Venetoclax–Rituximab and Emerging Treatment Strategies After c-BTKi Exposure in Relapsed/Refractory CLL: A Real-World Cohort and Literature Overview
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
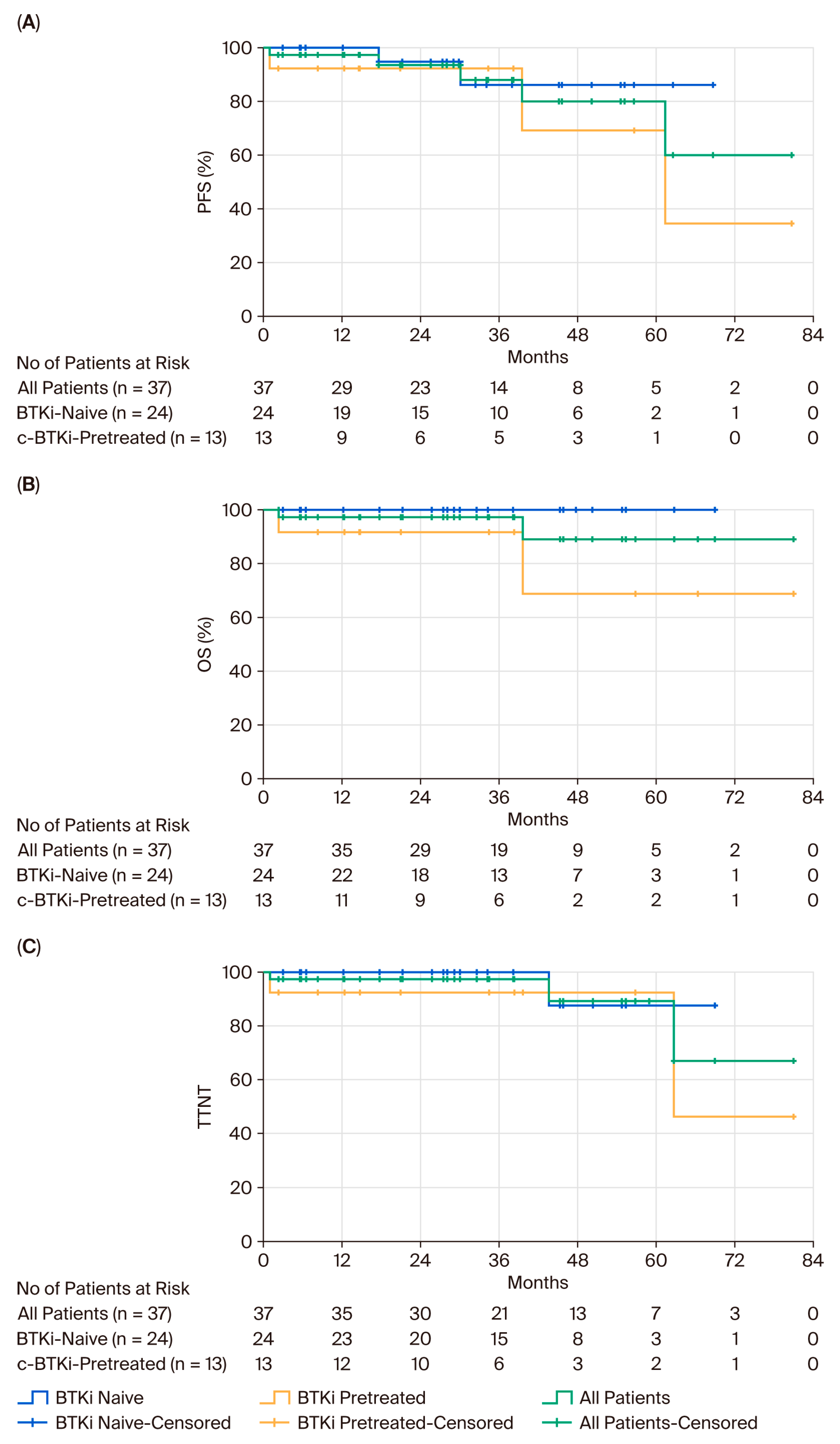
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scarfò, L.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Ghia, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 104, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Nadeu, F.; Colomer, D.; Campo, E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: From molecular pathogenesis to novel therapeutic strategies. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Barr, P.M.; Robak, T.; Owen, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Sarma, A.; Patten, P.E.; Grosicki, S.; McCarthy, H.; Offner, F.; et al. Final analysis of the RESONATE-2 study: Up to 10 years of follow-up of first-line ibrutinib treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma. Blood, 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Patel, K.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Hughes, M.; et al. Acalabrutinib-obinutuzumab improves survival vs chemoimmunotherapy in treatment-naive CLL in the 6-year follow-up of ELEVATE-TN. Blood 2025, 146, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, M.; Munir, T.; Robak, T.; Brown, J.R.; Kahl, B.S.; Ghia, P.; Giannopoulos, K.; Šimkovič, M.; Österborg, A.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Zanubrutinib Versus Bendamustine and Rituximab in Patients with Treatment-Naïve Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: Median 5-Year Follow-Up of SEQUOIA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Zhang, C.; Olivieri, S.; Chang, Y.M.; Fink, A.M.; Tausch, E.; Schneider, C.; Ritgen, M.; Kreuzer, K.-A.; et al. Venetoclax-obinutuzumab for previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 6-year results of the randomized phase 3 CLL14 study. Blood 2024, 144, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax–rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Wierda, W.; O’Brien, S. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukeia. The Lancet 2024, 404, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi-Sharifi, N.; Davids, M.S. Advances in the management of relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation. Hematol Oncol. 2025, 43, e70064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendrick, A.M. Real-World Evidence: An Additional Tool to Support Clinical Decision-Making. ISPOR. 2021. Available online: https://www.ispor.org/docs/default-source/strategic-initiatives/ispor-rwe-byline-article_10-25-21.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Booth, C.M.; Karim, S.; Mackillop, W.J. Real-world data: Towards achieving the achievable in cancer care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, H.G.; Bloechl-Daum, B.; Broich, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Oderkirk, J.; Rasi, G.; Santos Ivo, R.; Schuurman, A.; Senderovitz, T.; Slawomirski, L.; et al. Data Rich, Information Poor: Can We Use Electronic Health Records to Create a Learning Healthcare System for Pharmaceuticals? Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 105, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Fazi, C.; Agathangelidis, A.; Villamor, N.; Letestu, R.; Nomdedeu, J.; Palacio, C.; Stehlikova, O.; Kreuzer, K.-A.; Liptrot, S.; et al. A complementary role of multiparameter flow cytometry and high-throughput sequencing for minimal residual disease detection in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An European Research Initiative on CLL study. Leukemia 2016, 30, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0; NCI: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2017. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_8.5x11.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Venclyxto: Summary of Product Characteristics; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/venclyxto-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 29.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sachanas, S.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Angelopoulou, M.; Papageorgiou, S.; Spanoudakis, E.; Bouzani, M.; Dimou, M.; Panagiotidis, P. Greek Consensus on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Treatment. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2025, 17, e2025014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichhorst, B.; Ghia, P.; Niemann, C.U.; Kater, A.P.; Gregor, M.; Hallek, M.; Jerkeman, M.; Buske, C. ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline interim update on new targeted therapies in the first line and at relapse of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saburi, M.; Nishikawa, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kohno, K.; Sakata, M.; Okuhiro, K.; Nakayama, T.; Ohtsuka, E.; Ogata, M. Real-world outcomes of venetoclax and rituximab for chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma: A retrospective analysis of nine Japanese cases. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2024, 64, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Eyre, T.A.; Brown, J.R.; Lamanna, N.; Manzoor, B.S.; Coombs, C.C.; Tuncer, H.H.; Ujjani, C.; Leslie, L.A.; Roeker, L.E.; et al. Treatment effectiveness of venetoclax-based therapy after Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An international real-world study. Am. J. Hematol. 2024, 100, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, T.E.; Bennett, R.; Lin, V.S.; Whitechurch, A.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Marlton, P.; Shen, Y.; Mulligan, S.P.; Casan, J.; Blombery, P.; et al. Venetoclax-rituximab is active in patients with BTKi-exposed CLL, but durable treatment-free remissions are uncommon. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herishanu, Y.; Goldschmidt, N.; Itchaki, G.; Bronstein, Y.; Levi, I.; Aviv, A.; Fineman, R.; Dally, N.; Tadmor, T.; Ronson, A.; et al. P651: Real-world effectiveness of venetoclax-based regimens in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia in Israel: Update from the multicenter prospective REVEAL study. HemaSphere 2023, 7 (Suppl. 