Recent Advances in Ablative Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thermal Ablation Techniques
2.1. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
2.2. Microwave Ablation (MWA)
2.3. Cryoablation
2.4. Thermal Ablation Combined with Transarterial Chemoembolization
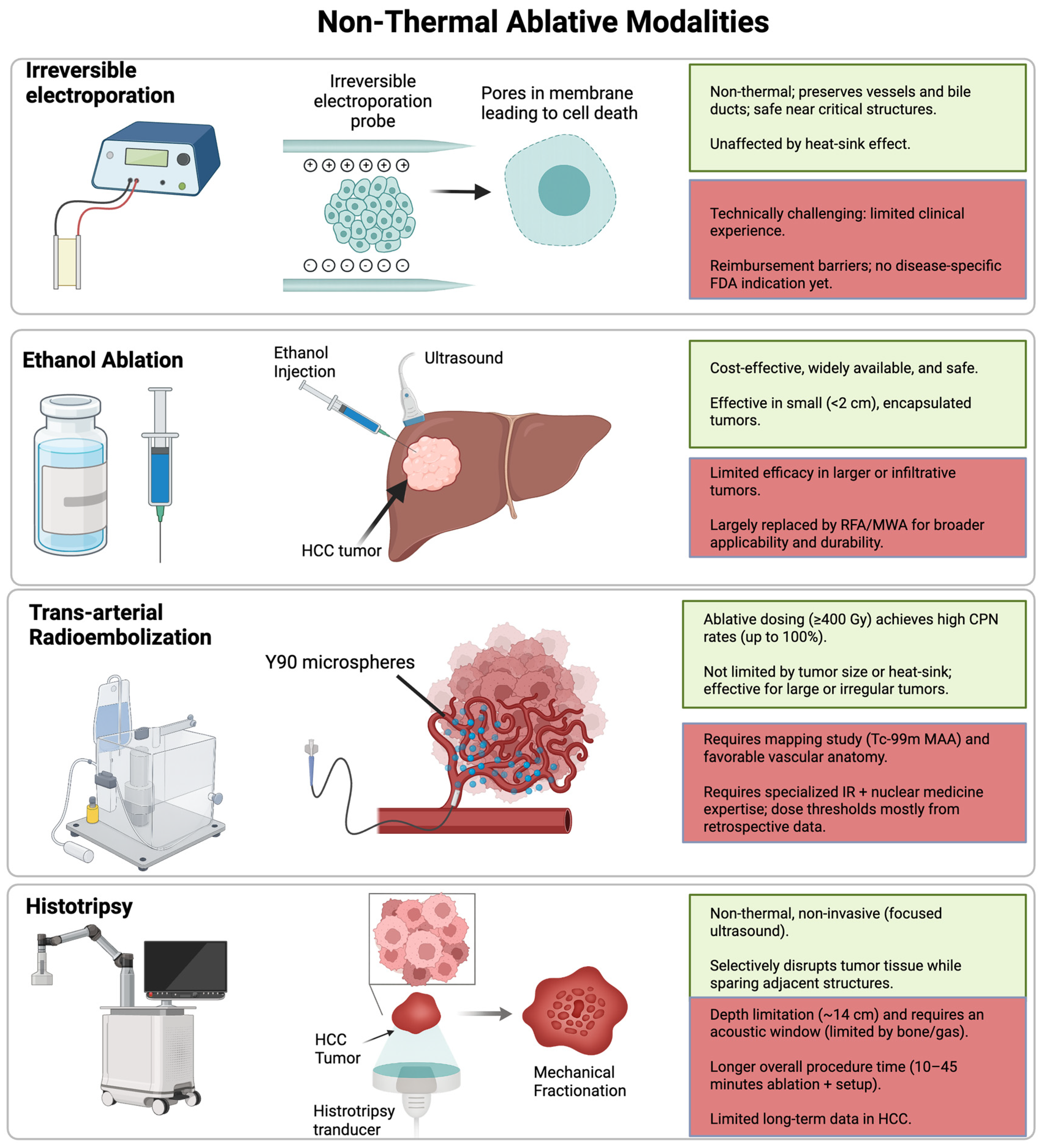
3. Non-Thermal Ablation Techniques
3.1. Irreversible Electroporation (IRE)
3.2. Percutaneous Ethanol Injection (PEI)
4. Radiation-Based Ablative Approaches
4.1. Trans-Arterial Radioembolization
4.2. External Beam Radiotherapy
5. Histotripsy
6. Imaging Advances in Ablation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCLC | Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer |
| CP | Child-Pugh |
| CPN | Complete pathological necrosis |
| CRCLM | Colorectal cancer liver metastases |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| mRECIST | Modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors |
| MWA | Microwave ablation |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PVTT | Portal vein tumor thrombosis |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| RFA | Radiofrequency ablation |
| RADSAG | Radiation segmentectomy |
| TACE | Transarterial chemoembolization |
| TARE | Transarterial radioembolization |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.-L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.B.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Abbott, D.E.; Anaya, D.A.; Anders, R.; Are, C.; Bachini, M.; Borad, M.; Brown, D.; Burgoyne, A.; et al. Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 541–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; Llovet, J.M.; Yarchoan, M.; Mehta, N.; Heimbach, J.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Jou, J.H.; Kulik, L.M.; Agopian, V.G.; Marrero, J.A.; et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1922–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, R.J.; Serhal, M.; Padia, S.A.; Kim, E.; Brown, D.B.; Tabori, N.E.; Toskich, B.B. The Evolving Application of Radiation Segmentectomy for the Treatment of Hepatic Malignancy. Radiology 2025, 316, e240333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Sher, A.; Abboud, G.; Schwartz, M.; Facciuto, M.; Tabrizian, P.; Knešaurek, K.; Fischman, A.; Patel, R.; Nowakowski, S.; et al. Radiation Segmentectomy for Curative Intent of Unresectable Very Early to Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma (RASER): A Single-Centre, Single-Arm Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, R.J.; Gabr, A.; Abouchaleh, N.; Ali, R.; Al Asadi, A.; Mora, R.A.; Kulik, L.; Ganger, D.; Desai, K.; Thornburg, B.; et al. Radiation Segmentectomy: Potential Curative Therapy for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2018, 287, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarini, E.; Savoia, A.; Brambilla, G.; Menozzi, F.; Reduzzi, L.; Strobel, D.; Hansler, J.; Buscarini, L.; Gaiti, L.; Zambelli, A. Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, L.; De Baere, T.; Lencioni, R. Quality Improvement Guidelines for Radiofrequency Ablation of Liver Tumours. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Kudo, M. Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Literature Review. Int. J. Hepatol. 2011, 2011, 104685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.K. Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Korean J. Radiol. 2000, 1, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, H.; Wakim, P.; Pritchard, W.F.; Castro, M.; Leonard, S.; Karanian, J.W.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Lencioni, R.; Wood, B.J. Radiofrequency Ablation Duration per Tumor Volume May Correlate with Overall Survival in Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Radiofrequency Ablation Plus Lyso-Thermosensitive Liposomal Doxorubicin. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, M.; Prakash, P.; Faridi, P.; Radosevic, A.; Curto, S.; Burdio, F.; Berjano, E. How Large Is the Periablational Zone after Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation? Computer-Based Comparative Study of Two Currently Used Clinical Devices. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, D.I.; Lee, M.W.; Song, K.D.; Ko, S.E.; Rhim, H. Ablative Outcomes of Various Energy Modes for No-Touch and Peripheral Tumor-Puncturing Radiofrequency Ablation: An Ex Vivo Simulation Study. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.-M.; Cui, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, M.-H.; Yan, K.; Goldberg, S.N. The 10-Year Survival Analysis of Radiofrequency Ablation for Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma 5 Cm or Smaller: Primary versus Recurrent HCC. Radiology 2021, 300, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agopian, V.G.; Morshedi, M.M.; McWilliams, J.; Harlander-Locke, M.P.; Markovic, D.; Zarrinpar, A.; Kaldas, F.M.; Farmer, D.G.; Yersiz, H.; Hiatt, J.R.; et al. Complete Pathologic Response to Pretransplant Locoregional Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Defines Cancer Cure after Liver Transplantation: Analysis of 501 Consecutively Treated Patients. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 536–545; discussion 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Bonder, A.; Hassan, L.; Malik, M.S.; Novack, V.; Curry, M.; Ahmed, M. Factors Associated With Complete Pathologic Necrosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Explant Evaluation After Locoregional Therapy: A National Analysis Using the UNOS Database. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2023, 220, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.; Cucchetti, A.; Felicani, C.; Mosconi, C.; De Cinque, A.; Golfieri, R.; Andreone, P.; Ercolani, G.; Maroni, L.; Ravaioli, M.; et al. Assessment of Radiofrequency Ablation Efficacy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Histology and Pretransplant Radiology. Liver Transpl. 2019, 25, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yan, L.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, H.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Y. A Randomized Trial Comparing Radiofrequency Ablation and Surgical Resection for HCC Conforming to the Milan Criteria. Ann. Surg. 2010, 252, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Kashiwabara, K.; Okamura, Y.; Kurosaki, M.; Kudo, M.; Shimada, M.; Yamanaka, N.; Inomata, M.