Investigating the Relationship Between Long Non-Coding RNAs and miR-200 Family Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
2.2. lncRNA Search
2.3. Database Search for miRNA-lncRNA Interactions
2.4. RNA Isolation from FFPE Tissue Samples
2.5. Analysis of Expression of miR-200 Family
2.5.1. Reverse Transcription (RT) of miRNAs
2.5.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.6. Analysis of Expression of lncRNAs
2.6.1. Reverse Transcription (RT) for lncRNAs
2.6.2. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR) and Probes
2.7. Expression of lncRNAs and miR-200 Family in KIRC (ccRCC) from RNA Sequencing Datasets Using the Cancer Genome Atlas
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
3.2. Indentification of Target lncRNAs
3.2.1. Identified lncRNAs with Potentially Regulatory Function Toward miR-200 Family
3.2.2. miRNA-lncRNA Interactions Identified from Cross-Database Search
3.3. Expression of miR-200 Family, Their Regulatory lncRNAs, and Correlation Between Them in ccRCC and sRCC
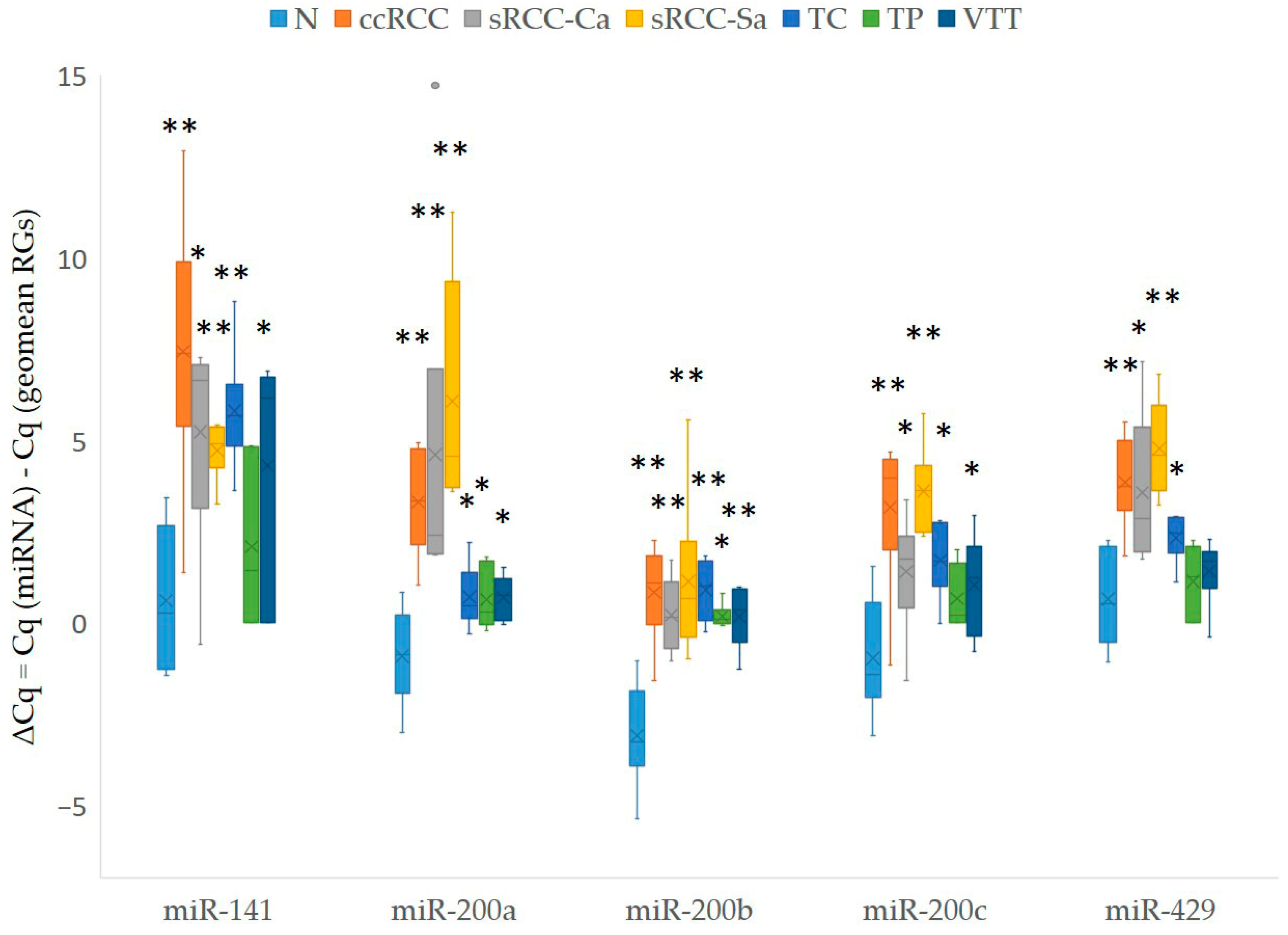
3.3.1. Expression of miR-200 Family in Our Cohort of Patients
3.3.2. Expression of lncRNAs in Our Cohort of Patients
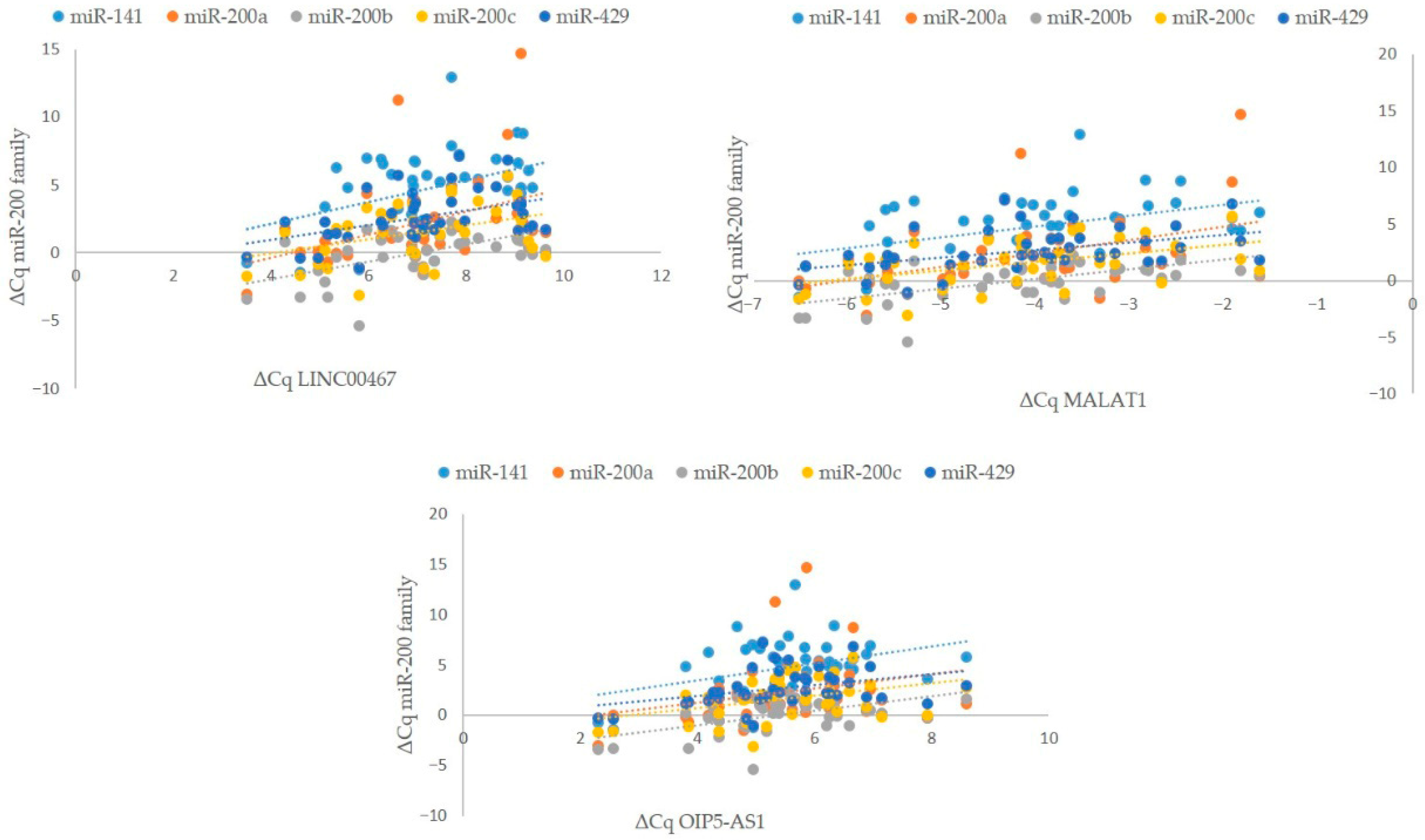
3.3.3. Correlation Between Expression of miR-200 Family and Expression of Potentially Regulatory lncRNAs
3.4. Expression of miR-200 Family, Their Potentially Regulatory lncRNAs, and Correlation Between Them in KIRC from TCGA
3.4.1. Expression of miR-200 Family in KIRC Samples from TCGA
3.4.2. Expression of lncRNAs in KIRC Samples from TCGA
3.4.3. Correlation Between miR-200 Family and Potentially Regulatory lncRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ccRCC | clear cell RCC |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| FPKM-UQ | fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads—upper quartile |
| GOI | gene of interest |
| HIF | hypoxia-inducible factor |
| ISUP | International Society of Urologic Pathologists |
| KIRC | kidney renal clear cell carcinoma |
| LINC00467 | large intergenic non-coding RNA 00467 |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| MALAT1 | metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| OIP5-AS1 | OPA-interacting protein 5 antisense transcript 1 |
| Qpcr | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| RG | reference gene |
| RPM | reads per million |
| RT | reverse transcriptase/transcription |
| sRCC | sarcomatoid RCC |
| TC | tumor center |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TNM | tumor node metastasis |
| TP | tumor periphery |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| VTT | venous tumor thrombus |
References
- Diamantopoulos, M.A.; Tsiakanikas, P.; Scorilas, A. Non-coding RNAs: The riddle of the transcriptome and their perspectives in cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassler, M.R.; Egger, G. Epigenomics of cancer—Emerging new concepts. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Mattick, J.S. Structure and function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kikyo, N. Strategies to identify long noncoding RNAs involved in gene regulation. Cell Biosci. 2012, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Kotake, Y.; Niida, H.; Ohhata, T. Cell cycle regulation by long non-coding RNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4785–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klicka, K.; Grzywa, T.M.; Mielniczuk, A.; Klinke, A.; Włodarski, P.K. The role of miR-200 family in the regulation of hallmarks of cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 965231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, V.; Burk, U.C.; Bajdak-Rusinek, K. Revisiting the miR-200 Family: A Clan of Five Siblings with Essential Roles in Development and Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Takenaka, K.; Xu, S.-M.; Cheng, Y.; Janitz, M. Recent advances in investigation of circRNA/lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks through RNA sequencing data analysis. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2025, 24, elaf005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhan, S.; Hauptman, N. Metastatic EMT Phenotype Is Governed by MicroRNA-200-Mediated Competing Endogenous RNA Networks. Cells 2021, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, X.; Zhu, X.W.; Yang, D.C.