3), e4428024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrens, J.; Lettens, T.; Gillon, B.; De Bevere, M.; Poedts, L. Real-world treatment usage of venetoclax-rituximab in relapsed/refractory CLL patients in Belgium: Results of the AREVEDECY study. In Proceedings of the ISPOR Europe 2024 Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 18–21 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Schwaner, I.; Hebart, H.F.; Losem, C.; Wolff, T.; Lehmann, C.; Huelsenbeck, J.; Schmidt, B.; Pichler, P.; Rossi, D. Clinical outcomes of CLL patients treated with venetoclax under real-world conditions in Austria, Germany, and Switzerland after treatment with ibrutinib. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Jaypirca (Pirtobrutinib): Summary of Product Characteristics. EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2024. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Woyach, J.A.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Roeker, L.E.; Patel, K.; Eyre, T.A.; Munir, T.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Lamanna, N.; Tam, C.S.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in post-cBTKi CLL/SLL: ~30 months follow-up and subgroup analysis with/without prior BCL2i from the phase 1/2 BRUIN study. In Proceedings of the 65th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sharman, J.P.; Munir, T.; Grosicki, S.; Roeker, L.E.; Burke, J.M.; Chen, C.I.; Grzasko, N.; Follows, G.; Mátrai, Z.; Sanna, A.; et al. Phase III trial of pirtobrutinib versus idelalisib/rituximab or bendamustine/rituximab in covalent Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor–pretreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (BRUIN CLL-321). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 2538–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.C.; Harrup, R.A.; Coombs, C.C.; Roeker, L.E.; Pu, J.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Barr, P.M.; Allan, J.N.; Šimkovič, M.; Leslie, L.; et al. Venetoclax retreatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia after a previous venetoclax-based regimen. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 4553–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kater, A.P.; Harrup, R.A.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.F.; Owen, C.J.; Assouline, S.; Lamanna, N.; Robak, T.; de la Serna, J.; Jaeger, U.; et al. The MURANO study: Final analysis and retreatment/crossover substudy results of VenR for patients with relapsed/refractory CLL. Blood 2025, 145, 2733–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.C.; Bhat, S.A.; Jurczak, W.; Patel, K.; Shah, N.N.; Woyach, J.A.; Coombs, C.C.; Eyre, T.A.; Danecki, M.; Dlugosz-Danecka, M.; et al. Outcomes of therapies following discontinuation of non-covalent Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation: Results from an international, multicenter study. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Male | 27 (73%) |
|---|---|
| Median age (range) | 67 (44–89) |
| Median prior trm lines (range) | 1 (1–4) |
| Pts with ≥2 prior trm lines | 11 (29.7%) |
| Time since last trm, mo (range) | 27 (0–128) |
| Prior CIT | 30 (81.1%) |
| Prior BTKi | 13 (35.1%) * |
| Reason for BTKi discontinuation | |
| disease progression | 8 (61.5%) |
| adverse event | 5 (38.5%) |
