Inverse Association Between METS-IR and Lung Cancer Risk: The Role of BMI in a Nationwide Korean Cohort
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
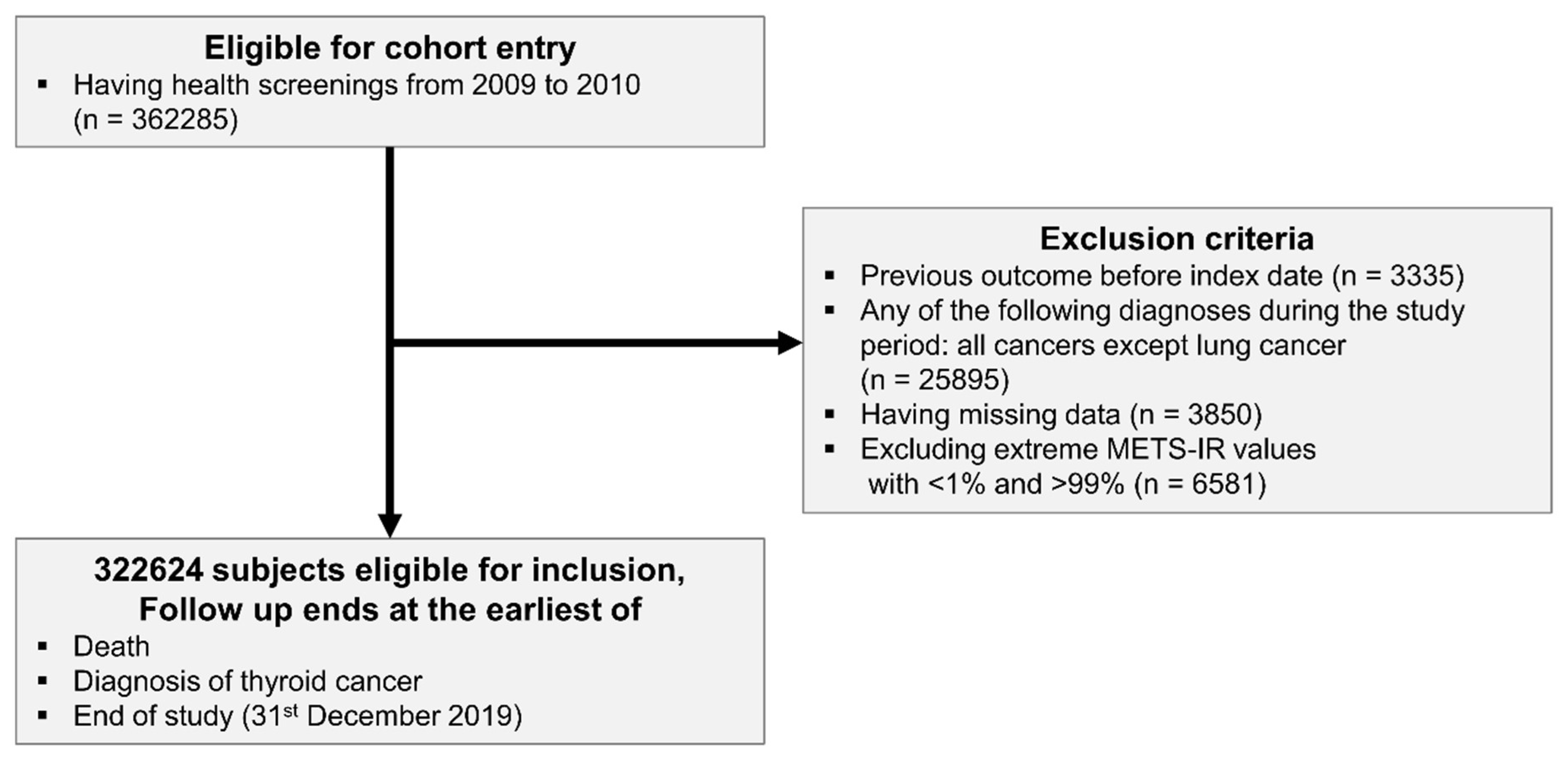
2.1. Data Source and Study Population
2.2. Definitions of Surrogate Markers for Insulin Resistance: METS-IR
2.3. Study Outcomes: Lung Cancer
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
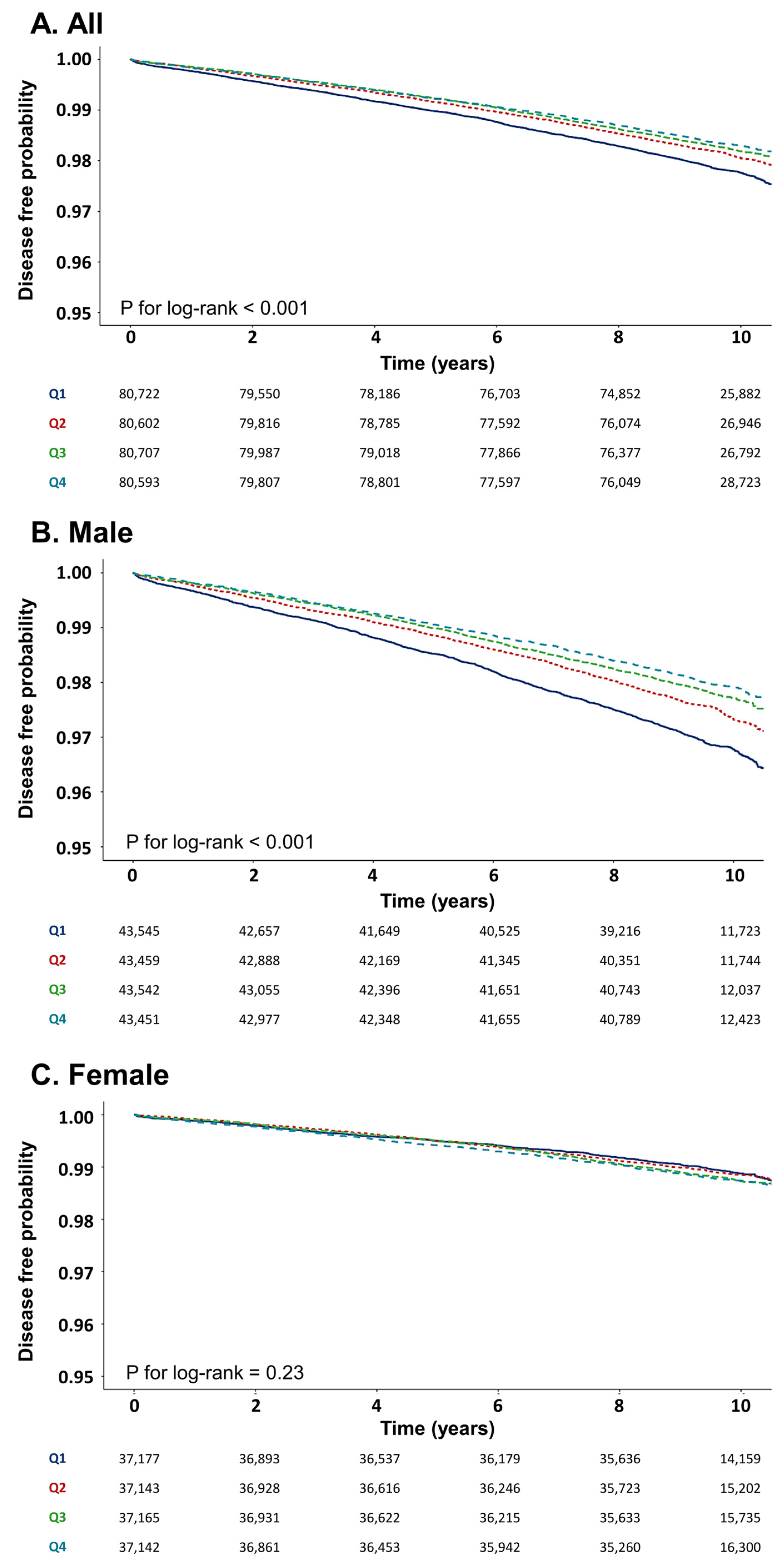
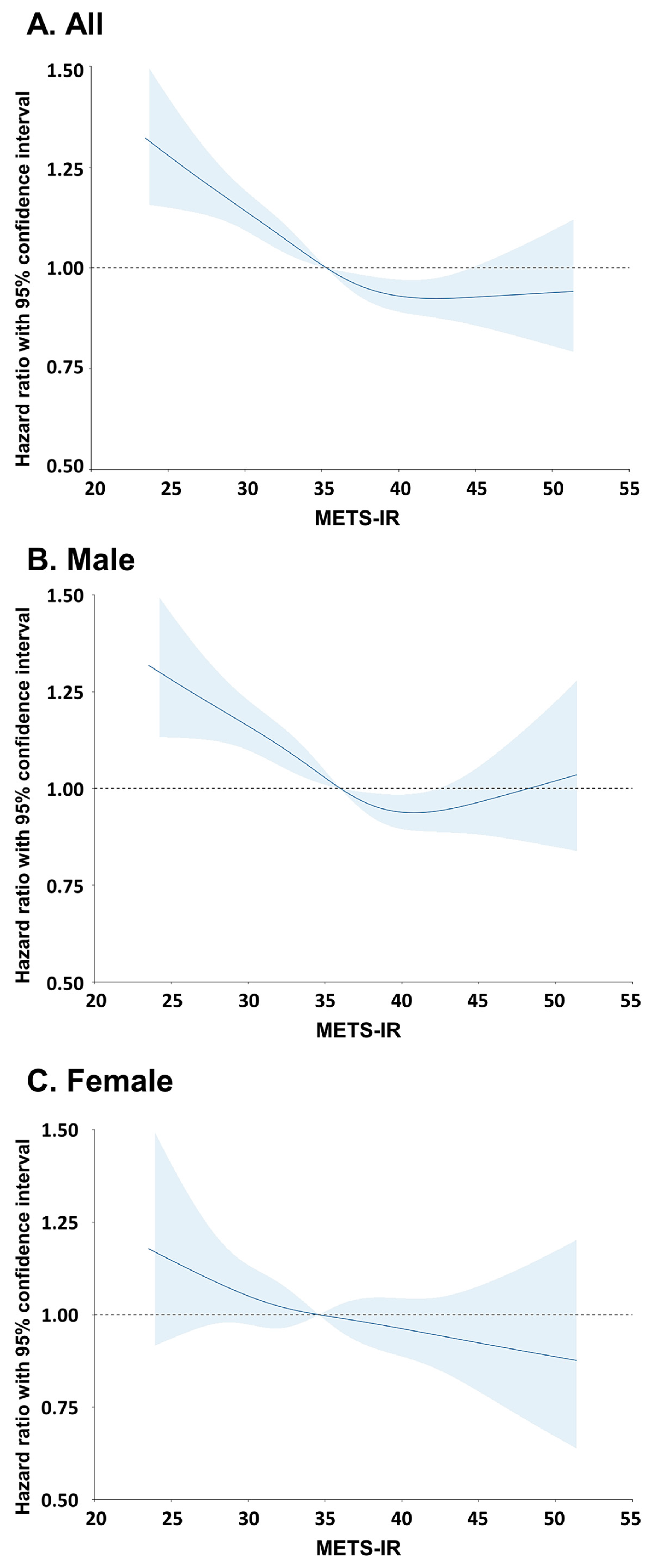
3.2. Incidence of Lung Cancer According to METS-IR
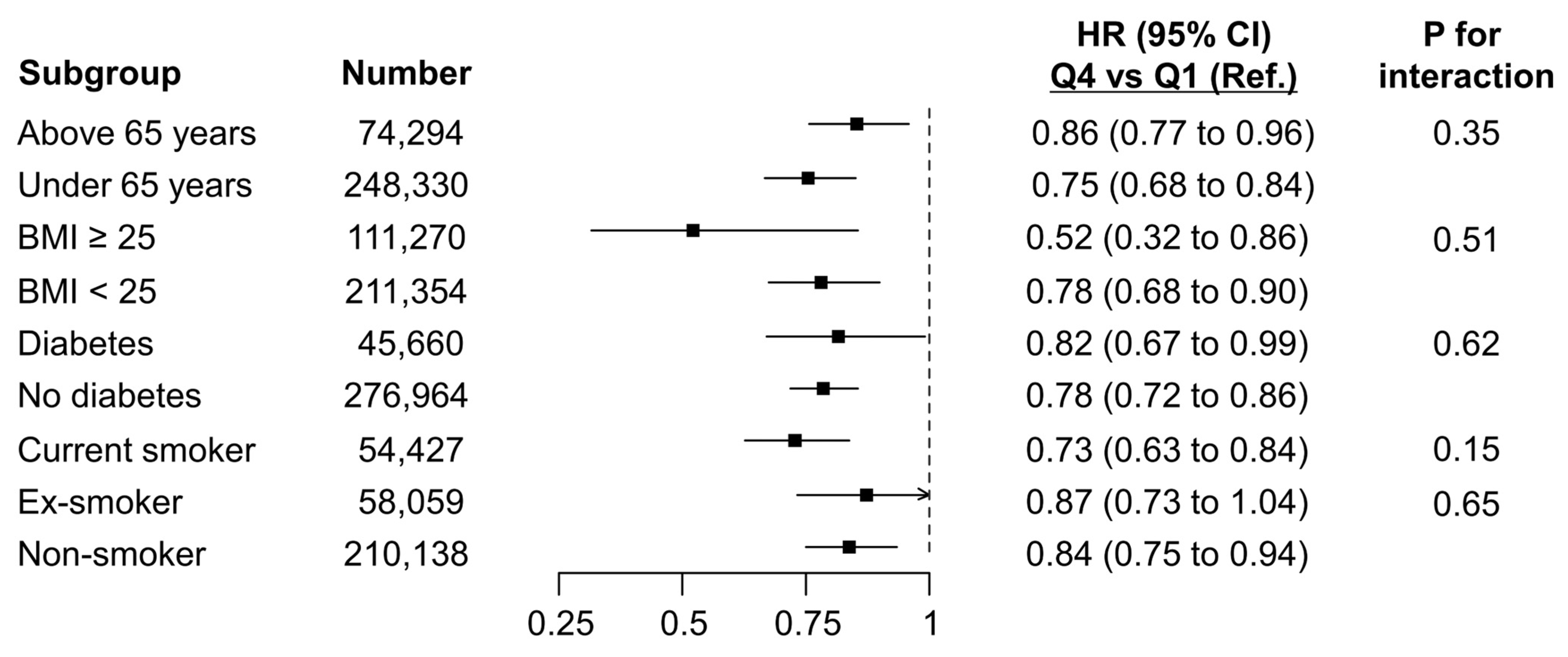
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| METS-IR | Metabolic score for insulin resistance |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| NHIS-HealS | National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, version 10 |
| FBG | Fasting blood glucose |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CCI | Charlson comorbidity index |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| BIA | Bioelectrical impedance analysis |
| DEXA | Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry |
References
- Leiter, A.; Veluswamy, R.R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. The global burden of lung cancer: Current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhikara, B.S.; Parang, K. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: The trends projection analysis. Chem. Biol. Lett. 2023, 10, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Tan, S.; Zhao, X.; Hou, A. Association between insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and its components and lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Pang, G.; Ge, W.; Ma, Z.; Ma, H.; Gong, L. The association between METS-IR, an indirect index for insulin resistance, and lung cancer risk. Eur. J. Public Health 2024, 34, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.Y.; Chang, Y.; Sung, E.; Park, B.; Kang, J.-H.; Shin, H.; Wild, S.H.; Byrne, C.D.; Ryu, S. Glycemic status, insulin resistance, and mortality from lung cancer among individuals with and without diabetes. Cancer Metab. 2024, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szablewski, L. Insulin resistance: The increased risk of cancers. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 998–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Mirabelli, M.; La Vignera, S.; Tanyolaç, S.; Foti, D.P.; Aversa, A.; Brunetti, A. Insulin resistance and cancer: In search for a causal link. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.; Moon, S.Y.; Koh, M.; Kang, Y.; Lee, J.Y. Association between Surrogate Markers of Insulin Resistance and the incidence of Colorectal Cancer in Korea: A Nationwide Population-based study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, H.; Mahmoudi, T.; Asadi, A.; Nobakht, H.; Dabiri, R.; Hamta, A. Insulin resistance and colorectal cancer risk: The role of elevated plasma resistin levels. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2020, 51, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Arzoun, H.; Gk, L.B.; Thangaraj, S.R. A systematic review: Does insulin resistance affect the risk and survival outcome of breast cancer in women? Cureus 2022, 14, e21712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.J.; Fei, K.; Feldman, S.M.; Port, E.; Friedman, N.B.; Boolbol, S.K.; Killelea, B.; Pilewskie, M.; Choi, L.; King, T. Insulin resistance contributes to racial disparities in breast cancer prognosis in US women. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome increase the risk of Relapse for Fertility preserving treatment in atypical endometrial hyperplasia and early endometrial Cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 744689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, S.Z.; Hennenlotter, J.; Franko, A.; Dannecker, C.; Fritsche, L.; Kantartzis, K.; Wagner, R.; Peter, A.; Stefan, N.; Fritsche, A. Diabetes and the prostate: Elevated fasting glucose, insulin resistance and higher levels of adrenal steroids in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-S.; Scherer, P.E. Obesity, diabetes, and increased cancer progression. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Chavolla, O.Y.; Almeda-Valdes, P.; Gomez-Velasco, D.; Viveros-Ruiz, T.; Cruz-Bautista, I.; Romo-Romo, A.; Sánchez-Lázaro, D.; Meza-Oviedo, D.; Vargas-Vázquez, A.; Campos, O.A. METS-IR, a novel score to evaluate insulin sensitivity, is predictive of visceral adiposity and incident type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Meng, L.; Lin, L.; Hu, X.; Li, X. The association between the metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) index and urinary incontinence in the United States: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001–2018. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, H.; OuYang, Z.; Hu, X.; Bao, Y.; Gao, T.; Hua, W. Association between METS-IR and female infertility: A cross-sectional study of NHANES 2013–2018. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1549525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.Y.; Son, M.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.I.; Han, J.M.; Bae, J.C.; Suh, S. Association Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2025, 35, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Kim, B.; Han, K. Big Data Research for Diabetes-Related Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database. Diabetes Metab. J. 2025, 49, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.S.; Park, M.; Back, J.H.; Lee, G.H.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, K.; Seo, H.J.; Kim, Y.A. Validation of Cancer Diagnosis Based on the National Health Insurance Service Database versus the National Cancer Registry Database in Korea. Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 54, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Li, B.; Couris, C.M.; Fushimi, K.; Graham, P.; Hider, P.; Januel, J.M.; Sundararajan, V. Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Zhang, X.; Yip, T.C.-F.; Liu, K.; Tse, Y.K.; Hui, V.W.-K.; Lai, J.C.-T.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Wong, V.W.-S. U-shaped relationship between urea level and hepatic decompensation in chronic liver diseases. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.L.; Yang, J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.-W. Non-insulin-based indices of insulin resistance for predicting incident albuminuria: A nationwide population-based study. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2024, 45, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Jung, D.; Lee, Y.; Park, B. The metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) as a predictor of incident ischemic heart disease: A longitudinal study among Korean without diabetes. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Xie, S.; Wang, F.; Chen, S.; Su, K.; Li, F.; Cui, H.; Cao, W.; Yu, Y.; Qin, C. BMI changes and the risk of lung cancer in male never—Smokers: A prospective cohort study. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Shao, F.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lange, T.; Ma, H.; Xu, H. Associations of genetic risk, BMI trajectories, and the risk of non-small cell lung cancer: A population-based cohort study. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, U.A.; Ballinger, T.J.; Bhandari, R.; Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Guertin, K.A.; Hibler, E.A.; Kalam, F.; Lohmann, A.E.; Ippolito, J.E. Imaging modalities for measuring body composition in patients with cancer: Opportunities and challenges. JNCI Monogr. 2023, 2023, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoke, D.B.; Atwood, G.S.; Bellefleur, E.R.; Stokes, A.M.; Toth, M.J. Body composition alterations in patients with lung cancer. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2025, 328, C872–C886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangalore, S.; Fayyad, R.; Laskey, R.; DeMicco, D.A.; Messerli, F.H.; Waters, D.D. Body-weight fluctuations and outcomes in coronary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Somers, V.K.; Sierra-Johnson, J.; Korenfeld, Y.; Boarin, S.; Korinek, J.; Jensen, M.D.; Parati, G.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Normal weight obesity: A risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, M.; Fukuda, A.; Onishi, S.; Ushiro, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Asai, A.; Kim, S.K.; Nishikawa, H. Insulin resistance: A marker for fat-to-lean body composition in Japanese adults. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, K.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Chatterjee, P.; Majhi, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Ghosh, S. Assessment of insulin resistance indices in individuals with lean and obese metabolic syndrome compared to normal individuals: A population based study. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2020, 68, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.-E.; Sung, M.-K. Sex and gender differences in obesity: Biological, sociocultural, and clinical perspectives. World J. Men’s Health 2025, 43, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, L.