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Surgery Versus Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized Controlled Trial (SURF-RCT Trial) and a Nonrandomized Prospective Observational Trial (SURF-Cohort Trial). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrafiello, G.; Laganà, D.; Ianniello, A.; Dionigi, G.; Novario, R.; Recaldini, C.; Mangini, M.; Cuffari, S.; Fugazzola, C. Post-radiofrequency Ablation Syndrome after Percutaneous Radiofrequency of Abdominal Tumours: One Centre Experience and Review of Published Works. Australas. Radiol. 2007, 51, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, S.J.; Lee, J.M. Incremental High Power Radiofrequency Ablation with Multi-Electrodes for Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prospective Study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Abe, H.; Ika, M.; Sakamoto, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Komazaki, S.; Takeda, S.; Ito, S.; Shimizu, S.; Matsuo, R. Efficacy of Fusion Imaging and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Poorly Visualized on Ultrasonography. Oncology 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Wang, J.; Tu, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hou, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Xie, H. Radiofrequency Ablation Combined with Toripalimab for Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Prospective Controlled Trial. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 20311–20320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Chen, S.; Bi, H.; Xia, F.; Feng, K.; Ma, K.; Ni, B. Combination Therapy with PD-1 Blockade and Radiofrequency Ablation for Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhim, H.; Lim, H.K. Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Pros and Cons. Gut Liver 2010, 4, S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Lu, F.; Ren, L.; Song, X.; Li, B.; Li, X. Efficacy and Safety of Microwave Ablation and Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e29321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darweesh, S.K.; Gad, A.A. Percutaneous Microwave Ablation for HCV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Efficacy, Safety, and Survival. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 30, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, K.; Seki, T.; Aoi, K.; Yamashina, M.; Murata, M.; Yamashiki, N.; Nishio, A.; Shimatani, M.; Naganuma, M. Efficacy of Microwave Ablation versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score Analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 3790–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solbiati, L.; Ierace, T.; Gennaro, N.; Muglia, R.; Cosman, E.R.; Goldberg, S.N. Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of HCC: Reduced Ablation Duration and Increased Ablation Size Using Single, Internally Cooled Electrodes with an Optimized Pulsing Algorithm. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietti Violi, N.; Duran, R.; Guiu, B.; Cercueil, J.-P.; Aubé, C.; Digklia, A.; Pache, I.; Deltenre, P.; Knebel, J.-F.; Denys, A. Efficacy of Microwave Ablation versus Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease: A Randomised Controlled Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuchte, K.; Staib, E.; Thelen, M.; Gödel, P.; Lechner, A.; Zentis, P.; Garcia-Marquez, M.; Waldschmidt, D.; Datta, R.R.; Wahba, R.; et al. Microwave Ablation Enhances Tumor-Specific Immune Response in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibollahi, P.; Sheth, R.A.; Cressman, E.N.K. Histological Correlation for Radiofrequency and Microwave Ablation in the Local Control of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) before Liver Transplantation: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2020, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Liu, P.; Xu, Z.; Wu, P.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B.; Qian, G. Microwave Ablation for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma That Met Up-to-Seven Criteria: Feasibility, Local Efficacy and Long-Term Outcomes. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 3877–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi, G.; Tosoratti, N.; Montagna, B.; Picchi, C. Microwave Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2578–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnon, J.; Cazzato, R.L.; Caudrelier, J.; Nouri-Neuville, M.; Rao, P.; Boatta, E.; Ramamurthy, N.; Koch, G.; Gangi, A. Adjunctive Thermoprotection During Percutaneous Thermal Ablation Procedures: Review of Current Techniques. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.A.; Ingram, L.; Wilson, I.D.C.; Breen, D.J. No-Touch Wedge Ablation Technique of Microwave Ablation for the Treatment of Subcapsular Tumors in the Liver. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, H.; Okamura, J. Microwave Thermosphere Ablation Versus Radiofrequency Ablation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Optimizing Treatment Strategies for Tumor Size and Malignancy Grade. Hepatol. Res. 2025, 55, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, K.; Lahat, A.; Levy, I.; Ben Horin, S. Gastric Perforation After Microwave Ablation to Adjacent Hepatocellular Lesion. ACG Case Rep. J. 2023, 10, e01082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, W.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Jia, W.; Ge, Y. Application of Indocyanine Green Fluorescence Imaging Combined with Laparoscopic Ultrasound in Laparoscopic Microwave Ablation of Liver Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e937832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Cristescu, M.; Lee, M.H.; Moreland, A.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Lee, F.T.; Brace, C.L. Effects of Microwave Ablation on Arterial and Venous Vasculature after Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Radiology 2016, 281, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccini, M.; Sehrt, D.; Pompeo, A.; Chicoli, F.A.; Molina, W.R.; Kim, F.J. Biophysiologic Considerations in Cryoablation: A Practical Mechanistic Molecular Review. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2011, 37, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenkle, P.C.; Mirabile, G.; Durak, E.; Edelstein, A.; Gupta, M.; Hruby, G.W.; Okhunov, Z.; Landman, J. The Effect of Argon Gas Pressure on Ice Ball Size and Rate of Formation. J. Endourol. 2010, 24, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, G.; Yu, M.; Zheng, M.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X. Effects of Radiofrequency Ablation versus Other Ablating Techniques on Hepatocellular Carcinomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazer, D.I.; Tatli, S.; Shyn, P.B.; Vangel, M.G.; Tuncali, K.; Silverman, S.G. Percutaneous Image-Guided Cryoablation of Hepatic Tumors: Single-Center Experience With Intermediate to Long-Term Outcomes. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toskich, B.B.; Bailey, R.E.; Alzubaidi, S.J.; Devcic, Z.; Frey, G.T.; Lewis, A.R.; Moynagh, M.R.; Mody, K.; Ritchie, C.A.; Sio, T.T.; et al. Advances in the Ablative Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Adv. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 1, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.; Kang, T.W.; Cha, D.I.; Song, K.D.; Lee, M.W.; Rhim, H.; Lim, H.K.; Sinn, D.H. Percutaneous Cryoablation for Perivascular Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Therapeutic Efficacy and Vascular Complications. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, X.; Sun, J.; Cheng, J.; Hu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Kong, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Percutaneous Argon-Helium Cryoablation for Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Located Adjacent to a Major Organ or Viscus: A Retrospective Study of 92 Patients at a Single Center. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e931473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Hu, K.; Xie, H.; Hu, K.; Bai, W.; Dong, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of Percutaneous Cryoablation versus Radiofrequency Ablation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1579–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ei, S.; Hibi, T.; Tanabe, M.; Itano, O.; Shinoda, M.; Kitago, M.; Abe, Y.; Yagi, H.; Okabayashi, K.; Sugiyama, D.; et al. Cryoablation Provides Superior Local Control of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinomas of >2 Cm Compared with Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Coagulation Therapy: An Underestimated Tool in the Toolbox. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Liu, H.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Li, Q. Cryoablation versus Microwave Ablation in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian J. Surg. 2025, 48, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.-Q. Advances in Clinical Application of Cryoablation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Metastatic Liver Tumor. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 48, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, J.-C.; Sutter, O.; Nahon, P.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Séror, O. Percutaneous Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: State of the Art and Innovations. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Xie, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Meng, Z. Potent Induction of Antitumor Immunity by Combining Cryo-thermal Ablation with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 723–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Han, Z. Modern Cancer Therapy: Cryoablation Meets Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1323070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Yu, Z.; Tang, X.; Chen, W.; Deng, X.; Zhu, X. Cryoablation Combined with Dual Immune Checkpoint Blockade Enhances Antitumor Efficacy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model Mice. Int. J. Hyperth. 2024, 41, 2373319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandt, T.; Bangar, A.; Sauceda, C.; Das, M.; Moderbacher, C.; Ghani, M.; Webster, N.; Newton, I. Stimulating Antitumoral Immunity by Percutaneous Cryoablation and Combination Immunoadjuvant Therapy in a Murine Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 34, 1516–1527.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, G.; Bai, W.; Dong, Z.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Qu, J.; Lou, M.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Percutaneous Cryoablation for Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma within Milan Criteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, M.S.; Chen, Y.; Lau, W.Y.; Peng, Z. Long-Term Outcomes of Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization Combined With Radiofrequency Ablation as an Initial Treatment for Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Am. Med. Assoc. Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2126992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Qi, L.; Liu, C.; Feng, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q. Combined Radiofrequency Ablation or Microwave Ablation with Transarterial Chemoembolization Can Increase Efficiency in Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma without More Complication: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yang, P.-P.; Xie, B.; Wei, J.; Qin, Z.; Qian, Z.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Fan, L.-F.; Qian, J.; et al. Single Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sequential Conventional Transarterial Chemoembolization (cTACE) and Microwave Ablation at 4 Weeks versus cTACE Alone: A Propensity Score. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 20, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarz, P.; Raman, S.S. Comparison of Combined Transarterial Chemoembolization and Ablations in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Fan, W.; Huang, K.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M.; Yao, W.; Li, J. Large Hepatocellular Carcinomas: Treatment with Transarterial Chemoembolization Alone or in Combination with Percutaneous Cryoablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 35, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.-Y.; Piao, X.-H.; Zou, Z.-Y.; Yang, Q.-F.; Qin, Z.-L.; Chen, J.-B.; Zhou, L.; Niu, L.-Z.; Liu, J.