Specialist Neurology Involvement and Impact in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Neurotoxicity: Experience in a Unified Healthcare System
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
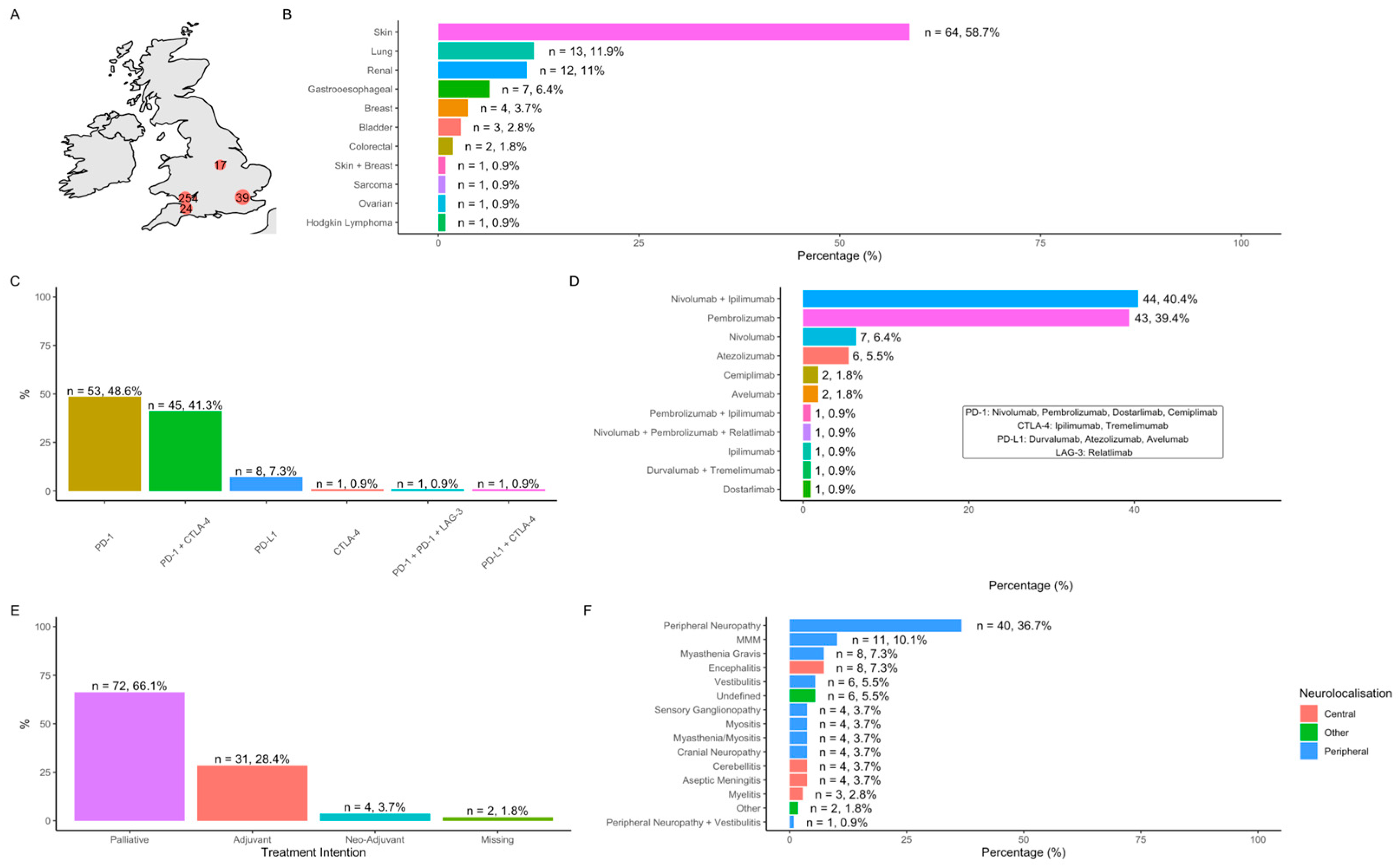
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
3.2. Neurological Immune-Related Adverse Events (N-irAEs)
3.2.1. Clinical Phenotypes
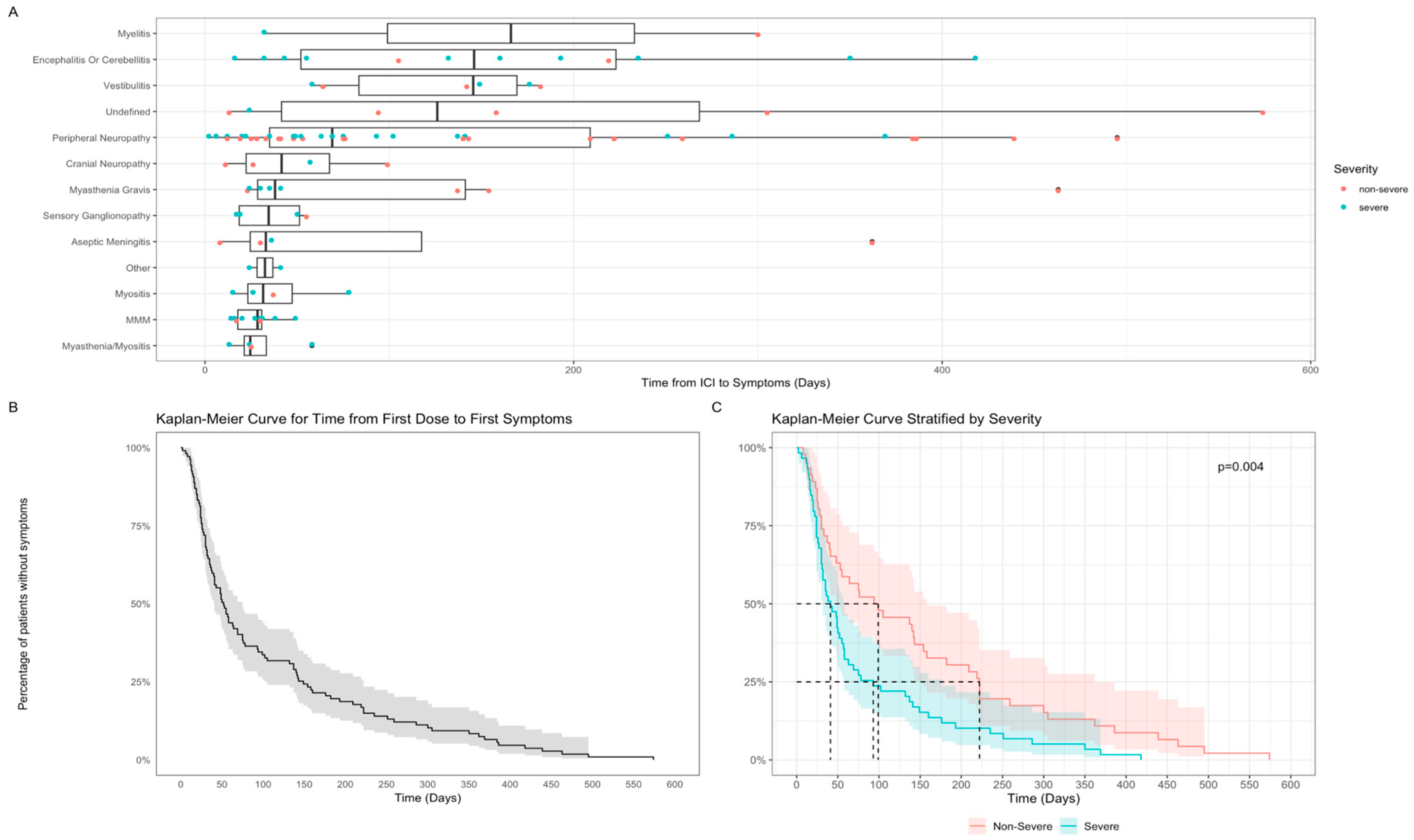
3.2.2. Time to N-irAE
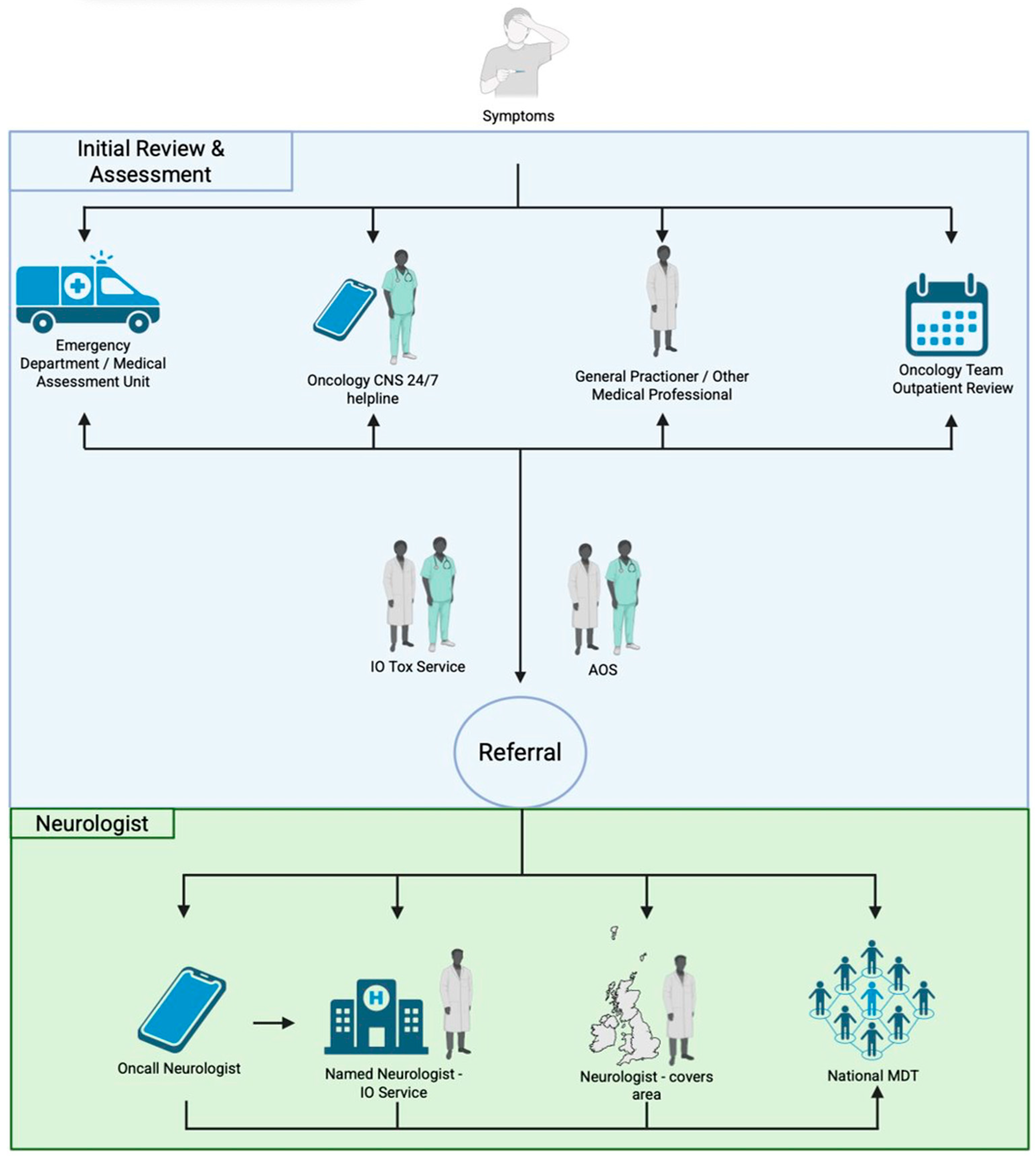
3.3. Neurology Service Models and Reasons for Referral
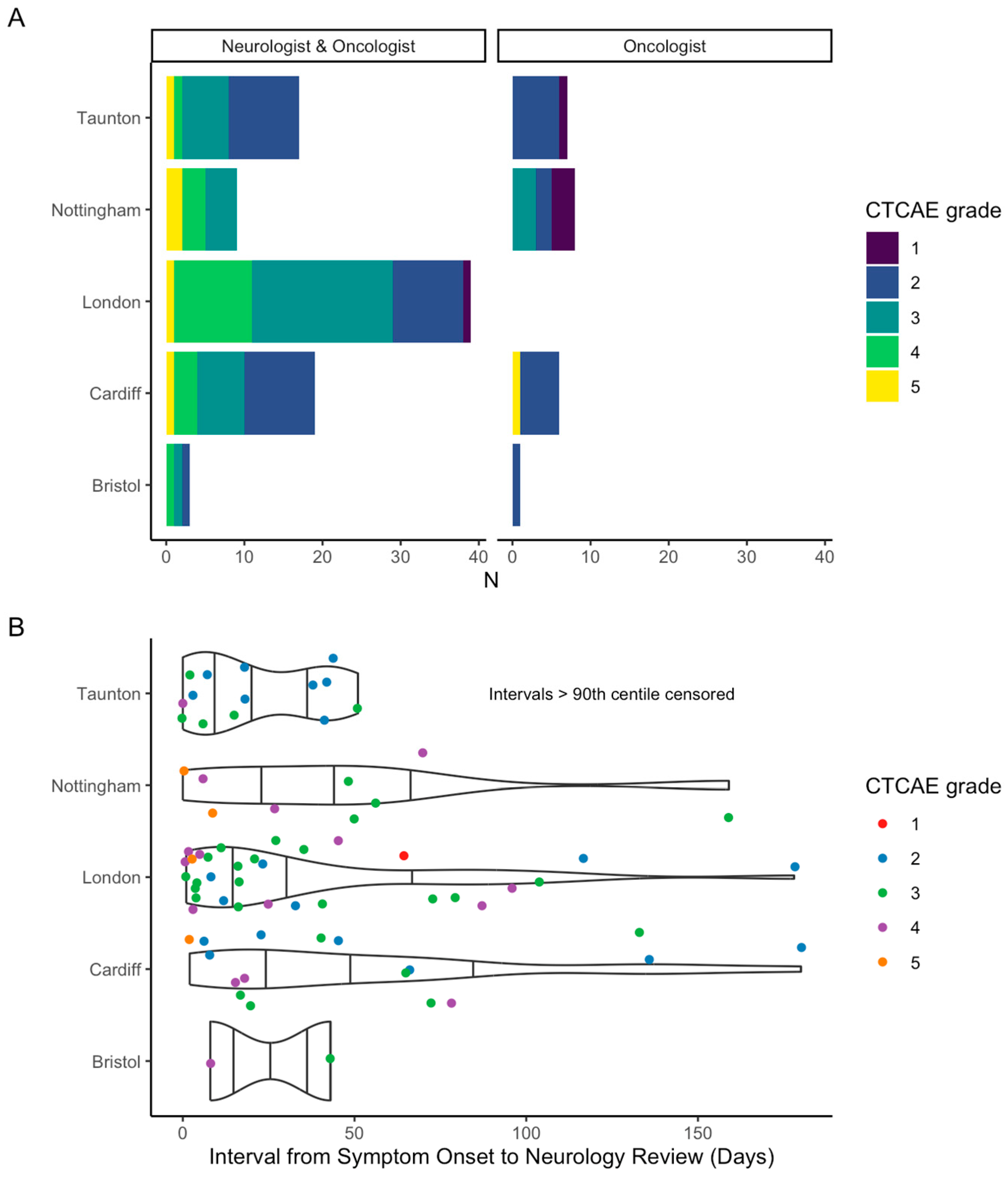
3.4. Specialist Neurology Involvement
3.4.1. Factors Associated with Neurology Involvement
3.4.2. Effect of Neurologist’s Involvement on Investigations and Diagnosis
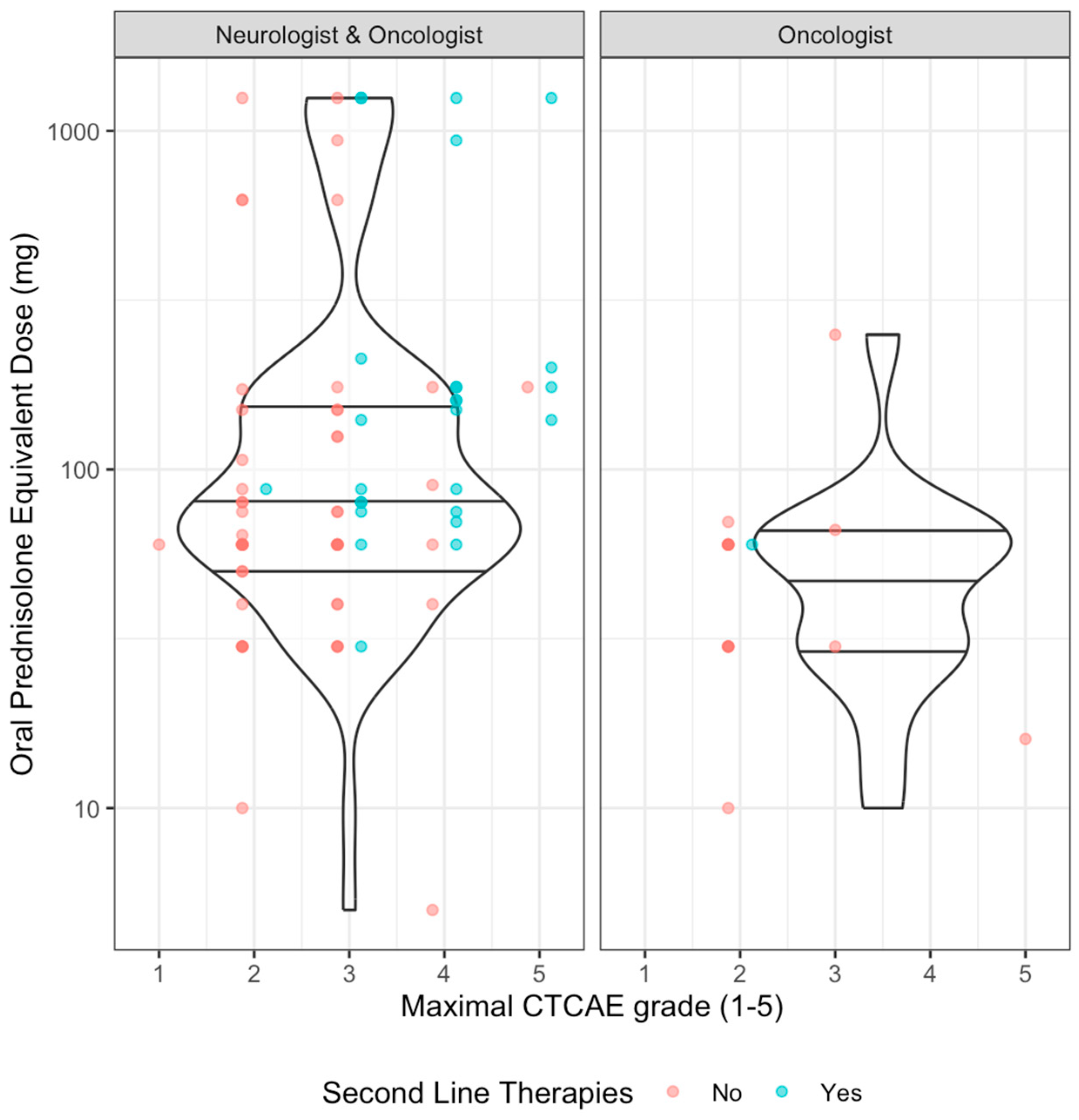
3.4.3. Effect of Neurologist’s Involvement on Clinical Management
3.4.4. Effect of Neurologist’s Involvement on Clinical Outcomes
3.4.5. Analysis of Immuno Oncology-Neurotoxicity Service
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Models of neurology services, reasons and rates of referral differ across the UK;
- Neurology opinion was associated with younger age and severity of neurotoxicity;
- Neurology opinion was universally sought for CNS toxicity (more than PNS) even though PNS complications were more common;
- Neurologists were more specific in their utilisation of investigations with a more diverse range of N-irAEs diagnoses with the added potential for identifying alternative diagnoses;
