Dynamic Reprogramming of Immune-Related Signaling During Progression to Enzalutamide Resistance in Prostate Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Cell Culture
2.2. Western Blot Analysis and Antibodies
2.3. Real-Time Quantitative RT-PCR
2.4. Cell Growth Assay
2.5. Clonogenic Assay
2.6. Luciferase Assay
2.7. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
2.8. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.9. Datasets and Patients’ Cohort
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
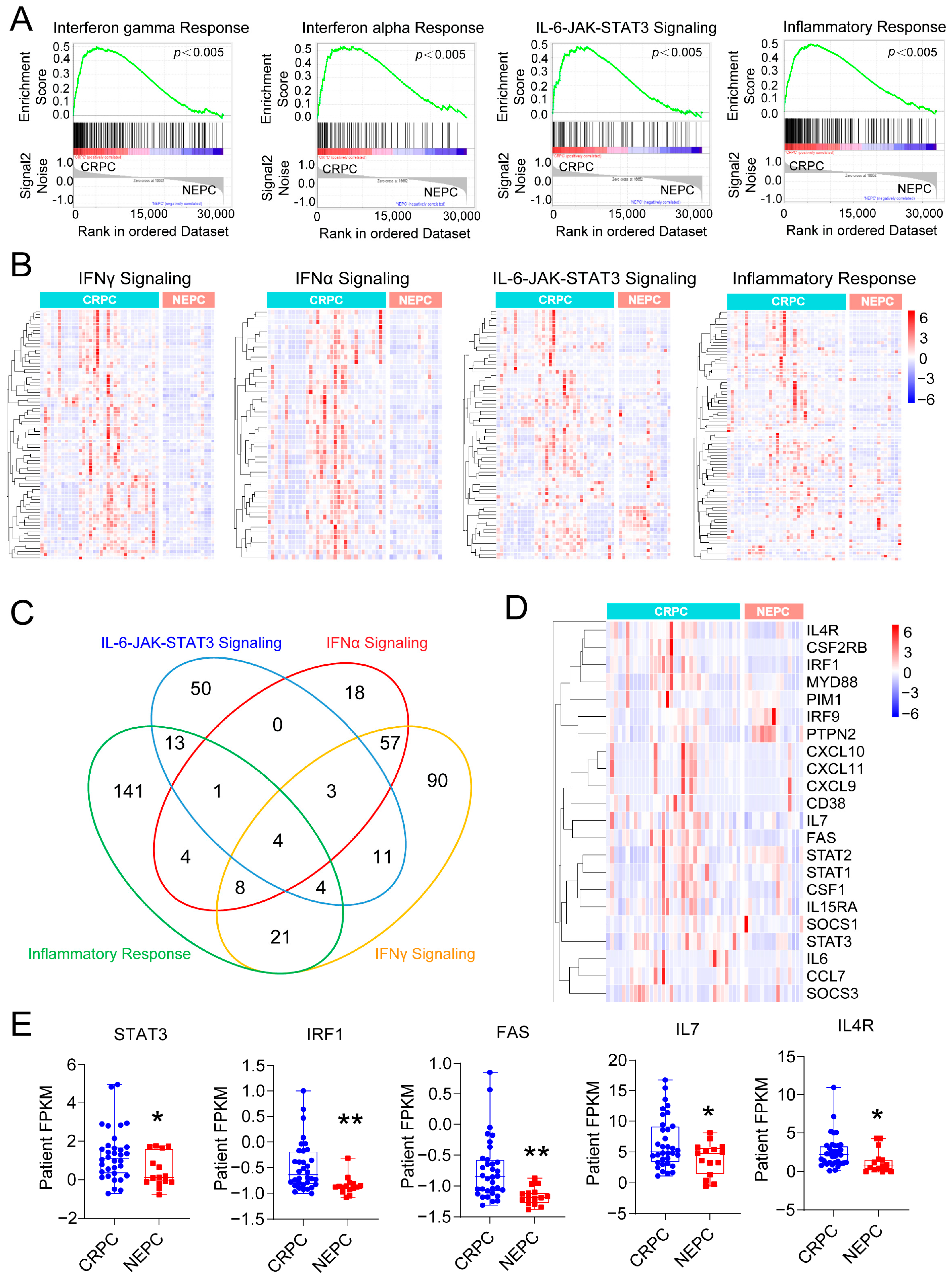
3.1. Inflammation-Associated Pathways Are Downregulated in NEPC
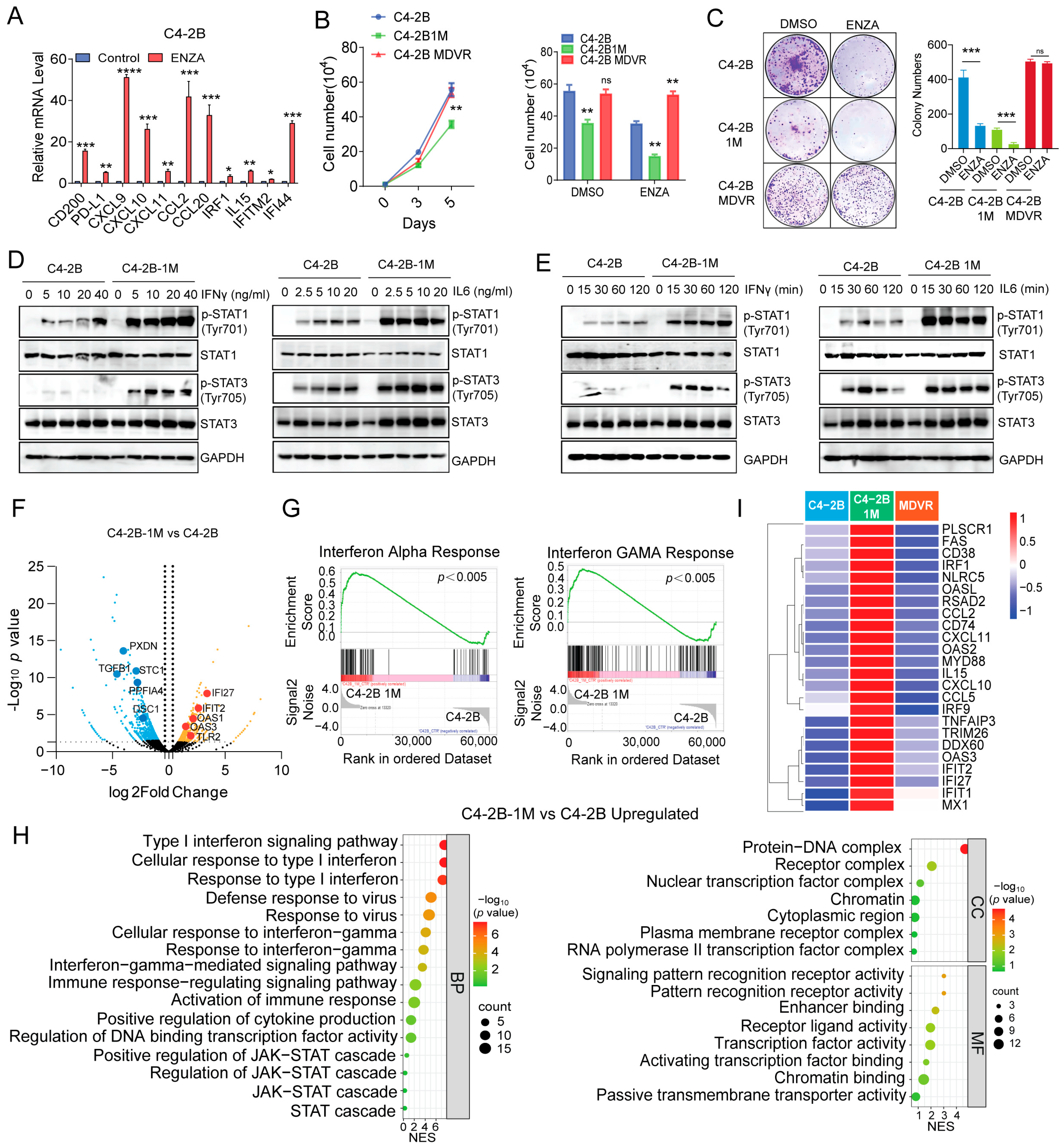
3.2. Enzalutamide-Resistant and NEPC Cells Exhibit Impaired IL-6 Signaling Pathways
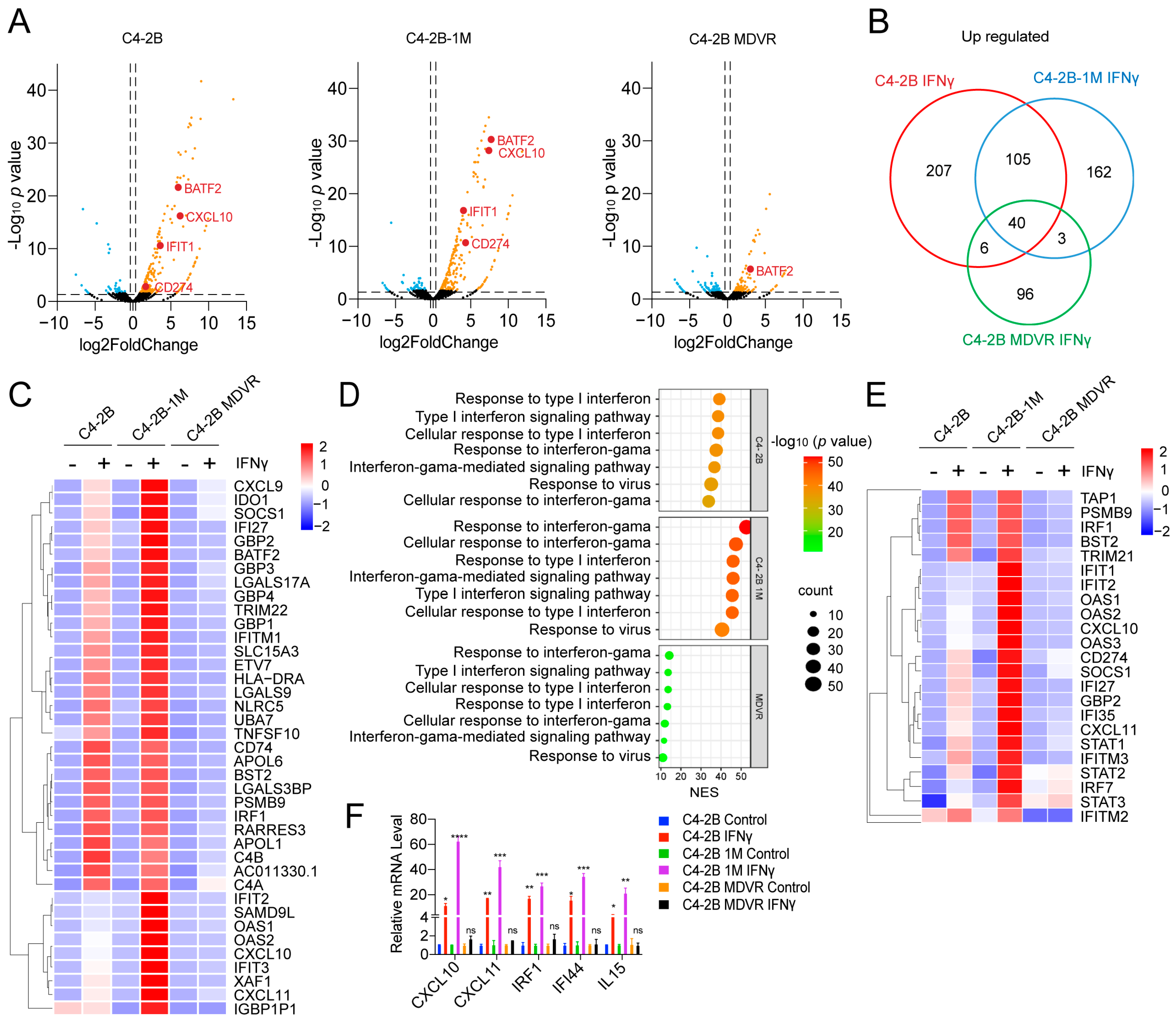
3.3. Enzalutamide Treatment Promotes Interferon Responsiveness at Early Stages
3.4. Early Enzalutamide Treatment Upregulates E2F Target Gene Expression Aligned with JAK/STAT Signaling Activation
3.5. Enzalutamide-Treated Prostate Cancer Cells in the Early Stage Are Highly Responsive to IFNγ
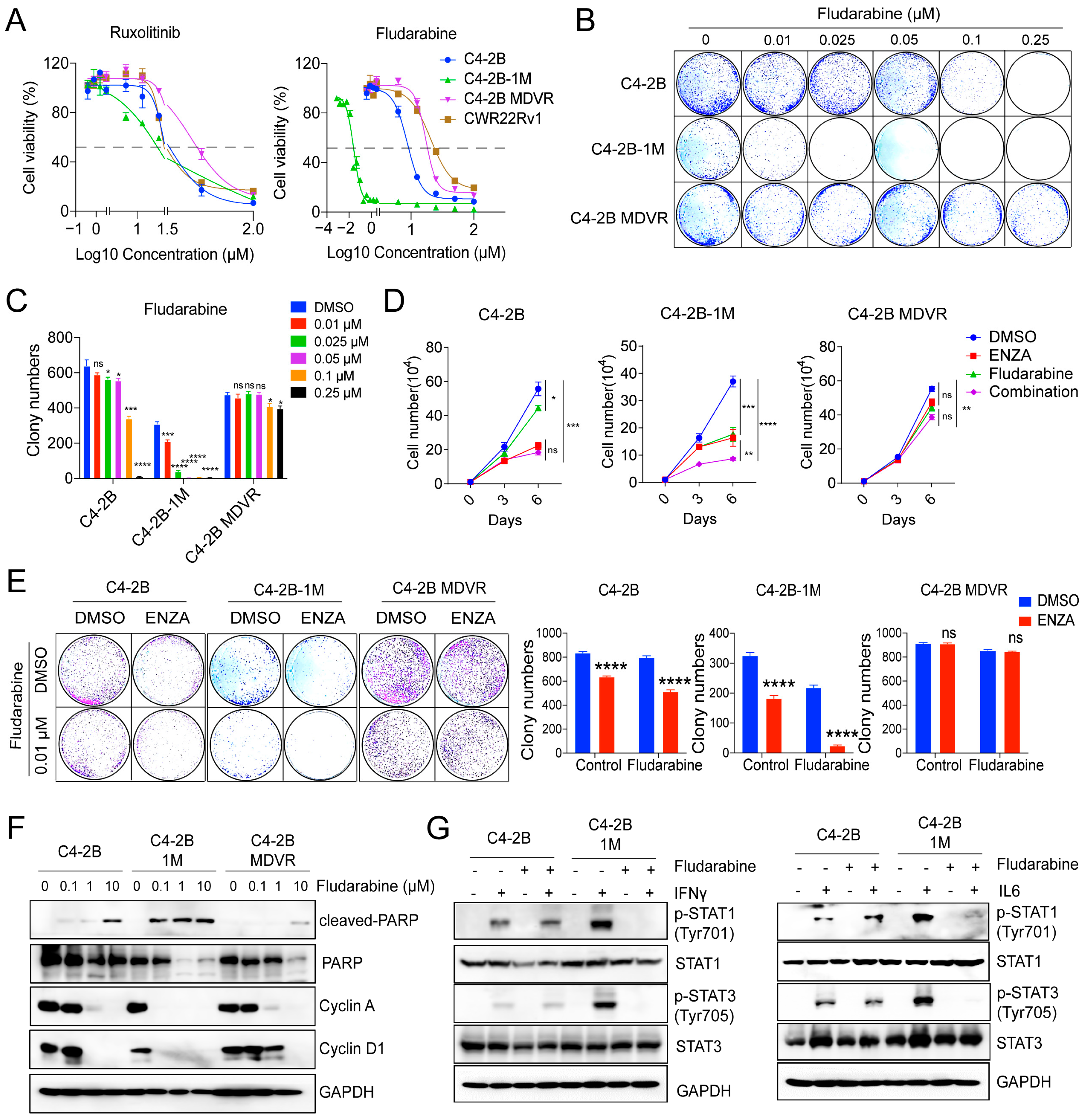
3.6. Early-Stage Enzalutamide Exposure Enhances Fludarabine Response in Prostate Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | Androgen Receptor |
| ADT | Androgen Deprivation Therapy |
| CRPC | Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer |
| tNEPC | Treatment-Induced Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer |
| IFNγ | Interferon gamma |
| IFNα | Interferon alpha |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| STAT1 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1 |
| EMT | Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
| MIP1α | Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 1 alpha |
| CCL3 | Chemokine (C C motif) ligand 3 |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| SDS PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| pSTAT1 | Phosphorylated STAT1 |
| pSTAT3 | Phosphorylated STAT3 |
| PARP | Poly (ADP ribose) polymerase |
| RT-PCR | Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| RNAseq | RNA sequencing |
| FPKM | Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads |
| GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| NES | Normalized Enrichment Score |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| G2M | Gap 2 Mitosis phase (cell cycle) |
| Myc | Myelocytomatosis oncogene |
| E2F | E2F Transcription Factor |
| PDL1 | Programmed Death Ligand 1 (also known as CD274) |
| SOCS1 | Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 |
| SOCS3 | Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 |