-G. Cryoablation with Drug-Loaded Bead Embolization in the Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Safety and Efficacy Analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7557–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.W.; Wong, D.; Prikhodko, S.V.; Perez, A.; Tran, C.; Loh, C.T.; Kee, S.T. Electron Microscopic Demonstration and Evaluation of Irreversible Electroporation-Induced Nanopores on Hepatocyte Membranes. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golberg, A.; Bruinsma, B.G.; Jaramillo, M.; Yarmush, M.L.; Uygun, B.E. Rat Liver Regeneration Following Ablation with Irreversible Electroporation. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.; Grand, D.; Charpentier, K. Irreversible Electroporation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Patient Selection and Perspectives. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2017, 4, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Huillier, R.; Dumortier, J.; Mastier, C.; Cayot, B.; Chambon, C.; Benech, N.; Stacoffe, N.; Valette, P.-J.; Milot, L. Robotic-Assisted Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2023, 104, 615–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hou, S.; Ni, J.; Sun, H.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L. Effectiveness and Safety of Irreversible Electroporation for Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Ineligible for Thermal Ablation after Surgery. J. Interv. Med. 2020, 3, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liang, B.; Li, R.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, M.; Niu, L. Irreversible Electroporation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Abutting the Diaphragm: A Prospective Single-Center Study. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, E.; Cheung, W.; Kavnoudias, H.; Majeed, A.; Kemp, W.; Roberts, S.K. Irreversible Electroporation For Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Longer-Term Outcomes At A Single Centre. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, E.; Cheung, W.; Ferdousi, S.; Kavnoudias, H.; Majeed, A.; Kemp, W.; Roberts, S.K. Irreversible Electroporation versus Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Single Centre Propensity-Matched Comparison. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, O.; Calvo, J.; N’Kontchou, G.; Nault, J.-C.; Ourabia, R.; Nahon, P.; Ganne-Carrié, N.; Bourcier, V.; Zentar, N.; Bouhafs, F.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Irreversible Electroporation for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Not Amenable to Thermal Ablation Techniques: A Retrospective Single-Center Case Series. Radiology 2017, 284, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niessen, C.; Thumann, S.; Beyer, L.; Pregler, B.; Kramer, J.; Lang, S.; Teufel, A.; Jung, E.M.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation: Long-Term Survival Analysis of 71 Patients with Inoperable Malignant Hepatic Tumors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollinger, M.; Zeman, F.; Niessen, C.; Lang, S.A.; Beyer, L.P.; Müller, M.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Bile Duct Injury after Irreversible Electroporation of Hepatic Malignancies: Evaluation of MR Imaging Findings and Laboratory Values. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, N.; Philips, P.; Scoggins, C.R.; McMasters, K.M.; Potts, M.H.; Martin, R.C.G. Evaluation of Tolerability and Efficacy of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) in Treatment of Child-Pugh B (7/8) Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). HPB 2016, 18, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Maralakunte, M.; Sagar, S.; Kumar-M, P.; Bhujade, H.; Chaluvashetty, S.B.; Kalra, N. Efficacy and Safety of Irreversible Electroporation for Malignant Liver Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6511–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.-H.; Choi, B.I.; De Baère, T.; Dodd, G.D.; et al. Image-Guided Tumor Ablation: Standardization of Terminology and Reporting Criteria—A 10-Year Update. Radiology 2014, 273, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühling, P.; Stillström, D.; Holmquist, F.; Nilsson, A.; Freedman, J. Irreversible Electroporation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases: A Nationwide Multicenter Study with Short- and Long-Term Follow-Up. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 49, 107046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, M.; Pan, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, K.; Xu, D.; Jing, X.; Lu, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Q.; et al. A Multicenter, Randomized, Parallel-Controlled Clinical Trial Protocol to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Irreversible Electroporation Compared with Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 22, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, A.I. Recent Advances in Multidisciplinary Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, R.M.; Bolus, D.N.; White, J.A. Irreversible Electroporation as a Bridge to Liver Transplantation. Am. Surg. 2019, 85, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H.; Fang, A.; Khorshidi, F.; Habibollahi, P.; Kutsenko, O.; Etezadi, V.; Hunt, S.; Nezami, N. New Developments in Image-Guided Percutaneous Irreversible Electroporation of Solid Tumors. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, C.B.; Sano, M.B.; Rossmeisl, J.H.; Caldwell, J.L.; Garcia, P.A.; Rylander, M.N.; Davalos, R.V. High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation (H-FIRE) for Non-Thermal Ablation without Muscle Contraction. BioMed Eng. Online 2011, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.; Wang, K.; Cartledge, J.; Ralph, C.; Jagdev, S.; Vasudev, N.; Bhattarai, S.; Wah, T.M. Ureteric Injury after Image-Guided Ablation of Renal Cell Cancer with Irreversible Electroporation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 32, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xue, W.; Yan, W.; Yin, L.; Dong, B.; He, B.; Yu, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, H.; et al. Extended Focal Ablation of Localized Prostate Cancer With High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation: A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. Surg. 2022, 157, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, L.P.; Pregler, B.; Michalik, K.; Niessen, C.; Dollinger, M.; Müller, M.; Schlitt, H.J.