Long-Acting Recombinant IL-7 (rhIL-7-hyFc) Enhances the Primary and Memory Neoantigen-Specific Immune Response to Breast Cancer Personalized Cancer Vaccines
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Tumor Cell Line
2.3. Polyepitope Neoantigen DNA Vaccination
2.4. rhIL-7-hyFc Treatment
2.5. ELISpot
2.6. Tumor Challenge
2.7. In Vivo Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. Flow Cytometry TIL Analysis
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
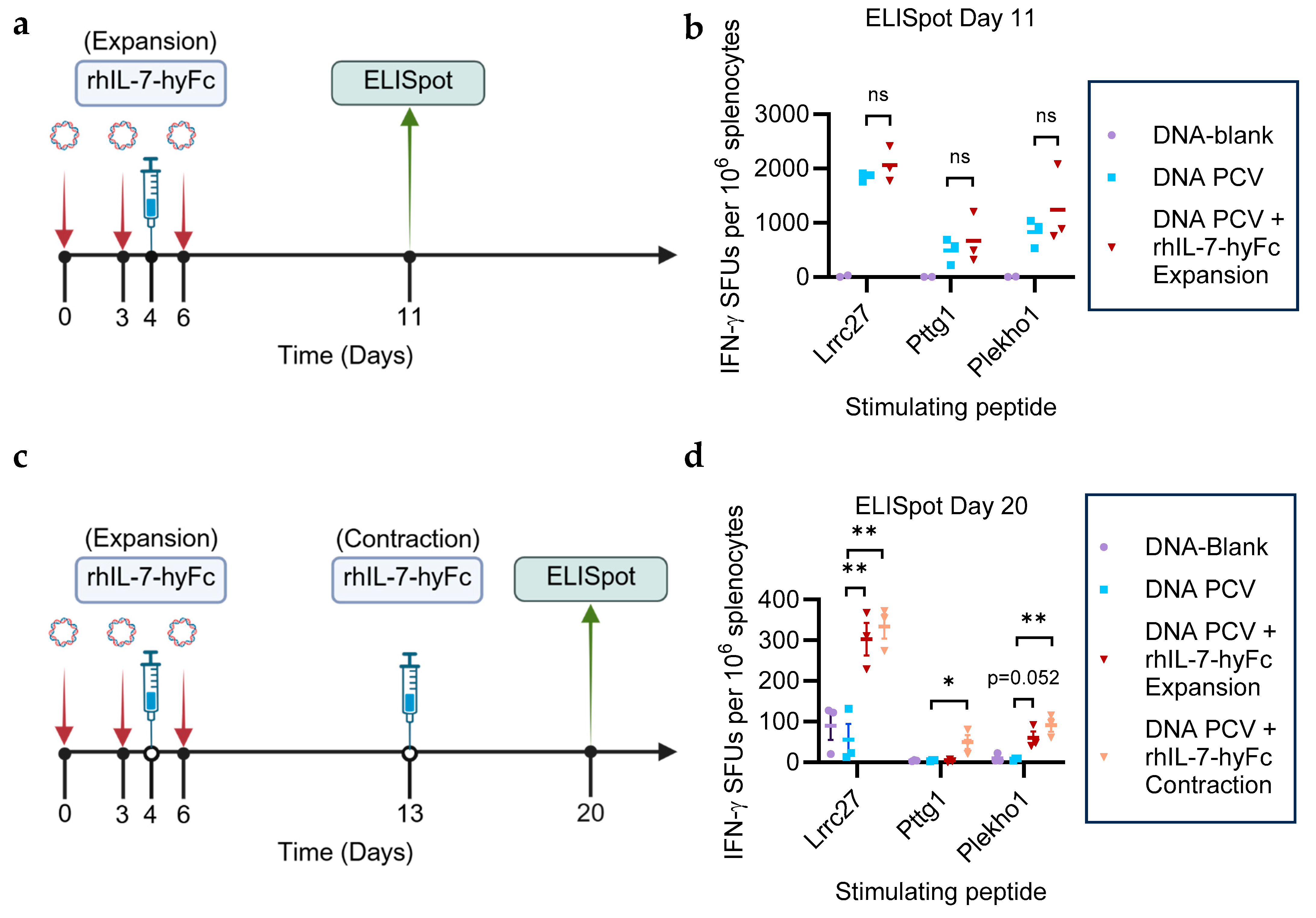
3.1. rhIL-7-hyFc Administered During the T Cell Expansion or Contraction Phase Prolongs Neoantigen-Specific T Cell Immunity
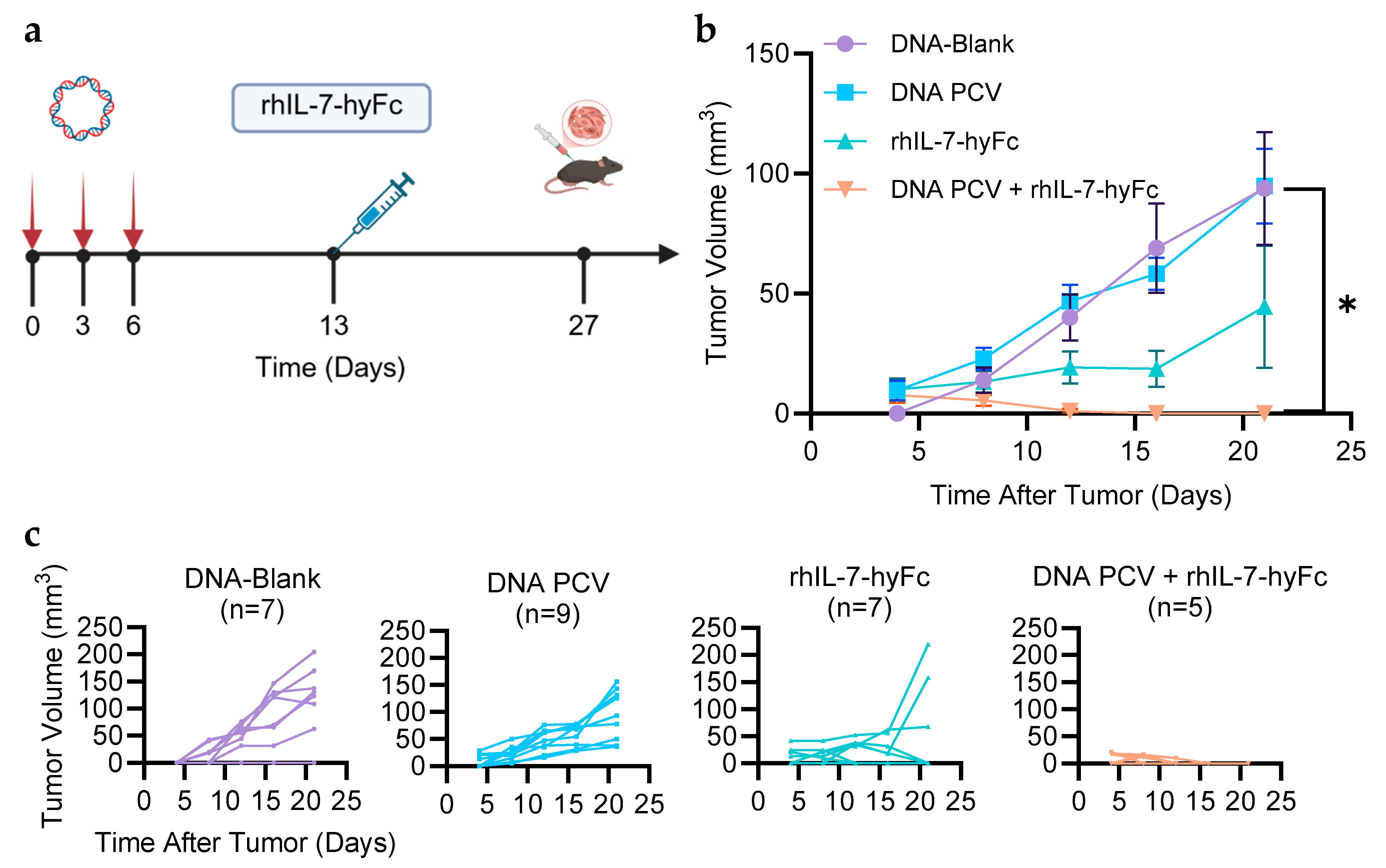
3.2. PCV + rhIL-7-hyFc Protects from Tumor Challenge
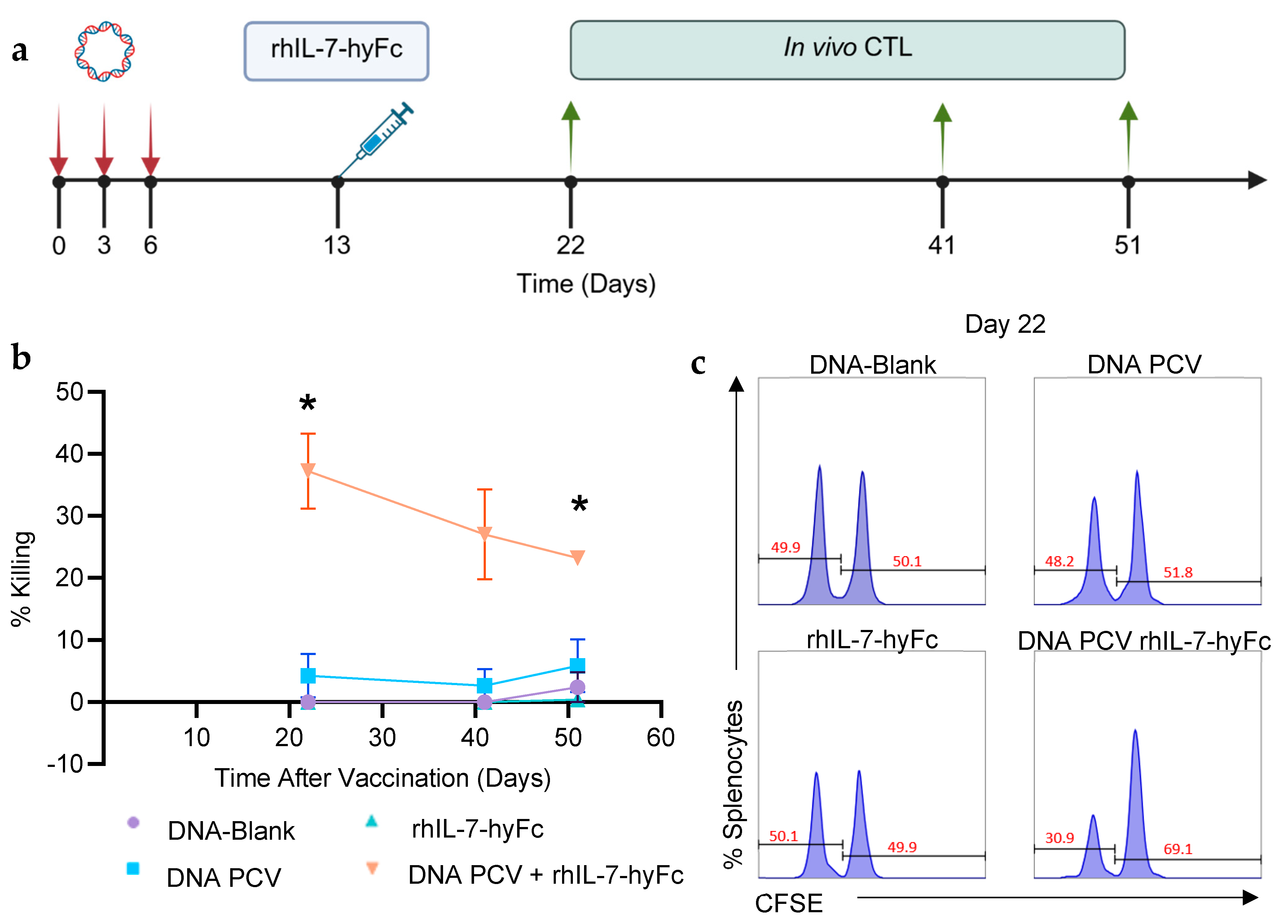
3.3. PCV + rhIL-7-hyFc Generates Stronger Neoantigen-Specific Killing and Memory CD8+ T Cell Responses
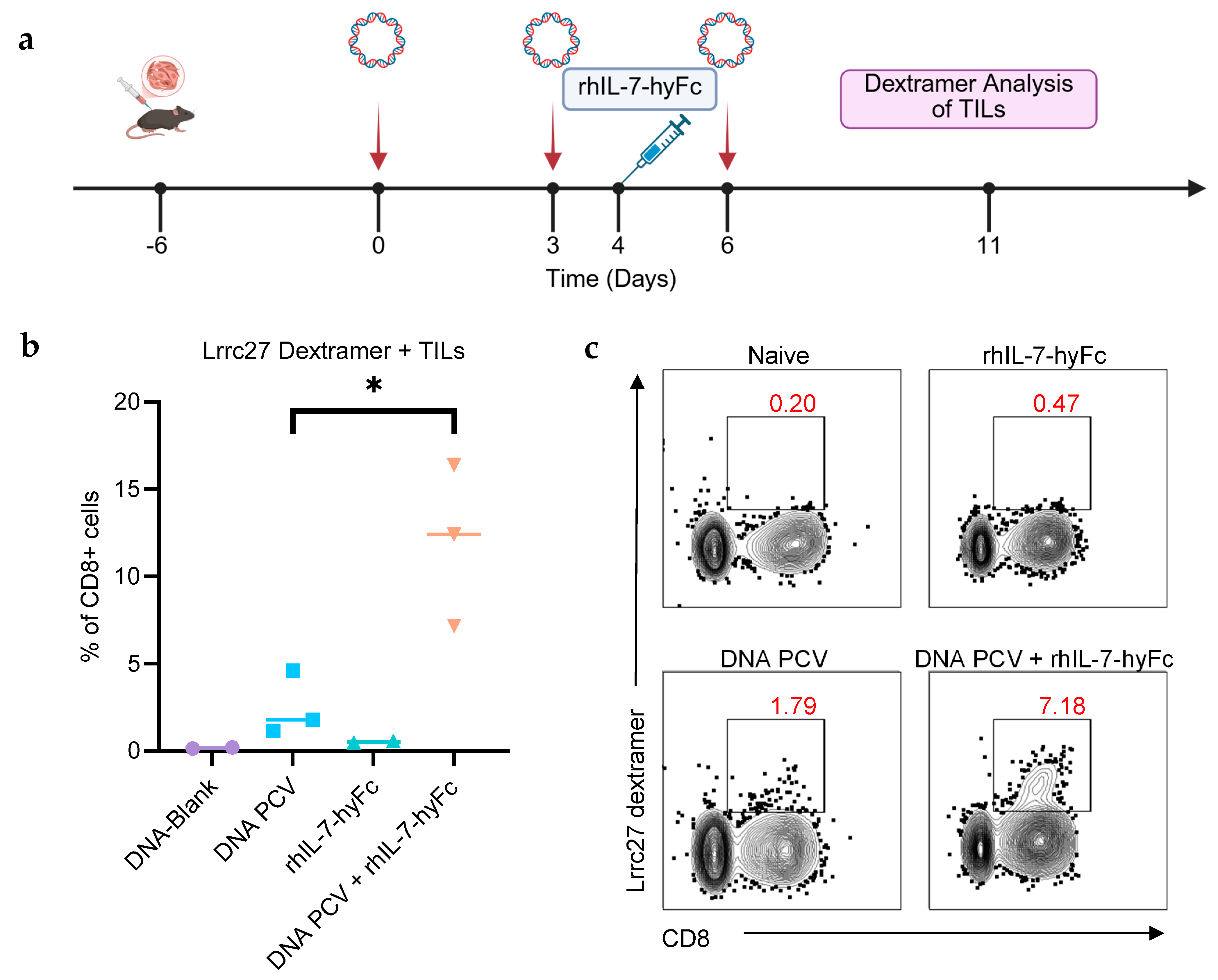
3.4. Combination of PCV and rhIL-7-hyFc Increases Neoantigen-Specific TILs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCV | Personalized Cancer Vaccine |
| IL-7 | Interleukin 7 |
| rhIL-7-hyFc | Recombinant Human Interleukin 7 Fused to an Antibody Fragment |
| TIL | Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocyte |
| GBM | Glioblastoma |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
| TCR | T cell Receptor |
References
- Liu, Z.; Lv, J.; Dang, Q.; Liu, L.; Weng, S.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Kong, Y.; Li, H.; Han, Y.; et al. Engineering neoantigen vaccines to improve cancer personalized immunotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5607–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pounraj, S.; Chen, S.; Ma, L.; Mazzieri, R.; Dolcetti, R.; Rehm, B.H. Targeting Tumor Heterogeneity with Neoantigen-Based Cancer Vaccines. Cancer Res. 2023, 84, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Hoang, M.H.; Schmidt, E.; Kiwala, S.; McMichael, J.; Skidmore, Z.L.; Fisk, B.; Song, J.J.; Hundal, J.; Mooney, T.; et al. pVACview: An interactive visualization tool for efficient neoantigen prioritization and selection. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londhe, V.Y.; Date, V. Personalized neoantigen vaccines: A glimmer of hope for glioblastoma. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2020, 19, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; You, J.; Hong, L.; Liu, W.; Guo, P.; Hao, X. Neoantigen cancer vaccines: A new star on the horizon. Cancer Biol. Med. 2023, 20230395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarayan, R.; Srinivasan, D.; Balakrishnan, R.; Kumar, A.; Usmani, S.S.; Srivastava, N. DNA Damage Response and Ne-oantigens: A Favorable Target for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Immunotherapy and Vaccine Development. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2024, 389, 104–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Goedegebuure, S.P.; Chen, M.Y.; Mishra, R.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Y.Y.; Singhal, K.; Li, L.; Gao, F.; Myers, N.B.; et al. Neoantigen DNA vaccines are safe, feasible, and induce neoantigen-specific immune responses in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundal, J.; Carreno, B.M.; Petti, A.A.; Linette, G.P.; Griffith, O.L.; Mardis, E.R.; Griffith, M. pVAC-Seq: A genome-guided in silico approach to identifying tumor neoantigens. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Arnaud, M.; Stevenson, B.J.; Michaux, J.; Benedetti, F.; Thevenet, J.; Bobisse, S.; Chiffelle, J.; Gehert, T.; Müller, M.; et al. A comprehensive proteogenomic pipeline for neoantigen discovery to advance personalized cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 43, 1360–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.A.; Moranzoni, G.; Chea, V.; McGregor, B.A.; Blass, E.; Tu, C.R.; Vanasse, A.P.; Forman, C.; Forman, J.; Afeyan, A.B.; et al. A neoantigen vaccine generates antitumour immunity in renal cell carcinoma. Nature 2025, 639, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethna, Z.; Guasp, P.; Reiche, C.; Milighetti, M.; Ceglia, N.; Patterson, E.; Lihm, J.; Payne, G.; Lyudovyk, O.; Rojas, L.A.; et al. RNA neoantigen vaccines prime long-lived CD8+ T