| IGHV status, unmutated (n = 23) | 12 (52.1%) |
| TP53 aberrations [del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations] (n = 26) | 4 (15.8%) |
| Complex karyotype (≥5 CA) (n = 29) | 4 (13.8%) |
| Study | n | TRM | Age, Median (Range) | Median FU, mo (Range) | Prior Trm Lines, Median (Range) | Prior c-BTKi, n (%) | Reason for c-BTKi Discontinuation, (%) | ORR, % | CR Rate, % | PFS | TTNT | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current cohort | 37 # | VR | 67 (44–89) # | 29.1 (2.3–80.9) # | 1 (1–4) # | 13 (35.1) | PD: 8 (61.5) AE: 5 (38) | 87.5 | 62.5 | 92.3% @30 mo | 92.3% @30 mo | 91.7% @30 mo |
| CORE study [22] | 64 | VR | NR | NR | NR | 64 (100) | PD: 43 AE: 37 | 71.4 | NR | 39.5 mo (median) | 37.4 mo (median) | NR |
| Australian RWD [23] | 32 | VR | 70.5 (49–84) | 20.6 (<1–58.6) | 2 (1–5) | 32 (100) | PD: 25 (78) AE: 7 (22) | 81 | 19 | 25.9 mo (median) | NR | 46.1 mo (median) |
| Austrian–German–Swiss RWD [26] | 28 | VR | 59 (NR) | 23 (NR) | 3 (1–10) | 28 (100) | PD: 10 (35.7) AE: 14 (50) | 100 | 54 | 72.9% @ 24 mo | NR | 76.6% @ 24 mo |
| Phase 1/2 BRUIN study [27] | 154 | Pirto | 69 (36–87) | 27.5 (22.2–31.6) | 4 (1–11) | 154 (100) | PD *: 76.9% AE *: 23.1% | 83.1 | 5 | 23 mo (median) | NR | NE |
| BRUIN 321 Phase 3 study [28] | 59 | Pirto | 67 (42–90) | NR | 3 (1–13) | 59 (100) | PD *: 71% AE *: 17% | NR | NR | NR | 29.5 mo | NR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimou, M.; Fioretzaki, R.; Zerzi, C.; Konstantinou, E.; Asimakopoulos, J.V.; Arapaki, M.; Piperidou, A.; Machairas, A.; Kopsaftopoulou, A.; Liaskas, A.; et al. Venetoclax–Rituximab and Emerging Treatment Strategies After c-BTKi Exposure in Relapsed/Refractory CLL: A Real-World Cohort and Literature Overview. Cancers 2025, 17, 3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193159
Dimou M, Fioretzaki R, Zerzi C, Konstantinou E, Asimakopoulos JV, Arapaki M, Piperidou A, Machairas A, Kopsaftopoulou A, Liaskas A, et al. Venetoclax–Rituximab and Emerging Treatment Strategies After c-BTKi Exposure in Relapsed/Refractory CLL: A Real-World Cohort and Literature Overview. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193159
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimou, Maria, Rodanthi Fioretzaki, Calliope Zerzi, Eliana Konstantinou, John V. Asimakopoulos, Maria Arapaki, Alexia Piperidou, Alexandros Machairas, Anastasia Kopsaftopoulou, Athanasios Liaskas, and et al. 2025. "Venetoclax–Rituximab and Emerging Treatment Strategies After c-BTKi Exposure in Relapsed/Refractory CLL: A Real-World Cohort and Literature Overview" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193159
APA StyleDimou, M., Fioretzaki, R., Zerzi, C., Konstantinou, E., Asimakopoulos, J. V., Arapaki, M., Piperidou, A., Machairas, A., Kopsaftopoulou, A., Liaskas, A., Bitsani, A., Belia, M., Panitsas, F., Benekou, A., Petsa, P., Plata, E., Tsaftaridis, P., Siakantaris, M., Vassilakopoulos, T. P., ... Angelopoulou, M. K. (2025). Venetoclax–Rituximab and Emerging Treatment Strategies After c-BTKi Exposure in Relapsed/Refractory CLL: A Real-World Cohort and Literature Overview. Cancers, 17(19), 3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193159