| IRF1 | Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 |
| CXCL10 | C X C Motif Chemokine Ligand 10 |
| CXCL11 | C X C Motif Chemokine Ligand 11 |
| IFI27 | Interferon Alpha Inducible Protein 27 |
| IFIT2 | Interferon Induced Protein with Tetratricopeptide Repeats 2 |
| OAS1 | 2 5 Oligoadenylate Synthetase 1 |
| OAS3 | 2 5 Oligoadenylate Synthetase 3 |
| TLR2 | Toll Like Receptor 2 |
| BATF2 | Basic Leucine Zipper ATF Like Transcription Factor 2 |
| IFIT1 | Interferon Induced Protein with Tetratricopeptide Repeats 1 |
| CD274 | Cluster of Differentiation 274 (also known as PDL1) |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute (refers to culture medium) |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
| HRP | Horseradish Peroxidase |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3 Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| HSP90 | Heat Shock Protein 90 |
| cBioPortal | cBio Portal for Cancer Genomics |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, M.; Hirst, C.; Crawford, E.D. Characterising the castration-resistant prostate cancer population: A systematic review. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2011, 65, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.K.; Sawyers, C.L. Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, F.; Dibitetto, F.; Ragonese, M.; Bassi, P. Mechanisms of Resistance to Second-Generation Antiandrogen Therapy for Prostate Cancer: Actual Knowledge and Perspectives. Med Sci. 2022, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluemn, E.G.; Coleman, I.M.; Lucas, J.M.; Coleman, R.T.; Hernandez-Lopez, S.; Tharakan, R.; Bianchi-Frias, D.; Dumpit, R.F.; Kaipainen, A.; Corella, A.N.; et al. Androgen Receptor Pathway-Independent Prostate Cancer Is Sustained through FGF Signaling. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 474–489.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Huang, J.; Alumkal, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Feng, F.Y.; Thomas, G.V.; Weinstein, A.S.; Friedl, V.; Zhang, C.; Witte, O.N.; et al. Clinical and Genomic Characterization of Treatment-Emergent Small-Cell Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer: A Multi-institutional Prospective Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2492–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abida, W.; Cyrta, J.; Heller, G.; Prandi, D.; Armenia, J.; Coleman, I.; Cieslik, M.; Benelli, M.; Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; et al. Genomic correlates of clinical outcome in advanced prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11428–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.; Conteduca, V.; Zoubeidi, A.; Beltran, H. Biological Evolution of Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Rickman, D.S.; Park, K.; Chae, S.S.; Sboner, A.; MacDonald, T.