RBE-Guided Treatment Planning, LET Optimization, and Implications of Proton Arc Therapy for the Sparing of Nervous Tissue in Head and Neck Proton Therapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- •
- Analyze the effect of LET on RBE for head and neck cancer patients, focusing on LET-dependent RBE dose to nervous tissue.
- •
- Explore the implications and impact of proton dynamic arc therapy on spatial LET distributions compared to conventional PBS.
- •
- Establish clinically feasible recommendations for the use of LET optimization in head and neck proton therapy by finding optimal LET optimization parameters to improve treatment safety and efficacy.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
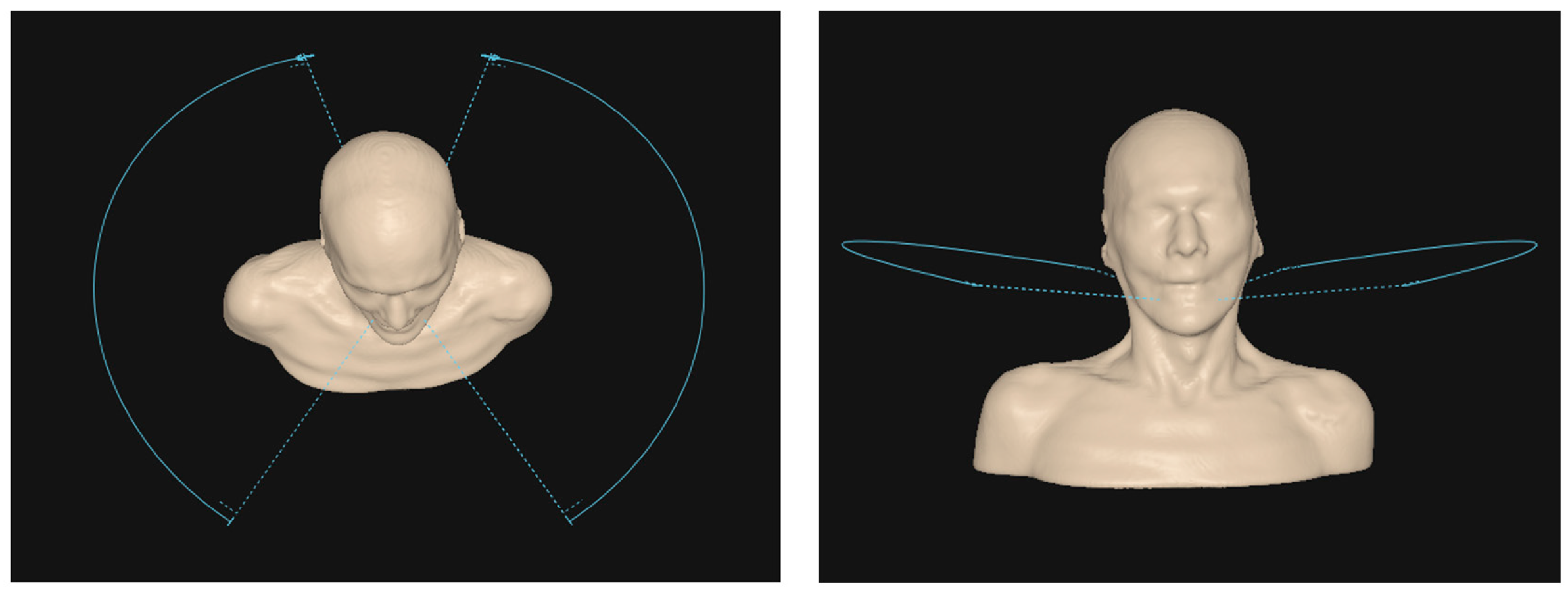
2.2. Treatment Plan Design & Prescription

2.3. LET-Based RBE Modeling
2.4. RBE Enhancement Metric
2.5. Plan Optimization
3. Results
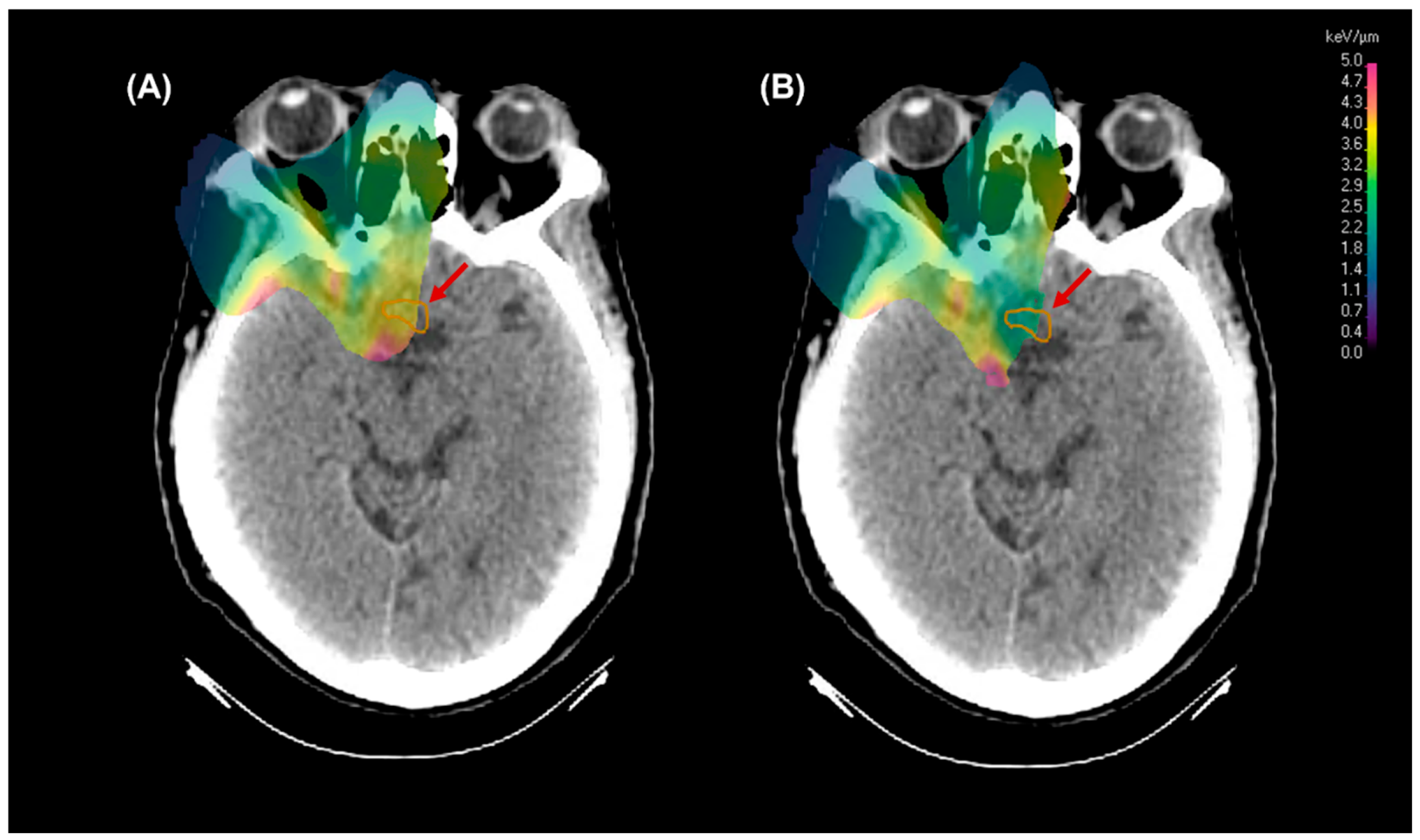
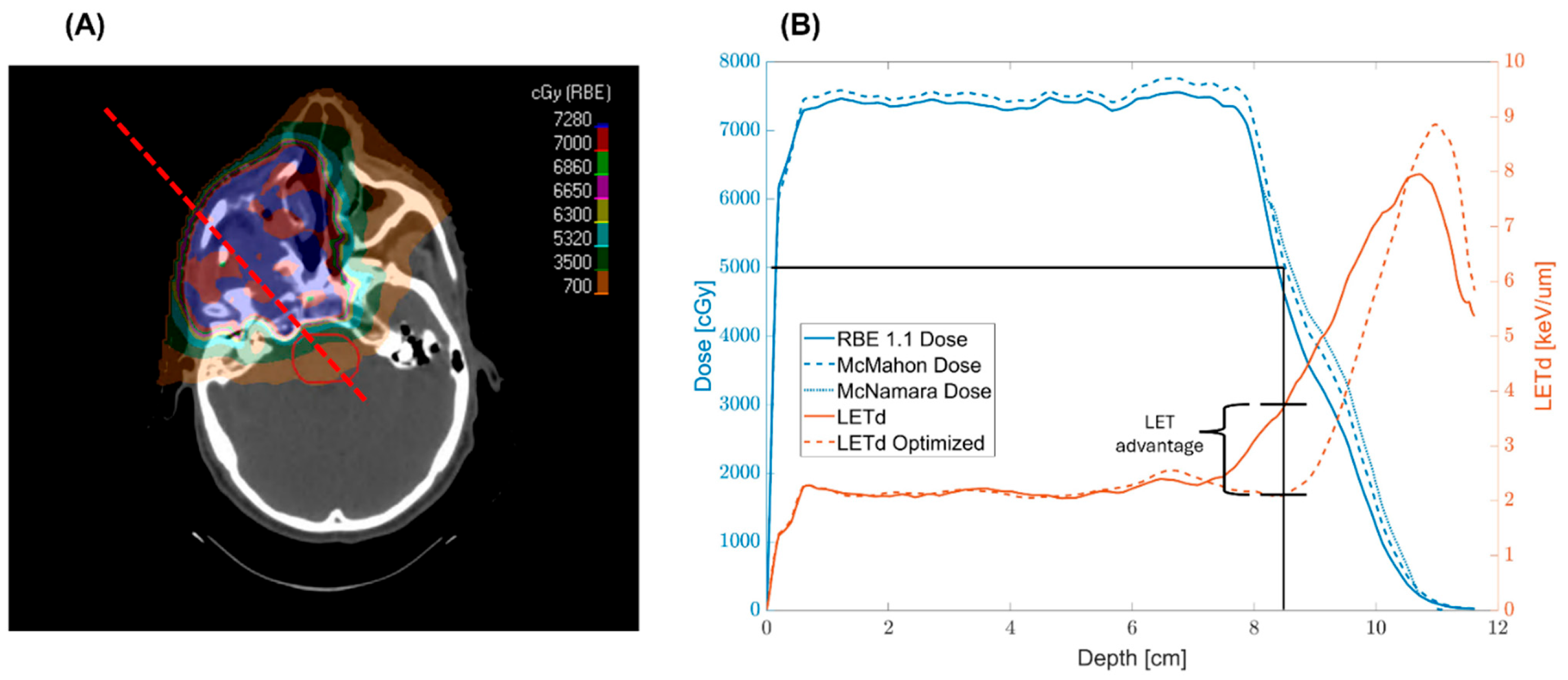
3.1. LETd and Dose Reduction
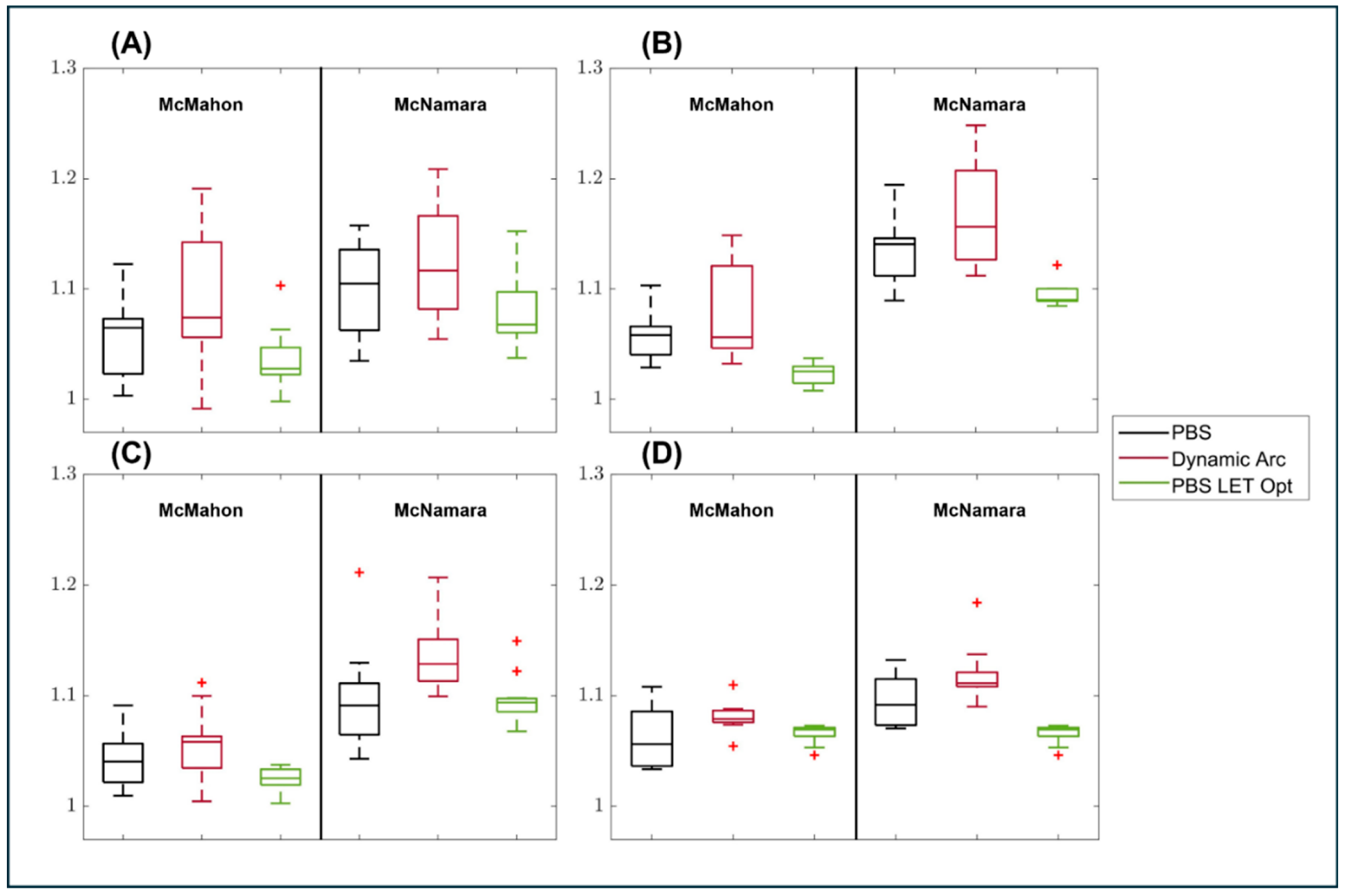
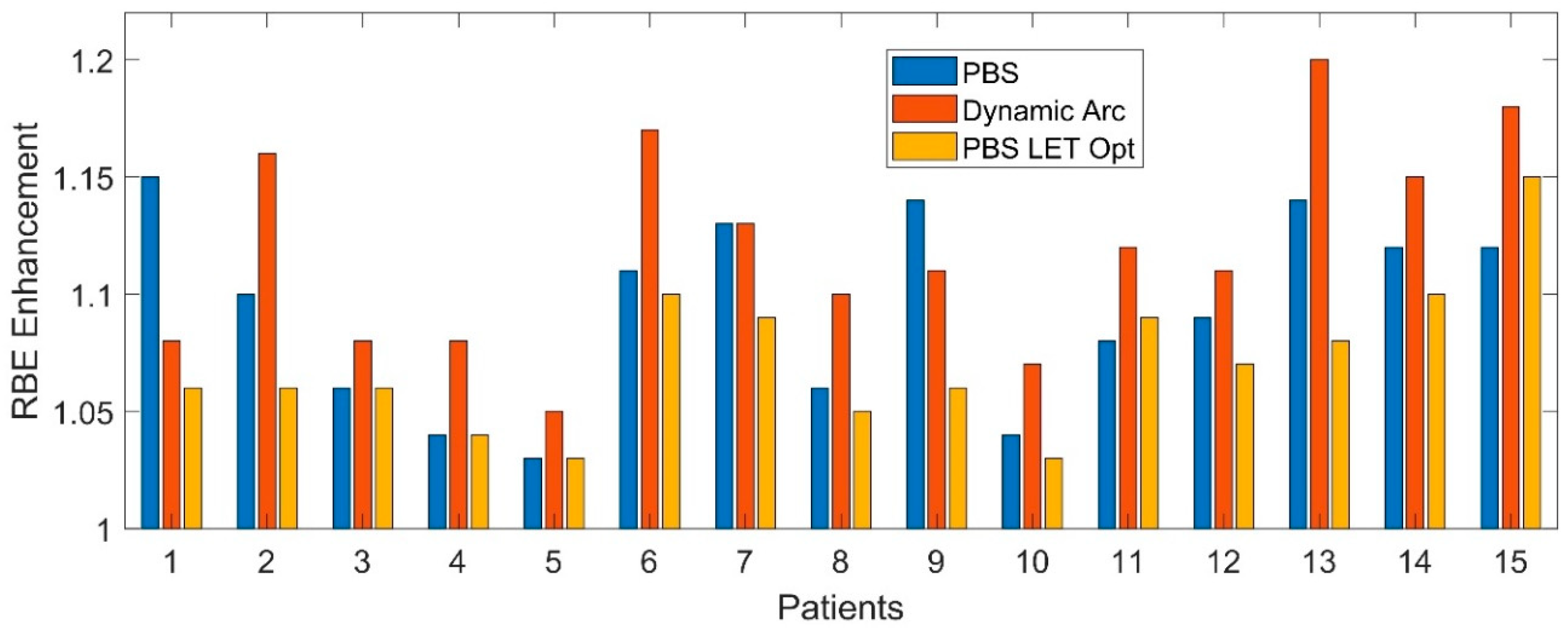
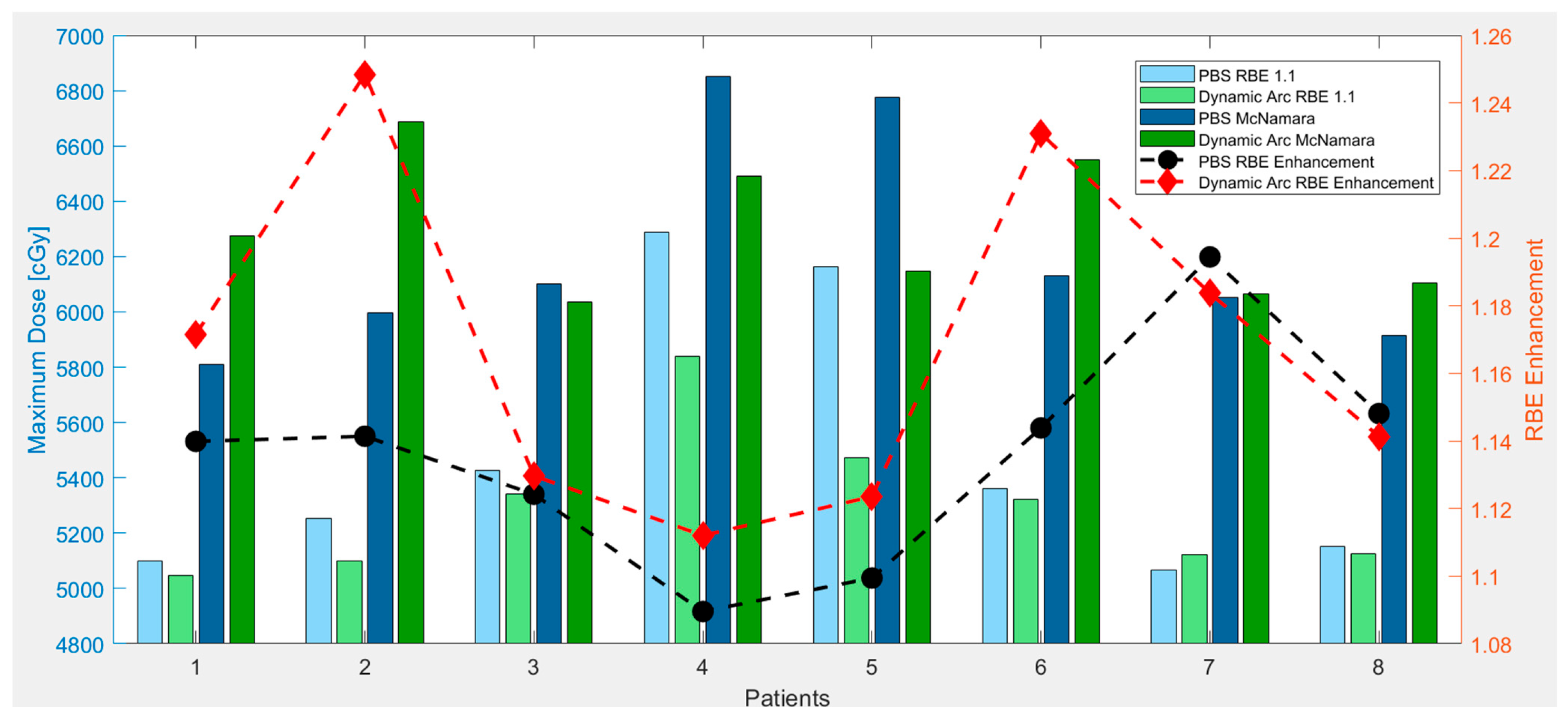
3.2. RBE Enhancement
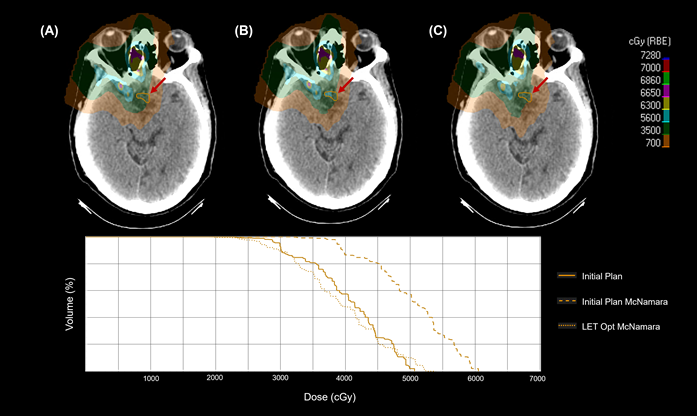
3.3. LET Optimization Variability
3.4. Effective Use of LETd Objectives
4. Discussion
4.1. LET Distributions & RBE Enhancement
4.2. Dynamic Arc Implications
4.3. Impact of LET Optimization
4.4. Clinical Deployment of LET Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreno, A.C.; Frank, S.J.; Garden, A.S.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Fuller, C.D.; Gunn, G.B.; Reddy, J.P.; Morrison, W.H.; Williamson, T.D.; Holliday, E.B.; et al. Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy (IMPT)—The Future of IMRT for Head and Neck Cancer. Oral Oncol. 2019, 88, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Water, T.A.; Lomax, A.J.; Bijl, H.P.; de Jong, M.E.; Schilstra, C.; Hug, E.B.; Langendijk, J.A. Potential Benefits of Scanned Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy Versus Advanced Photon Therapy with Regard to Sparing of the Salivary Glands in Oropharyngeal Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 79, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minatogawa, H.; Yasuda, K.; Dekura, Y.; Takao, S.; Matsuura, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Suzuki, R.; Yokota, I.; Fujima, N.; Onimaru, R.; et al. Potential Benefits of Adaptive Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy in Nasopharyngeal Carcinomas. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester-Coll, N.H.; Margalit, D.N. Modeling the Potential Benefits of Proton Therapy for Patients with Oropharyngeal Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 104, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.J.; Busse, P.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Hernandez, M.; Swanson, D.M.; Garden, A.S.; Sturgis, E.M.; Ferrarotto, R.; Gunn, G.B.; Patel, S.H.; et al. Phase III Randomized Trial of Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy (IMPT) versus Intensity-Modulated Photon Therapy (IMRT) for the Treatment of Head and Neck Oropharyngeal Carcinoma (OPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, P.; Gunn, G.B.; Lin, A.; Foote, R.L.; Lee, N.Y.; Frank, S.J. Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancers. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 28, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Leeman, J.E.; Riaz, N.; McBride, S.; Tsai, C.J.; Lee, N.Y. Proton Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2018, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steneker, M.; Lomax, A.; Schneider, U. Intensity Modulated Photon and Proton Therapy for the Treatment of Head and Neck Tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2006, 80, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, M.; Wilson, P.; Gorayski, P.; Bezak, E. A Systematic Review of LET-Guided Treatment Plan Optimisation in Proton Therapy: Identifying the Current State and Future Needs. Cancers 2023, 15, 4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, C.; Trofimov, A.; Lomax, A.; Paganetti, H. Variations in Linear Energy Transfer within Clinical Proton Therapy Fields and the Potential for Biological Treatment Planning. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, C.; Paganetti, H. Elevated LET Components in Clinical Proton Beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 6677–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedenberg, M.; Lind, B.K.; Hårdemark, B. A Model for the Relative Biological Effectiveness of Protons: The Tissue Specific Parameter α/β of Photons Is a Predictor for the Sensitivity to LET Changes. Acta Oncol. 