Targeting the MDM2-p53 Interaction with Siremadlin: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Treating TP53 Wild-Type Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Compound
2.2. Cell Viability Assay for the Cell Lines
2.3. Patient Samples
2.4. Patient Sample Information
2.5. Cell Viability Assay for the Primary Cells
2.6. Immunoblotting
2.7. Annexin V-FITC/PI Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TP53 Wild-Type B Cell Lines Demonstrate Sensitivity to MDM2 Inhibition Using HDM201
3.2. TP53 Wild-Type Primary CLL Samples Are Sensitive to MDM2 Inhibition Using HDM201
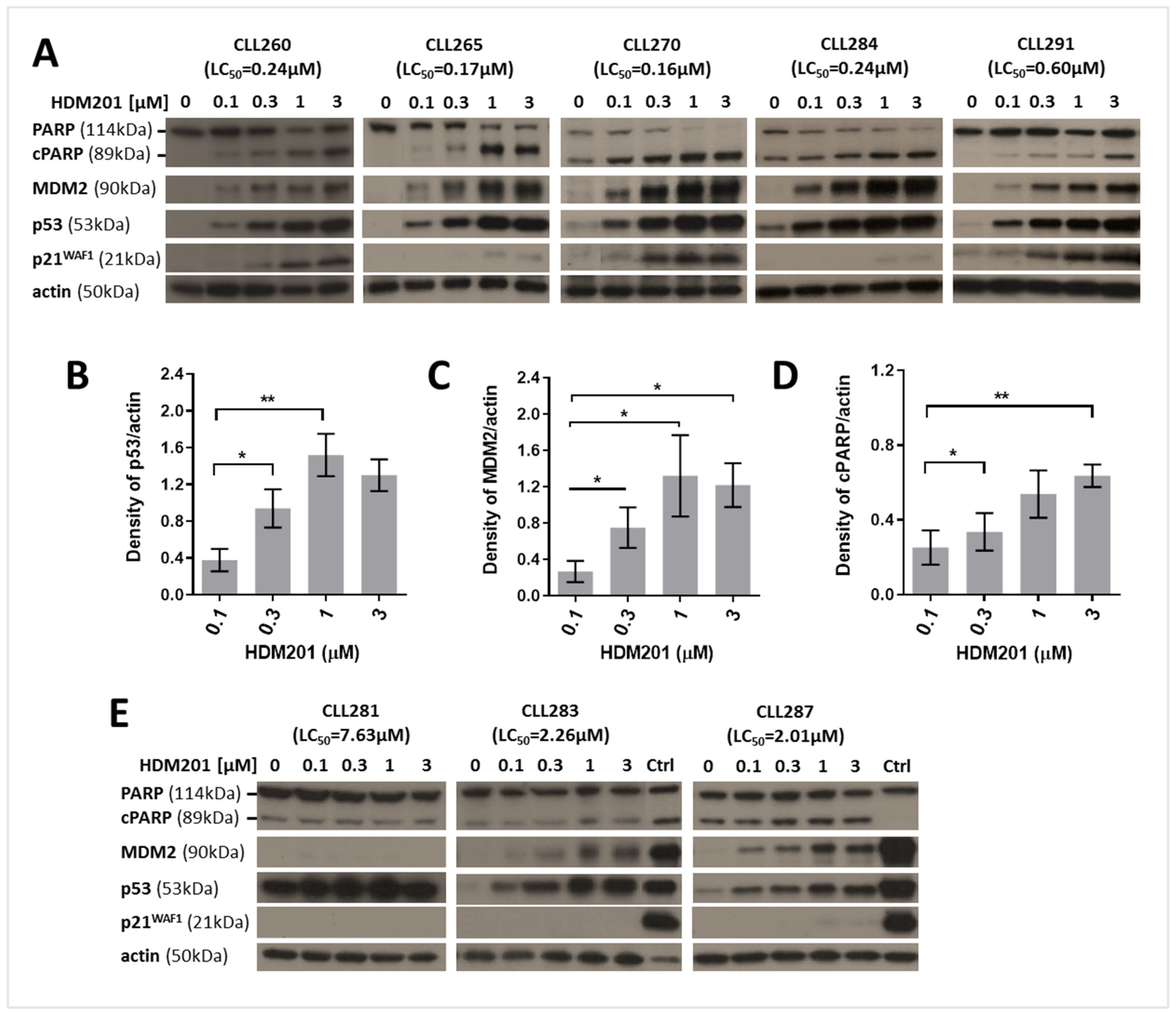
3.3. HDM201 Induces p53 Stabilization and Functional Activation in TP53 Wild-Type CLL Cells
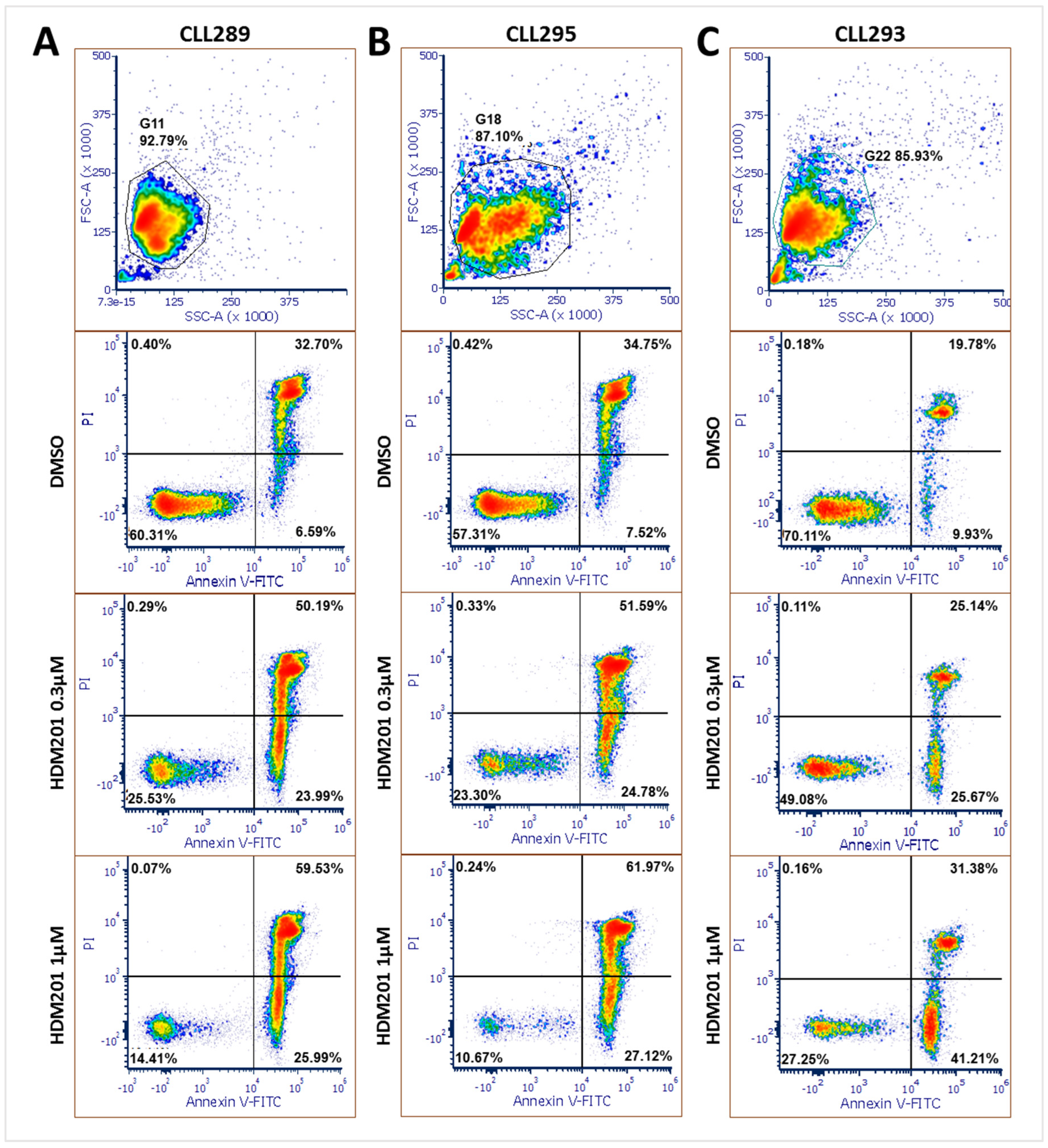
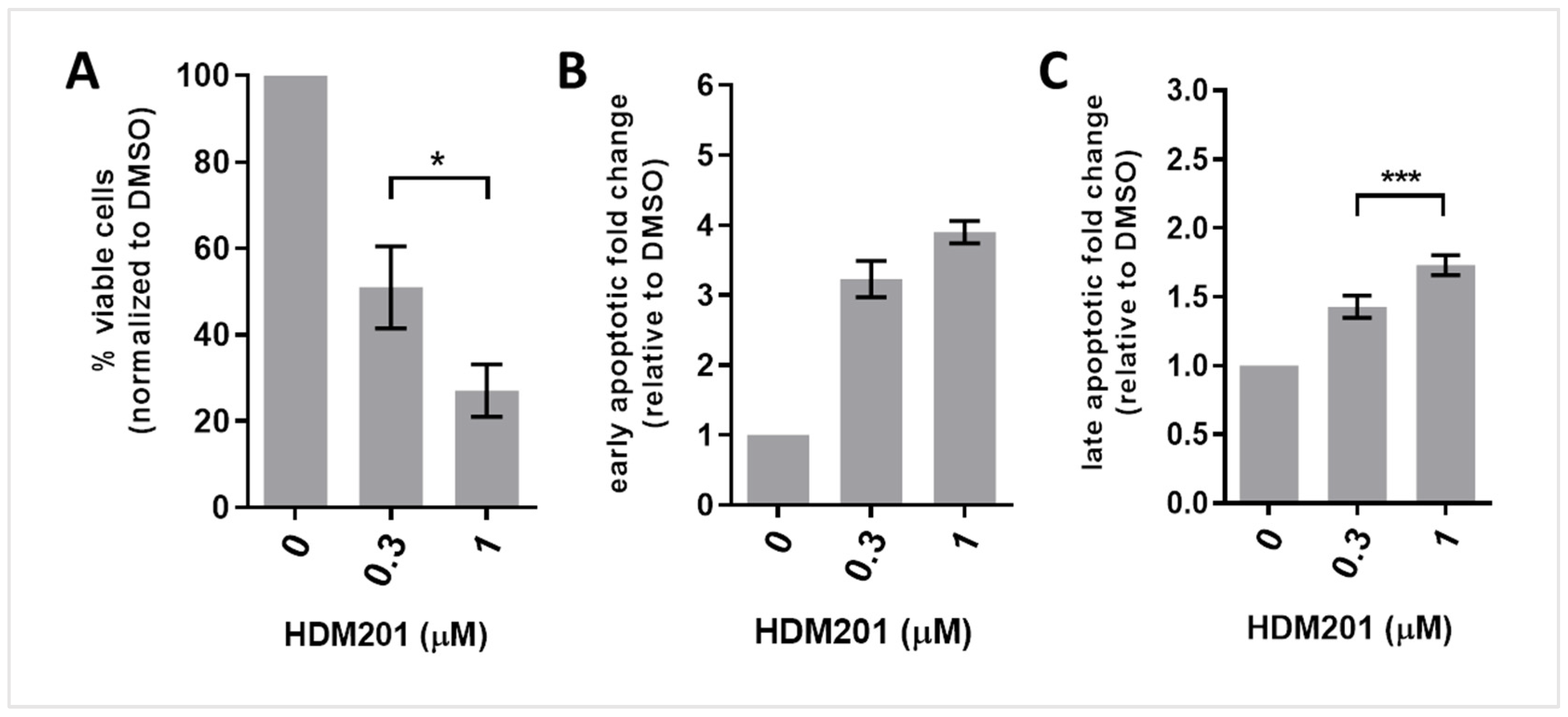
3.4. HDM201 Treatment Increases the Proportions of Early and Late Apoptotic CLL Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiorazzi, N.; Rai, K.R.; Ferrarini, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzoni, M.; Doglioni, C.; Caligaris-Cappio, F. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: The pathologist’s view of lymph node microenvironment. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2011, 28, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Ghia, P.; Rosenwald, A.; Caligaris-Cappio, F. The microenvironment in mature B-cell malignancies: A target for new treatment strategies. Blood 2009, 114, 3367–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damle, R.N.; Wasil, T.; Fais, F.; Ghiotto, F.; Valetto, A.; Allen, S.L.; Buchbinder, A.; Budman, D.; Dittmar, K.; Kolitz, J.; et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F.K. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, P.; Wang, L. Emerging Therapies in CLL in the Era of Precision Medicine. Cancers 2023, 15, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, S.E.; Mustafa, R.Z.; Gyamfi, J.A.; Pittaluga, S.; Chang, S.; Chang, B.; Farooqui, M.; Wiestner, A. Ibrutinib inhibits BCR and NF-kappaB signaling and reduces tumor proliferation in tissue-resident cells of patients with CLL. Blood 2014, 123, 3286–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, S.; Patel, K.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J. Ibrutinib (imbruvica): A novel targeted therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 483–519. [Google Scholar]