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Kararigas, G.; Ahmed, S.B.; Stallone, J.N. The role of sex differences in cardiovascular, metabolic, and immune functions in health and disease: A review for “Sex Differences in Health Awareness Day”. Biol. Sex Differ. 2025, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Befroy, D.; Dufour, S.; Dziura, J.; Ariyan, C.; Rothman, D.L.; DiPietro, L.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: Possible role in insulin resistance. Science 2003, 300, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Flores, R.E.; Poff, A.M.; D’Agostino, D.P. Cancer as a metabolic disease: Implications for novel therapeutics. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, G.-T.; Xie, H.-L.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Liu, C.-A.; Ge, Y.-Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.-W.; Zhang, X.; Tang, M.; Song, M.-M. A novel inflammation and insulin resistance related indicator to predict the survival of patients with cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 905266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Erbay, E. Nutrient sensing and inflammation in metabolic diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 923–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N. Metabolically healthy and unhealthy normal weight and obesity. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Shin, M.-J.; Magkos, F. When Being Lean Is Not Enough: The Metabolically Unhealthy Normal Weight Phenotype and Cardiometabolic Disease. CardioMetabolic Syndr. J. 2024, 4, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Miao, G.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhao, X. Metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in the general population: Evidence from NHANES 2001–2018. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.E.; Jung, D.H.; Heo, S.-J.; Park, B.; Lee, Y.J. METS-IR and all-cause mortality in Korean over 60 years old: Korean genome and epidemiology study-health examinees (KoGES-HEXA) cohorts. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1346158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ji, B.; Du, W.; Shi, S.; Zhao, H.; Sheng, J.; Jiang, X.; Ban, B.; Gao, G. METS-IR, a Novel simple insulin Resistance Index, is Associated with NAFLD in patients with type 2 diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 3481–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Heo, S.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Lee, J.E. Comparison of METS-IR and HOMA-IR for predicting new-onset CKD in middle-aged and older adults. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabczyk, M.; Nowak, J.; Jagielski, P.; Hudzik, B.; Kulik-Kupka, K.; Włodarczyk, A.; Lar, K.; Zubelewicz-Szkodzińska, B. Metabolic deregulations in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Metabolites 2023, 13, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| All Subjects (N = 322,624) | METS-IR | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Quartile, Q1 (N = 80,722) | 2nd Quartile, Q2 (N = 80,602) | 3rd Quartile, Q3 (N = 80,707) | 4th Quartile, Q4 (N = 80,593) | ||
| Demographics | |||||
| Age (years) | 58.4 (9.1) | 58.5 (8.6) | 58.9 (8.5) | 59.2 (8.6) | <0.001 |
| Sex (%) | 1.00 | ||||
| Male | 43,545 (53.9) | 43,459 (53.9) | 43,542 (54.0) | 43,451 (53.9) | |
| Female | 37,177 (46.1) | 37,143 (46.1) | 37,165 (46.0) | 37,142 (46.1) | |
| Income Level (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| 1st quartile | 11,572 (14.3) | 11,184 (13.9) | 11,105 (13.8) | 11,295 (14.0) | |
| 2nd quartile | 17,814 (22.1) | 16,675 (20.7) | 16,069 (19.9) | 16,062 (19.9) | |
| 3rd quartile | 23,198 (28.7) | 23,374 (29.0) | 23,914 (29.6) | 24,670 (30.6) | |
| 4th quartile | 28,138 (34.9) | 29,369 (36.4) | 29,619 (36.7) | 28,566 (35.4) | |
| Residence (%) | <0.001 | ||||
| Urban | 53,251 (66.0) | 52,349 (64.9) | 51,938 (64.4) | 50,273 (62.4) | |
| Rural | 27,471 (34.0) | 28,253 (35.1) | 28,769 (35.6) | 30,320 (37.6) | |
| Underlying disease | |||||
| Hypertension (%) | 26,472 (32.8) | 34,026 (42.2) | 40,506 (50.2) | 49,054 (60.9) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes (%) | 5112 (6.3) | 8514 (10.6) | 12,498 (15.5) | 19,536 (24.2) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 18,676 (23.1) | 26,325 (32.7) | 34,599 (42.9) | 48,544 (60.2) | <0.001 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | <0.001 | ||||
| 0 | 42,623 (52.8) | 38,925 (48.3) | 36,075 (44.7) | 31,887 (39.6) | |