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sheikh, K.L.; Terry, S.; Tagawa, S.T.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer and Identification of New Drug Targets. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.L.; Thaper, D.; Vahid, S.; Davies, A.; Ketola, K.; Kuruma, H.; Jama, R.; Nip, K.M.; Angeles, A.; Johnson, F.; et al. The Master Neural Transcription Factor BRN2 Is an Androgen Receptor–Suppressed Driver of Neuroendocrine Differentiation in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Benelli, M.; Karthaus, W.R.; Hoover, E.; Chen, C.-C.; Wongvipat, J.; Ku, S.-Y.; Gao, D.; Cao, Z.; et al. SOX2 promotes lineage plasticity and antiandrogen resistance in TP53- and RB1-deficient prostate cancer. Science 2017, 355, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfanos, K.S.; De Marzo, A.M. Prostate cancer and inflammation: The evidence. Histopathology 2011, 60, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; MacLennan, G.T.; Hartman, D.J.; Fu, P.; Resnick, M.I.; Gupta, S. Activation of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway promotes prostate cancer cell invasion. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, Z.; Puhr, M. Interleukin-6 and prostate cancer: Current developments and unsolved questions. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 462, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, D.R.; Hurt, E.M.; Farrar, W.L. The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K.L.; Gearing, L.J.; Zanker, D.J.; Brockwell, N.K.; Khoo, W.H.; Roden, D.L.; Cmero, M.; Mangiola, S.; Hong, M.K.; Spurling, A.J.; et al. Prostate cancer cell-intrinsic interferon signaling regulates dormancy and metastatic outgrowth in bone. Embo Rep. 2020, 21, e50162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marzo, A.M.; Platz, E.A.; Sutcliffe, S.; Xu, J.; Grönberg, H.; Drake, C.G.; Nakai, Y.; Isaacs, W.B.; Nelson, W.G. Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, R.; Soon, R.H.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, K.; Lim, C.T. Cancer Diagnosis: From Tumor to Liquid Biopsy and Beyond. Lab a Chip 2018, 19, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Wasielewski, L.J.; Yang, J.C.; Cai, D.; Evans, C.P.; Murphy, W.J.; Liu, C. The Immunotherapy and Immunosuppressive Signaling in Therapy-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, Z. Interleukin-6 Function and Targeting in Prostate Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol 2021, 1290, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Johnson, N.A.; Mukherji, A.; Lo, U.