- Seiler, T.; Dohner, H.; Stilgenbauer, S. Risk stratification in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Hu, B.; Wang, F.; Yan, Y.; Kim, E.; Vitale, C.; Patel, K.P.; Strati, P.; Gumbs, C.; Little, L.; et al. Clinical implications of cancer gene mutations in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with lenalidomide. Blood 2018, 131, 1820–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlette, E.J.; Admirand, J.; Wierda, W.; Abruzzo, L.; Lin, K.I.; O’Brien, S.; Lerner, S.; Keating, M.J.; Tam, C. p53 expression by immunohistochemistry is an important determinant of survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia receiving frontline chemo-immunotherapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2009, 50, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhibik, M.; Gaglione, E.M.; Eik, D.; Herrick, J.; Le, J.E.; Ahn, I.E.; Chiu, C.; Wielgos-Bonvallet, M.; Hiemstra, I.H.; Breij, E.C.W.; et al. Cytotoxicity of the CD3xCD20 bispecific antibody epcoritamab in CLL is increased by concurrent BTK or BCL-2 targeting. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 4089–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lam, C.K.; Long, V.; Widjaja, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, L.; Burke, S.; Gorlatov, S.; Brown, J.; et al. MGD011, A CD19 x CD3 Dual-Affinity Retargeting Bi-specific Molecule Incorporating Extended Circulating Half-life for the Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Woyach, J.A.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Patel, K.; Eyre, T.A.; Munir, T.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Lamanna, N.; Tam, C.S.; et al. Pirtobrutinib after a Covalent BTK Inhibitor in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, N.; Yu, D.; Zhou, C.; Shi, G.; Zhang, B.; Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; et al. Discovery of Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111), a Novel, Potent, and Selective Covalent Inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7923–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Furman, R.R.; Liu, T.M.; Ozer, H.G.; Zapatka, M.; Ruppert, A.S.; Xue, L.; Li, D.H.; Steggerda, S.M.; Versele, M.; et al. Resistance mechanisms for the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Jain, P.; Patel, K.P.; Routbort, M.