Revisiting p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and Its Prognostic Implications in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
2.2. p53 Protein Expression
2.3. TP53 Mutations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
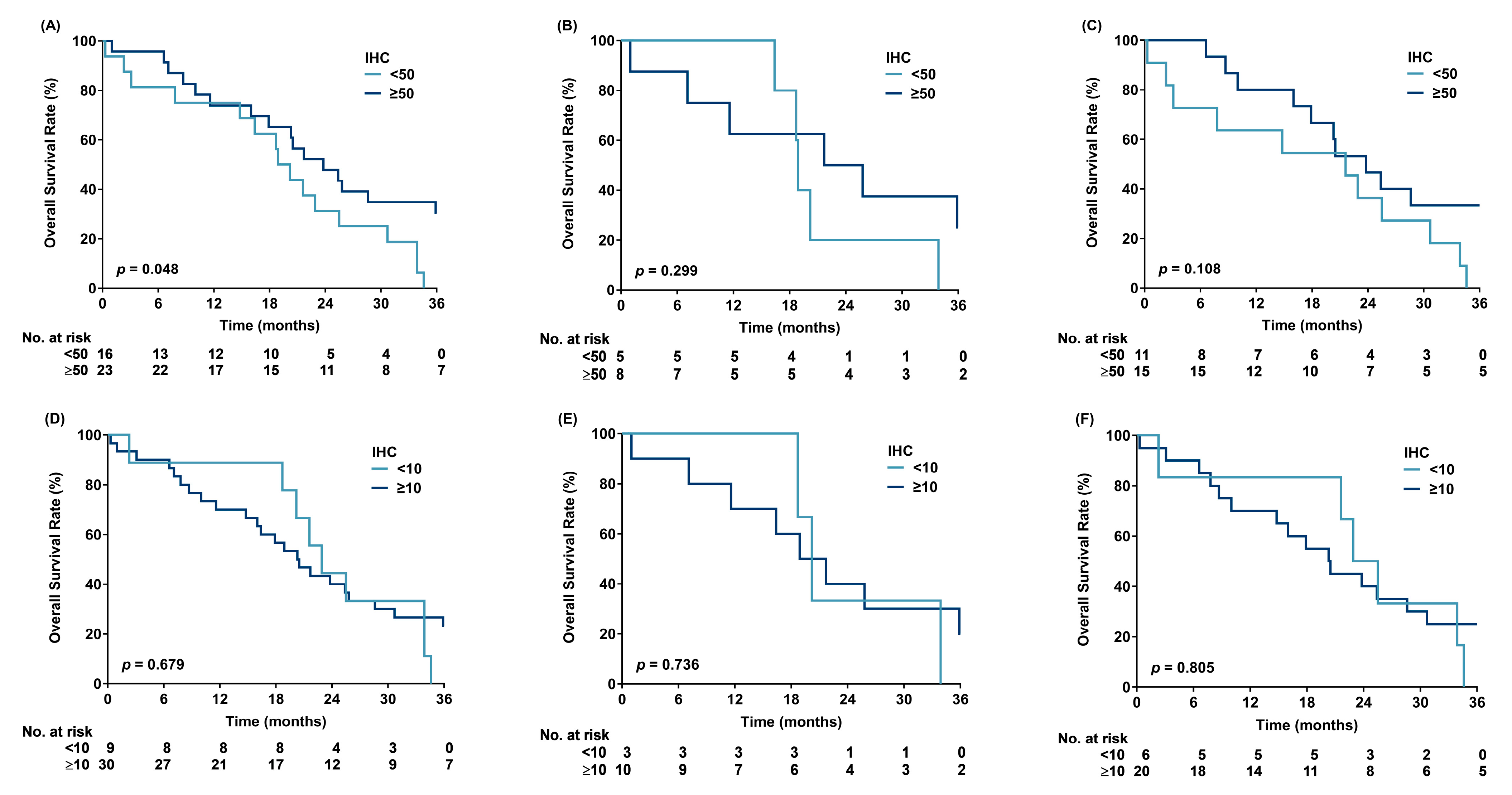
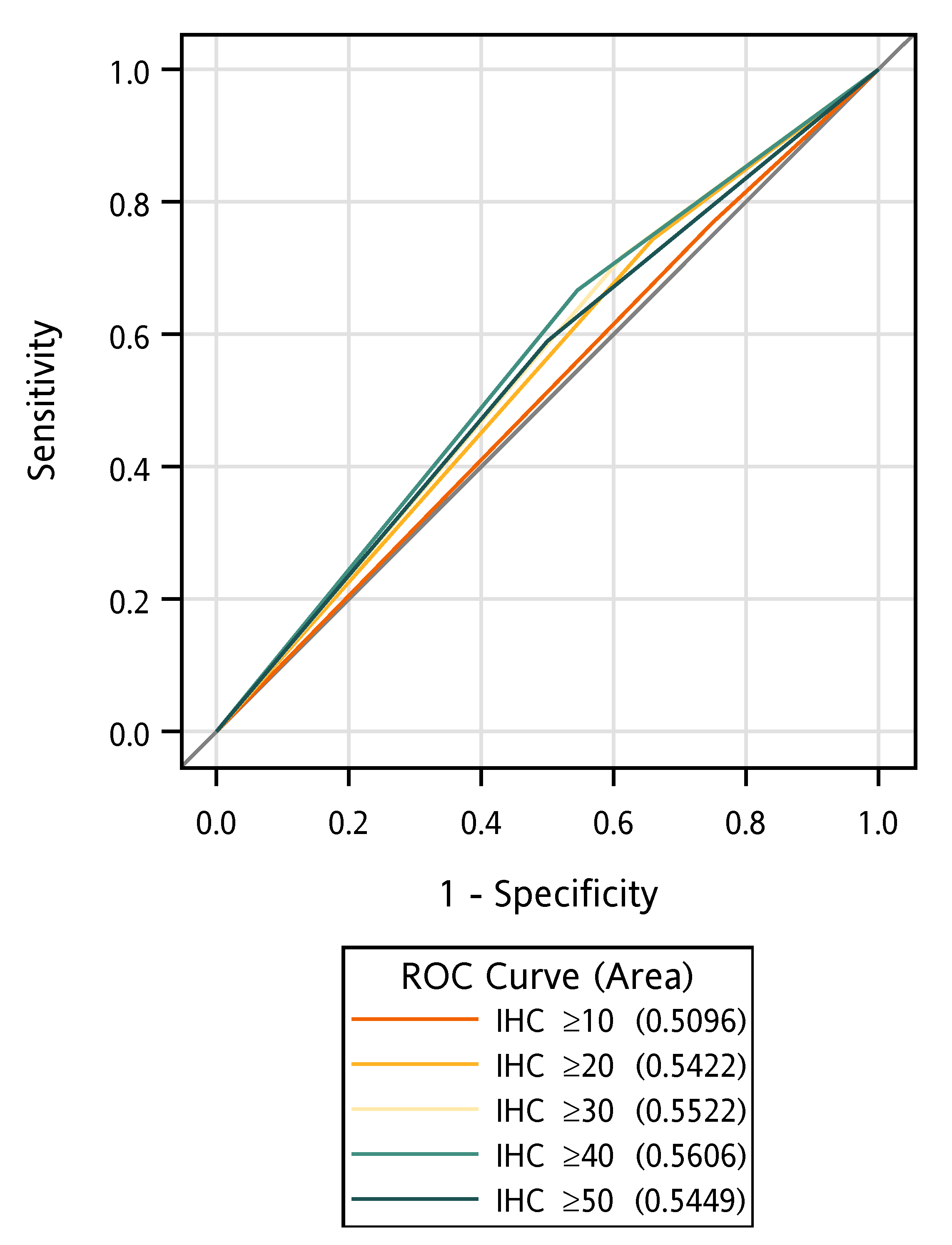
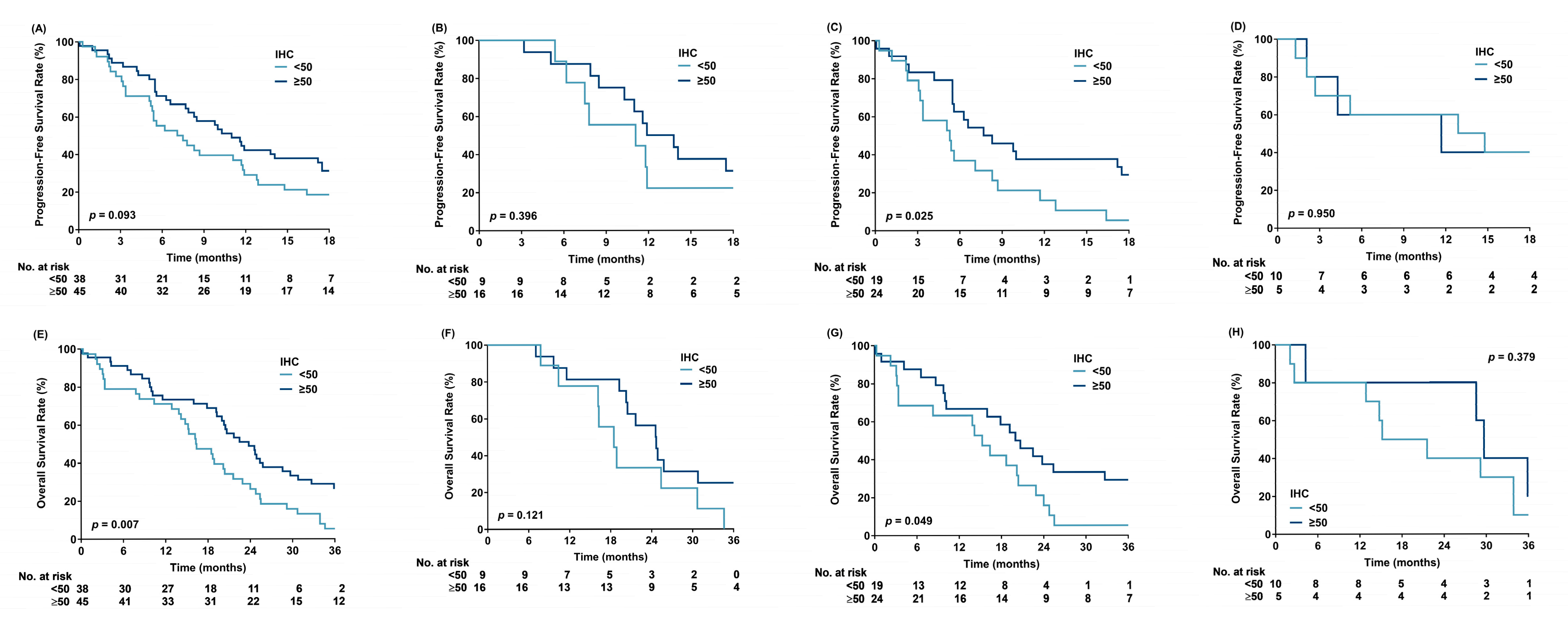
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| Del19 | Deletions in Exon 19 |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| TKI | Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor |
| WT | Wild-Type |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.-H.; Chu, D.-T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or Carboplatin–Paclitaxel in Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yang, P.-C. Precision Management of Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 71, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, C.M.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Wu, W.; Gini, B.; Chabon, J.J.; McCoach, C.E.; McGranahan, N.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Olivas, V.R.; et al. Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Su, W.; Dou, Z.; Zhao, D.; Jin, X.; Lei, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Cheng, B.; et al. Mutant p53 in cancer: From molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.G.; Belluomini, L.; Smimmo, A.; Sposito, M.; Avancini, A.; Giannarelli, D.; Milella, M.; Pilotto, S.; Bria, E. Meta-analysis of the prognostic impact of TP53 co-mutations in EGFR-mutant advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2023, 184, 103929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokes, N.I.; Chambers, E.; Nguyen, T.; Coolidge, A.; Lydon, C.A.; Le, X.; Sholl, L.; Heymach, J.V.; Nishino, M.; Van Allen, E.M.; et al. Concurrent TP53 Mutations Facilitate Resistance Evolution in EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 779–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockhammer, P.; Grant, M.; Wurtz, A.; Foggetti, G.; Expósito, F.; Gu, J.; Zhao, H.; Choi, J.; Chung, S.; Li, F.; et al. Co-Occurring Alterations in Multiple Tumor Suppressor Genes Are Associated With Worse Outcomes in Patients With EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 19, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobor, S.; Al Bakir, M.; Hiley, C.T.; Skrzypski, M.; Frankell, A.M.; Bakker, B.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Markovets, A.; Dry, J.R.; Brown, A.P.; et al. Mixed responses to targeted therapy driven by chromosomal instability through p53 dysfunction and genome doubling. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.B.; Chung, J.-H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.-T.; Jheon, S.; Sung, S.W. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation and p53 Overexpression during the Multistage Progression of Small Adenocarcinoma of the Lung. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halasova, E.; Adamkov, M.; Matakova, T.; Kavcova, E.; Poliacek, I.; Singliar, A. Lung cancer incidence and survival in chromium exposed individuals with respect to expression of anti-apoptotic protein survivin and tumor suppressor P53 protein. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2010, 15, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.T.; Chang, G.-C.; Ko, J.-L.; Liao, H.-Y.; Liu, H.-J.; Chen, C.-C.; Su, J.-M.; Lee, H.; Sheu, G.-T. Induction of tubulin by docetaxel is associated with p53 status in human non small cell lung cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Vila, M.A.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Gascó, A.; Mayo-De-Las-Casas, C.; Sánchez-Ronco, M.; Pujantell-Pastor, L.; Bonanno, L.; Favaretto, A.G.; Cardona, A.F.; Vergnenègre, A.; et al. Nondisruptive p53 Mutations Are Associated with Shorter Survival in Patients with Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4647–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, F.-C.; Li, S.-H.; Wang, C.-L.; Lin, M.-H.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Yang, C.-T. Analysis of progression-free survival of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring leu858Arg or exon 19 deletions. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 1343–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, F.-C.; Kuo, L.-T.; Chen, M.-C.; Yang, C.-T.; Shi, C.-S.; Teng, D.; Lee, K.-D. Overall survival benefits of first-line EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompkins, W.; Grady, C.B.; Hwang, W.-T.; Chandrasekhara, K.; McCoach, C.; Sun, F.; Liu, G.; Patel, D.; Nieva, J.; Herrmann, A.; et al. Characteristics of Long-Term Survivors With EGFR-Mutant Metastatic NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2024, 5, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, S.; Tsuda, T.; Gazdar, A.F. The TP53 gene, tobacco exposure, and lung cancer. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, I.F.; Finkelstein, S.D.; Woods, J.; Burnham, J.; Holmes, E.J.; Hamilton, R.L.; Yates, A.J.; Boyett, J.M.; Finlay, J.L.; Sposto, R. Expression of p53 and Prognosis in Children with Malignant Gliomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeta, M.L.; Manola, J.; Goldwasser, M.A.; Forastiere, A.; Benoit, N.; Califano, J.A.; Ridge, J.A.; Goodwin, J.; Kenady, D.; Saunders, J.; et al. TP53 Mutations and Survival in Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, A.; Buttitta, F.; Merlo, G.; Diella, F.; Pellegrini, S.; Pepe, S.; Macchiarini, P.; Chella, A.; Angeletti, C.A.; Callahan, R. p53 alterations in non-small cell lung cancers correlate with metastatic involvement of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes. Cancer Res 1993, 53, 2846–2851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Battifora, H. p53 immunohistochemistry: A word of caution. Hum. Pathol. 1994, 25, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Oyama, T.; Nishida, K.; Ogami, A.; Osaki, T.; Nakanishi, R.; Sugio, K.; Yasumoto, K.; Sugimachi, K. p53 nuclear immunostaining and gene mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer and their effects on patient survival. Ann. Oncol. 1995, 6, S9–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, J.G.; Jänne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR Mutations in Lung Cancer: Correlation with Clinical Response to Gefitinib Therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Di Maria, M.V.; Veve, R.; Bremnes, R.M.; Barón, A.E.; Zeng, C.; Franklin, W.A. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Non–Small-Cell Lung Carcinomas: Correlation Between Gene Copy Number and Protein Expression and Impact on Prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtĕsek, B.; Bártek, J.; Midgley, C.A.; Lane, D.P. An immunochemical analysis of the human nuclear phosphoprotein p53. New monoclonal antibodies and epitope mapping using recombinant p53. J. Immunol. Methods 1992, 151, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Yoon, A.; Kalapurakal, S.K.; Ro, J.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Tu, N.; Hittelman, W.N.; Hong, W.K. Expression of p53 oncoprotein in non-small-cell lung cancer: A favorable prognostic factor. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Lv, D.; Yang, L.; Ding, L.; Zhou, J.; Hong, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; He, S.; et al. Mefatinib as first-line treatment of patients with advanced EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase Ib/II efficacy and biomarker study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steendam, C.M.J.; Veerman, G.D.M.; Pruis, M.A.; Atmodimedjo, P.; Paats, M.S.; van der Leest, C.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Yick, D.C.Y.; Hoop, E.O.-D.; Koolen, S.L.W.; et al. Plasma Predictive Features in Treating EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachiglio, A.M.; Fenizia, F.