The Potential and Challenges of Proton FLASH in Head and Neck Cancer Reirradiation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Challenges in Head and Neck Cancer Recurrence or Reirradiation
1.2. Potential of Proton FLASH-RT for HN Cancer Treatment
2. Current Challenges in Proton FLASH Application
2.1. Insufficient Biological Evidence for FLASH Sparing Modeling
2.2. Absence of Optimal Regimens for FLASH-RT
2.3. Limited Availability of Proton Facilities
3. Strategies for Improved Implementation
3.1. Design Robust Clinical Trials for HN Cancers
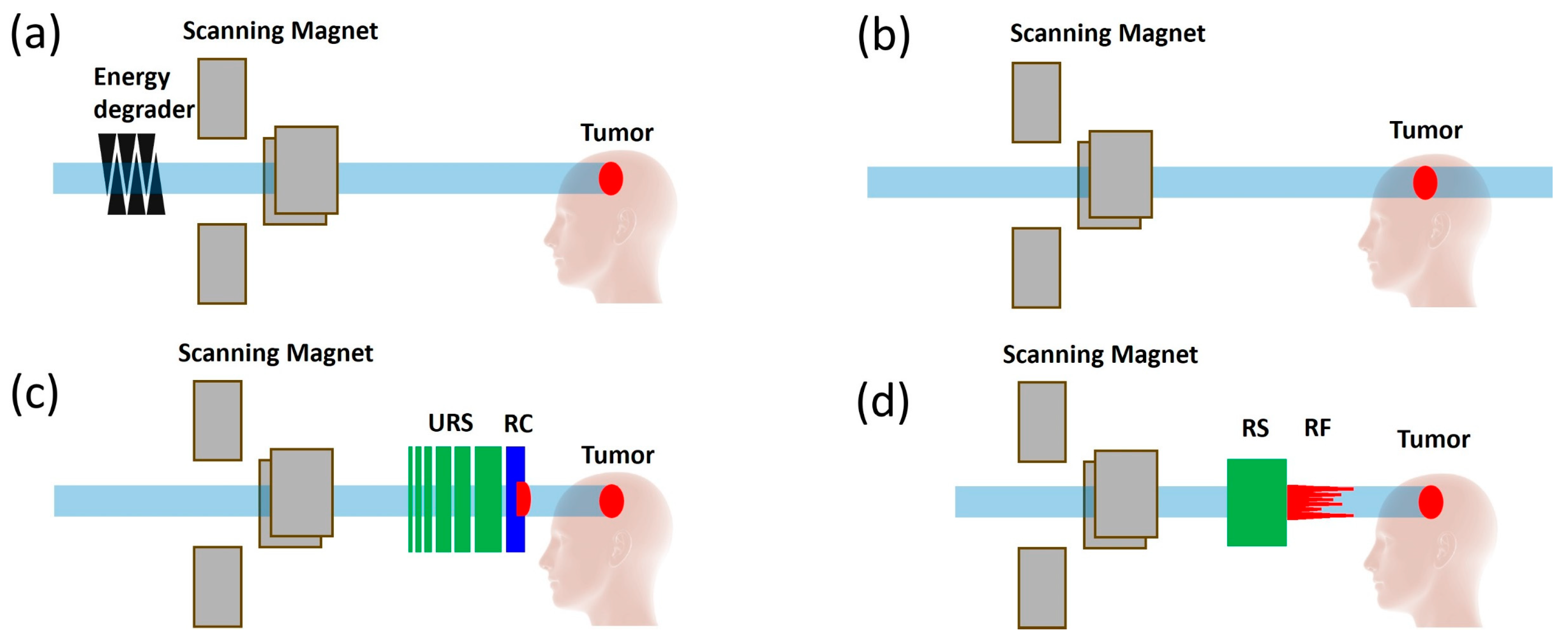
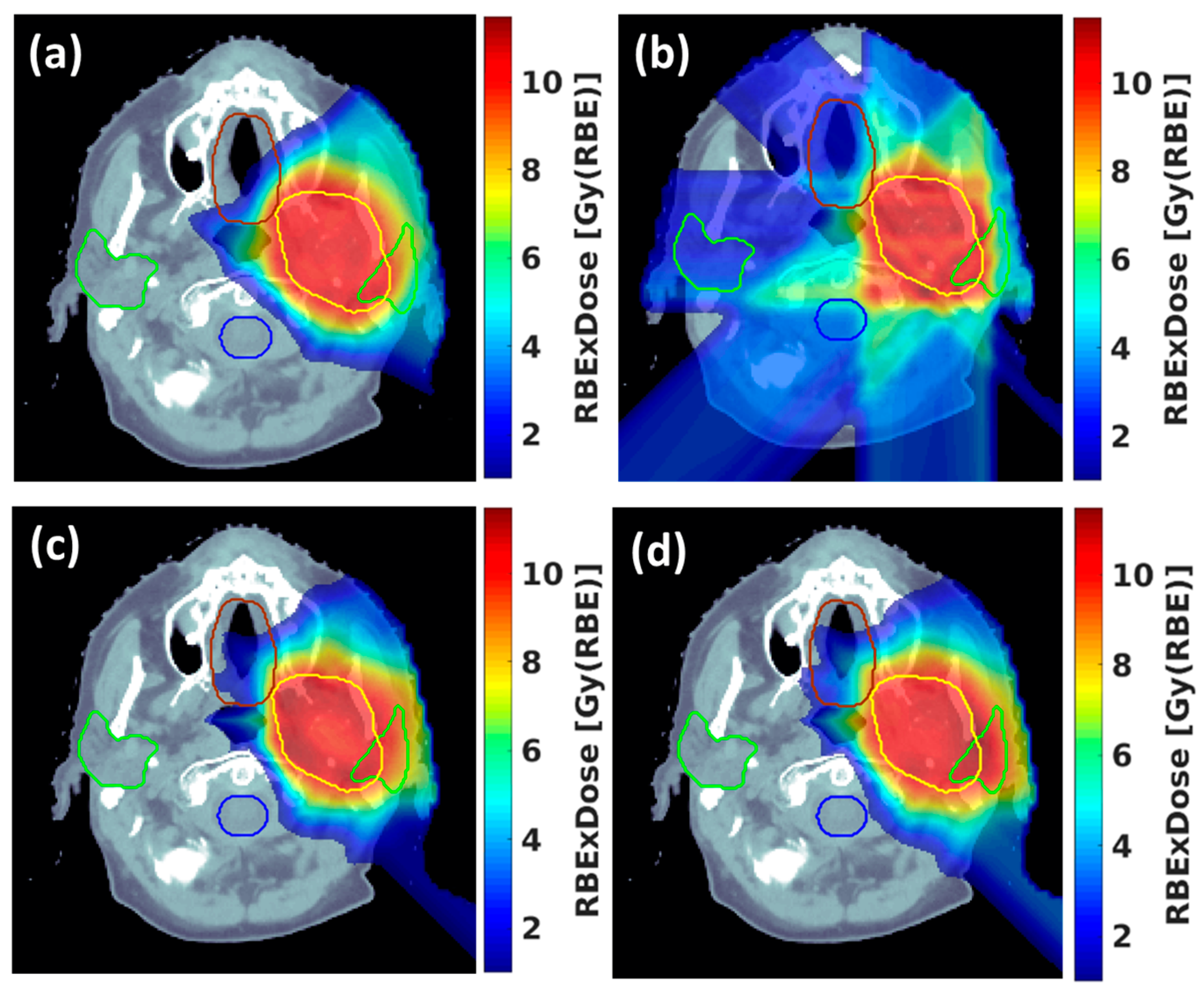
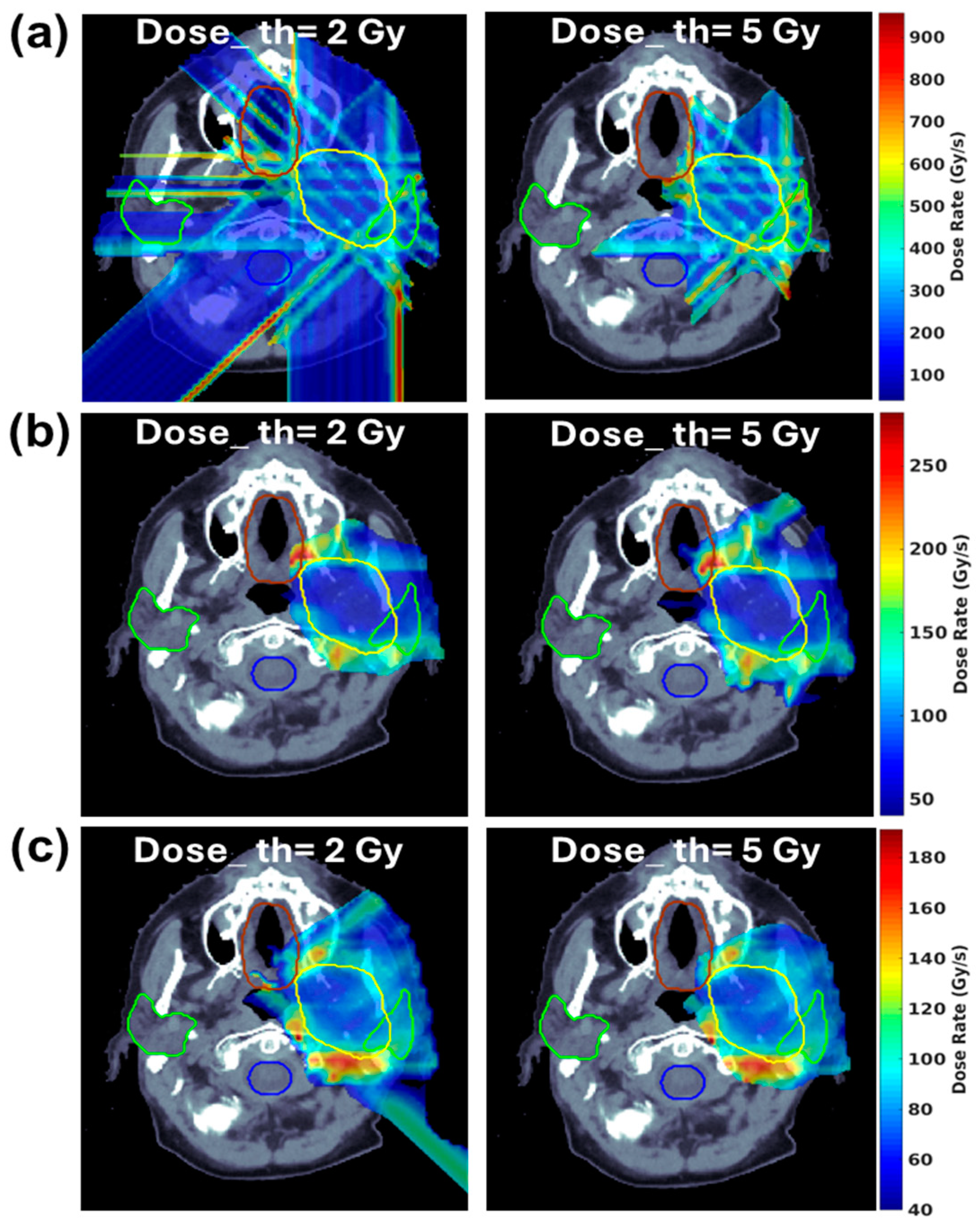
3.2. Development of Innovative Delivery Solutions
3.3. Development of Commercial TPSs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nenclares, P.; Rullan, A.; Tam, K.; Dunn, L.A.; St John, M.; Harrington, K.J. Introducing Checkpoint Inhibitors Into the Curative Setting of Head and Neck Cancers: Lessons Learned, Future Considerations. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2022, 42, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chow, L.Q. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadoni, G.; Giraldi, L.; Petrelli, L.; Pandolfini, M.; Giuliani, M.; Paludetti, G.; Pastorino, R.; Leoncini, E.; Arzani, D.; Almadori, G.; et al. Prognostic factors in head and neck cancer: A 10-year retrospective analysis in a single-institution in Italy. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anderson, G.; Ebadi, M.; Vo, K.; Novak, J.; Govindarajan, A.; Amini, A. An Updated Review on Head and Neck Cancer Treatment with Radiation Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nuyts, S.; Bollen, H.; Ng, S.P.; Corry, J.; Eisbruch, A.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Smee, R.; Strojan, P.; Ng, W.T.; Ferlito, A. Proton Therapy for Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck: Early Clinical Experience and Current Challenges. Cancers 2022, 14, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sharma, S.; Zhou, O.; Thompson, R.; Gabriel, P.; Chalian, A.; Rassekh, C.; Weinstein, G.S.; O’Malley, B.W., Jr.; Aggarwal, C.; Bauml, J.; et al. Quality of Life of Postoperative Photon versus Proton Radiation Therapy for Oropharynx Cancer. Int. J. Part Ther. 2018, 5, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Youssef, I.; Yoon, J.; Mohamed, N.; Zakeri, K.; Press, R.H.; Chen, L.; Gelblum, D.Y.; McBride, S.M.; Tsai, C.J.; Riaz, N.; et al. Toxicity Profiles and Survival Outcomes Among Patients With Nonmetastatic Oropharyngeal Carcinoma Treated with Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy vs Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2241538, Erratum in JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2250485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Rwigema, J.M.; Malyapa, R.S.; Regine, W.F.