cells in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2025, 639, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsikis, P.D.; Ishii, K.J.; Schliehe, C. Challenges in developing personalized neoantigen cancer vaccines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 24, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Su, X.; Qiu, L.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Wei, F.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, L.; Chen, G.; et al. Personalized neoantigen vaccine prevents postoperative recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with vascular invasion. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarchoan, M.; Gane, E.J.; Marron, T.U.; Perales-Linares, R.; Yan, J.; Cooch, N.; Shu, D.H.; Fertig, E.J.; Kagohara, L.T.; Bartha, G.; et al. Personalized neoantigen vaccine and pembrolizumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase 1/2 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xiao, H.; Wakefield, M.R.; Ding, V.A.; Bai, Q.; Fang, Y. The Role of IL-7 in Immunity and Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 963–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sportès, C.; Hakim, F.T.; Memon, S.A.; Zhang, H.; Chua, K.S.; Brown, M.R.; Fleisher, T.A.; Krumlauf, M.C.; Babb, R.R.; Chow, C.K.; et al. Administration of rhIL-7 in humans increases in vivo TCR repertoire diversity by preferential expansion of naive T cell subsets. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Han, S.; Ma, Z. Advances in IL-7 Research on Tumour Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tang, T.-X.; Deng, H.; Yang, X.-P.; Tang, Z.-H. Interleukin-7 Biology and Its Effects on Immune Cells: Mediator of Generation, Differentiation, Survival, and Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Kong, L.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Oh, S.; Jo, S.; Jang, I.; Kim, T.-D. The Role of IL-7 and IL-7R in Cancer Pathophysiology and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackall, C.L.; Fry, T.J.; Gress, R.E. Harnessing the biology of IL-7 for therapeutic application. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfarth, A.A.; Dhar, S.; Goon, J.B.; Ezeanya, U.I.; Ferrando-Martínez, S.; Lee, B.H. Advancements of Common Gamma-Chain Family Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy. Immune Netw. 2022, 22, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Jayasinghe, R.; Devenport, J.M.; Ritchey, J.K.; Rettig, M.P.; O’nEal, J.; Staser, K.W.; Kennerly, K.M.; Carter, A.J.; Gao, F.; et al. A long-acting interleukin-7, rhIL-7-hyFc, enhances CAR T cell expansion, persistence, and anti-tumor activity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campian, J.L.; Ghosh, S.; Kapoor, V.; Yan, R.; Thotala, S.; Jash, A.; Hu, T.; Mahadevan, A.; Rifai, K.; Page, L.; et al. Long-Acting Recombinant Human Interleukin-7, NT-I7, Increases Cytotoxic CD8 T Cells and Enhances Survival in Mouse Glioma Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswami, R.; Kask, A.S.; D’aMico, L.; Menon, M.P.; Lurain, K.; Yarchoan, R.; Ekwede, I.; Couey, P.; Burnham, E.; Angeldekao, A.; et al. Phase I study of efineptakin alfa (NT-I7) for the treatment of Kaposi sarcoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e010291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Naour, A.; Koffi, Y.; Diab, M.; Le Guennec, D.; Rougé, S.; Aldekwer, S.; Goncalves-Mendes, N.; Talvas, J.; Farges, M.-C.; Caldefie-Chezet, F.; et al. EO771, the first luminal B mammary cancer cell line from C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Kim, S.W.; Herndon, J.M.; Becker-Hapak, M.K.; Carreno, B.M.; Myers, N.B.; Sturmoski, M.A.; McLellan, M.D.; et al. Optimized polyepitope neoantigen DNA vaccines elicit neoantigen-specific immune responses in preclinical models and in clinical translation. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bins, A.D.; Jorritsma, A.; Wolkers, M.C.; Hung, C.-F.; Wu, T.-C.; Schumacher, T.N.M.; Haanen, J.B.A.G. A rapid and potent DNA vaccination strategy defined by in vivo monitoring of antigen expression. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Li, L.; McMurtrey, C.P.; Hildebrand, W.H.; Weidanz, J.A.; Gillanders, W.E.; Diamond, M.S.; Hansen, T.H. Single-Chain HLA-A2 MHC Trimers That Incorporate an Immundominant Peptide Elicit Protective T Cell Immunity against Lethal West Nile Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4423–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quah, B.J.; Parish, C.R. New and improved methods for measuring lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and in vivo using CFSE-like fluorescent dyes. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 379, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.-I.; Park, S.; Jeong, Y.L.; Kim, Y.-M.; Min, J.; Lee, C.; Choi, J.-A.; Choi, Y.H.; Kong, H.-J.; Choi, Y.; et al. Fc-fused IL-7 provides broad antiviral effects against respiratory virus infections through IL-17A-producing pulmonary innate-like T cells. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Im, S.-K.; Baek, S.; Ji, M.; Kim, M.; Lee, E.J.; Ji, S.T.; Ferrando-Martinez, S.; Wolfarth, A.; Lee, J.-Y.; et al. rhIL-7-hyFc and hIL-2/TCB2c combination promotes an immune-stimulatory tumor microenvironment that improves antitumor efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.M.; Kim, S.; Lee, M.A.; Byun, M.-S.; Choi, D.; Yang, S.H.; Woo, J.; Sung, Y.C.; Shin, E.-C.; Park, S.-H.; et al. GX-I7, a long-acting IL-7, safely and effectively increased peripheral CD8+/CD4+ T cells and TILs in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2025, 133, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leilei, Z.; Kewen, Z.; Biao, H.; Fang, H.; Yigang, W. The Role of Chemokine IL-7 in Tumor and Its Potential Antitumor Immunity. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2022, 42, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, M.; Calzascia, T.; Elford, A.R.; Shahinian, A.; Lin, A.E.; Dissanayake, D.; Dhanji, S.; Nguyen, L.T.; Gronski, M.A.; Morre, M.; et al. Adjuvant IL-7 antagonizes multiple cellular and molecular inhibitory networks to enhance immunotherapies. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wan, J.; He, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Fu, Z.F.; Zhao, L. IL-7 promotes mRNA vaccine-induced long-term immunity. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Heo, M.; Sung, Y.C.; Jeun, S. Compassionate use of recombinant human IL-7-hyFc as a salvage treatment for restoring lymphopenia in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 12, 6778–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.W.; Koh, J.-Y.; Choi, D.; Heo, M.; Chung, J.-Y.; Lee, B.H.; Yang, S.H.; Sung, Y.C.; Lee, H.; et al. A single administration of hIL-7-hyFc induces long-lasting T-cell expansion with maintained effector functions. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 6093–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liang, T.; Hutchins, L.E.; Wolfarth, A.A.; Ferrando-Martinez, S.; Lee, B.H.; Ho, M. rhIL-7-hyFc, a Long-Acting Inter-leukin-7, Improves Efficacy of CAR-T Cell Therapy in Solid Tumors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.M.; Bentzen, S.M.; Ahmad, H.; Pham, L.; Woodworth, G.F.; Mishra, M.V. Systematic review and pooled analysis of the impact of treatment-induced lymphopenia on survival of glioblastoma patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Dho, Y.-S.; Ock, C.-Y.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, S.-T.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, T.M.; Park, C.-K. Clinical observation of lymphopenia in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2019, 143, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afghahi, A.; Mathur, M.; Seto, T.; Desai, M.; Kenkare, P.; Horst, K.C.; Das, A.K.; Thompson, C.A.; Luft, H.S.; Yu, P.P.; et al. Lymphopenia after adjuvant radiotherapy (RT) to predict poor survival in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.D.; Mamdani, H.; Barve, M.A.; Johnson, M.L.; Murphy, J.A.; Trogun, L.; Ferrando-Martinez, S.; Lee, B.H.; Yang, S.H.; Chaney, M.F.; et al. A phase 2a study of NT-I7 (efineptakin alfa), a long-acting IL-7, and pembrolizumab to evaluate efficacy, including overall survival, in hard-to-treat gastrointestinal tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Luo, J.R.; Grote, C.; Nehring, L.; Katumba, R.; Etter, K.; Barozinsky, K.; Ferrando-Martinez, S.; Stermer, K.; Lee, B.H.; et