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Galetta, D.; Crinò, L.; Vincenzi, B.; Barletta, E.; Pinto, C.; Ferraù, F.; Lambiase, M.; et al. The Presence of Concomitant Mutations Affects the Activity of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellyer, J.A.; White, M.N.; Gardner, R.M.; Cunanan, K.; Padda, S.K.; Das, M.; Ramchandran, K.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A. Impact of Tumor Suppressor Gene Co-Mutations on Differential Response to EGFR TKI Therapy in EGFR L858R and Exon 19 Deletion Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Bai, H.; Li, T.; Gao, B.; Han, J.; Chang, G.; Zhang, P.; Fei, K.; He, X.; Wang, J. TP53 mutations in circulating tumor DNA in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients treated with gefitinib. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-L.; Taki, T.; Adachi, M.; Konishi, T.; Higashiyama, M.; Miyake, M. Mutations in exon 7 and 8 of p53 as poor prognostic factors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Petracci, E.; Delmonte, A.; Chiadini, E.; Dazzi, C.; Papi, M.; Capelli, L.; Casanova, C.; De Luigi, N.; Mariotti, M.; et al. Impact of TP53 Mutations on Outcome in EGFR-Mutated Patients Treated with First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, C.; Davis, C.W.; Mick, R.; Thompson, J.C.; Ahmed, S.; Jeffries, S.; Bagley, S.; Gabriel, P.; Evans, T.L.; Bauml, J.M.; et al. Influence of TP53 Mutation on Survival in Patients With Advanced EGFR-Mutant Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.L.F.; Lee, M.Y.; Goh, H.C.; Ng, G.Y.N.; Lee, J.J.H.; Kannan, S.; Lim, Y.T.; Zhao, T.; Lim, E.K.H.; Phua, C.Z.J.; et al. Domain-specific p53 mutants activate EGFR by distinct mechanisms exposing tissue-independent therapeutic vulnerabilities. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Jänne, P.A.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yanagitani, N.; Kim, S.-W.; Sugawara, S.; Yu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Geater, S.L.; et al. Osimertinib with or without Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Lu, S.; Felip, E.; Spira, A.I.; Girard, N.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Ostapenko, Y.; Danchaivijitr, P.; Liu, B.; et al. Amivantamab plus Lazertinib in Previously Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Nadal, E.; Garon, E.B.; Nishio, M.; Seto, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Park, K.; Shih, J.-Y.; Paz-Ares, L.; Frimodt-Moller, B.; et al. RELAY Subgroup Analyses by EGFR Ex19del and Ex21L858R Mutations for Ramucirumab Plus Erlotinib in Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5258–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | n | (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 83 | |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 48 | (57.8) |
