Diagnostic Accuracy of Ex Vivo Confocal Microscopy for Surgical Margin Assessment of High-Risk Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Material
2.3. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
2.4. EVCM- and Conventional Histopathology-Based PDEMA Workflow
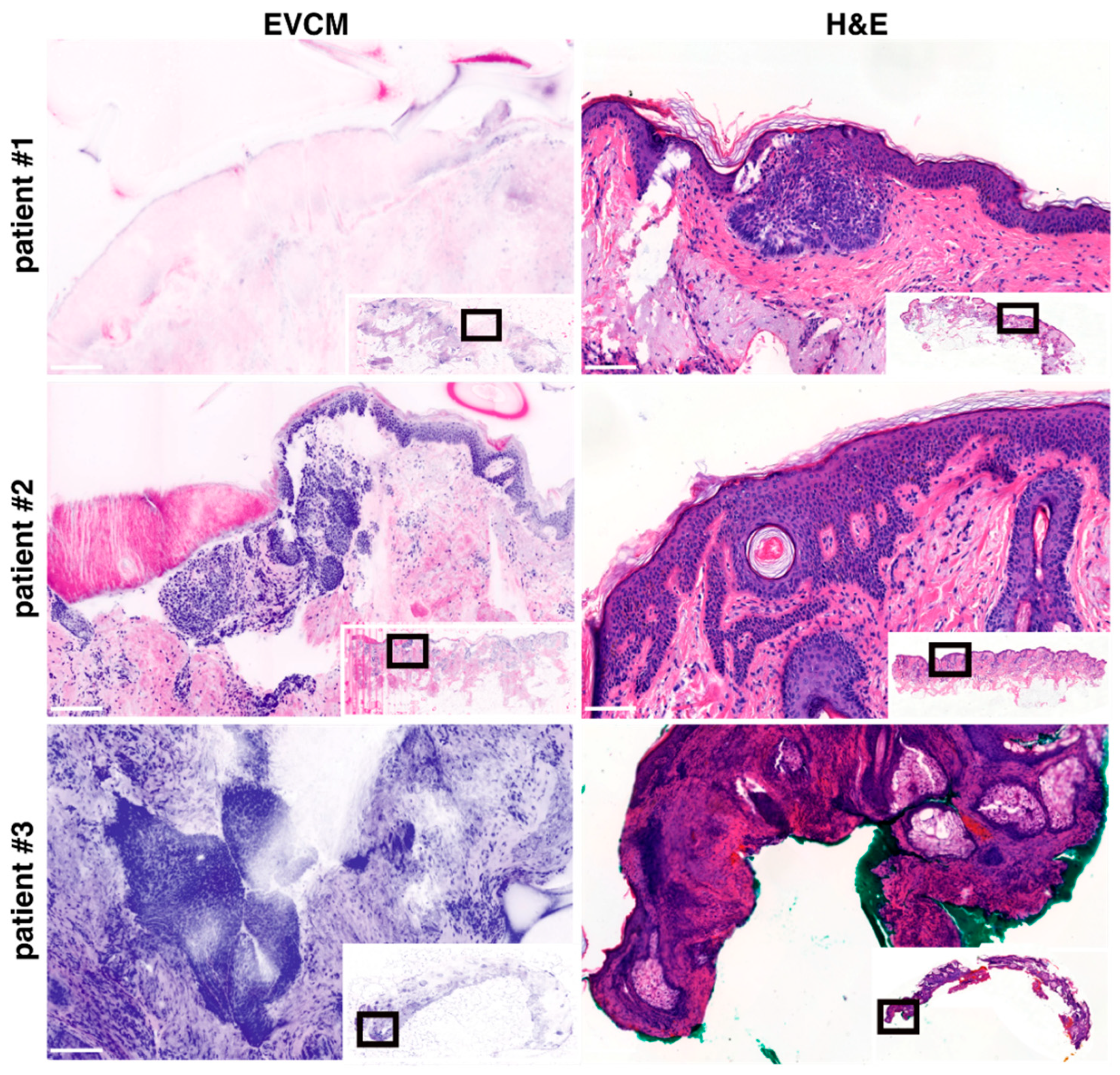
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCC | Basal cell carcinoma |
| PDEMA | Peripheral and deep en-face margin assessment |
| EVCM | Ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Peris, K.; Fargnoli, M.C.; Kaufmann, R.; Arenberger, P.; Bastholt, L.; Seguin, N.B.; Bataille, V.; Brochez, L.; Del Marmol, V.; Dummer, R.; et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for diagnosis and treatment of basal cell carcinoma—Update 2023. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 192, 113254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dika, E.; Scarfì, F.; Ferracin, M.; Broseghini, E.; Marcelli, E.; Bortolani, B.; Campione, E.; Riefolo, M.; Ricci, C.; Lambertini, M. Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. IJMS 2020, 21, 5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuninger, H.; Dietz, K. Prediction of Subclinical Tumor Infiltration in Basal Cell Carcinoma. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1991, 17, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, N.W.J.; Kuijpers, D.I.M.; Nelemans, P.; Ostertag, J.U.; Verhaegh, M.E.J.M.; Krekels, G.A.M.; Neumann, H.A.M. Mohs’ micrographic surgery for treatment of basal cell carcinoma of the face--results of a retrospective study and review of the literature. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 151, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delft, L.C.J.; Nelemans, P.J.; Loo, E.; Abdul Hamid, M.; Kelleners-Smeets, N.W.J. The illusion of conventional histological resection margin control. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 1240–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, P.N.; Lange, E.P.; Luna, N.M.; Miot, H.A.; Abbade, L.P.F. Efficacy of micrographic surgery versus conventional excision in reducing recurrence for basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosterd, K.; Krekels, G.A.; Nieman, F.H.; Ostertag, J.U.; Essers, B.A.; Dirksen, C.D.; Steijlen, P.M.; Vermeulen, A.; Neumann, H.A.M.; Kelleners-Smeets, N.W. Surgical excision versus Mohs’ micrographic surgery for primary and recurrent basal-cell carcinoma of the face: A prospective randomised controlled trial with 5-years’ follow-up. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvehy, J.; Pérez-Anker, J.; Toll, A.; Pigem, R.; Garcia, A.; Alos, L.L.; Puig, S. Ex vivo confocal microscopy: Revolution in fast pathology in dermatology. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, V.Q.; Dwyer, P.J.; Nehal, K.S.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Menaker, G.M.; Charles, C.; Jiang, S.B. Use of Ex Vivo Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy during Mohs Surgery for Nonmelanoma Skin Cancers. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, E.W.; Lewin, J.M.; Stevenson, M.L.; Meehan, S.A.; Carucci, J.A.; Gareau, D.S. Use of Digitally Stained Multimodal Confocal Mosaic Images to Screen for Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, M.; Gerger, A.; Koller, S.; Weger, W.; Langsenlehner, U.; Krippl, P.; Kerl, H.; Samonigg, H.; Smolle, J. The use of confocal laser-scanning microscopy in microsurgery for invasive squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, D.; Krammer, S.; Bachmann, M.R.; Mathemeier, L.; Ruzicka, T.; Bagci, I.S.; Von Braunmühl, T. Ex vivo confocal microscopy features of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, A.; Cinotti, E.; Habougit, C.; Labeille, B.; Rubegni, P.; Perrot, J. Ex vivo confocal microscopy for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Ski. Res. Technol. 