-G.; Xu, L.; Gonzalez, J.; et al. Ectopic JAK–STAT activation enables the transition to a stem-like and multilineage state conferring AR-targeted therapy resistance. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 1071–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lou, W.; Cui, Y.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Inhibition of constitutively active Stat3 reverses enzalutamide resistance in LNCaP derivative prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2013, 74, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Nadiminty, N.; Lou, W.; Gao, A.C. Interleukin-6 induces neuroendocrine differentiation (NED) through suppression of RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST). Prostate 2014, 74, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, U.; Chen, Y.; Cen, J.; Deng, S.; Luo, J.; Zhau, H.; Ho, L.; Lai, C.; Mu, P.; Chung, L.W.; et al. The driver role of JAK-STAT signalling in cancer stemness capabilities leading to new therapeutic strategies for therapy- and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhinder, B.; Ferguson, A.; Sigouros, M.; Uppal, M.; Elsaeed, A.G.; Bareja, R.; Alnajar, H.; Eng, K.W.; Conteduca, V.; Sboner, A.; et al. Immunogenomic Landscape of Neuroendocrine Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 2933–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, T.; Xiao, Y.-T.; Sheng, H.; Su, H.; Hollern, D.P.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Wen, S.; et al. FOXA1 overexpression suppresses interferon signaling and immune response in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e147025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.M.; Zaidi, S.; Love, J.R.; Zhao, J.L.; Setty, M.; Wadosky, K.M.; Gopalan, A.; Choo, Z.-N.; Persad, S.; Choi, J.; et al. Lineage plasticity in prostate cancer depends on JAK/STAT inflammatory signaling. Science 2022, 377, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, H.I.; Sawyers, C.L. Biology of Progressive, Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Directed Therapies Targeting the Androgen-Receptor Signaling Axis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8253–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh-Ghodsi, M.; Owen, K.L.; Townley, S.L.; Zanker, D.; Rollin, S.P.; Hanson, A.R.; Shrestha, R.; Toubia, J.; Gargett, T.; Chernukhin, I.; et al. Potent Stimulation of the Androgen Receptor Instigates a Viral Mimicry Response in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 