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Evaluation of a Robotic System for Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) of Malignant Liver Tumors: Initial Results. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baère, T.; Roux, C.; Deschamps, F.; Tselikas, L.; Guiu, B. Evaluation of a New CT-Guided Robotic System for Percutaneous Needle Insertion for Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors: A Prospective Pilot Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, K.P. Irreversible Electroporation for the Ablation of Liver Tumors: Are We There Yet? Arch. Surg. 2012, 147, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Xi, T.; Lau, W.-Y.; Dong, H.; Xian, Z.-H.; Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, F.; Wu, M.-C.; Cong, W.-M. Pathobiological Features of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Correlation between Tumor Size and Biological Behavior. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, S.; Tagawa, K.; Unuma, T.; Takanashi, R.; Yoshiura, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Hata, Y.; Niwa, Y.; Shiratori, Y.; Terano, A.; et al. Percutaneous Ethanol Injection Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. A Histopathologic Study. Cancer 1991, 68, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-M.; Lin, C.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Hsu, C.-W.; Chen, Y.-C. Radiofrequency Ablation Improves Prognosis Compared with Ethanol Injection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma ≤4 Cm. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwell, T.D.; Charboneau, J.W.; Que, F.G.; Rubin, J.; Lewis, B.D.; Nagorney, D.M.; Callstrom, M.R.; Farrell, M.A.; Pitot, H.C.; Hobday, T.J. Treatment of Neuroendocrine Cancer Metastatic to the Liver: The Role of Ablative Techniques. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2005, 28, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.A.; Allgaier, H.-P.; Cioni, D.; Olschewski, M.; Deibert, P.; Crocetti, L.; Frings, H.; Laubenberger, J.; Zuber, I.; Blum, H.E.; et al. Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhosis: Randomized Comparison of Radio-Frequency Thermal Ablation versus Percutaneous Ethanol Injection. Radiology 2003, 228, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasi, M.D.; Buscarini, L.; Livraghi, T.; Giorgoi, A.; Salmi, A.; Sio, I.D.; Brunello, F.; Solmi, L.; Caturelli, E.; Magnolfi, F.; et al. Percutaneous Ethanol Injection in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Survey of Evaluation Practices and Complication Rates. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardi, E.M.; Di Matteo, F.; Santini, D.; Uwechie, V.; Crucitti, P.; Carassiti, M.; Picardi, A.; Perrella, E.; Caricato, M.; Tonini, G.; et al. Pancreatitis after Percutaneous Ethanol Injection into HCC: A Minireview of the Literature. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 27, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, R.; Hunter, R.D. Yttrium-90 Microspheres for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 66, S83–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, R.; Thurston, K.G. Radioembolization with 90Yttrium Microspheres: A State-of-the-Art Brachytherapy Treatment for Primary and Secondary Liver Malignancies. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 17, 1251–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrfooh, A.; Patel, A.; Laroia, S. Transarterial Radioembolization Agents: A Review of the Radionuclide Agents and the Carriers. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 55, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. TheraSphere Y-90 Glass Microspheres for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC Strategy for Prognosis Prediction and Treatment Recommendation: The 2022 Update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin, E.; Tselikas, L.; Guiu, B.; Chalaye, J.; Edeline, J.; De Baere, T.; Assenat, E.; Tacher, V.; Robert, C.; Terroir-Cassou-Mounat, M.; et al. Personalised versus Standard Dosimetry Approach of Selective Internal Radiation Therapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (DOSISPHERE-01): A Randomised, Multicentre, Open-Label Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Sposito, C.; Bhoori, S.; Romito, R.; Chiesa, C.; Morosi, C.; Maccauro, M.; Marchianò, A.; Bongini, M.; Lanocita, R.; et al. Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for Intermediate-Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Phase 2 Study. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1826–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokabi, N.; Camacho, J.C.; Xing, M.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Spivey, J.R.; Knechtle, S.J.; Kim, H.S. Open-label Prospective Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Glass-based Yttrium 90 Radioembolization for Infiltrative Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis. Cancer 2015, 121, 2164–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.M.; Kulik, L.; Baker, T.; Ryu, R.K.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Abecassis, M.; Salem, R.; Lewandowski, R.J. Treating and Downstaging Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Caudate Lobe with Yttrium-90 Radioembolization. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 35, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, R.; Padia, S.A.; Toskich, B.B.; Callahan, J.D.; Fowers, K.D.; Geller, B.S.; Johnson, G.E.; Kulik, L.; Patel, T.C.; Lewandowski, R.J.; et al. Radiation Segmentectomy for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Curative. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, A.; Gates, V.L.; Atassi, B.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Mulcahy, M.F.; Ryu, R.K.; Sato, K.T.; Baker, T.; Kulik, L.; Gupta, R.; et al. Radiation Segmentectomy: A Novel Approach to Increase Safety and Efficacy of Radioembolization. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 79, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, R.; Johnson, G.E.; Kim, E.; Riaz, A.; Bishay, V.; Boucher, E.; Fowers, K.; Lewandowski, R.; Padia, S.A. Yttrium-90 Radioembolization for the Treatment of Solitary, Unresectable HCC: The LEGACY Study. Hepatology 2021, 74, 2342–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, A.; Riaz, A.; Johnson, G.E.; Kim, E.; Padia, S.