Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis and Experimental Verification of the Roles of Retinoid-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of the Key Features of RBP Family Members in Homo sapiens
2.2. TCGA Pan-Cancer Atlas Data Profile
2.3. Survival and Cox Analysis of RBP Family Expression
2.4. Genetic Alteration Analysis
2.5. Immune Infiltration Cells and Immune Checkpoint Correlation Analysis
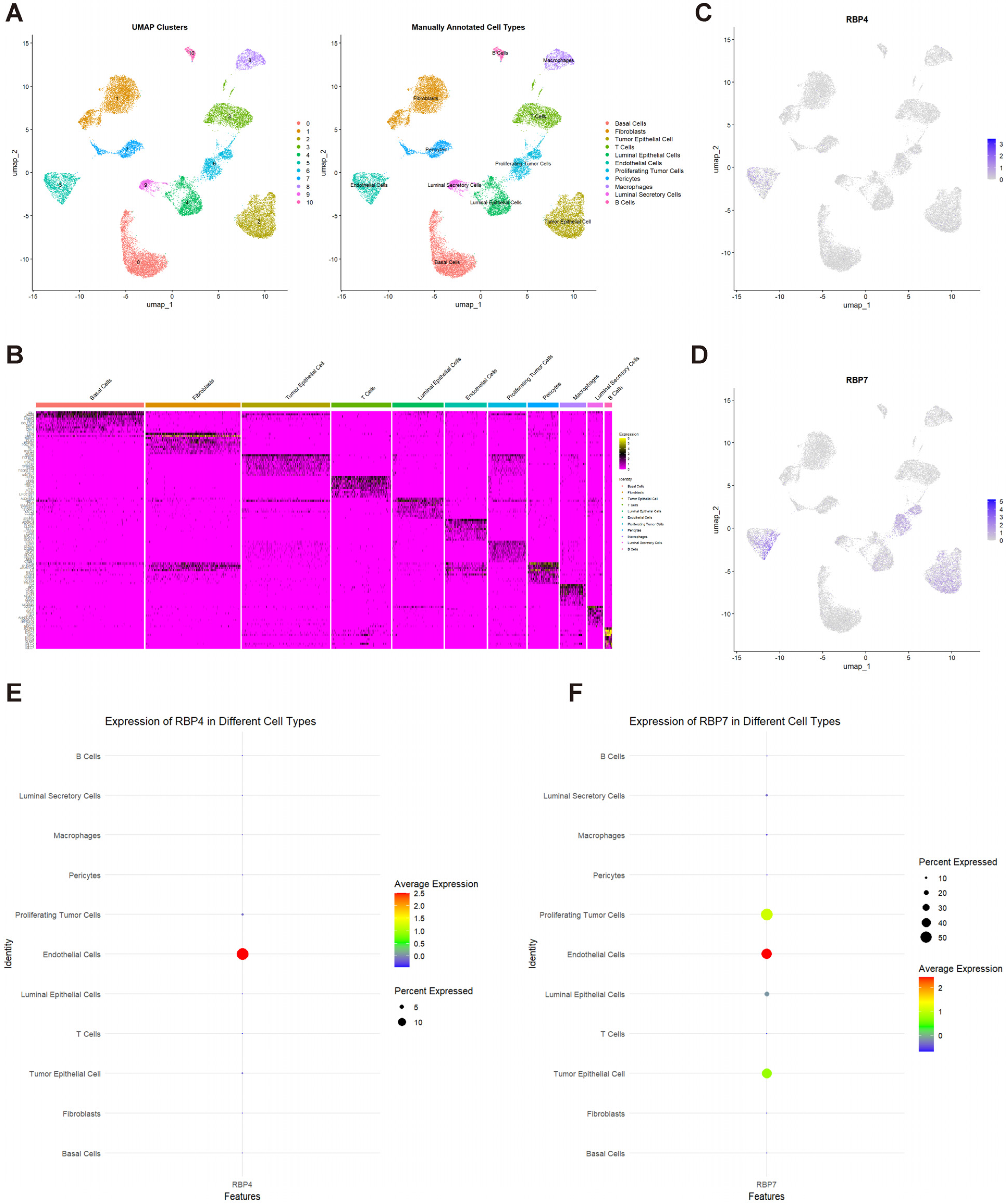
2.6. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis
2.6.1. Data Preprocessing
2.6.2. Dimensionality Reduction and Clustering
2.6.3. Marker Gene Identification
2.6.4. Cell Type Identification
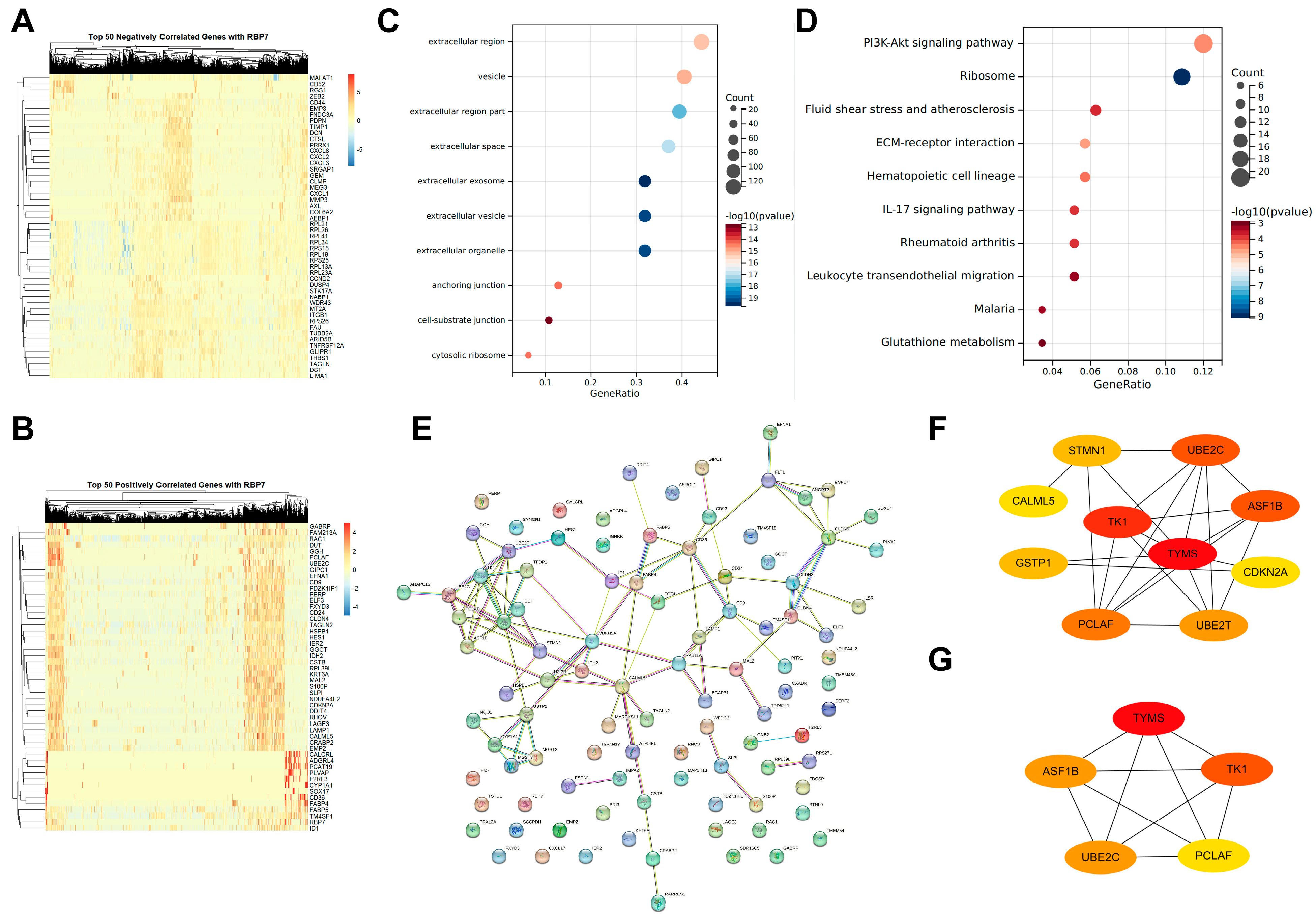
2.6.5. Genes Co-Expressed with RBP7 and Functional Analysis
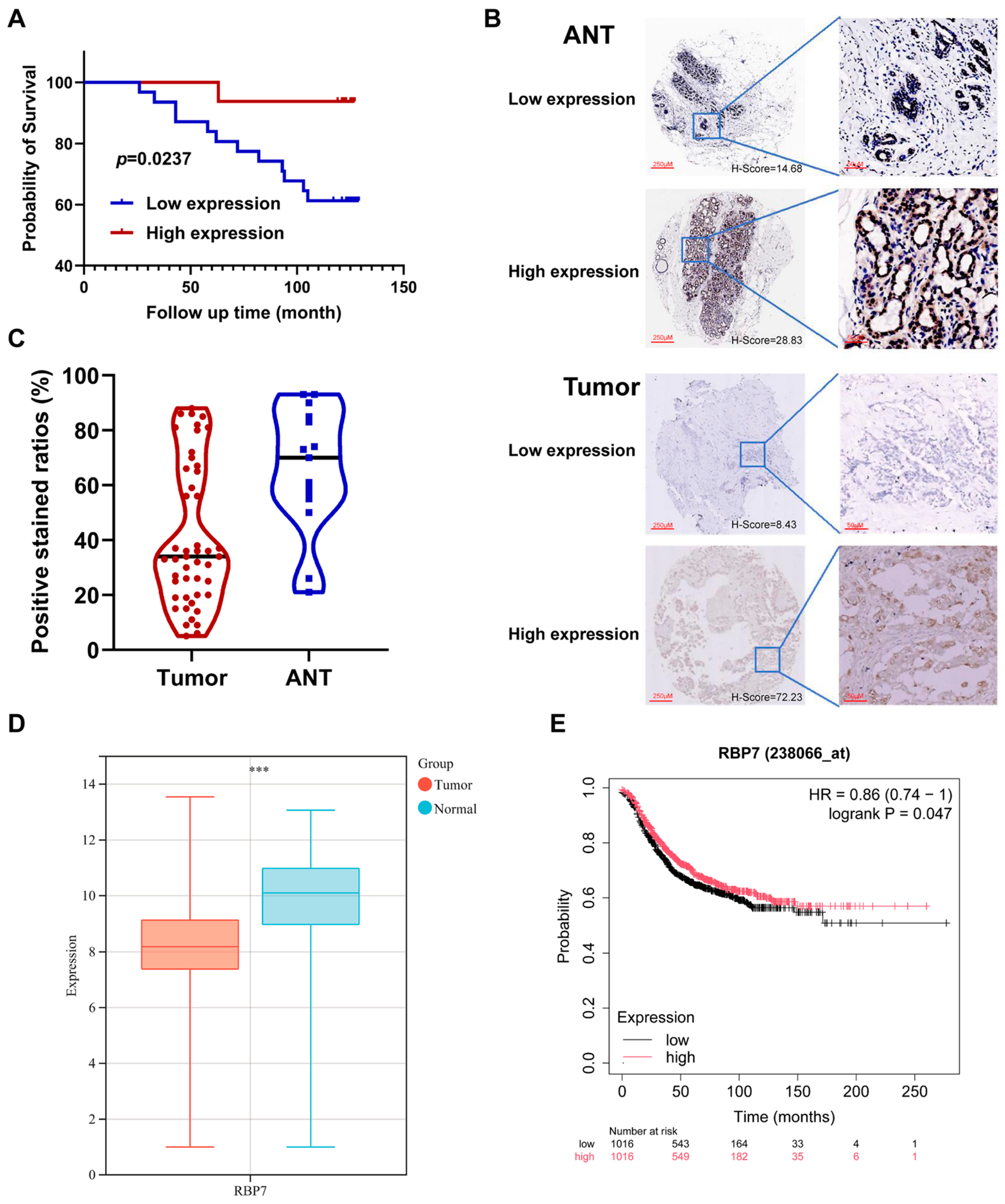
2.7. Tissue Microarray Methodology and Validation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Structure and Motif Composition of RBP Family Members in Homo sapiens
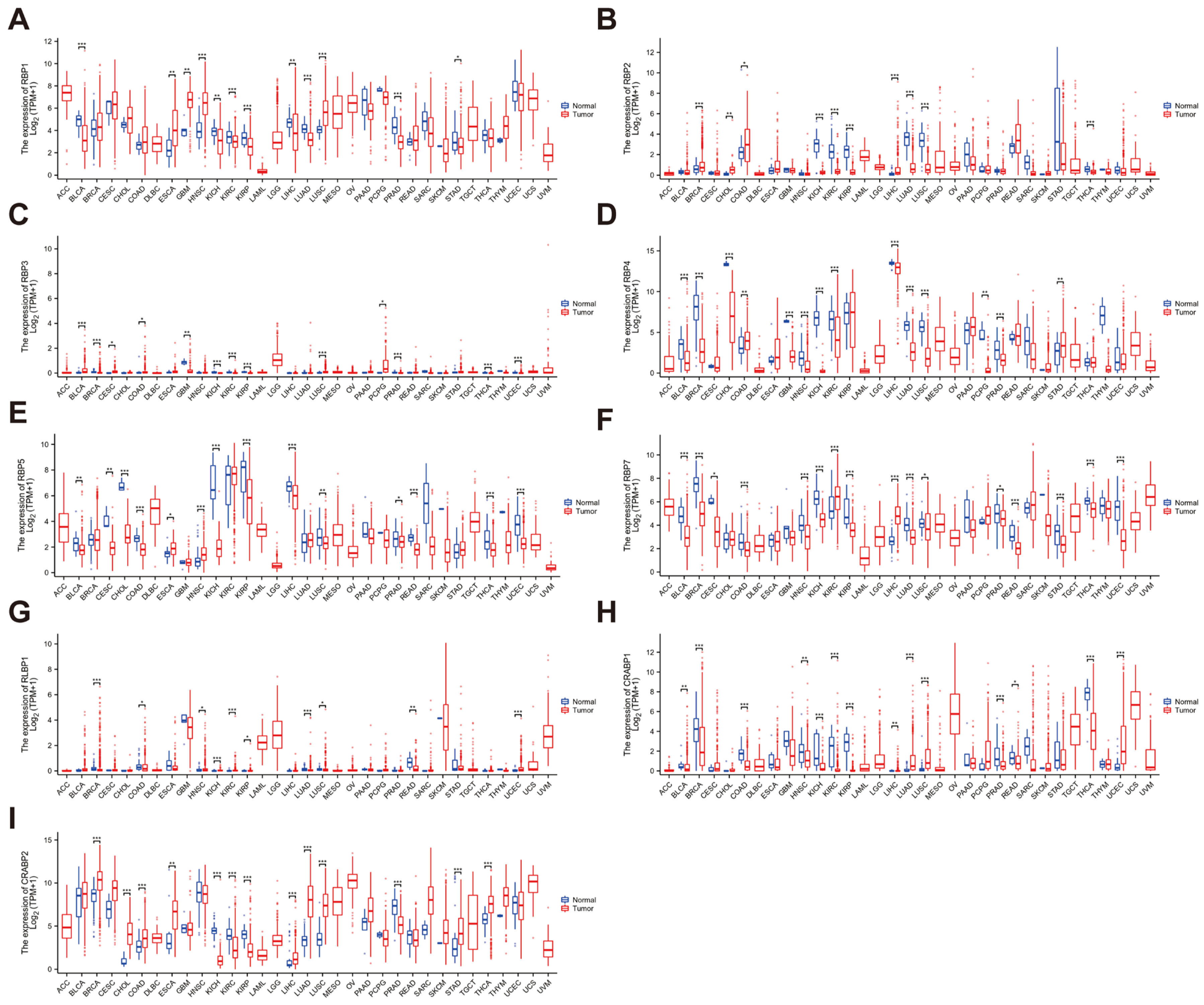
3.2. Expression Levels of the RBP Family in Pan-Cancer
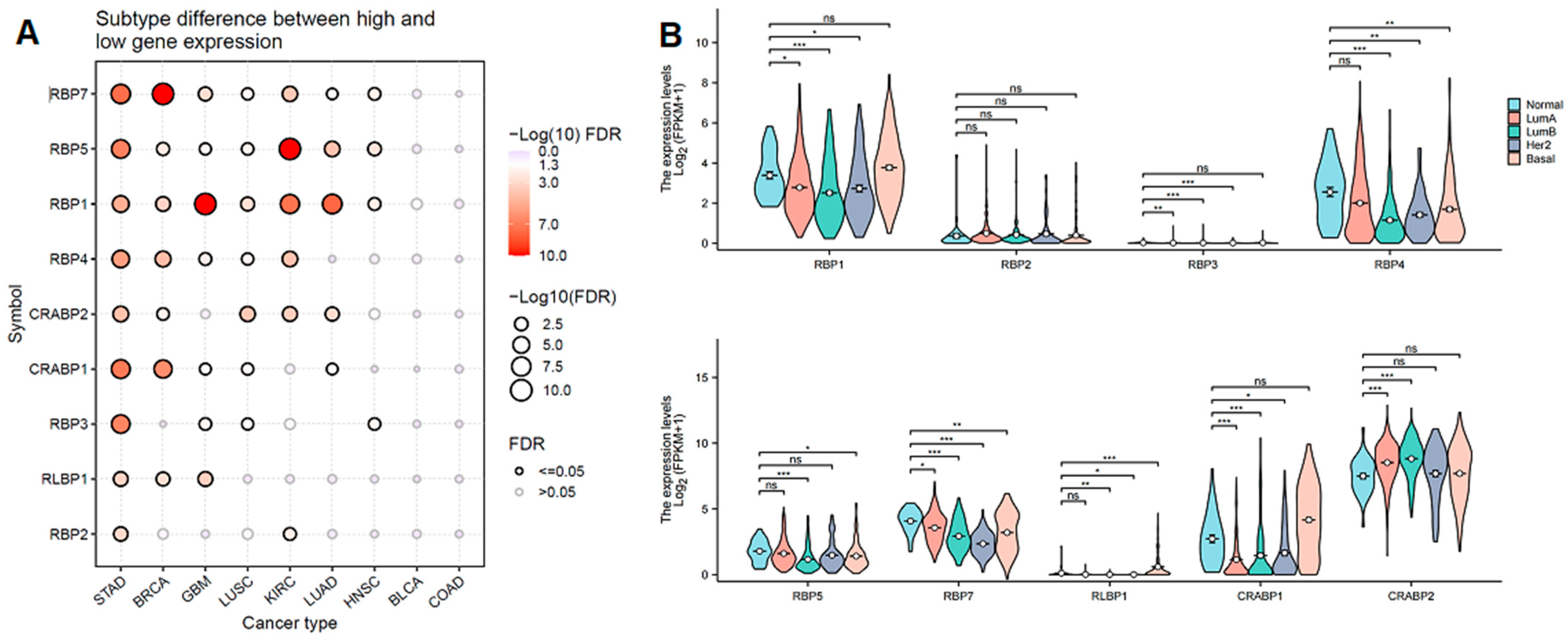
3.3. The Association Between Clinical Characteristics, Tumor Subtypes, and RBP Expression
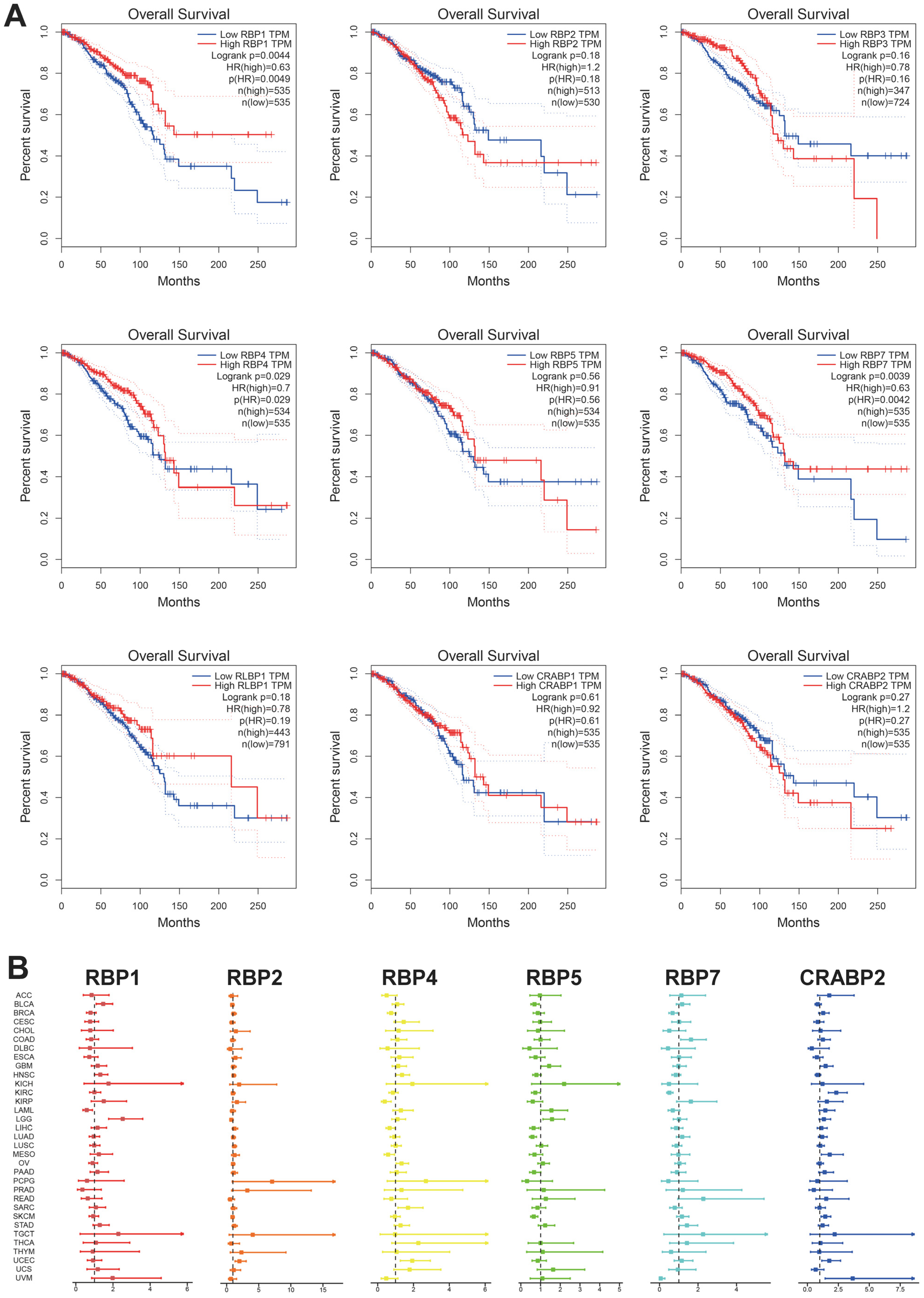
3.4. Prognostic Value of RBPs in Pan-Cancer
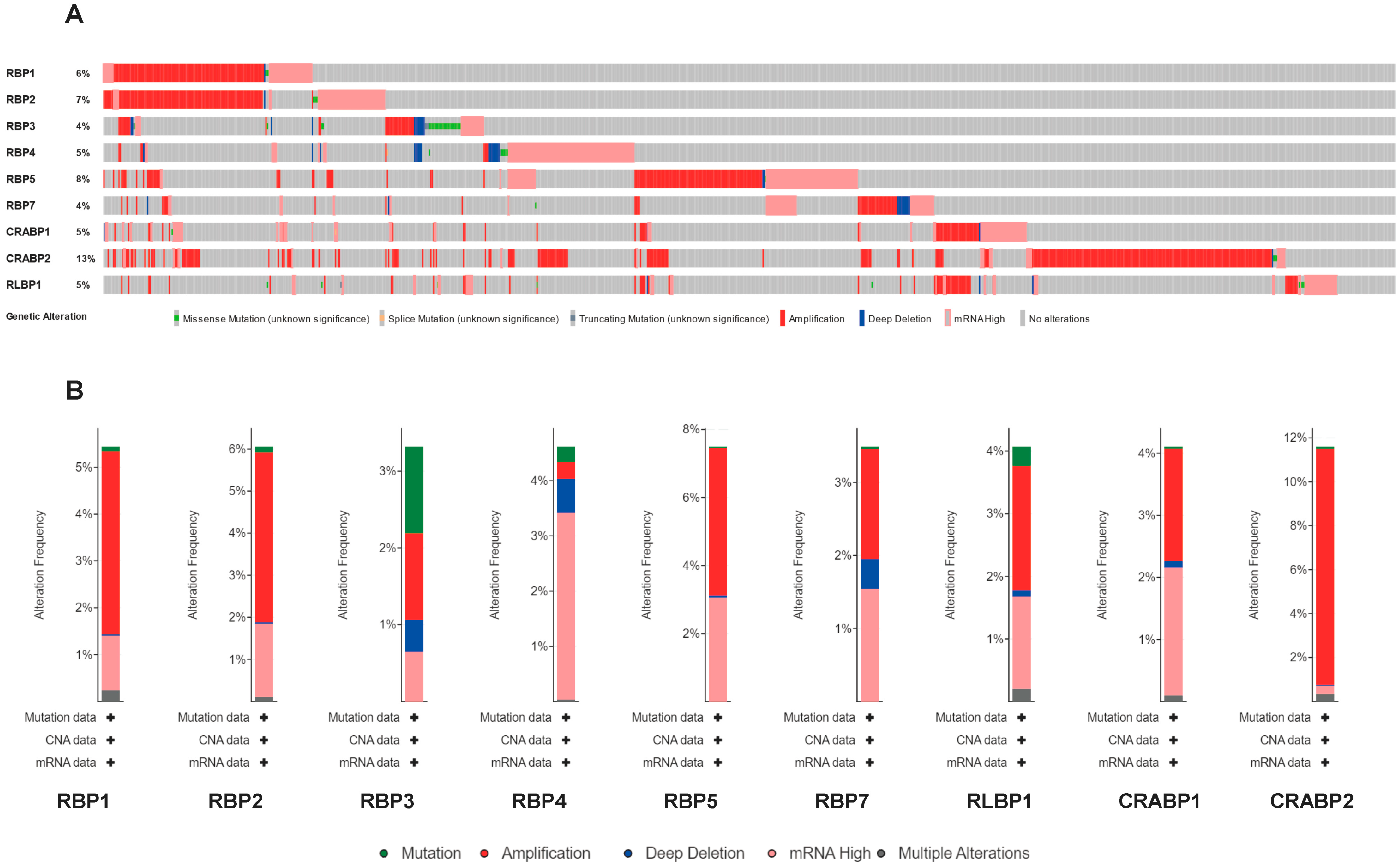
3.5. Genetic Alteration and Immune Checkpoint Correlation Analysis
3.6. Single-Cell Transcriptome Analysis of RBP4 and RBP7 in TNBC
3.7. Single-Cell Differential Gene Expression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RBPs | Retinoid-binding proteins |
| scRNA-seq | Single-cell RNA sequencing |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| TMA | Tissue microarray |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: Globocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Martinez, L.; Zhang, Y.; Nakata, Y.; Chan, H.L.; Morey, L. Epigenetic mechanisms in breast cancer therapy and resistance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabellini, N.; Cullen, J.; Cao, L.; Shanahan, J.; Hamerschlak, N.; Waite, K.