Evaluation of Mithramycin in Combination with Chemotherapeutic Agents Against Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Chemicals, Reagents, and Antibodies
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Flow Cytometry: PE Annexin-V Staining
2.5. Western Blot: C-PARP Expression
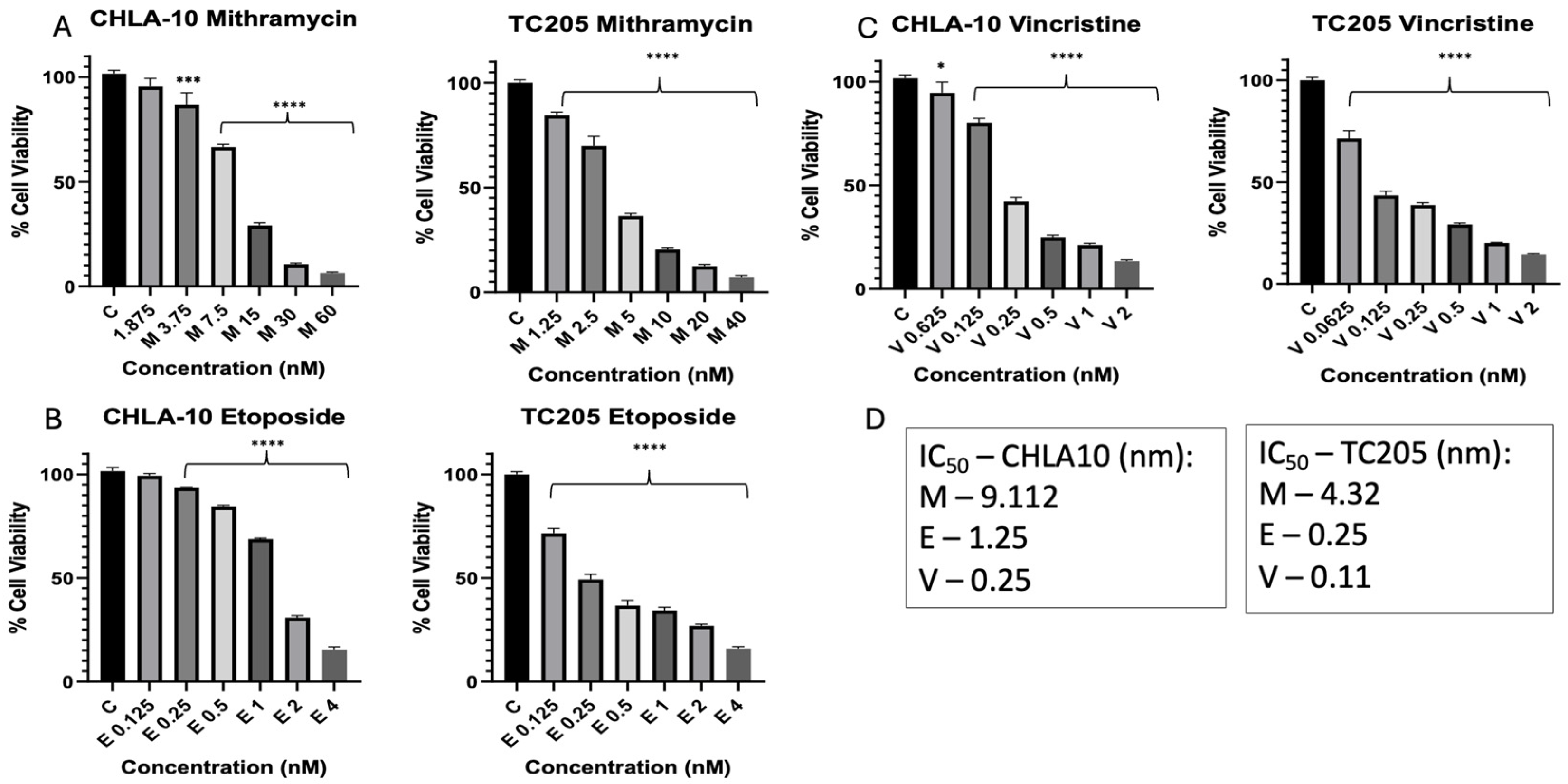
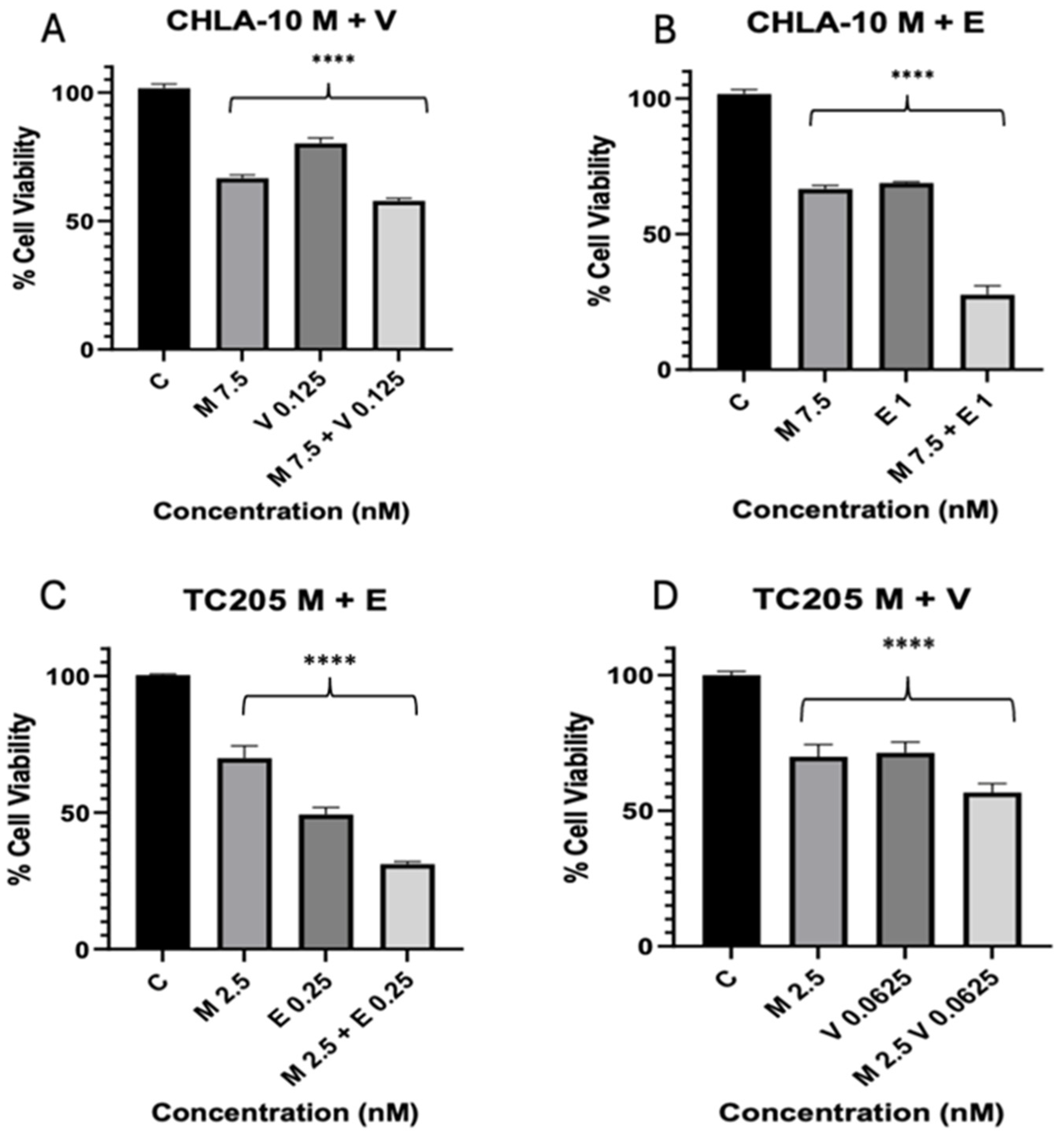
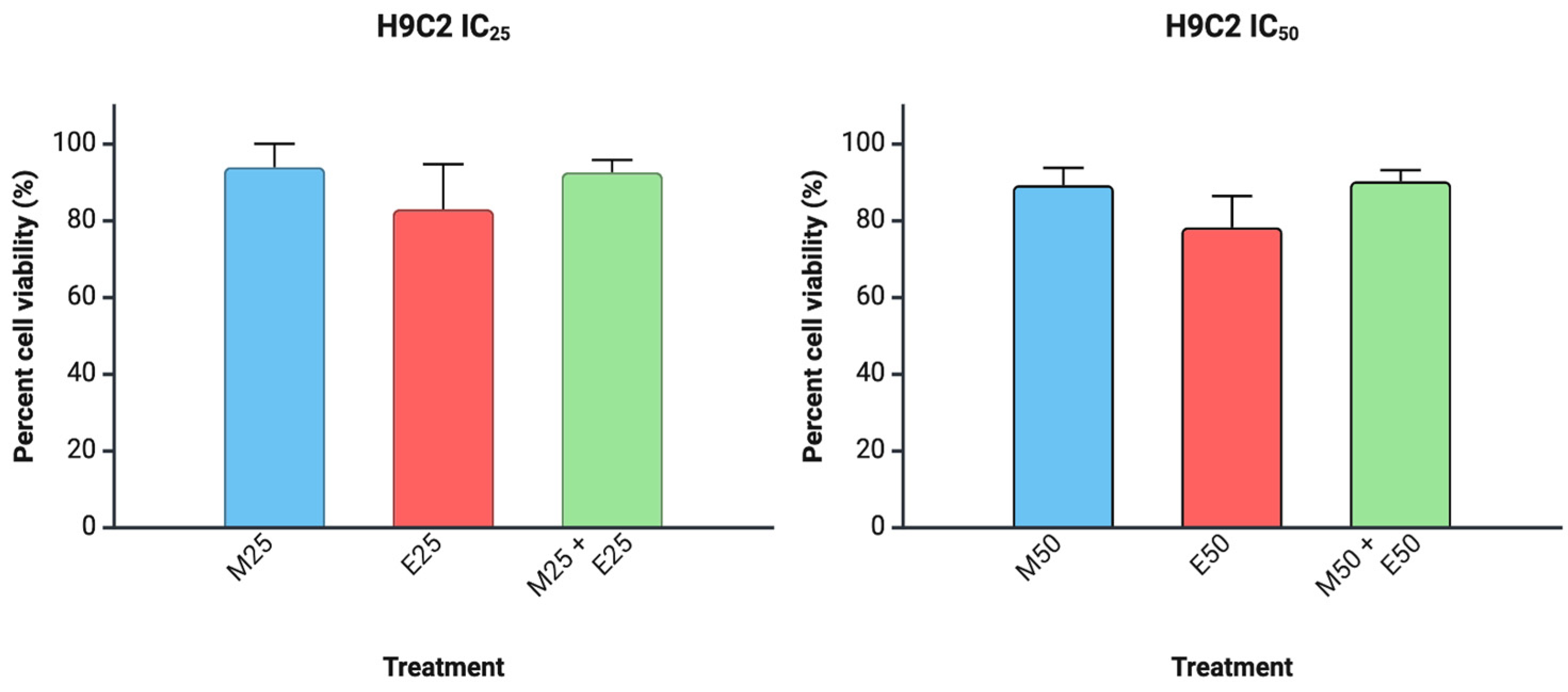
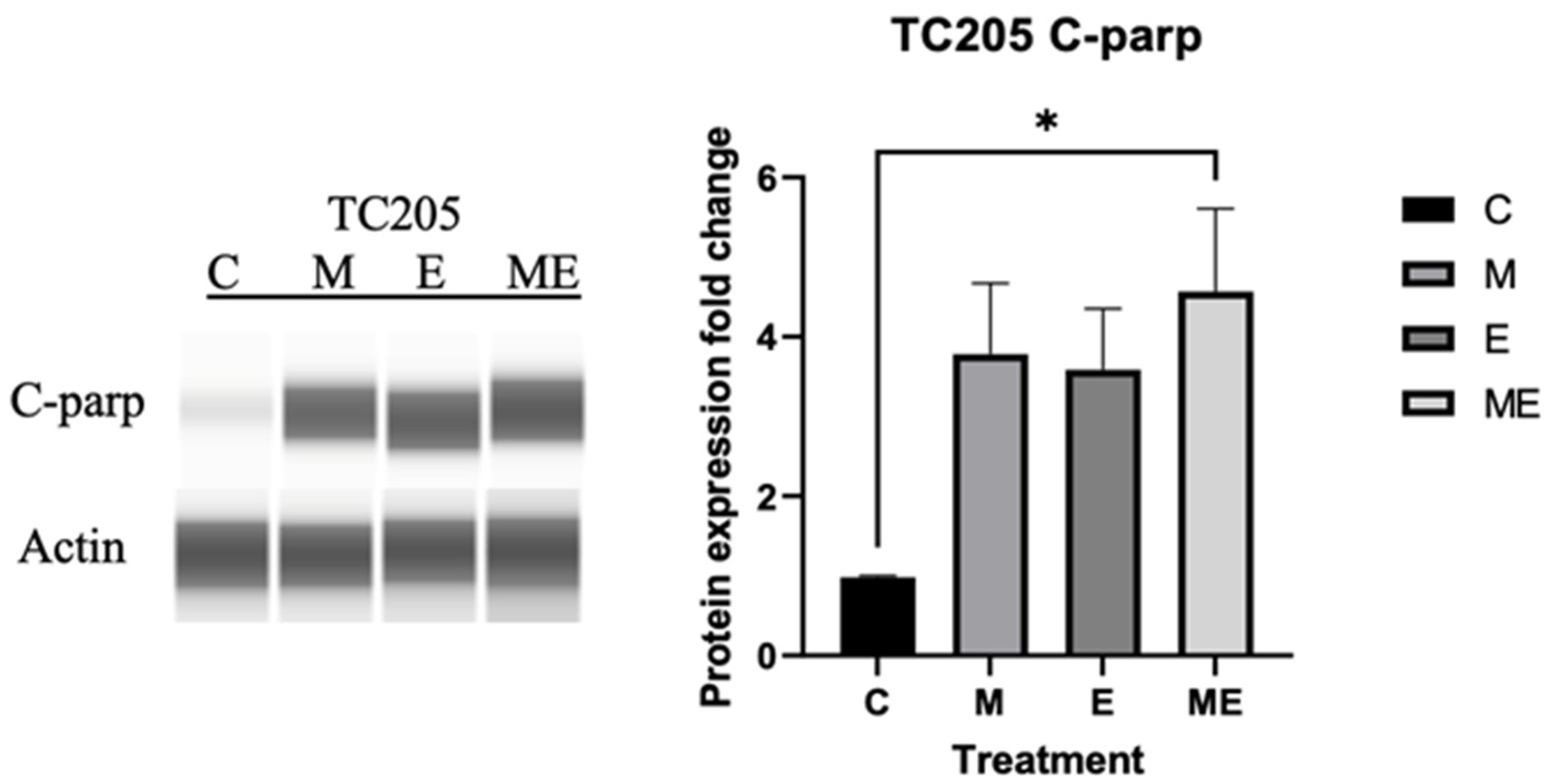
3. Results
3.1. Dose Response and Determination of IC50 Values
3.2. Combination Index
3.3. Mithramycin and Eto Effects on Apoptotic Cell Population
3.4. Cleaved PARP Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| c-PARP | Cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ED | Effective dose |
| ED50 | Median effective dose |
| ES | Ewing sarcoma |
| Eto | Etoposide |
| IC50 | Inhibitory concentration 50 |
| M | Molar |
| Mit | Mithramycin |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PNET | Primitive neuroectodermal tumor |
| VCR | Vincristine |
References
- Eaton, B.R.; Claude, L.; Indelicato, D.J.; Vatner, R.; Yeh, B.; Schwarz, R.; Laack, N. Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68 (Suppl. S2), e28355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.-Y.K.; Gardner, J.M.; Lucas, D.R.; McHugh, J.B.; Patel, R.M. Ewing sarcoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 31, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.D.; Lessnick, S.L. A transcriptional profiling meta-analysis reveals a core EWS-FLI gene expression signature. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohar, P.J.; Glod, J.; Peer, C.J.; Sissung, T.M.; Arnaldez, F.I.; Long, L.; Figg, W.D.; Whitcomb, P.; Helman, L.J.; Widemann, B.C. A phase I/II trial and pharmacokinetic study of mithramycin in children and adults with refractory Ewing sarcoma and EWS–FLI1 fusion transcript. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesla, A.C.; Papakonstantinou, A.; Tsagkozis, P. Current Status of Management and Outcome for Patients with Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Kridis, W.; Toumi, N.; Chaari, H.; Khanfir, A.; Ayadi, K.; Keskes, H.; Boudawara, T.; Daoud, J.; Frikha, M. A Review of Ewing Sarcoma Treatment: Is it Still a Subject of Debate? Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2017, 12, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miser, J.S.; Krailo, M.D.; Tarbell, N.J.; Link, M.P.; Fryer, C.J.; Pritchard, D.J.; Gebhardt, M.C.; Dickman, P.S.; Perlman, E.J.; Meyers, P.A.; et al. Treatment of metastatic Ewing’s sarcoma or primitive neuroectodermal tumor of bone: Evaluation of combination ifosfamide and etoposide—A Children’s Cancer Group and Pediatric Oncology Group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2873–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorthi, A.; Romero, J.C.; Loranc, E.; Cao, L.; Lawrence, L.A.; Goodale, E.; Iniguez, A.B.; Bernard, X.; Masamsetti, V.P.; Roston, S.; et al. EWS–FLI1 increases transcription to cause R-loops and block BRCA1 repair in Ewing sarcoma. Nature 2018, 555, 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahim, M.; Baker, C.H.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Safe, S. Tolfenamic acid and pancreatic cancer growth, angiogenesis, and Sp protein degradation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.; Pathi, S.; Jutooru, I.; Sreevalsan, S.; Basha, R.; Abdelrahim, M.; Samudio, I.; Safe, S. Metformin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell and tumor growth and downregulates Sp transcription factors. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2870–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Sankpal, U.T.; Hurtado, M.; Bowman, W.P.; Murray, J.; Borgmann, K.; Ghorpade, A.; Sutphin, R.; Eslin, D.; Basha, R. Combination of clotam and vincristine enhances anti-proliferative effect in medulloblastoma cells. Gene 2019, 705, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.