- Specialist second-line treatments were associated with neurology involvement.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, J.; Mitchell, A.P.; Kesselheim, A.S.; Rome, B.N. Overlapping and non-overlapping indications for checkpoint inhibitors in the US. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. 16), 11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, S.; Sopetto, G.B.; Bertalot, G.; Bortolotti, R.; Racanelli, V.; Caffo, O.; Giometto, B.; Berti, A.; Veccia, A. Immune-Related Adverse Events Due to Cancer Immunotherapy: Immune Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations. Cancers 2024, 16, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzzubbo, S.; Carpentier, A.F. Neurological adverse events of immune checkpoint blockade: From pathophysiology to treatment. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2022, 35, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, D.; David, W.S.; Reynolds, K.L.; Chute, D.F.; Clement, N.F.; Cohen, J.V.; Lawrence, D.P.; Morradian, M.J.; Sullivan, R.J.; Guidon, A.C. Severe Neurological Toxicity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Growing Spectrum. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Y.; Cohen, J.V.; Chandra, S.; Menzer, C.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S.; Das, S.; Beckermann, K.E.; Ha, L.; Rathmell, W.K.; et al. Fatal Toxic Effects Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, A.; Birzu, C.; Elsensohn, M.H.; Picca, A.; Muniz-Castrillo, S.; Vogrig, A.; Villagran-Garcia, M.; Ciano-Petersen, N.L.; Massacesi, L.; Hervier, B.; et al. Neurological outcomes in immune checkpoint inhibitor-related neurotoxicity. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, M.D.; Schroeder, B.; Marandino, L.; Turajlic, S.; Carr, A.S. Neurological immune-related adverse events with checkpoint inhibitor therapy: Challenges for the neurologist. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2025, 96, 1024–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, J.; Zhang, J.; Lipson, E.J.; Forde, P.M.; Suresh, K.; Moseley, K.F.; Mehta, S.; Kwatra, S.G.; Parian, A.M.; Kim, A.K.; et al. A Multidisciplinary Toxicity Team for Cancer Immunotherapy-Related Adverse Events. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 712–720. [Google Scholar]
- MDCalc. Available online: https://www.mdcalc.com/calc/2040/steroid-conversion-calculator (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- SERVICES_USDOHAH. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). Version 5.0; 2017. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Carr, A.S.; Vonberg, F.W.; Koay, S.; Young, K.; Shaw, H.; Olsson-Brown, A.; Willis, M. Neurological Complications of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Practical Guide. Pract. Neurol. 2025, 25, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Rutkowski, P.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Queirolo, P.; Dummer, R.; Butler, M.O.; Hill, A.G.; et al. Final, 10-year outcomes with nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, E.; Cabrera-Maqueda, J.M.; Ruiz-Garcia, R.; Naranjo, L.; Diaz-Pedroche, C.; Velasco, R.; Macias-Gomez, A.; Milisendra, J.C.; Munoz-Farjas, E.; Pascual-Goni, E.; et al. Neurological adverse events related to immune-checkpoint inhibitors in Spain: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haanen, J.; Obeid, M.; Spain, L.; Carbonnel, F.; Wang, Y.; Robert, C.; Lyon, A.R.; Wick, W.; Kostine, M.; Peters, S.; et