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Montero, A.J. Racial disparities in breast cancer treatment patterns and treatment related adverse events. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushue, N.; Wan, Y.-J.Y. Retinoid pathway and cancer therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, P.; Desmarchelier, C. Genetic Variations Associated with Vitamin A Status and Vitamin A Bioavailability. Nutrients 2017, 9, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, T.; Madigan, M.C.; Fernando, N.; Aggio-Bruce, R.; Zhou, F.; Pierce, M.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Natoli, R.; et al. Interphotoreceptor Retinoid-Binding Protein (IRBP) in Retinal Health and Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 577935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Han, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Z.; Luo, H.; Hao, Y.; Jiang, Y. Methylation-Mediated Silencing of Rbp7 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression through Ppar and Pi3k/Akt Pathway. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 9039110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasry, M.; Brandl, L.; Engel, J.; Jung, A.; Kirchner, T.; Horst, D. RBP7 is a clinically prognostic biomarker and linked to tumor invasion and EMT in colon cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4883–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Cui, L.; Ma, A.; Li, N.; Si, H. Elevated Serum Levels of Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Are Associated with Breast Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Q.; Baral, S.; Ding, J.; Zhao, F.; Yao, Q.; Gao, S.; Liu, B.; Wang, D. Retinol Binding Protein 4 Serves as a Potential Tumor Biomarker and Promotes Malignant Behavior in Gastric Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2024, 16, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, F.; Huang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.; Liang, L.; Qin, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Retinol-binding