706–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Herrmann, A.; Cherryholmes, G.; Kowolik, C.; Buettner, R.; Pal, S.; Yu, H.; Müller-Newen, G.; Jove, R. Loss of Androgen Receptor Expression Promotes a Stem-like Cell Phenotype in Prostate Cancer through STAT3 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstathiou, E.; Titus, M.; Wen, S.; Hoang, A.; Karlou, M.; Ashe, R.; Tu, S.M.; Aparicio, A.; Troncoso, P.; Mohler, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Enzalutamide-treated Bone Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Toivanen, R.; Mitrofanova, A.; Floch, N.; Hayati, S.; Sun, Y.; Le Magnen, C.; Chester, D.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Califano, A.; et al. Transdifferentiation as a Mechanism of Treatment Resistance in a Mouse Model of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, D.M.S.; Pal, S.K.; Moreira, D.; Duttagupta, P.; Zhang, Q.; Won, H.; Jones, J.; D’APuzzo, M.; Forman, S.; Kortylewski, M. TLR9-Targeted STAT3 Silencing Abrogates Immunosuppressive Activity of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells from Prostate Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3771–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, D.Y.; Spisák, S.; Seo, J.-H.; Bell, C.; O’cOnnor, E.; Korthauer, K.; Ribli, D.; Csabai, I.; Solymosi, N.; Szállási, Z.; et al. A Somatically Acquired Enhancer of the Androgen Receptor Is a Noncoding Driver in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2018, 174, 422–432.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yang, J.C.; Ning, S.; Chen, B.; Nip, C.; Wei, Q.; Liu, L.; Johnson, O.T.; Gao, A.C.; Gestwicki, J.E.; et al. Allosteric inhibition of HSP70 in collaboration with STUB1 augments enzalutamide efficacy in antiandrogen resistant prostate tumor and patient-derived models. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 189, 106692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, C.; Nadiminty, N.; Lou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Evans, C.P.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, A.C. Inhibition of Stat3 activation by sanguinarine suppresses prostate cancer cell growth and invasion. Prostate 2011, 72, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yang, J.C.; Chen, B.; Ning, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Nip, C.; Shen, Y.; Johnson, O.T.; Grigorean, G.; et al. Proteostasis perturbation of N-Myc leveraging HSP70 mediated protein turnover improves treatment of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, H.; Prandi, D.; Mosquera, J.M.; Benelli, M.; Puca, L.; Cyrta, J.; Marotz, C.; Giannopoulou, E.; Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Varambally, S.; et al. Divergent clonal evolution of castration-resistant neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, S.; Zhao, J.; Lombard, A.P.; D’aBronzo, L.S.; Leslie, A.R.; Sharifi, M.; Lou, W.