al. Management of toxicities from immunotherapy: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Shawer, O.; Singh, P.; Yenulevich, E.; Brito, A.; Ni, J.; Abdulnour, R.E.E.; Grover, S.; Manos, M.; Bowling, P.; LeBoeuf, N.R.; et al. Novel platform leveraging electronic medical record (EMR) to triage patients admitted with high-grade immune-related adverse events (irAEs) to the immune-toxicity (ITOX) service. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubiri, L.; Molina, G.E.; Mooradian, M.J.; Cohen, J.; Durbin, S.M.; Petrillo, L.; Boland, G.M.; Juric, D.; Dougan, M.; Thomas, M.F.; et al. Effect of a multidisciplinary Severe Immunotherapy Complications Service on outcomes for patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy for cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Neurotoxicity | N | Age 1 | Sex (M) | ICI | Cancer | MRI | CSF | NeuroPhy | Management | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peripheral Neuropathy/Neuritis | 40 | 67 (58, 77) | 25 | PD-1: 39 PD-L1: 0 CTLA-4: 20 LAG-3: 1 | Skin: 28 GI: 5 Renal: 3 Lung: 3 Breast: 1 Other: 1 | Yes: 26 No: 13 | Yes: 13 No: 27 | Yes: 29 No: 11 | Steroids: 32 IVIg: 4 PLEX: 1 | Resolution: 12 * Recurrence: 3 * Rechallenge: 12 * |
| MMM | 11 | 77 (61, 81) | 9 | PD-1: 10 PD-L1: 1 CTLA-4: 3 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 8 Renal: 1 GI: 1 Bladder: 1 | Yes: 7 No: 4 | Yes: 0 No: 11 | Yes: 1 No: 10 | Steroids: 11 IVIg: 3 | Resolution: 2 * Recurrence: 0 Rechallenge: 1 * |
