Endothelial Injury Following CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy for Hematological Malignancies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CRS: Basic Insights
3. ICANS and Neurotoxicity
4. Endothelial Injury Markers in CAR-T Cell Recipients
4.1. An Overview of Studies Investigating Endothelial Injury Markers in CAR-T Cell Recipients
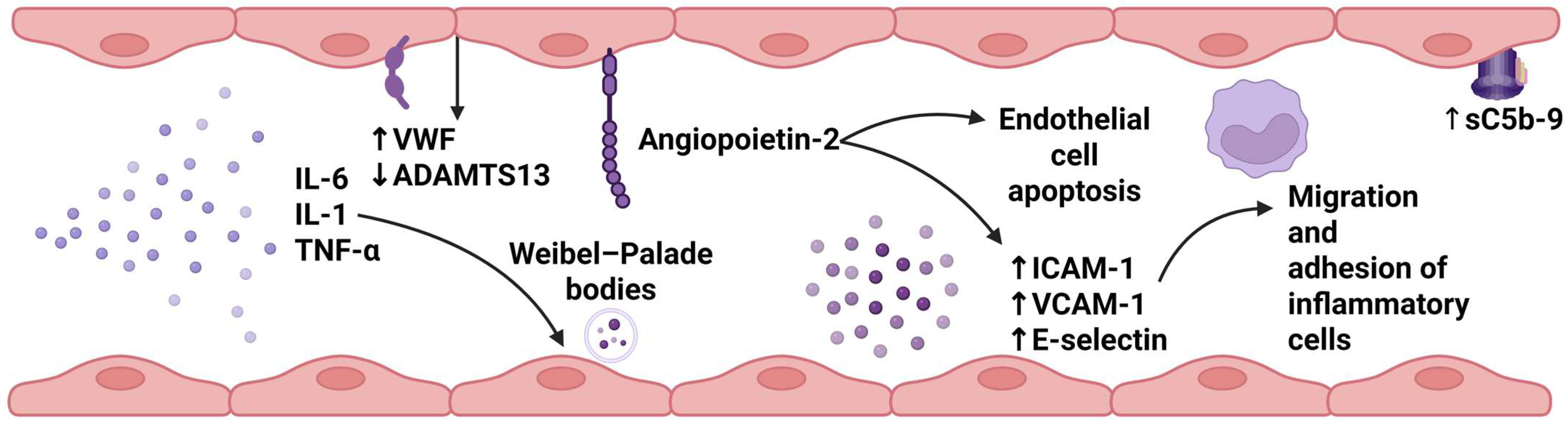
4.2. Mechanisms of Endothelial Injury in CAR-T Cell Recipients
4.2.1. Complement Activation
4.2.2. Endothelial Activation
4.2.3. Procoagulant State
5. Endothelial Injury Indices in the Prediction of CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy Outcomes
6. Therapeutic Implications
6.1. Statins
6.2. Defibrotide
6.3. TNF-α and IL-1β Blockade
7. Conclusions—Future Perspectives
- Conducting real-world studies to explore the role of endothelial injury indices in predicting infectious events, malignancy relapse, and severe cytopenias post-infusion.
- Performing meta-analyses, particularly individual patient data meta-analyses, to elucidate the role of these scores.
- Investigating ADAMTS13 activity, von Willebrand factor (VWF), and complement system activation in patients with severe toxicities through translational research approaches.
- Undertaking multicenter collaborative studies to identify cases of transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) post-infusion.
- Exploring the associations between EASIX scores, endothelial injury markers, and cognitive outcomes.
- Studying pre-infusion genetic susceptibility to endothelial injury syndromes.
- Assessing microcirculation with non-interventional methods in long-term CAR-T cell therapy survivors.