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Alhalouli, T.; Khoury, J.D.; Luthra, R.; Ferrajoli, A.; Keating, M.; et al. Targeted multigene deep sequencing of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia with disease progression and Richter transformation. Cancer 2019, 125, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhoda, S.; Vistarop, A.; Wang, Y.L. Resistance to Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chene, P. Inhibiting the p53-MDM2 interaction: An important target for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.J.; Lain, S.; Verma, C.S.; Fersht, A.R.; Lane, D.P. Awakening guardian angels: Drugging the p53 pathway. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenz, T.; Eichhorst, B.; Busch, R.; Denzel, T.; Habe, S.; Winkler, D.; Buhler, A.; Edelmann, J.; Bergmann, M.; Hopfinger, G.; et al. TP53 mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4473–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicker, F.; Herholz, H.; Schnittger, S.; Nakao, A.; Patten, N.; Wu, L.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. The detection of TP53 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia independently predicts rapid disease progression and is highly correlated with a complex aberrant karyotype. Leukemia 2009, 23, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Su, W.; Dou, Z.; Zhao, D.; Jin, X.; Lei, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Cheng, B.; et al. Mutant p53 in cancer: From molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollstein, M.; Sidransky, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Harris, C.C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science 1991, 253, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.E.; Chen, C.P.; Huang, W.K.; Pan, Y.R.; Aptullahoglu, E.; Yeh, C.N.; Lunec, J. p53 as a biomarker and potential target in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 872202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J.; Oren, M. The first 30 years of p53: Growing ever more complex. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momand, J.; Jung, D.; Wilczynski, S.; Niland, J. The MDM2 gene amplification database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 3453–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, H. MDM2 oncogene as a novel target for human cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2000, 6, 393–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, U.M.; Petrenko, O. The MDM2-p53 interaction. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.D. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, J.; Ross, T.M.; Chu, X.J.; Bartkovitz, D.; Podlaski, F.; Janson, C.; et al. Discovery of RG7388, a potent and selective p53-MDM2 inhibitor in clinical development. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5979–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furet, P.; Masuya, K.; Kallen, J.; Stachyra-Valat, T.; Ruetz, S.; Guagnano, V.; Holzer, P.; Mah, R.; Stutz, S.; Vaupel, A.; et al. Discovery of a novel class of highly potent inhibitors of the p53-MDM2 interaction by structure-based design starting from a conformational argument. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4837–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rew, Y.; Sun, D. Discovery of a small molecule MDM2 inhibitor (AMG 232) for treating cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6332–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnhold, V.; Schmelz, K.; Proba, J.; Winkler, A.; Wunschel, J.; Toedling, J.; Deubzer, H.E.; Kunkele, A.; Eggert, A.; Schulte, J.H.; et al. Reactivating TP53 signaling by the novel MDM2 inhibitor DS-3032b as a therapeutic option for high-risk neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmore, E.; Ahn, M.; Kyle, S.; Zhao, Y.; Thomas, H.; Rankin, K.S.; Bevan, L.; Fazal, L.; Hearn, K.; Wilsher, N.; et al. Targeting the MDM2-p53 interaction: Time- and concentration-dependent studies in tumor and normal human bone marrow cells reveal strategies for an enhanced therapeutic index. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y.J.; McEachern, D.; Meaux, I.; Barrière, C.; Stuckey, J.A.; Meagher, J.L.; Bai, L.C.; Liu, L.; et al. SAR405838: An Optimized Inhibitor of MDM2-p53 Interaction That Induces Complete and Durable Tumor Regression. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5855–5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardullo, C.; Aptullahoglu, E.; Woodhouse, L.; Lin, W.Y.; Wallis, J.P.; Marr, H.; Marshall, S.; Bown, N.; Willmore, E.; Lunec, J. Non-genotoxic MDM2 inhibition selectively induces a pro-apoptotic p53 gene signature