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, T. Long non-coding RNAs in Oral squamous cell carcinoma: Biologic function, mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, M.D.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA and cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, V.N. Processing of intronic microRNAs. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Fu, X.; Han, W. Long Noncoding RNAs: Insights from Biological Features and Functions to Diseases. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33, 517–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, E.A.; Brown, C.J.; Lam, W.L. The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetyan, A.R.; Buiting, C.; Kuiper, R.A.; Coolen, M.W. Regulatory Roles for Long ncRNA and mRNA. Cancers 2013, 5, 462–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanduri, C. Long noncoding RNAs: Lessons from genomic imprinting—PubMed. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1859, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cugura, T.; Bostjancic, E.; Uhan, S.; Hauptman, N.; Jeruc, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition associated markers in sarcomatoid transformation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 138, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukavina, L.; Bensalah, K.; Bray, F.; Carlo, M.; Challacombe, B.; Karam, J.A.; Kassouf, W.; Mitchell, T.; Montironi, R.; O’Brien, T.; et al. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma: 2022 Update. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, R.Y.; Haake, S.M. Hypoxia-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 487, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myszczyszyn, A.; Czarnecka, A.M.; Matak, D.; Szymanski, L.; Lian, F.; Kornakiewicz, A.; Bartnik, E.; Kukwa, W.; Kieda, C.; Szczylik, C. The Role of Hypoxia and Cancer Stem Cells in Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 919–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, D.A.; Drula, R.; Ott, L.; Fabris, L.; Slaby, O.; Calin, G.A.; Pichler, M. Circulating Non-coding RNAs in Renal Cell Carcinoma—Pathogenesis and Potential Implications as Clinical Biomarkers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 17, 1032. [Google Scholar]
- Moch, H.; Amin, M.B.; Berney, D.M.; Comperat, E.M.; Gill, A.J.; Hartmann, A.; Menon, S.; Raspollini, M.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. The 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs—Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Tang, Q.; He, J.; Li, L.; Yang, N.; Yu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Cui, T.; et al. RNAInter v4.0: RNA interactome repository with redefined confidence scoring system and improved accessibility. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D326–D332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Tastsoglou, S.; Skoufos, G.; Karavangeli, A.; Pierros, V.; Zacharopoulou, E.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-LncBase v3: Indexing experimentally supported miRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D101–D110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotschofsky, Z.; Meyer, H.A.; Jung, M.; Fendler, A.; Wagner, I.; Stephan, C.; Busch, J.; Erbersdobler, A.; Disch, A.C.; Mollenkopf, H.J.; et al. Reference genes for the relative quantification of microRNAs in renal cell carcinomas and their metastases. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardon, E.; Donada, M.; Bonin, S.; Dotti, I.; Stanta, G. Higher random oligo concentration improves reverse transcription yield of cDNA from bioptic tissues and quantitative RT-PCR reliability. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 87, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenn, S.T.; Jones, C.A.; Liang, P.; Kaushik, D.; Gross, K.W.; Kim, H.L. Expression profiling of archival renal tumors by quantitative PCR to validate prognostic markers. Biotechniques 2007, 43, 633–642, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Qin, T.; Yu, J.; Giordano, T.J.; Sartor, M.A.; Koenig, R.J. Novel role of ASH1L histone methyltransferase in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 8834–8845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, B.; Lu, H.; Ma, H. Long Non-Coding RNA CCAT2 Promotes the Development of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inhibiting miR-200b to Upregulate the IGF2BP2/TK1 Axis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 680642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayeldeen, G.; Shaker, O.G.; Amer, E.; Zaafan, M.A.; Herzalla, M.R.; Keshk, M.A.; Abdelhamid, A.M. The Impact of lncRNA-GAS5/miRNA-200/ACE2 Molecular Pathway on the Severity of COVID-19. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amicone, L.; Marchetti, A.; Cicchini, C. The lncRNA HOTAIR: A pleiotropic regulator of epithelial cell plasticity. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiyomaru, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Saini, S.; Majid, S.; Deng, G.; Shahryari, V.; Chang, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is targeted and regulated by miR-141 in human cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12550–12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossaghzadeh, F.; Hajjari, M.; Sheikhi, A.; Salahshourifar, I.; Irani, S. HOTAIR Induces the Downregulation of miR-200 Family Members in Gastric Cancer Cell Lines. Iran. Biomed. J. 2022, 26, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, W.; Wang, J.; Wei, Q. A LINC00341-mediated regulatory pathway supports chondrocyte survival and may prevent osteoarthritis progression. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 10812–10820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Z.; Jia, J.; Chen, C.H. lncRNA-KCNQ1OT1: A Potential Target in Exosomes Derived from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells for the Treatment of Osteoporosis. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 7690006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Yu, M.; He, X.; Wen, L.; Bu, Z.; Feng, J. KCNQ1OT1 promotes autophagy by regulating miR-200a/FOXO3/ATG7 pathway in cerebral ischemic stroke. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Xu, E.; Zhu, T.; Cai, X. KCNQ1OT1 mediates keratinocyte migration to promote skin wound healing through the miR-200b-3p/SERP1 axis. Burns 2023, 49, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Duan, H.; An, D.; Yi, X.; Li, J.; Liao, C. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA LINC00467 inhibits glioma cell progression via modulation of E2F3 targeted by miR-200a. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 2040–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yi, B.; Zhou, W.; Gong, W.; Li, G.; Yu, S. Linc00475 promotes the progression of glioma by regulating the miR-141-3p/YAP1 axis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 25, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Q.; Lu, J.; Zuo, L.; Liu, M. Linc00641 promotes the progression of gastric carcinoma by modulating the miR-429/Notch-1 axis. Aging 2021, 13, 8497–8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Zang, Y. LINC00667 Promotes Progression of Esophageal Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-200b-3p/SLC2A3 Axis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 2936–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Xu, S.; Song, H.; Zhang, W.; Sun, N. LINC00667 promotes Wilms’ tumor metastasis and stemness by sponging miR-200b/c/429 family to regulate IKK-β. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kang, J.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Pan, G.; Mao, A.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, J.; Ding, J.; Li, H. Docetaxel-resistant triple-negative breast cancer cell-derived exosomal lncRNA LINC00667 reduces the chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to docetaxel via targeting miR-200b-3p/Bcl-2 axis—PubMed. Eur. J. Histochem. 2022, 66, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Su, Z.; Kang, P.; Jiang, X.; Cui, Y. Yin Yang 1-induced LINC00667 up-regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 to promote proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells by sponging miR-200c-3p. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, M.; Zheng, L.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Yuan, C.; Ma, P.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, F.; Tang, W.; Sheng, M. ln RNA LINC01234 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression through regulating the miR-429/SYNJ1 axis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 11399–11412. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Shi, L. Long non-coding RNA LUCAT1 modulates methotrexate resistance in osteosarcoma via miR-200c/ABCB1 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; She, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Qin, S. LncRNA MAGI2-AS3 Is Regulated by BRD4 and Promotes Gastric Cancer Progression via Maintaining ZEB1 Overexpression by Sponging miR-141/200a. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.T.; Wan, C.H.; Guo, Q.H.; Yang, S.J.; Wu, J.D.; Cai, J. Long Noncoding RNA Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 (MALAT1) Promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression via Sponging miRNA-429. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Tang, K.; Liu, P.; Chen, K.; Hu, J.; Zeng, J.; Xiao, W.; Yu, G.; Yao, W.; Zhou, H.; et al. LncRNA MALAT1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate ZEB2 expression by sponging miR-200s in clear cell kidney carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 38005–38015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Lung Cancer Proliferation and Gefitinib Resistance by Acting as a miR-200a Sponge. Arch. Bronconeumol. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 55, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Ma, M.; Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Zuo, X.; Gu, X.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y. LncRNA MEG3 regulates breast cancer proliferation and apoptosis through miR-141-3p/RBMS3 axis. Genomics 2021, 113, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, M.; Lin, M.; Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, N.; Huang, J. Long non-coding RNA MIAT promotes gastric cancer growth and metastasis through regulation of miR-141/DDX5 pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Zhu, J.; Fang, C.L.; Jin, H.; Zhan, D.P.; Huang, J. Down-regulation of MIAT suppresses osteosarcoma progression by acting as a ceRNA for miR-141-3p to regulate SIX1-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Su, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Su, X. Emerging impact of the long noncoding RNA MIR22HG on proliferation and apoptosis in multiple human cancers. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; An, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, W. LncRNA MIR22HG negatively regulates miR-141-3p to enhance DAPK1 expression and inhibits endometrial carcinoma cells proliferation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, P.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Yang, K. Long non-coding RNA MIR22HG impedes the progression of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma via targeting miR-141-3p/PTEN/AKT axis. Endokrynol. Pol. 2025, 76, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ye, K.; Wang, D. Upregulation of HTRA1 mediated by the lncRNA NEAT1/miR-141-3p axis contributes to endometriosis development through activating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptotic cell death and cellular inflammation. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2023, 59, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, G.; Wang, X. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 transported by extracellular vesicles contributes to breast cancer development by sponging microRNA-141-3p and regulating KLF12. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, H.Y.; Yao, Z.X.; Zheng, Z.; Meng-Yan, S.; Wu, K. NEAT1/miR-200b-3p/SMAD2 axis promotes progression of melanoma. Aging 2020, 12, 22759–22775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L.; Li, R.; Xiao, D. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 suppresses lung adenocarcinoma progression and modulates macrophage polarization through the miR-429/DOCK4 regulatory axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1569644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.; Shao, Y. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 promotes the malignancy of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via regulating miR-429/FOXD1/ERK pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yuan, W.; Huang, C.; Luo, Q.; Xiao, R.; Chen, Z.H. LncRNA PCAT19 induced by SP1 and acted as oncogene in gastric cancer competitively binding to miR429 and upregulating DHX9. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Luo, H.; Deng, Z. PCAT19: The role in cancer pathogenesis and beyond. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1435717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.S.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, H.-L.; Li, Q.-P.; Miao, L. Long noncoding RNA SNHG6 mainly functions as a competing endogenous RNA in human tumors. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liang, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Su, L.; Kang, X. lncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression by modulating the miR-200c-5p/collagen type XI alpha1 chain pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3677–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xia, L.; Tan, X.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, W.; Tan, B.; Yu, X.; Fang, W.; Yang, Z. Molecular mechanism of lncRNA SNHG12 in immune escape of non-small cell lung cancer through the HuR/PD-L1/USP8 axis. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J. LncRNA SNHG15 contributes to proliferation, invasion and autophagy in osteosarcoma cells by sponging miR-141. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Wang, S.; Wen, X.; Han, X.R.; Wang, Y.J.; Shen, M.; Fan, S.H.; Zhang, Z.F.; Shan, Q.; Li, M.Q.; et al. LncRNA SNHG15 acts as a ceRNA to regulate YAP1-Hippo signaling pathway by sponging miR-200a-3p in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Tan, L.; Fu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wen, L.; Deng, Y.; Liu, K. LncRNA SNHG15 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-141-3p. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 19775–19783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y. Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer via sponging miR-200a-3p. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Zhou, R.; Fan, X.G. The long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 modulates HCC cell proliferation through miR-200a-dependent HMGB1/RAGE regulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Xu, F.; Zhang, D.; Yi, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, E. TP73-AS1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation through miR-200a-mediated TFAM inhibition. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Lu, J.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Li, X.; Lu, Y. LncRNA TP73-AS1 enhances the malignant properties of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by increasing MMP14 expression through miRNA -200a sponging. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 3654–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Li, F. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cervical cancer progression by regulating the miR-138-5p-SIRT1 axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, C.; Hou, L.; Wu, Y. Silencing of the lncRNA TUG1 attenuates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular epithelial cells by sponging miR-141-3p via regulating beta-catenin. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2020, 319, F1125–F1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Liao, W.; Li, E.; Wu, L. TUG1 promotes the expression of IFITM3 in hepatocellular carcinoma by competitively binding to miR-29a. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 6905–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Li, X. LncRNA TUG1 promoted viability and associated with gemcitabine resistant in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 137, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Han, W.; Ruan, A.