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. Systematic assessment of clinical outcomes and toxicities of proton radiotherapy for reirradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 125, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaudon, V.; Caplier, L.; Monceau, V.; Pouzoulet, F.; Sayarath, M.; Fouillade, C.; Poupon, M.F.; Brito, I.; Hupé, P.; Bourhis, J.; et al. Ultrahigh dose-rate FLASH irradiation increases the differential response between normal and tumor tissue in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 245ra93, Erratum in Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourhis, J.; Sozzi, W.J.; Jorge, P.G.; Gaide, O.; Bailat, C.; Duclos, F.; Patin, D.; Ozsahin, M.; Bochud, F.; Germond, J.F.; et al. Treatment of a first patient with FLASH-radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouillade, C.; Curras-Alonso, S.; Giuranno, L.; Quelennec, E.; Heinrich, S.; Bonnet-Boissinot, S.; Beddok, A.; Leboucher, S.; Karakurt, H.U.; Bohec, M.; et al. FLASH Irradiation Spares Lung Progenitor Cells and Limits the Incidence of Radio-induced Senescence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vozenin, M.C.; De Fornel, P.; Petersson, K.; Favaudon, V.; Jaccard, M.; Germond, J.F.; Petit, B.; Burki, M.; Ferrand, G.; Patin, D.; et al. The Advantage of FLASH Radiotherapy Confirmed in Mini-pig and Cat-cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, B.S.; Sitarz, M.K.; Ankjærgaard, C.; Johansen, J.G.; Andersen, C.E.; Kanouta, E.; Grau, C.; Poulsen, P. Pencil beam scanning proton FLASH maintains tumor control while normal tissue damage is reduced in a mouse model. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Petersson, K.; Jaccard, M.; Boivin, G.; Germond, J.F.; Petit, B.; Doenlen, R.; Favaudon, V.; Bochud, F.; Bailat, C.; et al. Irradiation in a flash: Unique sparing of memory in mice after whole brain irradiation with dose rates above 100 Gy/s. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Acharya, M.M.; Petersson, K.; Alikhani, L.; Yakkala, C.; Allen, B.D.; Ollivier, J.; Petit, B.; Jorge, P.G.; Syage, A.R.; et al. Long-term neurocognitive benefits of FLASH radiotherapy driven by reduced reactive oxygen species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10943–10951, Erratum in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 25946–25947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Levy, K.; Natarajan, S.; Wang, J.; Chow, S.; Eggold, J.T.; Loo, P.E.; Manjappa, R.; Melemenidis, S.; Lartey, F.M.; Schüler, E.; et al. Abdominal FLASH irradiation reduces radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity for the treatment of ovarian cancer in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Valdés Zayas, A.; Kumari, N.; Liu, K.; Neill, D.; Delahoussaye, A.; Gonçalves Jorge, P.; Geyer, R.; Lin, S.H.; Bailat, C.; Bochud, F.; et al. Independent Reproduction of the FLASH Effect on the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Multi-Institutional Comparative Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Okoro, C.M.; Schüler, E.; Taniguchi, C.M. The Therapeutic Potential of