- Investigating endothelial injury post-infusion in patients receiving CAR-T cell therapy for autoimmune diseases and examining the role of EASIX scores in these patients.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AL | Light-chain amyloidosis |
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| ANG-1 | Angiopoietin-1 |
| ANG-2 | Angiopoietin-2 |
| aPTT | Activated partial thromboplastin |
| ASTCT | American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| B-ALL | B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| BCMA | B-cell maturation antigen |
| BTK | Bruton’s tyrosine kinase |
| CAR-T | Chimeric antigen receptor-T |
| CLL1 | C-type lectin-like molecule 1 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CRS | Cytokine release syndrome |
| DAMPs | Danger associated molecular patterns |
| EASIX | Endothelial Activation and Stress Index |
| EASIX-F | Endothelial Activation and Stress Index score combined with ferritin values |
| ECs | Endothelial cells |
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FiO2 | Fraction of inspired oxygen |
| FRIDA | Frontal rhythmic intermittent delta activity |
| FVIII | Factor VIII |
| GDF-15 | Growth/differentiation factor 15 |
| GM-CSF | Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| HCT | Hematopoietic cell transplantation |
| HLH | Hemolytic lymphohistiocytosis |
| HMW | High molecular weight |
| ICAHT | Immune effector cell-associated hematotoxicity |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| ICANS | Immune effector cell-associated syndromes |
| ICE | Immune effector cell-associated encephalopathy |
| IL-1 | Interleukin 1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-6-mEASIX | IL-6 modified Endothelial Activation and Stress Index |
| INF-γ | Interferon-γ |
| JAK/STAT | Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription |
| LD | Lymphodepleting chemotherapy |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LMW | Low molecular weight |
| MAPK/NFκB | Mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| MAS | Macrophage activation syndrome |
| mEASIX | Modified Endothelial Activation and Stress Index |
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NETs | Neutrophil extracellular traps |
| NHL | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PLTs | Platelets |
| P-mEASIX | Phosphorus-modified Endothelial Activation and Stress Index |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| R/R | Relapsed/refractory |
| RES | Reticuloendothelial system |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristics |
| sC5b-9 | Soluble C5b-9 |
| sEASIX | Simplified Endothelial Activation and Stress Index |
| sICAM-1 | Soluble intracellular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| suPAR | Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor |
| sVCAM | Soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule |
| TA-TMA | Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy |
| TIE-2 | Angiopoietin-1 receptor |
| TLS | Tumor lysis syndrome |
| TNF-a | Tumor necrosis factor-a |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VWF | Von Willebrand factor |
References
- Lu, J.; Jiang, G. The Journey of CAR-T Therapy in Hematological Malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddie, C.; Rampotas, A. The Present and Future of CAR-T Cell Therapy for Adult B-Cell ALL. Blood J. 2024, 145, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, D.G.; Waghela, H.; Nuh, M.; Pan, J.; Lulla, P. Approved CAR-T Therapies Have Reproducible Efficacy and Safety in Clinical Practice. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2024, 20, 2378543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheykhhasan, M.; Ahmadieh-Yazdi, A.; Vicidomini, R.; Poondla, N.; Tanzadehpanah, H.; Dirbaziyan, A.; Mahaki, H.; Manoochehri, H.; Kalhor, N.; Dama, P. CAR T Therapies in Multiple Myeloma: Unleashing the Future. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 667–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, G.; Reed, M.R.; Bielamowicz, K.; Koss, B.; Rodriguez, A. CAR-T Therapies in Solid Tumors: Opportunities and Challenges. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schett, G.; Müller, F.; Taubmann, J.; Mackensen, A.; Wang, W.; Furie, R.A.; Gold, R.; Haghikia, A.; Merkel, P.A.; Caricchio, R.; et al. Advancements and Challenges in CAR T Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, A.; Gunning, T.S.; Della Pia, A.; Zhang, X.; Ahn, J.; Sinclaire, B.; Lukasik, B.; Cho, C.; Donato, M.L.; Kaur, S.; et al. Real-World Outcomes of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy for Third-Line Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Single-Center Study. Hemato 2025, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, C.A.; Munoz, J.; Sun, F.; Kanters, S.; Limbrick-Oldfield, E.H.; Spooner, C.; Mignone, K.; Ayuk, F.; Sanderson, R.; Whitmore, J.; et al. Real-World Outcomes with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapies in Large B Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2024, 30, 77.e1–77.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, S. CAR T-Cell Therapy: Adverse Events and Management. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2019, 10, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.C.; Neelapu, S.S.; Giavridis, T.; Sadelain, M. Cytokine Release Syndrome and Associated Neurotoxicity in Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangolo, A.; Amoozgar, B.; Mansour, C.; Zhang, L.; Gill, S.; Ip, A.; Cho, C. Comprehensive Review of Early and Late Toxicities in CAR T-Cell Therapy and Bispecific Antibody Treatments for Hematologic Malignancies. Cancers 2025, 17, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejeski, K.; Subklewe, M.; Aljurf, M.; Bachy, E.; Balduzzi, A.; Barba, P.; Bruno, B.; Benjamin, R.; Carrabba, M.G.; Chabannon, C.; et al. Immune Effector Cell–Associated Hematotoxicity: EHA/EBMT Consensus Grading and Best Practice Recommendations. Blood 2023, 142, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, M.R. Late Complications and Long-Term Care of Adult CAR T-Cell Patients. Hematology 2024, 2024, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelidis, P.; Tragiannidis, K.; Vyzantiadis, A.; Evangelidis, N.; Kalmoukos, P.; Vyzantiadis, T.-A.; Tragiannidis, A.; Kourti, M.; Gavriilaki, E. Invasive Fungal Disease After Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T Immunotherapy in Adult and Pediatric Patients. Pathogens 2025, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Dolgyras, P.; Dimou-Mpesikli, S.; Poulopoulou, A.; Evangelidis, P.; Evangelidis, N.; Demosthenous, C.; Zachrou, E.; Siasios, P.; Mallouri, D.; et al. Risk Factors, Prevalence, and Outcomes of Invasive Fungal Disease Post Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies: A Retrospective Monocenter Real-Life Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Doesum, J.A.; Salmanton-García, J.; Marchesi, F.; Di Blasi, R.; Falces-Romero, I.; Cabirta, A.; Farina, F.; Besson, C.; Weinbergerová, B.; Van Praet, J.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination and Monoclonal Antibodies on Outcome Post-CD19-Directed CAR T-Cell Therapy: An EPICOVIDEHA Survey. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelidis, P.; Evangelidis, N.; Kalmoukos, P.; Kourti, M.; Tragiannidis, A.; Gavriilaki, E. Genetic Susceptibility in Endothelial Injury Syndromes after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and Other Cellular Therapies: Climbing a Steep Hill. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4787–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Anyfanti, P. Editorial: Endotheliopathies: Current Concepts and Importance in Clinical Practice. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1162121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.; Nagle, S.; Randall, J.; Hinson, H.E. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell-Related Neurotoxicity: Mechanisms, Clinical Presentation, and Approach to Treatment. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2019, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Tang, C.; Zhang, G.; Wan, X. DAMPs Released by Pyroptotic Cells as Major Contributors and Therapeutic Targets for CAR-T-Related Toxicities. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Zhou, N.; Lv, J.; Tang, K.; et al. Gasdermin E-Mediated Target Cell Pyroptosis by CAR T Cells Triggers Cytokine Release Syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaax7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwameis, M.; Schörgenhofer, C.; Assinger, A.; Steiner, M.M.; Jilma, B. VWF Excess and ADAMTS13 Deficiency: A Unifying Pathomechanism Linking Inflammation to Thrombosis in DIC, Malaria, and TTP. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Xiao, Y. The Critical Role of Endothelial Cell in the Toxicity Associated with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy and Intervention Strategies. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudno, J.N.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Recent Advances in CAR T-Cell Toxicity: Mechanisms, Manifestations and Management. Blood Rev. 2019, 34, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, D.A.; Lee, D.W. Cytokine Release Syndrome Biology and Management. Cancer J. 2021, 27, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, M.R.; Knight, T.E.; McNerney, K.O.; Leick, M.B.; Jain, T.; Ahmed, S.; Frigault, M.J.; Hill, J.A.; Jain, M.D.; Johnson, W.T.; et al. Immune Effector Cell-Associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis-Like Syndrome. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2023, 29, 438.e1–438.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.K.; Turtle, C.J. Assessment and Management of Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurotoxicity Following CD19 CAR-T Cell Therapy. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegler, E.L.; Kenderian, S.S. Neurotoxicity and Cytokine Release Syndrome After Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: Insights Into Mechanisms and Novel Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.D.; Smith, M.; Shah, N.N. How I Treat Refractory CRS and ICANS Following CAR T-Cell Therapy. Blood 2023, 141, 2430–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Hu, K.; Si, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, H. Mechanisms of Immune Effector Cell-associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome after CAR-T Treatment. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2022, 14, e1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.N.; Krenciute, G. The Mechanisms of Altered Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in CD19 CAR T-Cell Recipients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, L.; Ricciotti, I.; Tosoni, A.; Di Nunno, V.; Bartolini, S.; Ranieri, L.; Franceschi, E. CAR-T Cells Neurotoxicity from Consolidated Practice in Hematological Malignancies to Fledgling Experience in CNS Tumors: Fill the Gap. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1206983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Ponce, R.; Liles, W.C.; Garden, G.A.; Turtle, C.J. Cytokines in CAR T Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 577027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strongyli, E.; Evangelidis, P.; Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, M.; Gavriilaki, E. Change in Neurocognitive Function in Patients Who Receive CAR-T Cell Therapies: A Steep Hill to Climb. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gust, J.; Taraseviciute, A.; Turtle, C.J. Neurotoxicity Associated with CD19-Targeted CAR-T Cell Therapies. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, V.S.; Gauthier, J. Taming the Beast: CRS and ICANS after CAR T-Cell Therapy for ALL. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Hay, K.A.; Hanafi, L.-A.; Li, D.; Myerson, D.; Gonzalez-Cuyar, L.F.; Yeung, C.; Liles, W.C.; Wurfel, M.; Lopez, J.A.; et al. Endothelial Activation and Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Neurotoxicity after Adoptive Immunotherapy with CD19 CAR-T Cells. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1404–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidi, Y.; Eckhardt, C.A.; Quadri, S.A.; Malik, P.; Firme, M.S.; Jones, D.K.; Jain, A.; Danish, H.H.; Rubin, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; et al. Forecasting Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome after Chimeric Antigen Receptor t-Cell Therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, S.J.; Grimshaw, A.A.; Silberstein, J.; Murdaugh, D.; Wildes, T.M.; Rosko, A.E.; Giri, S. Clinical Presentation, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome Following Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: A Systematic Review. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, J.H. Management of Immune Effector Cell-Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome (ICANS). In The EBMT/EHA CAR-T Cell Handbook; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Hernani, R.; Benzaquén, A.; Solano, C. Toxicities Following CAR-T Therapy for Hematological Malignancies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2022, 111, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Tummala, S.; Kebriaei, P.; Wierda, W.; Gutierrez, C.; Locke, F.L.; Komanduri, K.V.; Lin, Y.; Jain, N.; Daver, N.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy—Assessment and Management of Toxicities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Teachey, D.T.; Pequignot, E.; Frey, N.; Porter, D.; Maude, S.L.; Grupp, S.A.; June, C.H.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Lacey, S.F. Measuring IL-6 and SIL-6R in Serum from Patients Treated with Tocilizumab and/or Siltuximab Following CAR T Cell Therapy. J. Immunol. Methods 2016, 434, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelidis, P.; Gavriilaki, E.; Tsakiris, D.A. Thrombotic Complications after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Other Cellular Therapies. Thromb. Update 2024, 16, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castaño, A.B.; Fernández, S.; Ventosa, H.; Palomo, M.; Martinez-Sanchez, J.; Ramos, A.; Ortiz-Maldonado, V.; Delgado, J.; de Larrea, C.F.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; et al. Characterization of the Endotheliopathy, Innate-Immune Activation and Hemostatic Imbalance Underlying CAR-T Cell Toxicities: Laboratory Tools for an Early and Differential Diagnosis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, M.; Diaz-Ricart, M.; Carreras, E. Endothelial Dysfunction in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Clin. Hematol. Int. 2019, 1, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jess, J.; Yates, B.; Dulau-Florea, A.; Parker, K.; Inglefield, J.; Lichtenstein, D.; Schischlik, F.; Ongkeko, M.; Wang, Y.; Shahani, S.; et al. CD22 CAR T-Cell Associated Hematologic Toxicities, Endothelial Activation and Relationship to Neurotoxicity. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e005898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, K.A.; Hanafi, L.-A.; Li, D.; Gust, J.; Liles, W.C.; Wurfel, M.M.; López, J.A.; Chen, J.; Chung, D.; Harju-Baker, S.; et al. Kinetics and Biomarkers of Severe Cytokine Release Syndrome after CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor–Modified T-Cell Therapy. Blood 2017, 130, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Shi, M.