-Y.; Pei, L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Dou, H.; Shu, G.; Yuan, Z.-X.; Lin, J.; Peng, G.; Zhang, W.; et al. Isobologram Analysis: A Comprehensive Review of Methodology and Current Research. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapuis, J.-C.; Keng, P.C.; Siemann, D.W. Activity of etoposide (VP-16) and teniposide (VM-26) in exponential and plateau phase human tumor cell cultures. Anticancer Drugs 1992, 3, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, R.; Cotterill, S.J.; Stevens, M.C. Risk factors for nephrotoxicity after ifosfamide treatment in children: A UKCCSG Late Effects Group study. United Kingdom Children’s Cancer Study Group. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Scobioala, S.; Eich, H.T. Risk stratification of pulmonary toxicities in the combination of whole lung irradiation and high-dose chemotherapy for Ewing sarcoma patients with lung metastases: A review. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilari, I.; De Ioris, M.A.; Milano, G.M.; Pessolano, R.; De Lurentis, C.; De Sio, L.; Fidani, P.; Jenkner, A.; Cozza, R. Toxicity of high-dose chemotherapy with etoposide, thiotepa and CY in treating poor-prognosis Ewing’s sarcoma family tumors: The experience of the Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010, 45, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Subbiah, V.; Anderson, P.; Lazar, A.J.; Burdett, E.; Raymond, K.; Ludwig, J.A. Ewing’s sarcoma: Standard and experimental treatment options. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2009, 10, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Mellado-Lagarde, M.M.; Blankenship, K.; Ganguly, D.; Twarog, N.R.; Bianski, B.; Kieffer, M.; Atkinson, S.; Sheppard, H.; Gartrell, J.; et al. The Combination of PARP and Topoisomerase 1 Inhibitors Improves Radiation Therapy for Ewing Sarcoma. Cancer Sci. 2025, 116, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Yang, L.; Shao, R.; Xu, T.; Zhang, L. RNA-binding protein gene NOP58 exhibits crucial prognostic and therapeutic value in Ewing sarcoma. Hereditas 2025, 162, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiba, H.; Aso, A.; Righi, A.; Gambarotti, M.; Cammelli, S.; Spinnato, P.; Traversari, M.; Atherley, A.; Solou, K.; Kimura, H.; et al. Comparison of histological response across patients with Ewing sarcoma treated with preoperative chemotherapy with or without preoperative radiotherapy. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2025, 35, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.S.; Desai, R.T.; Pandya, A.J.; Kothari, N.R.; Patel, R.; Chorawala, M.R. Harnessing the immune responses: A new frontier in Ewing sarcoma treatment. Med. Oncol. 2025, 42, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, R.; Shen, L.; Luo, B.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Z.; Zhan, K.; et al. Aspirin enhances radio/chemo-therapy sensitivity in C. elegans by inducing germ cell apoptosis and suppresses RAS overactivated tumorigenesis via mtROS-mediated DNA damage and MAPK pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 735, 150828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, H.; Pawar, S.; Bahl, D. Curcumin in combination with anti-cancer drugs: A nanomedicine review. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankpal, U.T.; Ingersoll, S.B.; Ahmad, S.; Holloway, R.W.; Bhat, V.B.; Simecka, J.W.; Daniel, L.; Kariali, E.; Vishwanatha, J.K.; Basha, R. Association of Sp1 and survivin in epithelial ovarian cancer: Sp1 inhibitor and cisplatin, a novel combination for inhibiting epithelial ovarian cancer cell proliferation. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 14259–14269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelake, S.; Sankpal, U.T.; Eslin, D.; Bowman, W.P.; Simecka, J.W.; Raut, S.; Ray, A.; Basha, R. Clotam enhances anti-proliferative effect of vincristine in Ewing sarcoma cells. Apoptosis 2019, 24, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N.; Pandey, A.; Bajpai, J. Metastatic Ewing’s Sarcoma: Revisiting the “Evidence on the Fence”. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2017, 38, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, T. Diagnosis and treatment of Ewing sarcoma of the bone: A review article. J. Orthop. Sci. 2015, 20, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshram, G.G.; Kaur, N.; Hura, K.S. Ewing’s sarcoma with distant metastasis: A brief note on management and emerging therapies. Clin. Pract. 2019, 9, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.Y.; Damron, T.A.; Oest, M.E.; Horton, J.A. Mithramycin A Radiosensitizes EWS:Fli1+ Ewing Sarcoma Cells by Inhibiting Double Strand Break Repair. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 1454–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, M.F.; Surdez, D.; Faehling, T.; Ehlers, A.C.; Marchetto, A.; Grossetête, S.; Volckmann, R.; Zwijnenburg, D.A.; Gerke, J.S.; Zaidi, S.; et al. Systematic multi-omics cell line profiling uncovers principles of Ewing sarcoma fusion oncogene-mediated gene regulation. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grohar, P.J.; Helman, L.J. Prospects and challenges for the development of new therapies for Ewing sarcoma. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 137, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, J.E.; Riester, R.; Schleicher, S.B.; Handgretinger, R.; Boehme, K.A.; Traub, F. Interaction of arsenic trioxide and etoposide in Ewing sarcoma cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehme, K.A.; Nitsch, J.; Riester, R.; Handgretinger, R.; Schleicher, S.B.; Kluba, T.; Traub, F. Arsenic trioxide potentiates the effectiveness of etoposide in Ewing sarcomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sabei, F.Y.; Taratula, O.; Albarqi, H.A.; Al-Fatease, A.M.; Moses, A.S.; Demessie, A.A.; Park, Y.; Vogel, W.K.; Nazzaro, E.E.; Davare, M.A.; et al. A targeted combinatorial therapy for Ewing’s sarcoma. Nanomedicine 2021, 37, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Damron, T.A.; Horton, J.A. Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis are early events in radiosensitization of EWS::FLI1 + Ewing sarcoma cells by Mithramycin A. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2023, 99, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.J.; Arora, R.D.; Menezes, R.G. Vinca Alkaloid Toxicity; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Vormoor, B.; Curtin, N.J. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in Ewing sarcoma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2014, 26, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, J.L.; Amaral, A.T.; Carcaboso, A.M.; Herrero-Martín, D.; García-Macías, M.d.C.; Sevillano, V.; Alonso, D.; Pascual-Pasto, G.; San-Segundo, L.; Vila-Ubach, M.; et al. The PARP inhibitor olaparib enhances the sensitivity of Ewing sarcoma to trabectedin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18875–18890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, S.; Miyakita, H.; Shima, M.; Usui, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Uchida, T.; Terachi, T. Acute myocardial infarction during combined chemotherapy with bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin for testicular cancer. Hinyokika Kiyo 2006, 52, 723–726. [Google Scholar]