2013, 52, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Bues, M.; Mohan, R.; Wong, W.W.; Foote, R.H.; Patel, S.H.; Liu, W. A Critical Review of LET-Based Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy Plan Evaluation and Optimization for Head and Neck Cancer Management. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2021, 8, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, P.; Adair, A.; Frank, S.J.; Grosshans, D.R.; Liao, Z.; Liu, A.; Mirkovic, D.; Poenisch, F.; Titt, U.; Wang, Q.; et al. Fixed- versus Variable-RBE Computations for Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 4, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtzman, A.L.; Mohammadi, H.; Furutani, K.M.; Koffler, D.M.; McGee, L.A.; Lester, S.C.; Gamez, M.E.; Routman, D.M.; Beltran, C.J.; Liang, X. Impact of Relative Biologic Effectiveness for Proton Therapy for Head and Neck and Skull-Base Tumors: A Technical and Clinical Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossum, C.C.; Beltran, C.J.; Whitaker, T.J.; Ma, D.J.; Foote, R.L. Biological Model for Predicting Toxicity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Receiving Proton Therapy. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2017, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, D.; Bradley, J.A.; Mailhot Vega, R.B.; Zhang, Y.; Indelicato, D.J.; Mendenhall, N.; Liang, X. Incorporation of the LETd-Weighted Biological Dose in the Evaluation of Breast Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy Plans. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) Values for Proton Beam Therapy. Variations as a Function of Biological Endpoint, Dose, and Linear Energy Transfer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, R419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polster, L.; Schuemann, J.; Rinaldi, I.; Burigo, L.; McNamara, A.L.; Stewart, R.D. Extension of TOPAS for the Simulation of Proton Radiation Effects Considering Molecular and Cellular Endpoints. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 5053–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H.; Blakely, E.; Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Carlson, D.J.; Das, I.J.; Dong, L.; Grosshans, D.; Held, K.D.; Mohan, R.; Moiseenko, V.; et al. Report of the AAPM TG-256 on the Relative Biological Effectiveness of Proton Beams in Radiation Therapy. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e53–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, M.S.; Yeap, B.Y.; Paganetti, H.; Goebel, C.P.; Gaudet, D.E.; Gallotto, S.L.; Weyman, E.A.; Morgan, M.L.; MacDonald, S.M.; Giantsoudi, D.; et al. Brainstem Injury in Pediatric Patients with Posterior Fossa Tumors Treated with Proton Beam Therapy and Associated Dosimetric Factors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 100, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmin, M.; Rees, J. Radiation and the Nervous System. Pract. Neurol. 2022, 22, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Giraldo, M.A.; Carabe, A. A Critical Study of Different Monte Carlo Scoring Methods of Dose Average Linear-Energy-Transfer Maps Calculated in Voxelized Geometries Irradiated with Clinical Proton Beams. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 2645–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, D.; Tran, L.T.; Meijers, A.; Marmitt, G.G.; Souris, K.; Bolst, D. Validation of Linear Energy Transfer Computed in a Monte Carlo Dose Engine of a Commercial Treatment Planning System. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Parcerisa, D.; Cortés-Giraldo, M.A.; Dolney, D.; Kondrla, M.; Fager, M.; Carabe, A. Analytical Calculation of Proton Linear Energy Transfer in Voxelized Geometries Including Secondary Protons. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassler, N.; Jäkel, O.; Søndergaard, C.S.; Petersen, J.B. Dose- and LET-Painting with Particle Therapy. Acta Oncol. 2010, 49, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Khabazian, A.; Yepes, P.P.; Lim, G.; Poenisch, F.; Grosshans, D.R.; Grassberger, C.; Trofimov, A.; Lomax, A.; Paganetti, H. Linear Energy Transfer Incorporated Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy Optimization. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 63, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Shan, J.; Patel, S.H.; Wong, W.; Schild, S.E.; Ding, X.; Bues, M.; Liu, W. Robust Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy to Reduce High Linear Energy Transfer in Organs at Risk. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 6138–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieceli, M.; Park, J.; Hsi, W.C.; Saki, M.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Johnson, P.; Artz, M. Potential Therapeutic Improvements in Prostate Cancer Treatment Using Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy with LETd Optimization and Disease-Specific RBE Models. Cancers 2024, 16, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, A.L.; Schuemann, J.; Paganetti, H. A Phenomenological Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) Model for Proton Therapy Based on All Published in Vitro Cell Survival Data. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 8399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairani, A.; Dokic, I.; Magro, G.; Tessonnier, T.; Bauer, J.; Böhlen, T.T.; Ciocca, M.; Ferrari, A.; Sala, P.R.; Jäkel, O.; et al. A Phenomenological Relative Biological Effectiveness Approach for Proton Therapy Based on an Improved Description of the Mixed Radiation Field. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kabolizadeh, P.; Yan, D.; Qin, A.; Zhou, J.; Hong, Y. Improve Dosimetric Outcome in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Using SpotScanning Proton Arc (SPArc) Therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Cao, X.; Dalfsen, R.; Soukup, M.; Dolan, J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Mulhem, A.; Gao, X.; Liu, G.; et al. Investigate Potential Clinical Benefits and Linear Energy Transfer Sparing Utilizing Proton Arc Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Phys. Med. 2024, 126, 104816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.B.; Mamalui, M.; Brodin, P.; Janssens, G. Secondary Cancer Risk in Six Anatomical Sites When Using PAT, IMPT, and VMAT/IMRT Radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 199, 110421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toussaint, L.; Indelicato, D.J.; Holgersen, K.S.; Petersen, J.B.B.; Stokkevag, C.H.; LassenRamshad, Y. Towards Proton Arc Therapy: Physical and Biologically Equivalent Doses with Increasing Number of Beams in Pediatric Brain Irradiation. Acta Oncol 2019, 58, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrik Brodin, N.; Tomé, W.A. Revisiting the Dose Constraints for Head and Neck OARs in the Current Era of IMRT. Oral Oncol. 