Colony-Stimulating Factor 3 Receptor Mutations and Variants in Hematological Malignancies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
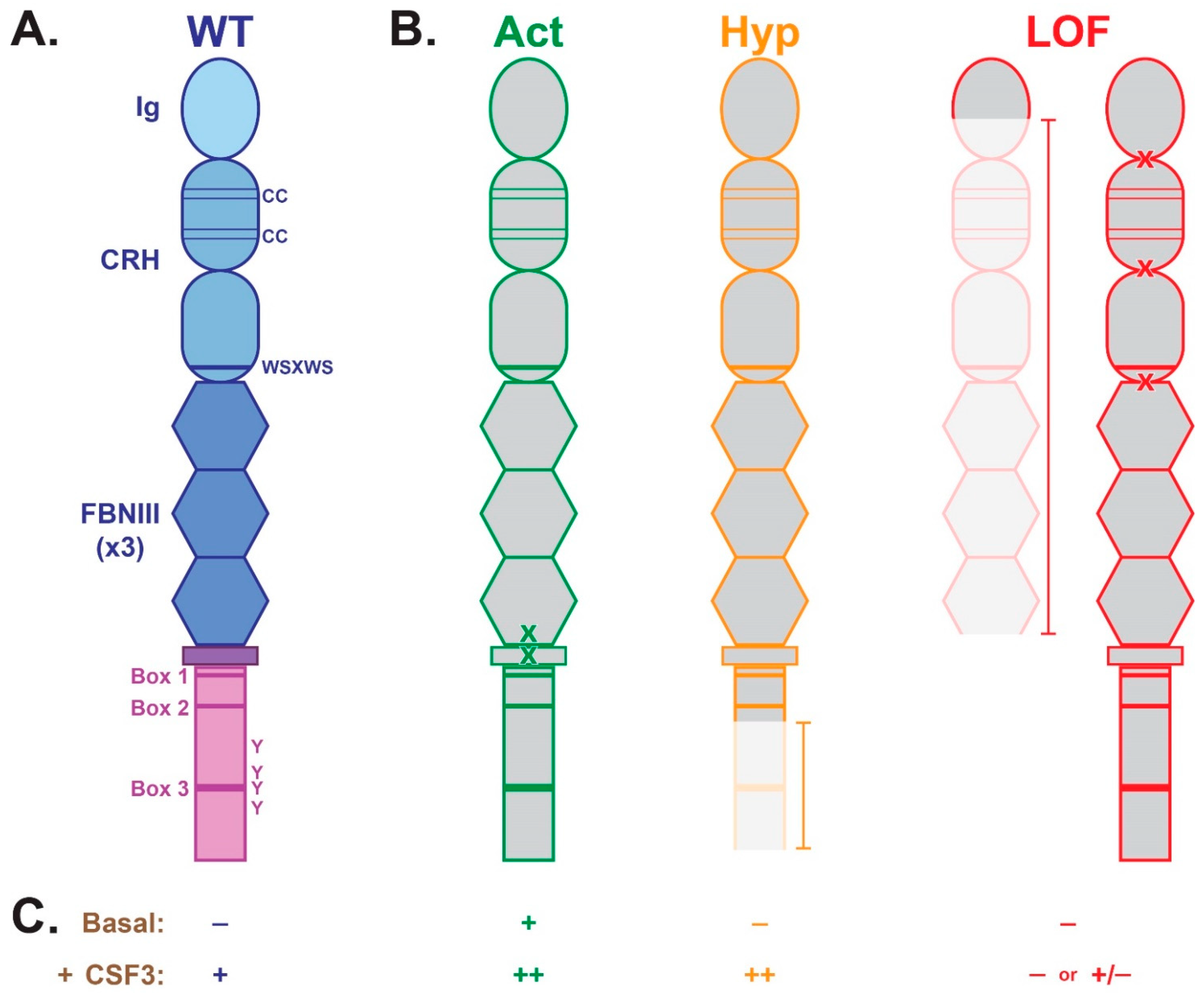
2. CSF3R Structure and Function
3. CSF3R Mutations and Variants Associated with Hematological Malignancy
3.1. Activating
3.2. Hyperactive
3.3. Loss-of-Function
4. Hematological Malignancies Associated with CSF3R Mutations/Variants
4.1. Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPNs)
4.2. Myelodysplastic Neoplasms (MDS)
4.3. MDS/MPN
4.4. Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
4.5. Lymphoid and Malignancies
5. Co-Operating Gene Mutations
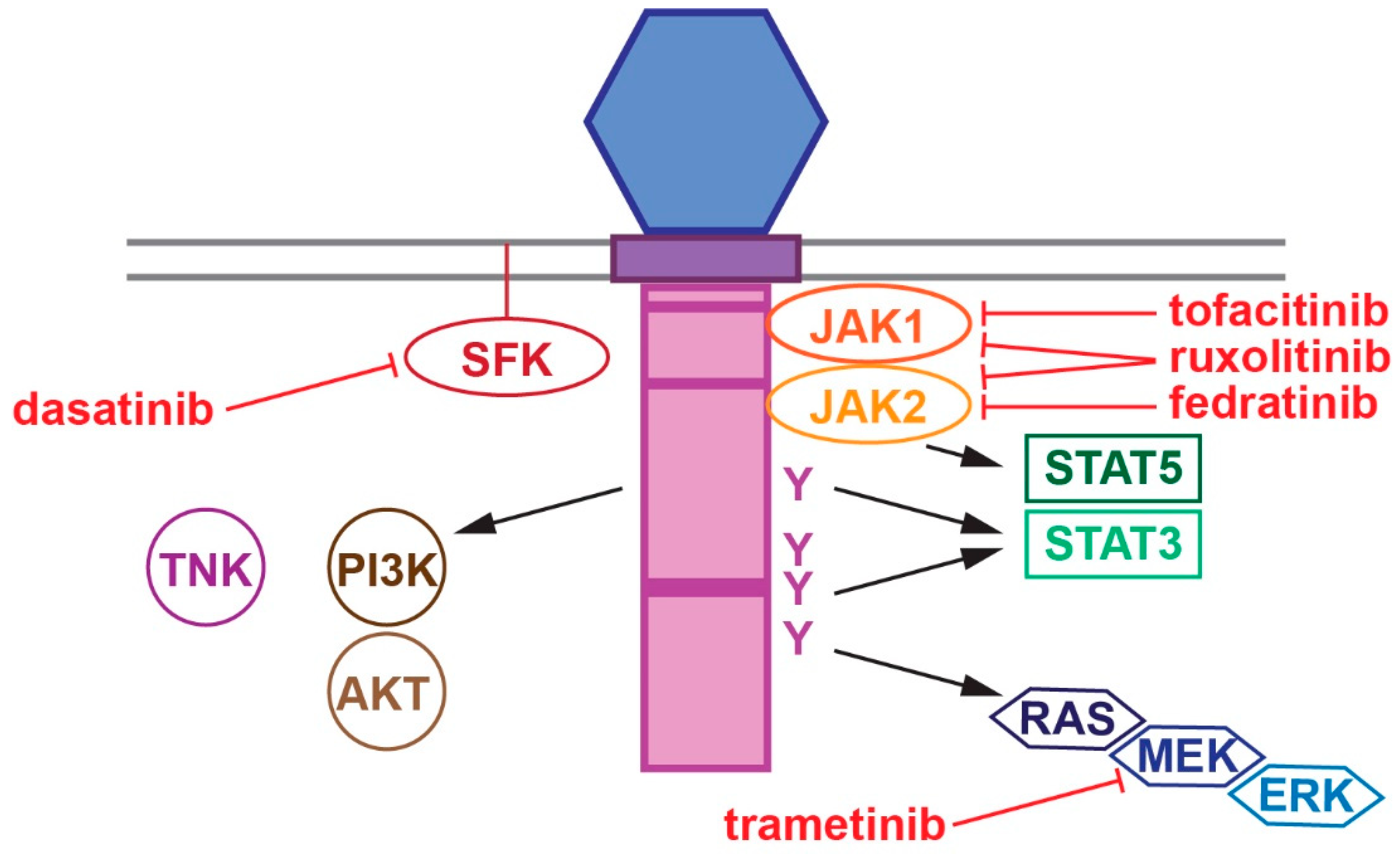
6. Therapeutic Considerations
7. Additional Oncogenic Roles for CSF3R
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, K.R.; Wong, H.L.; Witko-Sarsat, V.; Wicks, I.P. G-CSF—A double edge sword in neutrophil mediated immunity. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 54, 101516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herro, R.; Grimes, H.L. The diverse roles of neutrophils from protection to pathogenesis. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liongue, C.; Wright, C.; Russell, A.P.; Ward, A.C. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor: Stimulating granulopoiesis and much more. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 2372–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Brynes, R.K.; Tidow, N.; Welte, K.; Lowenberg, B.; Touw, I.P. Mutations in the gene for the granulocyte colony-stimulating-factor receptor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia preceded by severe congenital neutropenia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfler, A.; Erkeland, S.J.; Bodner, C.; Valkhof, M.; Renner, W.; Leitner, C.; Olipitz, W.; Pfeilstocker, M.; Tinchon, C.; Emberger, W.; et al. A functional single-nucleotide polymorphism of the G-CSF receptor gene predisposes individuals to high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2005, 105, 3731–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, J.E.; Gotlib, J.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fleischman, A.G.; Agarwal, A.; Eide, C.A.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; McWeeney, S.K.; Tognon, C.E.; et al. Oncogenic CSF3R mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, H.M.; Glaubach, T.; Long, A.; Lu, H.; Przychodzen, B.; Makishima, H.; McDevitt, M.A.; Cross, N.C.; Maciejewski, J.; Corey, S.J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor T595I (T618I) mutation confers ligand independence and enhanced signaling. Leukemia 2013, 27, 2407–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, A.M.; Druhan, L.J.; Kraft, I.L.; Lance, A.; Feurstein, S.; Helgeson, M.; Segal, J.P.; Das, S.; Avalos, B.R.; Godley, L.A. Heterozygous germ line CSF3R variants as risk alleles for development of hematologic malignancies. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5269–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Abaza, Y.; Altman, J.; Jennings, L.; Vormittag-Nocito, E.; Sukhanova, M.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q. CSF3R mutated myeloid neoplasms: Beyond chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Hum. Pathol. 2024, 149, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, R.; Ishizaka Ikeda, E.; Seto, Y.; Nagata, S. Expression cloning of a receptor for murine granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Cell 1990, 61, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Oates, A.C.; Harpur, A.G.; Ziemiecki, A.; Wilks, A.F.; Layton, J.E. Tyrosine kinase JAK1 is associated with the granulocyte-colony stimulating factor receptor and both become tyrosine phosphorylated after receptor activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2985–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, S.J.; Burkhardt, A.L.; Bolen, J.B.; Geahlen, R.L.; Tkatch, L.S.; Tweardy, D.J. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling involves the formation of a three-component complex with Lyn and Syk protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4683–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Novak, U.; Ziegler, S.F.; Layton, J.E. Distinct regions of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor are required for tyrosine phosphorylation of the signaling molecules JAK2, Stat3, and p42, p44 MAPK. Blood 1995, 86, 3698–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.C.; Monkhouse, J.L.; Csar, X.F.; Touw, I.P.; Bello, P.A. The Src-like kinase Hck is activated by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and docks to the activated G-CSF receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1998, 251, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.-S.; Lamb, P.; Seidel, H.M.; Stein, R.B.; Rosen, J. Rapid activation of the STAT3 transcription factor by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 1994, 84, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Liu, X.; de Koning, J.P.; Touw, I.P.; Henninghausen, L.; Larner, A.; Grimley, P.M. Stimulation of Stat5 by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) is modulated by two distinct cytoplasmic regions of the G-CSF receptor. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6503–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Koning, J.P.; Soede-Bobok, A.A.; Schelen, A.M.; Smith, L.; van Leeuwen, D.; Santini, V.; Burgering, B.M.T.; Bos, J.L.; Löwenberg, B.; Touw, I.P. Proliferation signaling and activation of Shc, p21Ras and Myc via tyrosine 764 of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor. Blood 1998, 91, 1924–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.S.; Robinson, L.J.; Roginskaya, V.; Corey, S.J. G-CSF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of Gab2 is Lyn kinase dependent and associated with enhanced Akt and differentiative, not proliferative, responses. Blood 2004, 103, 3305–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, H.M.; Corey, S.J. G-CSF, the guardian of granulopoiesis. Semin. Immunol. 2021, 54, 101515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieschke, G.J.; Grail, D.; Hodgson, G.; Metcalf, D.; Stanley, E.; Cheers, C.; Fowler, K.J.; Basu, S.; Zhan, Y.F.; Dunn, A.R. Mice lacking granulocyte colony-stimulating factor have chronic neutropenia, granulocyte and macrophage progenitor deficiency, and impaired neutrophil mobilization. Blood 1994, 84, 1737–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, F.; Rasighaemi, P.; Liongue, C.; Ward, A.C. Zebrafish granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor maintains neutrophil number and function throughout the life span. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, e00793-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, M.G.; Boettcher, S. Emergency granulopoiesis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, L.V.; Gale, R.E.; Pizzey, A.; Pouwels, K.; Nathwani, A.; Linch, D.C. An activating mutation in the transmembrane domain of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2002, 21, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plo, I.; Zhang, Y.; Le Couedic, J.P.; Nakatake, M.; Boulet, J.M.; Itaya, M.; Smith, S.O.; Debili, N.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Vainchenker, W.; et al. An activating mutation in the CSF3R gene induces a hereditary chronic neutrophilia. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, R.; Valkhof, M.; van Strien, P.; Valk, P.J.; Touw, I.P. Prevalence of a new auto-activating colony stimulating factor 3 receptor mutation (CSF3R-T595I) in acute myeloid leukemia and severe congenital neutropenia. Haematologica 2013, 98, e62–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, J.E.; Luty, S.B.; MacManiman, J.D.; Abel, M.L.; Druker, B.J.; Tyner, J.W. Ligand independence of the T618I mutation in the colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor (CSF3R) protein results from loss of O-linked glycosylation and increased receptor dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5820–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, M.J.; Malaker, S.A.; Riley, N.M.; Perez, I.; Abney, N.M.; Gray, M.A.; Maxson, J.E.; Cochran, J.R.; Bertozzi, C.R. Mutational screens highlight glycosylation as a modulator of colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor (CSF3R) activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, J.E.; Luty, S.B.; MacManiman, J.D.; Paik, J.C.; Gotlib, J.; Greenberg, P.; Bahamadi, S.; Savage, S.L.; Abel, M.L.; Eide, C.A.; et al. The colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor T640N mutation is oncogenic, sensitive to JAK inhibition, and mimics T618I. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, R.; Valkhof, M.G.; Sanders, M.A.; van Strien, P.M.; Haanstra, J.R.; Broeders, L.; Geertsma-Kleinekoort, W.M.; Veerman, A.J.; Valk, P.J.; Verhaak, R.G.; et al. Sequential gain of mutations in severe congenital neutropenia progressing to acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 5071–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lance, A.; Chiad, Z.; Seegers, S.L.; Paschall, S.C.; Drummond, K.; Steuerwald, N.M.; Yang, H.T.; Chen, J.; Voorhees, P.M.; Avalos, B.R.; et al. Hereditary chronic neutrophilic leukemia in a four-generation family without transformation to acute leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischman, A.G.; Maxson, J.E.; Luty, S.B.; Agarwal, A.; Royer, L.R.; Abel, M.L.; Macmaniman, J.D.; Loriaux, M.M.; Druker, B.J.; Tyner, J.W. The CSF3R T618I mutation causes a lethal neutrophilic neoplasia in mice that is responsive to therapeutic JAK inhibition. Blood 2013, 122, 3628–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Reister Schultz, A.; Luty, S.; Rofelty, A.; Su, Y.; Means, S.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; McWeeney, S.K.; Tyner, J.W. Characterization of the leukemogenic potential of distal cytoplasmic CSF3R truncation and missense mutations. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2752–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Coblentz, C.; Watanabe-Smith, K.; Means, S.; Means, J.; Maxson, J.E.; Tyner, J.W. Gain-of-function mutations in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (CSF3R) reveal distinct mechanisms of CSF3R activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 7387–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Qiao, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.J. Clinical significance of CSF3R, SRSF2 and SETBP1 mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20834–20841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Dale, D.C.; Bonilla, M.A.; Freedman, M.; Fasth, A.; Neijens, H.J.; Palmblad, J.; Briars, G.L.; Carlsson, G.; Veerman, A.J.; et al. Mutations in the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor gene in patients with severe congenital neutropenia. Leukemia 1997, 11, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touw, I.P.; Palande, K.; Beekman, R. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor signaling: Implications for G-CSF responses and leukemic progression in severe congenital neutropenia. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2013, 27, 61–73, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liongue, C.; Ward, A.C. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor mutations in myeloid malignancy. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Z.; Pan, J.; Wang, Q.; Wen, L.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, S. Identification of a novel CSF3R-SPTAN1 fusion gene in an atypical chronic myeloid leukemia patient with t(1;9)(p34;q34) by RNA-Seq. Cancer Genet. 2017, 216–217, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.C.; van Aesch, Y.M.; Schelen, A.M.; Touw, I.P. Defective internalization and sustained activation of truncated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor found in severe congenital neutropenia/acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 1999, 93, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.G.; Avalos, B.R. Deletion of a critical internalization domain in the G-CSFR in acute myelogenous leukemia preceded by severe congenital neutropenia. Blood 1999, 93, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Geijn, G.J.; Gits, J.; Aarts, L.H.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Touw, I.P. G-CSF receptor truncations found in SCN/AML relieve SOCS3-controlled inhibition of STAT5 but leave suppression of STAT3 intact. Blood 2004, 104, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Qiu, Y.; Yi, T.; Touw, I.P.; Larner, A.C. The carboxyl terminus of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor, truncated in patients with severe congenital neutropenia/acute myeloid leukemia, is required for SH2-containing phosphatase-1 suppression of Stat activation. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 6447–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkeland, S.J.; Aarts, L.H.; Irandoust, M.; Roovers, O.; Klomp, A.; Valkhof, M.; Gits, J.; Eyckerman, S.; Tavernier, J.; Touw, I.P. Novel role of WD40 and SOCS box protein-2 in steady-state distribution of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor and G-CSF-controlled proliferation and differentiation signaling. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.G.; Jacob, A.; O’donnell, L.C.; Agler, A.; Druhan, L.J.; Coggeshall, K.M.; Avalos, B.R. Loss of SHIP and CIS recruitment to the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor contribute to hyperproliferative responses in severe congenital neutropenia/acute myelogenous leukemia. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5036–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, M.H.A.; Antonissen, C.; Ward, A.C.; Mayen, A.E.M.; Ploemacher, R.E.; Touw, I.P. Sustained receptor activation and hyperproliferation in response to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in mice with a severe congenital neutropenia/acute myeloid leukemia-derived mutation in the G-CSF receptor gene. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gits, J.; van Leeuwen, D.; Carroll, H.P.; Touw, I.P.; Ward, A.C. Multiple pathways contribute to the hyperproliferative responses from truncated granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptors. Leukemia 2006, 20, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Larner, A.C. Activation of Akt kinase by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): Evidence for the role of a tyrosine kinase activity distinct from the Janus kinases. Blood 2000, 95, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.G.; Avalos, B.R. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor mutations in severe congenital neutropenia transforming to acute myeloid leukemia confer resistance to apoptosis and enhance cell survival. Blood 2000, 95, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.S.; Xia, L.; Mills, G.B.; Lowell, C.A.; Touw, I.P.; Corey, S.J. G-CSF induced reactive oxygen species involves Lyn-PI3-kinase-Akt and contributes to myeloid cell growth. Blood 2006, 107, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsen, P.A.; Bosch, D.A.; de Looper, H.W.J.; van Strien, P.M.H.; Hoogenboezem, R.M.; Roovers, O.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Bindels, E.M.J.; De Pater, E.M.; Touw, I.P. Truncated CSF3 receptors induce pro-inflammatory responses in severe congenital neutropenia. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, M.H.A.; Ward, A.C.; Antonissen, C.; Karis, A.; Lowenberg, B.; Touw, I.P. Perturbed granulopoiesis in mice with a targeted mutation in the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor gene associated with severe chronic neutropenia. Blood 1998, 92, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLemore, M.L.; Poursine-Laurent, J.; Link, D.C. Increased granulocyte colony-stimulating factor responsiveness but normal resting granulopoiesis in mice carrying a targeted granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor mutation derived from a patient with severe congenital neutropenia. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 102, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulleeraz, V.; Goy, M.; Basheer, F.; Liongue, C.; Ward, A.C. Leukemia-associated truncation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor impacts granulopoiesis throughout the life-course. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1095453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Kunter, G.; Krem, M.M.; Eades, W.C.; Cain, J.C.; Tomasson, M.H.; Hennighausen, L.; Link, D.C. Csf3r mutations in mice confer a strong clonal HSC advantage via activation of Stat5. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrabaugh, S.; Kesarwani, M.; Kincaid, Z.; Huber, E.; Leddonne, J.; Siddiqui, Z.; Khalifa, Y.; Komurov, K.; Grimes, H.L.; Azam, M. Enhanced MAPK signaling is essential for CSF3R-induced leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunter, G.; Woloszynek, J.R.; Link, D.C. A truncation mutant of Csf3r cooperates with PML-RARalpha to induce acute myeloid leukemia in mice. Exp. Hematol. 2011, 39, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awaya, N.; Uchida, H.; Miyakawa, Y.; Kinjo, K.; Matsushita, H.; Nakajima, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Kizaki, M. Novel variant isoform of G-CSF receptor involved in induction of proliferation of FDCP-2 cells: Relevance to the pathogenesis of myelodysplastic syndrome. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 191, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, G.; Aghajani, R.; Dance, B.; Othman, J.; Goodwin, L.; Stevenson, W.; Mackinlay, N. Chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm in adulthood in CBL syndrome harboring a splice-site CBL variant alongside a novel constitutional CSF3R variant. EJHaem 2024, 5, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Zhu, Q.S.; Romero, G.; Corey, S.J. Deletional mutation of the external domain of the human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor in a patient with severe chronic neutropenia refractory to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2003, 25, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, H.A.; Kosteas, T.; Gemetzi, C.; Damianaki, A.; Anagnou, N.P.; Eliopoulos, G.D. Acute myeloid/NK precursor cell leukemia with trisomy 4 and a novel point mutation in the extracellular domain of the G-CSF receptor in a patient with chronic idiopathic neutropenia. Ann. Hematol. 2004, 83, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druhan, L.J.; Ai, J.; Massullo, P.; Kindwall-Keller, T.; Ranalli, M.A.; Avalos, B.R. Novel mechanism of G-CSF refractoriness in patients with severe congenital neutropenia. Blood 2005, 105, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.C.; van Aesch, Y.M.; Gits, J.; Schelen, A.M.; de Koning, J.P.; van Leeuwen, D.; Freedman, M.H.; Touw, I.P. Novel point mutation in the extracellular domain of the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor in a case of severe congenital neutropenia hyporesponsive to G-CSF treatment. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyen, J.; Ernst, M.P.T.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Valk, P.J.M.; Broeders, L.; Touw, I.P.; Raaijmakers, M. A congenital CSF3R mutation in chronic neutropenia reveals a vital role for a cytokine receptor extracellular hinge motif in the response to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; van Paassen, M.; van Buitenen, C.; Hoefsloot, L.H.; Löwenberg, B.; Touw, I.P. A point mutation in the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (G-CSF-R) gene in a case of acute myeloid leukemia results in the overexpression of a novel G-CSF-R isoform. Blood 1995, 85, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardanani, A.; Lasho, T.L.; Laborde, R.R.; Elliott, M.; Hanson, C.A.; Knudson, R.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Maxson, J.E.; Tyner, J.W.; Tefferi, A. CSF3R T618I is a highly prevalent and specific mutation in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1870–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggendorfer, M.; Haferlach, T.; Alpermann, T.; Jeromin, S.; Haferlach, C.; Kern, W.; Schnittger, S. Specific molecular mutation patterns delineate chronic neutrophilic leukemia, atypical chronic myeloid leukemia, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2014, 99, e244–e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Li, B.; Gale, R.P.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Qin, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Z. CSF3R, SETBP1 and CALR mutations in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M.A.; Pardanani, A.; Hanson, C.A.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.M.; Belachew, A.A.; Tefferi, A. ASXL1 mutations are frequent and prognostically detrimental in CSF3R-mutated chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wilmot, B.; Bottomly, D.; Dao, K.T.; Stevens, E.; Eide, C.A.; Khanna, V.; Rofelty, A.; Savage, S.; Reister Schultz, A.; et al. Genomic landscape of neutrophilic leukemias of ambiguous diagnosis. Blood 2019, 134, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, K.T.; Gotlib, J.; Deininger, M.M.N.; Oh, S.T.; Cortes, J.E.; Collins, R.H., Jr.; Winton, E.F.; Parker, D.R.; Lee, H.; Reister, A.; et al. Efficacy of ruxolitinib in patients with chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Zuo, Q.; Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; et al. Bcl6 preserves the suppressive function of regulatory T cells during tumorigenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreno-Tarragona, G.; Alvarez-Larran, A.; Harrison, C.; Martinez-Avila, J.C.; Hernandez-Boluda, J.C.; Ferrer-Marin, F.; Radia, D.H.; Mora, E.; Francis, S.; Gonzalez-Martinez, T.; et al. CNL and aCML should be considered as a single entity based on molecular profiles and outcomes. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 1672–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Song, I.C.; Kim, J.; Kwon, G.C. Analysis of CSF3R mutations in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia and other myeloid malignancies. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 71, 152317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmider, O.; Itzykson, R.; Chesnais, V.; Lasho, T.; Laborde, R.; Knudson, R.; Gauthier, A.; Merlevede, J.; Ades, L.; Morabito, M.; et al. Mutation of the colony-stimulating factor-3 receptor gene is a rare event with poor prognosis in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, E.D.; Lasho, T.L.; Finke, C.M.; Saliba, A.N.; Elliott, M.A.; Pardanani, A.D.; Gangat, N.; Mangaonkar, A.A.; Ketterling, R.P.; Tefferi, A.; et al. CSF3R T618I mutant chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) defines a proliferative CMML subtype enriched in ASXL1 mutations with adverse outcomes. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, R.; Paolini, A.; Conte, B.; Riva, G.; Nasillo, V.; Creti, F.; Martinelli, S.; Giacobbi, F.; Corradini, G.; Pilato, F.; et al. Distribution of different classes of CSF3R mutations and co-mutational pattern in 360 myeloid neoplasia. Ann. Hematol. 2025, 104, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, J.E.; Ries, R.E.; Wang, Y.C.; Gerbing, R.B.; Kolb, E.A.; Thompson, S.L.; Guidry Auvil, J.M.; Marra, M.A.; Ma, Y.; Zong, Z.; et al. CSF3R mutations have a high degree of overlap with CEBPA mutations in pediatric AML. Blood 2016, 127, 3094–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Cao, P.; Ma, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. CSF3R mutations are frequently associated with abnormalities of RUNX1, CBFB, CEBPA, and NPM1 genes in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2018, 124, 3329–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlock, K.; Alonzo, T.; Wang, Y.C.; Gerbing, R.B.; Ries, R.E.; Hylkema, T.; Smith, J.L.; Maxson, J.E.; Meshinchi, S. Prognostic impact of CSF3R mutations in favorable risk childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wen, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Qiu, H. Differential implications of CSF3R mutations in t(8;21) and CEBPA double mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skokowa, J.; Steinemann, D.; Katsman-Kuipers, J.E.; Zeidler, C.; Klimenkova, O.; Klimiankou, M.; Unalan, M.; Kandabarau, S.; Makaryan, V.; Beekman, R.; et al. Cooperativity of RUNX1 and CSF3R mutations in severe congenital neutropenia: A unique pathway in myeloid leukemogenesis. Blood 2014, 123, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimiankou, M.; Mellor-Heineke, S.; Zeidler, C.; Welte, K.; Skokowa, J. Role of CSF3R mutations in the pathomechanism of congenital neutropenia and secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1370, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duployez, N.; Willekens, C.; Plo, I.; Marceau-Renaut, A.; de Botton, S.; Fenwarth, L.; Boyer, T.; Huet, G.; Nibourel, O.; Rose, C.; et al. Inherited transmission of the CSF3R T618I mutational hotspot in familial chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Blood 2019, 134, 2414–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, S. CSF3R P733T is a deleterious germline variant in acute leukaemia showing gain-of-function-like T618I mutation. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 204, e31–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szuber, N.; Orazi, A.; Tefferi, A. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical chronic myeloid leukemia: 2024 update on diagnosis, genetics, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 99, 1360–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxson, J.E.; Tyner, J.W. Genomics of chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Chen, X.; Gao, F.; Li, J.; Wang, H.W. Analysis of gene mutation characteristics in patients with chronic neutrophilic leukaemia. Hematology 2019, 24, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carratt, S.A.; Kong, G.L.; Curtiss, B.M.; Schonrock, Z.; Maloney, L.; Maniaci, B.N.; Blaylock, H.Z.; Baris, A.; Druker, B.J.; Braun, T.P.; et al. Mutated SETBP1 activates transcription of Myc programs to accelerate CSF3R-driven myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2022, 140, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Nakamaki, T.; Sakai, H.; Fukuchi, K.; Kabasawa, N.; Hattori, N.; Harada, H. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia preceded by myelodysplastic syndromes. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 118, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratt, S.A.; Brewer, D.; Maxson, J.E.; Druker, B.J.; Braun, T.P. Outgrowth of a CSF3R-mutant clone drives a second myeloproliferative neoplasm in a chronic myeloid leukemia patient: A case report. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotlib, J.; Maxson, J.E.; George, T.I.; Tyner, J.W. The new genetics of chronic neutrophilic leukemia and atypical CML: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 2013, 122, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druhan, L.J.; McMahon, D.P.; Steuerwald, N.; Price, A.E.; Lance, A.; Gerber, J.M.; Avalos, B.R. Chronic neutrophilic leukemia in a child with a CSF3R T618I germ line mutation. Blood 2016, 128, 2097–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellanne-Chantelot, C.; Rabadan Moraes, G.; Schmaltz-Panneau, B.; Marty, C.; Vainchenker, W.; Plo, I. Germline genetic factors in the pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood Rev. 2020, 42, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Aggarwal, A.; Sharma, S.; Bafana, V.; Sharma, S. Germline CSF3R, RUNX1 and ETV6 pathogenic variants in a case of atypical chronic myeloid leukemia: Individual to familial unravelling by next generation sequencing. Indian. J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2024, 40, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochicchio, M.T.; Micucci, G.; Asioli, S.; Ghetti, M.; Simonetti, G.; Lucchesi, A. Germline CSF3R variant in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: Linking genetic predisposition to uncommon hemorrhagic symptoms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Jo, I.; Jang, W.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; Kim, M. T618I-mutated colony stimulating factor 3 receptor in chronic neutrophilic leukemia and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia patients who underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, A.; Ibrahim, I.; Le, T.; Jaso, J.M.; Weinberg, O.; Fuda, F.; Chen, W. CSF3R T618I mutated chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: A proliferative subtype with a distinct mutational profile. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2022, 17, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ghiuzeli, C.; Jou, E.; Hsu, P.; Kolitz, J.; Brody, J.P. CSF3R T618I mutant myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm in the elderly: An age-related disease with unfavorable prognosis. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2022, 17, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasserjian, R.P. The spectrum of Ph-negative disease: CNL and CSF3R-related disorders. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2024, 2024, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastafierro, V.; Ubezio, M.; Manes, N.; Milanesi, C.; Della Porta, M.; Bonometti, A. CSF3R-mutant chronic myelomonocytic leukemia is a distinct clinically subset with abysmal prognosis: A case report and systematic review of the literature. Leuk. Lymphoma 2023, 64, 1566–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Rao, J.; Hu, W.; Cui, B.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Distinct genomic landscape of Chinese pediatric acute myeloid leukemia impacts clinical risk classification. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, R.; Feng, D.; Ni, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, R.; et al. CSF3R mutations in hematological disorders undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am. J. Hematol. 2025, 100, 925–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, X. A case of chronic eosinophilic leukemia with CSF3R-mutant clone and transformed to secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Lab. 2024, 70, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.S.; Wieduwilt, M.J. CSF3R truncation mutations in a patient with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia and a favorable response to chemotherapy plus dasatinib. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2020, 14, 100208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.C.; Szybinski, J.; Halter, J.P.; Cantoni, N.; Wenzel, F.; Leonards, K.; Brkic, S.; Passweg, J.R.; Touw, I.; Maxson, J.E.; et al. Co-occurring CSF3R W791* germline and somatic T618I driver mutations induce early CNL and clonal progression to mixed phenotype acute leukemia. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.W.; Yoon, J.; Jung, C.W.; Lee, K.O.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J. Next-generation sequencing reveals unique combination of mutations in cis of CSF3R in atypical chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschan, C.A.; Pilz, C.; Zeidler, C.; Welte, K.; Germeshausen, M. Time course of increasing numbers of mutations in the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor gene in a patient with congenital neutropenia who developed leukemia. Blood 2001, 97, 1882–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapeti, M.; Soede-Bobok, A.; Hochhaus, A.; Sill, H.; Touw, I.P.; Goldman, J.M.; Cross, N.C. Rarity of dominant-negative mutations of the G-CSF receptor in patients with blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia or de novo acute leukemia. Leukemia 1997, 11, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmusey, L.; Bagley, A.J.; Nguyen, T.T.; Carlson, H.L.; Blaylock, H.; Shrestha, S.B.; Pang, A.; Tauchmann, S.; Taylor, S.C.; Foley, A.C.; et al. Dual ASXL1 and CSF3R mutations drive myeloid-biased stem cell expansion and enhance neutrophil differentiation. Blood Adv. 2025, 9, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolarinwa, A.; Szuber, N.; He, R.; Pardanani, A.; Gangat, N.; Tefferi, A. CSF3R mutations and variants in myeloid neoplasms: Associated phenotypes, co-mutations, and survival trends. Haematologica 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallee, V.P.; Krosl, J.; Lemieux, S.; Boucher, G.; Gendron, P.; Pabst, C.; Boivin, I.; Marinier, A.; Guidos, C.J.; Meloche, S.; et al. Chemo-genomic interrogation of CEBPA mutated AML reveals recurrent CSF3R mutations and subgroup sensitivity to JAK inhibitors. Blood 2016, 127, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.P.; Okhovat, M.; Coblentz, C.; Carratt, S.A.; Foley, A.; Schonrock, Z.; Curtiss, B.M.; Nevonen, K.; Davis, B.; Garcia, B.; et al. Myeloid lineage enhancers drive oncogene synergy in CEBPA/CSF3R mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratt, S.A.; Kong, G.L.; Coblentz, C.; Schonrock, Z.; Maloney, L.; Weeder, B.; Yashar, W.; Callahan, R.; Blaylock, H.; Coleman, C.; et al. RUNX1::ETO translocations must precede CSF3R mutations to promote acute myeloid leukemia development. Leukemia 2023, 37, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Ward, A.C.; Touw, I.P.; Friedman, A.D. C/EBPalpha and G-CSF receptor signals cooperate to induce the myeloperoxidase and neutrophil elastase genes. Leukemia 2001, 15, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Jin, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, R.C. Interleukin-6 signaling regulates anchorage-independent growth, proliferation, adhesion and invasion in human ovarian cancer cells. Cytokine 2012, 59, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swoboda, A.S.; Arfelli, V.C.; Danese, A.; Windisch, R.; Kerbs, P.; Redondo Monte, E.; Bagnoli, J.W.; Chen-Wichmann, L.; Caroleo, A.; Cusan, M.; et al. CSF3R T618I collaborates with RUNX1-RUNX1T1 to expand hematopoietic progenitors and sensitizes to GLI inhibition. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Tan, Y.H.; Lin, H.; Han, W.; Yang, Y.P.; Liu, X.L.; Sun, J.N.; Liu, Q.J.; Gao, S.J. [Restratifying the prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia patients with CEBPA double mutations based on CSF3R mutations and measurable residual disease]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2022, 43, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Link, D.C.; Kunter, G.; Kasai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Miner, T.; McLellan, M.D.; Ries, R.E.; Kapur, D.; Nagarajan, R.; Dale, D.C.; et al. Distinct patterns of mutations occurring in de novo AML versus AML arising in the setting of severe congenital neutropenia. Blood 2007, 110, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, A.; Liu, L.; Qin, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, M.; Lou, Y.; Wang, L.; Ni, X.; Hu, X.; et al. The clinical impact of IKZF1 mutation in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsen, P.A.; Fatrai, S.; van Strien, P.M.H.; Obenauer, J.C.; de Looper, H.W.J.; Hoogenboezem, R.M.; Erpelinck-Verschueren, C.A.J.; Vermeulen, M.; Roovers, O.; Haferlach, T.; et al. Malignant transformation involving CXXC4 mutations identified in a leukemic progression model of severe congenital neutropenia. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, M.; Klimiankou, M.; Klimenkova, O.; Schambach, A.; Hoffmann, D.; Schmidt, A.; Kanz, L.; Link, D.C.; Welte, K.; Skokowa, J. Cooperating, congenital neutropenia-associated Csf3r and Runx1 mutations activate pro-inflammatory signaling and inhibit myeloid differentiation of mouse HSPCs. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinze, A.; Rinke, J.; Hochhaus, A.; Ernst, T. Durable remission with ruxolitinib in a chronic neutrophilic leukemia patient harboring a truncation and membrane proximal CSF3R compound mutation. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, N.; Yokoyama, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Kitahara, S.; Fujii, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Yusa, N.; Shimizu, E.; Imoto, S.; Tojo, A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of ruxolitinib on chronic neutrophilic leukemia harboring CSF3R-T618I mutation with bilateral renal abscesses. Leuk. Res. Rep. 2022, 18, 100348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P.; Muench, D.E.; Wagner, M.; Azam, M.; Grimes, H.L.; Greis, K.D. Time resolved quantitative phospho-tyrosine analysis reveals Bruton’s Tyrosine kinase mediated signaling downstream of the mutated granulocyte-colony stimulating factor receptors. Leukemia 2019, 33, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesarwani, M.; Kincaid, Z.; Azhar, M.; Azam, M. Enhanced MAPK signaling induced by CSF3R mutants confers dependence to DUSP1 for leukemic transformation. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2765–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parducci, N.S.; Garnique, A.; Lima, K.; Carlos, J.; Fonseca, N.P.; de Miranda, L.B.L.; de Almeida, B.O.; Rego, E.M.; Traina, F.; Machado-Neto, J.A. Antineoplastic effects of pharmacological inhibitors of aurora kinases in CSF3R(T618I)-driven cells. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2024, 104, 102799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannenmann, B.; Klimiankou, M.; Oswald, B.; Solovyeva, A.; Mardan, J.; Nasri, M.; Ritter, M.; Zahabi, A.; Arreba-Tutusaus, P.; Mir, P.; et al. iPSC modeling of stage-specific leukemogenesis reveals BAALC as a key oncogene in severe congenital neutropenia. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 906–922.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.M.; Ball, E.D.; Ehmann, W.C.; Rao, A.S.; Tweardy, D.J. Increased expression of the differentiation-defective granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor mRNA isoform in acute myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 1998, 12, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Kitabayashi, I.; Kamada, N.; Abe, T.; Maseki, N.; Suzukawa, K.; Ohki, M. AML1-MTG8 leukemic protein induces the expression of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor through the up-regulation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein epsilon. Blood 2000, 96, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, X. CSF3R as a potential prognostic biomarker and immunotherapy target in glioma. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2024, 49, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Guha, S. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor/granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor biological axis promotes survival and growth of bladder cancer cells. Urology 2007, 69, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, J.; Ward, A.C. Role of the interleukin 6 receptor family in epithelial ovarian cancer and its clinical implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 145, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.T.; Khan, H.; Ahmad, A.; Weston, L.L.; Nofchissey, R.A.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J. G-CSF and G-CSFR are highly expressed in human gastric and colon cancers and promote carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmen, M.; Karaman, S.; Schwager, S.; Lisibach, A.; Christiansen, A.J.; Maksimow, M.; Varga, Z.; Jalkanen, S.; Detmar, M. G-CSF regulates macrophage phenotype and associates with poor overall survival in human triple-negative breast cancer. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1115177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Lakoma, A.; Chen, Z.; Hicks, J.; Metelitsa, L.S.; Kim, E.S.; Shohet, J.M. G-CSF promotes neuroblastoma tumorigenicity and metastasis via STAT3-dependent cancer stem cell activation. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2566–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannidis, I.; Salataj, E.; Said Abu Egal, E.; Beswick, E.J. G-CSF in tumors: Aggressiveness, tumor microenvironment and immune cell regulation. Cytokine 2021, 142, 155479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, I.; de Santana Van Vilet, E.; Said Abu Egal, E.; Phinney, B.; Jacenik, D.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Beswick, E.J. G-CSF and G-CSFR induce a pro-tumorigenic macrophage phenotype to promote colon and pancreas tumor growth. Cancers 2020, 12, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannidis, I.; Jerman, S.J.; Jacenik, D.; Phinney, B.B.; Yao, R.; Prossnitz, E.R.; Beswick, E.J. G-CSF and G-CSFR modulate CD4 and CD8 T cell responses to promote colon tumor growth and are potential therapeutic targets. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Arias, J.; Meyers, P.A.; Bolontrade, M.F.; Rodriguez, N.; Zhou, Z.; Reddy, K.; Chou, A.J.; Koshkina, N.V.; Kleinerman, E.S. Expression of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor and its receptor in human Ewing sarcoma cells and patient tumor specimens: Potential consequences of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor administration. Cancer 2007, 110, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, K. Forty years of human G-CSF: A short history in time. Br. J. Haematol. 2024, 205, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, H.M.; Malandra, M.; Corey, S.J. G-CSF and GM-CSF in neutropenia. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Diseases | Genetics | Frequency | Major Mutation Type(s) | Common Concurrent Mutations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNL | Somatic, dominant | 76.0% | Act (T618I) 91% ⟶ with Hyp (various) 21% | ASXL1 82%, SETBP1 67%, SRSF2 30%, EZH2 20% | [6,9,34,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73] |
| aCML | Somatic, dominant | 18.5% | Act (T618I) 89% ⟶ with Hyp (various) 20% | ASXL1 65%, SETBP1 41%, SRSF2 41%, TET2 30% | [6,9,65,66,70,72,73] |
| CMML | Somatic, dominant | 1.6% | Act (T618I, P733T) 48% ⟶ with Hyp (various) 10% | ASXL1 85%, TET2 43%, SRSF2 33% | [9,34,66,69,74,75,76] |
| AML | Somatic, dominant | 1.7% | Act (T618*) 74%, Hyp (various) 25% | CBF 43%, CEBPA 35%, KIT 19%, FLT3 17% | [7,9,23,25,28,76,77,78,79,80] |
| AML: 2° to CN | Somatic, dominant | 88.9% | Hyp (various) 100% | RUNX1 67% | [81,82] |
| Hereditary neutrophilia | Germline, dominant | 100% penetrant | Act (T640N) 100% | ?? | [24] |
| Familial CNL | Germline, dominant | 100% penetrant | Act (T618I) 100% | ?? | [83] |
| Susceptibility to high-risk MDS | Germline, dominant | 9.7% [OR = 12.5] | LOF (E808K) | ?? | [5] |
| Susceptibility to AML/ALL | Germline, dominant | 1.9–7.8% [OR = 1.5 → 5] | Act (P733T) | ?? | [84] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liongue, C.; Ratnayake, T.; Ward, A.C. Colony-Stimulating Factor 3 Receptor Mutations and Variants in Hematological Malignancies. Cancers 2025, 17, 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203378
Liongue C, Ratnayake T, Ward AC. Colony-Stimulating Factor 3 Receptor Mutations and Variants in Hematological Malignancies. Cancers. 2025; 17(20):3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203378
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiongue, Clifford, Tarindhi Ratnayake, and Alister C. Ward. 2025. "Colony-Stimulating Factor 3 Receptor Mutations and Variants in Hematological Malignancies" Cancers 17, no. 20: 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203378
APA StyleLiongue, C., Ratnayake, T., & Ward, A. C. (2025). Colony-Stimulating Factor 3 Receptor Mutations and Variants in Hematological Malignancies. Cancers, 17(20), 3378. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17203378