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.C.; Evans, C.P.; et al. Activation of neural lineage networks and ARHGEF2 in enzalutamide-resistant and neuroendocrine prostate cancer and association with patient outcomes. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xu, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.-S.; Ren, Y.-Y.; Dong, X.-M.; Wu, P.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.-L. Prostate cancer microenvironment: Multidimensional regulation of immune cells, vascular system, stromal cells, and microbiota. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesner, L.N.; Polesso, F.; Graff, J.N.; Hawley, J.E.; Smith, A.K.; Lundberg, A.; Das, R.; Shenoy, T.; Sjöström, M.; Zhao, F.; et al. Androgen Receptor Inhibition Increases MHC Class I Expression and Improves Immune Response in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2024, 15, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettoun, D.J.; Scafonas, A.; Rutledge, S.J.; Hodor, P.; Chen, O.; Gambone, C.; Vogel, R.; McElwee-Witmer, S.; Bai, C.; Freedman, L.; et al. Interaction between the Androgen Receptor and RNase L Mediates a Cross-talk between the Interferon and Androgen Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38898–38901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.M.; Zhao, F.; Graff, J.N.; Chen, C.; Zhao, X.; Thomas, G.V.; Wu, H.; Kardosh, A.; Mills, G.B.; Alumkal, J.J.; et al. Androgen receptor activity inversely correlates with immune cell infiltration and immunotherapy response across multiple cancer lineages. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Polesso, F.; Wang, C.; Sehrawat, A.; Hawkins, R.M.; Murray, S.E.; Thomas, G.V.; Caruso, B.; Thompson, R.F.; Wood, M.A.; et al. Androgen receptor activity in T cells limits checkpoint blockade efficacy. Nature 2022, 606, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, R.A.; Karzai, F.; Donahue, R.N.; Al-Harthy, M.; Bilusic, M.; Rosner, I.I.; Singh, H.; Arlen, P.M.; Theoret, M.R.; Marté, J.L.; et al. Clinical and immunologic impact of short-course enzalutamide alone and with immunotherapy in non-metastatic castration sensitive prostate cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Moreira, D.; Won, H.; White, S.W.; Duttagupta, P.; Lucia, M.; Jones, J.; Hsu, J.; Kortylewski, M. Reduced T-cell