| Male | 35 | (42.2) |
| Age (years) | ||
| <70 | 41 | (49.4) |
| ≥70 | 42 | (50.6) |
| Median (range) | 71 | (41–91) |
| Smoking | ||
| Never | 55 | (66.3) |
| Ever/Current | 28 | (33.7) |
| Baseline brain metastasis | ||
| No | 63 | (75.9) |
| Yes | 20 | (24.1) |
| EGFR mutations | ||
| Del19 | 25 | (30.1) |
| L858R | 43 | (51.8) |
| Other | 15 | (18.1) |
| p53 positivity | ||
| <50 | 38 | (45.8) |
| ≥50 | 45 | (54.2) |
| p53 mutation | ||
| Nondisruptive MT * | 26 | (31.3) |
| WT + Disruptive MT | 57 | (68.7) |
| p53 mutation | ||
| Missense | 39 | (47.0) |
| WT | 44 | (53.0) |
| p53 intensity | ||
| Strong/Intermediate | 54 | (65.1) |
| Weak/Neg | 29 | (34.9) |
| TKIs | ||
| Afatinib | 6 | (7.2) |
| Erlotinib | 21 | (25.3) |
| Gefitinib | 56 | (67.5) |
| PFS | p-Value | OS | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR | (95% CI) | HR | (95% CI) | ||
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Male | 0.85 | (0.51–1.40) | 0.517 | 1.32 | (0.82–2.14) | 0.257 |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| <70 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| ≥70 | 0.58 | (0.34–0.96) | 0.035 | 1.19 | (0.74–1.90) | 0.477 |
| Smoking | ||||||
| Never | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Ever/Current | 1.01 | (0.65–1.85) | 0.722 | 1.65 | (1.00–2.70) | 0.050 |
| Baseline brain metastasis | ||||||
| No | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Yes | 1.25 | (0.71–2.18) | 0.440 | 1.55 | (0.90–2.66) | 0.117 |
| EGFR mutations | ||||||
| Del19 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| L858R | 1.68 | (0.95–2.97) | 0.076 | 1.24 | (0.72–2.13) | 0.438 |
| Other | 0.94 | (0.42–2.09) | 0.871 | 0.98 | (0.49–1.97) | 0.961 |
| p53 positivity | ||||||
| <50 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| ≥50 | 0.66 | (0.40–1.08) | 0.097 | 0.53 | (0.32–0.84) | 0.008 |
| p53 mutation | ||||||
| Nondisruptive MT | 0.93 | (0.54–1.58) | 0.781 | 0.85 | (0.51–1.42) | 0.531 |
| WT + Disruptive MT | Reference | Reference | ||||
| p53 mutation | ||||||
| Missense | 0.76 | (0.46–1.26) | 0.284 | 0.83 | (0.52–1.33) | 0.437 |
| WT | Reference | Reference | ||||
| p53 intensity | ||||||
| Strong/Intermediate | 0.90 | (0.54–1.52) | 0.696 | 0.77 | (0.48–1.26) | 0.298 |
| Weak/Neg | Reference | Reference | ||||
| TKIs | ||||||
| Afatinib | 0.62 | (0.19–2.01) | 0.426 | 0.65 | (0.23–1.80) | 0.404 |
| Erlotinib | 0.85 | (0.48–1.52) | 0.587 | 0.83 | (0.48–1.43) | 0.509 |
| Gefitinib | Reference | Reference | ||||
