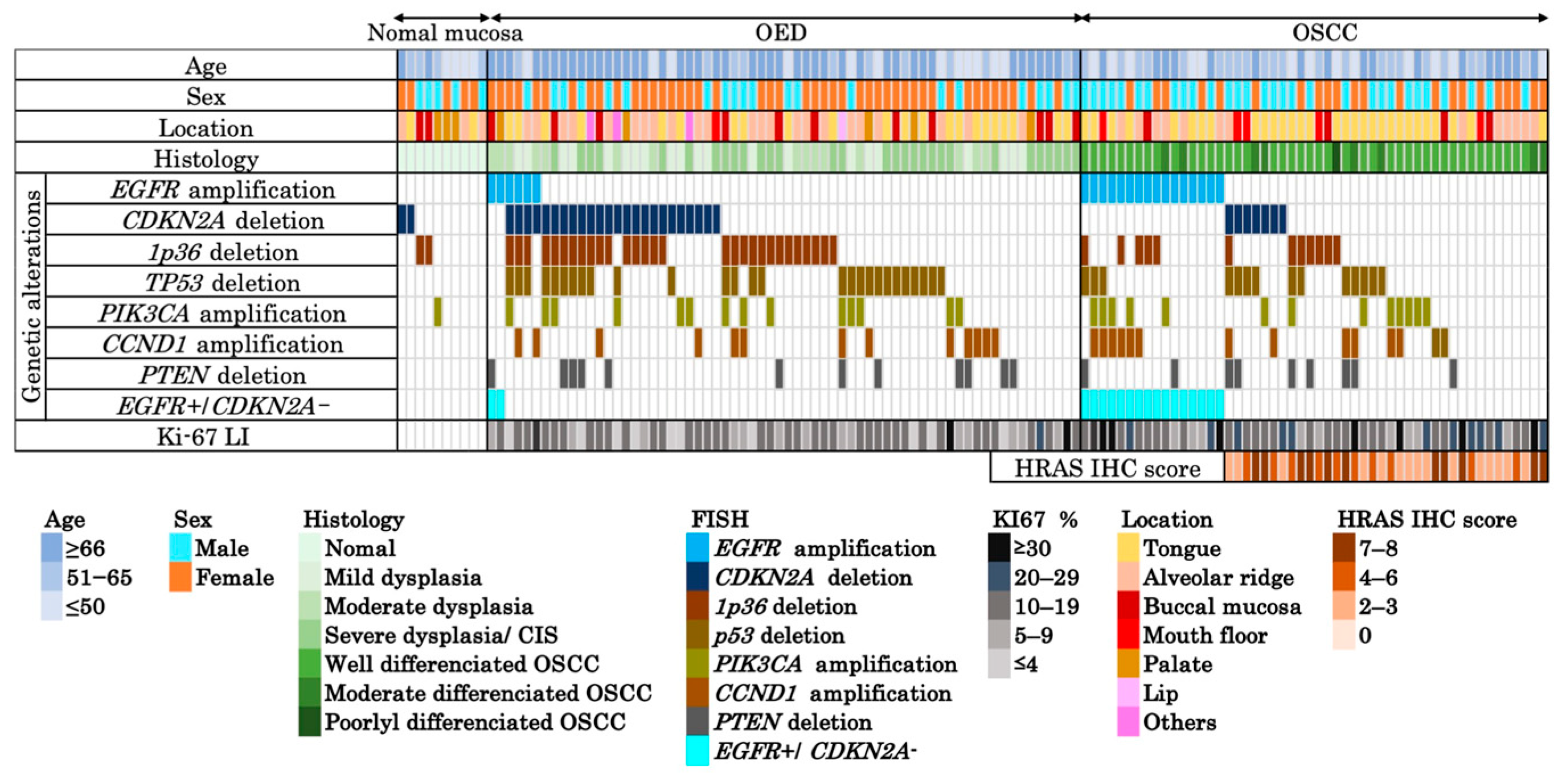
| Parameters | Normal Mucosa (n = 10) (%) | OED (n = 66) (%) | OSCC (n = 51) (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 5 (50.0) | 21 (31.8) | 29 (56.9) |
| Female | 5 (50.0) | 45 (68.2) | 22 (43.1) | |
| Age (y) | Average (range) | 57.0 (36–87) | 69.9 (25–97) | 58.9 (26–88) |
| Anatomical site | Tongue | 2 (20.0) | 22 (33.3) | 30 (58.8) |
| Gingiva | 3 (30.0) | 23 (34.8) | 12 (23.5) | |
| Buccal mucosa | 2 (20.0) | 11 (16.7) | 4 (7.9) | |
| Mouth floor | 0 | 1 (1.5) | 5 (9.8) | |
| Palate | 3 (30.0) | 5 (7.6) | 0 (0) | |
| Lip | 0 | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0) | |
| Others | 0 | 3 (4.6) | 0 (0) | |
| Epithelial dysplasia | Mild | - | 21 (31.8) | - |
| Moderate | - | 14 (21.2) | - | |
| Severe/CIS | - | 31 (47.0) | - | |
| Histopathological grade | Well differentiated | - | - | 42 (82.3) |
| Moderately differentiated | - | - | 8 (15.7) | |
| Poorly differentiated | - | - | 1 (1.9) | |
| Pathological tumor stage | T1 | - | - | 20 (39.2) |
| T2 | - | - | 23 (45.1) | |
| T3 | - | - | 3 (5.9) | |
| T4a | - | - | 5 (9.8) | |
| T4b | - | - | 0 (0) | |
| Pathological nodal stage | N0 | - | - | 33 (64.7) |
| N1 | - | - | 9 (17.6) | |
| N2a | - | - | 0 (0) | |
| N2b | - | - | 8 (15.7) | |
| N2c | - | - | 1 (2.0) | |
| N3 | - | - | 0 (0) | |
| Neck dissection | Not performed | - | - | 29 (56.9) |
| performed | - | - | 22 (43.1) | |
| Clinical TNM stage | I | - | - | 17 (33.3) |
| II | - | - | 12 (23.5) | |
| III | - | - | 9 (17.7) | |
| IV | - | - | 13 (25.5) | |
| Ki-67 index | Average | - | 12.48 (1–37.8) | 18.23 (5.2–38.7) |
| CCND1 amplification | Negative | 10 (100.0) | 53 (80.3) | 38 (74.5) |
| Positive | 0 (0) | 13 (19.7) | 13 (25.5) | |
| CDKN2A deletion | Negative | 8 (80.0) | 42 (63.6) | 44(86.3) |
| Positive | 2 (20.0) | 24 (36.4) | 7(13.7) | |
| EGFR amplification | Negative | 10 (100.0) | 60 (91.0) | 36 (70.6) |
| Positive | 0 (0) | 6 (9.0) | 15 (29.4) | |
| PIK3CA amplification | Negative | 9 (90.0) | 52 (78.8) | 38 (74.5) |
| Positive | 1 (10.0) | 14 (21.2) | 13 (25.5) | |
| PTEN deletion | Negative | 10 (100.0) | 54 (81.8) | 42 (82.4) |
| Positive | 0 (0) | 12 (18.2) | 9 (17.6) | |
| TP53 deletion | Negative | 10 (100.0) | 39 (59.1) | 37 (72.5) |
| Positive | 0 (0) | 27 (40.9) | 14 (27.5) | |
| 1p36 deletion | Negative | 8(80.0) | 37 (56.1) | 40 (78.4) |
| Positive | 2 (20.0) | 29 (43.9) | 11 (21.6) |