| Encephalitis or Cerebellitis | 12 | 64 (57, 73) | 5 | PD-1: 7 PD-L1: 1 CTLA-4: 2 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 5 Lung: 4 Renal: 2 Other: 1 | Yes: 12 | Yes: 10 No: 2 | Yes:1 No: 11 | Steroids: 11 IVIg: 1 PLEX: 4 | Resolution: 5 * Recurrence: 2 Rechallenge: 1 |
| Myasthenia Gravis (isolated) | 8 | 78 (63, 86) | 5 | PD-1: 6 PD-L1: 1 CTLA-4: 1 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 5 Renal: 1 Bladder: 1 CRC: 1 | Yes: 6 No: 2 | Yes: 0 No: 8 | Yes: 4 No: 4 | Steroid: 7 IVIg: 4 PLEX: 3 | Resolution: 4 Recurrence: 1 * Rechallenge: 0 |
| Vestibulitis | 6 | 63 (54, 67) | 3 | PD-1: 7 PD-L1: 1 CTLA-4: 4 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 3 Renal: 2 Lung: 1 | Yes: 6 | Yes: 1 No: 5 | Yes: 1 No: 5 | Steroid: 5 IVIg: 0 PLEX: 0 | Resolution: 1 Recurrence: 0 * Rechallenge: 0 |
| Unclear | 6 | 73 (61, 83) | 3 | PD-1: 4 PD-L1: 2 CTLA-4: 0 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 2 Lung: 2 Renal: 1 Breast: 1 | Yes: 5 No: 1 | Yes: 0 No: 6 | Yes: 2 No: 4 | Steroid: 6 IVIg: 0 PLEX: 0 | Resolution: * Recurrence: 2 Rechallenge: 2 |
| Sensory Ganglionopathy | 4 | 75 (66, 79) | 3 | PD-1: 4 PD-L1: 0 CTLA-4: 3 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 4 | Yes: 4 | Yes: 2 No: 2 | Yes: 4 | Steroid: 4 IVIg: 2 PLEX: 0 | Resolution: 1 Recurrence: 0 Rechallenge: 0 |
| Aseptic Meningitis | 4 | 50 (33, 60) | 1 | PD-1: 4 PD-L1: 0 CTLA-4: 3 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 3 GI: 1 | Yes: 4 | Yes: 3 No:1 | Yes: 0 No: 4 | Steroid: 4 IVIg: 0 PLEX: 0 | Resolution: 3 Recurrence: 1 Rechallenge: 1 |