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, P.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. miR-200c Targets CDK2 and Suppresses Tumorigenesis in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhu, X.; Chen, F.; Huang, C.; Ai, K.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X. LncRNA XIST/miR-200c regulates the stemness properties and tumourigenicity of human bladder cancer stem cell-like cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, T.; Yu, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L. LncRNA XIST accelerates cervical cancer progression via upregulating Fus through competitively binding with miR-200a. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wan, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, G.; Wang, S.; Su, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Lei, Z.; et al. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes TGF-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating miR-367/141-ZEB2 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 418, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-G.; Xu, Q. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-200b-3p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 9857–9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.J.; Fiechter, C.; Burton, J.; Hallion, J.; Paas, M.; Patel, A.; Patel, A.; Rochet, A.; Scheurlen, K.; Gardner, S.; et al. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 is a major regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through miR-200/ZEB1/E-cadherin, vimentin signaling in colon adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.S. MicroRNA function: Multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA 2005, 11, 1753–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamore, P.D.; Haley, B. Ribo-gnome: The big world of small RNAs. Science 2005, 309, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, S.; He, J. The Mechanism of Long Non-coding RNA in Cancer Radioresistance/Radiosensitivity: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 879704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooten, S.; Smith, K.N. Long non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 (Cyrano): A context-specific regulator of normal and disease processes. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Dashti, S.; Farsi, M.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M. A review on the role of oncogenic lncRNA OIP5-AS1 in human malignancies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cai, X.; Cai, Y.; Chang, Y. lncRNA OIP5-AS1 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Invasion of Endometrial Cancer by Regulating PTEN/AKT via Sponging miR-200c-3p. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 4861749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, H. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 predicts poor prognosis and regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in bladder cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 7499–7505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hou, J.; Ping, J.; Wen, D.; He, J. Opa interacting protein 5 acts as an oncogene in bladder cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 2221–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Pang, S.; Wang, F.P.; Li, X.Y.; Zou, Q. Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 exhibits oncogenic activity in bladder cancer through miR-217 and MTDH. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandi, F.; Taheri, F.; Kiani, A.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Expression analysis of OIP5-AS1 in bladder tissues. Genit. Mol. Res. 2018, 18, 260–263. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.X. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via binding to miR-30c-5p. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjazi, A.; Jasim, S.A.; Altalbawy, F.M.A.; Kaur, H.; Hamzah, H.F.; Kaur, I.; Deorari, M.; Kumar, A.; Elawady, A.; Fenjan, M.N. Relationship between lncRNA MALAT1 and Chemo-radiotherapy Resistance of Cancer Cells: Uncovered Truths. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 1613–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q. Regulatory Networks of LncRNA MALAT-1 in Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 10181–10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Wang, K.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z. LncRNA MALAT1 contributes to non-small cell lung cancer progression via modulating miR-200a-3p/programmed death-ligand 1 axis. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 2058738419859699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, R.; Xiong, H.; Qiu, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Disrupting MALAT1/miR-200c sponge decreases invasion and migration in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; Zou, H.; Li, B. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 knockdown inhibits progression of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma by regulating miR-200a-3p/FOXA1. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.B.; Chen, F.; Bai, X.F. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth Under Hypoxia via Sponging MicroRNA-200a. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Wen, G.; Ren, Y. miRNA-205-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating VEGFA and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in renal carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapinski, O.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs and human disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.E. Functional aspects of animal microRNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.; Guigo, R.; Johnson, R. The Long Non-Coding RNAs: A New (P)layer in the “Dark Matter”. Front. Genet. 2011, 2, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.S.; Krishna, B.; Chirala, R.; Amato, R.J.; Truong, L.D. Kidney-specific cadherin, a specific marker for the distal portion of the nephron and related renal neoplasms. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, E.D.; Zuk, A. Transformations between epithelium and mesenchyme: Normal, pathological, and experimentally induced. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1995, 26, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Nasrollahzadeh, D.; Egevad, L.; Banks, R.E.; Vasudev, N.; Holcatova, I.; Povysil, C.; Foretova, L.; Janout, V.; Mates, D.; et al. Morphological findings in frozen non-neoplastic kidney tissues of patients with kidney cancer from large-scale multicentric studies on renal cancer. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinnider, B.F.; Folpe, A.L.; Hennigar, R.A.; Lim, S.D.; Cohen, C.; Tamboli, P.; Young, A.; de Peralta-Venturina, M.; Amin, M.B. Distribution of cytokeratins and vimentin in adult renal neoplasms and normal renal tissue: Potential utility of a cytokeratin antibody panel in the differential diagnosis of renal tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenye, T. Do results obtained with RNA-sequencing require independent verification? Biofilm 2021, 3, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
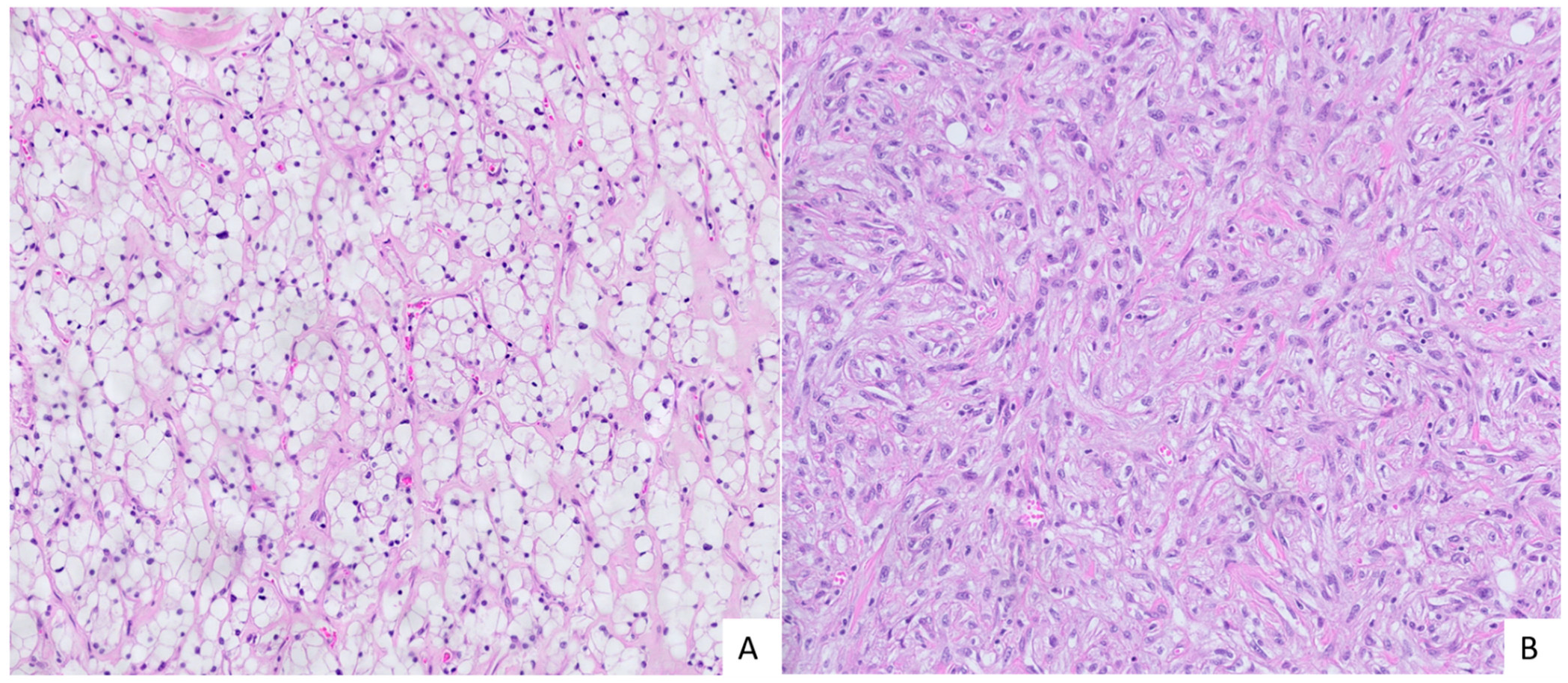




| Group | Age (Mean ± SD) | Male/Female | Tumor Size (Mean) | Nuclear Grade | Tissue Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early ccRCC | 62.7 ± 4.6 | 4:3 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 2 | Non-Tumorous Kidney (n = 3) |
| Carcinoma (n = 6) | |||||
| Advanced † ccRCC | 64.6 ± 8.9 | 10:0 | 6.3 ± 2.2 | 2 (n = 2) | Non-Tumorous Kidney (n = 3) |
| Carcinoma–Central Part (n = 6) | |||||
| 3 (n = 7) | Carcinoma–At Hilum (n = 6) | ||||
| Venous Tumor Thrombus (n = 6) | |||||
| sRCC § | 61.1 ± 13.4 | 6:2 | 8.9 ± 3.2 | 4 | Carcinomatous Component (n = 6) |
| Sarcomatous Component (n = 6) |
| lncRNA | Target miRNA | Associated Disease | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCAT1 | miR-200b | Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma | [33] |
| CCAT2 | miR-200b | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | [34] |
| GAS5 | miR-200 family | COVID-19 | [35] |