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zeng, L.; He, A.; et al. Predictive Role of Endothelial Cell Activation in Cytokine Release Syndrome after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 11063–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Gardner, R.; Porter, D.L.; Louis, C.U.; Ahmed, N.; Jensen, M.; Grupp, S.A.; Mackall, C.L. Current Concepts in the Diagnosis and Management of Cytokine Release Syndrome. Blood 2014, 124, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Finney, O.C.; Li, D.; Brakke, H.M.; Hicks, R.M.; Futrell, R.B.; Gamble, D.N.; Rawlings-Rhea, S.D.; Khalatbari, H.K.; Ishak, G.E.; et al. Glial Injury in Neurotoxicity after Pediatric CD19-directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, M.; Van Hoovels, L.; Benucci, M.; De Luca, R.; Coccia, C.; Bernardini, P.; Russo, E.; Amedei, A.; Guiducci, S.; Grossi, V.; et al. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (SuPAR) in Autoimmune Rheumatic and Non Rheumatic Diseases. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, L.J.H.; Petersen, J.E.V.; Eugen-Olsen, J. Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor (SuPAR) as a Biomarker of Systemic Chronic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 780641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehan, S.T.; Imran, L.; Eqbal, F.; Khan, Z.; Nashwan, A.J.; Asghar, M.S. Prognostic Role of SuPAR in Acute Pancreatitis: A Protocol for Systematic Review. Medicine 2024, 103, e37064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Demosthenous, C.; Evangelidis, P.; Bousiou, Z.; Batsis, I.; Vardi, A.; Mallouri, D.; Koravou, E.-E.; Spyridis, N.; Panteliadou, A.; et al. Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (SuPAR), Growth Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF-15), and Soluble C5b-9 (SC5b-9) Levels Are Significantly Associated with Endothelial Injury Indices in CAR-T Cell Recipients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischhusen, J.; Melero, I.; Fridman, W.H. Growth/Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF-15): From Biomarker to Novel Targetable Immune Checkpoint. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Brodsky, R.A. Complementopathies and Precision Medicine. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2152–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Yuan, X.; Ye, Z.; Ambinder, A.J.; Shanbhag, S.P.; Streiff, M.B.; Kickler, T.S.; Moliterno, A.R.; Sperati, C.J.; Brodsky, R.A. Modified Ham Test for Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazana, I. Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy in the Context of Allogenic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Where We Stand. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.S.; Koirala, A. Thrombotic Microangiopathy Following Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. Clin. Nephrol. Case Stud. 2023, 11, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Medvedovic, M.; Luebbering, N.; Chen, J.; Dandoy, C.E.; Laskin, B.L.; Davies, S.M. Interferon-Complement Loop in Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vythoulkas, D.; Lazana, I.; Kroupis, C.; Gavriilaki, E.; Konstantellos, I.; Bousiou, Z.; Chondropoulos, S.; Griniezaki, M.; Vardi, A.; Gkirkas, K.; et al. Endothelial Injury Syndromes after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Angiopetin-2 as a Novel Predictor of the Outcome and the Role of Functional Autoantibodies against Angiotensin II Type 1 and Endothelin A Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatekawa, S.; Kohno, A.; Ozeki, K.; Watamoto, K.; Ueda, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Yokota, I.; Teramukai, S.; Taniwaki, M.; et al. A Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Panel for Endothelial Cell Damage-Related Complications in Allogeneic Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.I.; Saxena, A.; Ahmad, F. Structure and Function of von Willebrand Factor. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2012, 23, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plautz, W.E.; Raval, J.S.; Dyer, M.R.; Rollins-Raval, M.A.; Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Neal, M.D. ADAMTS13: Origins, Applications, and Prospects. Transfusion 2018, 58, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, M.; Gavriilaki, E.; Ztriva, E.; Evangelidis, P.; Lefkou, E.; Vlachaki, E.; Bountola, S.; Perifanis, V.; Matsagkas, M.; Savopoulos, C.; et al. Prospective Study of ADAMTS13 and von Willebrand Factor’s Role in the Prediction of Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, S.; Lämmle, B.; Cataland, S.R. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korell, F.; Penack, O.; Mattie, M.; Schreck, N.; Benner, A.; Krzykalla, J.; Wang, Z.; Schmitt, M.; Bullinger, L.; Müller-Tidow, C.; et al. EASIX and Severe Endothelial Complications After CD19-Directed CAR-T Cell Therapy—A Cohort Study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 877477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, E.; Sorà, F.; Hohaus, S.; Fresa, A.; Pansini, I.; Autore, F.; Metafuni, E.; Innocenti, I.; Limongiello, M.A.; Giammarco, S.; et al. Endothelial Activation Predicts Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy, Cytokine Release Syndrome and Prognosis in Patients Treated with Anti-CD19 CAR-T Cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 201, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, T.; Benner, A.; Jodele, S.; Dandoy, C.E.; Storb, R.; Gooley, T.