2019, 25, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karen, J.K.; Gareau, D.S.; Dusza, S.W.; Tudisco, M.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Nehal, K.S. Detection of basal cell carcinomas in Mohs excisions with fluorescence confocal mosaicing microscopy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 160, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, B.; Abeytunge, S.; Seltzer, E.; Rajadhyaksha, M.; Nehal, K. Detection of skin cancer margins in Mohs excisions with high-speed strip mosaicing confocal microscopy: A feasibility study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennàssar, A.; Vilata, A.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J. Ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy for fast evaluation of tumour margins during Mohs surgery. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 170, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinasse, M.; Cinotti, E.; Grivet, D.; Labeille, B.; Prade, V.; Douchet, C.; Cambazard, F.; Thuret, G.; Gain, P.; Perrot, J.L. ‘En face’ ex vivo reflectance confocal microscopy to help the surgery of basal cell carcinoma of the eyelid. Clin. Exper. Ophthalmol. 2017, 45, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, C.; Pampena, R.; Bombonato, C.; Gardini, S.; Piana, S.; Mirra, M.; Raucci, M.; Kyrgidis, A.; Pellacani, G.; Ragazzi, M. Diagnostic accuracy of ex vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy in Mohs surgery of basal cell carcinomas: A prospective study on 753 margins. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, N.; Schubert, M.; Metzler, G.; Geppert, J.-P.; Moehrle, M. Diagnostic accuracy of a new ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscope compared to H&E-stained paraffin slides for micrographic surgery of basal cell carcinoma. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, L.; Kuonen, F. Ex vivo confocal microscopy for surgical margin assessment: A histology-compared study on 109 specimens. Ski. Health Dis. 2022, 2, e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Anker, J.; Ribero, S.; Yélamos, O.; García-Herrera, A.; Alos, L.; Alejo, B.; Combalia, M.; Moreno-Ramírez, D.; Malvehy, J.; Puig, S. Basal cell carcinoma characterization using fusion ex vivo confocal microscopy: A promising change in conventional skin histopathology. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 182, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razi, S.; Ouellette, S.; Khan, S.; Oh, K.S.; Truong, T.M.; Rao, B.K. Role of VivaScope 2500 ex vivo confocal microscopy in skin pathology: Advantages, limitations, and future prospects. Ski. Res. Technol. 2023, 29, e13388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thissen, M.R.T.M.; Neumann, M.H.A.; Schouten, L.J. A Systematic Review of Treatment Modalities for Primary Basal Cell Carcinomas. Arch. Dermatol. 1999, 135, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijałkowska, M.; Koziej, M.; Antoszewski, B. Detailed head localization and incidence of skin cancers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanadan, A.; Abdollahi, P.; Rabet, M.; Naraghi, Z.; Abbasi, M.A.; Moslehi, H.; Abbasi, A. Different Anatomical Distribution of Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes in Iranian Population: Association between Site and Subtype. Ann. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, M.C.; Lee, E.; Hibler, B.P.; Barker, C.A.; Mori, S.; Cordova, M.; Nehal, K.S.; Rossi, A.M. Basal cell carcinoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibovitch, I.; Huilgol, S.C.; Selva, D.; Richards, S.; Paver, R. Basal cell carcinoma treated with Mohs surgery in Australia II. Outcome at 5-year follow-up. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Anker, J.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J. A fast and effective option for tissue flattening: Optimizing time and efficacy in ex vivo confocal microscopy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, e157–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Anker, J.; Toll, A.; Puig, S.; Malvehy, J. Six steps to reach optimal scanning in ex vivo confocal microscopy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forchhammer, S.; Grunewald, S.; Möhrle, M.; Metzler, G.; Eigentler, T.; Münch, A.-K.; Ogrzewalla, H. Diagnosis of Basal Cell Carcinoma with Ex-vivo Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy in a Real-life Setting. Acta Dermato-Venereol. 2023, 103, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Puram, S.V.; Silverman, D.A.; Old, M.O.; Rocco, J.W.; Kang, S.Y. Margin Analysis in Head and Neck Cancer: State of the Art and Future Directions. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4070–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shavlokhova, V.; Vollmer, M.; Gholam, P.; Saravi, B.; Vollmer, A.; Hoffmann, J.; Engel, M.; Freudlsperger, C. Deep Learning on Basal Cell Carcinoma In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy Data. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| All | Peripheral Margins | Deep Margins | |
|---|---|---|---|
| True positive (n) | 15 | 11 | 4 |
| False positive (n) | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| True negative (n) | 153 | 108 | 45 |
| False negative (n) | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 93.8 (95% CI: 71.7–98.9) | 91.7 (95% CI: 61.5–98.7) | 100.0 (95% CI: 51.0–100.0) |
| Specificity (%) | 98.7 (95% CI: 95.2–99.7) | 98.2 (95% CI: 93.5–99.6) | 100.0 (95% CI: 92.1–100.0) |
| Positive predictive value (%) | 88.2 (95% CI: 63.6–97.4) | 84.6 (95% CI: 54.6–96.9) | 100.0 (95% CI: 51.0–100.0) |
| Negative predictive value (%) | 99.4 (95% CI: 96.4–99.9) | 99.1 (95% CI: 94.9–99.9) | 100.0 (95% CI: 92.1–100.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stramke, W.; Tonellotto, L.; Guenova, E.; Kuonen, F. Diagnostic Accuracy of Ex Vivo Confocal Microscopy for Surgical Margin Assessment of High-Risk Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183019
Stramke W, Tonellotto L, Guenova E, Kuonen F. Diagnostic Accuracy of Ex Vivo Confocal Microscopy for Surgical Margin Assessment of High-Risk Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183019
Chicago/Turabian StyleStramke, William, Luca Tonellotto, Emmanuella Guenova, and François Kuonen. 2025. "Diagnostic Accuracy of Ex Vivo Confocal Microscopy for Surgical Margin Assessment of High-Risk Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 18: 3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183019
APA StyleStramke, W., Tonellotto, L., Guenova, E., & Kuonen, F. (2025). Diagnostic Accuracy of Ex Vivo Confocal Microscopy for Surgical Margin Assessment of High-Risk Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(18), 3019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183019