al. CTIM-24. PHASE II TRIAL OF RHIL-7-HYFC IN PATIENTS WITH HIGH-GRADE GLIOMA DEMONSTRATED ACCEPTABLE SAFETY PROFILE AND REDUCED LYMPHOPENIA. Neuro-Oncology 2024, 26, viii90–viii91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, W.E.; Yu, H.; Dierksheide, J.; Pfeffer, K.; Bouchard, P.; Clark, R.; Durbin, J.; Baldwin, A.S.; Peschon, J.; Johnson, P.R.; et al. A fatal cytokine-induced systemic inflammatory response reveals a critical role for NK cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4943–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Kane, T.; Chen, I.; Supabphol, S.; Zhang, X.; Wolfarth, A.A.; Choi, D.; Li, L.; Goedegebuure, S.P.; Gillanders, W.E. Long-Acting Recombinant IL-7 (rhIL-7-hyFc) Enhances the Primary and Memory Neoantigen-Specific Immune Response to Breast Cancer Personalized Cancer Vaccines. Cancers 2025, 17, 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193177
Chen M, Kane T, Chen I, Supabphol S, Zhang X, Wolfarth AA, Choi D, Li L, Goedegebuure SP, Gillanders WE. Long-Acting Recombinant IL-7 (rhIL-7-hyFc) Enhances the Primary and Memory Neoantigen-Specific Immune Response to Breast Cancer Personalized Cancer Vaccines. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193177
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Michael, Thomas Kane, Ina Chen, Suangson Supabphol, Xiuli Zhang, Alexandra A. Wolfarth, Donghoon Choi, Lijin Li, S. Peter Goedegebuure, and William E. Gillanders. 2025. "Long-Acting Recombinant IL-7 (rhIL-7-hyFc) Enhances the Primary and Memory Neoantigen-Specific Immune Response to Breast Cancer Personalized Cancer Vaccines" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193177
APA StyleChen, M., Kane, T., Chen, I., Supabphol, S., Zhang, X., Wolfarth, A. A., Choi, D., Li, L., Goedegebuure, S. P., & Gillanders, W. E. (2025). Long-Acting Recombinant IL-7 (rhIL-7-hyFc) Enhances the Primary and Memory Neoantigen-Specific Immune Response to Breast Cancer Personalized Cancer Vaccines. Cancers, 17(19), 3177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193177