FLASH-RT for Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chow, R.; Kang, M.; Wei, S.; Choi, J.I.; Press, R.H.; Hasan, S.; Chhabra, A.M.; Cengel, K.A.; Lin, H.; Simone, C.B. FLASH radiation therapy: Review of the literature and considerations for future research and proton therapy FLASH trials. Appl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 10, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børresen, B.; Arendt, M.L.; Konradsson, E.; Bastholm Jensen, K.; Bäck, S.Å.; Munck Af Rosenschöld, P.; Ceberg, C.; Petersson, K. Evaluation of single-fraction high dose FLASH radiotherapy in a cohort of canine oral cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1256760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Konradsson, E.; Arendt, M.L.; Bastholm Jensen, K.; Børresen, B.; Hansen, A.E.; Bäck, S.; Kristensen, A.T.; Munck Af Rosenschöld, P.; Ceberg, C.; Petersson, K. Establishment and Initial Experience of Clinical FLASH Radiotherapy in Canine Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 658004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sørensen, B.S.; Kanouta, E.; Ankjærgaard, C.; Kristensen, L.; Johansen, J.G.; Sitarz, M.K.; Andersen, C.E.; Grau, C.; Poulsen, P. Proton FLASH: Impact of Dose Rate and Split Dose on Acute Skin Toxicity in a Murine Model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 120, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esplen, N.; Mendonca, M.S.; Bazalova-Carter, M. Physics and biology of ultrahigh dose-rate (FLASH) radiotherapy: A topical review. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 23TR03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Wei, S.; Choi, J.I.; Lin, H.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. A Universal Range Shifter and Range Compensator Can Enable Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Single-Energy Bragg Peak FLASH-RT Treatment Using Current Commercially Available Proton Systems. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Marlen, P.; Dahele, M.; Folkerts, M.; Abel, E.; Slotman, B.J.; Verbakel, W.F.A.R. Bringing FLASH to the Clinic: Treatment Planning Considerations for Ultrahigh Dose-Rate Proton Beams. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 106, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattery, G.; Kaulfers, T.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, X.; Selvaraj, B.; Lin, H.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Choi, J.I.; Chang, J.; Kang, M. Pencil Beam Scanning Bragg Peak FLASH Technique for Ultrahigh Dose Rate Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy in Early-Stage Breast Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2023, 15, 4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaulfers, T.; Lattery, G.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, X.; Selvaraj, B.; Wu, H.; Chhabra, A.M.; Choi, J.I.; Lin, H.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; et al. Pencil Beam Scanning Proton Bragg Peak Conformal FLASH in Prostate Cancer Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kang, M.; Wei, S.; Lin, H.; Choi, J.I.