protein 4 as a promising serum biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular Carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 45, 101979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-L.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Jhuang, J.-Y.; Li, Y.-S.; Cheng, S.-P. CRABP2 Is Associated with Thyroid Cancer Recurrence and Promotes Invasion via the Integrin/FAK/AKT Pathway. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqac171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-I.; Lin, Y.-P.; Tseng, C.-W.; Chen, H.-J.; Wang, L.-H. Crabp2 Promotes Metastasis of Lung Cancer Cells via HuR and Integrin β1/FAK/ERK Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, L. Reduced Expression of RBP7 is Associated with Resistance to Tamoxifen In Luminal A Breast Cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xu, R.; Xu, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Huang, X.; et al. RBP7 functions as a tumor suppressor in HR+ breast cancer by inhibiting the AKT/SREBP1 pathway and reducing fatty acid. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, H. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Expression Analysis of the Jaz Gene Family in Resistance to Gray Leaf Spots in Tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Luthe, D. Identification and evolution analysis of the JAZ gene family in maize. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Yoon, B.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.Y. Gent2: An Updated Gene Expression Database for Normal and Tumor Tissues. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12 (Suppl. S5), 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posta, M.; Győrffy, B. Pathway-level mutational signatures predict breast cancer outcomes and reveal therapeutic targets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 182, 