Comprehensive Evaluation of Hepatotoxicity Following Radiation Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
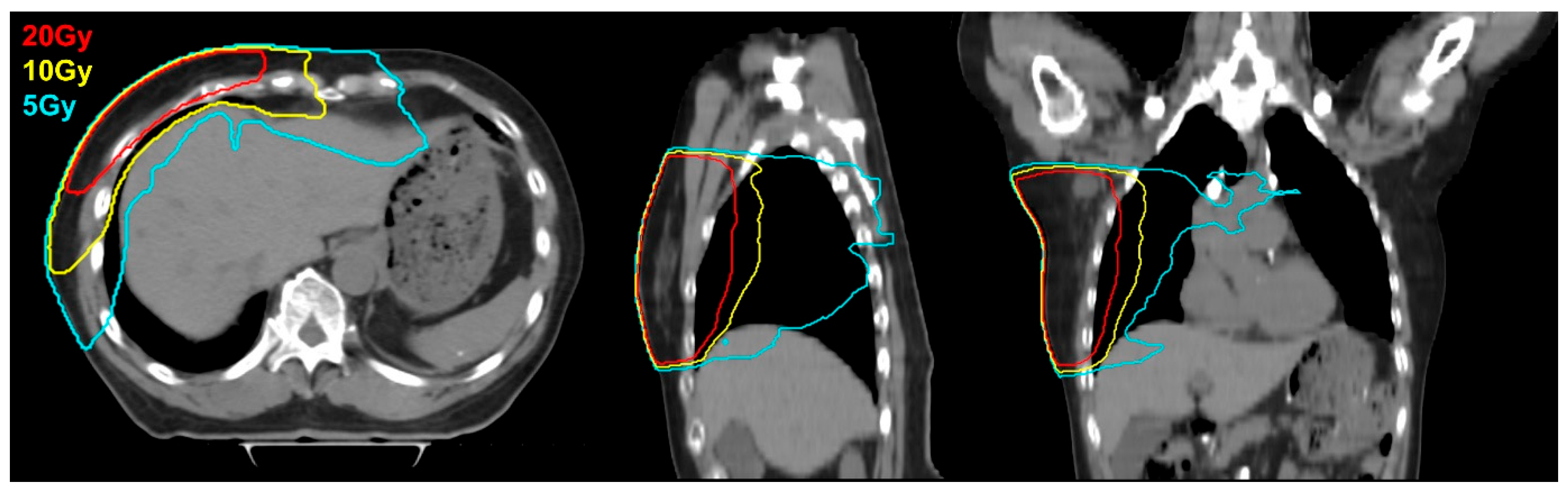
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. LEE and RILD
3.3. Univariate Analysis of DVH Parameters
3.4. Multivariate Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, S.A.; Alam, F.; Adams, L.; Boon, I.S.; Callaghan, J.; Conti, I.; Copson, E.; Carson, V.; Davidson, M.; Fitzgerald, H.; et al. Global Funding for Cancer Research between 2016 and 2020: A Content Analysis of Public and Philanthropic Investments. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meattini, I.; Becherini, C.; Caini, S.; Coles, C.E.; Cortes, J.; Curigliano, G.; de Azambuja, E.; Isacke, C.M.; Harbeck, N.; Kaidar-Person, O.; et al. International Multidisciplinary Consensus on the Integration of Radiotherapy with New Systemic Treatments for Breast Cancer: European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO)-Endorsed Recommendations. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, e73–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.J.; Jung, K.W.; Bang, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, E.H.; Hwa Yun, E.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, H.J.; Im, J.S.; Seo, H.G. Cancer Statistics in Korea: Incidence, Mortality, Survival, and Prevalence in 2020. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 55, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jung, Y. Radiation-Induced Liver Disease: Current Understanding and Future Perspectives. Exp Mol Med. 2017, 49, e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, H.; Turner, S.S. I/II Clinical Trials Management of Patients with Liver Metastases: Results of the RTOG Dose Escalating. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1993, 27, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T.S.; Robertson, J.M.; Anscher, M.S.; Jirtle, R.L.; Ensminger, W.D.; Fajardo, L.F. Hepatic Toxicity Resulting from Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 31, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.H.; Wu, J.K.; Lee, P.C.T.; Liu, H.S.; Jian, J.J.M.; Lin, Y.M.; Sung, J.L.; Jan, G.J. Biologic Susceptibility of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Radiotherapy to Radiation-Induced Liver Disease. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 60, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, L.A.; Ten Haken, R.K. Partial Volume Tolerance of the Liver to Radiation. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2005, 15, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudd, T.W.; Guddati, A.K. Management of Hepatotoxicity of Chemotherapy and Targeted Agents. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3461–3474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, J.; Tai, A.; Arthur, D.; Buchholz, T.; MacDonald, S.; Marks, L.; Pierce, L.; Recht, A.; Rabinovitch, R.; Taghian, A.; et al. Breast Cancer Atlas for Radiation Therapy Planning: Consensus Definitions. Available online: www.srobf.cz/downloads/cilove-objemy/breastcanceratlas.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Liu, X. Classification Accuracy and Cut Pointselection. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 2676–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güzelöz, Z.; Ayrancıoğlu, O.; Aktürk, N.; Güneş, M.; Alıcıkuş, Z.A. Dose Volume and Liver Function Test Relationship Following Radiotheraphy for Right Breast Cancer: A Multicenter Study. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 8763–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauffer, D.C.; Miglierini, P.; Kuhn, P.A.; Thalmann, S.U.; Gutierres-Demierre, N.; Khomsi, F.; Tercier, P.A.; Allal, A.S. Impact of Adjuvant Radiotherapy on Biological and Clinical Parameters in Right-Sided Breast Cancer. Cancer Radiothérapie 2021, 25, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.F.; Wei, W.; Smithy, J.W.; Acs, B.; Toki, M.I.; Blenman, K.R.M.; Zelterman, D.; Kluger, H.M.; Rimm, D.L. Multiplex Quantitative Analysis of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Immunotherapy Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.C.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Dawson, L.A.; Li, X.A.; Das, S.K.; Miften, M.; Ten Haken, R.K. Radiation-Associated Liver Injury. Int J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, S94–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koay, E.J.; Owen, D.; Das, P. Radiation-Induced Liver Disease and Modern Radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 28, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Cheong, K.H.; Koo, T.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, K.J.; Park, S.; Han, T.; Kang, S.K.; Ha, B.; Yoon, J.W.; et al. Effects of Radiation Dose on Liver after Free-Breathing Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy for Breast Cancer. Vivo 2022, 36, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offersen, B.V.; Boersma, L.J.; Kirkove, C.; Hol, S.; Aznar, M.C.; Biete Sola, A.; Kirova, Y.M.; Pignol, J.P.; Remouchamps, V.; Verhoeven, K.; et al. ESTRO Consensus Guideline on Target Volume Delineation for Elective Radiation Therapy of Early Stage Breast Cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jian, C.; Li, Y.; Pan, Z.; Yang, G.; Sun, X. Clinical Benefits of Deep Inspiration Breath-Hold in Postoperative Radiotherapy for Right-Sided Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, H.; Hoofnagle, M.D. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547852/ (accessed on 24 October 2024).