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Becker, N.; Radujkovic, A.; Dreger, P.; et al. EASIX in Patients with Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e414–e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, A.; Salas, M.Q.; Rodríguez-Lobato, L.G.; Escribano-Serrat, S.; Suárez-Lledo, M.; Martínez-Cebrian, N.; Solano, M.T.; Arcarons, J.; Rosiñol, L.; Gutiérrez-García, G.; et al. Easix Score Correlates With Endothelial Dysfunction Biomarkers and Predicts Risk of Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease After Allogeneic Transplantation. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2024, 30, 187.e1–187.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Sakellari, I.; Chatzikonstantinou, T.; Mallouri, D.; Batsis, I.; Vardi, A.; Bousiou, Z.; Koravou, E.-E.; Masmanidou, M.; Touloumenidou, T.; et al. Endothelial and Complement Activation As Predictors of Survival in Adult Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Hemasphere 2021, 5, e487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, M.; Anagnostopoulos, A. A New Era in Endothelial Injury Syndromes: Toxicity of CAR-T Cells and the Role of Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, M.; Sanchez-Escamilla, M.; Flynn, J.R.; Shouval, R.; Alarcon Tomas, A.; Silverberg, M.L.; Batlevi, C.; Brentjens, R.J.; Dahi, P.B.; Devlin, S.M.; et al. Modified EASIX Predicts Severe Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurotoxicity after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3397–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, U.; Strati, P.; Saliba, R.M.; Torres, J.; Rondon, G.; Nieto, Y.; Hosing, C.; Srour, S.A.; Westin, J.; Fayad, L.E.; et al. CRP and Ferritin in Addition to the EASIX Score Predict CAR-T–Related Toxicity. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2799–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Tzannou, I.; Batsis, I.; Tsonis, I.; Liga, M.; Gkirkas, K.; Ximeri, M.; Dolgyras, P.; Bampali, V.; Evangelidis, P.; et al. EASIX and M-EASIX Predict Severe Cytokine Release Syndrome and Overall Survival after CAR T-Cell Therapy. Blood Vessel. Thromb. Hemost. 2024, 1, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta-Medina, A.A.; Johnson, I.M.; Bansal, R.; Hathcock, M.; Kenderian, S.J.; Durani, U.; Khurana, A.; Wang, Y.; Paludo, J.; Villasboas, J.C.; et al. Pre-Lymphodepletion & Infusion Endothelial Activation and Stress Index as Predictors of Clinical Outcomes in CAR-T Therapy for B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, J.W.; Keijzer, K.; Pennings, E.R.A.; van Doesum, J.A.; Spanjaart, A.M.; Jak, M.; Mutsaers, P.G.N.J.; van Dorp, S.; Vermaat, J.S.P.; van der Poel, M.W.M.; et al. Population-Based External Validation of the EASIX Scores to Predict CAR T-Cell-Related Toxicities. Cancers 2023, 15, 5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.P.; Peters, C.W.; Quiros, C.; Wang, X.; Klomhaus, A.M.; Yamada, R.E.; Timmerman, J.M.; Moore, T.B.; Nowicki, T.S. Hypophosphatemia Due to Increased Effector Cell Metabolic Activity Is Associated with Neurotoxicity Symptoms in CD19-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2022, 10, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K.; Koza, S.; Katsanis, E.; Husnain, M. Hypophosphatemia and Pre-Infusion Thrombocytopenia as Biomarkers for CRS and ICANS after CAR T Therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023, 58, 1267–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K.; Marco, T.; Husnain, M.; Katsanis, E. Addition of Phosphorous and IL6 to M-EASIX Score Improves Detection of ICANS and CRS, as Well as CRS Progression. Cancers 2025, 17, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandaki, D.; Selukar, S.; Bi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zinsky, M.; Bonifant, C.L.; Epperly, R.; Keerthi, D.; Triplett, B.M.; Gottschalk, S.; et al. EASIX and M-EASIX Predict CRS and ICANS in Pediatric and AYA Patients after CD19-CAR T-Cell Therapy. Blood Adv. 2025, 9, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, J.; Avni, B.; Grisariu, S.; Elias, S.; Zimran, E.; Stepensky, P.; Basak, G.W. Endothelial Activation and Stress Index Score as a Prognostic Factor of Cytokine Release Syndrome in CAR-T Patients—A Retrospective Analysis of Multiple Myeloma and Large B-Cell Lymphoma Cohorts. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2024, 72, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marvin-Peek, J.; Savani, B.N.; Olalekan, O.O.; Dholaria, B. Challenges and Advances in Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rhenen, A.; van Dongen, G.A.M.S.; Kelder, A.; Rombouts, E.J.; Feller, N.; Moshaver, B.; Walsum, M.S.-V.; Zweegman, S.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Schuurhuis, G.J. The Novel AML Stem Cell Associated Antigen CLL-1 Aids in Discrimination between Normal and Leukemic Stem Cells. Blood 2007, 110, 2659–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Guo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; et al. Modified EASIX Scores Predict Severe CRS/ICANS in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Following CLL1 CAR-T Cell Therapy. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xu, J.; Mei, H.; Hu, Y. IL-10 plus the EASIX Score Predict Bleeding Events after Anti-CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 3575–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenking, J.H.; Zhou, X.; Wagner, V.; Hielscher, T.; Kauer, J.; Mai, E.K.; Friedrich, M.J.; Michel, C.S.; Hajiyianni, M.; Breitkreutz, I.; et al. EASIX-Guided Risk Stratification for Complications and Outcome after CAR T-Cell Therapy with Ide-Cel in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e009220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Colio, L.M.; Tuñón, J.; Martín-Ventura, J.L.; Egido, J. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Statins. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.K.; Sehgal, V.S.; Kashfi, K. Molecular Targets of Statins and Their Potential Side Effects: Not All the Glitter Is Gold. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 922, 174906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adroja, S.; Burns, E.A.; Giese, N.; Mathur, S.; Khosla, M.; Rios, J.; Hassanain, H.S.; Lulla, P.D.; Ramos, C.A.; Yuen, C.; et al. Statins May Improve Outcomes and Toxicities in Patients Undergoing CD19-Specific CAR T-Cell Therapy for Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas. Blood 2024, 144, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.L.; Abdulhaleem, M.; Abedin, M.S.U.; Holley, N.; Al-saeed, N.; Anaum, S.; Saifuddin, A.; Safi, S. The Effect of Statin Use on Outcome in Patients Receiving Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2025, 31, S247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumransub, N.; Seichter, C.; Kent, K.; Shanley, R.; Hu, M.; O’Leary, D.; El Jurdi, N.H.; Holtan, S.G.; Betts, B.; Juckett, M.; et al. Simvastatin with Intrathecal Dexamethasone Reduces Neurotoxicity in Adults Receiving Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cells Treatment. Blood 2023, 142, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, E.; Mo, C.C.; Calabretta, E.; Corrado, F.; Kocoglu, M.H.; Baron, R.M.; Connors, J.M.; Iacobelli, M.; Wei, L.-J.; Benjamin, E.J.; et al. Defibrotide for Protecting Against and Managing Endothelial Injury in Hematologic Malignancies and COVID-19. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauffal, M.; Kim, H.T.; Richardson, P.G.; Soiffer, R.J.; Antin, J.H.; Cutler, C.; Nikiforow, S.; Gooptu, M.; Koreth, J.; Romee, R.; et al. Defibrotide: Real-World Management of Veno-Occlusive Disease/Sinusoidal Obstructive Syndrome after Stem Cell Transplant. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, C.A.; Rosenthal, A.C.; Arnason, J.; Agarwal, S.; Zhang, P.; Wu, W.; Amber, V.; Yared, J.A. A Phase 2 Trial of Defibrotide for the Prevention of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell–Associated Neurotoxicity Syndrome. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 6790–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Shang, S.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Therapeutic Potential of TNFα and IL1β Blockade for CRS/ICANS in CAR-T Therapy via Ameliorating Endothelial Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 623610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Grade | CRS | ICANS |
|---|---|---|
| I | Fever ≥ 38.0 °C | ICE score: 7–9 Depressed level of consciousness, awakens spontaneously |
| II | Fever ≥ 38.0 °C with hypotension requiring IV fluids but not requiring vasopressors and/or hypoxia requiring oxygen via LFNC (≤6/L minute) 1 | ICE score: 3–6 Depressed level of consciousness, awakens to voice |
| III | Fever ≥ 38.0 °C with hypotension requiring one vasopressor (±vasopressin) and/or hypoxia requiring oxygen via HFNC (≥6/L minute), facemask, non-breather or venturi mask 1 | ICE score: 0–2 Depressed level of consciousness, awakens to tactile stimulus Seizure: Any clinical seizure, focal or generalized, that resolves rapidly, or nonconvulsive seizures on EEG that resolve with intervention Cerebral edema: Focal/local edema on neuroimaging |
| IV | Fever ≥ 38.0 °C with hypotension requiring multiple vasopressors (not vasopressin) and/or hypoxia requiring positive pressure oxygenation (e.g., CPAP, BiPAP, intubation and mechanical ventilation 1 | ICE score: 0 Depressed level of consciousness: Unarousable patient, or requiring vigorous or repetitive tactile stimuli to arouse or stupor or coma Motor findings: Deep focal motor weakness such as hemiparesis or paraparesis Elevated ICP: Diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging, decerebrate or decorticate posturing, cranial nerve VI palsy, papilledema, or Cushing’s triad |
| First Author, Year, Reference | Study Design | Control Group | Patient Population | Markers of Endothelial Injury | Significant Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moreno-Castaño et al., 2023 [46] | Prospective study | Healthy controls (n = 49) | CAR-T cell recipients who developed CRS/ICANS (n = 19) | s-VCAM1, STNFRI, TM, ST2, ADAMTS13 activity, Ang-2, NETs, sC5b-9, VWF antigen, a2-AP, PAI-1 Ag |