| 1 | 21,672 (26.8) | 22,307 (27.7) | 22,424 (27.8) | 21,939 (27.2) | |
| 2 | 9481 (11.7) | 10,540 (13.1) | 11,429 (14.2) | 12,523 (15.5) | |
| ≥3 | 6946 (8.6) | 8830 (11.0) | 10,779 (13.4) | 14,244 (17.7) | |
| Health Screening | |||||
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 21.1 (1.6) | 23.2 (1.4) | 24.8 (1.5) | 27.0 (2.1) | <0.001 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 121.5 (15.3) | 124.3 (15.0) | 126.4 (14.8) | 128.8 (14.8) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 75.4 (9.9) | 77.0 (9.8) | 78.2 (9.8) | 79.7 (9.8) | <0.001 |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 94.1 (16.5) | 98.1 (20.2) | 102.0 (23.7) | 109.3 (32.3) | <0.001 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 197.7 (35.3) | 200.5 (36.8) | 201.6 (38.0) | 201.6 (39.0) | <0.001 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 93.0 (48.7) | 117.4 (56.0) | 144.3 (70.7) | 193.4 (103.2) | <0.001 |
| HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 64.7 (27.3) | 55.8 (12.0) | 50.9 (10.8) | 45.1 (9.7) | <0.001 |
| LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 115.8 (35.6) | 121.2 (35.9) | 122.0 (37.6) | 118.2 (39.3) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.6 (1.4) | 13.8 (1.5) | 13.9 (1.5) | 14.1 (1.5) | <0.001 |
| Glomerular Filtration Rate (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 80.4 (30.3) | 79.1 (30.3) | 77.8 (30.9) | 76.9 (32.4) | <0.001 |
| Current Smoker (%) | 15,015 (18.6) | 12,925 (16.0) | 12,877 (16.0) | 13,610 (16.9) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol Drink (%) | 32,892 (40.7) | 32,877 (40.8) | 32,220 (39.9) | 30,843 (38.3) | <0.001 |
| Regular Exercise (%) | 3909 (4.8) | 3948 (4.9) | 3724 (4.6) | 3418 (4.2) | <0.001 |
| METS-IR | 28.6 (2.0) | 33.2 (1.3) | 36.9 (1.4) | 42.7 (3.0) | <0.001 |
| Subjects (N = 322,624) | Events | Follow-up Duration (Person-Years) | Incidence Rate (per 1000 Person-Years) | Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Intervals) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | p-Value | Adjusted * | p-Value | ||||
| Total | |||||||
| Q1 (N = 80,722) | 1722 | 758,787 | 2.27 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| Q2 (N = 80,602) | 1480 | 765,719 | 1.93 | 0.85 (0.79–0.91) | <0.001 | 0.91 (0.85–0.98) | 0.009 |