- Chia, H.C.; Chen, P.J.; Lee, P.H.; Cheng, A.L.; Hsu, H.C.; Cheng, J.C.H. Radiation-Induced Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Liver Mediated by the Bystander Effect from Irradiated Endothelial Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | n = 529 | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age, yr, median (range) | 51 | (27–86) |
| Laterality | ||
| Right | 392 | 74.1% |
| Left | 137 | 25.9% |
| Pathologic T stage | ||
| 0, in situ | 42 | 7.9% |
| 1 | 317 | 59.9% |
| 2 | 137 | 25.9% |
| 3 | 26 | 4.9% |
| 4 | 7 | 1.3% |
| Pathologic N stage | ||
| X | 35 | 6.6% |
| 0 | 315 | 59.5% |
| 1 | 118 | 22.3% |
| 2 | 43 | 8.1% |
| 3 | 18 | 3.4% |
| Surgery, Primary lesion | ||
| Breast-conserving surgery | 414 | 78.3% |
| Mastectomy | 115 | 21.7% |
| Surgery, Nodal | ||
| No axillary surgery | 55 | 10.4% |
| SLNB | 353 | 66.7% |
| SLNB with ALND | 121 | 22.9% |
| Neoadjuvant therapy | 146 | 27.6% |
| Targeted therapy | 79 | 14.9% |
| Endocrine therapy | 359 | 67.9% |
| Cytotoxic chemotherapy | 261 | 49.3% |
| Adriamycin | 135 | 25.5% |
| Taxane | 257 | 48.6% |
| Platinum-based | 43 | 8.1% |
| Cyclophosphamide | 240 | 45.4% |
| Breast RT dose, Gy, median (range) | 42.56 | (38.5–50.06) |
| Boost radiotherapy | 321 | 60.7% |
| Boost dose, Gy, median (range) | 9.6 | (7.5–17.5) |
| Mean dose to liver (cGy) | 168.9 | (0.8–984.1) |
| V5Gy (%) | 6.1 | (0–83.7) |
| V10Gy (%) | 0.75 | (0–33.0) |
| V20Gy (%) | 0.04 | (0–12.35) |
| IMRT | 414 | 78.3% |
| 3D-CRT | 115 | 21.7% |
| Pre-Radiotherapy | Post-Radiotherapy | p | Change * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | |||
| AST | <0.001 | AST | ||||||
| −1 | 4 | 0.8% | ||||||
| CTCAE grade 0 | 523 | 98.9% | 521 | 98.5% | 0 | 519 | 98.1% | |
| CTCAE grade 1 | 6 | 1.1% | 8 | 1.5% | 1 | 6 | 1.1% | |
| ALT | <0.001 | ALT | ||||||
| −1 | 11 | 2.1% | ||||||
| CTCAE grade 0 | 514 | 97.2% | 517 | 97.7% | 0 | 509 | 96.2% | |
| CTCAE grade 1 | 15 | 2.8% | 10 | 1.9% | 1 | 8 | 1.5% | |
| CTCAE grade 2 | 0 | 0.0% | 2 | 0.4% | 2 | 1 | 0.2% | |
| ALP | <0.001 | ALP | ||||||
| −1 | 16 | 3.0% | ||||||
| CTCAE grade 0 | 506 | 95.7% | 497 | 94.0% | 0 | 488 | 92.2% | |
| CTCAE grade 1 | 23 | 4.3% | 32 | 6.0% | 1 | 25 | 4.7% | |
| Characteristics | Elevation | Logistic Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AST elevation | Yes | No | OR | 95% CI | p |
| Mean dose (cGy) | 151.97 | 223.49 | 0.990 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.371 |
| V5Gy | 7.01 | 12.98 | 0.97 | 0.89–1.04 | 0.385 |
| V10Gy | 1.48 | 3.86 | 0.88 | 0.66–1.17 | 0.38 |
| V20Gy | 0.36 | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.31–1.79 | 0.507 |