| HOTAIR | miR-141, miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-200c | RCC Cell Lines, Gastric Carcinoma Cell Line, Ovarian Carcinoma | [36,37,38] |
| LINC00341 | miR-141 | Osteoarthritis | [39] |
| KCNQ1OT1 | miR-141/-200a/b | Osteoporosis, Cerebral Ischemic Stroke, Skin Wound Healing | [40,41,42] |
| LINC00467 | miR-200a | Glioma Cell Line | [43] |
| LINC00475 | miR-141 | Glioma | [44] |
| LINC00641 | miR-429 | Gastric Cancer | [45] |
| LINC00667 | miR-200b/c/429 | Wilms Tumor, Esophageal Carcinoma, Breast Carcinoma, Cholangiocarcinoma | [46,47,48,49] |
| LINC01234 | miR-429 | Breast Carcinoma | [50] |
| LUCAT1 | miR-200c | Osteosarcoma | [51] |
| MAGI2-AS3 | miR-141/200a | Gastric Carcinoma | [52] |
| MALAT1 | miR-200 family | RCC, Lung Carcinoma | [53,54,55] |
| MEG3 | miR-141, miR-200a/c | Breast Carcinoma, Lung Carcinoma Cell Line | [56] |
| MIAT | miR-141 | Gastric Carcinoma, Osteosarcoma | [57,58] |
| MIR22HG | miR-141 | Endometrial Carcinoma, Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma | [59,60,61] |
| NEAT1 | miR-141, miR-200b | Endometriosis, Breast Carcinoma, Melanoma | [62,63,64] |
| OIP5-AS1 | miR-429, miR-200c | Lung Adenocarcinoma, Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma, Endometrial Carcinoma | [65,66] |
| PCAT19 | miR-429 | Gastric Carcinoma, Lung Adenocarcinoma | [67,68] |
| SNHG6 | miR-141, miR-429 | Osteosarcoma, Wilms Tumor | [69] |
| SNHG12 | miR-200c, miR-429 | Renal Cell Carcinoma, Lung Adenocarcinoma | [70,71] |
| SNHG15 | miR-141, miR-200a | Osteosarcoma, Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma | [72,73,74] |
| SNHG16 | miR-200a | Colorectal Carcinoma | [75] |
| TP73-AS1 | miR-141, miR-200a | Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma, Breast Carcinoma | [76,77,78] |
| TUG1 | miR-138, miR-141 | Renal Interstitial Fibrosis Cervical Carcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Pancreatic Carcinoma | [79,80,81,82] |
| XIST | miR-141, miR-200a, miR-200b, miR-200c, miR-429 | Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Bladder Carcinoma, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Cervical Carcinoma | [83,84,85,86,87] |
| ZFAS1 | miR-200b, miR-200c | Colorectal Carcinoma | [88] |
| Database | miR-200a | miR-200b | miR-200c | miR-141 | miR-429 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIANA-lncBase v3 | 178 | 140 | 204 | 229 | 174 |
| ENCORI | 26 | 23 | 24 | 26 | 24 |
| RNA Interactome | 116 | 123 | 118 | 120 | 131 |
| miR-200a | miR-200b | miR-200c | miR-141 | miR-429 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MALAT1 | MALAT1 | MALAT1 | MALAT1 | MALAT1 |
| SNHG16 | OIP5-AS1 | OIP5-AS1 | SNHG16 | OIP5-AS1 |
| XIST | XIST | XIST | XIST |
| DIANA-lncBase v3 | ENCORI | RNA Interactome |
|---|---|---|
| AC010342.1 | AL049840.5 | AQP4-AS1 |
| AL118506.1 | KCNQ1OT1 | ASTN2-AS1 |
| AP000926.1 | MALAT1 | ATP2B1-AS1 |
| GAS5 | NEAT1 | ATXN8OS |
| MALAT1 | OIP5-AS1 | C5orf56 |
| NAP1L1P3 | XIST | DRAIC |
| NEAT1 | H19 | |
| OIP5-AS1 | HAND2-AS1 | |
| PVT1 | LINC00341 | |
| RPL23AP73 | LINC00461 | |
| SNHG15 | LINC00667 | |
| TDGP1 | LINC01140 | |
| XIST | LINC01312 | |
| XLOC_006069 | LINC02120 | |
| XLOC_008185 | LOC256880 | |
| LOC285074 | ||
| LOC401021 | ||
| MALAT1 | ||
| MSC-AS1 | ||
| PART1 | ||
| TTTY4B | ||
| ZEB1-AS1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čugura, T.; Hauptman, N.; Jeruc, J.; Boštjančič, E. Investigating the Relationship Between Long Non-Coding RNAs and miR-200 Family Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193123
Čugura T, Hauptman N, Jeruc J, Boštjančič E. Investigating the Relationship Between Long Non-Coding RNAs and miR-200 Family Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193123
Chicago/Turabian StyleČugura, Tanja, Nina Hauptman, Jera Jeruc, and Emanuela Boštjančič. 2025. "Investigating the Relationship Between Long Non-Coding RNAs and miR-200 Family Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193123
APA StyleČugura, T., Hauptman, N., Jeruc, J., & Boštjančič, E. (2025). Investigating the Relationship Between Long Non-Coding RNAs and miR-200 Family Expression in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(19), 3123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193123