| Q3 (N = 80,707) | 1390 | 766,717 | 1.81 | 0.79 (0.74–0.85) | <0.001 | 0.86 (0.79–0.92) | <0.001 |
| Q4 (N = 80,593) | 1320 | 765,634 | 1.72 | 0.75 (0.70–0.81) | <0.001 | 0.80 (0.74–0.86) | <0.001 |
| Male | |||||||
| Q1 (N = 43,545) | 1318 | 400,614 | 3.29 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| Q2 (N = 43,459) | 1068 | 404,169 | 2.64 | 0.80 (0.74–0.87) | <0.001 | 0.92 (0.85–0.99) | 0.04 |
| Q3 (N = 43,542) | 938 | 409,295 | 2.29 | 0.70 (0.64–0.76) | <0.001 | 0.85 (0.78–0.93) | <0.001 |
| Q4 (N = 43,451) | 861 | 408,439 | 2.11 | 0.64 (0.59–0.70) | <0.001 | 0.80 (0.73–0.88) | <0.001 |
| Female | |||||||
| Q1 (N = 37,177) | 404 | 356,899 | 1.13 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | ||
| Q2 (N = 37,143) | 412 | 360,287 | 1.14 | 1.01 (0.88–1.16) | 0.87 | 0.94 (0.82–1.07) | 0.35 |
| Q3 (N = 37,165) | 452 | 360,501 | 1.25 | 1.11 (0.97–1.27) | 0.14 | 0.94 (0.82–1.08) | 0.36 |
| Q4 (N = 37,142) | 459 | 360,277 | 1.27 | 1.13 (0.98–1.29) | 0.08 | 0.88 (0.76–1.01) | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shine, B.-K.; Jeong, I.H.; Son, M.; Kim, B.; Moon, S.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Huh, S.J. Inverse Association Between METS-IR and Lung Cancer Risk: The Role of BMI in a Nationwide Korean Cohort. Cancers 2025, 17, 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233727
Shine B-K, Jeong IH, Son M, Kim B, Moon SY, Lee JY, Kim HR, Huh SJ. Inverse Association Between METS-IR and Lung Cancer Risk: The Role of BMI in a Nationwide Korean Cohort. Cancers. 2025; 17(23):3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233727
Chicago/Turabian StyleShine, Bo-Kyung, In Hwa Jeong, Minkook Son, Bongjo Kim, Sang Yi Moon, Jong Yoon Lee, Hye Ryeon Kim, and Seok Jae Huh. 2025. "Inverse Association Between METS-IR and Lung Cancer Risk: The Role of BMI in a Nationwide Korean Cohort" Cancers 17, no. 23: 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233727
APA StyleShine, B.-K., Jeong, I. H., Son, M., Kim, B., Moon, S. Y., Lee, J. Y., Kim, H. R., & Huh, S. J. (2025). Inverse Association Between METS-IR and Lung Cancer Risk: The Role of BMI in a Nationwide Korean Cohort. Cancers, 17(23), 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233727