| ALT elevation | Yes | No | OR | 95% CI | p |
| Mean dose (cGy) | 223.2 | 190.4 | 0.99 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.632 |
| V5Gy | 12.99 | 7.79 | 0.97 | 0.92–1.03 | 0.380 |
| V10Gy | 3.86 | 2.47 | 0.95 | 0.81–1.11 | 0.541 |
| V20Gy | 0.86 | 0.59 | 0.89 | 0.53–1.50 | 0.673 |
| ALP elevation | Yes | No | OR | 95% CI | p |
| Mean dose (cGy) | 293.4 | 219.2 | 1 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.063 |
| V5Gy | 19.15 | 12.6 | 1.02 | 0.99–1.04 | 0.054 |
| V10Gy | 5.72 | 0.84 | 1.04 | 0.98–1.09 | 0.128 |
| V20Gy | 0.99 | 0.84 | 1.04 | 0.85–1.29 | 0.681 |
| Any LEE | Yes | No | OR | 95% CI | p |
| Mean dose (cGy) | 263.3 | 219.8 | 1 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.196 |
| V5Gy | 16.2 | 12.67 | 1.01 | 0.99–1.03 | 0.218 |
| V10Gy | 4.83 | 3.77 | 1.02 | 0.98–1.07 | 0.336 |
| V20Gy | 0.85 | 0.85 | 1 | 0.82–1.21 | 0.996 |
| Characteristics | Logistic Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AST | OR | 95% CI | p |
| V5Gy (>3.54% vs. <3.54%) | 0.76 | 0.15–3.78 | 0.732 |
| V10Gy (>1.74% vs. <1.74%) | 0.67 | 0.12–3.68 | 0.642 |
| V20Gy (>0.01% vs. <0.01%) | 3.78 | 0.44–32.54 | 0.227 |
| Mean Dose (>135.2cGy vs. <135.2cGy) | 0.74 | 0.15–3.72 | 0.718 |
| ALT | OR | 95% CI | p |
| V5Gy (>3.54% vs. <3.54%) | 2.30 | 0.46–11.49 | 0.311 |
| V10Gy (>1.74% vs. <1.74%) | 0.80 | 0.19–3.39 | 0.764 |
| V20Gy (>0.01% vs. <0.01%) | 2.26 | 0.45–11.32 | 0.320 |
| Mean Dose (>135.2cGy vs. <135.2cGy) | 2.26 | 0.45–11.32 | 0.320 |
| ALP | OR | 95% CI | p |
| V5Gy (>3.54% vs. <3.54%) | 0.76 | 0.15–3.78 | 0.732 |
| V10Gy (>1.74% vs. <1.74%) | 0.67 | 0.12–3.68 | 0.642 |
| V20Gy (>0.01% vs. <0.01%) | 3.78 | 0.44–32.54 | 0.227 |
| Mean Dose (>135.2cGy vs. <135.2cGy) | 0.74 | 0.15–3.72 | 0.718 |
| All | OR | 95% CI | p |
| V5Gy (>3.54% vs. <3.54%) | 2.30 | 1.06–5.01 | 0.036 |
| V10Gy (>1.74% vs. <1.74%) | 1.65 | 0.83–3.28 | 0.156 |
| V20Gy (>0.01% vs. <0.01%) | 1.68 | 0.81–3.51 | 0.166 |
| Mean Dose (>135.2cGy vs. <135.2cGy) | 2.26 | 1.04–4.93 | 0.040 |
| Characteristics | Logistic Regression | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| V5Gy | OR | 95% CI | p |
| V5Gy (>1.78% vs. <1.78%) | 2.05 | 0.72–5.83 | 0.179 |
| RT Plan (IMRT vs. 3D) | 1.36 | 0.45–4.16 | 0.587 |
| Neoadjuvant therapy (Yes vs. No) | 2.69 | 1.09–6.65 | 0.032 |
| Cyclophosphamide (Yes vs. No) | 0.34 | 0.06–1.78 | 0.201 |
| Taxane (Yes vs. No) | 2.07 | 0.37–11.49 | 0.404 |
| Adriamycin (Yes vs. No) | 2.78 | 0.84–9.18 | 0.093 |
| Platinum (Yes vs. No) | 2.41 | 0.49–11.92 | 0.282 |
| Tamoxifen (Yes vs. No) | 0.42 | 0.17–1.05 | 0.065 |