| Cranial Neuropathy | 4 | 65 (50, 72) | 1 | PD-1: 3 PD-L1: 1 CTLA-4: 1 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 1 Breast: 2 Bladder: 1 | Yes: 3 No: 1 | Yes: 1 No: 3 | Yes: 0 No: 4 | Steroid: 4 IVIg: 0 PLEX: 0 | Resolution: 0 * Recurrence: 0 Rechallenge: 1 |
| Myasthenia Gravis and Myositis | 4 | 73 (70, 76) | 4 | PD-1: 4 PD-L1: 0 CTLA-4: 3 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 2 Lung: 2 | Yes: 2 No: 2 | Yes: 0 No: 4 | Yes: 3 No: 1 | Steroid: 4 IVIg: 2 PLEX: 1 | Resolution: 1 * Recurrence: 0 Rechallenge: 1 |
| Myositis | 4 | 85 (74, 88) | 2 | PD-1: 3 PD-L1: 1 CTLA-4: 1 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 2 Renal: 2 | Yes: 3 No: 1 | Yes: 0 No: 4 | Yes: 2 No: 2 | Steroid: 4 IVIg: 0 PLEX: 1 | Resolution: 2 * Recurrence: 0 Rechallenge: 4 |
| Myelitis | 3 | 76 (55, 77) | 1 | PD-1: 3 PD-L1: 0 CTLA-4: 0 LAG-3: 0 | Skin: 1 Lung: 1 CRC: 1 | Yes: 3 No: 0 | Yes: 3 No: 0 | Yes: 0 No: 3 | Steroid: 3 IVIg: 0 PLEX: 1 | Resolution: 0 Recurrence: 1 * Rechallenge: 0 |
| Other | 2 | 58 (55, 61) | 1 | PD-1: 1 PD-L1: 1 CTLA-4: 1 LAG-3: 0 | Breast: 1 Other: 1 | Yes: 2 No: 0 | Yes: 2 No: 0 | Yes: 1 No: 1 | Steroid: 2 IVIg: 1 PLEX: 1 | Resolution: 1 Recurrence: 1 * Rechallenge: 0 |
| Peripheral neuropathy and vestibulitis | 1 | 68.4 | 1 | PD-1: 1 | Skin: 1 | Yes: 1 | No: 1 | Yes: 1 | Steroid: 1 IVIg: 0 PLEX: 0 | Resolution: * Recurrence: 0 Rechallenge: 0 |
| Steroids | Steroid Dose (Median, Range) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | |
| Yes (n = 81) | Yes (n = 17) | |||
| Grade 1 | 1/1 (100%) | 0/4 (0%) | 1/1, 60 (60–60) | 0/0 |
| Grade 2 | 26/28 (92.9%) | 13/14 (92.9%) | 26/26, 60 (10–1240) | 12/13 60 (10–70) |
| Grade 3 | 31/35 (88.6%) | 3/3 (100%) | 30/31, 77.5 (30–1250) | 3/3 66.3 (30–250) |