Numbers and Elevated Levels of Immunomodulatory Cytokines in Metastatic Prostate Cancer Patients De Novo Resistant to Abiraterone and/or Enzalutamide Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho-Schwermann, M.; Carneiro, B.A.; Carlsen, L.; Huntington, K.E.; Srinivasan, P.R.; George, A.; Tajiknia, V.; MacDonald, W.; Purcell, C.; Zhou, L.; et al. Androgen receptor signaling blockade enhances NK cell-mediated killing of prostate cancer cells and sensitivity to NK cell checkpoint blockade. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, C.R.; Udartseva, O.; Ramsey, K.D.; Bush, C.; Gollnick, S.O. Enzalutamide, an Androgen Receptor Antagonist, Enhances Myeloid Cell–Mediated Immune Suppression and Tumor Progression. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yang, J.C.; Chen, B.; Nip, C.; Van Dyke, J.E.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.-W.; Evans, C.P.; Murphy, W.J.; Liu, C. Androgen receptor blockade resistance with enzalutamide in prostate cancer results in immunosuppressive alterations in the tumor immune microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.-D.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Wu, X.-L.; Yang, C.-X.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yu, T.; Qi, H.-X.; Zhou, G.-P. Transcription factor E2F1 positively regulates interferon regulatory factor 5 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 6907–6915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, R.A.; Aboelenein, H.R.A.; Sourour, S.K.N.; Fawzy, I.O.; Salah, S.; Abdelaziz, A. Targeting E2F1 and c-Myc expression by microRNA-17-5p represses interferon-stimulated gene MxA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Discov. Med. 2015, 19, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spitschak, A.; Dhar, P.; Singh, K.P.; Garduño, R.C.; Gupta, S.K.; Vera, J.; Musella, L.; Murr, N.; Stoll, A.; Pützer, B.M. E2F1-induced autocrine IL-6 inflammatory loop mediates cancer-immune crosstalk that predicts T cell phenotype switching and therapeutic responsiveness. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1470368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Kang, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, B.; Ma, J.; Zheng, C.; Sun, J.; Tian, Z.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W. E2F1 renders prostate cancer cell resistant to ICAM-1 mediated antitumor immunity by NF-κB modulation. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; He, Q.; Li, C.; Alsharafi, B.L.M.; Deng, L.; Long, Z.; Gan, Y. Focus on the tumor microenvironment: A seedbed for neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 955669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigore, A.D.; Ben-Jacob, E.; Farach-Carson, M.C. Prostate Cancer and Neuroendocrine Differentiation: More Neuronal, Less Endocrine? Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Nadiminty, N.; Gaikwad, N.W.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Intracrine Androgens and AKR1C3 Activation Confer Resistance to Enzalutamide in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westbrook, T.C.; Guan, X.; Rodansky, E.; Flores, D.; Liu, C.J.; Udager, A.M.; Patel, R.A.; Haffner, M.C.; Hu, Y.-M.; Sun, D.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of matched patient biopsies clarifies molecular determinants of enzalutamide-induced lineage plasticity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Ko, H.; Shi, K.; Pittsenbarger, J.; Dao, L.V.; Shi, K.; Libmann, M.; Geng, H.; Qian, D.Z. Understanding Enzalutamide-Resistance Based on a Functional Single-Cell Approach. Prostate 2025, 85, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.A.; Mahajan, S.; Ritz, J. Fludarabine-induced immunosuppression is associated with inhibition of STAT1 signaling. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallen, H.A.; Thompson, J.; Reilly, J.Z.; Rodmyre, R.M.; Cao, J.; Yee, C. Fludarabine Modulates Immune Response and Extends In Vivo Survival of Adoptively Transferred CD8 T Cells in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, P.; Qu, H.; Yang, J.C.; Wei, F.; Zhao, J.; Tang, M.; Wang, L.; Nip, C.; Li, H.; Gao, A.C.; et al. Dynamic Reprogramming of Immune-Related Signaling During Progression to Enzalutamide Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193187
Xu P, Qu H, Yang JC, Wei F, Zhao J, Tang M, Wang L, Nip C, Li H, Gao AC, et al. Dynamic Reprogramming of Immune-Related Signaling During Progression to Enzalutamide Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193187
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Pengfei, Huan Qu, Joy C. Yang, Fan Wei, Junwei Zhao, Menghuan Tang, Leyi Wang, Christopher Nip, Henson Li, Allen C. Gao, and et al. 2025. "Dynamic Reprogramming of Immune-Related Signaling During Progression to Enzalutamide Resistance in Prostate Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193187
APA StyleXu, P., Qu, H., Yang, J. C., Wei, F., Zhao, J., Tang, M., Wang, L., Nip, C., Li, H., Gao, A. C., Lam, K., Dall'Era, M., Li, Y., & Liu, C. (2025). Dynamic Reprogramming of Immune-Related Signaling During Progression to Enzalutamide Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 17(19), 3187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193187