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Salem, R. Correlation of Y90-Absorbed Radiation Dose to Pathological Necrosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Confirmatory Multicenter Analysis in 45 Explants. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Nasser, I.; Weinstein, J.L.; Odeh, M.; Babar, H.; Dinh, D.; Curry, M.; Bullock, A.; Eckhoff, D.; Dib, M.; et al. Histopathologic Outcomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Transarterial Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 Resin Microspheres. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, A.; Todd, R.I.; Shilo, D.; Garcia-Reyes, K.I.; Bishay, V.L.; Patel, R.I.; Patel, R.S.; Fischman, A.M.; Nowakowski, F.S.; Lookstein, R.A.; et al. Histopathologic Response and Oncologic Outcomes after Segmental and Subsegmental Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radioembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2025, 36, 1285–1295.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biederman, D.M.; Titano, J.J.; Bishay, V.L.; Durrani, R.J.; Dayan, E.; Tabori, N.; Patel, R.S.; Nowakowski, F.S.; Fischman, A.M.; Kim, E. Radiation Segmentectomy versus TACE Combined with Microwave Ablation for Unresectable Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Up to 3 Cm: A Propensity Score Matching Study. Radiology 2017, 283, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Sinn, D.H.; Hur, M.H.; Hong, J.H.; Park, M.K.; Cho, H.J.; Choi, N.R.; Lee, Y.B.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Transarterial Radioembolization for Large Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comparison to Resection. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La Garza-Ramos, C.; Montazeri, S.A.; Croome, K.P.; LeGout, J.D.; Sella, D.M.; Cleary, S.; Burns, J.; Mathur, A.K.; Overfield, C.J.; Frey, G.T.; et al. Radiation Segmentectomy for the Treatment of Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Outcomes Compared with Those of Surgical Resection. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 33, 775–785.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padia, S.A.; Johnson, G.E.; Horton, K.J.; Ingraham, C.R.; Kogut, M.J.; Kwan, S.; Vaidya, S.; Monsky, W.L.; Park, J.O.; Bhattacharya, R.; et al. Segmental Yttrium-90 Radioembolization versus Segmental Chemoembolization for Localized Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of a Single-Center, Retrospective, Propensity Score–Matched Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 777–785.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vouche, M.; Habib, A.; Ward, T.J.; Kim, E.; Kulik, L.; Ganger, D.; Mulcahy, M.; Baker, T.; Abecassis, M.; Sato, K.T.; et al. Unresectable Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Not Amenable to Radiofrequency Ablation: Multicenter Radiology-Pathology Correlation and Survival of Radiation Segmentectomy: VOUCHE ET AL. Hepatology 2014, 60, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.C.; Zahra, S.A.; Serhal, M.; Kircher, S.M.; Kalyan, A.; Sato, K.; Riaz, A.; Hohlastos, E.; Salem, R.; Lewandowski, R.J. Escalated Segmental and Modified Radiation Lobectomy Dosing for Yttrium-90 Radioembolization of Liver-Dominant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: 10-Year Outcomes. Clin. Color. Cancer 2025, 24, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, E.; Shin, S.S.; Cho, S.B.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.K.; Rew, J.S. Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer-Stage C Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Novel Approach to Subclassification and Treatment. Medicine 2017, 96, e6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokken, R.P.; Kerlan, R.K.; Chung, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-F.; Mehta, N.J.; Yao, F.Y.; Fidelman, N. Hepatic Toxicity After Selective Chemoembolization Is Associated With Decreased Survival Among Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, M.M.; Voigtländer, T.; Schweitzer, N.; Gebel, M.; Hinrichs, J.B.; Rodt, T.; Manns, M.P.; Wacker, F.; Potthoff, A.; Vogel, A. Retrograde Portal Vein Flow and Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma—A Case–Control Study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Chung, J.W.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.-C.; Hur, S.; Lee, M.; Jae, H.J. Portal Hypertension Is Associated with Poor Outcome of Transarterial Chemoembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 2184–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, R.J.; Sato, K.T.; Atassi, B.; Ryu, R.K.; Nemcek, A.A.; Kulik, L.; Geschwind, J.-F.; Murthy, R.; Rilling, W.; Liu, D.; et al. Radioembolization with 90Y Microspheres: Angiographic and Technical Considerations. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 30, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.; Lau, W.Y.; Leung, T.W.T.; Chan, M.; Johnson, P.J.; Li, A.K.C. Clinical Evaluation of the Partition Model for Estimating Radiation Doses from Yttrium-90 Microspheres in the Treatment of Hepatic Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1997, 24, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, C.; Mahler, M.; Soulen, M.C. Curative-Intent Therapies in Localized Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2020, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, T.K.; Tepper, J.E.; Moon, A.M.; Barry, A.; Molla, M.; Seong, J.; Torres, F.; Apisarnthanarax, S.; Buckstein, M.; Cardenes, H.; et al. Defining Minimum Treatment Parameters of Ablative Radiation Therapy in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Expert Consensus. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 14, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, R.C.-E.; Lee, C.-H.; Huang, H.-C.; Wu, S.-W.; Chou, C.-Y.; Hung, S.-P.; Lee, C.-W.; Krishnan, S.; Venkatesulu, B.P.; Lee, J.-C.; et al. Clinical and Dosimetric Results of Proton or Photon Radiation Therapy for Large (>5 Cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 118, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Garza-Ramos, C.; Montazeri, S.A.; LeGout, J.; Lewis, A.; Frey, G.; Paz-Fumagalli, R.; Hallemeier, C.; Rutenberg, M.; Ashman, J.; Toskich, B. Radiation Segmentectomy or Ablative External Beam Radiation Therapy as Initial Treatment for Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Experience. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2025, 12, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-W.; Kim, Y.; Maxwell, A.D.; Wang, T.-Y.; Hall, T.L.; Xu, Z.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Cain, C.A. Histotripsy beyond the Intrinsic Cavitation Threshold Using Very Short Ultrasound Pulses: Microtripsy. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-W.; Hall, T.L.; Xu, Z.; Cain, C.A. Histotripsy Lesion Formation Using an Ultrasound Imaging Probe Enabled by a Low-Frequency Pump Transducer. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 2148–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-W.; Duryea, A.P.; Kim, Y.; Hall, T.L.; Xu, Z.; Cain, C.A. Dual-Beam Histotripsy: A Low-Frequency Pump Enabling a High-Frequency Probe for Precise Lesion Formation. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Control 2014, 61, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaisavljevich, E.; Aydin, O.; Yuksel Durmaz, Y.; Lin, K.-W.; Fowlkes, B.; ElSayed, M.; Xu, Z. Effects of Ultrasound Frequency on Nanodroplet-Mediated Histotripsy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2015, 41, 2135–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, A.D.; Cain, C.A.; Hall, T.L.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Xu, Z. Probability of Cavitation for Single Ultrasound Pulses Applied to Tissues and Tissue-Mimicking Materials. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baac, H.W.; Lee, T.; Ok, J.G.; Hall, T.; Jay Guo, L. Dual-Frequency Focused Ultrasound Using Optoacoustic and Piezoelectric Transmitters for Single-Pulsed Free-Field Cavitation in Water. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 234103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HistoSonics, Inc. Multi-Center, Open-Labeled, Non-Randomized Study to Evaluate the Acute Technical Performance and Safety Profile of the VORTX Rx® for Ablation of Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors (Theresa Study); HistoSonics, Inc.: Plymouth, MN, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal-Jove, J.; Serres, X.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Cannata, J.; Duryea, A.; Miller, R.; Merino, X.; Velat, M.; Kam, Y.; Bolduan, R.; et al. First-in-Man Histotripsy of Hepatic Tumors: The THERESA Trial, a Feasibility Study. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggermann, P.; Pech, M.; Serres-Créixams, X.; White, S.B.; Davis, C.; Ahmed, O.; Parikh, N.D.; Planert, M.; Thormann, M.; Xu, Z.; et al. The #HOPE4LIVER Single-Arm Pivotal Trial for Histotripsy of Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors. Radiology 2024, 312, e233051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemlewicz, T.J.; Critchfield, J.J.; Mendiratta-Lala, M.; Wiggermann, P.; Pech, M.; Serres-Créixams, X.; Lubner, M.; Wah, T.M.; Littler, P.; Davis, C.R.; et al. The #HOPE4LIVER Single-Arm Pivotal Trial for Histotripsy of Primary and Metastatic Liver Tumors: 1-Year Update of Clinical Outcomes. Ann. Surg. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiina, S.; Tateishi, R.; Imamura, M.; Teratani, T.; Koike, Y.; Sato, S.; Obi, S.; Kanai, F.; Kato, N.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Percutaneous Ethanol Injection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 20-year Outcome and Prognostic Factors. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hall, T.L.; Vlaisavljevich, E.; Lee, F.T. Histotripsy: The First Noninvasive, Non-Ionizing, Non-Thermal Ablation Technique Based on Ultrasound. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X. Research Progress and Clinical Evaluation of Histotripsy: A Narrative Review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2023, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, M.; Wehrle, C.J.; Satish, S.; Knott, E.; Hong, H.; Allkushi, E.; Schlegel, A.; Berber, E.; Aucejo, F.; Kim, J.; et al. Histotripsy of Liver Tumors: Patient Selection, Ethical Discussions, and How We Do It. Cancers 2025, 17, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Gelehrter, S.K.; Fifer, C.G.; Lu, J.C.; Owens, G.E.; Berman, D.R.; Williams, J.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Ives, K.A.; Xu, Z. Non-invasive Pulsed Cavitational Ultrasound for Fetal Tissue Ablation: Feasibility Study in a Fetal Sheep Model. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 37, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrle, C.J.; Burns, K.; Ong, E.; Couillard, A.; Parikh, N.D.; Caoili, E.; Kim, J.; Aucejo, F.; Schlegel, A.; Knott, E.; et al. The First International Experience with Histotripsy: A Safety Analysis of 230 Cases. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2025, 29, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knott, E.A.; Swietlik, J.F.; Longo, K.C.; Watson, R.F.; Green, C.M.; Abel, E.J.; Lubner, M.G.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Smolock, A.R.; Xu, Z.; et al. Robotically-Assisted Sonic Therapy for Renal Ablation in a Live Porcine Model: Initial Preclinical Results. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styn, N.R.; Hall, T.L.; Fowlkes, J.B.; Cain, C.A.; Roberts, W.W. Histotripsy of Renal Implanted VX-2 Tumor in a Rabbit Model: Investigation of Metastases. Urology 2012, 80, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, Z.T.; Patel, T.; Burgoyne, A.M.; Clary, B.M. Hyperprogression and Systemic Metastasis of Cholangiocarcinoma after Histotripsy Therapy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2025, 36, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Sun, X.; Sun, H.; Qi, J.; Li, H.; Luan, J.; Zhai, D. Fusion Imaging versus Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Liver Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Acta Radiol. 2023, 64, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, D.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Chang, W. Utility of Real-Time CT/MRI-US Automatic Fusion System Based on Vascular Matching in Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinomas: A Prospective Study. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 44, 1579–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, R.; Cong, L.; Liu, B.; Xie, X.; Huang, G. Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Fusion Imaging in Precise Needle Placement for Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Hyperth. 2024, 41, 2316097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, S.M.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Yu, S.J.; Han, J.K. Real-Time US-CT/MR Fusion Imaging for Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zensen, S.; Bücker, A.; Meetschen, M.; Haubold, J.; Opitz, M.; Theysohn, J.M.; Schramm, S.; Jochheim, L.; Kasper, S.; Forsting, M.; et al. Current Use of Percutaneous Image-Guided Tumor Ablation for the Therapy of Liver Tumors: Lessons Learned from the Registry of the German Society for Interventional Radiology and Minimally Invasive Therapy (DeGIR) 2018–2022. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 3322–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Aoki, T.; Hagiwara, S.; Kudo, M. Tips for Preparing and Practicing Thermal Ablation Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Ye, J.; Huang, T.; Cong, L.; Xie, X.; Huang, G. 3D Fusion Is Superior to 2D Point-to-Point Contrast-Enhanced US to Evaluate the Ablative Margin after RFA for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 34, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonschot, K.H.M.; Arts, S.; Van Den Boezem, P.B.; De Wilt, J.H.W.; Fütterer, J.J.; Stommel, M.W.J.; Overduin, C.G. Ablative Margins in Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Hepatic Tumors: A Systematic Review. Expert. Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2023, 23, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdonschot, K.H.M.; Jenniskens, S.F.M.; Van Den Boezem, P.B.; Tjwa, E.T.T.L.; Wilt, J.H.W.; Fütterer, J.J.; Stommel, M.W.J.; Overduin, C.G. CT-Guided Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumors Using Intraprocedural CT-CT Fusion for Applicator Position and Ablation Completeness Assessment: A Single-Center Comparative Analysis. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2025, 48, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arellano, R.S. What’s New in Percutaneous Ablative Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Colorectal Hepatic Metastases? 2020 Update. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.; Ansari, M.Y.; Warfa, M.; Al-Hamar, H.; Abinahed, J.; Barah, A.; Dakua, S.P.; Balakrishnan, S. Efficacy of Fusion Imaging for Immediate Post-ablation Assessment of Malignant Liver Neoplasms: A Systematic Review. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 14225–14251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukund, A.; Tripathy, T.P.; Patel, R.K.; Chandel, K.; Patidar, Y.; Jindal, A.; Sarin, S.K. Percutaneous Ablative Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Caudate Lobe of the Liver: Efficacy and Outcome. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
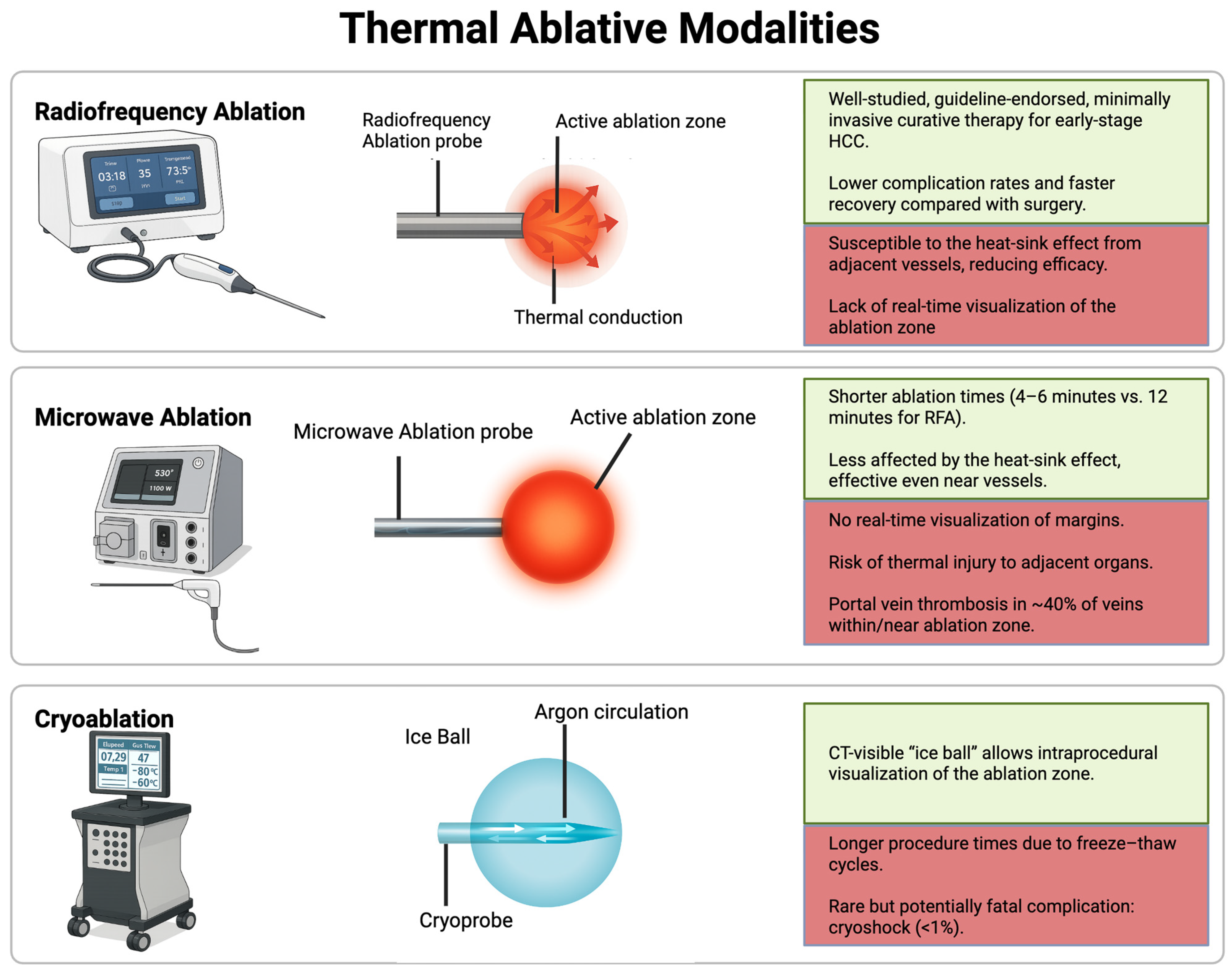
| Modality * | Complete Pathologic Necrosis (CPN) ** | Overall Survival (OS) ** | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiofrequency ablation | 61.6% overall in explant series; median tumor size 2.0 cm (range, 1.6–2.6) [20] | 54.8% 5-year OS (vs. 75.6% for resection, RCT, n = 230) [21] | Heat-sink near vessels; smaller single-applicator zones; overlaps often needed; tumor visibility/adjacent structures can limit use |
| Microwave ablation | 92.8% histology-confirmed with biopsies; mean tumor size 4.1 ± 1.9 cm (range, 1.2–8.0) [35] | 50.6% 5-year OS (single-center prospective, n = 142, 294 nodules, median size ≤7 cm) [36] | Collateral thermal injury risk near critical structures; may require hydrodissection |
| Cryoablation | NR (imaging complete response 97% within Milan criteria cohort) [60] | 40.0% 5year OS (vs. 38% RFA, comparative cohort, n = 360) [51] | Longer procedure times; minimal coagulative hemostasis; rare cryoshock <1% |
| Trans-arterial Radioembolization-Radiation Segmentectomy | 100% CPN achieved when absorbed doses exceeded: 400 Gy with glass microspheres (median tumor size 2.5 cm, range 1.3–8.0). 433 Gy with resin microspheres (median tumor size 2.6 cm, range 1.9–3.4) [8,110,111,112] | 75.0% 5-year OS for solitary tumors ≤3 cm and 57.0% for tumors ≤ 5 cm [9,108]. | Requires mapping study (MAA); anatomy must permit selective delivery; lung-shunting may limit dosing/safety; early stasis (resin microspheres) can cap achievable dose; specialized expertise |
| Ethanol Ablation | 72% CPN; tumor size range 1.6–5.0 cm (average, 2.9 cm) [93] | 49.0% % 5-year OS (single center retrospective cohort, n = 685) [140]. | Multiple sessions usually needed; Limited to small encapsuled tumors; tumor capsule limits any potential for ablation margin |
| Irreversible electroporation | 83% CPN in explant series of transplanted patients; median tumor size 2.2 cm (range, 1.6–2.6) [84] | 40.9% 3-year OS (meta-analysis, n = 776, 285 HCC) [79] | Requires GA with neuromuscular blockade; parallel multi-probe placement; tissue-impedance variability; reimbursement barriers |
| Histotripsy | NR | 73.3% 1-year OS (HOPE4LIVER prospective trial, n = 44, liver tumors including 31 HCC) [139] | Tumor must be sonographically visible. Depth limit ~14 cm; requires clear acoustic window (blocked by gas or bone); efficacy reduced in deep lesions/obesity; possible vascular thrombosis; multi-target patient repositioning |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu Zahra, S.; Nadeem, A.; Kundu, A.; Gibson, N.; Haggaz, A.; Sato, K.T.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Gordon, A.C. Recent Advances in Ablative Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193251
Abu Zahra S, Nadeem A, Kundu A, Gibson N, Haggaz A, Sato KT, Lewandowski RJ, Gordon AC. Recent Advances in Ablative Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193251
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu Zahra, Saad, Arsalan Nadeem, Ashima Kundu, Nick Gibson, Ali Haggaz, Kent T. Sato, Robert J. Lewandowski, and Andrew C. Gordon. 2025. "Recent Advances in Ablative Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193251
APA StyleAbu Zahra, S., Nadeem, A., Kundu, A., Gibson, N., Haggaz, A., Sato, K. T., Lewandowski, R. J., & Gordon, A. C. (2025). Recent Advances in Ablative Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(19), 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193251