in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aptullahoglu, E.; Ciardullo, C.; Wallis, J.P.; Marr, H.; Marshall, S.; Bown, N.; Willmore, E.; Lunec, J. Splicing Modulation Results in Aberrant Isoforms and Protein Products of p53 Pathway Genes and the Sensitization of B Cells to Non-Genotoxic MDM2 Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, K.B.; Zimmerman, M.S.; Dmytrenko, I.V.; Gao, F.; Link, D.C. Idasanutlin and navitoclax induce synergistic apoptotic cell death in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2023, 37, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seipel, K.; Schmitter, K.; Bacher, U.; Pabst, T. Rationale for a Combination Therapy Consisting of MCL1- and MEK-Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2019, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotaslou, A.; Samii, A.; Boustani, H.; Kiani Ghalesardi, O.; Shahidi, M. AMG-232, a New Inhibitor of MDM-2, Enhance Doxorubicin Efficiency in Pre-B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 11, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, H.L.; Blair, H.J.; Jepson Gosling, S.J.; Galler, M.; Astley, D.; Moorman, A.V.; Heidenreich, O.; Veal, G.J.; van Delft, F.W.; Lunec, J.; et al. Combination p53 activation and BCL-x(L)/BCL-2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in high-risk and relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungordu, S.; Aptullahoglu, E. Targeting MDM2-mediated suppression of p53 with idasanutlin: A promising therapeutic approach for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Investig. New Drugs 2024, 42, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, E.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Chromik, J.; Chatterjee, M.; Bauer, S.; Lin, C.C.; Suarez, C.; de Vos, F.; Steeghs, N.; Cassier, P.A.; et al. Results from a First-in-Human Phase I Study of Siremadlin (HDM201) in Patients with Advanced Wild-Type TP53 Solid Tumors and Acute Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kojima, Y.; Sudo, K.; Okuma, H.S.; Shimoi, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Sadachi, R.; Hirakawa, A.; et al. Clinical Activity and Exploratory Resistance Mechanism of Milademetan, an MDM2 Inhibitor, in Intimal Sarcoma with MDM2 Amplification: An Open-Label Phase Ib/II Study. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1814–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.G.; Dail, M.; Garcia, J.S.; Jonas, B.A.; Yee, K.W.L.; Kelly, K.R.; Vey, N.; Assouline, S.; Roboz, G.J.; Paolini, S.; et al. Venetoclax and idasanutlin in relapsed/refractory AML: A non-randomized, open-label phase 1b trial. Blood 2022, 141, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopleva, M.Y.; Rollig, C.; Cavenagh, J.; Deeren, D.; Girshova, L.; Krauter, J.; Martinelli, G.; Montesinos, P.; Schafer, J.A.; Ottmann, O.; et al. Idasanutlin plus cytarabine in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia: Results of the MIRROS trial. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4147–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Razak, A.R.; Bauer, S.; Suarez, C.; Lin, C.C.; Quek, R.; Hutter-Kronke, M.L.; Cubedo, R.; Ferretti, S.; Guerreiro, N.; Jullion, A.; et al. Co-Targeting of MDM2 and CDK4/6 with Siremadlin and Ribociclib for the Treatment of Patients with Well-Differentiated or Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma: Results from a Proof-of-Concept, Phase Ib Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, J.; Muftuoglu, M.; Ishizawa, J.; Abbas, H.A.; Loghavi, S.; Borthakur, G.; Yilmaz, M.; Issa, G.C.; Dara, S.I.; Basyal, M.; et al. A Phase I study of Milademetan (DS3032b) in combination with low dose cytarabine with or without venetoclax in acute myeloid leukemia: Clinical safety, efficacy, and correlative analysis. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Marechal, V.; Levine, A.J. Mapping of the p53 and mdm-2 interaction domains. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4107–4114. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, E.M.; Chromik, J.; Carpio, C.; Mous, R.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Alatrash, G.; Curti, A.; Craddock, C.; Schmid, C.; Zeiser, R.; et al. Siremadlin (HDM201) Is Well Tolerated and Demonstrates Clinical Activity in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Who Have Relapsed after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Subset Analysis of Safety and Preliminary Efficacy. Blood 2021, 138, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, N.; So, S.; Iiizumi, S.; Nomura, Y.; Murai, K.; Yamakawa, C.; Miyagawa, K.; Koyama, H. The human pre-B cell line Nalm-6 is highly proficient in gene targeting by homologous recombination. DNA Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Dohner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.J.; Montserrat, E.; Rai, K.R.