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. Flash Radiotherapy Systems and Methods of Use. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20220323791A1/en (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Zhang, G.; Gao, W.; Peng, H. Design of static and dynamic ridge filters for FLASH-IMPT: A simulation study. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 5387–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Butkus, M.; Wu, X. Conformal Dose Modulator for Proton Beam Therapy: A Simulation Study. PREPRINT (Version 1). Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-2488761/v1 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Roddy, D.; Béllnger-Champagne, C.; Tattenberg, S.; Yen, S.; Trinczek, M.; Hoehr, C. Design, optimization and testing of ridge filters for proton FLASH radiotherapy at TRIUMF: The HEDGEHOG. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 2024, 1063, 169284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeonov, Y.; Weber, U.; Schuy, C.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R.; Penchev, P.; Flatten, V.; Zink, K. Development, Monte Carlo simulations and experimental evaluation of a 3D range-modulator for a complex target in scanned proton therapy. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2022, 8, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Zhou, J.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, Y.; Patel, P.R.; Yu, D.S.; Tian, S.; Yang, X. Streamlined pin-ridge-filter design for single-energy proton FLASH planning. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennock, M.; Wei, S.; Cheng, C.; Lin, H.; Hasan, S.; Chhabra, A.M.; Choi, J.I.; Bakst, R.L.; Kabarriti, R.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; et al. Proton Bragg Peak FLASH Enables Organ Sparing and Ultrahigh Dose-Rate Delivery: Proof of Principle in Recurrent Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krieger, M.; van de Water, S.; Folkerts, M.M.; Mazal, A.; Fabiano, S.; Bizzocchi, N.; Weber, D.C.; Safai, S.; Lomax, A.J. A quantitative FLASH effectiveness model to reveal potentials and pitfalls of high dose rate proton therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2026–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Friedl, A.A.; Prise, K.M.; Butterworth, K.T.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Favaudon, V. Radiobiology of the FLASH effect. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 1993–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hageman, E.; Che, P.P.; Dahele, M.; Slotman, B.J.; Sminia, P. Radiobiological Aspects of FLASH Radiotherapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bogaerts, E.; Macaeva, E.; Isebaert, S.; Haustermans, K. Potential Molecular Mechanisms behind the Ultrahigh Dose Rate “FLASH” Effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, G. Mechanisms underlying FLASH