| Grade 4 | 18/18 (100%) | 0/0 | 16/18, 120 (5–1250) | 0/0 |
| Grade 5 | 5/5 (100%) | 1/1 (100%) | 5/5, 175 (140–1250) | 1/1, 16 (16–16) |
| IVIg | PLEX | SSA/Biologic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | |
| Treatment received | N = 17 | N = 0 | N = 12 | N = 1 | N = 13 | N = 1 |
| Grade 1 | 0/1 | 0/4 | 0/1 | 0/4 | 0/1 | 0/4 |
| Grade 2 | 1/28 (3.6%) | 0/14 | 0/28 | 1/14 (7.1%) | 0/28 | 1/14 (7.1%) |
| Grade 3 | 5/35 (14.3%) | 0/3 | 2/35 (5.7%) | 0/3 | 8/35 (22.9%) | 0/3 |
| Grade 4 | 9/18 (50%) | 0/0 | 7/18 (38.9%) | 0/0 | 4/18 (22.2%) | 0/0 |
| Grade 5 | 2/5 (40%) | 0/1 | 3/5 (60%) | 0/1 | 1/5 (20%) | 0/1 |
| Resolution | Recurrence | Rechallenge | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | Neurologist and Oncologist (n = 87) | Oncologist only (n = 22) | |
| Data available | N = 70 (80.5%) | N = 15 (68.2%) | N = 77 (88.5%) | N = 17 (77.3%) | N = 85 (97.7%) | N = 21 (95.4%) |
| Grade 1 | 1/1 (1.4%, 100%) | 2/3 (13.3%, 50%) | 0/1 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 2/4 (9.5%, 50%) |
| Grade 2 | 10/19 (14.3%, 52.6%) | 4/8 (26.7%, 50%) | 2/27 (2.6%, 7.4%) | 2/12 (11.8%, 16.7%) | 3/27 (3.5%, 11.1%) | 8/13 (38.1%, 61.5%) |
| Grade 3 | 8/29 (11.4%, 27.6%) | 1/3 (6.7%, 33.3%) | 5/29 (6.5%, 17.2%) | 0/1 | 5/35 (5.9%, 14.3%) | 1/3 (4.8%, 33.3%) |
| Grade 4 | 6/17 (8.6%, 35.3%) | 0/0 | 2/17 (2.6%, 11.8%) | 0/0 | 1/17 (1.2%, 5.9%) | 0/0 |