5734–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Q.; Ren, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Dou, Z.; Kong, X.; Liang, X.; Zhi, K. The Rbp1-Ckap4 Axis Activates Oncogenic Autophagy and Promotes Cancer Progression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, D.; Williams, S.J.; Hamilton, T.C. Loss of Cellular Retinol-Binding Protein 1 Gene Expression in Microdissected Human Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Kuppumbatti, Y.S.; Rexer, B.; Nakajo, S.; Nakaya, K.; Mira-Y-Lopez, R. CRBP suppresses breast cancer cell survival and anchorage-independent growth. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7413–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, A.; Ferlosio, A.; Ciucci, A.; Francesconi, A.; Lifschitz-Mercer, B.; Gabbiani, G.; Spagnoli, L.G.; Czernobilsky, B. Cellular retinol binding protein-1 expression in endometrial hyperplasia and carcinoma: Diagnostic and possible therapeutic implications. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ren, J.; Bi, Z.; Fu, Z. Positive Expression of Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Is Related to the Malignant Clinical Features Leading to Poor Prognosis of Glioblastoma. Genet. Res. 2022, 2022, 5435523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Adipokine Rbp4 Drives Ovarian Cancer Cell Migration. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, H.; Takahashi, T.; Izumi, K. Induction of retinol-binding protein 4 and placenta-specific 8 expression in human prostate cancer cells remaining in bone following osteolytic tumor growth inhibition by osteoprotegerin. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papiernik, D.; Urbaniak, A.; Kłopotowska, D.; Nasulewicz-Goldeman, A.; Ekiert, M.; Nowak, M.; Jarosz, J.; Cuprych, M.; Strzykalska, A.; Ugorski, M.; et al. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Accelerates Metastatic Spread and Increases Impairment of Blood Flow in Mouse Mammary Gland Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.C.Y.; Cheung, S.T.; Poon, W.S.; Lee, Y.T.; Ng, I.O.L.; Fan, S.T. Down-regulation of retinol binding protein 5 is associated with aggressive tumor features in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 133, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boylan, J.F.; Gudas, L.J. Overexpression of the Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein-I (Crabp-I) Results in a Reduction in Differentiation-Specific Gene Expression in F9 Teratocarcinoma Cells. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 112, 965–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornic, M.; Delva, L.; Castaigne, S.; Lefebvre, P.; Balitrand, N.; Degos, L.; Chomienne, C. In Vitro All-Trans Retinoic Acid (Atra) Sensitivity and Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein (Crabp) Levels in Relapse Leukemic Cells after Remission Induction by Atra in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. Leukemia 1994, 8, 914–917. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, N.; Park, J.; Lee, J.S.; Yoe, J.; Park, G.Y.; Kim, E.; Jeon, H.; Cho, Y.M.; Roh, T.Y.; Lee, Y. Mir-93/Mir-106b/Mir-375-Cic-Crabp1: A Novel Regulatory Axis in Prostate Cancer Progression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.-Z.; Garcia, E.; Glubrecht, D.D.; Poon, H.Y.; Mackey, J.R.; Godbout, R. CRABP1 is associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer: Adding to the complexity of breast cancer cell response to retinoic acid. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Imoto, I.; Inoue, J.; Kozaki, K.; Tsuda, H.; Shimada, Y.; Aiko, S.; Yoshizumi, Y.; Iwai, T.; Kawano, T.; et al. Frequent methylation-associated silencing of a candidate tumor-suppressor, CRABP1, in esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6456–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.C.; Hallam, S.J.; Lee, S.J.; Klein, R.S.; Wiernik, P.H.; Tallman, M.S.; Gallagher, R.E. Constitutive Expression of Cellular Retinoic Acid Binding Protein Ii and Lack of Correlation with Sensitivity to All-Trans Retinoic Acid in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia Cells. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5770–5776. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, C.S.; ChinAleong, J.-A.; Kocher, H.M. CRABP2 and FABP5 expression levels in diseased and normal pancreas. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 47, 151557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuducu, A.F.; Janzen, V.; Ko, Y.; Hahne, J.C.; Lu, H.; Ma, Z.L.; Albers, P.; Sahin, A.; Wellmann, A.; Scheinert, P.; et al. Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 is down-regulated in prostate cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, B.; Zhou, C.; Mu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Liu, P. Crabp2 Regulates Invasion and Metastasis of Breast Cancer through Hippo Pathway Dependent on ER Status. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Identification of Novel Biomarkers Associated with the Prognosis and Potential Pathogenesis of Breast Cancer via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 1533033821992081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Keen, H.L.; Lu, K.T.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Davis, D.R.; Ibeawuchi, S.C.; Vogel, S.; Quelle, F.W.; Sigmund, C.D. Retinol-Binding Protein 7 Is an Endothelium-Specific Pparγ Cofactor Mediating an Antioxidant Response through Adiponectin. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e91738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.X.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Yang, X.X.; Shen, W.R.; Yuan, L.W.; Ding, X.; Yu, Y.; Cai, W.Y. Unveiling the Impact of Lipid Metabolism on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth and Treatment Options. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1579423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Yu, Q.; Zeng, X.; Feng, J.; Yang, R.; Wan, H.