| Laterality (Right vs. Left) | 2.44 | 0.82–7.25 | 0.108 |
| V10Gy | OR | 95% CI | p |
| V10Gy (>0.55% vs. <0.55%) | 0.92 | 0.38–2.26 | 0.861 |
| RT Plan (IMRT vs. 3D) | 1.97 | 0.65–5.95 | 0.23 |
| Neoadjuvant therapy (Yes vs. No) | 2.64 | 1.07–6.50 | 0.035 |
| Cyclophosphamide (Yes vs. No) | 0.32 | 0.06–1.73 | 0.187 |
| Taxane (Yes vs. No) | 2.25 | 0.41–12.45 | 0.352 |
| Adriamycin (Yes vs. No) | 3 | 0.91–9.92 | 0.072 |
| Platinum (Yes vs. No) | 2.37 | 0.47–12.03 | 0.298 |
| Tamoxifen (Yes vs. No) | 0.43 | 0.17–1.06 | 0.067 |
| Laterality (Right vs. Left) | 2.91 | 0.89–9.50 | 0.077 |
| V20Gy | OR | 95% CI | p |
| V20Gy (>0.59% vs. <0.59%) | 0.79 | 0.35–1.80 | 0.576 |
| RT Plan (IMRT vs. 3D) | 1.99 | 0.71–5.62 | 0.192 |
| Neoadjuvant therapy (Yes vs. No) | 2.68 | 1.09–6.60 | 0.033 |
| Cyclophosphamide (Yes vs. No) | 0.31 | 0.06–1.68 | 0.175 |
| Taxane (Yes vs. No) | 2.32 | 0.42–12.89 | 0.335 |
| Adriamycin (Yes vs. No) | 3.04 | 0.92–10.00 | 0.067 |
| Platinum (Yes vs. No) | 2.38 | 0.47–12.16 | 0.298 |
| Tamoxifen (Yes vs. No) | 0.43 | 0.17–1.06 | 0.067 |
| Laterality (Right vs. Left) | 3.09 | 1.00–9.54 | 0.050 |
| Mean Dose | OR | 95% CI | p |
| Mean Dose (>99.6 Gy vs. <99.6 Gy) | 1.95 | 0.69–5.46 | 0.206 |
| RT Plan (IMRT vs. 3D) | 1.35 | 0.43–4.22 | 0.604 |
| Neoadjuvant therapy (Yes vs. No) | 2.72 | 1.10–6.72 | 0.030 |
| Cyclophosphamide (Yes vs. No) | 0.33 | 0.06–1.71 | 0.184 |
| Taxane (Yes vs. No) | 2.15 | 0.39–11.71 | 0.377 |
| Adriamycin (Yes vs. No) | 2.78 | 0.85–9.16 | 0.092 |
| Platinum (Yes vs. No) | 2.4 | 0.49–11.87 | 0.282 |
| Tamoxifen (Yes vs. No) | 0.43 | 0.17–1.06 | 0.068 |
| Laterality (Right vs. Left) | 2.7 | 0.92–7.95 | 0.071 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.Y.; Hong, S.W.; Kang, S.-W.; Jang, B.-S.; Kim, I.A. Comprehensive Evaluation of Hepatotoxicity Following Radiation Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2025, 17, 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193252
Song JY, Hong SW, Kang S-W, Jang B-S, Kim IA. Comprehensive Evaluation of Hepatotoxicity Following Radiation Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193252
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jun Yeong, Soon Woo Hong, Sang-Won Kang, Bum-Sup Jang, and In Ah Kim. 2025. "Comprehensive Evaluation of Hepatotoxicity Following Radiation Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193252
APA StyleSong, J. Y., Hong, S. W., Kang, S.-W., Jang, B.-S., & Kim, I. A. (2025). Comprehensive Evaluation of Hepatotoxicity Following Radiation Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers, 17(19), 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193252