| Grade 5 | 0/4 (0%, 0%) | 0/1 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 0/5 | 0/1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schroeder, B.; Prasad, P.; Gbadegesin, O.; Gupta, S.; Frazer, R.; Heaney, S.; Franks, H.; Blair, C.; Stuttard, M.; Barlow, C.; et al. Specialist Neurology Involvement and Impact in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Neurotoxicity: Experience in a Unified Healthcare System. Cancers 2025, 17, 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243935
Schroeder B, Prasad P, Gbadegesin O, Gupta S, Frazer R, Heaney S, Franks H, Blair C, Stuttard M, Barlow C, et al. Specialist Neurology Involvement and Impact in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Neurotoxicity: Experience in a Unified Healthcare System. Cancers. 2025; 17(24):3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243935
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchroeder, Benjamin, Prakrit Prasad, Ope Gbadegesin, Senjuti Gupta, Ricky Frazer, Smilla Heaney, Hester Franks, Cameron Blair, Matthew Stuttard, Clare Barlow, and et al. 2025. "Specialist Neurology Involvement and Impact in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Neurotoxicity: Experience in a Unified Healthcare System" Cancers 17, no. 24: 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243935
APA StyleSchroeder, B., Prasad, P., Gbadegesin, O., Gupta, S., Frazer, R., Heaney, S., Franks, H., Blair, C., Stuttard, M., Barlow, C., Cook, H., Winter, H., d’Arienzo, P., Symington, J., Radif, Y., Rampes, S., Nathan, P., Young, K., Shaw, H., ... Willis, M. (2025). Specialist Neurology Involvement and Impact in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Neurotoxicity: Experience in a Unified Healthcare System. Cancers, 17(24), 3935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17243935