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Lu, J.; et al. Single-Cell Rna Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis Revealed the Immune Microenvironment and Gene Markers of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 3205–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Kang, Z.; Mei, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, H. Promising Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Six Genes in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1239–1254. [Google Scholar]
| Gene Symbol | Ensembl | Protein Length (aa) | Subcellular Location | Qualified GO Term | Ligand | Oncogene | Tumor Suppressor Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBP1 | ENSG00000114115 | 135 | Cytoplasm; lipid droplet | Is active in nucleus; located in nucleoplasm; cytoplasm; located in lipid droplet; located in cytosol | Retinol | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [26] | Ovarian cancer [27]; breast cancer [28]; endometrial cancer [29] |
| RBP2 | ENSG00000114113 | 134 | Cytoplasm | Is active in nucleus; cytoplasm; located in cytosol | Retinol | ||
| RBP3 | ENSG00000265203 | 1247 | Extracellular matrix; secreted | Involved in retinoid metabolic process; involved in proteolysis; involved in lipid metabolic process; involved in visual perception | Retinoids | ||
| RBP4 | ENSG00000138207 | 201 | Secreted | Retinoid binding; enables protein binding; enables retinal binding; enables retinol binding; enables retinol transmembrane transporter activity | Retinol | Glioblastoma [30]; ovarian cancer [31]; prostate cancer [32]; breast cancer [10,33] | |
| RBP5 | ENSG00000139194 | 135 | Cytoplasm | Enables retinoid binding; enables fatty acid binding; enables protein binding; lipid binding; enables retinal binding | Retinol | Hepatocellular carcinoma [34] | |
| RBP7 | ENSG00000162444 | 134 | Cytoplasm | Retinoid binding; enables fatty acid binding; enables protein binding; lipid binding; enables retinal binding | Retinol | Breast cancer [15] | |