|
| Jess et al., 2023 [48] | Prospective study | Patients without ICANS (n = 33) or coagulopathy (n = 30) post-infusion | Patients who developed ICANS (n = 20) or coagulopathy (n = 18) post-infusion | Ang-2, Ang-2:Ang-1 ratio, fibrinogen nadirs, protein C, S, factor VIII, antithrombin, VWF antigen and activity, VEGF |
|
| Hong et al., 2021 [50] | Prospective study | Healthy controls (n = 7) and patient with mild CRS (n = 24) | CAR-T cell recipients (n = 30) and patients with severe CRS (n = 6) | VWF, Ang-1, Ang-2, Ang-2:Ang-1 ratio, sVCAM, sICAM-1, E-selectin 1 | Peak levels of these markers were significantly elevated in post-CAR-T cell therapy patients and in patients with severe CRS, compared to healthy controls and those without severe CRS, respectively |
| Hay et al., 2017 [49] | Phase 1 clinical trial | CAR-T cell recipients with CRS grade 1–3 (n = 51) | Patients experiencing severe CRS, defined as grade ≥ 4 (n = 9) | VFW, Ang-2, Ang-1 and Ang-2:Ang-1 ratio | The levels of the assessed markers were significantly associated with CRS severity |
| Gust et al., 2019 [52] | Prospective study | CAR-T cell recipients without ICANS (n = 24) | CAR-T cell recipients with ICANS (n = 19) | VEGF-A, Ang-1, Ang-2 | No statistically significant differences were identified between the two groups |
| Gust et al., 2017 [38] | Prospective study | CAR-T cell recipients with grade 0–3 ICANS (multiple subgroups were assessed for comparison) | Patients developing grade ≥ 4 ICANS | Ang-1, Ang-2, Ang-2:Ang-1 ratio, VWF (including LMW and HMW VWF), ADAMTS13:VWF ratio |
|
| Gavriilaki et al., 2024 [56] | Prospective study | Healthy controls (n = 20) | CAR-T cell recipients (n = 45) | suPAR, GDF-15, sC5b-9 2 | These biomarkers were significantly higher in patients treated with CAR-T cells |
| Category | Marker of Endothelial Injury | Pathophysiological Role | Significant Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complement | sC5b-9 |
| Increased in CAR-T cell recipients compared to normal controls and in CRS, ICANS | [46,56] |
| Endothelium | VCAM-1 |
| Increased in CRS, ICANS | [46,50] |
| ICAM-1 |
| Increased in CRS and severe CRS | [50] | |
| E-selectin |
| Increased in CRS and severe CRS | [50] | |
| Ang-2 |
| Increased in CRS and severe CRS | [38,46,48,49,50,69] | |
| Procoagulant molecules | TM |
| Increased in CRS, ICANS | [46,69] |
| ADAMTS13 activity |
| Decreased in CRS, ICANS | [46] | |
| VWF |
| Increased in CRS, ICANS Association with severe ICANS | [38,46,70] | |
| Proinflammatory molecules | STNFRI |
| Increased in CRS, ICANS | [46] |
| ST2 | Disruption of vascular integrity | Increased in CRS, ICANS | [46,69] | |
| NETs | Systemic inflammation and cytokine surge | Increased in CRS, ICANS | [46] |
| Predictive Endpoint | Endothelial Injury Indices | Time Point of Assessment | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe CRS (grade ≥ 3) | EASIX | pLD, infusion, days 1 to 3 post-infusion | [69,75,76,77,82,83] |
| mEASIX | pLD, infusion, days 1 to 3 post-infusion | ||
| EASIX-F | pLD | ||
| P-mEASIX | Day 1 post-infusion | ||
| IL6-mEASIX | Day 1 post-infusion | ||
| Severe (grade ≥ 3) | EASIX | pLD, infusion | [69,75,76,78,79,82,83] |
| mEASIX | pLD, infusion, day 3 post-infusion | ||
| EASIX-F | pLD | ||
| sEASIX | pLD | ||
| P-mEASIX | Day 1 post-infusion | ||
| Hematological toxicity, DIC, bleeding events | EASIX | pLD | [70,88,89] |
| mEASIX | pLD | ||
| Complete response | mEASIX | Days 1 to 3 post-infusion, on CRS onset | [75] |
| Overall survival | EASIX | Day 14 post-infusion | [56,77] |
| mEASIX | Day 14 post-infusion | ||
| sEASIX | Infusion, day 14 post-infusion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demosthenous, C.; Evangelidis, P.; Gatsis, A.; Mitroulis, I.; Vakalopoulou, S.; Vardi, A.; Bountoura, S.; Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, E. Endothelial Injury Following CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy for Hematological Malignancies. Cancers 2025, 17, 2876. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172876
Demosthenous C, Evangelidis P, Gatsis A, Mitroulis I, Vakalopoulou S, Vardi A, Bountoura S, Sakellari I, Gavriilaki E. Endothelial Injury Following CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy for Hematological Malignancies. Cancers. 2025; 17(17):2876. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172876
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemosthenous, Christos, Paschalis Evangelidis, Athanasios Gatsis, Ioannis Mitroulis, Sofia Vakalopoulou, Anna Vardi, Stefania Bountoura, Ioanna Sakellari, and Eleni Gavriilaki. 2025. "Endothelial Injury Following CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy for Hematological Malignancies" Cancers 17, no. 17: 2876. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172876
APA StyleDemosthenous, C., Evangelidis, P., Gatsis, A., Mitroulis, I., Vakalopoulou, S., Vardi, A., Bountoura, S., Sakellari, I., & Gavriilaki, E. (2025). Endothelial Injury Following CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy for Hematological Malignancies. Cancers, 17(17), 2876. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172876