- Herradón, E.; González, C.; González, A.; Uranga, J.A.; López-Miranda, V. Cardiovascular Toxicity Induced by Chronic Vincristine Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 692970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Stamenkovic, I.; Longo, D.L. Ewing’s Sarcoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.M.; Tu, Z.J.; Kilpatrick, S.E.; Trucco, M.; Hanna, R.; Chan, T. Routine EWS Fusion Analysis in the Oncology Clinic to Identify Cancer-Specific Peptide Sequence Patterns That Span Breakpoints in Ewing Sarcoma and DSRCT. Cancers 2023, 15, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, P.Y.; Omer, N.; Wong, J.K.M.; Tu, C.; Alim, L.; Rossi, G.R.; Victorova, M.; Tompkins, H.; Lin, C.; Mehdi, A.M.; et al. Enhancement of anti-sarcoma immunity by NK cells engineered with mRNA for expression of a EphA2-targeted CAR. Clin. Transl. Med. 2025, 15, e70140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lambring, C.B.; Albeer, L.; Negrete, A.O.; Fure, K.; Basha, R. Evaluation of Mithramycin in Combination with Chemotherapeutic Agents Against Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines. Cancers 2025, 17, 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182977
Lambring CB, Albeer L, Negrete AO, Fure K, Basha R. Evaluation of Mithramycin in Combination with Chemotherapeutic Agents Against Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182977
Chicago/Turabian StyleLambring, Christoffer Briggs, Lina Albeer, Aneth Ochoa Negrete, Kayla Fure, and Riyaz Basha. 2025. "Evaluation of Mithramycin in Combination with Chemotherapeutic Agents Against Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines" Cancers 17, no. 18: 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182977
APA StyleLambring, C. B., Albeer, L., Negrete, A. O., Fure, K., & Basha, R. (2025). Evaluation of Mithramycin in Combination with Chemotherapeutic Agents Against Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines. Cancers, 17(18), 2977. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182977