2018, 86, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines Detail. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1437 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- McMahon, S.J.; Paganetti, H.; Prise, K.M. LET-Weighted Doses Effectively Reduce Biological Variability in Proton Radiotherapy Planning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 225009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Klinge, T.; Hopewell, J.W. The Influence of the α/β Ratio on Treatment Time Iso-Effect Relationships in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, C.M.; Oei, A.L.; Crezee, J.; Bel, A.; Franken, N.A.P.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Kok, H.P. The Alfa and Beta of Tumours: A Review of Parameters of the Linear-Quadratic Model, Derived from Clinical Radiotherapy Studies. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Bradley, J.; Mendenhall, N.; Mailhot, R.; Bruchianti, T.; Zhang, Y.; Grewal, H.; Saki, M.; Willoughby, T.; Johnson, P.; et al. Radiation-Induced Acute Lung Pneumonitis after PBS Proton Treatment for Breast Cancer: Correlation with Dose-Volume Parameters and Optimization Objectives to Reduce Lung Toxicities. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, A.; Casper, A.; Dagan, R.; Grewal, H.S.; Park, J.; Brooks, E.D.; Traneus, E.; Glimelius, L.; Johnson, P.B.; Saki, M.; et al. Brachial Plexopathy in Head and Neck Cancer Potentially Related to LET-Dependent RBE. Biophysica 2025, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Oglesby, R.; Tran, A.; Guryildirim, M.; Miller, M.; Sheikh, K.; Li, H.; Ladra, M.; Hrinivich, W.T.; Acharya, S. The Association of Linear Energy Transfer and Dose with Radiation Necrosis After Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Therapy in Pediatric Posterior Fossa Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2025, 121, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeler, C.R.; Mirkovic, D.; Titt, U.; Blanchard, P.; Gunther, J.R.; Mahajan, A.; Mohan, R.; Grosshans, D.R. Clinical Evidence of Variable Proton Biological Effectiveness in Pediatric Patients Treated for Ependymoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 121, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handeland, A.H.; Indelicato, D.J.; Fredrik Fjæra, L.; Ytre-Hauge, K.S.; Pettersen, H.E.S.; Muren, L.P.; Lassen-Ramshad, Y.; Stokkevåg, C.H. Linear Energy Transfer-Inclusive Models of Brainstem Necrosis Following Proton Therapy of Paediatric Ependymoma. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 27, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ding, X.; Zheng, W.; Liu, G.; Janssens, G.; Souris, K.; Barragán-Montero, A.M.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P. Linear Energy Transfer Incorporated Spot-Scanning Proton Arc Therapy Optimization: A Feasibility Study. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 698537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karger, C.P.; Glowa, C.; Peschke, P.; Kraft-Weyrather, W. The RBE in Ion Beam Radiotherapy: In Vivo Studies and Clinical Application. Z. Für Med. Phys. 2021, 31, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkens, J.J.; Oelfke, U. Optimization of Radiobiological Effects in Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy. Med. Phys. 2005, 32, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Ding, X.; Younkin, J.E.; Shen, J.; Bues, M.; Schild, S.E.; Patel, S.H.; Liu, W. Hybrid 3D Analytical Linear Energy Transfer Calculation Algorithm Based on Precalculated Data from Monte Carlo Simulations. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ödén, J.; Toma-Dasu, I.; Witt Nyström, P.; Traneus, E.; Dasu, A. Spatial Correlation of Linear Energy Transfer and Relative Biological Effectiveness with Suspected Treatment-Related Toxicities Following Proton Therapy for Intracranial Tumors. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.P.; Li, X.Q.; Cao, W.H.; Zhang, X.D. Influence of Robust Optimization in Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy with Different Dose Delivery Techniques. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giantsoudi, D.; Grassberger, C.; Craft, D.; Niemierko, A.; Trofimov, A.; Paganetti, H. Linear Energy Transfer (LET)-Guided Optimization in Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy (IMPT): Feasibility Study and Clinical Potential. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Energy Layer Spacing | Spot Spacing | Target Margins (Lateral) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | Automatic with scale = 1 | Automatic with scale = 0.7 | Automatic with scale = 0.7 |