| CRABP1 | ENSG00000166426 | 137 | Cytoplasm | Enables retinoic acid binding; enables retinoid binding; enables fatty acid binding; enables protein binding; lipid binding | Retinoic acid | Teratocarcinoma [35]; acute promyelocytic leukemia [36]; prostate cancer [37]; breast cancer [38] | Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma [39] |
| CRABP2 | ENSG00000143320 | 138 | Cytoplasm; endoplasmic reticulum; nucleus | Enables retinoic acid binding; enables retinoid binding; enables fatty acid binding; enables protein binding; lipid binding | Retinoic acid; synthetic retinoid | Acute promyelocytic leukemia [40]; lung cancer [14]; pancreatic cancer [41] | Prostate cancer [42]; breast cancer [43] |
| RLBP1 | ENSG00000140522 | 317 | Cytoplasm | Enables 11-cis retinal binding; enables protein binding; enables retinol binding; enables phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding | 11-cis-retinaldehyde/retinol/retinal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, Y.; Du, D.; Su, Y.; Guo, L.; Chen, S. Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis and Experimental Verification of the Roles of Retinoid-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223706
Xiang Y, Du D, Su Y, Guo L, Chen S. Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis and Experimental Verification of the Roles of Retinoid-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(22):3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223706
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Yuchu, Dan Du, Yaoxi Su, Linghong Guo, and Siliang Chen. 2025. "Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis and Experimental Verification of the Roles of Retinoid-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 22: 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223706
APA StyleXiang, Y., Du, D., Su, Y., Guo, L., & Chen, S. (2025). Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis and Experimental Verification of the Roles of Retinoid-Binding Proteins in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 17(22), 3706. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223706