| PFS | p-Value | OS | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HRadj. * | (95% CI) | HRadj. | (95% CI) | ||
| Sex | ||||||
| Female | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Male | 0.40 | (0.15–1.07) | 0.068 | 0.84 | (0.33–2.11) | 0.707 |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| <70 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| ≥70 | 0.50 | (0.28–0.88) | 0.017 | 1.59 | (0.93–2.72) | 0.088 |
| Smoking | ||||||
| Never | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Ever/Current | 2.11 | (0.77–5.81) | 0.148 | 1.94 | (0.76–4.93) | 0.165 |
| Baseline brain metastasis | ||||||
| No | Reference | Reference | ||||
| Yes | 1.23 | (0.68–2.22) | 0.495 | 1.84 | (1.03–3.30) | 0.041 |
| EGFR mutations | ||||||
| Del19 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| L858R | 1.81 | (0.99–3.30) | 0.053 | 1.15 | (0.66–2.01) | 0.623 |
| Other | 1.08 | (0.43–2.71) | 0.878 | 0.74 | (0.34–1.59) | 0.441 |
| p53 positivity | ||||||
| <50 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| ≥50 | 0.70 | (0.41–1.20) | 0.194 | 0.49 | (0.30–0.81) | <0.001 |
| p53 mutation | ||||||
| Missense | 0.68 | (0.40–1.15) | 0.151 | 0.88 | (0.56–1.42) | 0.599 |
| WT | Reference | Reference | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuan, F.-C.; Chang, S.-F.; Yang, Y.-R.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Chen, F.-F.; Lee, K.-F.; Chi, C.-L.; Lin, M.-H.; Shi, C.-S. Revisiting p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and Its Prognostic Implications in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213577
Kuan F-C, Chang S-F, Yang Y-R, Wu Y-Y, Chen F-F, Lee K-F, Chi C-L, Lin M-H, Shi C-S. Revisiting p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and Its Prognostic Implications in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(21):3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213577
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuan, Feng-Che, Shun-Fu Chang, Yao-Ren Yang, Yu-Ying Wu, Fen-Fen Chen, Kam-Fai Lee, Chen-Lin Chi, Meng-Hung Lin, and Chung-Sheng Shi. 2025. "Revisiting p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and Its Prognostic Implications in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 21: 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213577
APA StyleKuan, F.-C., Chang, S.-F., Yang, Y.-R., Wu, Y.-Y., Chen, F.-F., Lee, K.-F., Chi, C.-L., Lin, M.-H., & Shi, C.-S. (2025). Revisiting p53 Immunohistochemical Staining and Its Prognostic Implications in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 17(21), 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213577