| Arc | Automatic with scale = 0.25 | Constant = 0.6 cm | Constant = 0.5 cm |
| McMahon: | Brainstem | Optic Chiasm | Optic Nerves | Brachial Plexus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = | 15 | 8 | 14 | 9 |
| PBS | 1.05 | 1.05 | 1.04 | 1.06 |
| Dynamic Arc | 1.09 | 1.18 | 1.05 | 1.08 |
| PBS LET Opt | 1.03 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 1.02 |
| McNamara: | Brainstem | Optic Chiasm | Optic Nerves | Brachial Plexus |
| N = | 15 | 8 | 14 | 9 |
| PBS | 1.09 | 1.13 | 1.09 | 1.09 |
| Dynamic Arc | 1.12 | 1.16 | 1.13 | 1.11 |
| PBS LET Opt | 1.07 | 1.09 | 1.09 | 1.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reiners, K.; Artz, M.; Bryant, C.M.; Dagan, R.; Grewal, H.S.; Johnson, P.B.; Li, Z.; Park, J.; Vieceli, M.; Zhang, Y. RBE-Guided Treatment Planning, LET Optimization, and Implications of Proton Arc Therapy for the Sparing of Nervous Tissue in Head and Neck Proton Therapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233724
Reiners K, Artz M, Bryant CM, Dagan R, Grewal HS, Johnson PB, Li Z, Park J, Vieceli M, Zhang Y. RBE-Guided Treatment Planning, LET Optimization, and Implications of Proton Arc Therapy for the Sparing of Nervous Tissue in Head and Neck Proton Therapy. Cancers. 2025; 17(23):3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233724
Chicago/Turabian StyleReiners, Keaton, Mark Artz, Curtis M. Bryant, Roi Dagan, Hardev S. Grewal, Perry B. Johnson, Zuofeng Li, Jiyeon Park, Michael Vieceli, and Yawei Zhang. 2025. "RBE-Guided Treatment Planning, LET Optimization, and Implications of Proton Arc Therapy for the Sparing of Nervous Tissue in Head and Neck Proton Therapy" Cancers 17, no. 23: 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233724
APA StyleReiners, K., Artz, M., Bryant, C. M., Dagan, R., Grewal, H. S., Johnson, P. B., Li, Z., Park, J., Vieceli, M., & Zhang, Y. (2025). RBE-Guided Treatment Planning, LET Optimization, and Implications of Proton Arc Therapy for the Sparing of Nervous Tissue in Head and Neck Proton Therapy. Cancers, 17(23), 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233724