| Parameters | OED (n = 66) (%) | OSCC (n = 51) (%) | Univariate OR (95% CI) | Univariate p | Multivariate OR (95% CI) | Multivariate p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDKN2A gene deletion | 24 (36.4) | 7 (13.7) | 0.28 (0.11–0.71) | 0.006 | - | - |
| EGFR gene amplification | 6 (9.0) | 15 (29.4) | 4.17 (1.48–11.71) | 0.007 | - | - |
| EGFR amplification-positive/CDKN2A deletion-negative | 2 (3.0) | 15 (29.4) | 13.33 (2.88–61.63) | <0.0001 | 10.9 (2.73–74.21) | 0.0003 |
| 1p36 deletion | 29 (43.9) | 11 (21.6) | 0.35 (0.15–0.80) | 0.018 | 2.24 (0.90–5.86) | 0.081 |
| Ki-67 labeling index (%, mean) | 12.48 | 18.23 | 1.10 (1.04–1.16) | 0.001 | 1.08 (1.02–1.15) | 0.004 |
| DFS | OS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age (y) | ||||||||
| >60 | 2.13 (0.77–5.89) | 0.170 | 0.99 (0.28–3.64) | 0.980 | ||||
| ≤60 | ||||||||
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 0.72 (0.29–1.78) | 0.480 | 1.13 (0.39–3.30) | 0.820 | ||||
| Female | ||||||||
| Tumor site | ||||||||
| Tongue | 1.20 (0.47–3.06) | 0.700 | 0.53 (0.11–2.64) | 0.440 | ||||
| Others | ||||||||
| Tumor size (cm) | ||||||||
| T1–T2 | 1.61 (1.38–17.51) | 0.041 | 0.45 (0.12–1.67) | 0.23 | 2.23 (1.81–6.74) | 0.017 | 0.49 (0.07–3.24) | 0.190 |
| T3–T4 | ||||||||
| Nodal status | ||||||||
| Positive | 4.10 (1.37–12.27) | 0.026 | 3.96 (1.05–15.02) | 0.004 | 3.81 (1.14–12.82) | 0.083 | ||
| Negative | ||||||||
| Histologic grade | 1.69 (0.39–7.37) | 0.320 | ||||||
| Well diff. | 12.81 (1.07–15.38) | 0.049 | 1.16 (0.27–4.94) | 0.280 | ||||
| Moderate + poorly diff. | ||||||||
| EGFR amplification-positive/CDKN2A deletion-negative | ||||||||
| Positive | 3.16 (1.28–7.83) | 0.014 | 5.08 (1.36–18.96) | 0.016 * | 3.20 (1.10–9.33) | 0.033 | 6.10 (1.36–10.69) | 0.047 † |
| Negative | ||||||||
| Clinical stage | ||||||||
| I, II | 4.11 (1.47–11.48) | 0.007 | 9.37 (2.11–41.66) | 0.006 * | 3.45 (1.94–12.71) | 0.043 | 2.93 (0.78–11.04) | 0.11 † |
| III, IV | ||||||||
| DFS | OS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univari ate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age (y) | ||||||||
| >60 | 2.22 (0.59–8.29) | 0.230 | 1.21 (0.30–7.4) | 0.620 | ||||
| ≤60 | ||||||||
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 0.22 (0.01–0.89) | 0.036 | 0.41 (0.08–2.02) | 0.066 | 0.40 (0.073–2.22) | 0.280 | ||
| Female | ||||||||
| Tumor site | ||||||||