radiotherapy, a novel way to enlarge the differential responses to ionizing radiation between normal and tumor tissues. Radiat. Med. Prot. 2020, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, R.; Esipova, T.V.; Allu, S.R.; Ashraf, R.; Rahman, M.; Gunn, J.R.; Bruza, P.; Gladstone, D.J.; Williams, B.B.; et al. Quantification of Oxygen Depletion During FLASH Irradiation In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Slyke, A.L.; El Khatib, M.; Velalopoulou, A.; Diffenderfer, E.; Shoniyozov, K.; Kim, M.M.; Karagounis, I.V.; Busch, T.M.; Vinogradov, S.A.; Koch, C.J.; et al. Oxygen Monitoring in Model Solutions and In Vivo in Mice During Proton Irradiation at Conventional and FLASH Dose Rates. Radiat. Res. 2022, 198, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cooper, C.R.; Jones, D.; Jones, G.D.; Petersson, K. FLASH irradiation induces lower levels of DNA damage ex vivo, an effect modulated by oxygen tension, dose, and dose rate. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Perstin, A.; Poirier, Y.; Sawant, A.; Tambasco, M. Quantifying the DNA-damaging Effects of FLASH Irradiation With Plasmid DNA. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diffenderfer, E.S.; Verginadis, I.I.; Kim, M.M.; Shoniyozov, K.; Velalopoulou, A.; Goia, D.; Putt, M.; Hagan, S.; Avery, S.; Teo, K.; et al. Design, Implementation, and in Vivo Validation of a Novel Proton FLASH Radiation Therapy System. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 106, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mascia, A.; McCauley, S.; Speth, J.; Nunez, S.A.; Boivin, G.; Vilalta, M.; Sharma, R.A.; Perentesis, J.P.; Sertorio, M. Impact of Multiple Beams on the FLASH Effect in Soft Tissue and Skin in Mice. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 118, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanisce, L.; Koshkareva, Y.; Xu, Q.; Patel, A.; Squillante, C.; Ahmad, N.; Rajagopalan, K.; Kubicek, G.J. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Treatment for Recurrent, Previously Irradiated Head and Neck Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1533033818780086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Quan, K.; Xu, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Clump, D.A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lalonde, R.; Burton, S.A.; Heron, D.E. Toxicities Following Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Treatment of Locally-Recurrent and Previously Irradiated Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 26, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, D.C.; Vargo, J.A.; Heron, D.E. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Recurrent Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer J. 2016, 22, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comet, B.; Kramar, A.; Faivre-Pierret, M.; Dewas, S.; Coche-Dequeant, B.; Degardin, M.; Lefebvre, J.L.; Lacornerie, T.; Lartigau, E.F. Salvage stereotactic reirradiation with or without cetuximab for locally recurrent head-and-neck cancer: A feasibility study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargo, J.A.; Ferris, R.L.; Ohr, J.; Clump, D.A.; Davis, K.S.; Duvvuri, U.; Kim, S.; Johnson, J.T.; Bauman, J.E.; Gibson, M.K.; et al. A prospective phase 2 trial of reirradiation with stereotactic body radiation therapy plus cetuximab in patients with previously irradiated recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, D.C.; Vargo, J.A.; Ferris, R.L.; Ohr, J.; Clump, D.A.; Yau, W.W.; Duvvuri, U.; Kim, S.; Johnson, J.T.; Bauman, J.E.; et al. Risk of Severe Toxicity According to Site of Recurrence in Patients Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Recurrent Head and Neck Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrer Bley, C.; Wolf, F.; Gonçalves Jorge, P.; Grilj, V.; Petridis, I.; Petit, B.; Böhlen, T.T.; Moeckli, R.; Limoli, C.; Bourhis, J.; et al. Dose- and Volume-Limiting Late Toxicity of FLASH Radiotherapy in Cats with Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Nasal Planum and in Mini Pigs. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3814–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Corde, S.; Laissue, J.A.; Bazalova-Carter, M. FLASH radiotherapy with photon beams. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyreuther, E.; Brand, M.; Hans, S.; Hideghéty, K.; Karsch, L.; Leßmann, E.; Schürer, M.; Szabó, E.R.; Pawelke, J. Feasibility of proton FLASH effect tested by zebrafish embryo irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesulu, B.P.; Sharma, A.; Pollard-Larkin, J.M.; Sadagopan, R.; Symons, J.; Neri, S.; Singh, P.K.; Tailor, R.; Lin, S.H.; Krishnan, S. Ultra high dose rate (35 Gy/sec) radiation does not spare the normal tissue in cardiac and splenic models of lymphopenia and gastrointestinal syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17180, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, D.; Sforza, D.; Wong, J.; Rezaee, M. Dosimetric characterization of a rotating anode x-ray tube for FLASH radiotherapy research. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 1474–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maxim, P.G.; Tantawi, S.G.; Loo, B.W., Jr. PHASER: A platform for clinical translation of FLASH cancer radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascia, A.E.; Daugherty, E.C.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, E.; Xiao, Z.; Sertorio, M.; Woo, J.; Backus, L.R.; McDonald, J.M.; McCann, C.; et al. Proton FLASH Radiotherapy for the Treatment of Symptomatic Bone Metastases: The FAST-01 Nonrandomized Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 62–69, Erratum in JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daugherty, E.C.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Mascia, A.E.; Sertorio, M.; Woo, J.; McCann, C.; Russell, K.J.; Sharma, R.A.; Khuntia, D.; et al. FLASH radiotherapy for the treatment of symptomatic bone metastases in the thorax (FAST-02): Protocol for a prospective study of a novel radiotherapy approach. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartsell, W.F.; Simone, C.B., II; Godes, D.; Maggiore, J.; Mehta, M.P.; Frank, S.J.; Metz, J.M.; Choi, J.I. Temporal Evolution and Diagnostic Diversification of Patients Receiving Proton Therapy in the United States: A Ten-Year Trend Analysis (2012 to 2021) From the National Association for Proton Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 119, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burus, T.; VanHelene, A.D.; Rooney, M.K.; Lang Kuhs, K.A.; Christian, W.J.; McNair, C.; Mishra, S.; Paulino, A.C.; Smith, G.L.; Frank, S.J.; et al. Travel-Time Disparities in Access to Proton Beam Therapy for Cancer Treatment. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2410670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Maradia, V.; Colizzi, I.; Meer, D.; Weber, D.C.; Lomaxs, A.J.; Actis, O.; Psoroulas, S. Universal and dynamic ridge filter for pencil beam scanning particle therapy: A novel concept for ultra-fast treatment delivery. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 225005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Lin, H.; Isabelle Choi, J.; Shi, C.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Kang, M. Advanced pencil beam scanning Bragg peak FLASH-RT delivery technique can enhance lung cancer planning treatment outcomes compared to conventional multiple-energy proton PBS techniques. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, B.; Lowe, M.; Traneus, E.; Krieger, M.; Schuemann, J. Treatment planning considerations for the development of FLASH proton therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 175, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.; Xu, L.; Jing, H.; Selvaraj, B.; Lin, H.; Pennock, M.; Chhabra, A.M.; Hasan, S.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The Potential and Challenges of Proton FLASH in Head and Neck Cancer Reirradiation. Cancers 2024, 16, 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193249
Cheng C, Xu L, Jing H, Selvaraj B, Lin H, Pennock M, Chhabra AM, Hasan S, Zhai H, Zhang Y, et al. The Potential and Challenges of Proton FLASH in Head and Neck Cancer Reirradiation. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193249
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chingyun, Liming Xu, Hao Jing, Balaji Selvaraj, Haibo Lin, Michael Pennock, Arpit M. Chhabra, Shaakir Hasan, Huifang Zhai, Yin Zhang, and et al. 2024. "The Potential and Challenges of Proton FLASH in Head and Neck Cancer Reirradiation" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193249
APA StyleCheng, C., Xu, L., Jing, H., Selvaraj, B., Lin, H., Pennock, M., Chhabra, A. M., Hasan, S., Zhai, H., Zhang, Y., Nie, K., Bakst, R. L., Kabarriti, R., Choi, J. I., Lee, N. Y., Simone, C. B., II, Kang, M., & Wu, H. (2024). The Potential and Challenges of Proton FLASH in Head and Neck Cancer Reirradiation. Cancers, 16(19), 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193249