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood 2008, 111, 5446–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Saba, N.; Austin, C.P.; Wiestner, A.; Auld, D.S. Identification of therapeutic candidates for chronic lymphocytic leukemia from a library of approved drugs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangary, S.; Qin, D.; McEachern, D.; Liu, M.; Miller, R.S.; Qiu, S.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; et al. Temporal activation of p53 by a specific MDM2 inhibitor is selectively toxic to tumors and leads to complete tumor growth inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3933–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangary, S.; Ding, K.; Qiu, S.; Nikolovska-Coleska, Z.; Bauer, J.A.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y.; McEachern, D.; Bernard, D.; et al. Reactivation of p53 by a specific MDM2 antagonist (MI-43) leads to p21-mediated cell cycle arrest and selective cell death in colon cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1533–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stühmer, T.; Chatterjee, M.; Hildebrandt, M.; Herrmann, P.; Gollasch, H.; Gerecke, C.; Theurich, S.; Cigliano, L.; Manz, R.A.; Daniel, P.T.; et al. Nongenotoxic activation of the p53 pathway as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma. Blood 2005, 106, 3609–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptullahoglu, E.; Wallis, J.P.; Marr, H.; Marshall, S.; Bown, N.; Willmore, E.; Lunec, J. SF3B1 Mutations Are Associated with Resistance to Non-Genotoxic MDM2 Inhibition in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, S.H.; Desnoyers, S.; Ottaviano, Y.; Davidson, N.E.; Poirier, G.G. Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: An early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aptullahoglu, E.; Nakjang, S.; Wallis, J.P.; Marr, H.; Marshall, S.; Willmore, E.; Lunec, J. RNA Sequencing Reveals Candidate Genes and Pathways Associated with Resistance to MDM2 Antagonist Idasanutlin in TP53 Wild-Type Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
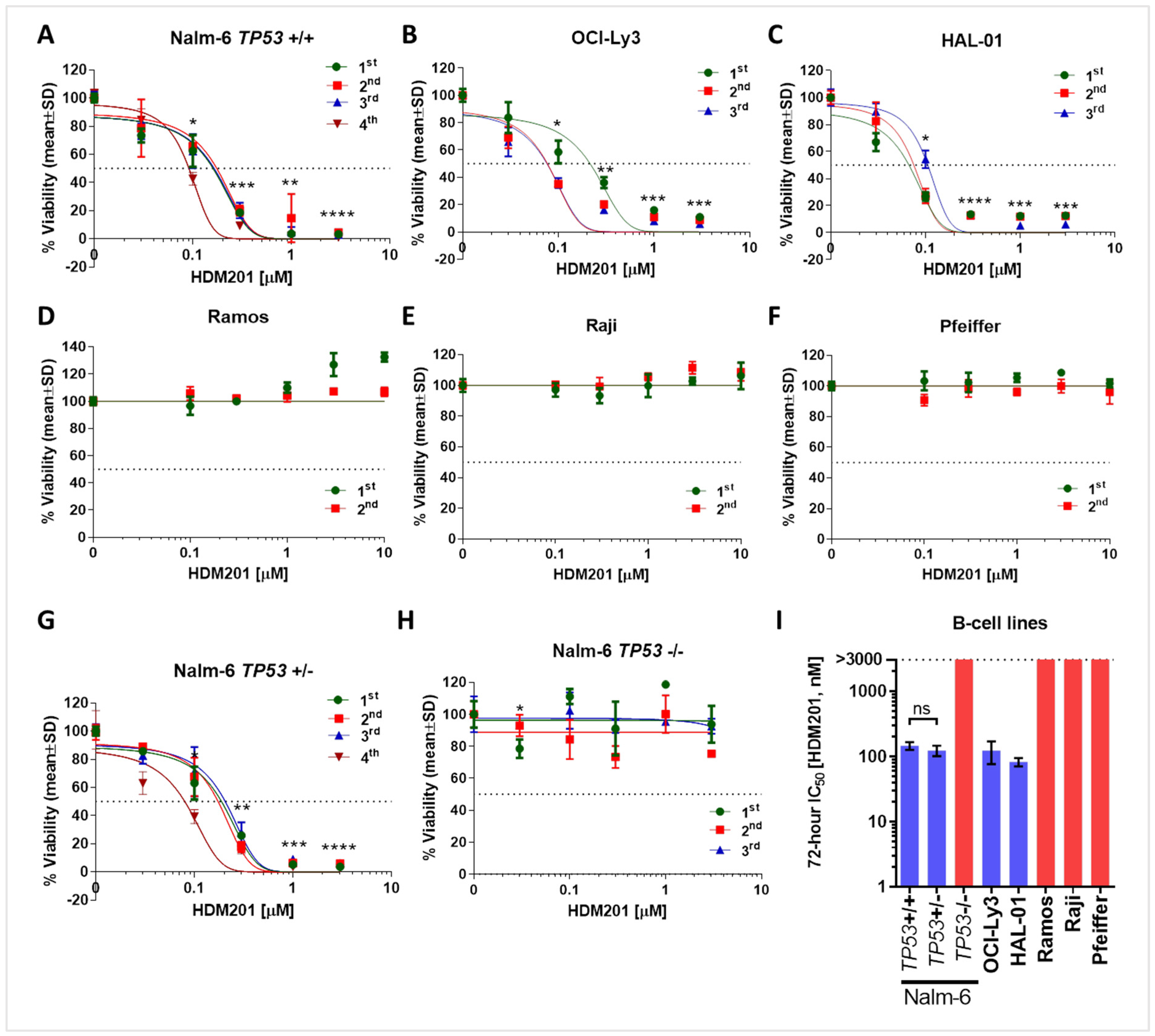

| Cell Line | TP53 Gene Status | HDM201 IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| OCI-Ly3 | Wild-type | 123 ± 47 |