| Tongue | 2.18 (0.59–8.14) | 0.250 | 0.53 (0.11–2.64) | 0.440 | ||||
| Others | ||||||||
| Tumor size (cm) | ||||||||
| T1–T2 | 0.34 (0.072–1.67) | 0.150 | 5.83 (1.06–32.0) | 0.035 | 3.12 (0.53–18.28) | 0.190 | ||
| T3–T4 | ||||||||
| Nodal status | ||||||||
| Positive | 17.4 (2.16–23.9) | <0.001 | 9.86 (1.22–79.60) | 0.006 | 8.64 (1.01–74.07) | 0.019 | 3.45 (0.38–31.35) | 0.220 |
| Negative | ||||||||
| Histologic grade | 0.40 (0.097–1.57) | 0.210 | 0.52 (0.095–2.85) | 0.470 | ||||
| Well diff. | ||||||||
| Moderate + poorly diff. | ||||||||
| HRAS IHC | ||||||||
| High | 3.22 (1.85–8.91) | 0.001 | 5.91 (1.09–19.63) | 0.022 * | 10.18 (1.78–12.91) | 0.017 | 6.15 (1.36–10.69) | 0.043 † |
| Low | ||||||||
| Clinical stage | ||||||||
| I, II | 3.05 (1.63–88.69) | 0.002 | 6.11 (1.66–49.15) | 0.035 * | 6.83 (2.79–58.53) | 0.038 | 3.18 (0.37–27.37) | 0.29 † |
| III, IV | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okubo, S.; Miyabe, S.; Fukumura, M.; Sasaki, J.; Fujii, H.; Terasawa, F.; Watanabe, S.; Okada, S.; Miyabe, M.; Miyabe, K.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using EGFR, CDKN2A, and HRAS Alterations. Cancers 2025, 17, 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243949
Okubo S, Miyabe S, Fukumura M, Sasaki J, Fujii H, Terasawa F, Watanabe S, Okada S, Miyabe M, Miyabe K, et al. Molecular Characterization of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using EGFR, CDKN2A, and HRAS Alterations. Cancers. 2025; 17(24):3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243949
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkubo, Satoshi, Satoru Miyabe, Masahiro Fukumura, Jun Sasaki, Hitoshi Fujii, Fumitaka Terasawa, Satoshi Watanabe, Soma Okada, Megumi Miyabe, Katsuyuki Miyabe, and et al. 2025. "Molecular Characterization of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using EGFR, CDKN2A, and HRAS Alterations" Cancers 17, no. 24: 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243949
APA StyleOkubo, S., Miyabe, S., Fukumura, M., Sasaki, J., Fujii, H., Terasawa, F., Watanabe, S., Okada, S., Miyabe, M., Miyabe, K., Sugita, Y., Maeda, H., Nakaya, S., Sakane, K., Yamada, S., Bhola, N., Warnakulasuriya, S., Nagao, T., & Goto, M. (2025). Molecular Characterization of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using EGFR, CDKN2A, and HRAS Alterations. Cancers, 17(24), 3949. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243949