| HAL-01 | Wild-type | 83 ± 12 |
| Nalm-6 | +/+ | 146 ± 20 |
| +/− | 123 ± 22 | |
| −/− | >3000 | |
| Ramos | Mutant (Homozygous) c.761T > A; p.I254N | >10,000 |
| Raji | Mutant (Heterozygous) c.638G > A; p.R213Q c.700T > C; p.Y234H | >10,000 |
| Pfeiffer | Null c.(del) | >10,000 |
| Tumor ID | 1 VAF (%) | 2 CDS Mutation | Amino Acid Mutation | HDM201 LC50 (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLL258 | 35 | c.626_627delGA | p.R209fs*6 (Deletion—Frameshift) | 0.82 |
| CLL261 | 97 | c.626_627delGA | p.R209fs*6 (Deletion—Frameshift) | >3 |
| CLL273 | 20 | c.1067G > C | p.G356A | >3 |
| 20 | c.1069A > C | p.K357Q | ||
| CLL281 | 28 | c.623A > T | p.D208V | >3 |
| 66 | c.659A > G | p.Y220C | ||
| CLL283 | 48 | c.745A > G | p.R249G | 2.26 |
| CLL287 | 50 | c.524G > A | p.R175H | 2.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aptullahoglu, E.; Howladar, M.; Wallis, J.P.; Marr, H.; Marshall, S.; Irving, J.; Willmore, E.; Lunec, J. Targeting the MDM2-p53 Interaction with Siremadlin: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Treating TP53 Wild-Type Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2025, 17, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020274
Aptullahoglu E, Howladar M, Wallis JP, Marr H, Marshall S, Irving J, Willmore E, Lunec J. Targeting the MDM2-p53 Interaction with Siremadlin: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Treating TP53 Wild-Type Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers. 2025; 17(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020274
Chicago/Turabian StyleAptullahoglu, Erhan, Mohammed Howladar, Jonathan P. Wallis, Helen Marr, Scott Marshall, Julie Irving, Elaine Willmore, and John Lunec. 2025. "Targeting the MDM2-p53 Interaction with Siremadlin: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Treating TP53 Wild-Type Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" Cancers 17, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020274
APA StyleAptullahoglu, E., Howladar, M., Wallis, J. P., Marr, H., Marshall, S., Irving, J., Willmore, E., & Lunec, J. (2025). Targeting the MDM2-p53 Interaction with Siremadlin: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Treating TP53 Wild-Type Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers, 17(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020274





